










Preview text:
Logistics
Gồm: plans, implements, control Have
Logistics: movement of materials in whole supply chain k thay đổi bản chất hàng hóa
Logistics is a service cung cấp dv vận chuyển sp ( transportation ) can by modes Air (
means airplane ), Sea ( ship ), rail ( train ), Road (truck, traler ), Pilelines trong chuỗi cung ứng
Cung cấp cho thuê kho bãi ( warehousing ) can nhận, chứa, giao hàng và xây dựng kênh
phân phối, thu mua trong nc và ngoài nc
( 3 & 4 PL ) 2 dạng cty cung cấp dvu logistics
3PL: logistics được bên thứ ba cung cấp, phải cung cấp dịch vụ kết hợp nhìu dvu.
4PL: Chuỗi logistics, dịch vụ logistics được cung cấp đầy đủ, chuyên gia, được quản lí
chặt chẽ theo hệ thống từ đầu tới cuối, tối ưu hóa chi phí
Nếu hàng hư, ng tiêu dùng mún trả, logistics có thể giúp ng dùng trả ngc lại ( reverse
logistics ) trả lại, sdung lại, tái chế, tiêu hủy
Seven Right’s of Logistics là ( trọng tâm) gồm Product Đúng sp Quantity Đúng số lượng
Condition Đúng chất lượng Place, Time, Customer, Price
Và nhập khẩu xuất khẩu cũng là chuỗi cung ứng
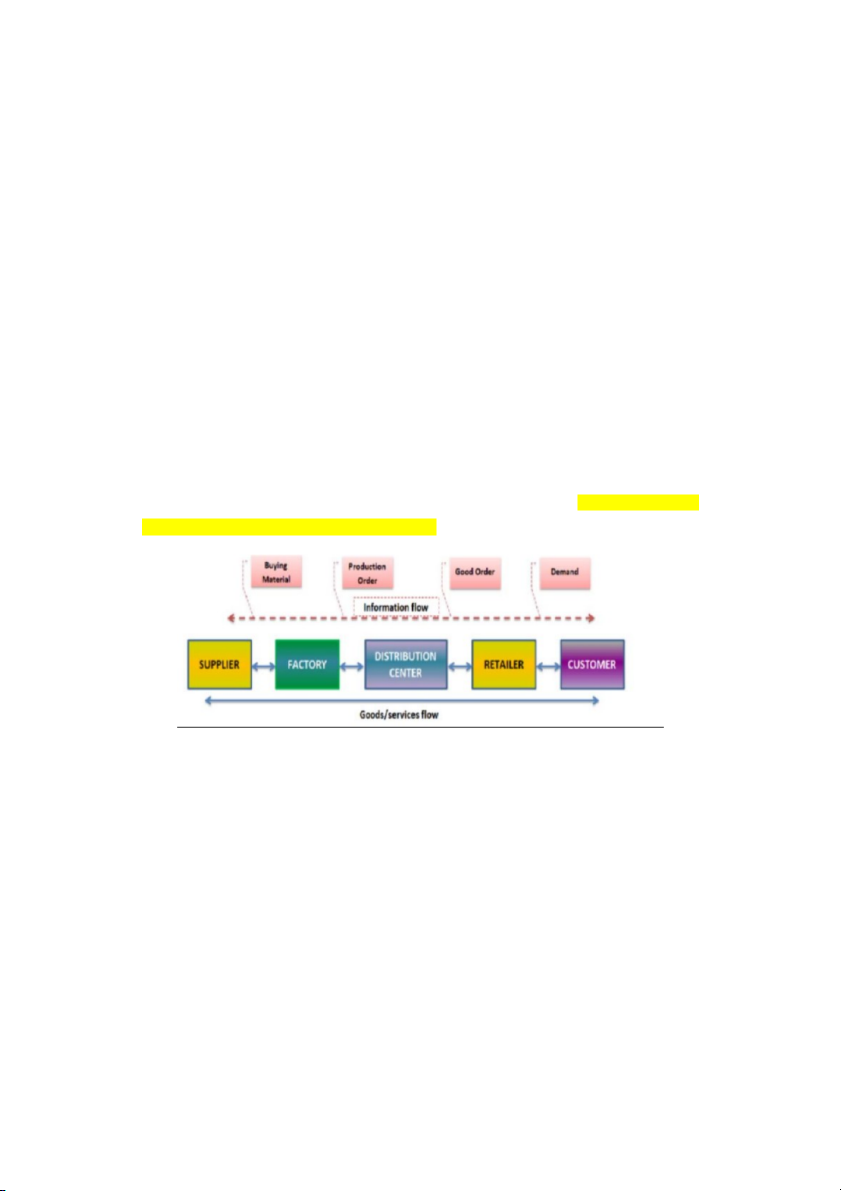
Đầu chuỗi: nhà cung ứng nvl ( supplier ) =>( giữa chuỗi ) bán cho nsx nhà máy => ( thành tố
t3 ) là nhà phân phối [ distributing] có thể mua nhìu bán ít => ( thành tố cuối cùng ) là ng tiêu dùng
=> logistics là dịch vụ ngta làm k dc thì mình làm cho ( làm tất cả nghiệp vụ cho chuỗi cung ứng vận hành )
=> K có ngành nào mà k cần logistics Câu hỏi thi
1. Các mô hình nào là mô hình qtri chuỗi cung ứng hiệu quả: SCOR
2. Môn hình SCOR gồm mấy hoạt động: 6
3. Nêu ra các thành tố: plan => source => make => deliver => return => enable 4. Tác giả là ai ?
C2: INTRO TO SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
Supply chain : chuỗi cung ứng nghĩa là 1 loại hd nhầm cung cấp, phân phối ( Transforming a raw
materials into products and getting it to customers ) thay đổi bản chất 1 dạng hàng hóa 5 Key Supply Chain Values:
1. Lowest end user prices and percentage of supply chain costs is the goal to make supply chains more competitive.
2. End user metrics are necessary.
3. Where can trading partners "buy time" to cut the overall supply chain cycle that moves a
product through the supply chain?
4. Collaborative planning among trading partners ( điểm mấu chốt ), with shared management of resources, is required.
5. Visibility of usage, forecasts, orders, shipments, and inventories is crucial.
Sự liên thông của các thành tố trên chuỗi cung ứng là điểm mấu chốt
Ng qtri phải bít lập kế hoạch, phải bít tổ chức, hướng dẫn tổ chức thực hiện plan, kiểm tra và kiểm soát kết quả
Procurement: tìm kiếm và tuyển chọn nhà cung cấp cho vc thu mua nvl đi kèm theo các tiêu chí tốt cho mình. Quiz c1 2
1. Logistics offers many companies an important route for creating makerting superiority A. True B. False
2. The movement and storage of materials into a firm refers to: A. Materials management B. Material handing C. Physical distribution D. Supply chain management
3. The activities related to ___________ include warehousing, repair, refurbishment,
recyling, return, aftermakert, call centre support, field service and many others. A. Outbound logistics B. Reverse logistics C. Inbound logistics D. Forward logistics
4. The supply chain management concept originated in what discipline? A. Production B. Logistics C. Marketing D. Operations
5. An individual firm can only be involved in one supply chain at a time A. True B. False
6. ___________ refers to being out of an item at the same time there is demand for it: A. Stockout B. Intensive distribution C. Tailored logistics D. Supplier indifference
7. Logistics clearly contributes to ___________ and ___________ utility. A. Place, form B. Possession, time C. Form, time D. Time, place
8. ___________ utility refers to having products available where they are needed by A. Possession B. Time C. Place D. Form
9. The most costly logistics activity in many firms is ____________. A. Transportation management B. Order management C. Industrial packaging D. Warehousing management
10. Which concept refers to the storage of finished product and movernernt to the customer? A. materials management B. physical distribution C. supply chain managerment D. business logistics
11. ____________usually specialize in warehousing and transportation services that can be
customced to customers needs based on market conditions and delivery service
requirements for their products and materials
A. Second-party logstics providers
B. Third-party logistics providers
C. Fourth-party logistics providers
D. Finst-party logistics providers
12. Supply chain activities____________ natural resources, raw materials and components
into a finished product that is delivered to the end customer A. Change B. Pass C. Transform D. Move
13. involves the activites of receiving, storing and distributing raw materials for use in
production. It is an integral element of business operations for a manufacturing firm. A. Outbound Logstics
B. None of the above andior beiow is correct C. Inbound Logstics D. Reverse Logstics
14. ____________refers to the removal of intermediaries between producer and consumer. A. Consolidation B. Market demassification C. Direct channels D. Disintermediation
15. The general idea behind ____________ is that one company allows a specialist company
to provide it with one or more logistics functions. A. Multichannel marketing
B. Cross-organizational collaboration C. Third-party logistics D. Supply chain management
16. According to APICS, Supply Chain is the global network used to deliver products and
services from raw materials to end customers through an engineered flows of____________ A. Cash B. Physical distribution
C. All the above and/or below options are correct D. Information
17. Supply chains are a new concept in the sense that they were first identified in the 1970s and 1980s A. True B. False
18. The primary objective of supply chain management is to fulfil____________ through the
most efficient use of resources including distribution capacity, inventory and labor.
A. All the above and/on below options are correct B. Customer's needs C. Manufacturers needs D. Supplers needs
19. What is a fourth-party logistics provider?
A. a third-party logistics provider that has achieved ISO 9000 certification
B. a logistics intermediary that specializes in one logistics activity such as warehousing or transportation
C. a third-party logistics provider that has been in existence for at least 25 years
D. a company that ensures that various third-party logistics companies are working
toward the relevant supply chain goals and objectives
20. primary objective of supply chain management is to optimize the performance of the supply chain as a whole A. True B. False
21. The process related to the storage (dự trữ) and movement of the final product and the
related information flows from the end of the production line to the end user. A. Reverse logistics B. Outbound logistics
C. All the above and/or below options are correct D. Inbound logistics
22. Supply chain managers make decisions at different levels as follows A. Operational level B. Tactical level
C. All the above and/or below options are correct D. Strategic level
23. Long production runs sometimes result in excessive inventory of products with limited demand for them. A. True B. False
24. The current definition of logistics, as promulgated by the Council of Supply Chain
Management Professionals, suggests that logistics is part of the supply chain process. A. True B. False
25. Which of the following is not a barrier to supply chain management?
A. Lack of top management commitment
B. All of the above and/or below are barriers
C. Regulatory and political considerations
D. Reluctance to share, or use, relevant
CHAPTER 3: PROCUREMENT & PURCHASING
Thu mua lquan tới hdong đặt hàng, vận tải
Step 1 Indetification of requirement
Step 2 determination of the specific: mún sx dc 1 món hàng phải có những cái cơ bản, liệt kê rõ ràng
Step 3 sourcing: đi tìm nguồn cung ứng
Step 4 Negotiation and finalization
Step 5 purchase requisition and order
Step 6 Delivery of the purchase order Step 7 Expediting = deadline Step 8 Recevie and inspection Step 9 Payment process
Step 10 Record keeping and review Quiz c3 4
1. The percentage of orders that can be completely and immediately filled from existing
stock is the ____________ rate A. Order fill B. Optimal inventory C. Order cycle D. Perfect order
2. Procurement and____________ are viewed as synonymous terms. A. Materials management B. Inbound logistics C. Purchasing D. Supply management
3. Demand management is NOT important because efficient and effective supply chains
have learned to match both supply and demand A. True B. False
4. Procuring products from suppliers close to one’s own facilities refers to____________. A. Outsourcing B. Dovetailing C. Agglomeration D. Near-sourcing
5. Forecasting accuracy refers to the relationship between the actual and forecasted demand. A. True B. False
6. The ability of logistics management to satisfy users in terms of time, dependability,
communication, and convenience is the definition of____________ A. Customer satisfaction B. The order cycle C. Customer service D. A perfect order
7. Single sourcing consolidates purchase volume with a single supplier in hopes of
increasing cooperation and communication in the supply relationship as well as ____.
A. Increased amounts of competition
B. Improved market intelligence
C. Greater supply risk mitigation D. Lower costs per unit
8. Buying the right products, at the right price, from the right source, at the right
specifications, in the right quantity, for delivery at the right time to the right internal
customer is associated with what procurement objective?
A. Supporting operational requirements
B. Supporting organizational goals and objectives
C. Managing the purchasing process effeciently D. Managing the supply base




