


Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 23136115 REVIEW QUESTIONS RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
-------------------------------------------------------- 1.
How do you come up with the research project idea?
The most convincing way to generate the new research idea is reading literature reviews to
explore the research gaps in a specific field which interest you.
However, you can also apply the following steps to come up with new idea:
● Step 1: Brainstorm for ideas.
● Step 2: Read General Background Information.
● Step 3: Focus on Your Topic.
● Step 4: Make a List of Useful Keywords. ● Step 5: Be Flexible.
● Step 6: Define Your Topic as a Focused Research Question.
● Step 7: Research and Read More About Your Topic.
● Step 8: Formulate a Thesis Statement. 2.
Why researchers create theoretical framework?
● to provide the theoretical framework for the research project;
● to establish their expertise in this area;
● to detail the current state of knowledge in the area;
● to highlight what is known and to highlight any gaps in what is known;
● to detail the theory from which the research has emerged;
● to outline the theory to which the research will ultimately contribute. 3.
How to generate theory from your own research?
● Your review of the literature gives you material from which you develop questions to ask in data gathering.
● When you analyse the data gathered, you begin the process of theorising your data.
● You do this by establishing where and how your data supports, and/or contradicts, the
theory in the literature review.
● This is the process of establishing how your data fits with the theory in the field. 4.
Before building theoretical framework, what should researchers do?
The researchers can build the theoretical framework through 4 main steps as follows:
● Step 1: Define problem statement lOMoAR cPSD| 23136115 ●
● Step 2: Clarify aims and objectives
Step 3: Present research questions
● Step 4: Finding appropriate literature review
Link for reference: https://ca.indeed.com/career-advice/career-
development/theoreticalframework 5.
Steps in creating theoretical framework
● Step 1: Identify your key concepts
The first step in constructing theoretical framework is to decide the key concepts/terms from
the problem statement and research questions, and clearly define those terms. ● Step 2:
Evaluate and explain relevant theories
After identifying key concepts, it is necessary to compare and critically evaluate the approaches
that different authors have proposed. In this step, researchers should choose the most important
theories related to main concepts.
● Step 3: Evaluate and explain related literatures, show how your research fits in
Importantly, researchers need to search for the most relevant readings regarding the
topic, explaining and showing that your own research project will make use of these ideas.
Link for reference: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4y1BAqOnhMM 6.
Presenting the purpose of LR
LR is regarded as the collection of academic and peer-reviewed writing on any given subject.
LR plays a vital role in research process for the reasons:
● LR provides historical background for your research: you need to know what has been
written about your research, so you can explore something new and significant about
the field in which you are studying.
● LR gives an overview of the current context in which your research is situated by
referring to comtemparary debates, issues, and questions in the field. This is because
the research fields have been updated continuously.
● LR includes a discussion of relevant theories and concepts which underpin your research.
● LR introduces relevant terminology and provides definitions to clarify how terms are
being used in the context of your own work. lOMoAR cPSD| 23136115 ●
● LR describes related research in the field and shows how your work extends or
challenges this, or addresses a gap in work in the field.
• LR assists creating a theoretical framework for the research project, the theoretical
framework is contained in the literature review. It is the content of the literature review.
Link for reference: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1nqzcfw1wDE
Extra question 1: How to be expert in LR?
● Search for relevant papers about your research theme, ensuring that approaching top
journals of business such as Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, Journal of
International Economics, Journal of International Business, Asia Pacific Journal of
Marketing and Logistics, The World Economy Journal, and other prestigious jounals.
● Make sure you use the right key words and terms in LR
● Exploit deeply relevant papers to get comprehensive understand regarding the topic
● Follow the citations of articles you do seek
Link for reference: https://www.editage.com/insights/5-tips-to-write-a-great-literature-review
Extra question 2: How to identify appropriate LR? ● Be discerning
● Check the date of publication
● Try to be as up-to-date as possible
● Be sure, also, to include seminal works
● Check the credentials of the authors
● Read the written account of the research ● Be critical
● Trace the steps of the research process through your reading of the research 7.
What’s the block of theory?
Four building blocks of theory include concepts, propositions, logic, and assumptions. ● Concepts/contructs
Concepts are the building blocks of theory. Concept is basic idea and communication
that helps in giving some order and sence to experimental knowledge. Concept is an accepted
collection of meanings or characteristics associated with certain events, objects, conditions,
situations, and behaviors. All theories and ideas are based on concept. lOMoAR cPSD| 23136115 ●
Constructs are abstract concepts specified at a high level of abstraction that are chosen
specifically to explain the phenomenon of interest.
Propositions: are associations postulated between constructs based on deductive logic.
Propositions are stated in declarative form and should ideally indicate a causeeffect relationship.
● Logic: Speaks to the "why" and acts like a "glue" that interfaces the theoretical
constructs and gives significance and importance to the connections between these constructs.
● Assumptions: Inspects the "who, when and where." All theories are obliged by
assumptions about time, space, values, and boundary conditions that oversee where the
theory can be connected and where it can't be connected. Link for reference:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AHGcIg_Fa44 8.
In the methodology, what the researchers needs to address? Link: Research Methodology ● What data
+ Qualitative or quantitative research, mixed-method research?
+ Secondary data or primary data? ● Sampling
+ What is your population, sampling? ● Data collection methods
+ Probability sampling or Non-probability sampling? ● Data analysis
+ Descriptive statistics, correlation matrix, multicollinearity, heteroskedasticity, regression, … 9.
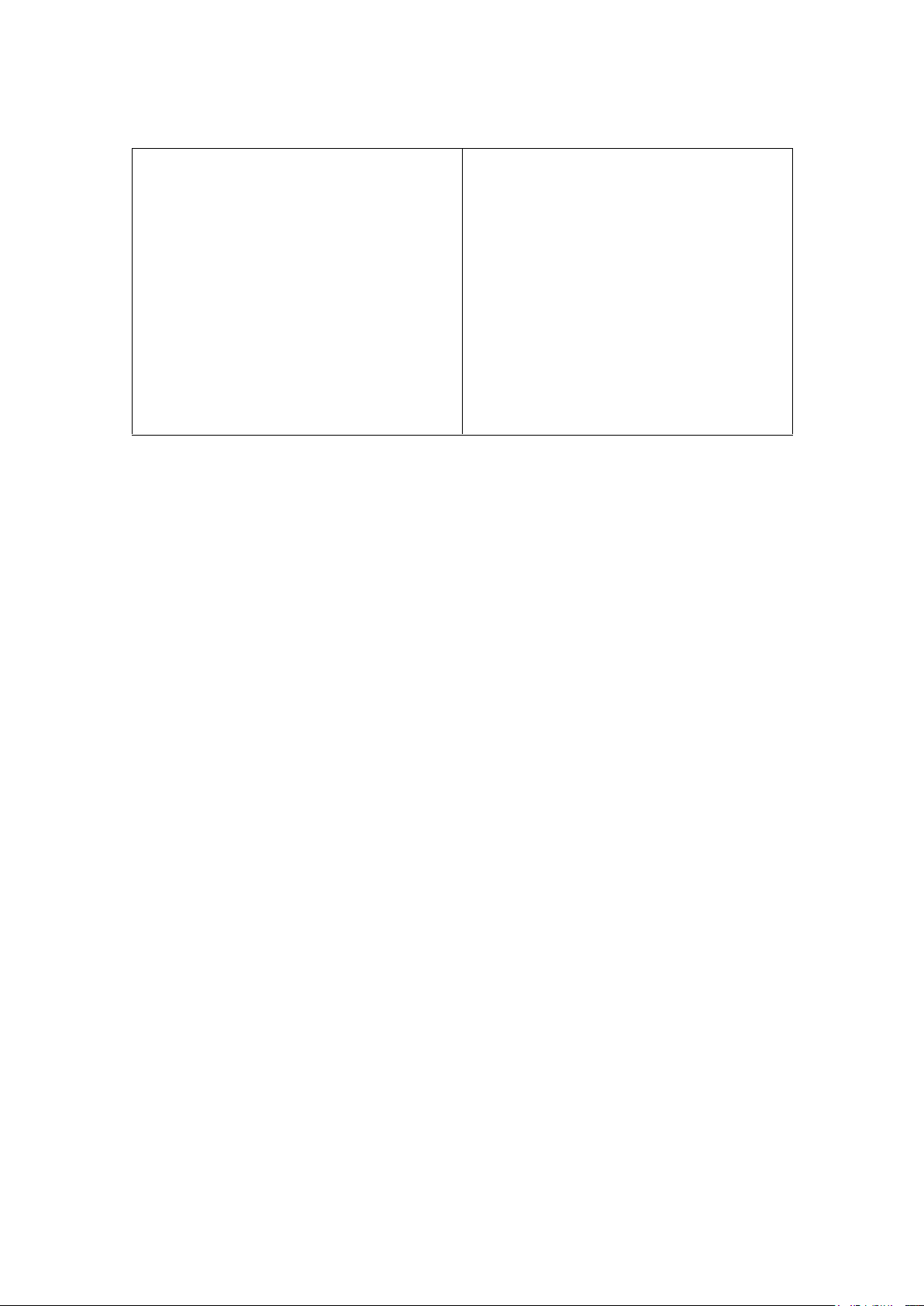
Make a comparison between qualitative research and quantitative research
Qualitative research
Quantitative research lOMoAR cPSD| 23136115 ● •
Qualitative research is expressed in
• Quantitative research is expressed in
words. -It is used to understand concepts, numbers and graphs. thoughts or experiences.
-It is used to test or confirm theories and
-This type of research enables you to gather assumptions.
in-depth insights on topics that are not well
-This type of research can be used to understood.
establish generalizable facts about a topic.
• Common quantitative methods include •
Common qualitative methods include experiments, observations recorded as
interviews with open-ended questions,
numbers, and surveys with closed-ended
observations described in words, and
literature reviews that explore concepts and lOMoAR cPSD| 23136115 theories. questions.
• It’s quite common for a qualitative
• A quantitative methodology is typically
methodology to be used when the research
used when the research aims and objectives
aims and objectives are exploratory in nature. are confirmatory in nature.
Extra question: Is it better to have only one method or mixed-method? 10.
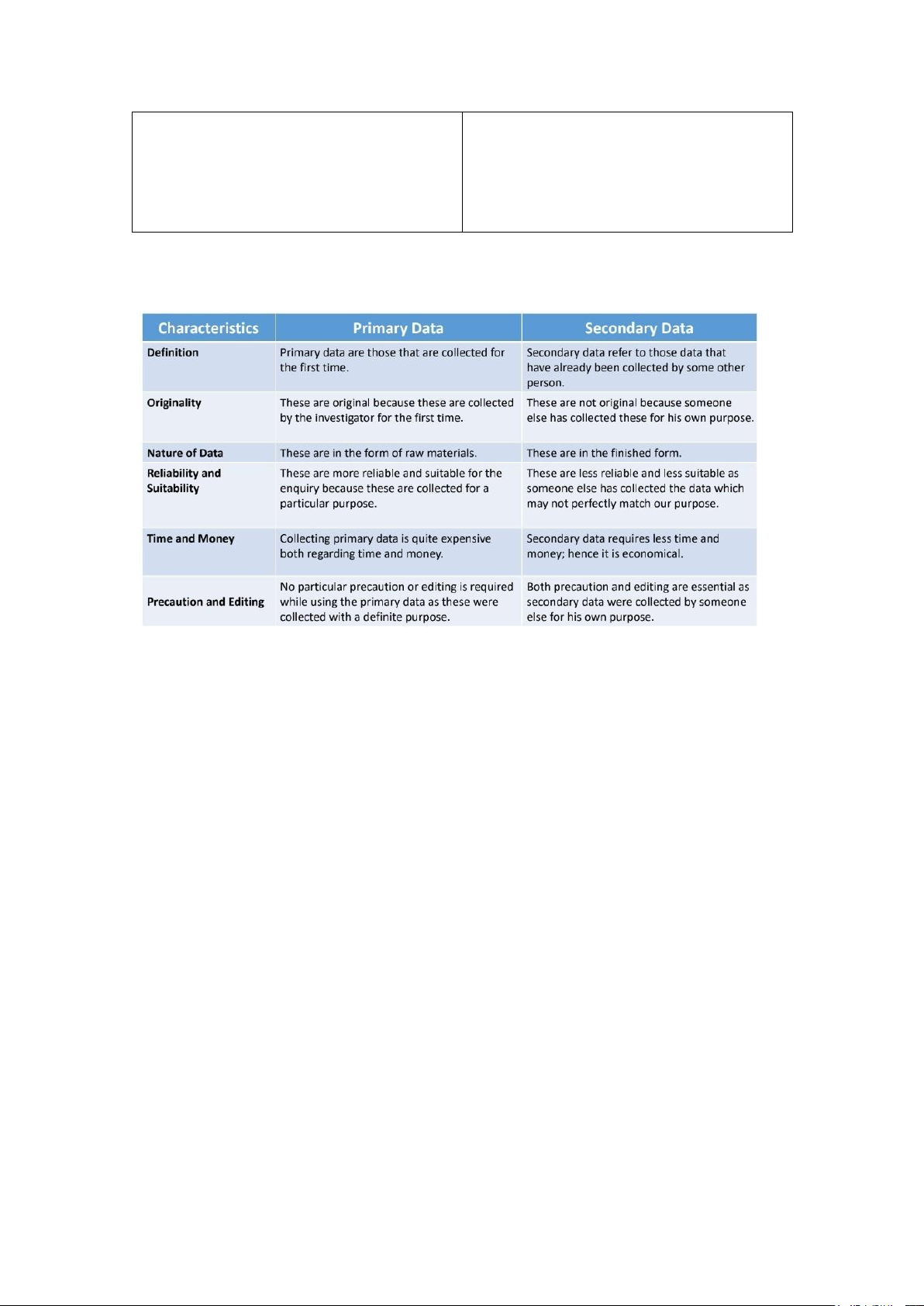
Make a comparison between secondary data and primary data
Extra question: Should we use primary or secondary data? 11.
The importance of theory in the research
● Theory is of the most fundamental importance in research.
● Research that is theorised makes a contribution to the body of knowledge – it connects with the body of knowledge.
● Such research becomes part of the ‘what is known’ about the phenomenon under investigation. 12.
How many types of variables we have learned? Which are they? Explained There
are five types of variables: dependent variable, independent variable, mediating
variable, moderating variable, and control variable.
● Variables that explain other variables are called independent variables.
● Variables that are explained by other variables are dependent variables.
● Variables that are explained by independent variables while also explaining dependent
variables are mediating variables (or intermediate variables).
● Variables that influence the relationship between independent and dependent variables
are called moderating variables. lOMoAR cPSD| 23136115
● Variables that are not pertinent (relevant) to explaining a given dependent variable, but
may have some impact on the dependent variable are control variables. 13.
How many types of standard scales? Explained
● Nominal scales (also called categorical scales), measure categorical data. These scales
are used for variables or indicators that have mutually exclusive attributes.
● Ordinal scales are those that measure rank-ordered data, such as the ranking of students
in a class as first, second, third, and so forth, based on their grade point average or test scores.
● Interval scales are those where the values measured are not only rank-ordered, but are
also equidistant from adjacent attributes.
● Ratio scales are those that have all the qualities of nominal, ordinal, and interval scales,
and in addition, have a “true zero” point (where the value zero implies lack or non-
availability of the underlying construct). 14.
Key ethical principles and issues ● Do not harm ● Integrity ● Plagiarism ● Validity ● Power ● Transparency 15.
What is sampling method? Probability sampling
● Sample random sampling: all possible subsets of a population are given an equal
probability of being selected.
● Systematic sampling: sampling frame is ordered according to some criteria and
elements are selected at regular intervals through that ordered list.
● Stratified sampling: the sampling frame is divided into homogeneous and
nonoverlapping subgroups (called “strata”), and a simple random is drawn within each subgroup
Non-probability sampling
● Convenience sampling: this is a technique in which a sample is drawn from that part
of the population that is close to hand, readily available, or convenient. lOMoAR cPSD| 23136115
● Quota sampling: the population is segmented into mutually-exclusive subgroups of
respondents to meet a predefined quota.
● Expert sampling: this is a technique in which respondents are chosen in a non-random
manner based on their expertise on the phenomenon being studied.
● Snowball sampling: you start by identifying a few respondents that match criteria for
inclusion in your study, then ask them to recommend others they know who also meet your selection criteria. 16.
Levels to contribute to scientific research ● Replicate
● Develop new measurement method
● Expand the existing theory ● Develop new theory 17.
How to test hypotheses? ● Measurement ● Data collection ● Data analysis




