



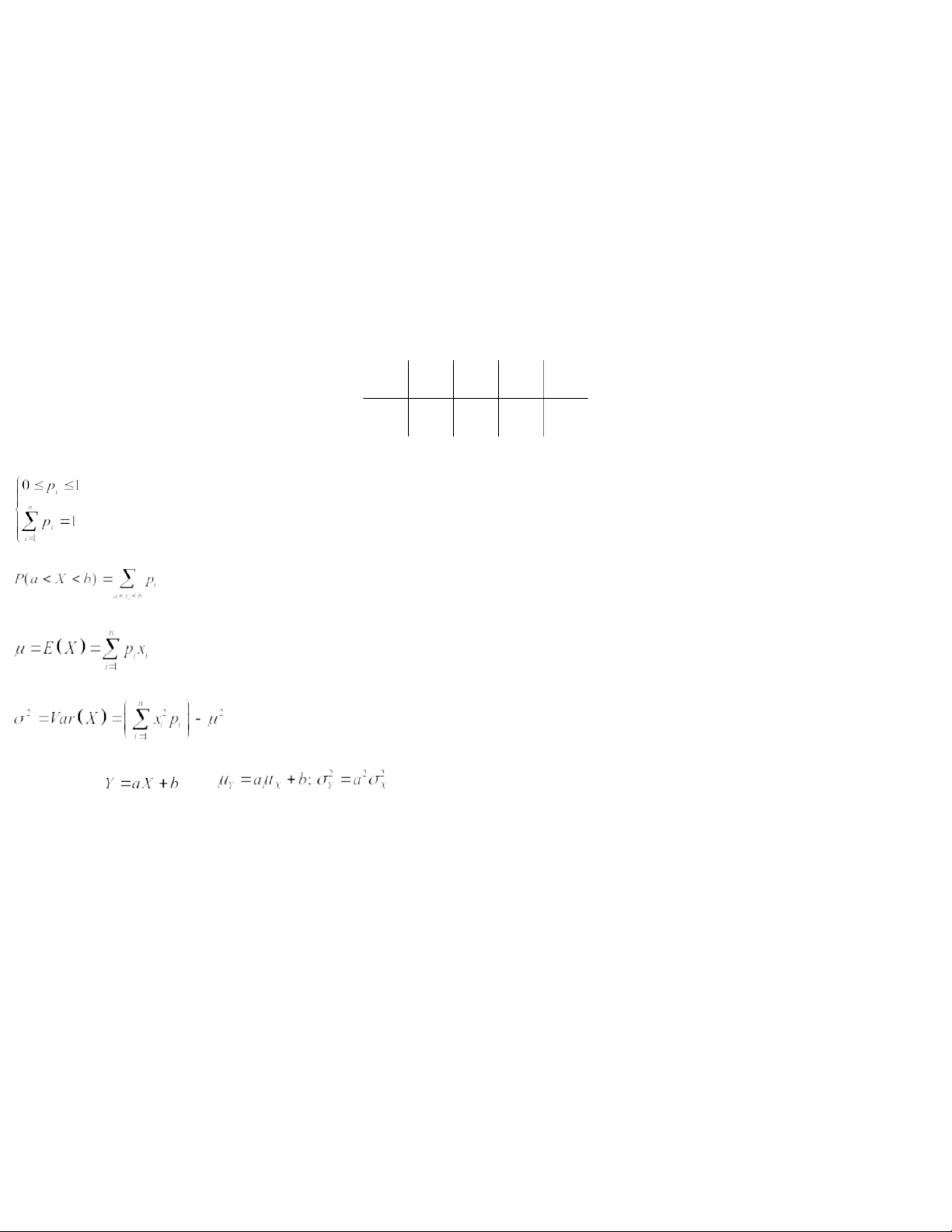






Preview text:
20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu
Question 1. (2 marks) Given that 10% of the people who come into the showroom and talk to a salesperson will purchase a car. To increase
he chances of success, you propose to offer a free dinner with a salesperson. The project is conducted, and 40% of the people who
purchased cars had a free dinner. In addition, 10% of the people who did not purchase cars had a free dinner.
a. (1 mark) What is the probability that a person will have a free dinner?
b. (0,5 marks) What is the probability that a person who accepts a free dinner will purchase a car?
c. (0,5 marks) What is the probability that a person who does not accept a free dinner will purchase a car?
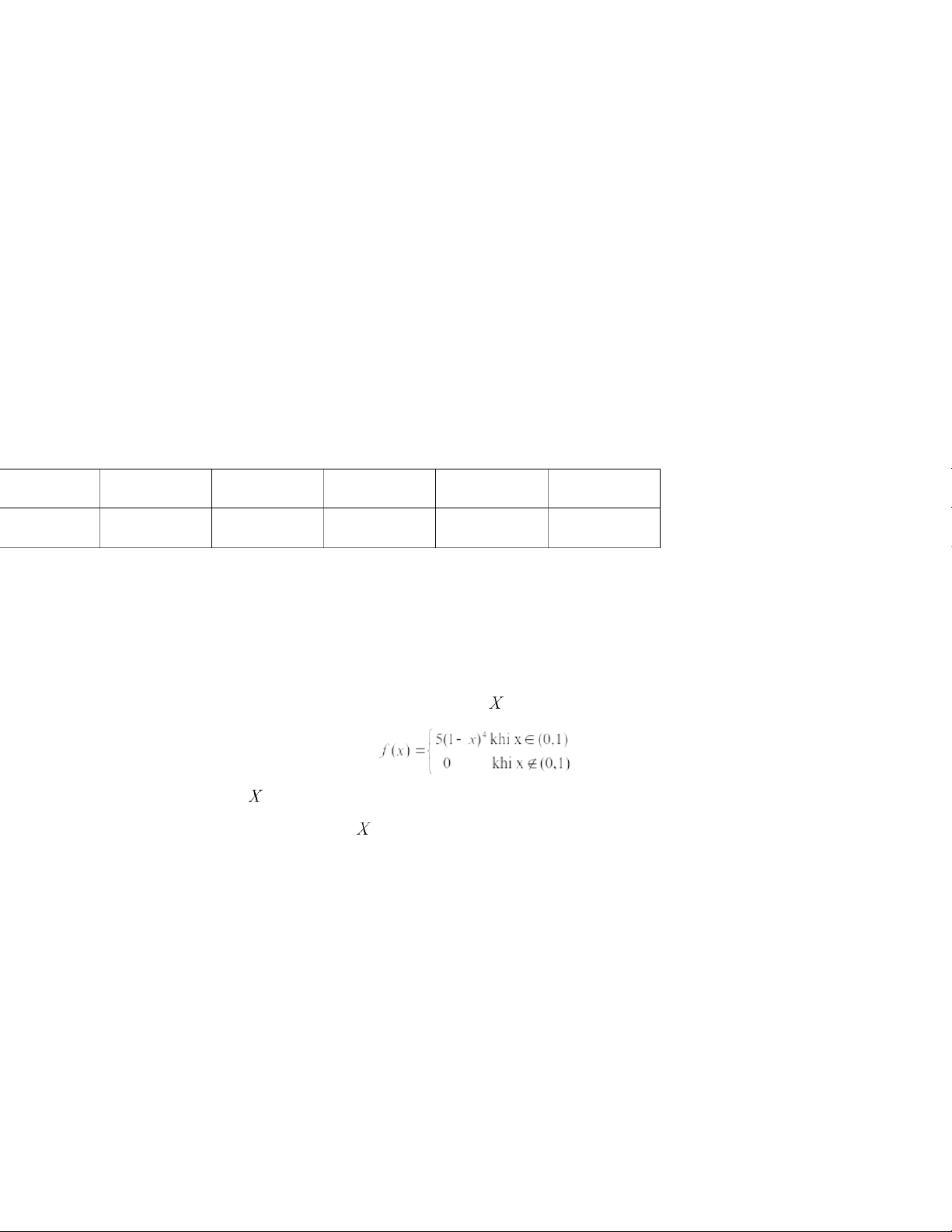
Question 2. (2 marks) A contractor estimates the probabilities for the number of days required to complete a certain type of construction project as follows: Time (days) 1 2 3 4 5 Probability 0,05 0,20 0,35 0,30 0,1
a. (1 mark) What is the probability that a randomly chosen project will take less than 3 days to complete?
b. (1 mark) The contractor’s project cost is made up of two parts—a fixed cost of $20,000, plus $2,000 for each day taken to complete the
project. Find the mean and standard deviation of total project cost.
Question 3. (1 mark) The number of accidents in a production facility has a Poisson distribution with a mean of 2.6 per month. For a given
month what is the probability there will be more than 3 accidents?
Question 4. (2 marks) Given the density function of a random variable .
a. (1 mark) Find the probability that is less than or equal to 0,3.
b. (1 mark) Find the expected value and variance of . 20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu
Question 5. (2 marks) It is estimated that the time that a well-known rock band, the Living Ingrates, spends on stage at its concerts follows
a normal distribution with a mean of 200 minutes and a standard deviation of 20 minutes.
a. (1 mark) An audience member smuggles a tape recorder into a Living Ingrates concert. The reel-to-reel tapes have a capacity of 245
minutes. What is the probability that this capacity will be insufficient to record the entire concert?
b. (1 mark) The probability is 0.2 that a Living Ingrates concert will last less than how many minutes?
Question 6. (1 mark) Package I has 5 products of type A, 1 product of type B. Package II has 2 products of type A, 4 products of type B
From each package, 1 product is randomly selected to deliver to the customer. Then the remaining products are put together into empty
package III. If we randomly select 2 products from package III, calculate the probability that there is at least 1 type B product among the 2 selected products? TEST 7 Time: 60 minutes
Question 1. (1 mark) Suppose 20 % of the employees of company ABC have only a high school diploma, 60 % have bachelor degrees, and
20 % have graduate degrees. Of those with only a high school diploma, 15 % hold management positions; whereas, of those having
bachelor degrees, 30 % hold management positions. Finally, 60 % of the employees who have graduate degrees hold management
positions. What percentage of employees holds management positions?
Question 2. (1 mark) Suppose you play a game with a biased coin. You play each game by tossing the coin once. Given P(heads) = 2/3. If
you toss a head, you pay $6. If you toss a tail, you win $10. What is your expected profit of playing the game over the long term?
Question 3. (1 mark) Text message users receive or send an average of 41,5 text messages per day.
a. (0,5 marks) What is the probability that a text message user receives or sends two messages per hour?
b. (0,5 marks) What is the probability that a text message user receives or sends more than two messages per hour?
Question 4. (1 mark) A company wants to estimate the proportion of people who are likely to purchase electric shavers from those who
watch the nationally telecast baseball playoffs. A random sample obtained information from 120 people who were identified as persons
who watch baseball telecasts. Suppose that the proportion of those likely to purchase electric shavers in the population who watch the
elecast is 0,25. The probability is 0.05 that the sample proportion is lower than the population proportion by how much? 20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu
Question 5. (2 marks) You do a study of hypnotherapy to determine how effective it is in increasing the number of hours of sleep subjects
get each night. You measure hours of sleep for 12 subjects with the following results.
8,2 9,1 7,7 8,6 6,9 11,2 10,1 9,9 8,9 9,2 7,5 10,5
a. (1 mark) Construct a 95% confidence interval for the mean number of hours slept for the population (assumed normal) from which you ook the data.
b. (1 mark) At 90% confidence, what is the width of the confidence interval?
Question 6. (3 marks) At the insistence of a government inspector, a new safety device is installed in an assembly-line operation. After the
nstallation of this device, a random sample of 8 days’ output gave the following results for numbers of finished components produced: 618 660 638 625 571 598 639 582
a. (1 mark) Calculate the samle mean and deviation.
b. (1 mark) Contruct a 95% confidence interval for the population mean.
c. (1 mark) Management is concerned about the variability of daily output and views any variance above 500 as undesirable. Test, at the
10% significance level, the null hypothesis that the population variance for daily output does not exceed 500.
Question 7. (1 mark) In a promotion for a particular airline, customers and potential customers were given vouchers. A 1/325 proportion of
hese were worth a free round-trip ticket anywhere this airline flies. How many vouchers would an individual need to collect in order to
have a 50% chance of winning at least one free trip?
*Critical Values for the standard normal distribution: CHAPTER 1. PROBABILITY I. Solution Steps 20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu
+ Step 1: Define the events from the problem.
+ Step 2: Define the probabilities and conditional probabilities for the events defined in Step 1.
+ Step 3: Find the system of events which is both mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive (compute the complement if needed). + Step 4: Apply the formula. II. Probability rules 1. Complement rule: . 2. Addition rule: . n particular, if are mutually exclusive, then . 3. Conditional probability: . 4. Multiplication rule: Events
are said to be statistically independent if and only if . 5. Total probability: Given the system of events
that are both mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive, then 20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu or 20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu
CHAPTER 2. DISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLES I. Distribution table Given the distribution table: Xx1x2….xn Pp1p2….pn Then 1. . 2. . 3. . 4. . n particular, if then . 20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu
II. Binomial Distribution Suppose that
a random experiment can result in two possible outcomes, “success” and “failure,”
and that p is the probability of a success in a single trial.
Let X be the the number of resulting successes in n independent trials.
The probability distribution of X is called binomial distribution.
III. Poisson Distribution
Let X be the number of occurrences in a given continuous interval (such as time, surface area, or length). Then the probability distribution
of X is called the Poisson distribution. 20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu
CHAPTER 3. CONTINUOUS RANDOM VARIABLES I. Density Function Given the density function
of a continuous random variable . Then i) ii) iii) iv) v) vi) 20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu II. Normal Distribution f
follows the normal distribution with the mean and variance , then The values of
can be found in Appendix Table 1 with the notices ) . i) ii) Moreover, if and , then
also follows the normal distribution 20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu
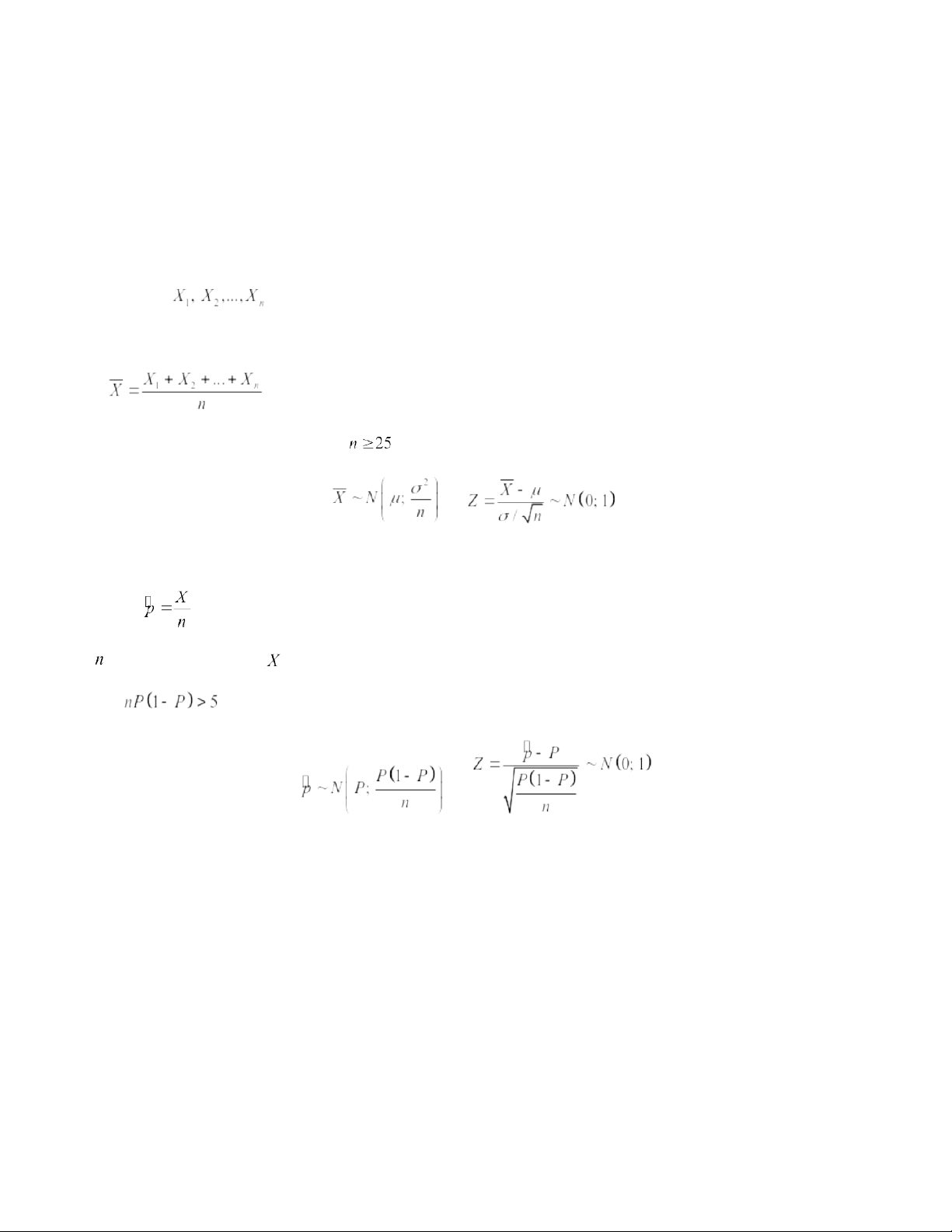
CHAPTER 4. SAMPLING DISTRIBUTION Let the random variables
denote a random sample from a population. I. Sample mean Sample mean: .
If the parent population distribution is normal (or ) then or . II. Sample proportion Sample proportion: where is the sample size and
is the number of objects having the characteristic of interest. When n is large ( ), we have or 20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu III. Sample variance Sample variance: .
If the parent population distribution is normal then 20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu
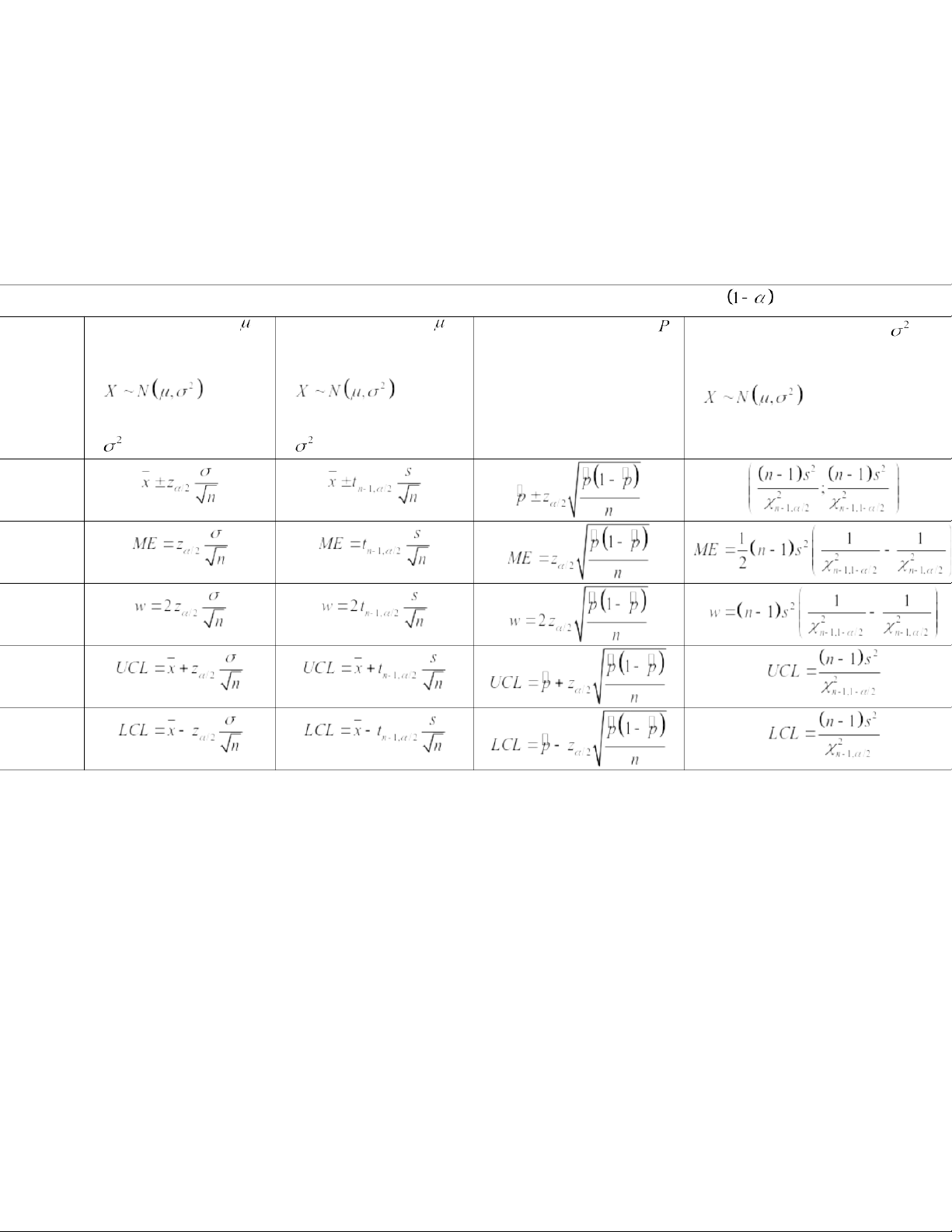
CHAPTER 5. CONFIDENCE INTERVAL ESTIMATION I. Formulas
Confidence Interval Estimation with the sample n and the confidence level Population mean Population mean Population proportion Population variance Given Given Given Estimation Given + n is large for + (or n is + (or n is + large) large) + is known + is unknown Confidenc e interval Margin of error Width Upper confidence limit Lower confidence limit 20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu II. Critical values
1. Critical values for the standard normal distribution: is a value such that Some critical values: Given the critical value
, we can determine the significant level (or confidence level ) by the following formula where
can be found in Appendix Table 1.
2. Critical values for the Student’s t distribution is a value such that The value
can be found in Appendix Table 8.
3. Critical values for the Chi-squared distribution is a value such that The value
can be found in Appendix Table 7a and 7b. 20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu
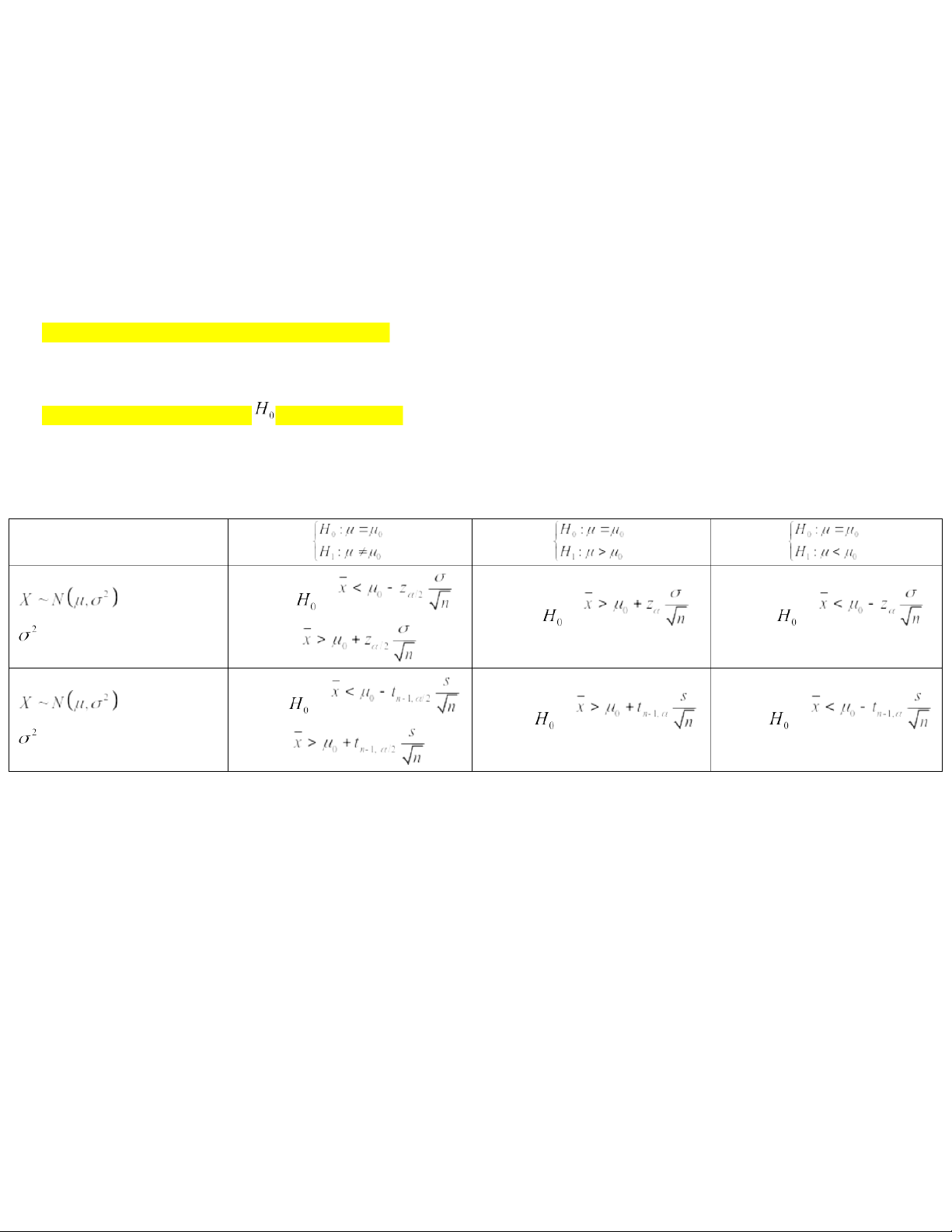
CHAPTER 6. HYPOTHESIS TESTS I. Solution steps
+ Step 1: State the null and alternative hypotheses.
+ Step 2: Summarize all information.
+ Step 3: Decision rule: reject if …… (Formula)
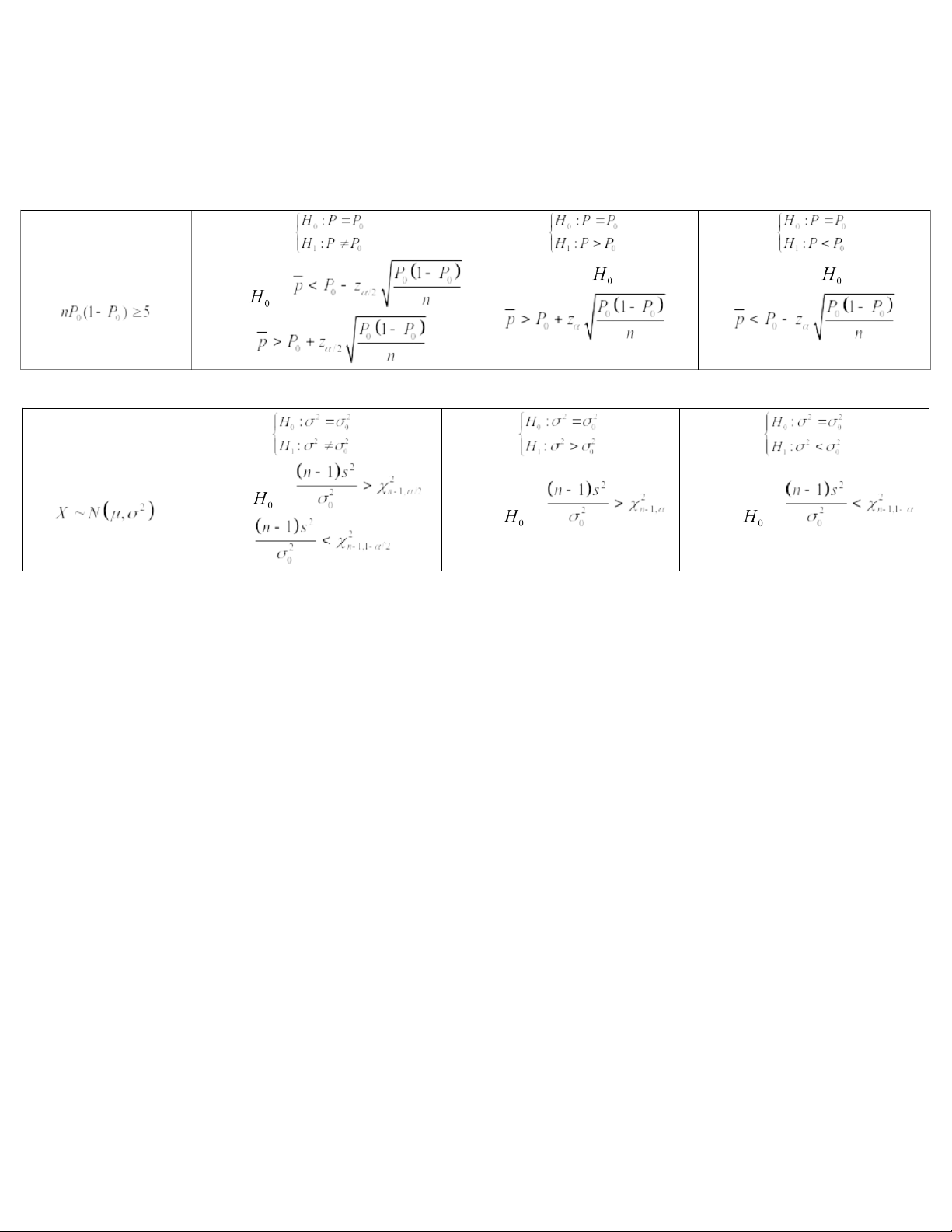
+ Step 4: Random sample => conclusion II. Decistion rule For population mean (or n is large) Reject if Reject if Reject if is known or (or n is large) Reject if Reject if Reject if is unknown or 20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu For population proportion Reject if Reject if Reject if or For population variance Reject if Reject if Reject if or 20:59, 27/01/2026
Probability and Statistics Review - Combo Đề 67 Exam Notes - Studocu




