Preview text:
PRACTICE 1 Q1.
Healthy Foods Inc. sells 50-pound bags of grapes to the military for $10 a bag. The fixed costs of this operation are
$80,000, while the variable costs of grapes are $0.10 per pound.
a. What is the break-even point in bags?
b. Calculate the profit or loss on 12,000 bags and on 25,000 bags.
c. What is the degree of operating leverage at 20,000 bags and at 25,000 bags? Why does the degree of operating
leverage change as the quantity sold increases?
d. If Healthy Foods has an annual interest expense of $10,000, calculate the degree of financial leverage at both 20,000 and 25,000 bags.
e. What is the degree of combined leverage at both sales levels? Q2.
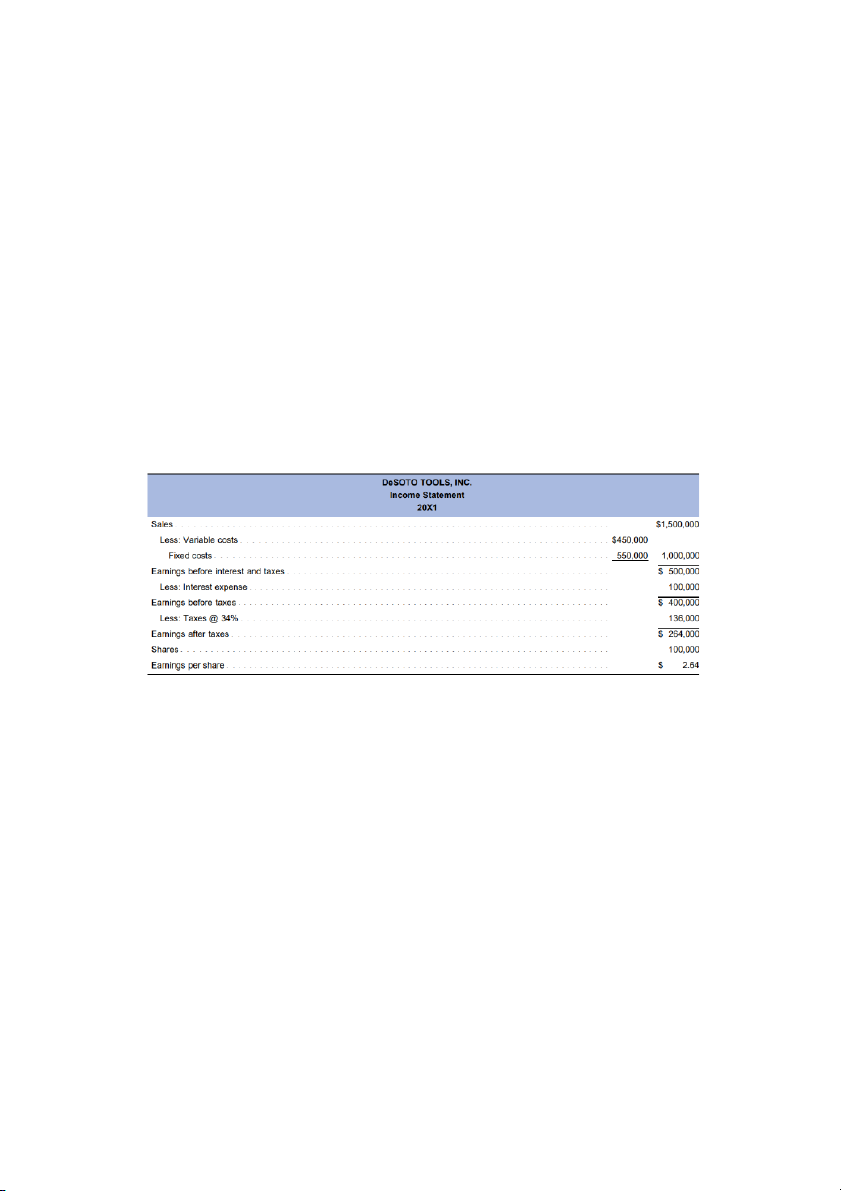
DeSoto Tools Inc. is planning to expand production. The expansion will cost $300,000, which can be financed either
by bonds at an interest rate of 14 percent or by selling 10,000 shares of common stock at $30 per share. The
current income statement before expansion is as follows:
After the expansion, sales are expected to increase by $1,000,000. Variable costs will remain at 30 percent of sales,
and fixed costs will increase to $800,000. The tax rate is 34 percent.
a. Calculate the degree of operating leverage, the degree of financial leverage, and the degree of combined leverage before expansion.
b. Construct the income statement for the two alternative financing plans.
c. Calculate the degree of operating leverage, the degree of financial leverage, and the degree of combined leverage, after expansion.
d. Explain which financing plan you favor and the risks involved with each plan
Q3. Cox Media Corporation pays an 11 percent coupon rate on debentures that are due in 10 years. The current
yield to maturity on bonds of similar risk is 8 percent. The bonds are currently callable at $1,110. The theoretical
value of the bonds will be equal to the present value of the expected cash flow from the bonds.
a. Find the market value of the bonds using semiannual analysis.
b. Do you think the bonds will sell for the price you arrived at in part a? Why?
Q4. A $1,000 par value bond was issued 25 years ago at a 12 percent coupon rate. It currently has 15 years
remaining to maturity. Interest rates on similar obligations are now 8 percent.
a. What is the current price of the bond? (Look up the answer in Table 16-2.)
b. Assume Ms. Bright bought the bond three years ago when it had a price of $1,050. What is her dollar profit
based on the bond’s current price? Đáp án PRACTICE 1
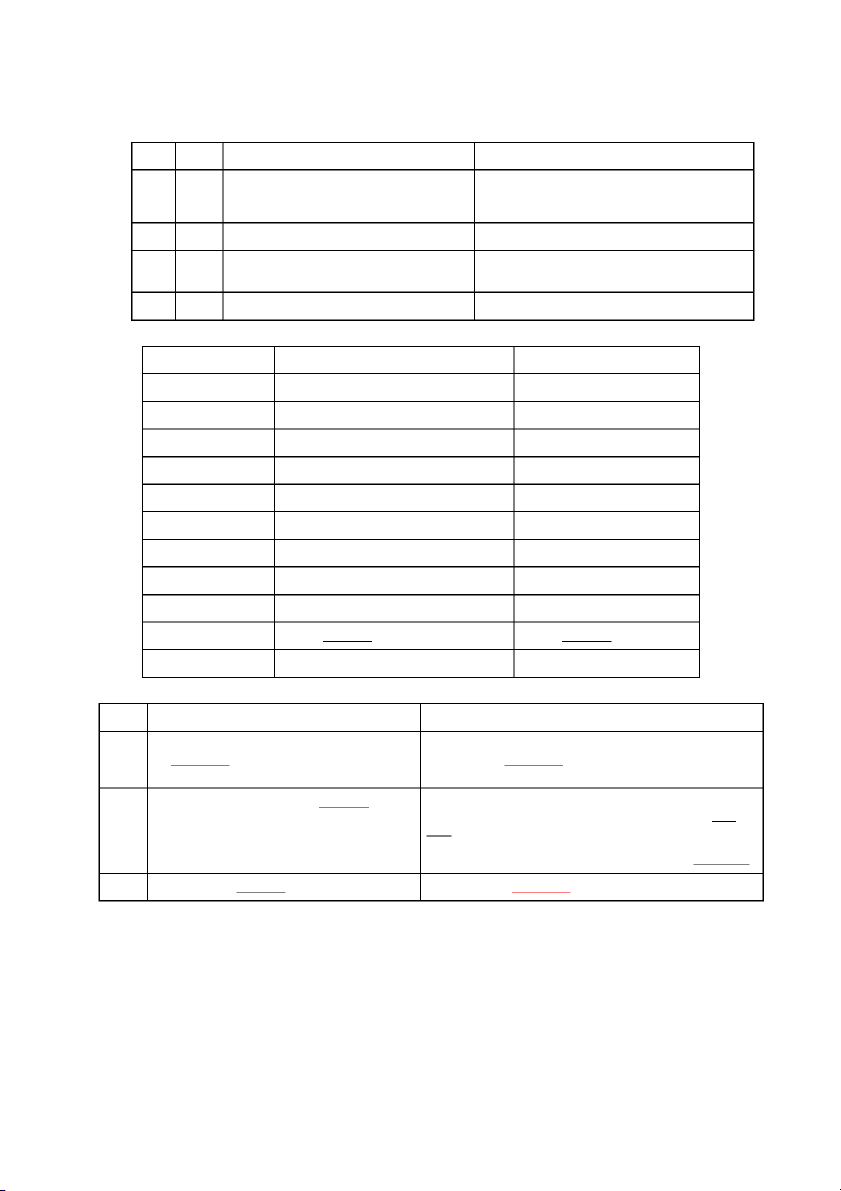
Tính đòn bẩy DOL, DFL và DTL trước và sau khi mở rộng hdsxkd Trước khi mở Sau khi mở
Dữ liệu báo cáo kết quả kinh Doanh thu mới? (cho trong đề)
Tổng chi phí biến đổi mới? DOL = Q(P-v)/Q(p-v)-F Chi phí cố định mới? = (tổng doanh thu- tổng
*nếu cty huy động vốn chủ để
chi phí biến đổi)/(Tổng doanh bổ sung vốn thì chi phí lãi vay
thu-tổng chi phí biến đổi- chi không đổi: phí cố đinh) = (1,500,000- DOL = Q(P-v)/Q(p-v)-F
450,000)/(1,500,000-450,000- = (tổng doanh thu mới- 550,000) tổng chi phí biến đổi DFL = Q(P-v)-F/Q(p-v)-F-I
mới)/(Tổng doanh thu mới- = (tổng doanh thu- tổng
tổng chi phí biến đổi mới- chi
chi phí biến đổi-CP cố phí cố đinh mới)
định)/(Tổng doanh thu-tổng DFL =(tổng doanh thu mới-
chi phí biến đổi- chi phí cố
tổng chi phí biến đổi mới- chi
đinh-cp lãi vay) =(1,500,000-
phí cố đinh mới)/(Tổng doanh
450,000-450,000)/(1,500,000- thu mới-tổng chi phí biến đổi 450,000-550,000-100,000)
mới- chi phí cố đinh mới -chi =EBIT/EBIT – I = phí lãi vay) 500,000/(500,000-100,000) DTL = DOLxDFL *Nếu công ty vốn vay: DOL = Q(P-v)/Q(p-v)-F = (tổng doanh thu mới- tổng chi phí biến đổi
mới)/(Tổng doanh thu mới-
tổng chi phí biến đổi mới- chi phí cố đinh mới) DFL =(tổng doanh thu mới-
tổng chi phí biến đổi mới- chi
phí cố đinh mới)/(Tổng doanh
thu mới-tổng chi phí biến đổi
mới- chi phí cố đinh mới -chi
phí lãi vay cũ+ CP lãi vay mới)
CP lãi vay mới = 14%x300,000 DOL DFL DTL (DCL)
Câu 1. a/ Q= 80.000/(10-0.1x50) =16.000 (0.5 điểm) Điểm Q=12.000 Q=25.000 0.5 Câu b
LN = 12.000x(10-0.1x50)-80.000 = -20.000
LN = 25.000x(10-0.1x50)-80.000 = 45.000 0.5 câu c
DOL=20.000x(10-5)/(20.000x(10-5)-80.000)=5
DOL=25.000x(10-5)/(25.000x(10-5)-80.000)=2.78 0.5 câu d
DFL=(20.000x(10-5)-80.000)/(20.000x(10-5)-
DFL=(25.000x(10-5)-80.000)/(25.000x(10-5)-80.000- 80.000-10.000)=2 10.000)=1.286 0.5 câu e 5x2 = 10 2.78x1.286 =3.5
Câu 2: b Construct the income statement for the two alternative financing plans. p/án vcsh p/an vay Dthu 2.500.000 2.500.000 CPBD 750.000 750.000 CPCD 800.000 800.000 Lãi gộp 950.000 950.000 CP lãi vay 100.000 142.000 CPBH 0 CP QLDN 0 LNTN 850.000 808.000 Thuế 289.000 274.720 LNST 561.000 (0.5 điểm) 533.280 (0.5 điểm) EPS LNST/số cổ phần Câu a và c. Trước mở rộng (câu a) Sau mở rộng (câu c) DOL
(1.500.000-450.000)/(1.500.000-450.000-550.000) =
(1.500.000+1.000.000-30%x2.500.000)/(2.500.000-30%x2.500.000- 2.1 (0.25 điểm)
800.000) = 1.84 (0.25 điểm) DFL
500.000/(500.000-100.000) =1.25 (0.2 điểm)
(2.500.000-30%x2.500.000-800.000)/(2.500.000-30%x2.500.000-
800.000-(1.00.000+42.000)) = 1.176 (t/h sử dụng vốn vay) (0.15 điểm)
(2.500.000-30%x2.500.000-800.000)/(2.500.000-30%x2.500.000-
800.000-1.00.000 =1.118 (t/h sử dụng vốn chủ sở hữu) (0.15 điểm) DTL
2.1x1.25 =2.625 (0.25 điểm)
1.84x1.176 =2.17 (0.125 điểm)-vay
1.84x1.118 = 2.06 (0.125 điểm)- (vốn chủ sở hữu)
Câu 3: Tiền lãi coupon 6 tháng= 11%x1.000/2 = 55 USD
PB = 55x(1/4% - 1/(8%x(1+4%)20) +1000/(1+4%)20 =1203.85 (2.5 diem)
Câu 4: . PB = 120x(1/8% - 1/(8%x(1+8%)10) +1000/(1+8%)10 =1268.4 (1.5 điểm) a.
profit = 1268.4-1050=218.4 (1 điểm)




