









Preview text:
Quiz 3 True/False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false. __ T __ rue
1. Probability is the tool that allows the statistician to use sample information to make inferences about
or describe the population from which the sample was drawn. __ T __ rue
2. Relative frequency histograms are constructed for a sample of measurements drawn from the n
population, while the probability histogram is constructed as a model for the entire population of measurements. ____ False
3. When a patient who is complaining of several specific symptoms arrives at a doctor's office, the
doctor who makes the diagnosis says that she is 90% certain that the patient has the flu, it is likely
that she is basing her assessment on relative frequency approach of assigning probabilities. ____ False
4. If P(A) > 0, P(B) > 0, and P(A B) = 0, then the events A and B are independent. ____ False
5. The time required to assemble a computer is an example of a discrete random variable. continuous Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
____ 1. Which of the following statements is true?
a. An experiment is the process by which an observation or measurement is obtained.
b. An event that cannot be decomposed is called a simple event.
c. An event is the collection of one or more simple events.
d. Only an experiment is the process by which an observation or measurement is
obtained and an event is the collection of one or more simple events are true. e.
____ 2. The set of all simple events of an experiment is called: a. a compound event c. a population d. a random sample e. all of these
____ 3. Which of the following correctly describes experiments?
a. They are two random events, A and B, such that the probability of one event is not
affected by the occurrence of the other event; therefore, P(A) = P(A|B).
b. They are different events that have no outcomes in common. c. d. All of the above. e. None of these.
____ 4. Any subset of the sample space is called: a. an event b. an experiment c. mutually exclusive events d. independent events e. None of these
____ 5. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. The experiment of tossing a single coin once contains 1 simple event.
c. The experiment of spinning the Monte Carlo roulette wheel once contains 27 simple events.
d. The experiment of drawing a single card once from a standard deck contains 4 events.
e. The experiment of tossing a coin twice contains 2 simple events.
____ 6. When Cynthia enters a grocery store, there are three simple events: buy nothing, buy a small
amount, or buy a large amount. In this situation, if Cynthia buys a small amount, she cannot also buy
a large amount or buy nothing. Thus the three events are: a. b. not mutually exclusive c. dependent events d. independent events e. none of these
____ 7. Which of the following statements if false?
a. The set of all simple events of an experiment is called the sample space. TRUE
c. The sum of the probabilities for all simple events in the sample space equals 1. TRUE
d. The probability of an event A is equal to the sum of the probabilities of the simple events contained in A.
e. The probability for any event in the sample space is between 0 and 1 inclusive.
____ 8. Which one of the following is always true for two events, A and B?
a. If A and B are independent, they are also mutually exclusive.
b. If A and B are dependent, they are also mutually exclusive.
c. If P(A / B) = P(A B), A and B are independent. e. All of these.
____ 9. If P(A/B) = P(A), or P(B/A) = P(B), then events A and B are said to be: a. mutually exclusive b. disjoint c. d. dependent e. B contains A.
____ 10. A false negative in screening tests (e.g., Steroid testing of athletes) represents the event that:
a. the test is negative for a given condition, given that the person does not have the condition
b. the test is positive for a given condition, given that the person does not have the condition c. d.
the test is positive for a given condition, given that the person has the condition
____ 11. A false positive in screening (e.g., home pregnancy tests) represents the event that:
a. the test is negative for a given condition, given that the person does not have the condition
c. the test is negative for a given condition, given that the person has the condition
d. the test is positive for a given condition, given that the person has the condition
____ 12. Screening tests (e.g., AIDS testing) are evaluated on the probability of a false negative or a false
positive, and both of these are: a.
b. probability of the intersection of two events
c. probability of the union of two events d. marginal probabilities
e. probability of dependent events
____ 13. The expected number of heads in 500 tosses of an unbiased coin is: a. 150 b. 200 c. d. 300 e. 500
____ 14. Which of the following correctly describes the nature of discrete quantitative variables?
a. They are characteristics possessed by persons or objects, called elementary units, y p y p j y in which we are interested.
b. They can assume values only at specific points on a scale of values, with
between successive observations
c. When dealing with such variables, we can count all possible observations and,
with some exceptions, that count leads to a
d. Is correctly described by “they are characteristics possessed by persons or objects,
called elementary units, in which we are interested” and “when dealing with such
variables, we can count all possible observations and, with some exceptions, that
count leads to a finite result.” e.
____ 15. The mean of a discrete random variable : x a. is denoted by
b. is denoted by E( ), because it is the value of x
one can expect to find on average by x
numerous repetitions of the random experiment that generates the variable's actual values
c. is correctly described by both “is denoted by ” and “is denoted by d. is always = 0 e. is none of these Problem
1. How many permutations of 3 colors can be drawn from a group of 20 colors? _______ 6840 _______
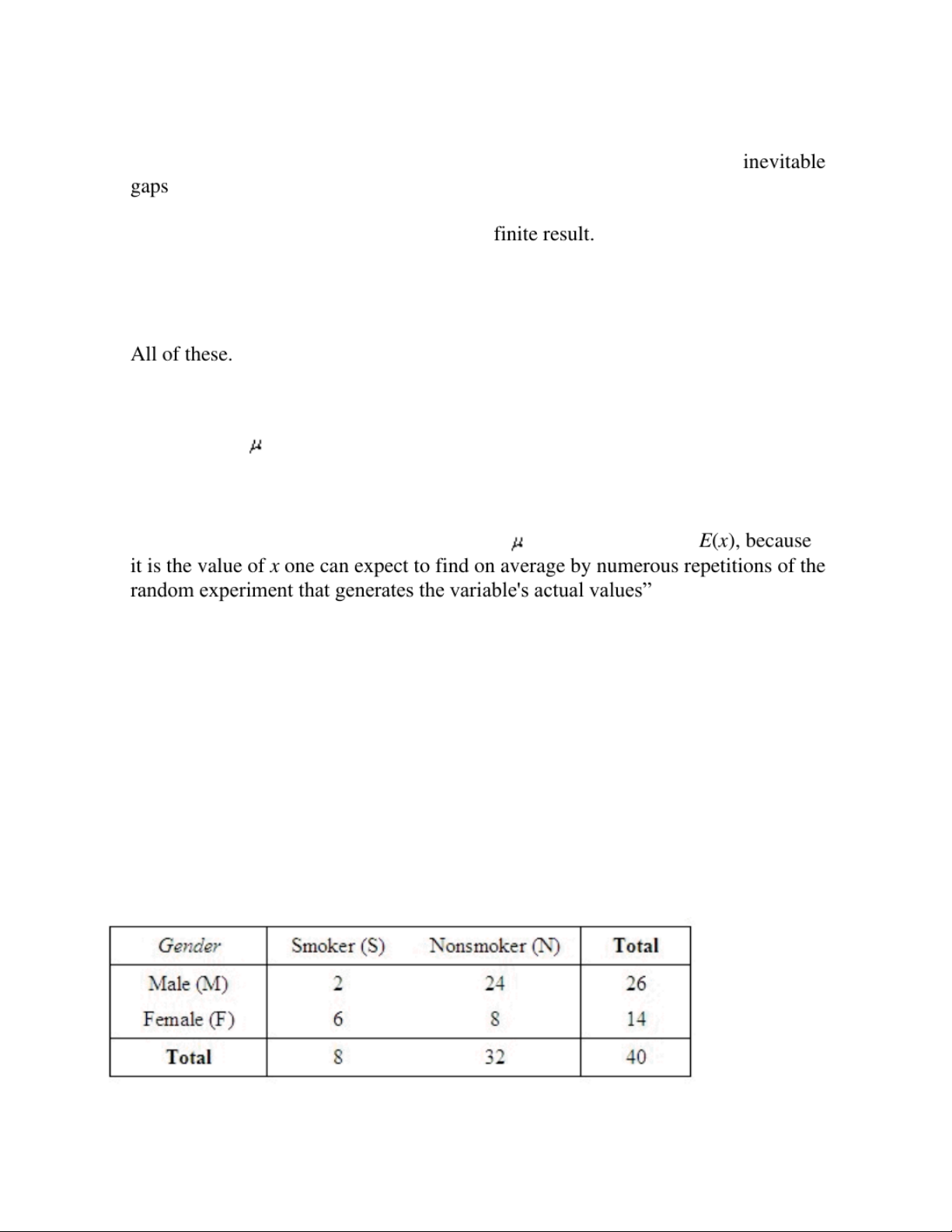
2. A group of forty people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown below:
Round your answers to four decimal places, if necessary.
a. One person is selected at random from that group of forty people. What is the probability the person smokes? ______________ 0.2
b. What is the probability the person is female but does not smoke? ______________ 0.2
c. What is the probability the person is male? ______________ 0.65
e. What is the probability the person is female? ______________ 0.35
f. What is the probability the person is male and smokes? ______________ 0.05
g. If the person was male, what is the probability he smokes? ______________ 0.0769
h. If the person was female, what is the probability she does not smoke? _____________ 0.5714




