
Preview text:
Macroeconomics - Market Equilibrium Supply and Demand - CDs
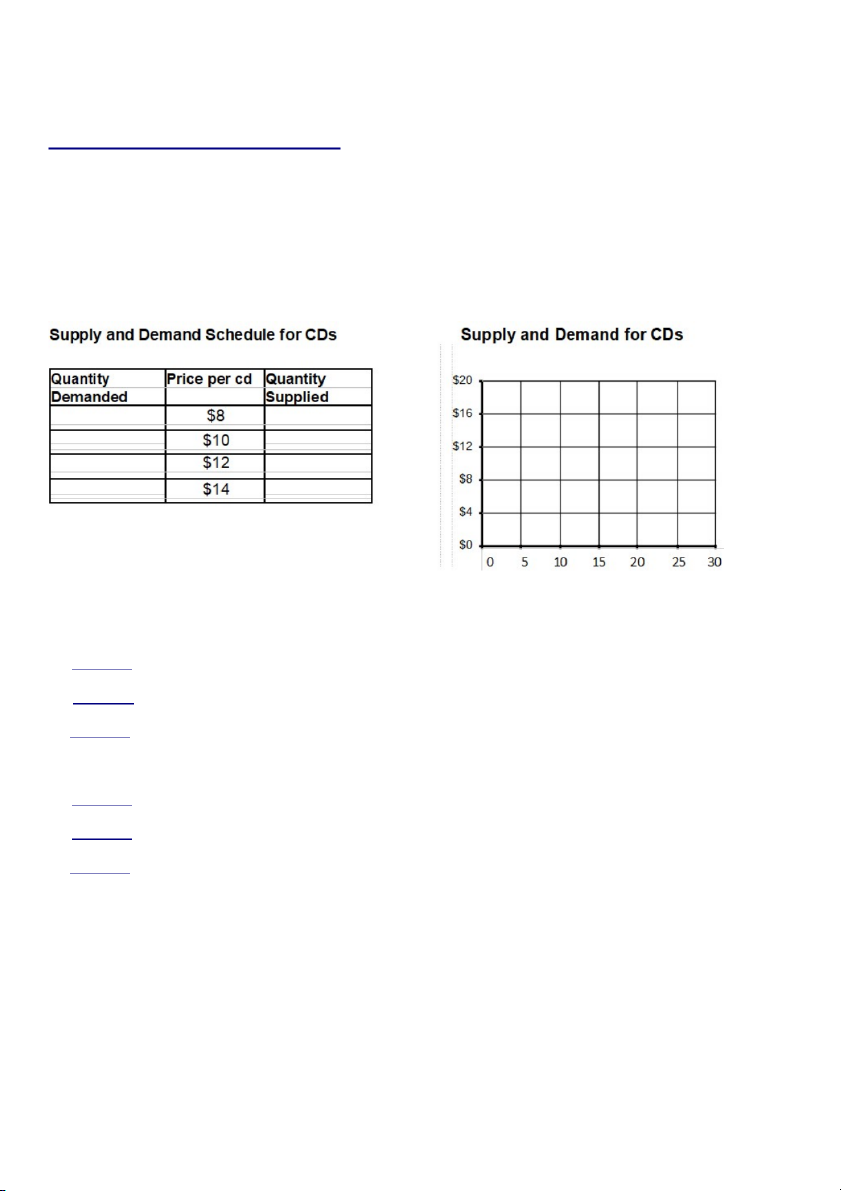
The following equations are for the supply and demand of CDs in the United States. Qd = -2P + 29 QS = 0.5P-1
QD = Quantity Demanded; QS = Quantity Supplied; P = Price
Complete the supply and demand schedule by calculating the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded at the various prices.
1. Question: What is the equilibrium price and quantity of CDs
2a. Question: How many CDs will be produced at $14 per CD?
2b. Question: Will there be a shortage or surplus of CDs? How many units will the surplus or shortage be?
2c. Question: What will happen to price (assuming markets can function without intervention)?
3a. Question: How many CDs will be produced at $8 per CD?
3b. Question: Will there be a shortage or surplus? How many units will the surplus or shortage be?
3c. Question: What will happen to price (assuming markets can function without intervention)? Page 1
Supply and Demand - Multiple Choice Questions
1. Question: Which of the following demonstrates a market equilibrium?
a. Quantity supplied equals quantity demanded.
b. Quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded.
c. Quantity supplied is less than quantity demanded.
d. The shortage is greater than the surplus.
2. Question: The invisible hand is a mechanism that?
a. Ensures government intervention will assist markets to reach equilibrium.
b. Shifts the supply curve when consumers desires are too great.
c. Prevents commercialization of commodities.
d. Automatically works to bring markets into equilibrium.
3. Question: What happens when price is higher than the equilibrium price?
a. There will be surplus putting downward pressure on price.
b. There will be a shortage putting downward pressure on price.
c. There will be a surplus putting upward pressure on price.
d. There will be a shortage putting upward pressure on price.
4. Question: What happens when price is lower than the equilibrium?
a. There will be surplus putting downward pressure on price.
b. There will be a shortage putting downward pressure on price.
c. There will be a surplus putting upward pressure on price.
d. There will be a shortage putting upward pressure on price.
5. Question: What moves markets toward equilibrium price and quantity?
a. Government sets price where supply is equal to demand.
b. Nothing. Most markets are not even close to equilibrium.
c. Price signals to producers and consumers help eliminate any surplus or shortage.
d. Government purchase of market surplus. Page 2




