I. Advanced sorting
1. Merge sort O(n log n)
[64, 34, 25, 12 | 22, 11, 90]
[64, 34 | 25, 12] [22, 11 | 90]
[64 | 34] [25 | 12] [22 | 11] [90]
[34, 64] [12, 25] [11, 22] [90]
[12, 25, 34, 64] [11, 22, 90]
[11, 12, 22, 25, 34, 64, 90]
time complexity is O(nlog n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
public class MergeSort {
public void mergeSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr.length < 2) return;
int mid = arr.length / 2;
int[] left = new int[mid];
int[] right = new int[arr.length - mid];
System.arraycopy(arr, 0, left, 0, mid);
System.arraycopy(arr, mid, right, 0, arr.length - mid);
mergeSort(left);
mergeSort(right);
merge(arr, left, right);
}
private void merge(int[] arr, int[] left, int[] right) {
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (i < left.length && j < right.length) {
if (left[i] <= right[j]) {
arr[k++] = left[i++];
} else {
arr[k++] = right[j++];
}
}
while (i < left.length) {
arr[k++] = left[i++];
}
while (j < right.length) {
arr[k++] = right[j++];
}
}

}
2. Shell sort O(n log n) to O(n^2)
Gap sequence: N/2, N/4, ..., 1
Gap = 3:
Position: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Initial: 64 34 25 12 22 11 90
Step 1: 12 34 25 64 22 11 90
Step 2: 12 11 25 64 22 34 90
Step 3: 12 11 22 64 25 34 90
Gap = 1 (Regular Insertion Sort):
Step 1: 11 12 22 64 25 34 90
Step 2: 11 12 22 25 64 34 90
Step 3: 11 12 22 25 34 64 90
Time Complexity:
Space Complexity: O(n)
public class ShellSort {
public void shellSort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
for (int gap = n/2; gap > 0; gap /= 2) {
for (int i = gap; i < n; i++) {
int temp = arr[i];
int j;
for (j = i; j >= gap && arr[j - gap] > temp; j -= gap) {
arr[j] = arr[j - gap];
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
3. Quick sort O(n log n) average, O(n^2) worst case
First partition (pivot = 90):
[64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11] 90
Pivot: 90
Less than pivot: [64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11]
Greater than pivot: []
Second partition (pivot = 11):

11 [64, 34, 25, 12, 22] 90
Pivot: 11
Less than pivot: []
Greater than pivot: [64, 34, 25, 12, 22]
11 12 [34, 25, 22] 64 90
11 12 22 [34, 25] 64 90
11 12 22 25 34 64 90
Time complexity: O(n^2)
Space Complexity: O(n)
public class QuickSort {
public void quickSort(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
private int partition(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = low - 1;
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (arr[j] <= pivot) {
i++;
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
int temp = arr[i + 1];
arr[i + 1] = arr[high];
arr[high] = temp;
return i + 1;
}
}
II. Binary Search Tree
small: left
big: right
If = : phải nhất quán (trái hết hoặc phải hết)
first number will be the root

Case 1: Node has no children: delete directly
Case 2: Node has one child: replace the node with its child
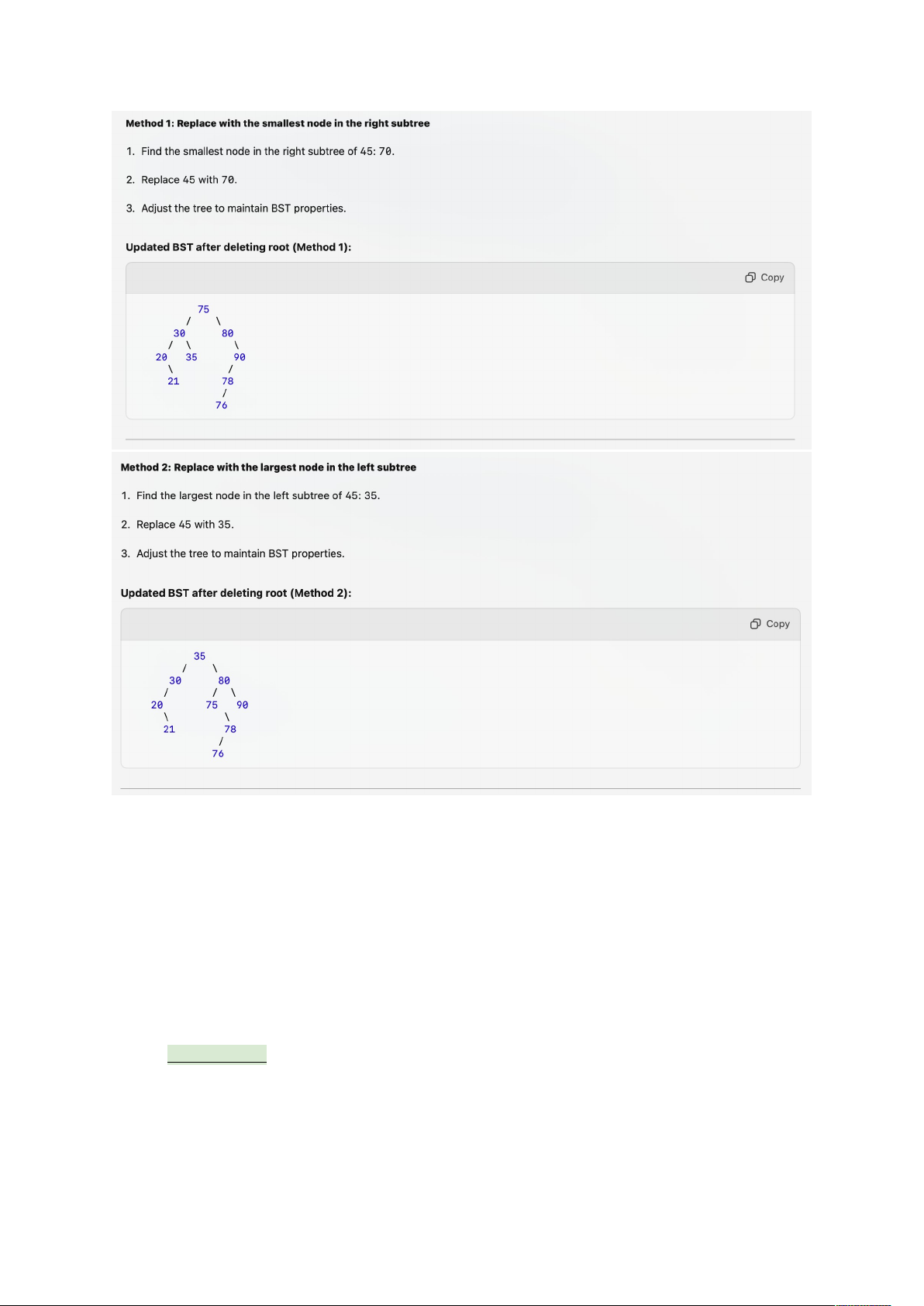
Case 3: Node has two children:
- Method 1: Replace with the smallest node in the right
- Method 2: Replace with the biggest node in the left
Explain why you should or should not ignore duplicates
● Reason to ignore (recommended)
- Based on the definition of bst: BST does not allow duplicate values and all must be
unique
- Simpler tree structure
- More efficient when sorting and deleting or inserting
● Reason not to ignore
- Application requirements: some apps need to store duplicate values, when
duplication is crucial.
Operations:
- Insert a node
// Insert a node - Duplicates are ignored
public void insert(int data) {
root = insertRec(root, data);
}

private Node insertRec(Node root, int data) {
if (root == null) {
return new Node(data);
}
if (data < root.data) {
root.left = insertRec(root.left, data);
} else if (data > root.data) {
root.right = insertRec(root.right, data);
}
// If data equals root.data, ignore duplicate
return root;
}
- Find a node
// Find a node
public boolean find(int data) {
return findRec(root, data);
}
private boolean findRec(Node root, int data) {
if (root == null) return false;
if (root.data == data) return true;
if (data < root.data) {
return findRec(root.left, data);
}
return findRec(root.right, data);
}
- Find min/max
// Find minimum value
public int findMin() {
if (root == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Tree is empty");
Node current = root;
while (current.left != null) {
current = current.left;
}
return current.data;
}
// Find maximum value
public int findMax() {
if (root == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Tree is empty");
Node current = root;

while (current.right != null) {
current = current.right;
}
return current.data;
}
- inorder/preorder/postorder traversal (for drawing binary tree)
// Inorder traversal
public void inorder() {
inorderRec(root);
}
private void inorderRec(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
inorderRec(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
inorderRec(root.right);
}
}
// Preorder traversal
public void preorder() {
preorderRec(root);
}
private void preorderRec(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
preorderRec(root.left);
preorderRec(root.right);
}
}
// Postorder traversal
public void postorder() {
postorderRec(root);
}
private void postorderRec(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
postorderRec(root.left);
postorderRec(root.right);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
}
}
// Find and print out values divisible by 5
static void findAndPrintDivisibleByFive(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (root.val % 5 == 0) {
System.out.print(root.data + " "); // Print if divisible by 5
}
findAndPrintDivisibleByFive(root.left); // Recursively check left subtree
findAndPrintDivisibleByFive(root.right); // Recursively check right subtree
}
// Print leaves
static void printLeaves(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return; // Base case: empty tree
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
System.out.print(root.data + " "); // Print if it's a leaf (no children)
return; // Important: Return after printing a leaf
}
printLeaves(root.left); // Recursively check left subtree
printLeaves(root.right); // Recursively check right subtree
}
// BFS
class BinaryTreeTraversal {
// BFS Implementation
public static void bfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
System.out.print("BFS: ");
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode current = queue.poll();
System.out.print(current.val + " ");
// Add left child to the queue
if (current.left != null) {
queue.add(current.left);
}
// Add right child to the queue

if (current.right != null) {
queue.add(current.right);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// DFS
DFS Preorder Traversal (Root, Left, Right)
// Preorder DFS Implementation
public static void dfsPreorder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// Visit the root
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
// Recur on the left subtree
dfsPreorder(root.left);
// Recur on the right subtree
dfsPreorder(root.right);
}
DFS Inorder Traversal (Left, Root, Right)
// Inorder DFS Implementation
public static void dfsInorder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// Recur on the left subtree
dfsInorder(root.left);
// Visit the root
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
// Recur on the right subtree
dfsInorder(root.right);
}
DFS Postorder Traversal (Left, Right, Root)
// Postorder DFS Implementation
public static void dfsPostorder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {

return;
}
// Recur on the left subtree
dfsPostorder(root.left);
// Recur on the right subtree
dfsPostorder(root.right);
// Visit the root
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
}
Tree: find and print out all the odd numbers in a tree, find depth,use BFS to traverse
and print out the nodes.
static void printOddNumbers(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (root.val % 2 != 0) {
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
}
printOddNumbers(root.left);
printOddNumbers(root.right);
}
static int findDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = findDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = findDepth(root.right);
return 1 + Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth);
}
static void bfsTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
System.out.print(node.val + " ");
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
- Find depth
// Find depth/height
public int findDepth() {
return findDepthRec(root);
}
private int findDepthRec(Node root) {
if (root == null) return -1;
return Math.max(findDepthRec(root.left), findDepthRec(root.right)) + 1;
}
- Delete (0/1/2 children)
// Delete a node
public void delete(int data) {
root = deleteRec(root, data);
}
private Node deleteRec(Node root, int data) {
if (root == null) return null;
// Find the node to delete
if (data < root.data) {
root.left = deleteRec(root.left, data);
} else if (data > root.data) {
root.right = deleteRec(root.right, data);
} else {
// Case 1: No children (leaf node)
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return null;
}
// Case 2: One child

else if (root.left == null) {
return root.right;
} else if (root.right == null) {
return root.left;
}
// Case 3: Two children
else {
// Find successor (smallest value in right subtree)
root.data = findMin(root.right);
// Delete the successor
root.right = deleteRec(root.right, root.data);
}
}
return root;
}
private int findMin(Node root) {
int min = root.data;
while (root.left != null) {
min = root.left.data;
root = root.left;
}
return min;
}
- Find successor
Duplicate Nodes
• If duplicates are ignored: The search only traverses the tree without
considering duplicates.
• If duplicates are allowed: Successor logic can remain unchanged, but
duplicate values could complicate finding exact successors for non-standard BSTs.
// Find successor
public Integer findSuccessor(int data) {
Node node = findNode(root, data);
if (node == null) return null;
// Case 1: Node has right subtree
if (node.right != null) {
Node current = node.right;
while (current.left != null) {
current = current.left;
}
return current.data;
}

// Case 2: No right subtree - find the ancestor where node is in left subtree
Node successor = null;
Node ancestor = root;
while (ancestor != node) {
if (node.data < ancestor.data) {
successor = ancestor;
ancestor = ancestor.left;
} else {
ancestor = ancestor.right;
}
}
return successor != null ? successor.data : null;
}
private Node findNode(Node root, int data) {
if (root == null || root.data == data) return root;
if (data < root.data) return findNode(root.left, data);
return findNode(root.right, data);
}
}
III. Hash Table
1. Linear Probing
Successful search: 1/2(1 + 1/(1-α))
Unsuccessful search: 1/2(1 + 1/(1-α)²) where α = load factor
We want to insert the keys: 10, 22, 31, 40, 55, 71
The hash function is: h(x) = x % 7
Insert 10:
• Hash: 10 % 7 = 3.
• Place 10 at index 3.
Insert 22:
• Hash: 22 % 7 = 1.
• Place 22 at index 1.
Insert 31:
• Hash: 31 % 7 = 3.
• Collision at index 3 (already occupied by 10).
• Linearly probe to the next index: index 4 is free.
• Place 31 at index 4.
Insert 40:
• Hash: 40 % 7 = 5.
• Place 40 at index 5.
Insert 55:
• Hash: 55 % 7 = 6.
• Place 55 at index 6.
Insert 71:
• Hash: 71 % 7 = 1.
• Collision at index 1 (occupied by 22).
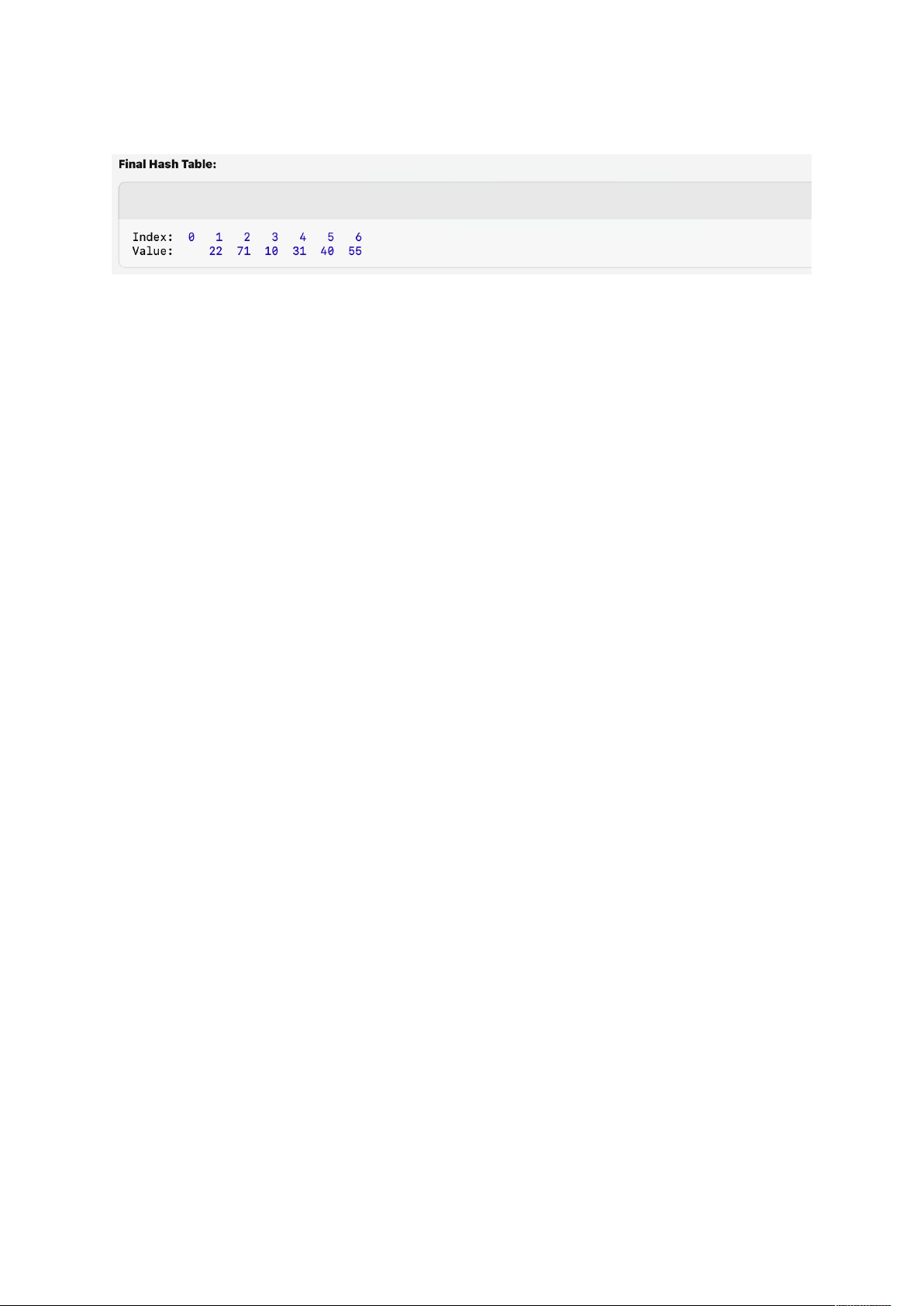
• Linearly probe: index 2 is free.
• Place 71 at index 2.
class HashTable {
private int[] table;
private int capacity;
private final int DELETED = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // Marker for deleted slots
public HashTable(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.table = new int[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
table[i] = -1; // Initialize all slots as empty (-1)
}
}
// Hash function
private int hash(int key) {
return key % capacity;
}
// Insert a key into the hash table
public void insert(int key) {
int index = hash(key);
int originalIndex = index;
while (table[index] != -1 && table[index] != DELETED) {
index = (index + 1) % capacity; // Linear probing
if (index == originalIndex) {
System.out.println("HashTable is full, cannot insert key: " + key);
return;
}
}
table[index] = key;
}
// Find a key in the hash table
public boolean find(int key) {
int index = hash(key);
int originalIndex = index;
while (table[index] != -1) {
if (table[index] == key) {
return true; // Key found
}
index = (index + 1) % capacity; // Linear probing
if (index == originalIndex) {
break;
}
}
return false; // Key not found
}

// Delete a key from the hash table
public void delete(int key) {
int index = hash(key);
int originalIndex = index;
while (table[index] != -1) {
if (table[index] == key) {
table[index] = DELETED; // Mark the slot as deleted
return;
}
index = (index + 1) % capacity; // Linear probing
if (index == originalIndex) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println("Key " + key + " not found for deletion.");
}
// Display the hash table
public void display() {
System.out.println("HashTable:");
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
if (table[i] == -1) {
System.out.println(i + ": Empty");
} else if (table[i] == DELETED) {
System.out.println(i + ": Deleted");
} else {
System.out.println(i + ": " + table[i]);
}
}
}
}
2. Quadratic Probing
Keys to insert: 10, 22, 31, 40, 55, 68, 75, 81, 93
Hash table size ( m ): 11
Hash function: h(k) = k \% m
Quadratic Probing Formula: h(k, i) = (h(k) + i^2) % m
Insert 10:
• Hash: 10 % 11 = 10 .
• Place 10 at index 10.
Insert 22:
• Hash: 22 % 11 = 0 .
• Place 22 at index 0.
Insert 31:
• Hash: 31 % 11 = 9 .
• Place 31 at index 9.
Insert 40:
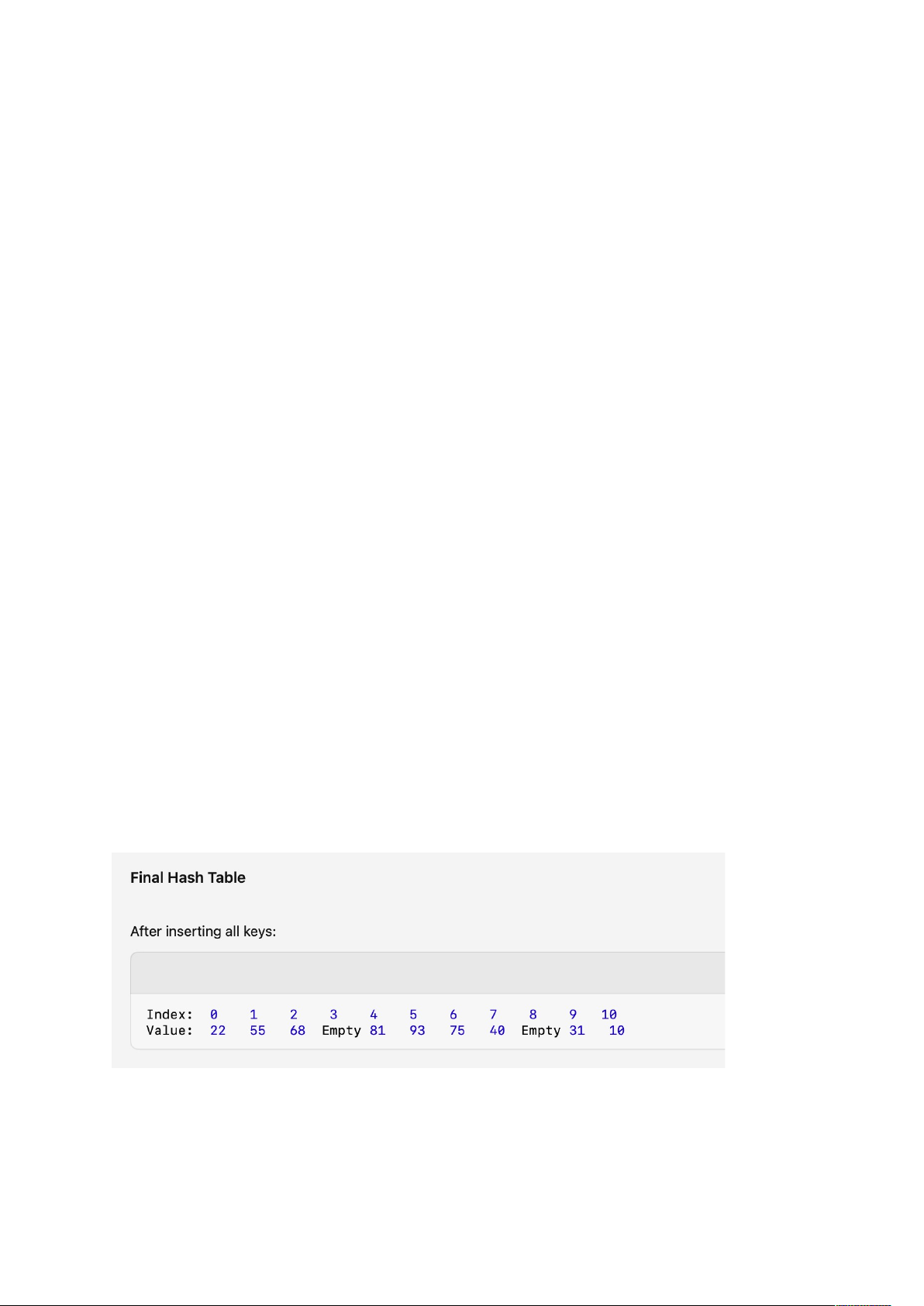
• Hash: 40 % 11 = 7 .
• Place 40 at index 7.
Insert 55:
• Hash: 55 % 11 = 0 (collision at index 0).
• Quadratic Probing:
• i = 1 : (0 + 1^2) % 11 = 1 .
• Place 55 at index 1.
Insert 68:
• Hash: 68 % 11 = 2 .
• Place 68 at index 2.
Insert 75:
• Hash: 75 % 11 = 9 (collision at index 9).
• Quadratic Probing:
• i = 1 : (9 + 1^2) % 11 = 10 (collision).
• i = 2 : (9 + 2^2) % 11 = 1 (collision).
• i = 3 : (9 + 3^2) % 11 = 6 .
• Place 75 at index 6.
Insert 81:
• Hash: 81 % 11 = 4 .
• Place 81 at index 4.
Insert 93:
• Hash: 93 % 11 = 5 .
• Place 93 at index 5.
class HashTable {
private int[] table;
private int capacity;
private final int DELETED = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // Marker for deleted slots

public HashTable(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.table = new int[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
table[i] = -1; // Initialize all slots as empty (-1)
}
}
// Hash function
private int hash(int key) {
return key % capacity;
}
// Insert a key into the hash table
public void insert(int key) {
int index = hash(key);
int i = 0;
// Quadratic probing to find an empty slot
while (table[(index + i * i) % capacity] != -1 && table[(index + i * i) % capacity] !=
DELETED) {
i++;
if (i >= capacity) {
System.out.println("HashTable is full. Cannot insert key: " + key);
return;
}
}
table[(index + i * i) % capacity] = key;
}
// Find a key in the hash table
public boolean find(int key) {
int index = hash(key);
int i = 0;
// Quadratic probing to search for the key
while (table[(index + i * i) % capacity] != -1) {
if (table[(index + i * i) % capacity] == key) {
return true; // Key found
}
i++;
if (i >= capacity) {
break;
}
}
return false; // Key not found
}

// Delete a key from the hash table
public void delete(int key) {
int index = hash(key);
int i = 0;
// Quadratic probing to locate the key
while (table[(index + i * i) % capacity] != -1) {
if (table[(index + i * i) % capacity] == key) {
table[(index + i * i) % capacity] = DELETED; // Mark the slot as deleted
return;
}
i++;
if (i >= capacity) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println("Key " + key + " not found for deletion.");
}
// Display the hash table
public void display() {
System.out.println("HashTable:");
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
if (table[i] == -1) {
System.out.println(i + ": Empty");
} else if (table[i] == DELETED) {
System.out.println(i + ": Deleted");
} else {
System.out.println(i + ": " + table[i]);
}
}
}
}
3. Separate Chaining
• Keys to Insert: 10, 21, 32, 43, 12, 35, 67
• Hash Table Size: m = 5
• Hash Function: h(k) = k % m
Insert 10:
• 10 \% 5 = 0 .
• Place 10 in the list at index 0.
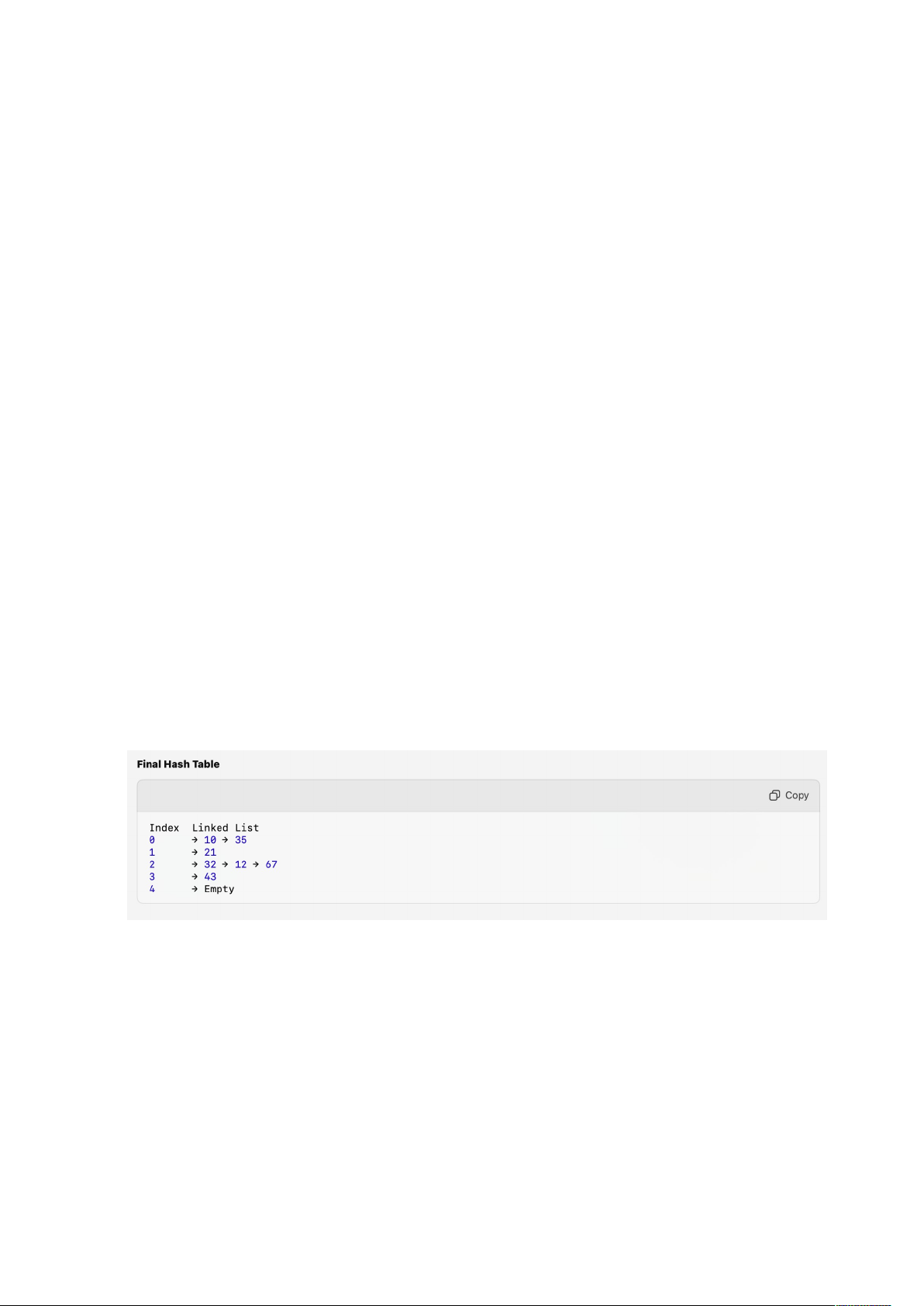
Insert 21:
• 21 \% 5 = 1 .
• Place 21 in the list at index 1.
Insert 32:
• 32 \% 5 = 2 .
• Place 32 in the list at index 2.
Insert 43:
• 43 \% 5 = 3 .
• Place 43 in the list at index 3.
Insert 12:
• 12 \% 5 = 2 (collision at index 2).
• Add 12 to the linked list at index 2.
Insert 35:
• 35 \% 5 = 0 (collision at index 0).
• Add 35 to the linked list at index 0.
Insert 67:
• 67 \% 5 = 2 (collision at index 2).
• Add 67 to the linked list at index 2.
class HashTable {
private LinkedList<Integer>[] table;
private int capacity;
// Constructor
public HashTable(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.table = new LinkedList[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
table[i] = new LinkedList<>(); // Initialize each slot with a linked list
}
}

// Hash function
private int hash(int key) {
return key % capacity;
}
// Insert a key
public void insert(int key) {
int index = hash(key);
table[index].add(key); // Add key to the linked list at the computed index
}
// Find a key
public boolean find(int key) {
int index = hash(key);
return table[index].contains(key); // Check if the key exists in the linked list
}
// Delete a key
public void delete(int key) {
int index = hash(key);
if (table[index].contains(key)) {
table[index].remove((Integer) key); // Remove the key from the linked list
} else {
System.out.println("Key " + key + " not found.");s
}
}
// Display the hash table
public void display() {
System.out.println("HashTable:");
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
System.out.print(i + ": ");
for (int key : table[i]) {
System.out.print(key + " → ");
}
System.out.println("null");
}
}
}
4. Double Hashing
Bấm Tải xuống để xem toàn bộ.