














Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392 BANKING ACADEMY ADVANCED PROGRAM
GROUP ASSIGNMENT: COMMERCIAL BANKING MODULE CODE : FIN09H TOPIC:
‘THE ROLE OF COMMERCIAL BANKS IN PROMOTING SUSTAINABLE
DEVELOPMENT OF ECONOMY’
Group 2 - Class K24CLCTCB
Instructor : Ts. Nguyen Thi Diem Huong Group members:
Vu Thu Thao ( leader) 23A4010609
Pham Thuy Nhung 24A4012965
Tran Thi Hong Nhung 24A4013122
Nguyen Nhat Minh 24A4010767
Huynh Ngoc Mai 24A4013111 lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392 Ha Noi, 2023 lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392 TABLE OF CONTENT
1. Liturature review ............................................................................................... 1
1.1. Definition and frameworks to calculate sustainable development of economy ... 1
1.2. Role of commercial banks in promoting sustainable development (NCKH) ...... 2
2. Liturature Sustainable developed activites of Vietnam commercial banks ............... 4
2.1. Green banks development ............................................................................ 4
2.1.1 Environmental policy in credit appraisal ................................................... 5
2.1.2. Green credit........................................................................................... 6
2.1.3. Green bond............................................................................................ 9
2.1.4. Community social activities .................................................................. 11
2.2. Digital banks development ......................................................................... 12
2.2.1 Payment ............................................................................................... 12
2.2.2 Lending ............................................................................................... 13
2.2.3 Saving ................................................................................................. 16
2.2.4 Blockchain ........................................................................................... 17
3. Assessment of the activity of Commercial Bank ................................................. 18
3.1. Assessment of the activity of Green Bank .................................................... 18
3.1.1. Achievements ...................................................................................... 18
3.1.2 Limitations ........................................................................................... 19
3.1.3 Solution ............................................................................................... 20
3.2. Assessment of the activity of Digital Bank ................................................... 21
3.2.1. Achievements ...................................................................................... 21
3.2.2. Limitations .......................................................................................... 22
3.2.3. Solution .............................................................................................. 23
4. References ....................................................................................................... 25 lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392 1. Liturature review
1.1. Definition and frameworks to calculate sustainable development of economy
There are different definitions of sustainable development of the economy,
depending on the perspective and context of research. (1) Economic sustainability is a
broad set of decision-making principles and business practices aimed at achieving
economic growth without engaging in the harmful environmental trade-offs that
historically accompany growth. Ideally, sustainable development creates operational
systems that consume natural capital (also known as natural resources) slowly enough that
future generations can also use those resources) (MasterClass, 2022). (2) Sustainable
development of the economy is a concept that aims to balance the economic, social and
environmental aspects of human activity, while ensuring that the needs of the present
generation are met without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their
own needs. (Barbie, E., 1987). It is based on the recognition that natural resources are finite
and that human activities have impacts on the environment that need to be managed and
minimized. (Kieren Mayers, Tom Davis, Luk N. Van Wassenhove, 2021).
There are various frameworks and indicators that can be used to assess and compare
the environmental, social, and governance performance of different entities. Some of the
most widely used frameworks and indicators are the ESG Metrics, the Global Reporting
Initiative (GRI), and The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The E in ESG,
environmental criteria, includes the energy your company takes in and the waste it
discharges, the resources it needs, and the consequences for living beings as a result. Not
least, E encompasses carbon emissions and climate change. Every company uses energy
and resources; every company affects, and is affected by, the environment. S, social criteria,
addresses the relationships your company has and the reputation it fosters with people and
institutions in the communities where you do business. S includes labor relations and
diversity and inclusion. Every company operates within a broader, diverse society. G,
governance, is the internal system of practices, controls, and procedures your company
adopts in order to govern itself, make effective decisions, comply with the law, and meet
the needs of external stakeholders. Every company, which is itself a legal creation, requires
governance. (Witold Henisz, Tim Koller, and Robin Nuttal, 2019). lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
GRI Standards are based on a Triple Bottom Line, disclosing information about the
achievement of specific economic, social and environmental results.Sustainable
development indicators are combined into three thematic standards: economic standard –
6 indices, environmental standard – 8 indices and social standard – 19 ones (Vera Samarina,
Tatiana Skufina, and Aleksandr Samarin, 2020)
To sum up, this research would consider that sustainable economic development
involves balancing economic growth with social and environmental considerations, while
ensuring intergenerational equity.
1.2. Role of commercial banks in promoting sustainable development (NCKH)
Lala, Stone (2023) states that commercial banks can help promoting sustainable development in four methods:
Financing renewable energy projects: invest in renewable energy projects, such as wind
and solar power, as a result reduce reliance on fossil fuels and support the growth of the renewable energy sector.
Green loans: make loans to businesses and individuals who have investment in sustainable
technologies, such as energy-efficient buildings and electric vehicles. Risk management:
identify and assess climate change risks, therefore banks can take steps to mitigate these
risks and ensure the long-term sustainability of their lending and investment activities.
Innovation: develop new financial products and services such as green bonds and other
financial instruments to finance sustainable projects.
Nguyễn Khánh Duyên (2018) indicates banks may create sustainable business
development through their credit policies, such as providing capital and encouraging
environmentally friendly projects, making an impact through service activities like
investment consulting. Moreover, commercial banks can offer "green" or "sustainable"
loans not only for large infrastructure projects but also in various sectors of the economy,
such as projects aimed at energy efficiency. Adhering to industry sustainability standards
can help banks better assess and manage environmental and social risks in projects and
avoid negative impacts on the environment. Additionally, banks contribute to sustainable
development by promoting comprehensive finance. Comprehensive finance involves
providing suitable and convenient financial services to all individuals and organizations,
especially those with low incomes and vulnerabilities, to enhance access to financial
resources, contribute to livelihood opportunities, circulate investment capital, and savings lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
in society, thereby driving economic growth. Therefore, banks play a specific role in
achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) as outlined in the tasks assigned to
the banking sector in the National Action Plan for Implementing the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Ryszawska (2018) emphasizes the importance of digital banks in promoting a
sustainable economy. Thanks to technology development such as climate finance, green
finance, carbon finance, banks support sustainability transitions. It may be observed that
traditional banks are changing to adjust digital innovation, decentralized and sustainable
production and consumption. Moreover, banks play an important role in financing
production of energy from renewable sources, waste recycling, reduction of greenhouse
gas emission, modern products and technologies with improved energy efficiency,
sustainable transportation, sustainable supply chains, and sustainable consumption.
It was revealed by Khaliun’s research (2015) that when commercial banks invest in
environmentally oriented projects, they may effectively manage their resources as well as
fulfill social responsibility and thereby build confidence in present and future customers..
For the effective development of the investment credit organizations need to balance the
supply and demand of the real sector. Commercial banks fulfill their social responsibility
as well as solve the problem of cash flow balance when sending their financial resources
to environmentally oriented investment projects.
Standard Bank Limited has categorized green banking products into several items
to emphasize diversification and promote sustainable development. 1. Renewable energy
a. Solar energy: solar home system, solar micro/mini grid, solar iIrrigation pumping
system, surface water purification plant using solar pump, solar photovoltaic (PV) assembly plant, …
b. Bio-gas: organic manure from slurry, mid range bio-gas plant, biomass based large
scale bio-gas plant, poultry & dairy based large scale bio-gas Plant
c. Hydro-power: hydropower (Pico, Micro & Mini)
d. Wind-power: wind energy driven power plant
2. Energy efficiency: substitution of conventional lighting system, electronic material,
boiler with energy efficient alternatives on the basis of Energy Audit; auto sensor
power switch assembly plant, energy efficient Improved Cook Stove (ICS)/ICS lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
Renewable/Hybrid Cook Stove Assembly Plant
3. Recycling & Recyclable Initiatives: PET Bottle Recycling Plant, Plastic Waste
Recycling Plant (PVC/PP/LDPE/HDPE,PS), Wastage Paper Recycling Plant for
Production of recycled paper, plate, mug, glass, Recyclable Baggage Manufacturing Plant
In addition, there are some outstanding digital banking products to pursue the goal of
sustainable development:(Sayan Das, 2022): (1)Savings accounts: easy access to banking
services and preserve money's purchasing power with interest; (2)Current accounts: make
multiple transactions daily; (3)Cash withdrawals and deposits: withdraw from or deposit
cash into these accounts. (4)Fund Transfers: users can transfer money between bank
accounts, e-commerce services, or other business transactions. (5)Bank statements:
generate bank statements online using the bank's mobile application or website; (6)Loans:
give loans to their users through digital means only.
In conclusion, many researchers conclude that commercial banks have a positive
influence on sustainable development. Banks promote economy’s sustainable development
by enhancing comprehensive finance, offering green loans and mobilizing fund for economic development.
2. Liturature Sustainable developed activites of Vietnam commercial banks
Recently, the Vietnamese government has actively participated in implementing
international commitments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, minimize the impact of
climate change, towards sustainable development goals as committed to implementing the
2030 Agenda for the sustainable development at the United Nations Summit. In particular,
the banking industry is always identified with its roles in "greening" investment capital
flows for sustainable development goals. Within the framework of the green banking and
green growth development plan proposed by the Government, commercial banks have also
made changes to suit the new market.
2.1. Green banks development
Within the framework of promoting and developing green banking, commercial
banks have been researching and proposing new policies to promote sustainable
development, including: Environmental policy in credit appraisal, green credit, green bond
and community social activities. lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
2.1.1 Environmental policy in credit appraisal
According to an assessment by PanNature, before 2015, Vietnam had not issued any
environmental safety policies for credit granting activities, and a number of banks had
developed environmental and social risk management policies. The association is still
relatively small. However, recognizing the importance of environmental risk management
in credit granting, the State Bank of Vietnam has taken many different steps to promote
sustainable finance, and at the same time, provide directions. guidelines to promote green
credit growth and manage environmental and social risks in credit granting activities.
Currently, some commercial banks have basically built and completed their internal
Environmental and Social Management System (ESMS) to serve the assessment of
environmental and social impacts during the appraisal process. determining and granting
credit, usually includes the following steps:
Source: author's compilation
In 2012, Sacombank was the first bank to deploy the ESMS system with a
combination of the following elements: Strategy, governance model, environmental and
social policy (E&S) integrated into the credit granting process. application, an Excel toolkit
including a questionnaire to assess E&S impacts on customers, establishing an ESMS team
at the Head Office.to conduct training for personnel to directly perform the assessment and
participate in the appraisal process, environmental and social impacts on customers. By
2016, the Credit Department (State Bank) said that two more banks had built internal
environmental risk management systems: Vietnam Technological and Commercial Bank
(TechcomBank) and Vietnam Bank for Industry and Trade. (VietinBank). Up to now, many
commercial banks have paid more attention and partly integrated environmental and social
risks in the appraisal of loan projects. For example, BIDV does not approve credit for
unplanned projects, professionalizing environmental and social risk management in the
credit granting process; promulgate a sustainable loan framework to provide green loans
and sustainable linked loans for businesses. Vietcombank only approves credit for projects
that have been approved for environmental impact assessment and requires project owners
to provide information related to technology and environment in the loan application. At
VPBank, since 2016, the bank has issued policies on environmental and social risk lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
management, by 2018 it has completed the environmental and social risk management
system (ESMS) and in 2022, the ESMS system credit granting became part of the bank- wide ESG policy.
Additionally, in February 2023, BIDV was the first bank to successfully develop a
sustainable loan framework based on advice from the Carbon Trust, designed to provide
the most popular sustainable loan products on the market. The global market today includes
thematic loans and sustainability-linked loans. This sustainable loan framework includes
Green Loan Principles, Social Loan Principles, and Sustainability-Linked Loan Principles.
The promulgation of the Sustainable Loan Framework helps position BIDV as a reputable
bank, with an active role in implementing the Sustainable Development Strategy of the Government of Vietnam.
However, the actual implementation of the environmental and social risk assessment
system in credit granting activities of most banks only stops at integrating requirements on
projects that have been approved for assessment. In addition, the sustainable development
reports of commercial banks show that there are no significant actual or potential negative
environmental impacts on the banks' product supply chains, nor are there any complaints.
Complaints about environmental impacts, no loan case has been closed due to
environmental issues of the project. This practice shows that many banks have not fully
assessed environmental and social risks in granting credit and monitoring E&S risks after
capital transactions with customers. 2.1.2. Green credit
In Vietnam, there are many different definitions of green credit, but in general, green
credit can be understood as credits supported by the banking industry for production and
business projects that do not cause environmental risks. environment, or for the purpose of
protecting the environment, contributing to protecting the general ecology.For example,
Techcombank has signed a credit cooperation contract with IFC to sponsor energy saving
and clean production projects of small and medium-sized enterprises in Vietnam.
Accordingly, Techcombank and IFC will finance businesses to change equipment, upgrade
technology and systems to improve energy saving efficiency, expand production, cut costs,
and reduce gas emissions. waste. In addition, Techcombank, along with ACB and VIB, also
plays a role in supporting financial appraisal and providing credit at the Green Credit Trust
Fund established by the Swiss Federal Economic Department (SECO). The fund's lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
operating purpose is to provide financial support for clean technology investment projects
of domestic enterprises, and at the same time, encourage customers to develop investment
products that bring environmental benefits to the community. copper.
Survey results on the application of "green credit" in the banking industry by the
State Bank show that 19 credit institutions have developed environmental and social risk
management strategies, of which 13 credit institutions have integrated risk management
content. environmental and social risks into the green credit operating process, 10 credit
institutions have built banking credit products for green credit, 17 credit institutions have
used environmental and social risk assessment handbooks for 10 Economics. Along with
that, preferential/support policies for banks lending to environmentally and
climatesensitive fields (providing preferential loans or applying low interest rates or
compensating for interest rate differences) …) has also been done. In addition, commercial
banks with a high proportion of green credit loans are also given priority in accessing
preferential loans from international organizations and development partners.
Green credits lending incentives of some Commercial Banks Banks Loan purposes Loan rate Tenor BIDV and Clean energy, green Medium and long Minimum 2 years Agribank
agriculture and projects to term: 8,7%/year in reduce pollution and treat the first 3 years waste From 4th year: 12 months saving + 4% margin VietinBank Energy saving and Medium and long Minimum 2 years efficiency projects under term: 8,1%/year EIB environmental credit program, GCPF credit program, REDP renewable energy projects Sacombank Development strategies, Medium and long Maximum 8 years lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392 production processes or term: 8,5%/year in loan use purposes that no the 1st year risk to environment, From the contributing to protect the following years: common ecosystem 9,5% Nam A Environment friendly Short term: Maximum 2 years Bank investment. The projects 7%/year promote reduction of CO2 Medium term: emissions, and save 20% 8,8%/year in the energy first 24 months Incentive package: 7,7%/year MBBank Renewable energy
Medium and long Maximum 15 years industry, green building term: Apply loan products, lending for margin 2,8%/year projects on waste (normally margin treatment 3%/year) HDBank Renewable energy and
Approval depends Maximum 10 years high tech agriculture on each case projects SHB Projects for renewable Preferential Maximum 10 - 15 energy and clean energy interest rates from years 1% - 1,5% compared to market interest rates
Sources: Banking Magazine lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
Commercial banks actively complete the development of internal regulations on
environmental and social risk management in credit granting activities, which has brought
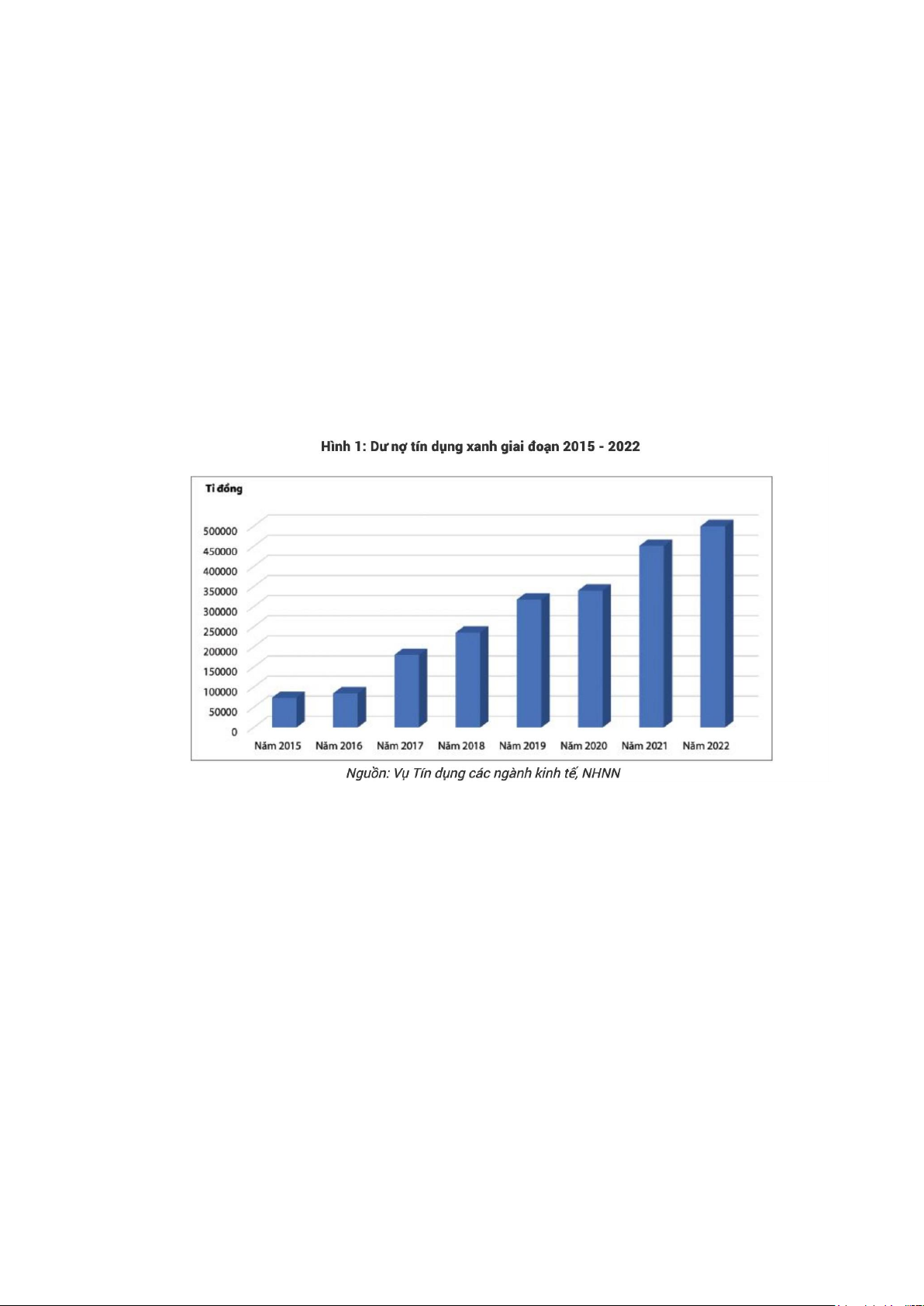
encouraging results. By the end of 2022, outstanding credit for green projects (12 green
projects built and issued by the State Bank since 2015) reached nearly 500,000 billion VND
(accounting for about 4.2% of the total outstanding debt of the economy). economy),
focusing on areas such as renewable energy, clean energy (accounting for the highest
proportion of 47%), followed by green agriculture (accounting for over 30%). Credit
institutions actively evaluate environmental and social risks in credit granting activities
with outstanding loans reaching more than 2.2 million billion VND with more than 1.1 million loans.
Green credit loans are mainly focused on green agriculture (accounting for about
46%), sustainable water management (accounting for about 13%), and recently tend to shift
to a number of fields. other such as renewable energy and clean energy (Tran The Anh,
2022). Many important fields in environmental protection and response to climate change
such as waste management, transportation and sustainable construction... are still very limited. 2.1.3. Green bond
Compared to other countries in the world, the green bond market in Vietnam is being
implemented more slowly. However, in recent years, there have been a number of green
bond-financed projects implemented in Vietnam. Domestic banks have only issued 216
million USD in green bonds in the past 5 years, although there are many environmental,
social and governance (ESG) projects that are looking for capital and investors looking for lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
them. investment opportunities. The majority of proceeds from bond issuance (57%) are
used for renewable energy - the main industry of interest to Vietnam, in addition to the
water, waste and agriculture sectors (MOF, 2021).
The overall picture of the green bond market in Vietnam is currently assessed to be
in its early form, undeveloped, the scale, type and foundation of supply and demand for
green bonds are all uncertain, in particular, the system The information system, propaganda
and understanding of investors in particular and the market in general about green bonds
are still very limited. In terms of structure, green bonds in Vietnam today are mainly local
government bonds financing green projects, Vietnamese commercial banks are only in the
early stages of developing products and services. green bond projects, 40% of Vietnamese
banks do not have green investment projects in their investment portfolio.
In October 2023, BIDV successfully became the first bank to issue green bonds
worth VND 2,500 billion according to the Green Bond Principles of the International
Capital Market Association (ICMA) in the domestic market. Accordingly, BIDV has
achieved Moody's rating for the Green Bond Framework of credit institutions, confirming
compliance and high-level transparency in project selection, appraisal, lending,
management and reporting regimes. Proceeds from bond issuance will be used to finance
green projects, save energy, reduce emissions, and protect the environment. BIDV's bond
issuance is also the first green bond issuance in Vietnam with a no-collateral structure, no
secondary debt and no need for payment guarantees, demonstrating a high level of
credibility. capacity and reputation of the issuing organization. All investors participating
in the transaction are insurance companies and fund management companies belonging to
the world's leading insurance groups. BIDV's Green Bond framework is highly rated by
Moody's Credit Rating Organization with the SQS2 (very good - very good) rating being
the second highest in a total of five rating levels.
BIDV's successful issuance of green bonds according to ICMA standards not only
has good meaning, contributing to the operations and reputation of the business but also
inspires other corporations and commercial banks to do the same. efforts to green the economy. lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
2.1.4. Community social activities
In addition to continuously building, innovating and providing modern and digital
financial products and services, green banking is also demonstrated through socially responsible investing.
Currently, most commercial banks in Vietnam have a separate fund serving community
activities. Among investments in social security, investments in improving the quality of
education and health care receive the most attention and investment from banks. In
addition, banks also sponsor volunteer and charity activities with the goal of sharing
difficulties and improving the quality of life of the community.
For example, Vietcombank said that community contribution is a core goal in the
bank's development strategy, focusing on the fields of health, education, supporting the
construction of charity houses, and giving gifts to the poor and families. policy families,
wounded and sick soldiers... The implementation of these activities spans all parts of the
country, from urban to rural areas, with a focus on mountainous areas, ethnic minorities,
and islands. Some welfare and charity activities that Vietcombank supports include Hoang
Tru primary school (Kim Lien, Nghe An) with a budget of 8 billion VND, Vang Anh
kindergarten (Ca Mau) with a cost of 13 billion VND, charity houses for the poor Quang
Ngai province worth 5 billion VND,... Besides sponsoring the construction of schools and
classrooms, the bank also focuses on supporting health insurance and social insurance
payments for the poor. At the end of November 2022, the bank transferred 1,000 social
insurance cards and 9,968 health insurance cards, with a total value of 5 billion VND, to
give to people in difficult circumstances.
In the period 2017 - 2022, in addition to implementing financial and monetary tasks
to serve the country's economic development programs, BIDV has also pioneered and
proactively allocated funding from the bank's operations. as well as mobilize employees to
contribute to implementing social security programs. The total cost of BIDV implementing
social security programs in the past 5 years is nearly 1,500 billion VND. Funding areas
focus mainly on education, health care, eliminating temporary housing for the poor, and
overcoming the consequences of natural disasters...
In addition, as of June 2023, Agribank has donated 215 billion VND for social
security activities in localities across the country, of which, separate funds are for building
charity houses and charity houses. for the poor, the great solidarity house is 56 billion VND, lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
the budget for educational activities is 69 billion VND, and nearly 55 billion VND for health care.
In general, community activities for social security are one of the activities that have
long been promoted in the tradition of commercial banks and have brought many benefits
not only to the environment but also to the people. contributing to social stability and
development background terrible international.
2.2. Digital banks development
With the strong development of the new technology era, applying technology to
banking services not only increases convenience for customers but also promotes
sustainable development by contributing to reducing printed documents, as well as
reducing the number of vehicles having to travel to the bank building. Those developments
can be mentioned such as online banking, online lending, saving and blockchain. 2.2.1 Payment
Vietnam has welcomed the e-banking trend since the mid-2000s. Although there are
still many shortcomings in banking service supervision, the Government is also trying to
create conditions for banks to exploit their potential and develop the above services. A sign
that the e-banking trend is gaining a foothold in Vietnam is the explosion of digital
payments. Vietnamese people increasingly prefer this payment service instead of using
cash. Especially in the early stages of the Covid-19 pandemic, in the first months of 2020,
digital payment figures skyrocketed. Compared to the same period in 2019, the value of
payment channels via the Internet increased by nearly 50%, payments via smartphones
increased by nearly 160%. During the period of social isolation, electronic payment
activities increased in number. quantity, price and transactions. volume also increased.
Since then, people have gradually become accustomed to the convenience that digital
payments bring. Even after the epidemic passed, the proportion of cash payments still decreased significantly.
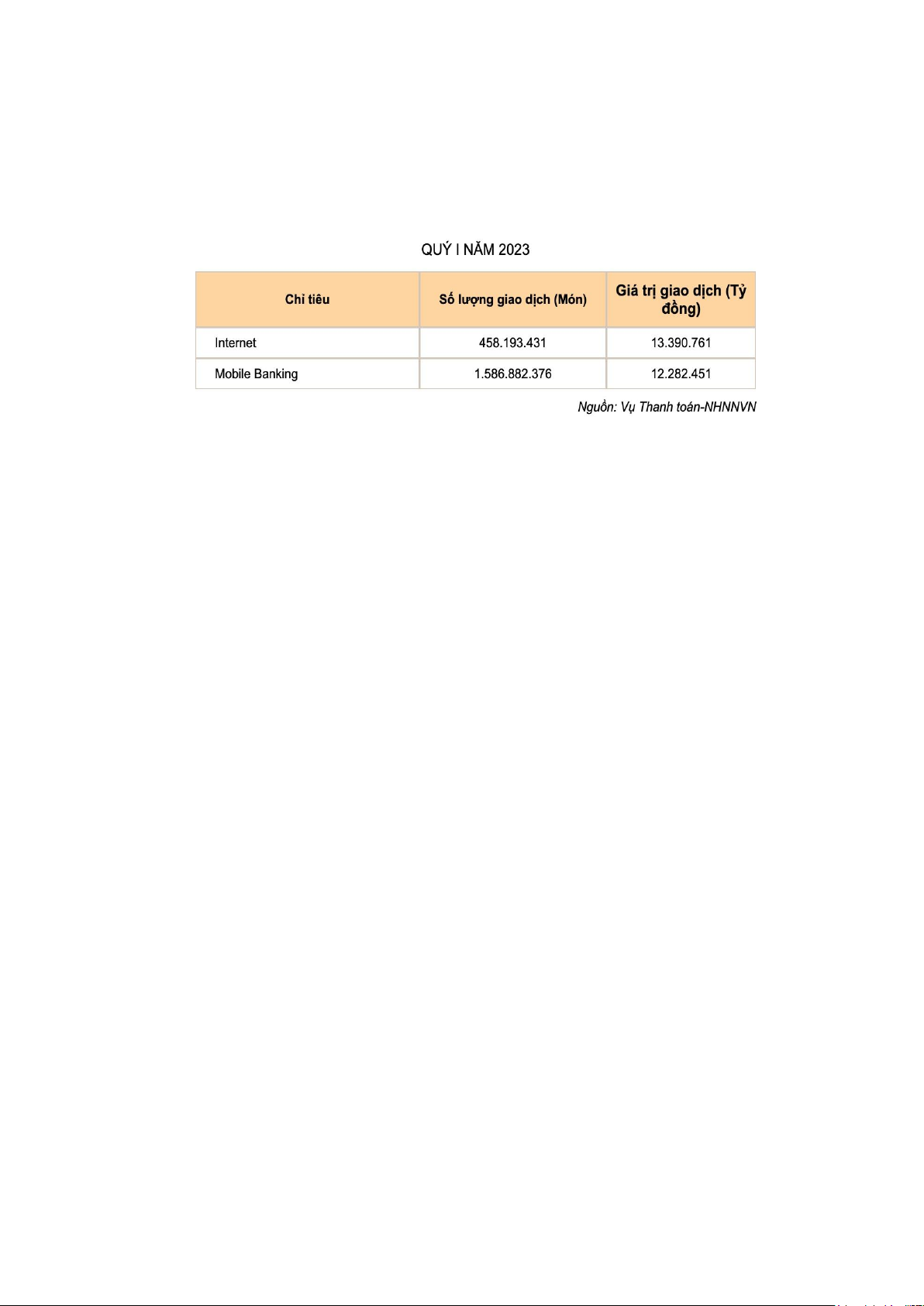
According to data published by the Payment Department - State Bank of Vietnam,
in the first 7 months of 2023 compared to the same period in 2022, non-cash payments
increased by 51.14% in quantity, via Internet channels increased by 66.46%. % in quantity,
via mobile phone channel increased by 63.09% in quantity; via QR Code increased by
124.15% in quantity. Online account opening will be carried out from the end of March
2021. As of June 2023, there were nearly 27 million accounts opened using the eKYC lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
electronic method. There are 10.8 million cards in circulation using the eKYC method.
This is the result of the banking digital transformation process that has changed customers'
behavior in using banking services, contributing to accelerating the banking digitization process.
The increasing demand for digital payment makes the race between banks more
exciting than ever as the goal of digital transformation and cashless payment is being
promoted. According to a report by the State Bank, currently 94% of commercial banks
have initially researched and implemented digital transformation strategies. Of these, more
than 50% of banks have been implementing this strategy in practice. Many commercial
banks have identified digital banking as an inevitable trend in future business activities.
Commercial banks in Vietnam are increasingly making changes to keep up with the
market, most banks have developed their own digital banking applications. For example,
Vietcombank and BIDV have replaced the previous Internet Banking and Mobile Banking
services with digital banking applications VCB Digibank and BIDV Smart banking. With
this application, customers can easily track transactions, bank account balances as well as
online savings on digital banking applications. In addition, commercial banks also
strengthen cooperation with Fintech to provide digital products and services based on
multi-channel platforms to ensure a rich experience for customers (the combination of
Techcombank Joint Stock Commercial Bank Vietnam
(Techcombank) and Fastcash Company, VIB and Vietnam Company Weezi Digital,
VietinBank and ON Company (UK), BE GROUP (Sweden)...). Thanks to the support of
Fintech, many digital models and products have appeared such as: Mobile Wallet, PeerTo-
Peer Transfer, mobile payment (Mobile Payment). ), Mobile Banking. 2.2.2 Lending
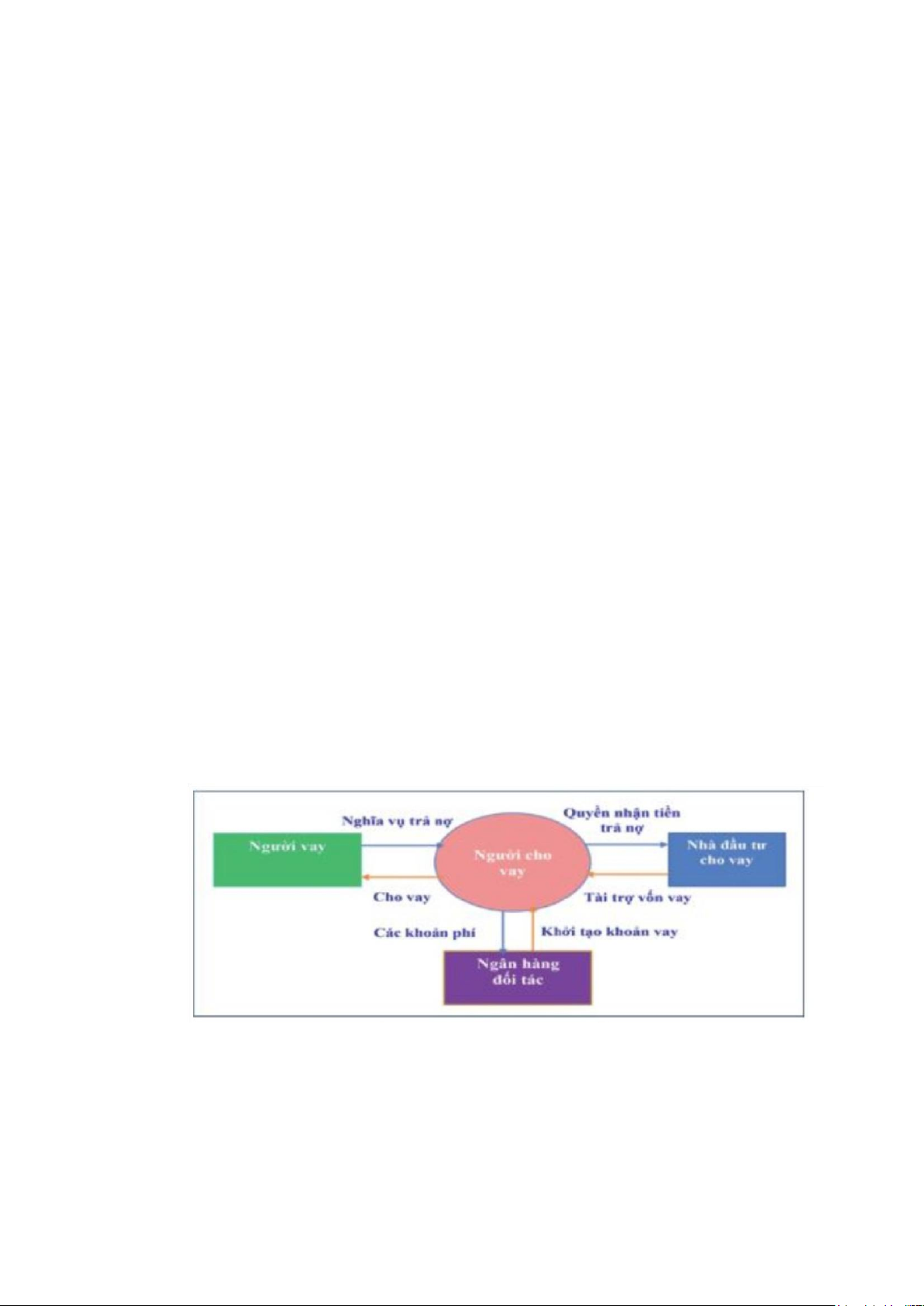
With the development of digital technology, a new online lending method has
appeared: peer-to-peer lending (P2P Lending). P2P Lending is an activity designed and lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
built on a digital technology application platform to directly connect borrowers with
lenders without going through financial intermediaries. Thanks to the application of digital
technology platforms, loan and disbursement procedures and processes are also simplified,
saving time. In Vietnam, a company operating like the P2P Lending model began to appear
in 2016 with the website huydong.com. Since then, many other P2P Lending companies
have gradually come into operation, such as Tima, SHA, Mobivi, Vaymuon.vn, etc. Among
more than 100 licensed Fintech companies, there are up to 40 companies with P2P Lending
services. . Some are operating quite effectively, especially lending companies targeting the
small and medium-sized enterprise segment, gradually helping this market become a
potential capital mobilization channel for businesses which are the target group. Capital
needs for production and business activities change greatly during operations and often
have to mobilize capital from unofficial sources.
P2P Lending development models in Vietnam are also quite diverse. In addition to
direct models from companies directly providing peer-to-peer lending services, indirect
models have also been deployed. According to this model, P2P Lending companies will
transfer the loan request of the person in need to an affiliated commercial bank. If the loan
proposal is approved, the bank will issue a debt receipt to the P2P Lending company so
that customers can receive disbursement at commercial banks using this debt receipt. Then,
when a lender is found, the P2P Lending company will pay this debt to the bank with the
lender's money and issue a loan certificate to the lender.
With the indirect lending model, P2P Lending companies cooperate with banks and
credit institutions to lend to customers. Accordingly, some banks combine with technology
companies to lend to small business and individual customers such as Dragon Bank, The
Bank, Gobear are three joint stock companies that cooperate and connect with banks in
finding customers. Cooperative banks are very diverse. Dragon Bank Joint Stock Company lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
cooperates with banks: OCB, Shinhan Bank, HDBank, ACB, UOB, VPBank, TPBank,
MSB. Gobear Joint Stock Company connects with BaovietBank, Citibank, DongA Bank,
Eximbank, HD Bank. The Bank has financial partners: FE Credit, Techcombank, Manulife,
VPBank, UOB, Shinhan Bank, BIDV, ABBank, Sacombank,... In general, P2P Lending
companies connected to banks will cooperate with many financial institutions.
In addition, a technological development that has been successfully applied in
lending activities is the application of blockchain in the documentary credit (L/C) method.
Blockchain technology acts as a ledger for all transactions, with the ability to share data
information transparently in real time, save storage space and be highly secure. To limit the
risks of late payment or refusal of payment, letters of credit can be modeled as smart
contracts capable of self-processing on the blockchain. This type of contract automatically
checks and determines the compatibility of delivery information with contract terms. This
approach increases the possibility of quick payment for sellers by preventing disputes
arising due to ambiguity in payment contracts.
HSBC is the first bank to successfully have a letter of credit transaction on the
blockchain platform in 2019 between Duy Tan Plastic Manufacturing Joint Stock Company
of Vietnam and INEOS Styrolution Korea Company of Korea. Transactions are conducted
from start to finish on a single shared application, Voltron, the goal of this platform is to
provide a single, simplified channel to support the digitalization of trade finance, from L/C
issuance until presentation/exchange of documents. lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392 2.2.3 Saving
According to the General Statistics Office, Vietnam has a large population, reaching
98.51 million people in 2021, with a relatively high young population (50.5 million people
aged 15 and over). However, about half of the population currently does not have access to
financial services through banks. With these potentials, developing personal financial
services is becoming one of the strategic directions of commercial banks. The strong
development of the consumer loan market is considered a good signal in the financial
market, especially microfinance and personal finance. To develop personal financial
services, commercial banks often promote consumer lending to improve quality and
diversify types of personal credit products. Personal financial management (PFM): is a tool
that helps build personal financial plans through managing financial data on software and
phone applications. PFM allows customers to manage their deposits in different banks or
loans from different lenders in the same application.
For example: Personal Finance Management (PFM) feature is integrated on the
MBBank App: Supports users to compile personal financial situation statistics, provide
financial advice and investment instructions. Effective investment to help customers
achieve their goals in life, with a modern, user-friendly interface. Fintech offers
customization tools and savings performance tracking. Users can set savings goals, receive
notifications, and track progress automatically. Fintechs can provide smart suggestions
based on customers' data and savings behavior, helping them optimize their savings and
investment strategies. Integration with other services: Fintechs often have integration
capabilities with other services such as electronic payments, loans, or investments, creating
a comprehensive financial ecosystem. Reduce costs and Increase competition: Using
fintech can reduce operating costs for banks, which in turn can provide higher benefits to
users through higher interest rates or other incentives.




