





















































Preview text:
PORTFOLIO
Course: READING & WRITING 2
Course timing: September – December 2023
Textbook: Skillful Reading and Writing 4
Instructor: Tran Thi Khanh Tung GROUP 6 Class: LT_02 UNIT 1: GATHERING Discussion point
1. Which statistic in the infographic surprises you the most? Why?
In the graphic, the information that surprised me the most was that less than 20%
of Americans use click buttons to make purchases on social networks. Because, for
a developed country like America, social networks are not strange, but people do
not use them as much as possible in online shopping. For my country, which has a
less developed economy and social networks have only become essential in recent
years, I see that people now buy things online very popularly.
2. How has social media influenced or changed shopping habits?
Social networks have a huge impact on shopping: they change people's shopping
habits and thinking. Shopping becomes easier when you just need to sit at home
and click on the item you want to buy, this is very convenient and makes us less
effortful when going out to buy directly and that makes us happy. we are more comfortable
3. Do you find targeted advertising on social media useful or invasive? Why?
The usefulness or invasiveness of targeted advertising on social media can vary
depending on individual preferences and experiences. In my opinion, it’s invasive.
Targeted advertising relies on collecting and analyzing user data, which can raise
privacy concerns for some individuals. The extent of data collection and how it is used can be seen as invasive. Before you watch 1b 2d 3a 4c While you watch 1F 2F 3T 4F 5T After you watch 1. Yes, it brings many useful 2. I will consequence it
3. Not very favorable due to climate, weather, and road conditions
READING 1: The rise of crowding Summary:
Crowdfunding vs. Venture Capital:
Crowdfunding: bypasses traditional investors, reaches a wider audience, suitable
for smaller projects (69% raise under $10,000), 35% success rate, relies heavily on social networks.
Venture Capital: offers larger investments, expertise, and support, better suited for
large projects or those needing guidance.
Launching a Successful Campaign:
Be realistic: Understand average funding levels (3% raise over $100,000), accept the 65% failure rate.
High-quality perception: Invest in a well-produced video pitch, emphasize frequent
updates, showcase professionalism.
Leverage networks: 30% of funding comes from friends and family, tap into your
social circles for initial momentum.
Campaign Types and Rewards:
Lending/Donation: philanthropic, for research or humanitarian projects.
Equity: offer investors company shares in exchange for funding.
Reward-based: most common, provide backers with the product itself or related
experiences (limited editions, merchandise).
Tiered rewards: offer different investment levels with varying benefits to attract diverse contributors. Funding Models:
Keep-it-all: entrepreneurs keep all investments regardless of reaching the target
(riskier, perceived as less trustworthy).
All-or-nothing: investors get their money back if the target isn't reached (safer, more successful).
Overall: Crowdfunding offers a dynamic alternative for entrepreneurs, but
understanding its limitations, crafting a compelling campaign, and utilizing
social networks effectively are crucial for success. A. Vocabulary preview Words Transcription MeaningVN Meaning Example Backers (n) /ˈbæk.ɚ/ (Người ủng someone who I was looking hộ) gives financial supp for a backer to ort to something assist me in the attempted buyout. Crowdfunding / (Huy động the practice of The project was (n) kra ˈ d.f ʊ n.d ʌ ɪŋ/ vốn từ cộng getting a large financed đồng, gây number of people through quỹ) to each give small crowdfunding. amounts of money i n order to provide th e finance for a project, typically u sing the internet Entrepreneur /ˌɑːn.trə.prə (Doanh nhân) Someone who This next (n) n ˈ / ɝː starts their own famous
business, especially entrepreneur when this involves was a high seeing a new school dropout. opportunity Equity (n) /ˈek.wə.ti/ (Công bằng) the value of To capture her
a company, divided equity, Linda into many equal must either sell parts owned by or refinance. the shareholders, or one of the equal parts into which the value of a company is divided Philanthropic /ˌfɪl.æn (Từ thiện)
helping poor people, Many (adj) θr ˈ ɑː.pɪk/
especially by giving philanthropic them money institutions were founded. Start-up (phr (Bắt đầu, If a business or Fine, I thought I v) khởi nghiệp)
other organization st would start up arts up, or if stairs today. someone starts one up, it is created and starts to operate Tangible (adj) /ˈtæn.d ə.bəl/ ʒ (Hữu hình) real and not I put less hope imaginary; able to in tangible
be shown, touched, things, but in or experienced thoughts and words. Venture (liên doanh the activity of The deal made capital (n) vốn) lending money to record returns someone to start a for venture new business, capital backers. especially one that involves risks a nd will make large profits if successful bypass /ˈba .p ɪ ɑːs/
đường vòng/ avoid something by We took the lách luật going around it road that bypasses the town notable /ˈnə .tə.bəl/ ʊ đáng chú ý important and What are your deserving attention notable strengths? merchandise
/ˈmɜː.tʃən.daɪz/ hàng hoá goods that are Shoppers bought and sold complained about poor quality merchandise and high prices
Complete the sentences with the words in the box 1. Entrepreneur 2. Venture capital 3. Start-up 4. Equity 5. Crowdfunding 6. Backers 7. Tangible 8. Philanthropic B. Before you read 1.
There are several key factors that have contributed to the rise of crowdfunding as a
popular means of gaining investment:
Accessibility and democratization: Crowdfunding platforms provide direct
access to a vast pool of potential investors, bypassing traditional gatekeepers
like venture capitalists. This opens up opportunities for diverse projects and
entrepreneurs who might not fit the mold of typical venture capital investments.
Lower barriers to entry: Compared to traditional funding methods,
crowdfunding requires less upfront capital and paperwork, making it more
accessible for startups and individuals with limited resources. This allows
small ventures and creative ideas to get off the ground without significant financial hurdles.
Community engagement and validation: Crowdfunding campaigns foster a
sense of community and engagement around the project. Backers feel like
they're not just investing, but actively participating in the creation and
success of something they believe in. This community involvement can
generate valuable feedback and build brand loyalty.
Viral potential and media reach: Effective crowdfunding campaigns can go
viral through social media and online engagement, generating significant
media attention and boosting project visibility. This organic reach can attract
even more investors and supporters beyond the initial platform audience. 2.
High-quality presentation: Invest in a professional video pitch that visually
explains your project and grabs attention within seconds. Create a well-
designed campaign page with clear details, captivating visuals, and transparent communication.
Realistic goals and budget: Set achievable funding targets based on your
project's needs and average funding levels in your category. Overly
ambitious goals can deter potential backers, while underestimating needs can compromise the final product.
Engaging rewards and tiers: Offer attractive rewards (copies of the product,
exclusive experiences, limited editions) at different investment levels to
cater to diverse budgets and motivations. Tiered systems increase
accessibility and attract a wider range of backers.
Strong social media presence: Leverage social media platforms to spread the
word, build hype, and engage with potential backers. Share updates, answer
questions, and cultivate a community around your project.
Authenticity and transparency: Be genuine, passionate, and honest about
your project's strengths and weaknesses. Communicate openly with backers,
address their concerns, and provide regular updates throughout the campaign and beyond. C. Global reading 4a 3b 1c 6d 5e 2f D. Close reading 1. Geography 2. Smaller 3. Early 4. Network 5. Tiers 6. Riskier E. Critical thinking
Instead, let's consider some broader observations about funding access:
Traditional investment structures: These have historically favored established
businesses and industries, often overlooking ventures led by women or minorities
due to unconscious biases and a lack of representation in decision-making roles.
Crowdfunding: This presents a more democratized approach, offering access to a
wider pool of potential investors beyond traditional gatekeepers. This can benefit
projects led by diverse individuals, including women, as it relies on broader appeal
and potential for public engagement.
However, it's important to avoid oversimplification:
Individual factors: Regardless of gender, success in attracting any type of
investment hinges on the merits of the business idea, the competence of the team,
and the ability to present a compelling case.
Evolving landscape: Both traditional and alternative funding structures are
constantly evolving, with a growing awareness of the need for diversity and
inclusion in investment decisions. READING 2:
Are online “friends” a threat to development? Summary: Childhood Friendships:
Crucial for emotional development, building trust, compromise, and conflict resolution.
Provide support and feedback for identity exploration and growth. Technology's Impact:
Debates about negative effects on friendship due to online connections.
Research shows socially adjusted teens engage more with social media,
highlighting its potential to complement real-world relationships and offer diverse connections.
Virtual friendships contribute social benefits and well-being.
Concerns of a Hyper-Connected World:
Potential downsides of excessive social media use: narcissism, reduced empathy, and lack of self-reflection.
Professor Rosen's research in "iDisorder" suggests young people may become vain,
aggressive, and display antisocial behavior.
College students exhibit a 40% decline in empathy compared to 30 years ago,
raising concerns about future relationships.
Sherry Turkle observes the "alone together" phenomenon, where constant mobile
engagement hinders real connection and self-reflection.
Recommendations for Nurturing Development:
Focus on fostering healthy face-to-face friendships while guiding children in modifying online behavior.
Address potential negative effects like narcissism and reduced empathy to ensure balanced social development. Overall message:
While technology offers new ways to connect, real-world friendships remain
essential for healthy development. Guide children to navigate both worlds safely
and prioritize genuine human connection while mitigating potential drawbacks of the hyper-connected age. A. Vocabulary preview New words Phonetics Meaning VN Meaning Examples ENG excerpt (n) / ek.s ˈ ɜːpt/ đoạn trích a short part An excerpt taken from a from her new speech, book, thriller will film, etc. appear in this weekend's magazine. compromise / thỏa hiệp an agreement It is hoped that (n) k ˈ m.prə.ma ɒ z/ ɪ in an argument a compromise in which the will be reached people in today's involved talks. reduce their demands or change their opinion in order to agree much-debated /mʌtʃd be ɪˈ t/ ɪ
gây tranh cãi a topic or issue The potential (adj) nhiều has been health risks discussed or associated with argued about a vaping is much lot debated. meteoric (adj) / mi ˌ ː.ti r. ˈɒ ɪk/ Nhanh chóng, used to The group had vượt bậc describe a meteoric rise something that to fame in the develops very 70s. fast and attracts a lot of attention Advancement /əd sự tiến bộ the All she was (n) v ˈ ɑːns.mənt/ development interested in or was the improvement advancement of something of her own career. empirical (adj) / m ɪ p ˈ r. ɪ ɪ.kəl/ thực nghiệm based on what This theory is experienced needs to be or seen rather backed up with than on theory solid empirical data/evidence. differentiate / d ˌ f.ə ɪ phân biệt to show or We do not (v) ren. ˈ i.e ʃ t/ ɪ find the differentiate difference between our between things employees on that are the basis of compared their race, religion, or national origin. fiction (n) / f ˈ k. ɪ ən/ ʃ hư cấu the type of The book is a book or story work of fiction that is written and not about intended as a imaginary historical characters and account. events and not based on real people and facts unfounded /ʌnˈfaʊn.d d/ ɪ vô căn cứ If a claim or Our fears (adj) piece of news about the is unfounded, weather it is not based proved totally on fact unfounded. adjusted (adj) /əˈd st/ ʒʌ
được điều to be change it is socially chỉnh something adjusted slightly, adolescents especially to who are more make it more likely to have a correct, social effective, or networking suitable profile adolescent (n) / æd. ˌ ə les.ənt/ ˈ thanh niên a young "many parents person who is find it hard to developing understand into an adult their adolescent children" substitute (v) / s ˈ b.st ʌ .t ɪ ʃu t/ ː thay thế to use He made his something or film debut someone when he was instead of substituted for another thing the actor who or person was originally cast. companions /kəm pæn.jən/ ˈ
người bạn a person you The dog has (n) đồng hành spend a lot of been her time with often constant because you companion are friends or these past ten because you years. are travelling together evolve (v) / v ɪˈ lv/ ɒ phát triển to develop Did humans gradually, or to evolve from cause apes? something or someone to develop gradually acquaintance /ə kwe ˈ n.təns/ ɪ người quen a person that a business (n) you have met acquaintance but do not know well ties (n) /ta /ɪ quan hệ the friendly Family ties are feelings that weaker if you people have move a long for other way away. people, or special connections with places hyper- / hīpərkə ˌ siêu kết nối characterized "in our connected nektəd/ ˈ by the hyperconnecte (adj) widespread or d world, habitual use of employees devices that expect to work have internet from connectivity. anywhere" narcissists (n) / n ˈ .s ɑː .s ɪ st/ ɪ
người ái kỷ someone who "narcissists người tự ái has too much who think the admiration for world revolves himself or around them" herself vain (adj) /ve n/ ɪ vô ích unsuccessful; The doctors of no value gave him more powerful drugs in the vain hope that he might recover. aggressive /ə res. ˈɡ v/ ɪ hung hăng showing anger The stereotype (adj) and a is that men willingness to tend to be attack other more people aggressive than women. mean-spirited ˈmin sp ˈ r ɪ t ɪ d ɪ xấu tính characterized While most are (adj) by or supportive, a displaying a fair number are propensity to critical, even be mean; mean-spirited. selfish, malicious, etc disturbing /də stərbiNG/ ˈ lo ngại causing (adj) anxiety; worrying. "disturbing unemployment figures" repercussion / ri ˌ .pə ː k ˈ .ən/ ʌʃ hậu quả the effect that President (n) an action, Kennedy's event, or assassination decision has on had far- something, reaching especially a repercussions. bad effect empathy (n) /ˈem.pə.θi/ sự đồng cảm the ability to He loves share someone children and else's feelings has a certain or experiences empathy with by imagining them. what it would be like to be in that person's situation empathetic / em.pə ˌ θet. ˈ k/ ɪ đồng cảm having the a kind and (adj) ability to empathetic imagine how friend someone else feels decline (v) /d kla ɪˈ n/ ɪ suy giảm to gradually His interest in become less, the project worse, or declined after lower his wife died. eradicate (v) / ræd. ɪˈ .ɪkeɪt/
diệt trừ, loại bỏ to get rid of The something government completely or claims to be destroy doing all it can something bad to eradicate corruption. self-reflect tự suy ngẫm the activity of He seems to (adj) thinking about be incapable of your own self-reflection. feelings and behaviour, and the reasons that may lie behind them frustration (n) /fr s ʌ ˈtre . ɪ ʃən/ sự thất vọng the feeling of I could sense being annoyed his frustration or less at not being confident able to help. because you cannot achieve what you want, or something that makes you feel like this disconcerting / d ˌ s.kən ɪ lo ngại making His message is (adj) s ˈ ɜː.tɪŋ/ someone feel deeply uncertain and disconcerting uncomfortable for anyone or worried who values democracy. foster (v) / f ˈ s.tə ɒ r/
bồi dưỡng, to take care of Would you nuôi dưỡng a child, usually consider for a limited fostering (a time, without child)? being the child's legal parent tendency (n) /ˈten.dən.si/
xu hướng, If someone His tendency khuynh hướng has a tendency to exaggerate to do or like is well known. something, they will probably do it or like it modify (v) / m ˈ d. ɒ ɪ.faɪ/ biến đổi to change Instead of something simply such as a plan, punishing opinion, law, them, the or way of system behaviour encourages slightly, offenders to usually to modify their improve it or behaviour. make it more acceptable well-adjusted
/ˌwel ə điều chỉnh tốt A well a quiet, well- (adj) ˈd s.t ʒʌ ɪd/ adjusted adjusted man person is reasonable and has good judgment and their behaviour is not difficult or strange B. Before you read
Advantages and Disadvantages of Social Media for Young People: Advantages:
Connection and communication: Social media allows young people to connect
with friends and family, both near and far, fostering a sense of belonging and
community. It provides platforms for communication, sharing experiences, and offering support.
Information and learning: Social media offers access to a vast amount of
information on various topics, potentially fostering curiosity and expanding
knowledge. It can connect young people with educational resources, diverse
perspectives, and opportunities for learning beyond traditional classroom settings.
Entertainment and relaxation: Social media offers various forms of entertainment,
from games and videos to memes and online communities. It can be a source of
relaxation, stress relief, and enjoyment for young people. Disadvantages:
Privacy concerns and data breaches: Sharing personal information on social media
raises concerns about privacy and data breaches. Young people may be unaware of
the risks of online sharing and vulnerable to exploitation or identity theft.
Addiction and excessive use: Social media can be highly addictive, leading to
excessive screen time and neglecting real-world interactions, hobbies, and
responsibilities. This can impact sleep, academic performance, and personal relationships.
Unrealistic comparisons and social pressure: Social media often presents carefully
curated and idealized versions of life, which can lead to feelings of inadequacy,
low self-esteem, and social pressure to conform to unrealistic beauty standards or lifestyles. C. Global reading
2. There are advantages to having online friends.
4. Social networking is changing young people’s personalities D. Close reading 1b 2d 3a 4c E. Critical thinking 1. Benefits:
Connection and Belonging: Social media can foster connection with friends,
family, and like-minded individuals, combatting loneliness and promoting a sense
of belonging. This can positively impact mental health by providing support,
reducing stress, and boosting self-esteem.
Information and Support: Social media platforms offer access to information and
support groups related to mental health issues, reducing stigma and offering
valuable resources for coping and recovery.
Identity Exploration and Expression: Social media can provide a safe space for
exploring and expressing identities, building confidence, and connecting with
communities for validation and acceptance. Drawbacks:
Cyberbullying and Harassment: Online harassment and bullying can lead to
anxiety, depression, and other negative mental health consequences. The
anonymity and disinhibition effect online can exacerbate these issues.
Social Comparison and FOMO: Exposure to curated and idealized online
portrayals can lead to feelings of inadequacy, social pressure, and fear of missing
out (FOMO), negatively impacting self-esteem and mental well-being.
Addiction and Excessive Use: Excessive social media use can displace real-world
interactions, hobbies, and responsibilities, leading to isolation, sleep problems, and decreased life satisfaction. 2. Potential Negative Impacts:
Reduced Empathy and Compassion: Overreliance on online interactions and focus
on digital personas can weaken real-world social skills and reduce empathy for others' experiences.
Increased Narcissism and Antisocial Behavior: Some studies suggest excessive
social media use might correlate with narcissistic tendencies and aggressive behavior offline.
Erosion of Attention Span and Critical Thinking: Constant multitasking and
exposure to short-form content online may negatively impact attention span and critical thinking skills. Potential Positive Impacts:
Increased Awareness and Activism: Social media can raise awareness about social
issues and mobilize individuals for positive change, fostering civic engagement
and a sense of global community.
Promoting Creativity and Self-Expression: Social media platforms provide avenues
for sharing talents, artistic endeavors, and unique perspectives, enhancing
creativity and self-expression.
Networking and Building Bridges: Connecting with diverse individuals and
communities online can broaden perspectives, challenge biases, and promote cross- cultural understanding. 3. Young People:
Limit screen time and practice digital detox.
Be mindful of content consumed and cultivate critical thinking skills.
Prioritize real-world interactions and maintain healthy offline relationships.
Report cyberbullying and seek support if needed. Parents:
Open communication and set clear boundaries for social media use.
Educate children about online safety and privacy risks.
Monitor online activity without invading privacy.
Encourage alternative activities and real-world social interaction. Schools:
Digital literacy and cyberbullying prevention programs.
Promote healthy technology use and responsible online behavior.
Provide support systems for students struggling with online issues.
Model responsible technology use within the school community. Government:
Regulation of social media platforms and content moderation policies.
Mental health resources and support for online issues.
Promoting public awareness campaigns about healthy technology use.
Investing in digital literacy education and cybercrime prevention. VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT Words Transcription Meaning Example Included / n ɪ klu ˈ ː.dɪd/ containing something Please make sure all (adj) as a part of something necessary documents else, or making something are included in the part of something else submission. (Bao gồm) Developmen /dɪ the process in which Continuous learning t (n) vel.əp.mənt/ ˈ someone or something and skill development grows or changes and are essential for becomes more advanced personal and (Phát triển) professional growth Ask for /æsk/ to say that you would Can I ask for your someone like to see or speak to opinion on this (phr v) someone (Nhờ ai đó) matter? Shown (v) /ʃo n/ ʊ Trình diễn The graph shown
indicates a significant increase in sales over the past year. Part (n) /pɑːrt/
mostly or usually (chủ yếu) I am proud to be a part of this amazing team Effect (n) /əˈfekt/ To produce or achieve The medication had a the results you want (để positive effect on her sản xuất) overall well-being. Happening /ˈhæp.ən.ɪŋ/ something that has What's happening at (n) happened (Đang xảy ra) the party tonight? Let (v) /let/ used after a negative Let me know if you statement to emphasize need any assistance. how unlikely a situation is because something much more likely has never happened (Cho phép) Decide (v) /d sa ɪˈ d/ ɪ to be the reason or I need to decide which situation that makes
restaurant to go to for a particular result dinner. happen (Quyết định) Remove (v) /rɪˈmuːv/ to force someone I need to remove the to leave an important stains from the fabric job or a position of power because they have behaved badly or not in a way you approve of (Di dời) States firmly The teacher states firmly that cheating
will not be tolerated in the classroom. Worrying /ˈw .i. ɝː ŋ/ ɪ making you feel unhappy I find the current (adj) and frightened (Lo lắng) situation very worrying. 1. 1. Comprised 2. Advancements 3. Seek 4. Proven 5. Element 6. Repercussion 7. Occurring 8. Permit 9. Determine 10.Eradicate 11.Asserts 12.Disconcerting
2. Replace the underlined words with the more formal synonyms in the box. 1. Repercussion, disconcerting 2. Permits to, distant 3. Element, establish 4. Are able to, seek, diverse 5. Comprehend, gravity ACADEMIC WORDS Words Transcription Meaning Example Aid (n) /e d/ ɪ A piece of She has no sense for equipment that first aid, either. helps you to do something (Sự giúp đỡ) Differentiate /ˌd f.ə ɪ ren. ˈ ʃi.eɪt/ To show or find It’s important to (v) the difference differentiate between
between things that the two concepts. are compared (Phân biệt) Empirical /emˈpɪr.ɪ.kəl/ Based on what is His method was (adj) experienced or
empirical, and the laws
seen rather than on which he established theory (Thực were generally the nghiệm) result of repeated experiment. Evolve (v) / v ɪˈ lv/ ɑː To develop
It took millions of years gradually, or to for early hominids to
cause something or evolve into modern someone to man. develop gradually (Tiến hóa, phát triển) Modify (v) /ˈm .də.fa ɑː /ɪ To change We may modify his
something such as arrangement as follows. a plan, opinion, law, or way of behavior slightly, usually to improve it or make it more acceptable (Biến đổi) Perception /pəˈsep.ʃən/ A belief on Dean smiled at the (n)
opinion, often held young lady’s by many people perception. and based on how things seem (Sự nhận thức) Pursue (v) /pɚˈsuː/ To follow s.o or
I really want to pursue sth, usually to try
this, but I don’t know to catch him, her, how or it (Theo đuổi) Resolve (v) /r z ɪˈ lv/ ɑː To solve or end a
In spite of her resolve, problem or she responded. difficulty (Giải quyết)
1. Complete the questions with words from Ex 1. Change the form if necessary 1. Pursue 2. Aids 3. Resolve 4. Empirical 5. Differentiate 6. Modify 7. Perceptions 8. Evolve CRITICAL THINKING
1. Advancement in mobile technology and social networking websites mean we
spend more time online than ever before.
2. The biggest criticism leveled at social networking is that young people are
losing their offline friends to online friends… these criticisms are generally unfounded.
3. A study conducted by Michigan State University provide social benefits and
friendships provide social benefits and improve our psychological well-being.
4. Pr. Larry D. Rosen, in his book iDisorder, presents evidence that social
networking is turning us into narcissists
5. She has noticed that these devices permit us to have complete control over our
friendships… Young people device who they communicate with, when and how…
6. It appears that people are no longer comfortable being alone…
7. The impact of “being alone together” is one that should concern parents GRAMMAR
1. Match (1-6) to (a-f) to concede or contrast idea. 1d 2c 3e 4a 5f 6b
2. Write sentences giving your opinions on the topics in bold, using the prompts
provided and the words in parentheses.
1. Even though mobile phones are necessary for the safety of children as they
allow parents to constantly check in, too much screen time at an early age
can be dangerous for their health.
2. Although smartphones used in school can distract pupils, they can very
much enhance those pupil’s learning.
3. In spite of the fact that some apps can aid our sleep, smartphones and other
devices are more likely to disrupt our sleep, especially when we forget to turn them off at night.
4. It is true that the use of social media by employees in the workplace can
reduce their productivity. Nevertheless, the ability to communicate faster
with others increases productivity.
5. Despite the privacy issues that social media raises, the benefits from using it are far greater.
Question multiple choice
1.Which word is antonym with the word "danger" in the following words? A. Peaceful B. Peril C. Safety ** D. Security
2. Which of the following words can we replace the word "changing" with? A. Modifying** B. Showing C. Demonstrating D. Replacing
3.Which word is synonymous with the word “cognition”in the following word? A. Perception ** B. Knowledge C. Greenness D. Inexperience
4. Which of the following words can replace the word “product” in the sentence:
“One of the company's products was recalled for contamination”? A. Trade B. Merchandise** C. Retail D. Handle
5. Which word is synonymous with the word “ Supporter” in the sentence: “We need
financial supporter for the project” ? A. Critic B. Rival C. Backer*** D. Opponent UNIT 2: GAMES Discussion point
1. Do you think video games have a positive impact on children in your country? Why / why not?
The impact of video games on children in a country can vary depending on
multiple factors. While some argue that video games can have positive
effects, such as improving cognitive skills, problem-solving abilities, and
hand-eye coordination, others express concerns about potential negative
impacts. These may include excessive screen time, sedentary behavior, and
potential desensitization to violence. It is important to consider the content
of the games, the amount of time spent playing, and the balance with other
activities and responsibilities.
2. Do you think video games are socially isolating? Why / why not?
The social impact of video games is a topic of debate. Some argue that video
games can be socially isolating as excessive gaming may lead to reduced
face-to-face interactions and decreased participation in offline social
activities. On the other hand, online multiplayer games can provide
opportunities for social interaction and collaboration with other players,
fostering teamwork and communication skills. The extent of social isolation
or engagement depends on the individual's gaming habits and the balance
maintained between virtual and real-life social interactions.
3. What effects do video games have on academic performance and health?
The effects of video games on academic performance and health can vary.
Excessive gaming can potentially lead to poorer academic performance if it
interferes with study time, sleep patterns, or other essential activities.
Additionally, prolonged sitting and sedentary behavior associated with
gaming can contribute to a sedentary lifestyle, which may impact physical health negatively. Before you watch 1. d 2. c 3. a 4. b While you watch
1. F (It will rise to $45 billion over the next 3 years.) 2. T 3. T
4. F (Despite their increasing market share, mobile games form only a small
part of this ever-popular industry).
READING 1: Instant satisfaction Summary:
The report highlights the exponential growth of streaming and on-demand
services, attributing it to improved internet connectivity. The origins of
streaming can be traced back to the early 80s when the hacking community
used it for file sharing. Over the years, video-sharing sites have transformed
media consumption. The shift away from physical media is evident, with the
music industry experiencing a significant decline in physical sales and a rise
in digital consumption. Online subscription video and on-demand TV
services, such as Amazon Prime and Netflix, have also seen a surge in
popularity. YouTube remains the leading video-sharing site globally.
Generational differences exist, with younger individuals favoring digital
platforms, while older individuals still consume traditional broadcast
television. The video game sector still sees physical sales dominating, but
cross-platform games and in-game purchases are expected to drive growth.
Overall, digital media sales are surpassing physical sales in many industries,
and the trend is likely to continue, particularly with the younger generation's
preference for digital formats. A. Vocabulary preview Words Transcription Meaning Example subscription(v) /səbˈskraɪb/ to pay money to She subscription
an organization in to several
order to receive a women’s product, use a magazines service regularly, or support the organization (đăng ký) dominate (v) /ˈd m. ɒ .ne ɪ t/ ɪ To have control They work as a over a place or group – no one person (thống trị) person is allowed to dominate norm(n) /nɔːm/ An accepted Europe’s varied
standard or a way cultural, political of behaving or and ethical norms doing things that most people agree with (chuẩn mực) staggering(adj) / stæ ˈ . ə r. ɡ ŋ / ɪ Very shocking It costs a and surprising staggering (sửng sốt) $50,000 per week to keep the museum open to the public embrace(v) / m ɪ bre ˈ s / ɪ To accept this was an something opportunity that enthusiastically he would (ôm ấp) embrace sector(n) /ˈsek.tər/ One of the areas The country has a into which the new policy of
economic activity transferring state of a country is industries from
divided (lĩnh vực) the public sector to the private sector feasible(adj) /ˈfiː.zə.bəl/
Able to be made, With the extra
done, or achieved resources, the (khả thi) project now seems feasible Consumption(n) / kənˈs mp. ʌ ə n / ʃ
The amount used We need to cut or eaten (sự tiêu down on our fuel thụ) consumption by having fewer cars on the road Exponential /ˌek.spəˈnen.ʃəl/
An exponential rate We are looking of increase for exponential becomes quicker growth in our and quicker as the investment thing that increases becomes larger (lũy thừa) Exemplify /ɪɡˈzem.plɪ.faɪ/ To be or give a This painting
typical example of perfectly something (nêu exemplifies the gương) naturalistic style which was so popular at the time. Vinyl / va ˈ .nəl/ ɪ Strong plastic that Today's music can be bent, used lovers growing for making floor up with iPods coverings, may never know
furniture, clothing, the sound of etc., or (especially in the past) records vinyl. (chất nhựa) Pensioner /ˈpen.ʃən.ər/ A person who Students and
receives a pension, pensioners are especially the entitled to a government discount pension given to old people (Người về hưu) Counterintuitive / ka ˌ n.tər. ʊ n ɪ Something that is It may seem t ˈ u ʃ . ː .t ɪ ɪv/ counterintuitive counterintuitive
does not happen in to open a shop in
the way you would the middle of a expect it to (phản recession trức giác) B. Before you read
The past 50 years have witnessed a breathtaking revolution in technology,
transforming every facet of our lives. From the rise of personal computers to the
ubiquity of smartphones and the internet, technological advancements have
brought both immense benefits and unforeseen challenges to society. Let's explore
some key areas of advancement and their impacts: Positive Impacts:
Healthcare and medicine: Technological advancements in medical imaging,
diagnostics, and treatments have dramatically improved healthcare outcomes and
life expectancy. Telemedicine connects patients with healthcare professionals
remotely, and wearable devices monitor health in real-time.
Productivity and efficiency: Automation and robotics have transformed industries,
boosting productivity and efficiency. Online tools and services streamline business
processes, while apps simplify daily tasks from banking to grocery shopping.
Entertainment and leisure: Technology has redefined entertainment with streaming
services, video games, and virtual reality experiences. Online platforms offer
diverse content catering to a wide range of interests. Negative Impacts:
Digital divide and inequality: Unequal access to technology creates a digital
divide, exacerbating existing inequalities in education, employment, and
healthcare. Access to technology and digital literacy become crucial factors in
determining life opportunities.
Privacy concerns and data security: As we generate and store more data online,
concerns about privacy, data breaches, and surveillance rise. Balancing innovation
with privacy protections is a crucial challenge.
Addiction and mental health: Excessive screen time and social media use can lead
to addiction, anxiety, and depression. The curated online world can fuel unrealistic
expectations and social comparison, negatively impacting self-esteem and mental well-being. C. Global reading 1b 2f 3d 4a 5c 6e D. Close reading 1. 1. Exceeded 2. No 3. Doubled 4. Steady 2. 1. 20 2. 11.9 3. 12.6 4. 2.1 5. 11.9 3.
1. Total revenue has decreased—the industry is making less money than it did
ten years ago; physical sales have steadily generated less revenue; digital
sales have steadily generated more revenue.
2. Illegal downloads and the rise of legal streaming services seem to have had
a significant impact on the industry as a whole, driving down revenue
overall, but driving up digital sales at the expense of physical sales E. Critical thinking
1. Surveys should be conducted by an independent company—a games
company might be biased and either have written the survey in such a way
that it elicits the answers they want or misrepresented their findings to make
themselves look better and therefore sell more games.
2. 20 is not a very large sample size—good studies focus on much larger groups.
3. Presumably people that describe themselves as “gamers” enjoy playing
video games and are therefore less likely to have a negative view of them.
The survey should have asked a range of people who spend varying levels of time playing computer games.)
READING 2: Gaming, society, and the individual Summary:
Based on the provided text, it suggests that the commonly held beliefs that video
games lead to violent behavior and are socially isolating are not supported by the
evidence. The text mentions research that challenges these beliefs, indicating that
gaming, particularly massively multiplayer online gaming (MMOG), encourages
collaboration, and social interaction, and can enhance fine motor skills.
Additionally, it suggests that gaming may have benefits for mental health and
could even help prevent neurodegenerative diseases.
However, the text also acknowledges that excessive gaming has been correlated
with poor academic performance, possibly due to sleep deficit and skipping
classes. It also raises concerns about sedentary behavior and its potential
contribution to childhood obesity, although it emphasizes that gaming alone should
not be solely blamed for this issue.
Overall, the text suggests that the effects of gaming are not solely negative and that
there are potential positive impacts on social skills, fine motor skills, mental health,
and decision-making abilities. However, it acknowledges the need for continued
research to fully understand the impact of gaming on various aspects of our lives.
It's important to note that this summary is based solely on the provided text.
Additional research and studies would be necessary to form a more comprehensive
and nuanced understanding of the effects of gaming. A. Vocabulary preview Words Transcription Meaning Example peers(v) /pɪər/ to look carefully When no one or with difficulty answered the (đồng nghiệp) door, she peered through the window to see if anyone was there. aggression(n) / əˈɡre . ən / ʃ
spoken or physical Some types of dog behaviour that is are bred for threatening or aggression. involves harm to someone or something (hiếu chiến, xâm lược) interaction(n) /ˌɪn.tə ræk. ˈ ʃən/
an occasion when The play follows two or more the interactions of people or things three very
communicate with different or react to each characters. other (sự tương tác) prolonged(adj) /prəˈl ŋd/ ɒ continuing for a Prolonged use of long time (kéo the drug is known dài) to have harmful side-effects analytical(adj) /ˌæn.əˈlɪt.ɪ.kəl/ examining or Some students
liking to examine have a more
things in detail, in analytical order to discover approach to more about them learning. (phân tích) awareness(adj) /əˈweər/ knowing that Were you aware
something exists, of the risks at the or having time? knowledge or experience of a particular thing (nhận thức) deficit(n) /ˌaɪ.səlˈeɪ.ʃən/ the condition of
The prisoner had being alone, been kept in especially when isolation for three this makes you days. feel unhappy (thiếu hụt) Solely (adv) / sə ˈ l.li/ ʊ only and not I bought it solely
involving anyone for that purpose. or anything else: (cô đô •c) dedicated core / ded. ˈ .ɪke .t ɪ d/ /k ɪ r/ ɔː very important the center part of something (lõi chuyên dụng) Equivalent (a) / kw ɪˈ v.əl.ənt/ ɪ same, equal Is $50 equivalent (tương đương) to about £30? Ingrained (a) / n ɪ re ˈɡ nd/ ɪ (of beliefs, Such ingrained attitudes, or prejudices cannot habits) so be corrected established that easily. they are difficult to change (ăn sâu vào) Reputed (a) /rɪˈpjuː.tɪd/
said to be the true She is reputed to
situation although be 25 years this is not known younger than her to be certain and husband. may not be likely (có uy tín) Emerging (a) /ɪˈm .d ɜː ŋ/ ʒɪ starting to exist Western ( mới nổi) governments should be giving more aid to the emerging democracies of the Third World. Cite (v) /sa t/ ɪ to mention She cited three something as reasons why
proof for a theory people get into
or as a reason why debt. something has happened (trích dẫn) Detrimental (a) / det.r ˌ men.təl/ ɪˈ causing harm or These chemicals damage (có hại) have a detrimental effect/impact on the environment. Robust (a) /rə b ʊˈ st/ ʌ strong and He looks robust unlikely to break and healthy or fail enough. (khỏe mạnh) Insular (a) /ˈɪn.sjə.lər/ interested only in We believe that
your own country this insular or group and not approach now willing to accept needs to be different or challenged. foreign ideas (đảo) Propensity (n) /prə pen.sə.ti/ ˈ the fact that He's well-known
someone is likely for his natural to behave in a propensity for particular way, indiscretion. especially a bad way (khuynh hướng) B. Before you read
The impact of gaming on individuals and society is a complex and multifaceted
issue, with both positive and negative aspects to consider. Determining which side
outweighs the other depends on several factors, including the type of game, the
amount of time spent playing, and individual motivations for playing. Positive Impacts:
Cognitive benefits: Studies have shown that certain types of games, such as
strategy games and puzzles, can improve cognitive skills like memory, attention,
and problem-solving. They can also stimulate creativity and spatial reasoning abilities.
Social engagement and connection: Online multiplayer games offer opportunities
for socialization and teamwork, connecting individuals with friends and
communities around the world. They can foster communication, collaboration, and leadership skills.
Emotional well-being and stress relief: Gaming can be a fun and engaging way to
relax, unwind, and escape from daily stressors. It can provide a sense of
accomplishment and mastery, contributing to positive emotions and well-being.
Educational and therapeutic potential: Educational games can make learning more
engaging and interactive, improving knowledge retention and motivation. Games
are also being used in therapeutic settings to address anxiety, depression, and motor skills development. Negative Impacts:
Addiction and excessive play: Gaming can be highly addictive, especially certain
genres that exploit reward systems and encourage compulsive behavior. Excessive
play can lead to neglecting responsibilities, neglecting sleep and physical health, and harming relationships.
Negative health effects: Spending too much time playing can lead to sedentary
lifestyles, obesity, and potential problems with eyesight and posture. Sleep
disturbances and social isolation can also be detrimental to physical and mental health.
Exposure to violence and inappropriate content: Some games contain graphic
violence, sexual content, and offensive language, which can be harmful, especially
for young audiences. Parental guidance and age-appropriate restrictions are crucial. C. Global reading 1d 2e 3a 4b 5c 6f D. Close reading
1. N—frankly (Para 2: the author believes there is evidence that is contrary to this) 2. Y—actually 3. Y—undoubtedly 4. NG 5. Y—counter-intuitively 6. NG
7. N—reasonably (Para 5: the author thinks it’s reasonable to consider gaming
a contributory factor in childhood obesity) 8. NG E. Critical thinking
1. The text does not provide enough information to determine whether the
effects of gaming are mainly positive or negative. It primarily focuses on the
growth of streaming and on-demand services, briefly mentioning the video
game sector without explicitly discussing the effects of gaming. To form a
comprehensive opinion, it would require additional information beyond what
is provided in the text, such as the content and context of the games, the
amount of time spent playing, and individual differences in gaming habits.
2. If there were specific studies mentioned in the reading, it would be valuable
to know their methodology, sample size, duration, and specific findings.
Additionally, understanding the scope of these studies (e.g., focusing on
children, specific game genres, or specific outcomes) would provide more
context. This information could help in assessing the impact of gaming on
children and potentially influence one's stance on the positive or negative effects of gaming. VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT 1. 1. exceed 2. overwhelming majority 3. negligibly 4. sizable 5. account for 6. flatten out 7. vastly 8. significant proportion 2. 1. vastly 2. exceeded 3. accounted for 4. negligibly 5. significant proportion 6. overwhelming majority 7. sizable 8. flattening out ACADEMIC WORDS Words Transcription Meaning Example Attribute / æt.r ˈ ɪ.bjuːt/ a quality or characteristic
Organizational ability is (v)
that someone or something an essential attribute for a has (thuộc tính) good manager Bulk (n) /b lk ʌ / something or someone
She eased her large bulk out
that is very large (số lượng of the chair lớn) Constitute / k ˈ ɑːn.stə.tuːt/ to be or be considered
This latest defeat constitutes (v) as something (cấu tạo) a major setback for the Democrats Format (n) /ˈfɔːr.mæt/ a pattern, plan, The meeting will have
or arrangement (định dạng) the usual
format- introductory session, group work and then
a time for reporting back. Infer (v) / n ɪ f ˈ ɝː/ to form an opinion or
What do you infer from her guess that something refusal? is true because of the information that you have (suy luận) Intrinsic / n ɪ tr ˈ n.z ɪ k ɪ / Being an extremely
Maths is an intrinsic part of (adj) important and basic the school curriculum. characteristic of a person or thing (nội tại) Proportion /prəˈpɔːr.ʃən/ the number or amount of Children make up (n) a group or part of
a large proportion of the
something when compared world's population to the whole (tỷ lệ) Solely /soʊl/
being one only; single (độc My sole objective is to make (adv) nhất)
the information more widely available 1. 1. d 2. g 3. a 4. b 5. f 6. h 7. c 8. e 2. 1. intrinsic 2. bulk 3. attributed 4. constitutes 5. proportion 6. infer 7. formats 8. solely CRITICAL THINKING 1.
1. We don’t know. If it was a small sample, the result is arguably less
impressive, or even inaccurate.
2. We don’t know. The measure used could be subjective, which potentially
lessens the importance of the results.
3. The age of the children—those approaching adolescence might show a
greater propensity toward violence in general; how much sleep the children
were getting—a lack of sleep could make them prone to angrier outbursts, etc. 2.
1. No. The sample size is too small. Also, the case study only looked at boys,
but the interpretation claims all children are affected.
2. No. It’s only 3% in one year. We also do not know the raw number, so it
could be quite a small number of actual crimes.
3. No. No evidence is presented in the data that this is a cause-and-effect
relationship. It could merely be a correlation. Other factors need to be
considered. We also do not know the sample size GRAMMAR 1.
1. Should sales of e-books continue to stagnate, companies may stop investing in them.
2. Should people continue to stream content on mobile devices, traditionally
broadcasted TV may become a thing of the past.
3. Were sales to decline any further, investors might well lose faith in the project
4. Should companies choose not to invest in mobile gaming, they may well see
a decline in revenue over the next decade.
5. Were e-readers easier to navigate, they would undoubtedly be more popular amongst consumers.
6. Were consumers not to adopt early, the product might fail in its first year.
Question multiple choice
1. Which word is CLOSET in meaning to the underlined part in the following question?
Maths is an intrinsic part of the school curriculum. A. fundamental B. acquired C. optional D. insignificant
2. Which word is OPPOSITE in meaning to the underlined part in the following question?
This candidate is vastly more experienced than the others. A. massively B. extremely C. slightly D. enormously
3. Which of the following words refers to fairly large? A. Miniature B. Sizable C. Unnoticeable D. Moderate
4. Which word indicates the correct answer to the following question?
Do you think it's true that teenage girls are less self-confident than their male ______? A. Peers B. Adults C. Acquaintances D. Volunteers
5. Which of the following words refers to the amount by which money spent or owed is
greater than money earned in a particular period of time? A. Surplus B. Deficit C. Excess D. Sufficiency
6.Which of the following words is synonymous with the word "cite"? A. Quote B. show C. Reveal D. Deal
7. Which of the following words is the opposite of the word "detrimental"? A. Harmful B. Dangerous C. Noxious D. Beneficial
8. What can the underlined word in the sentence below be replaced by?
The project implementation plan has been assessed as feasible within the government budget. A. suitable B. fit C. possible D. replace
9.Which of the following words is synonymous with the word "retiree"? A. Pensioner B. patriot C. revolutionary D. Buddhist
10.Which word below is the opposite of the underlined word in the following sentence?
The prosecutor's speculations are just based on intuition. A. Feeling B. 6th Sense C. Counterintuitive D. Option.
Answer key: 1. A 2. C 3. B 4. A 5. B 6.A 7.D 8.C 9.A 10.C UNIT 3: ENERGY Discussion point 1.
What are the main sources of energy in your country?
Currently, the main energy source in Vietnam is still fossil energy such as coal and
oil, accounting for about 50% of total electricity output. Besides, coal is the most
widely used energy source in Vietnam, accounting for about 41.6% (2019) of total
energy output, and is used mainly to produce electricity 2.
What energy does your country produce?
Hydropower is a strongly developed energy source in Vietnam, accounting for
about 37.7% (2019) of total electricity output. The largest hydroelectric plants in
Vietnam are Son La, Hoa Binh, and Lai Chau. 3.
Do you think we should continue to use fossil fuels? Why / why not?
I think we shouldn’t continue to use fossil fuels. Because fossil fuels are a major
contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, which are the primary cause of climate
change. Continued reliance on fossil fuels exacerbates climate change and its
associated impacts, such as rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and sea-
level rise. Additionally, fossil fuels are non-renewable resources, meaning they are
finite and will eventually run out. As extraction becomes more difficult and costly,
it may lead to price volatility and energy insecurity in the long term. Before you watch 1c 2e 3b 4d 5a While you watch
1. Whether to use nuclear power or renewable energy sources
2. Nuclear power poses a significant safety risk
3. Energy prices will rise if nuclear plants are closed
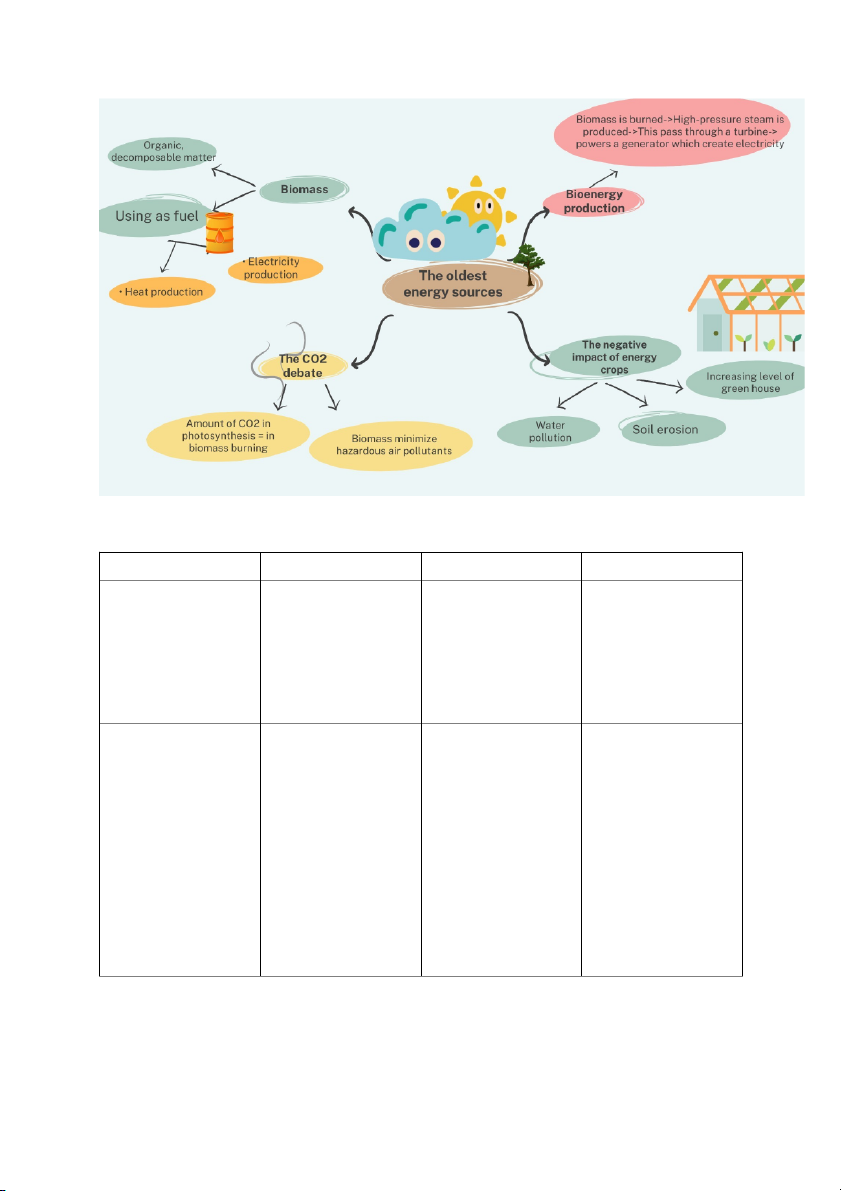
READING 1: The oldest energy source Summary: A. Vocabulary preview Words Transcription Meaning Example Adverse (adj) /ædˈv s ɝː /
Having a negative The doctor or harmful effect warned of on sth (Xấu) the adverse effects of the medication Carbon-neutral / k ˌ ɑːr.bən If sth such as an How can we (adj) nu ˈ ː.trəl/ organization or carbon-neutral activity is carbon our homes? neutral, it removes the same amount of carbon dioxide from the environment as it releases into the environment (Trung hòa carbon) Cultivate (v) /ˈkʌl.tə.ve t/ ɪ To prepare land The farmer is
and grow crops on cultivating the it, or to grow a land to prepare it particular crop for planting. (Trồng trọt) Excessive (n) / ek.ses ˈ /
An amount that is The movie was more than criticized for its acceptable, excessive violence expected, or reasonable (Quá) Inedible (adj) / n ˌɪ ed.ə.b ˈ əl/ Not suitable or The food was so good enough to overcooked that it eat (Không ăn was inedible được) Minimize (v) / m ˈ ɪn.ə.ma z ɪ / To reduce sth to The doctor is the least possible trying to minimize level or amount the risk of (Giảm thiểu) infection Proponents (n) /prə po ˈ .nənt ʊ / A person who She is a vocal
speaks publicly in proponent of support of a climate change particular idea or action plan of action (Người đề xuất) Renewable (adj) /r nu ɪˈ .ə.b ː əl/
Renewable forms Solar and wind of energy can be power are produced as renewable energy
quickly as they are sources. used (Tái tạo)
Complete the sentences with the words in the box. 1. Inedible 2. Carbon-neutral 3. Proponents 4. Renewable 5. Excessive 6. Cultivate 7. Minimize 8. Adverse B. Before you read Advantages:
Renewable resource: Unlike fossil fuels which are finite, biomass can be
continuously replenished through farming and sustainable forest management. This
helps reduce dependence on non-renewable energy sources and contributes to energy security.
Carbon neutrality: When biomass is burned, the carbon released is typically
reabsorbed by growing plants, leading to a balanced carbon cycle. This makes it a
potentially carbon-neutral option compared to fossil fuels, which contribute
significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
Waste utilization: Burning biomass provides a way to utilize organic waste from
agricultural and forestry activities, reducing landfill waste and potential methane
emissions. Additionally, animal waste can be converted into biogas for electricity generation. Disadvantages:
Deforestation and land-use change: Increased demand for biomass can lead to
deforestation and conversion of natural habitats to energy plantations, reducing
biodiversity and ecosystem services. Sustainable practices are crucial to avoid these negative impacts.
Greenhouse gas emissions: Although considered carbon-neutral, biomass burning
does release other greenhouse gases like methane and nitrous oxide, which can
contribute to climate change, especially if sourced or managed unsustainably.
Air pollution: While cleaner than coal, burning biomass can still generate
particulate matter and nitrogen oxides, potentially impacting air quality in
surrounding areas. Efficient combustion technologies and proper emission controls
are necessary to mitigate these effects. C. Global reading A-5 B-4 C-6 D-1 E-3 F-2 D. Close reading 1. 1. Biomass 2. Methane gas 3. High-pressure steam 4. Turbine 5. Generator 6. Electricity 7. Transformer 8. Voltage 2. 1. T 2. NG 3. T 4. T 5. F E. Critical thinking Technical Feasibility:
Fuel source: They need to demonstrate a reliable and sustainable source of
biomass, considering factors like availability, transportation logistics, and long- term supply chain stability.
Technology: The proposed technology needs to be proven efficient and reliable,
with minimal emissions and environmental impact.
Grid integration: The ability to safely and efficiently integrate the generated
electricity into the existing grid infrastructure must be assured.
Environmental Impact Assessment:
Emissions: The company must thoroughly assess the potential air, water, and soil
pollution impact of the plant, including emissions of greenhouse gases, particulate
matter, and other pollutants. Mitigation strategies for reducing these impacts need to be presented.
Land use and sustainability: The impact on land use, including potential
deforestation, soil erosion, and habitat destruction, needs to be comprehensively
evaluated. Plans for minimizing these impacts and promoting sustainable land
management practices must be included.
Waste management: An effective plan for handling and disposing of solid waste
and wastewater generated by the plant is crucial. Social and Economic Impacts:
Community engagement: Open and transparent communication with the local
community about the project's potential benefits and drawbacks is essential.
Addressing concerns and mitigating potential social impacts is necessary.
Economic benefits: The company needs to demonstrate the economic benefits of
the project for the local community and region, such as job creation, economic
development, and energy security.
Health and safety: Compliance with health and safety regulations for both workers
and the surrounding community must be guaranteed.
READING 2: Fracking – the future? Summary: A. Vocabulary preview Words Transcription Meaning Example Additives (n) / æd.ə. ˈ tɪv/ A substance that is
This margarine is full of
added to food in order additives - just look at the to improve its taste or label! appearance or to keep it fresh and stop it from decaying (chất gây nghiện)
Contaminate /kən tæm.ə.ne ˈ tɪ/ To make sth less pure
The food which had been (v) or make it poisonous contaminated (làm ô uế) was destroyed. Drill (n) /drɪl/
A tool or machine that Do you know how to use makes holes (máy a power drill? khoan) Formations /f r ɔː me ˈ ɪ.ʃən/ The way sth is
The team was lined up in (n) naturally made or the a punting formation. way it has been arranged (sự hình thành) Horizontal / h ˌ ɔːr. z ɪˈ n.
ɑː təl/ Parallel to the ground Draw a horizontal line (adj)
or to the bottom or top across the bottom of edge of sth (nằm the page. ngang) Mining (n) / ma ˈ ɪ.nɪŋ/ The industry or
"Mining" is the discovery activity of removing of new bitcoins—just substances such as like finding gold. coal or metal from the ground by digging (khai thác mỏ) Pump (n) /p mp/ ʌ To force liquid or gas The pump to move somewhere is driven by steam. (bơm) Vertical /ˈv . ɝː ə.k t əl/ Standing or pointing She looked over (adj) straight up or at an
the cliff and found she angle of 90 to a
was standing at the edge horizontal surface or of a vertical drop. line (thẳng đứng)
Complete the sentences with the words in the box. 1. Drill 2. Pump 3. Additives 4. Horizontal 5. Contaminate 6. Mining 7. Formation 8. Vertical B. Before you read
The extraction of fossil fuels plays a crucial role in the global energy mix, but
responsible practices are essential to minimize environmental impact and ensure
long-term sustainability. Technological advancements, stricter regulations, and
investments in renewable energy sources are key to navigating this complex
landscape and securing a cleaner future.
Understanding where fossil fuels come from and how they are extracted is a vital
step toward making informed decisions about their use and exploring alternative
energy sources. By considering both the benefits and drawbacks of these resources,
we can strive for a more sustainable and responsible relationship with the Earth's hidden treasures. C. Global reading
A-3 B-4 C-5 D-1 E-6 F-7 G-2 H-8 D. Close reading 1. a) Porous b) Well c) Fissures d) Leach e) Magnitude 2. 1. T 2. NG 3. F 4. T 5. F 6. T E. Critical thinking Regulation and Policy:
Environmental regulations: Strengthening existing environmental regulations and
implementing new ones to set stricter limits on emissions, pollution, and resource
extraction. These regulations should be enforced effectively with clear penalties for non-compliance.
Carbon pricing: Implementing carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems puts a price
on carbon emissions, making it more expensive for companies to pollute and
incentivizing them to reduce their environmental impact.
Subsidies and incentives: Providing subsidies and incentives for renewable energy,
energy efficiency, and sustainable practices can make them more attractive and
cost-competitive for businesses, encouraging them to adopt these solutions. Market Mechanisms:
Corporate social responsibility (CSR): Encouraging corporations to adopt CSR
practices that prioritize environmental sustainability alongside financial
performance. This can be achieved through investor pressure, consumer demand
for sustainable products, and transparency initiatives.
Environmental disclosure: Requiring companies to disclose their environmental
impact transparently, including their greenhouse gas emissions and resource
consumption. This can help investors and consumers make informed decisions and hold companies accountable.
Green bonds and sustainable finance: Promoting the development of green bonds
and other financial instruments specifically designed to fund environmentally
friendly projects and businesses. Societal Change:
Consumer awareness: Educating consumers about the environmental impact of
their choices and encouraging them to demand sustainable products and services.
This can be done through public education campaigns, labeling initiatives, and awareness-raising programs.
Community engagement: Empowering local communities to participate in
decision-making processes related to environmental issues and hold corporations
and governments accountable for their actions.
Investing in education and research: Supporting research and development in
renewable energy, clean technologies, and sustainable practices. Investing in
education and training programs can also help create a workforce equipped with
the skills needed for a green economy. VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT Words Transcription Meaning Example Dam (v) /dæm/
To build a dam across a The Aswan High Dam river in order to store
is on the River Nile in Egypt. water (con đập) Flow (n) /floʊ/ Movement of a liquid Many short rivers flow (chảy)
into the Pacific Ocean. Gears (n) / r ɡɪ /
To start to do sth better Icouldn't find reverse gear or faster(tăng tốc) Generator
/ˈdʒen.ər.e .ɪtɚ/ A machine that
The hospital's emergency (n) prroduces electrical generators power (máy phát điện) are designed to cope with power cuts. Kinetic /kɪ ne ˌ t.ɪk Energy that an object The energy of disturbances is energy (n) ˈen. .d ɚ i ʒ / or system has because
primarily kinetic energy. it is moving (động năng) Shaft (n) / æft ʃ / A beam of light
His fingers tightened around
the shaft of the golf club. Transmission It must also be suitable for lines (n) the
transmission line along which it goes. Turbine (n) / t ˈ .ba ɝː ɪn/ A type of machine The third loop is a
through which liquid or steam turbine cycle. gas flows and turns a special wheel with blades in order to produce power (tua- bin) 1. 1. Dam 2. Shaft 3. Turbine 4. Kinetic energy, flows 5. Gears 6. Generator 7. Transmission lines ACADEMIC WORDS
1. Match the words in bold with the correct definitions. 1h 2f 3c 4a 5d 6b 7e 8g
2. Complete the sentences with words from Ex 1. Change the form if necessary 1. Sustainable 2. Restricted 3. Cited 4. Predominantly 5. Parallel 6. Diminishing 7. Dispose 8. Erosion CRITICAL THINKING
1. Read the text and answer the questions
1. No, the writer seems biased about fracking
2. Environmental lobbyists and Kilnbrook 3. Limited, weak, experts 2.
1. One-sided, no atternative perspective included.
2. Other influences –i.e Fracking UK funded the research
3. Emotive language – clearly, aggressively, vast, dubious, fragile. GRAMMAR 1. 1. Blows
2. Converts into the low-speed rotation 3. Uses the kinetic energy
4. Generate the electrical electricity 5. Be transmitted 6. To measure the speech 7. Is transmitted 8. To rotate the turbine 9. Are applied UNIT 4: RISK Discussion point
1. The biggest risks in business are often the ones that are the most unpredictable
and difficult to mitigate. These risks can include things like economic recessions,
natural disasters, and changes in government regulations. While it is impossible to
eliminate all risk from business, there are a number of things that business people
can do to mitigate risks, such as diversifying their operations, having a solid
business plan, and having a team of experienced advisors.
2. Risk is an inherent part of business. It is the possibility of something happening
that could negatively impact a business's financial performance, reputation, or
ability to operate. While there is no way to eliminate all risk from business, there
are things that business people can do to mitigate it.
Why is risk important in business?
Risk is important in business because it can have a significant impact on a
company's bottom line. For example, a company that experiences a data breach
could lose customers and revenue. A company that launches a new product that
fails could incur significant losses. And a company that is caught in a scandal
could see its stock price plummet.
In addition to the financial impact, risk can also damage a company's reputation
and make it difficult to attract and retain customers and employees.
How can business people mitigate risks?
There are a number of things that business people can do to mitigate risk. These include:
- Identifying risks: The first step to mitigating risk is to identify it. This means
understanding what risks a company faces and assessing the likelihood and potential impact of each risk.
- Developing risk management plans: Once risks have been identified, business
people can develop plans to mitigate them. These plans may include things like
purchasing insurance, implementing security measures, or diversifying business operations.
- Monitoring and reviewing risks: Risks are not static. They change over time, so it
is important to monitor and review risks on a regular basis. This will help to ensure
that risk management plans are effective and up-to-date.
3. People take many different risks in their family life, social life, work life, and
leisure time. These risks can be big or small, and they can have positive or negative consequences. Family life
Financial risks: Many people take financial risks in their family life, such as
buying a house or starting a business. These risks can pay off, but they can
also lead to financial hardship if things don't go as planned.
Relationship risks: People also take relationship risks in their family life,
such as getting married or having children. These risks can lead to great joy
and fulfillment, but they can also lead to pain and heartache.
Health risks: People also take health risks in their family life, such as
making lifestyle choices that could affect their long-term health. These risks
can be difficult to assess, but they can have a significant impact on their quality of life. Social life
Social risks: People take social risks by putting themselves out there and
making new friends. This can be scary, but it can also lead to great friendships and experiences.
Reputational risks: People also take reputational risks by doing things that
could damage their reputation. This can be a major concern, especially in a professional setting.
Safety risks: People also take safety risks by engaging in activities that could
put them in danger. This is especially true for young people, who are more
likely to take risks without thinking about the consequences. Work life
Career risks: People take career risks by taking on new challenges or
pursuing new opportunities. These risks can lead to great success, but they can also lead to failure.
Financial risks: People also take financial risks in their work life, such as
taking a job that pays less but offers more opportunities for advancement.
These risks can be difficult to assess, but they can have a significant impact on their financial security.
Health risks: People also take health risks in their work life, such as working
long hours or sitting for extended periods of time. These risks can lead to health problems down the road. Leisure time
Physical risks: People take physical risks by engaging in activities that could
put them in danger, such as rock climbing or skydiving. These risks can be
exhilarating, but they can also lead to serious injury or death.
Financial risks: People also take financial risks in their leisure time, such as
going to the casino or gambling online. These risks can lead to financial
losses, but they can also lead to short-term financial gains.
Social risks: People also take social risks in their leisure time, such as going
to a party or attending a social event. These risks can lead to awkward social
situations, but they can also lead to new friendships and experiences.
In conclusion, people take many different risks in their family life, social life, work
life, and leisure time. These risks can have positive or negative consequences, and
it is important to weigh the risks and benefits before making a decision. Before you watch 1a 2d 3e 4b 5c While you watch 1T 2F 3F 4F 5F
READING 1: The credit crunch: Whose fault was it anyway? Summary: A. Vocabulary preview
Complete the definitions with the words or phrases in the box. 1. Credit crunch 2. Default on your mortgage 3. Housing bubble 4. Regulator 5. File for bankruptcy 6. Bail them out 7. Recession 8. Stimulate the economy B. Before you read 1. Increasing Internet Rates:
Homeowners: Higher internet bills can strain household budgets, especially for
families relying on internet access for work, education, and entertainment. They
may need to adjust their spending habits or seek cheaper internet plans.
Savers: As household spending on internet decreases, this could potentially free up
some savings for individuals. However, the overall impact on savings rates might
be negligible compared to other factors.
Companies: Businesses heavily reliant on internet connectivity for operations and
online interactions could face increased costs, impacting their profitability and
potentially leading to price hikes for customers.
Banks: Banks may see a slight increase in revenue if people use debit or credit
cards to pay for higher internet bills. However, this could be offset by a decrease in
overall consumer spending due to tighter budgets. Decreasing Internet Rates:
Homeowners: Lower internet bills free up disposable income, potentially boosting
consumer spending and stimulating the economy. This could also increase
affordability and access to online resources.
Savers: Reduced internet costs could contribute to higher savings rates for
individuals, especially for budget-conscious households.
Companies: Businesses can benefit from lower internet costs, potentially
improving their profitability and competitiveness. This could also lead to lower prices for consumers.
Banks: While lower internet bills may result in fewer debit/credit card transactions,
banks could benefit from increased consumer spending spurred by savings generated from the lower cost. 2. Causes:
Subprime lending: Banks lent large amounts of money to high-risk borrowers with
poor credit history, often packaged into mortgage-backed securities (MBS) and sold to investors.
Housing bubble: Easy credit fueled a housing bubble, leading to inflated property
prices beyond their sustainable value.
Financial deregulation: Lack of adequate regulations allowed risky financial
practices to flourish, amplifying the potential for disaster.
Credit default swaps: These complex financial instruments magnified losses when borrowers defaulted on loans. Effects:
Bank failures: Major banks and financial institutions collapsed, leading to
widespread financial panic and loss of jobs.
Global recession: The crisis triggered a global recession, impacting employment,
trade, and investment worldwide.
Stock market crash: Stock markets around the world plummeted, wiping out
wealth and eroding confidence in the financial system.
Loss of trust: Public trust in financial institutions and regulators was shaken,
leading to long-lasting repercussions. Long-term impacts:
Increased regulations: The crisis led to stricter financial regulations to prevent similar events in the future.
Economic uncertainty: The lasting effects of the crisis continue to pose challenges
for many economies, with slower growth and higher unemployment.
Social and political consequences: The crisis widened inequalities and contributed
to political unrest in some countries. C. Global reading 1d 2b 3f 4a 5e 6c D. Close reading f-a-e-b-g-c-d-j-i-h E. Critical thinking
2. In the daily lives of ordinary people, money plays a crucial role. It enables them
to meet their basic needs, pursue their aspirations, and build a secure future.
However, handling money also involves inherent risks, which, if not managed
effectively, can lead to financial difficulties and setbacks. Let's explore the
common money-related risks faced by ordinary people and discuss strategies to mitigate these risks. Common Money-Related Risks
1. Overspending: Overspending is a prevalent risk that can quickly deplete
one's financial resources. This can be caused by impulse purchases, a lack of
budgeting, or an unrealistic lifestyle.
2. Debt Accumulation: Debt, when managed responsibly, can be a useful tool
to finance large purchases or investments. However, excessive debt can
become a burden, leading to high interest payments and a strained financial situation.
3. Lack of Savings: Saving money is essential for financial security and the
ability to handle unexpected expenses or emergencies. However, many
people struggle to save regularly, leaving them vulnerable to financial shocks.
4. Investment Risks: Investing can be a great way to grow one's wealth over
time. However, investments carry inherent risks, such as market fluctuations or potential losses.
5. Financial Fraud: Ordinary people are not immune to financial fraud, which
can take various forms, such as identity theft, scams, or Ponzi schemes.
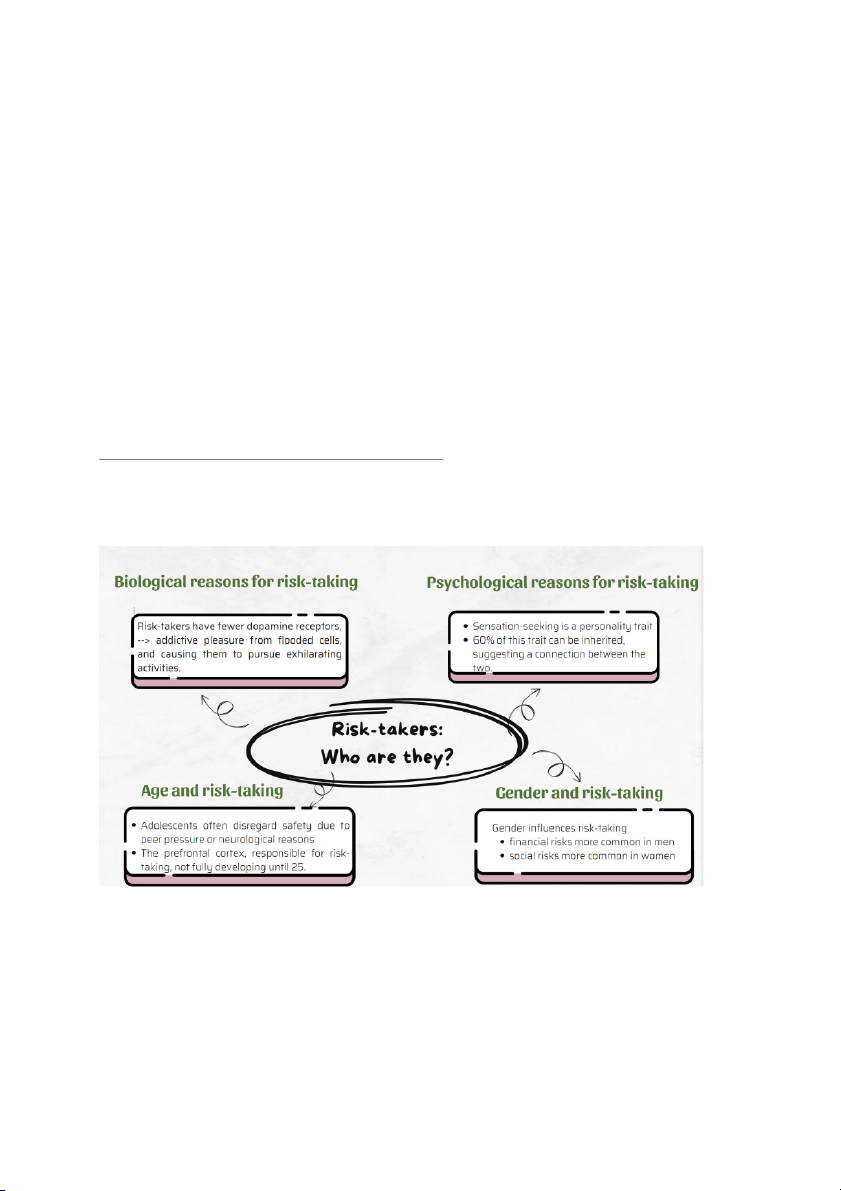
READING 2: Risk-takers: Who are they? Summary: A. Vocabulary preview
Complete the paragraph with the words in the box. 1. Disregard 2. Personality trait 3. Susceptible 4. Sound judgment 5. Peer pressure 6. Triggered 7. Addictive 8. Gene Before you read
A typical risk-taker is often an adventurous person who is always up for a new
challenge. They are often seen as thrill-seekers and adrenaline junkies, and they are
not afraid to take risks in order to achieve their goals. Risk-takers are often very
confident and self-assured, and they believe in themselves and their abilities. They
are also often very optimistic and have a positive outlook on life.
Here are some of the characteristics of a typical risk-taker:
Age: Risk-takers are often young adults, between the ages of 18 and 25. This
is because this is a time when people are exploring their identity and trying
to figure out who they are. They are also more likely to take risks because they have less to lose.
Character: Risk-takers are often outgoing and extroverted. They are also
often very curious and have a thirst for knowledge. They are also often very independent and self-reliant.
Gender: Risk-taking is more common in men than in women. This is
because men are often socialized to take risks, while women are often
socialized to be more cautious.
Job: Risk-takers are often drawn to jobs that are exciting and challenging.
They may work as firefighters, police officers, or entrepreneurs.
Social life: Risk-takers often have a large group of friends and are very social.
They enjoy spending time with others and trying new things. C. Global reading
1. Brain chemicals, genetic factors, gender, age
2. Wittman (2012) suggests that age, gender, brain, and biology cause risk-taking. 3. 1. Active 2. Cautions 3. Rats 4. Addictive 5. Pleasure 6. Four D. Close reading 1F 2T 3F 4NG 5NG 6F E. Critical thinking
1. Yes, it is generally true that young people take more risks than older people.
Young people are more likely to engage in sensation-seeking behaviors. This
is due to changes in the brain that occur during adolescence. The prefrontal
cortex, which is responsible for planning, impulse control, and risk
assessment, is not fully developed in adolescents. This can lead to them
taking more risks without fully considering the potential consequences.
Young people are more likely to be optimistic and have a positive outlook
on life. This can make them more likely to take risks, as they believe that
they are more likely to succeed than fail.
Young people have more time to recover from mistakes. If a young person
takes a risk and fails, they have more time to learn from their mistake and
recover. Older people may be more risk-averse because they have less time to recover from mistakes.
Of course, there are always exceptions to the rule. Some young people are
very cautious and risk-averse, while some older people are more
adventurous and willing to take risks. However, in general, young people are
more likely to take risks than older people.
2. In many countries, parents, schools, and the government work
collaboratively to minimize the risks that young people take. The efforts are
generally focused on ensuring the well-being, safety, and positive
development of the younger population. The extent to which each entity is
involved and the specific strategies employed can vary. Parents:
Parents play a crucial role in guiding and supervising their children.
They often educate them about potential risks, set boundaries, and
instill values that promote responsible decision-making.
Monitoring and controlling access to certain activities, such as
limiting screen time, supervising social interactions, and ensuring a
safe home environment, are common ways parents try to minimize risks. Schools:
Schools contribute to risk reduction through educational programs that
focus on health, safety, and personal development. This may include
sex education, drug prevention programs, and courses on responsible internet use.
Teachers and school counselors often serve as mentors, providing
guidance and support to students facing challenges or difficult decisions. Government:
Governments implement policies and regulations to protect young
people. This can include laws on the legal age for various activities,
such as driving, voting, and consuming certain substances.
Educational initiatives, public health campaigns, and social programs
may be funded and implemented by the government to address
specific risks facing young people.
Whether it is the responsibility of parents, schools, and the government to
minimize the risks for young people is a matter of societal perspective and often
depends on cultural and political values. Here are some arguments:
Yes, it is their responsibility:
Young people are often considered vulnerable and in need of guidance
and protection until they reach adulthood.
These entities have a duty to create an environment that fosters the
physical, emotional, and intellectual well-being of young individuals.
Society benefits when its young population is healthy, educated, and
capable of making informed decisions. VOCABULARY DEVELOPMENT 2. 1. Endorsed 2. Examined 3. Disagree 4. Predominantly 5. Make 6. Compare 3. 1. According to 2. Observation 3. Concluded 4. Evidence 5. Writing 6. Recommended 7. Further 8. Advised ACADEMIC WORDS Words Transcription Meaning Example Deduction /d d ɪˈ k. ʌ ʃən/ The process of reaching a All we can do is make (n) decision or answer by
deductions from the thinking about the known available facts.
facts, or the decision that is reached (khấu trừ) Orientation / r.i.en ˌɔː The particular things that a We employ people withou (n) te ˈ .ɪʃən/ person prefers, believe, t
thinks, or usually does (định regard to their political hướng) orientation Precede (v) /pri si ːˈ ːd/
To be or go before sth or s.o It would be helpful if you in time or space (đứng were to precede trước) the report with an introduction. Fund (v) /fʌnd/
An amount of money saved, Contributions are being
collected, or provided for a sought for particular purpose (quỹ) the disaster fund. Inspect (v) / n ɪ spekt ˈ / To look at sth or s.o She held the bank note carefully in order to up to the light and discover information,
inspected it carefully. especially about their quality or condition (quan sát) Allocation /ˌæl.ə ke ˈ .ɪʃən/ The process of giving s.o
Allocation of the grants (n) their part of a total amount
was handled by a charity of sth to use in a particular that provides support way (phân bổ)
and advocacy for disable d children. Offset (v) / f ˌɑː set ˈ / To balance one influence
The extra cost of travellin
against opposing influence, g so that there is no great to work is difference as a result (bù
offset by the lower lại) price of houses here. Transmit /trænsˈmɪt/
To broadcast sth, or to send Department stores use (v) out or carry signals or EDI to messages using radio, TV
transmit orders to supplie (chuyển giao) rs. Complete the statements 1. Allocate 2. Transmitting 3. Funding 4. Deduce 5. Offset 6. Orientation 7. Precede 8. Inspections CRITICAL THINKING 2.
1. Study at VANDERBILT University and Albert Einstein College of Medicine
2. Marvin Zuckerman’s sensation-seeking scale 3. Zuckerman’s twin study
4. National Institute of Mental Health, U. S. , study
5. Columbia Business School research
6. Columbia Business School research GRAMMAR 1.
1. Sentence a refers to the present (habit) and sentence b refers to the past
2. Sentence a refers to the present (in progress) and sentence n refers to the past
3. Sentence a refers to the present (habit) and sentence n refers to the past
4. Sentence a is active and sentence b is passive; but use present perfect
5. The time is emphasized in sentence a, i.e., now, immediately 2. 1. To be protecting 2. Be given 3. To have learned 4. Be needed 5. To be missing out 6. To have enjoyed 7. Be nurtured 8. Be provided
Question multiple choice
1.What is the type of word "mitigate" in the sentence "there are a number of things
that business people can do to mitigate risks"? a. Verb b. Noun c. Adverb d. Adjective
2.In the sentence "Risk is important in business because it can have a significant
impact on a company's bottom line," what does the word "bottom line" mean? a. Revenue b. Profit c. total d. Rule
3.What does the word "static" in the sentence "Risks are not static" mean? a. Quiet b. Electrostatic c. Stillness d. Static degree
4.What does the word "exhilarating" in the sentence "These risks can be
exhilarating, but they can also lead to serious injury or death" mean? a. Cause excitement b. Disappointing c. Causes boredom d. Causes anxiety
5.What does the word "prevalent" in the sentence "Overspending is a prevalent risk
that can quickly deplete one's financial resources" mean? a. Popular b. Rarely c. Primarily d. Accumulation Answer 1.A 2.B 3.C 4.A 5.A UNIT 5: SPRAWL Discussion point
1. Why do you think the cities have expanded at a faster rate than the suburbs?
There are a number of reasons why cities have expanded at a faster rate than the
suburbs in recent years. Some of the most significant factors include:
The rise of the knowledge economy: Cities are increasingly becoming centers for
innovation and knowledge creation, which has attracted a large number of highly
skilled workers. These workers are often drawn to the amenities and opportunities
that cities offer, such as access to world-class universities, research institutions, and cultural attractions.
Changes in transportation: The development of new transportation options, such as
light rail and bus rapid transit, has made it easier for people to live and work in
cities without relying on cars. This has made cities more attractive to people who
are concerned about the environment and who want to live a more sustainable lifestyle.
A renewed interest in urban living: There has been a growing interest in urban
living in recent years, as people are increasingly drawn to the vibrant energy and
diverse communities that cities offer. This has led to a resurgence of investment in
urban neighborhoods, which has helped to revitalize cities and make them more attractive places to live.
2. Why might poverty be a greater issue in the suburbs?
Poverty is often thought of as a problem that is primarily associated with inner
cities. However, poverty is also a significant issue in the suburbs. In fact, the
poverty rate in the suburbs has been increasing in recent years, while the poverty
rate in cities has been declining.
There are a number of reasons for this trend. One reason is that the suburbs are
becoming more economically diverse. In the past, the suburbs were primarily home
to middle- and upper-income families. However, as the cost of living in cities has
increased, more low-income families have been moving to the suburbs.
Another reason for the increase in poverty in the suburbs is that the suburbs are
losing jobs. Many of the jobs that were once located in the suburbs have been
outsourced or moved to other parts of the country. This has left many suburban
residents without jobs or with jobs that pay lower wages.
3. Why might the number of jobs within a typical commute distance be
decreasing in both suburbs and cities?
The number of jobs within a typical commute distance is decreasing in both
suburbs and cities for a number of reasons. One reason is that the economy is
becoming more globalized. This means that companies are increasingly able to
source their labor from all over the world, which has led to a decline in the number of jobs in many countries.
Another reason for the decline in the number of jobs is that the economy is
becoming more automated. This means that many jobs that were once done by
humans are now being done by machines. This has led to job losses in a variety of
industries, including manufacturing, retail, and transportation.
Finally, the decline in the number of jobs is also being driven by changes in the
way that people work. More and more people are now working remotely, which
means that they do not need to live near their jobs. This has led to a decline in the
demand for office space in both cities and suburbs. Before you watch 1a 2b 3e 4d 5c While you watch 1T 2T 3F 4F 5T
READING 1: Rust Belt dystopia Summary:
The Rust Belt, a region in the U.S., has experienced economic decline, population
loss, and urban decay over the past three decades. Three initiatives to revitalize the
region include increased tourism, economic restructuring, and smart decline. The
factory belt decline was caused by the industrial landscape shifting, leading to a
smaller share of manufacturing jobs and a heavy reliance on social security and
government spending. To create a successful tourist industry, planners must
develop a total tourism portfolio, focusing on natural features, urban parks, and
local culture. Economic restructuring involves diversifying the economy through
new knowledge, innovations, and technologies, but can be costly and costly to
local taxpayers. Smart decline, focusing on improving the lives of existing
residents rather than increasing population, has not been implemented in sufficient breadth to prove its efficacy. A. Vocabulary preview Words Transcription Meaning Example Automation
/ˌɑː.təˈme .ɪʃən/ The use of machines Automation and robotics have (n) and computers that
decreased the need for can operate without
a large, highly skilled needing human
control (tự động hóa) work force. Booming / bu ˈ .m ː ɪŋ/ Making a deep and The van turns up, fully (adj) loud hollow sound equipped with a (đang bùng nổ) booming sound system. Coal (n) /ko l ʊ / A hard, black How much coal was mined
substance that is dug here? from the earth in pieces, and can be burned to produce heat or power, or a single piece of this (than đá) Desired /dɪˈza rd ɪ / That is wanted
His words had the desired (adj) (mong muốn) effect. Domestically /də mes.t ˈ .k ɪ əl.i/ Inside a particular
The movie made $76 million (adv)
country rather than in domestically but only $1.3
other countries (trong million abroad. nước) Fallout (n) / f ˈ l.a ɑː t ʊ /
The radioactive dust The political fallout of the in the air after a revelations has nuclear explosion been immense. (phóng xạ) Impacted /ɪmˈpæk.tɪd/ An impacted tooth The asteroid impacted the (adj) cannot grow in the Earth right way, usually with devastating force because it is growing against another tooth below the gum (bị ảnh hưởng) Restructure / ri ˌ str ːˈ k.t ʌ ʃɚ/ To organize a
The government restructured (v) company, business,
the coal industry before or system in a new
selling it to private owners. way to make it operate more effectively (tái cơ cấu)
Complete the paragraph with the following words 1. Automation 2. Booming 3. Restructure 4. Coal 5. Domestically 6. Fallout 7. Impacted 8. Desired B. Before you read C. Global reading D. Close reading
3. Complete the sentences with no more than two words from the paper. 1. Transport links 2. Free trade 3. Pride 4. Tax payers 5. Vacant buildings 6. Regenerating E. Critical thinking Potential benefits:
Cost reduction: By adapting existing infrastructure and services to a smaller
population, municipalities can potentially reduce operational costs and optimize resource allocation.
Community building: Focusing on existing communities and utilizing vacant
spaces can foster stronger social ties and enhance local identity.
Environmental benefits: Reduced urban sprawl and resource consumption can
contribute to lower carbon emissions and environmental impact. Potential drawbacks:
Social and economic hardship: Depopulation and job losses can lead to increased
poverty, decreased tax revenue, and reduced access to essential services.
Difficulty in implementation: Shifting resources and adapting existing
infrastructure can be complex and politically challenging.
Risk of neglecting marginalized communities: Ensuring equitable access to
resources and opportunities for all residents during the decline process is crucial to
avoid exacerbating existing inequalities.
READING 2: Suburb of the future? Summary:
Shifting from Sprawl to Density:
Future suburbs will focus on density instead of sprawl, with mixed-use
developments offering housing, offices, shops, and entertainment in one place.
This can reduce infrastructure costs and commuting while benefiting the environment. Challenges and Opportunities:
Affordability is a major concern, as developments need to cater to diverse income
levels and prevent gentrification.
Ecologically sustainable construction is crucial, including energy-saving features
and carbon-neutral options (depending on location).
Mixed-use developments may increase parking needs and emissions in some areas,
requiring careful planning and alternative transportation options. Economic and Social Impacts: