













Preview text:
HOA SEN UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF TOURISM
COURSE: LEADERSHIP & MANAGEMENT IN HOSPITALITY INDUSTRY Group 9
Supervisor: Võ Thị Nga Ph.D Students: Phạm Anh Vũ – 2172173
Trần Phương Nhi – 2184751
Nguyễn Thị Thu Thủy – 2194508 HO CHI MINH CITY, 2021 HOA SEN UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF TOURISM
COURSE: LEADERSHIP & MANAGEMENT IN HOSPITALITY INDUSTRY Group 9
Supervisor: Võ Thị Nga Ph.D Students: Phạm Anh Vũ – 2172173
Trần Phương Nhi – 2184751
Nguyễn Thị Thu Thủy – 2194508 2 HO CHI MINH, 2021 3 DUTY ROSTER Ordinal Full name Student ID no Duty Rate of progress 1 Phạm Anh Vũ 2172173 - Chapter 1 & 4 100% - Power point - Abstract - Word 2 Trần Phương Nhi 2184751 - Chapter 2 100% (word + ppt) - Q&A 3 Nguyễn Thị Thu 2194508 - Chapter 3 100% Thủy (word + ppt) - Q&A 4 ABSTRACT
Leadership is a lifelong learning process. Every great leader always looks for ways
to improve. No one ever wakes up and says, “I know everything there is to know about
leadership. I’m a perfect leader.”
Leadership can be especially challenging for entrepreneurs. Balancing the need to
run a business (products, investors, customers, etc.) and the need to lead company personnel is quite a task.
In this report, I will introduce the delegation of leaders in the organization, the
processes and responsibilities of delegation will be evident in this article. 5 TABLE OF CONTENTS
ABSTRACT.......................................................................................................................4
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION......................................................................................7
CHAPTER 2: CONTENT..................................................................................................9
1. What is delegation leadership style?........................................................................9
2. Essentials of Delegation...........................................................................................9
3. Conditions for delegating successfully include......................................................10
3.1. Advance planning............................................................................................10
3.2. A positive attitude toward your people............................................................10
3.3. Trust................................................................................................................10
3.4. The ability to let go and take risk....................................................................10
3.5. Good communications.....................................................................................11
3.6. Commitment....................................................................................................11
4. The steps in delegation leadership..........................................................................11
4.1. The first step is planning..................................................................................11
4.2. The second step is developing the task in detail..............................................11
4.3. The third step is delegating..............................................................................12
4.4. The fourth step is follow up.............................................................................12
CHAPTER 3: DICUSSION.............................................................................................13
5. Benefits or advantages of delegation of authority..................................................13
5.1. Specialization..................................................................................................13
5.2. Reduce Pressure And Workload.......................................................................13
5.3. Quick Decisions..............................................................................................13
5.4. Employee Development..................................................................................13
5.5. On-the-job Training.........................................................................................13
5.6. Better Understanding.......................................................................................13
5.7. Expansion And Diversification........................................................................14
5.8. Suitability........................................................................................................14
6. Drawbacks Or Disadvantages Of Delegation Of Authority....................................14 6
6.1. Misunderstanding And Conflict.......................................................................14
6.2. Poor Results.....................................................................................................14
6.3. Misuse Of Power.............................................................................................14
6.4. Burden On Subordinates..................................................................................15
6.5. Lack Of Self Confidence.................................................................................15
6.6. Low Quality Of Work......................................................................................15
6.7. Not Suitable.....................................................................................................15
7. Common mistakes in delegation and Improve.......................................................16
7.1. Giving Vague Instructions...............................................................................16
7.2. Using Delegation to Avoid Difficult Decisions................................................16
7.3. Delegating Tasks to the Wrong Person............................................................17
7.4. Failing to Empower Delegates to Complete Projects.......................................17
7.5. Forgetting Who You Delegate Tasks To...........................................................18
7.6. Waiting Until a Task is Complete to Check Progress.......................................18
CHAPTER 4: CONCLUSION.........................................................................................20
REFERENCES................................................................................................................21 7 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
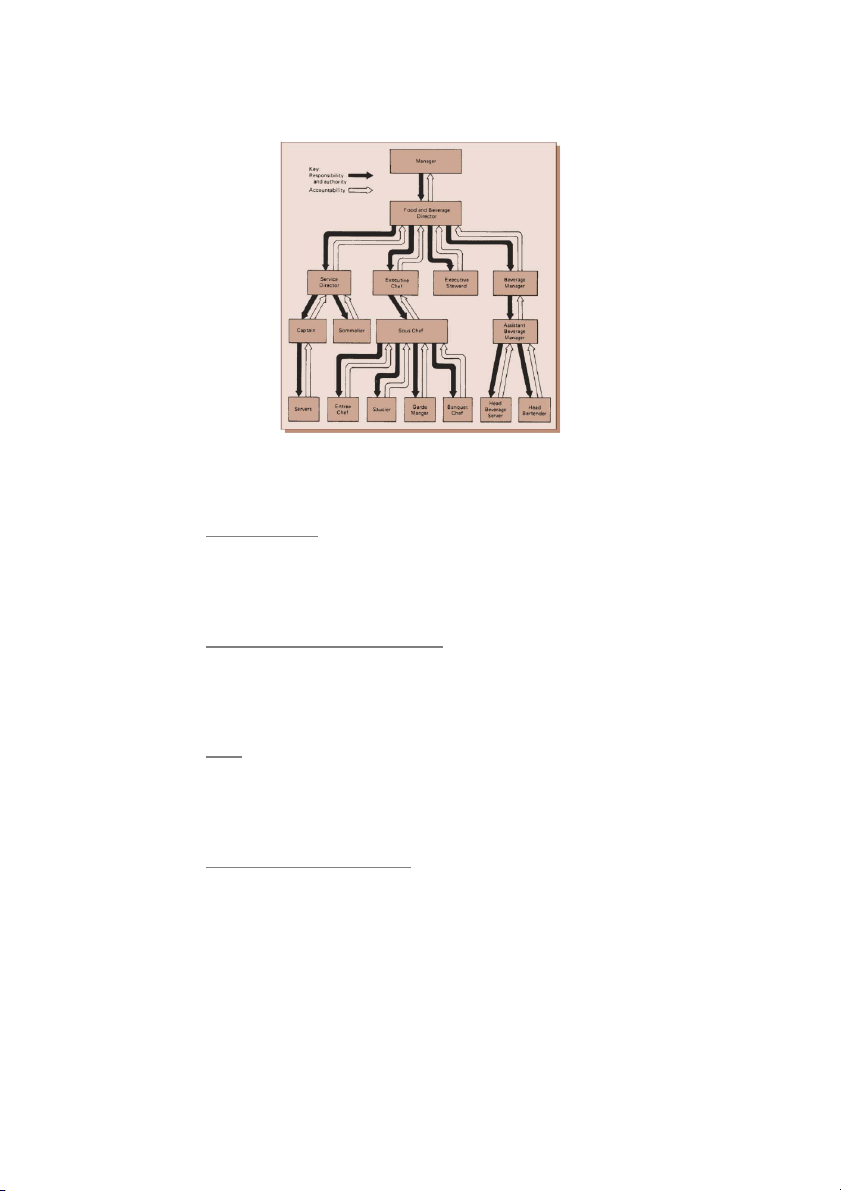
Delegation is basically a process of assigning responsibility, sharing authority, and
producing accountability in organizations. The process of delegation is adjusted
according to the nature of the work itself, and by the type of person who will be
completing the work. Delegation is a crucial expertise for managers to use to make the
best of their own time and resources. The manager who is skilled in delegation
overcomes the problems by establishing clearly understood plans and standards,
instructing his people to carry work through. As he knows that result are the final
measure and there are different ways to arrive at equally satisfactory results. (Henry
Mintzberg 1973) “views delegation as the most significant managerial problem. He
argues that while managers tend to delegate tasks involving only one specialist function,
they feel cold footed on the prospects of delegating tasks that cut across specialties or that
involve the managers’ special information”. “Empirical research has illuminated our
understanding of why managers delegate and the outcomes of delegation, there is a
paucity of research on the conditions under which delegation is effective (Leana, 1986,
1987) (Schriesheim et al., 1998) (Yukl, 1998) and why delegation is related to its
demonstrated outcomes”. This paper is review work in field of delegation; the main
purpose is to understand the delegation process and describe the standards, skills of the
managers and to suggest the delegation path model and explaining various benefits to managers and subordinates.
In the modern organizational structure, delegation of authority has become the
focus of the researchers and scholars. These are constantly keeping close eye on the
decentralization of the organizations and the impact of delegation on the performance of
organization in general and employees in particular. 8
Objectives of the delegation of authority include: a reduction of the excessive
burden of work on superiors (e.g., executives and managers); provision of opportunities
for growth and self-development to junior executives; establishment of a team of
experienced and matured managers for the organization; and improvement of individual
and overall organizational efficiency. 9 CHAPTER 2: CONTENT
1. What is delegation leadership style?
A leadership style refers to a leader’s methods and behaviors when directing, motivating,
and managing others. A person’s leadership style also determines how they strategize and
implement plans while accounting for the expectations of stakeholders and the wellbeing of their team.
Leadership is the assignment of one or more meaningful tasks or responsibilities, either
operational or managerial in nature, to a subordinate or subordinates. Delegate responsibility
Managers are responsible for the entire output of department, they delegate responsibility
for certain parts of the work to people they hire to do certain jobs.
Example: delegate cooking to the cooks, front desk work to the front desk clerks.
2. Essentials of Delegation
There are 3 aspects of delegation:
Responsibility: Something that it is your job or duty to deal with
Authority: The rights and powers to make the necessary decisions and take the
necessary actions to get the job done
Accountability: Means the answerability of the subordinate to those above him in
the chain of command for his work’s responsibility
In short, as a supervisor you have been given the responsibility for certain activities and
the results they are expected to produce, the authority (or rights and powers) to carry out
your responsibilities, and the accountability (or obligation to your boss) to produce these results. 10
3. Conditions for delegating successfully include 1.1. Advance planning
This should include an overall review of who is responsible for what in your
department at this time, what further responsibilities could be delegated, who is qualified
to assume greater responsibilities, what training would be necessary… 1.2. A po
sitive attitude toward your people
You must have good relationships with your employees, know their interests and
their capabilities, and be sensitive to their needs and their potential. You must respect
them as individuals and be interested in developing them, for both your sake and theirs. 1.3. T rust
You trust them enough to share your responsibility with them, and they trust you
not to put something over on them or get them in over their heads. Only if you both have
this trust can you get the commitment necessary to make delegation work. 1.4.
The ability to let go and take risk 11
Each time you delegate a responsibility it is going to be new for you and new for
the other person, and some mistakes are bound to be made. But when a mistake happens,
the worker learns under your leadership, and you improve your leadership skills. You can
both learn something from every mistake, and that is how you both grow 1.5. Good communications
Make sure that the people to whom you delegate know the terms of their authority
and the extent of their responsibility 1.6. Commitment
The employees will become committed to achieving the results. You, in turn, must
be committed to train, coach, and support as needed.
4. The steps in delegation leadership 1.7.
The first step is planning
- Need to identify tasks that can be assigned to someone else.
- Need to figure out which of your people are able and willing to take them on.
- Listing all the things you do.
- Keep a chart for several days on which you note absolutely everything you do in each quarter – hour.
- Sort out your activities and responsibilities into groups.
- Arrange things that should and could be delegated in some kind of order: order of
importance, or ease of delegating, or time saved.
- Choose which one or two you will tackle first. 1.8.
The second step is developing the tas k in detail
- Define the area of responsibility
- The activities that must be carried out - The results you expect
- The authority necessary to fulfill the responsibility
- Use a system of performance standards as an excellent tool for use in delegating responsibility.
- You have told them exactly what you want, have set the achievement goals, and
have trained them in the skills needed.
- They can take the responsibility from there and leave you free to manage. 12 1.9. The thir d step is delegating
- Delegate responsibility for the task and the results expected.
- Delegate the authority necessary to carry it out. - Establish accountability.
When you delegate, you meet with the chosen employees in a private interview, you describe:
- The task, the results you expect
- The responsibility and authority it entails
It should be an informal person - to - person discussion and there must be agreement on
the employee’s part to accept the delegation.
There are 3 right things in delegation: you have matched the right person with the right
assignment and have communicated it in the right way, employees will be interested,
pleased, motivated, challenged, and glad to have more responsibility
1.10. The fourth step is follow up
Train your people as needed. This is something they have never done before, so
you go through the whole story: what you want done, how you want it done, to what standard 13 CHAPTER 3: DICUSSION
5. Benefits or advantages of delegation of authority
The main advantages of delegation of authority can be studied as follows: 1.11. Specialization
Authorities and responsibilities are delegated as per the skills, abilities, knowledge
and experience of subordinates. So, delegation of authority promotes specialization and
division of work in the organization. 1.12. Reduce Pr essure And Workload
In delegation, routine routine tasks are assigned to middle level and lower level
managers. It reduces the pressure, stress and workload of top level manager. Manager get
enough time to conduct other important creative and productive activities. 1.13. Quick Decisions
Lower level managers get the authority to make decisions which helps to improve
their decision making power. They do not need to consult top managers to take decision
which ensures prompt decisions at the workplace.
1.14. Employee Development
Delegation of authority helps to develop skills and capabilities of subordinates. It
helps them to perform challenging jobs which helps to develop managerial qualities. 1.15. On-the-job T raining
Delegation of authority is a kind of on-the-job training where subordinates can
learn, improve skills and develop managerial abilities at the workplace.
1.16. Better Understanding
It helps to build trust and better understanding between managers and subordinates
in the organization. It promotes effective communication and sense of team spirit while performing the job. 14 1.17. Expansion And Diversification
Delegation creates well-trained, dedicated and competent team of subordinates.
So, it is helpful for expansion, growth and diversification of organization. 1.18. Suitability
Delegation of authority is suitable for large organizations with different
departments, branches and units with various organizational activities
6. Drawbacks Or Disadvantages Of Delegation Of Authority
The major disadvantages of delegation can be studied as follows:
1.19. Misunderstanding A nd Conflict
Because of lack of proper communication and coordination, there exists a chance
of misunderstanding and conflict between managers and subordinates. It may negatively
affect the performance and productivity of the firm. 1.20. Poor Results
It authority and responsibility is delegated to unskilled and incompetent
subordinate, then the organization cannot achieve desired results because of poor performance. 1.21. Misuse Of Power 15
Another drawback of delegation is that the subordinate can misuse his.her power
by taking wrong decisions for personal benefit. 1.22. Bur den On Subordinates
Delegation of authority increases the workload and stress of subordinates. Pressure
of work may lose interest and lower the motivation towards the job.
1.23. Lack Of Self Confidence
Superior tries to delegate boring and not properly defined tasks to the
subordinates. In most cases, very limited power is given to them which reduce the self confidence of the employees. 1.24. Low Quality Of W ork
If authority is not delegated properly to the proper person, then the quality of work
will be affected. It negatively affects productivity, goodwill and image of the business. 1.25. Not Suitable
Delegation of authority is not suitable for small firms with limited organizational activities. 16
7. Common mistakes in delegation and Improve 1.26. Giving V ague Instructions
Your employees cannot read your mind. The top delegation mistake leaders make
is assigning employees tasks without providing clear expectations. There are only three
cases when you’re likely to have a successful outcome when you give vague instructions:
You’re delegating a task to someone who has completed it several times before
and already knows your preferences.
You only care about the results, and you empower the person you delegate to do
the work however they think is best.
You’re open to a variety of outcomes and curious about what your employee will
produce when they’re not influenced by your guidance.
Without one of those conditions, employees are likely to be confused and interrupt you
with lots of questions and/or make unintentional mistakes because they don’t understand what you want from them. Fix this error:
Give people specific instructions that detail what you want them to accomplish
and how. Make sure the person you delegate to has an opportunity to ask questions before they begin working.
1.27. Using Delegation to
Avoid Difficult Decisions 17
A study published in Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes
found that people tend to delegate decisions that involve unattractive options and are
likely to create poor outcomes for others. These are the worst types of tasks to pass off.
You are responsible for your strategic work. Assigning critical tasks to other
people often leads to poor outcomes and creates resentment toward you and delegated work in general. Fix this error:
Only delegate tasks that are not part of your responsibilities or that you know
will likely result in someone else taking the blame for a difficult decision that
should have been yours to make. 1.28. Delegating T
asks to the Wrong Person
Assigning work based on who first comes to mind, sets yourself up for failure.
Who you choose to delegate to impacts the speed and accuracy of project completion and
your team’s overall perception toward delegation.
If you assign work to a mid to upper-level professional who is stressed out with
their work, they’re unlikely to give your task the needed effort and may resent you for
adding more to their workload. Likewise, if you pass on a complicated project to an
employee in a junior or a support staff role, they’re likely to fail. Fix this error:
Consider people’s availability, skills, position, and interests when deciding who to
delegating to. Though it will take a few extra minutes to make a decision, they will
complete the work much more efficiently.
1.29. Failing to Empower Delegates to Complete P rojects
When delegating one-off tasks, leaders often forget that their subordinates don’t
have the same ability to complete work. Setbacks that can occur from this are:
Not having access to necessary tools
Being blocked by individuals who think they don’t have the authority to
complete the work you assigned them 18
Having inadequate access to knowledge and materials that would help them work more effectively
Lacking the power to make decisions necessary to complete the task Fix this error:
Before delegating tasks, think about what you would use to complete them and
empower your delegate with the same access and authority that you do. 1.30. For
getting Who You Delegate Tasks To
If you’re distractedly delegating work while juggling several other tasks, you’re
setting yourself up for confusion when assignments are due. Forgetting who you assign
work to creates two tense and avoidable conflicts:
If a job isn’t completed by its due date, you don’t remember who to reach out to
for a progress update. This limits accountability and may force you to redo work
by the unknown person you delegated to.
You may incorrectly recall who you assigned a task to and which may lead you to
hold someone responsible for work that you never gave them. Fix this error:
Make a note in your task management tool whenever you delegate a task. This
ensures that you always know who to hold accountable. 1.31. W
aiting Until a Task is Complete to Check Progress
Even if leaders remember who they delegate tasks to, they often forget about work
while it’s in progress. The danger of waiting until a job is complete to check-in is that you
don’t have any time to identify and correct errors before they affect the entire project.
Even if you delegate small tasks on an ongoing basis, such as scheduling
and expense management, it’s vital to have brief syncs with your team to ensure they meet expectations. Fix this error: For lar ge projects: 19 o
Check-in, at a minimum, mid-way through its timeline. Add additional
progress updates if it’s challenging and/or requires a high degree of accuracy. For small, fr equent tasks: o
Set up a brief sync two to four times per month to offer feedback and
identify opportunities for improvement. 20