
Preview text:
SLIDE 1: DEFINITION OF L/C
A letter of credit is a document sent from a bank or financial institute that
guarantees that a seller will receive a buyer’s payment on time and for the full amount.
Letters of credit are often used within the international trade industry.
There are many different letters of credit including one called a revolving letter of credit.
Banks collect a fee for issuing a letter of credit.
(Chào iêm, Ếch đến đây từ sáng để làm slide :3) SLIDE 2: TYPES OF L/C
1. Irrevocable LC: Cannot be cancelled or modified without consent of the beneficiary.
2. Revocable LC: Can be cancelled or modified by the Bank at the customer's
instructions without prior agreement of the beneficiary.
3. Confirmed LC. In addition to the Bank guarantee of the LC issuer, this LC
type is confirmed by the Seller's bank or any other bank.
4. Transferable LC: Enables the Seller to assign part of the letter of credit to other party(ies).
5. Back-to-Back LC: Considers issuing the second LC on the basis of the first letter of credit. SLIDE 3: PROS AND CONS SLIDE 4: PROS ● For seller:
○ The seller is reassured that providing they present documents in order
and within an agreed timeframe, they will receive their money in full and on time.
○ A letter of credit is one of the most secure methods of payment for
exporters as long as they meet all the terms and conditions
○ The risk of non-payment is transferred from the seller to the bank. ● For buyer:
○ Only when the goods are actually delivered does the consignee have to
pay. The consignee can rest assured that the shipper will have to do
everything as stipulated in the L/C to ensure the shipper's satisfaction will be paid.
○ Control through requiring exporters to present documents on the
quality/quantity of goods issued by an independent inspection agency. SLIDE 5: CONS - Costly. - Sensitive expiration dates.
- Require amendments if there’re any changes,thereby delaying the transaction.
- The reliability of payment under the L/C is dependent on the issuing bank.
SLIDE 6: PROCESS (nhi) (in đậm bỏ dô slide)
Step 1: open Letter of credit
Step 2: send draft to Advising bank
Step 3: Send LC to the seller to check the information Step 4: Delivery
Step 5: The seller sends the document to AdviDocument sing bank
Step 6: The document is sent to Issuing bank (recheck-correct and full information)
Step 7: Ask the buyer to pay money (70%) and receive a set of documents
Step 8: Advising bank receive money from buyer
Step 9: Money is transferred to the bank account Nghi:
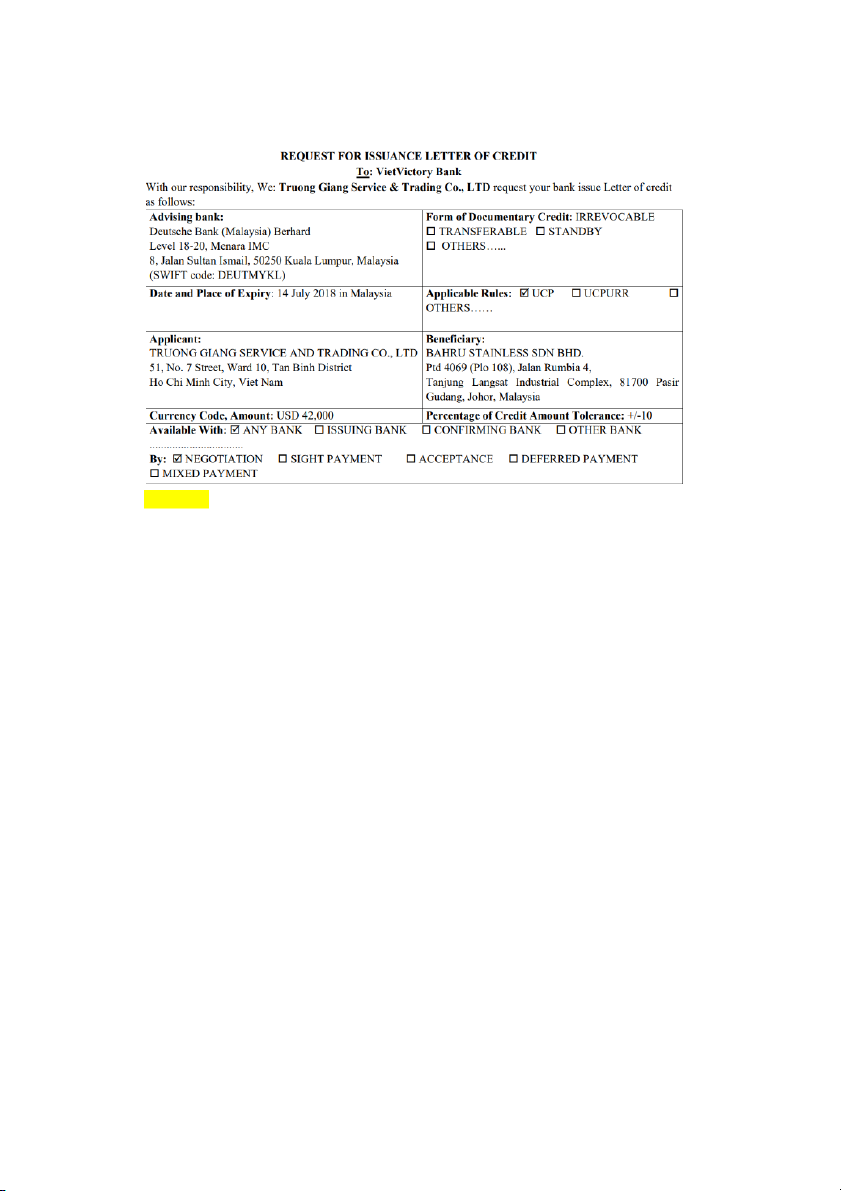
SLIDE 1: LETTER OF CREDIT (OR DOCUMENTARY CREDIT) APPLICATION SLIDE 2: Highlight màu vàng: - Date of Place of Expiry
- Currency Currencycode, Amount
Chú thích = cách khoanh tròn rồi chĩa mũi tên ra ngoài:
- Khoanh SWIFT code: also called a BIC number, identifies banks and financial
institutions globally (contains 8-11 character code that identifies country, city, bank, and branch)
- Khoanh Form of Documentary Credit: An irrevocable LC guarantees the
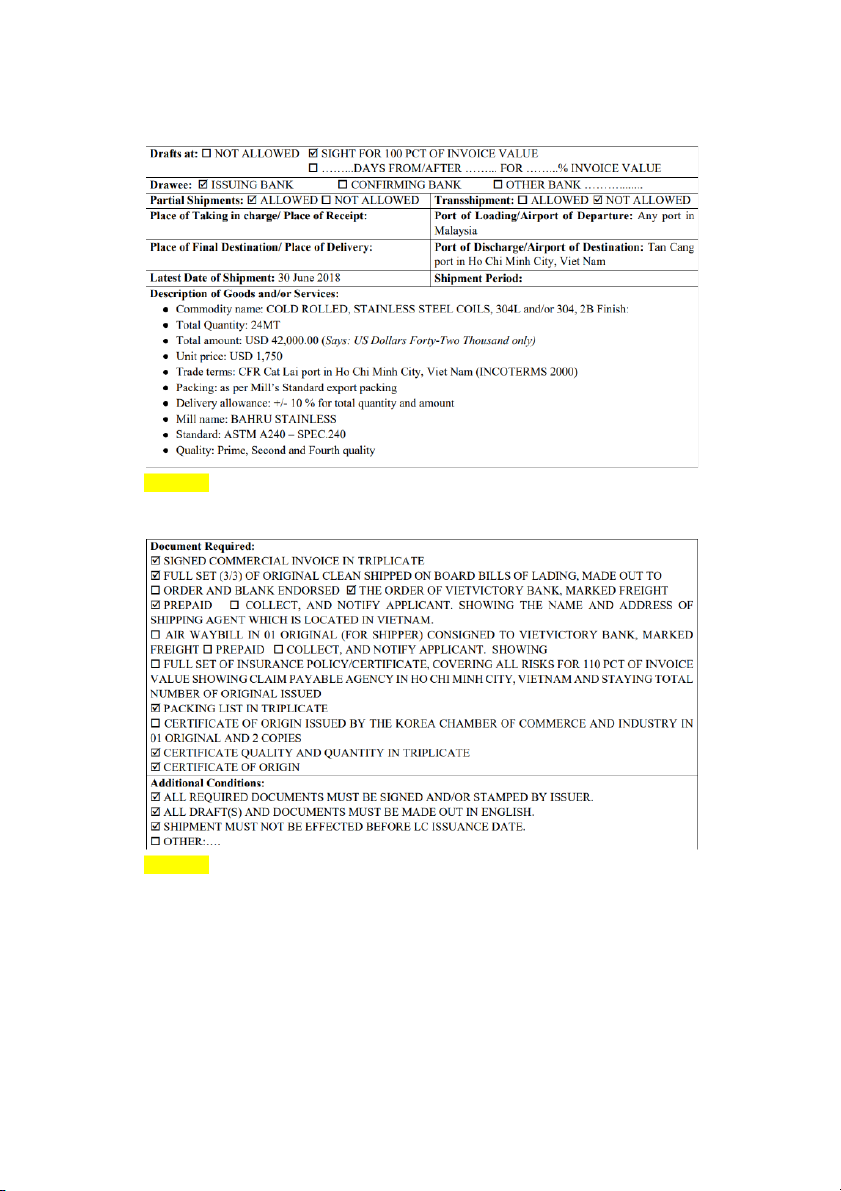
seller's rights (Issuing bank is responsible for paying the seller within the validity period). SLIDE 3: Highlight màu vàng: - Latest Date of Shipment
- Description of Goods and/or Services
Chú thích = cách khoanh tròn rồi chĩa mũi tên ra ngoài:
- Khoanh Latest Date of Shipment: must be within the validity period of the L/C
and must not coincide with the validity expiration date of the L/C, and must be
a reasonable time after the L/C opening date
- Khoanh Drawee: This section usually records the SWIFT code and detailed
information of the issuing bank (VVTBVNVX) SLIDE 4:
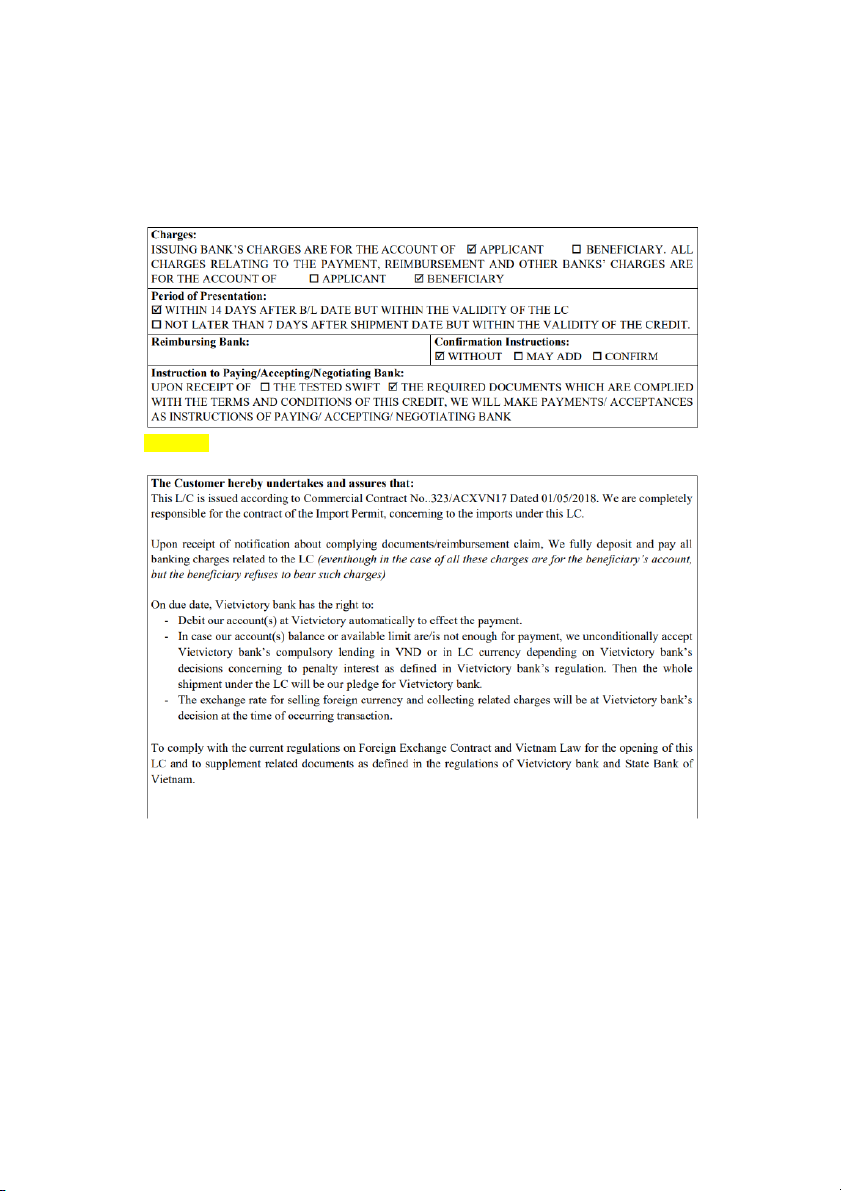
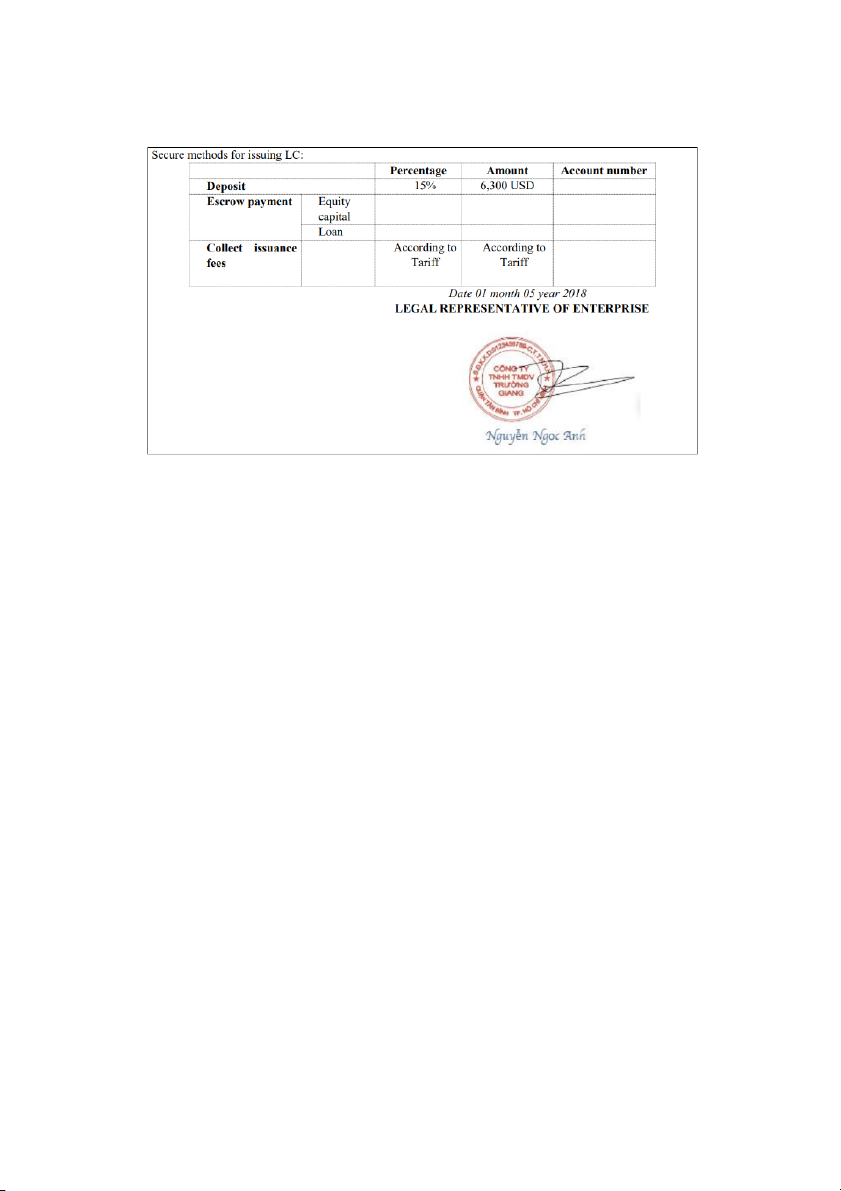
Highlight: Document Required SLIDE 5:
Highlight: Period of Presentation
Chú thích = cách khoanh tròn rồi chĩa mũi tên ra ngoài: -
Noted: If not specifically specified, according to article 14c of UCP 600: L/C
Issuing bank will refuse documents presented after 21 days from the date of delivery. SLIDE 6:




