
Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 45254322
SESSION 13: THE NATURAL WORLD – READING & WRITING I. READING
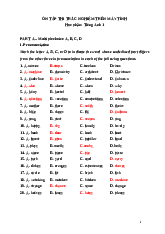
1. The following words refer to the natural world. Use the words to label the pictures below. bay valley cliff waterfall
2. The words below refer to similar things, but they are not interchangeable. Choose the correct words to complete the sentences. soil sand land ground
a. The house we are buying comes with a lot of _____________.
b. Children love playing in the _____________.
c. There were no chairs in the garden so we all sat on the ______.
d. I have bought a big bag of _________ so I can plant some flowers in these pots.
3. Look at the four questions below and think about how you will find the information in the text that
follows. Then skim-read the text to find the answers to the questions as quickly as you can. a. What do jellyfish look like? b. What are barnacles? c. How are fossils formed? d. How are seashells formed?
The beach, a natural treasure trove
When you are walking on the beach, you may be able to spot tracks. Birds and crabs leave
footprints behind, especially in wet sand. On sandy beaches you will also be able to find interesting holes
made by crabs that were digging for food in the mud.
You may also come across jellyfish as these are often washed up on the beach. They have no eyes,
ears, heart or head and are mostly made of water. They look like a bag with arms, which are called
tentacles. These contain poison that helps them catch food. Even when jellyfish are out of the water or
in pieces, their tentacles may sting.
Other animals you may find are coral and barnacles. The latter are marine animals related to
crabs and lobsters and live in shallow waters. They like to attach themselves to hard materials, so you
are likely to find them stuck to pieces of wood.
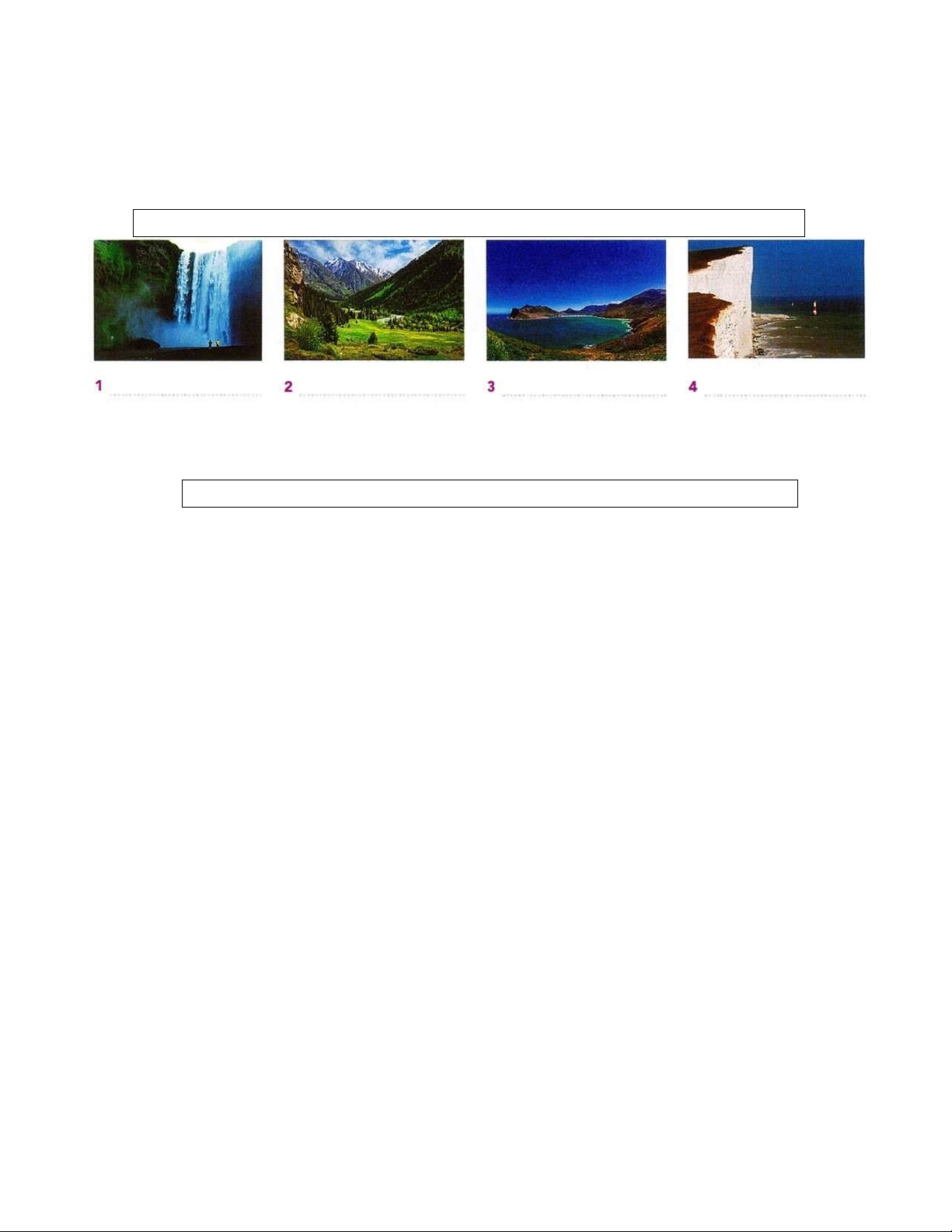
If you are lucky, you may find a fossil. In essence, this is an animal that died and got buried in a
sea bed. Fossils are likely to look like pieces of rock with an imprint of an animal skeleton. Their history is
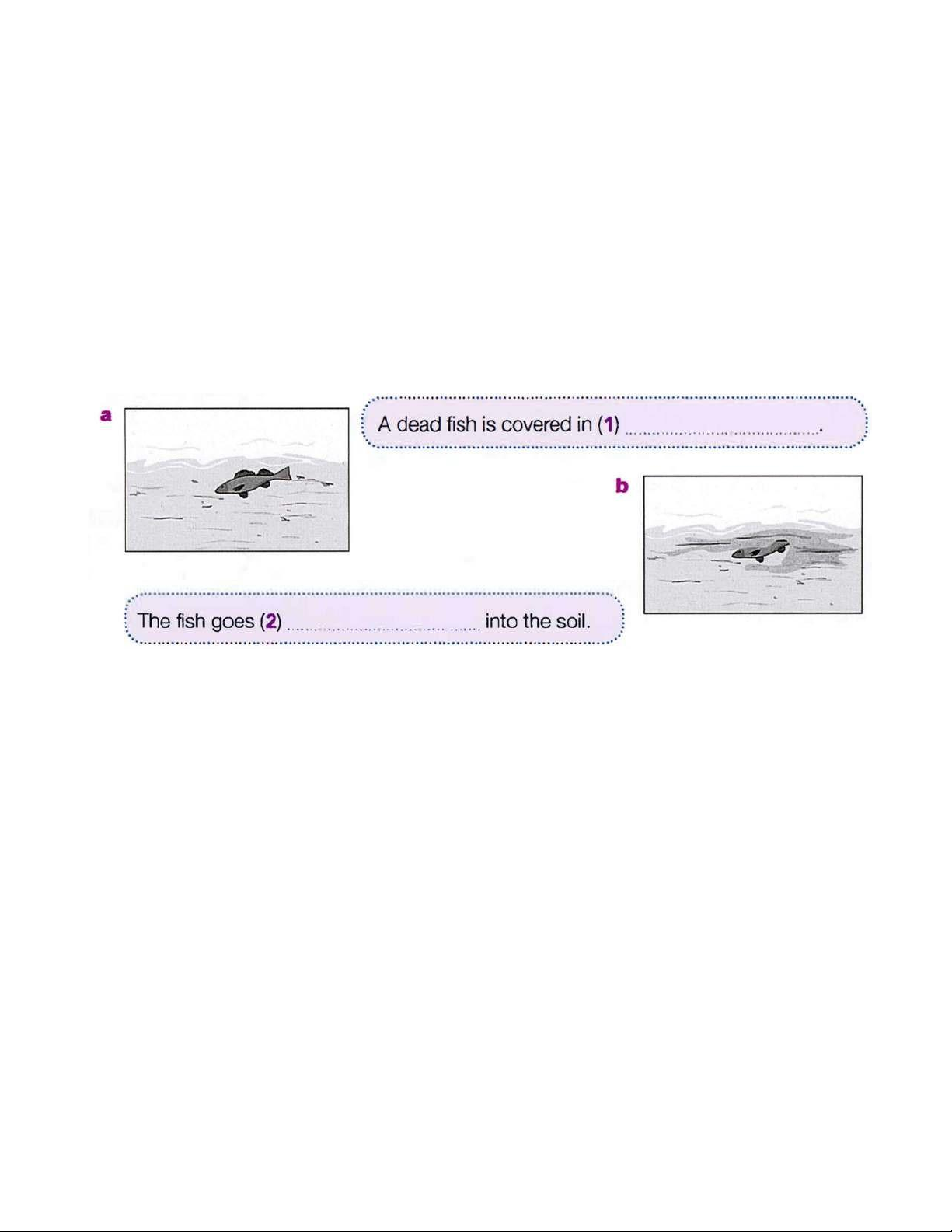
very interesting. For an animal to become fossilized, it has to be buried in mud, sand or soil; if a dead lOMoAR cPSD| 45254322
animal is not buried, it is more likely to rot away or be eaten by another animal. Over millions of years,
the animal remains become buried deeper and deeper; the mud, sand or soil compresses and slowly
becomes rock. The bone or shell of the animal starts to crystallize because of surrounding minerals and
chemicals. Ideally, the temperature stays relatively constant throughout this process. Sometimes the
fossil dissolves completely and just leaves an imprint. At other times, waves, tides and currents slowly
erode the rock, which allows the animal remains to break off, ready for you to find.
What you will definitely find on a beach are shells. These were once the homes of animals such
as snails or mussels, consisting of a hard layer that the animal created for protection as part of its body.
After the animal has died, its soft parts have rotted or been eaten by other animals. What is left is a
beautiful seashell for you to admire.
4. Using NO MORE THAN FOUR WORDS from the passage, complete each gap in the diagram. lOMoAR cPSD| 45254322 PRACTICE FOR THE TEST
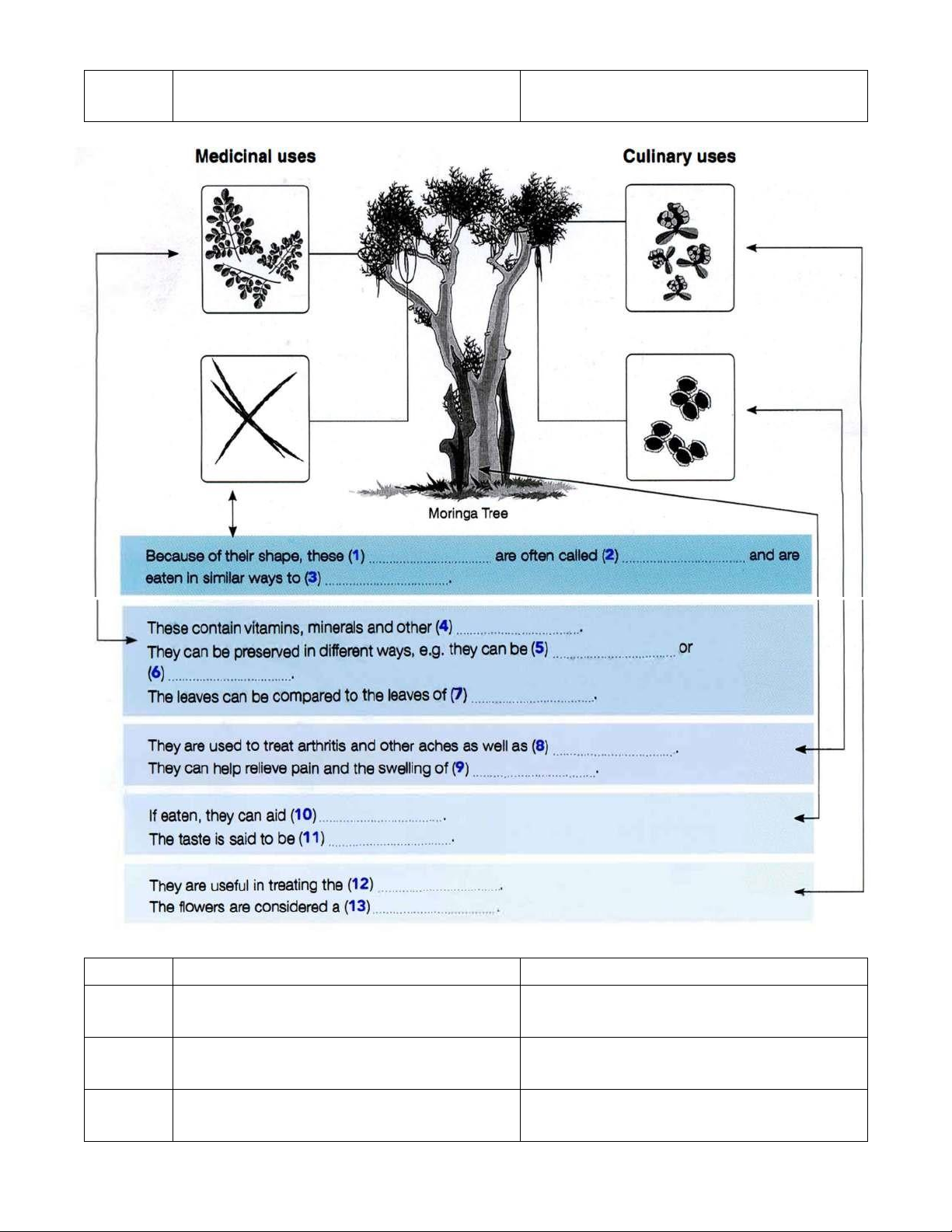
Using NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage, complete each gap in the diagram. The many uses of the Moringa tree
The Moringa tree, Saragwa, or Drumstick tree, is relatively unknown in the West despite the fact that it
is incredibly useful. Miriam Tayne reports about its culinary, medicinal and other uses.
The Moringa tree is a relatively small tree that typically grows to between three and ten metres
tall. Its flowers are creamy-colored and have been compared to small orchids. The plant has long green
pods that can grow up to 30 centimetres and which look a bit like drumsticks, hence the tree's common
name. The pods contain round, dark brown seeds. The tree is propagated by planting the seeds or cuttings
in sand or muddy soil. It does not tolerate frost but thrives in hot climates. It is very common in South
and South-east Asia, Africa and America.
The leaves are reputed to have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties and so are used
for eye and ear infections, fevers, etc. They are also held against the forehead to reduce headaches, or
made into tea to treat stomach complaints. As they contain a lot of iron, they have been used for the
treatment of anaemia, a medical condition in which there are too few red cells in the blood, causing lOMoAR cPSD| 45254322
tiredness. The plant also contains many other nutrients, such as phosphorus, calcium, potassium and vitamins A and C.
The ground-up seeds are commonly used to treat certain skin infections but can be used for much
more. Ground seeds can be mixed with salt or oils and applied to the body to treat cramp, backache and
forms of arthritis, a medical condition in which the joints are swollen and painful. The oil, called Ben oil
because it contains behenic acid, is also used as a hair treatment or a perfume, and to deter mosquitoes
and treat their bites. The by-products of the oil manufacturing process are used as a fertilizer and in water purification.
The roots work in exactly the same way as the seeds, but are much stronger, so are not used as
often. They have additional uses for heart and circulation problems, whereas the gum is sometimes used
to treat asthma. The bark has quite a pleasant taste and is sometimes eaten to encourage digestion.
The plant's main use, however, is as food for livestock and human beings because it contains high
concentrations of fibre and protein. The drumsticks are eaten in soup or as vegetables, like green beans,
and often in combination with shrimps (see picture), whereas the seeds are eaten like peas or roasted.
The leaves are eaten fresh or cooked in similar ways to spinach. Chopped, they are used as a garnish on soups and salads.
They are often pickled or dried so that they are always available to use in sauces, stir-fries, soups
and in sweet and sour or spicy curries.
Like every other part of the tree, the decorative flowers are also useful. They taste a bit like wild
mushrooms and are considered a delicacy. They are used to make tea to treat the common cold and
mixed with honey to make cough medicine.
All parts of the Moringa are used, which makes it one of the most beneficial trees in the world. KEYWORD TABLE Question Keyword in the question Keyword in the passage 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. lOMoAR cPSD| 45254322 9. Question Keyword in the question Keyword in the passage 10. 11. 12. lOMoAR cPSD| 45254322 13. II. WRITING – BAR CHART
1. Put each one next to a noun in the table to make a collocation. (You can use each verb more than once,
and each noun can have more than one verb.) take sit do give write make pass fail get study Verbs nouns Verbs nouns take an exam a an essay a subject qualification a (e.g. biology) a course presentation
2. Complete the text with verbs from the table.
Mustafa: I've just finished school. I (1) _______________ all my exams, so I'm really happy! I'm
going to university. I want to (2) ________________ engineering. I have to (3) ________________ an
entrance exam for my English because I want to study in Australia. The course sounds really good. It's at
a really good university and has a mixture of assessments; I'll need to (4) ________________essays, (5)
________________ presentations and (6) ________________ exams. I'll also get some work experience!
It's a lot of work but I think I'll (7) ________________ a really good qualification.
3. Now look at the verb + noun collocations in the sentences below. Circle the correct verbs.
a. Amil took/gave an online test to find out how good his grammar was.
b. When the course finished, all of the students had to complete a feedback form and make /give
our opinions about the university and the teaching staff.
c. Our students take/have lectures in the mornings and self-study in the afternoons.
d. At the end of the course you get / give a certificate of attendance.
e. Did you make/do your maths homework?
f. It's a good idea to get / take some work experience while you are at university. It could help you find a job later.
g. I have two assignments to make/do before Friday.
h. Can you take / give us examples of the essay questions we might have to answer?
4. The notes show what the class of 2013 did after they left school. Read the notes and complete the
sentences with the correct information and the correct form of the verbs in brackets.
Destinations of school leavers, 2013
University: 12 boys - 14 girls
Local college: 7 boys - 1 girl Work: 5 boys – 8 girls
a. ________________ girls________________ (go) to university after leaving school.
b. ________________ girl________________ (start) courses at the local further education college.
c. ________________ boys and ________________ girls ________________(find) jobs straight after leaving high school. lOMoAR cPSD| 45254322
d. ________________ school leavers ________________ (continue) studying after leaving school.
e. Only ________________ school leavers________________ (not go) to university or college.
f. ________________ school leavers________________ (decide) to go to college.
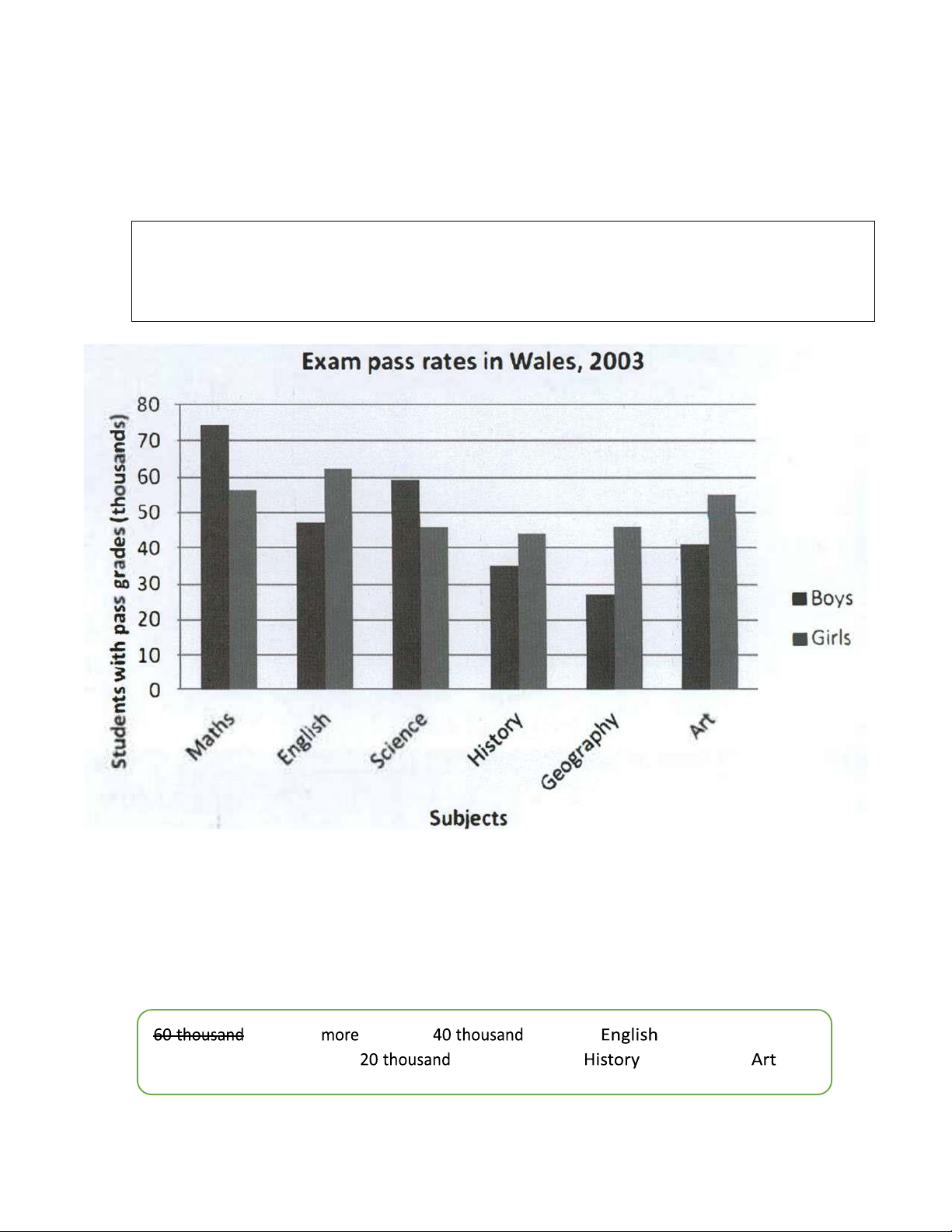
5. Look at the written information about primary students and the same information in the bar chart.
Answer the questions about the bar chart.
Exam pass rates in Wales in 2003
Maths: 75.000 boys, 56.000 girls
History: 35.000 boys, 44.000 girls
English: 48.000 boys, 62.000 girls
Geography: 28.000 boys, 46.000 girls
Science: 59.000 boys, 46.000 girls
Art: 41.000 boys, 55.000 girls
a. What do the numbers on the vertical axis measure?
b. How is the information grouped on the horizontal axis?
c. What do the different shades of the bars show?
d. When was the data collected?
6. Look at the bar chart in Exercise 6 again. Read the introduction to a text about the bar chart. Complete
the paragraph about the girls using the phrases below. Geography lOMoAR cPSD| 45254322
This bar chart shows the numbers (in thousands) of students with pass grades in different subject exams
in Wales in 2003. The chart groups the students according to subject and divides these subject groups
into boys and girls. There are clear differences between the boys and the girls.
Similar numbers of girls achieved pass grades in all the subjects. The number of girls with pass grades
ranged from the highest number of just over (1) 60 thousand to the lowest number of just over (2)
_________a difference of around (3) _________. Girls did best in Art, Maths and (4) _________, while
their lowest pass rate was in (5) _________. Girls achieved (6) _________ passes than boys in four
subjects: English, (7) ________, History and (8) _________.
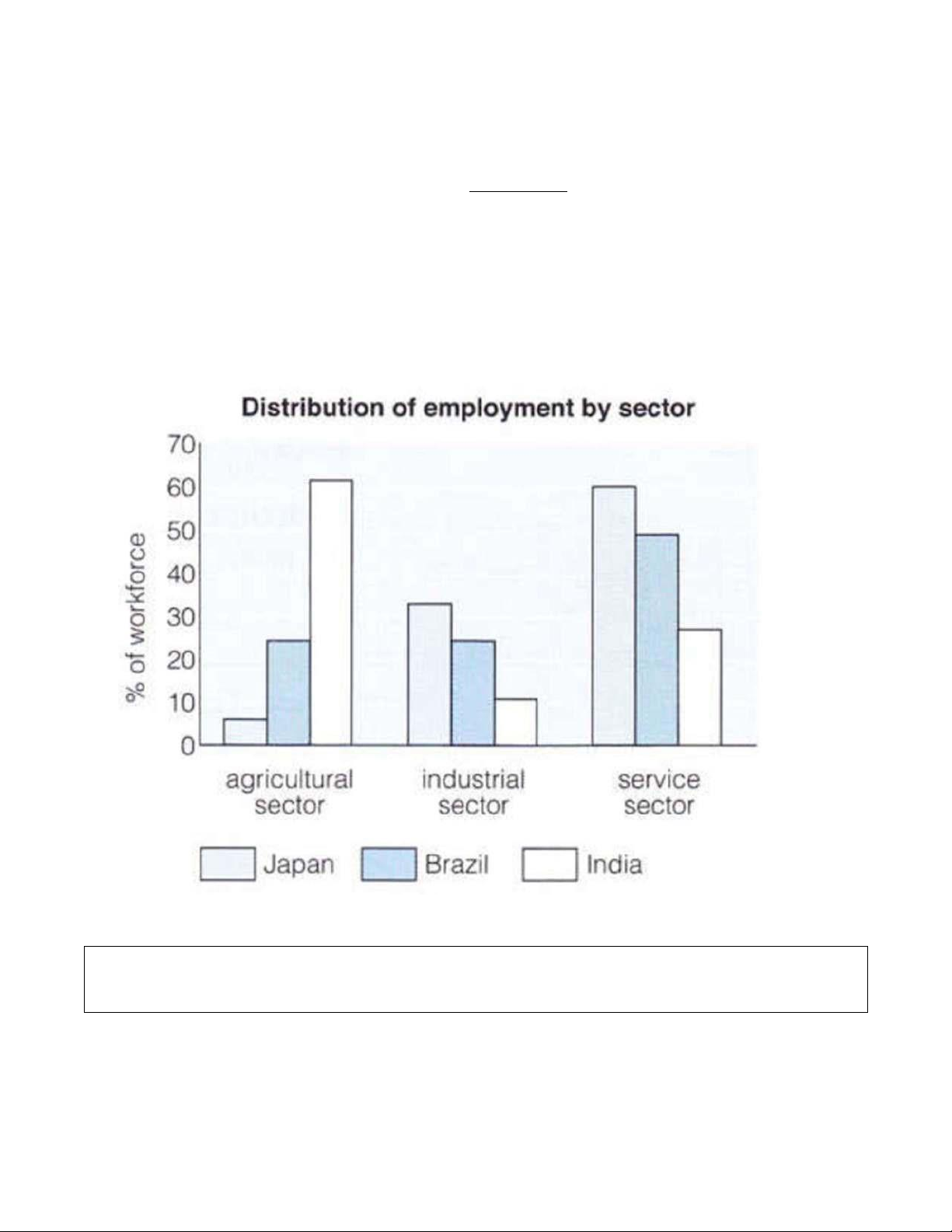
The bar chart gives information about the percentage of workers in different sectors of employment in
three countries at different stages of economic development.
Write a report for a university lecturer describing the information shown.
7. Use the information in the Writing task to fill gaps with words from the box. Use each expression once only. as as many fewer largest highest a larger percentage lowest proportion majority more developed most more
a. In Japan the _____________ proportion of the workforce is in the service sector.
b. India has many _____________ people employed in the agricultural sector than either Japan or
Brazil, but it has _____________ workers in the industrial sector.
c. Brazil has _____________ workers in the agricultural sector it has in the industrial sector.
d. In India, _____________ people work in the agricultural sector. lOMoAR cPSD| 45254322
e. The _____________ of workers in Brazil are in the service sector.
f. The _____________ of Japanese workers are employed in the agricultural sector.
g. Of the three countries, Japan has the _____________ percentage of employees in the industrial sector.
h. Countries which have_____________ economies seem to have _____________ of the workforce in the service sector.
8. Match the expressions below with parallel expressions from the box. the majority of the same number of the largest percentage of the the fewest lowest percentage of the workforce the working population a. the highest proportion of = the largest percentage of b. people employed = ____________________ c. an equal number of = ____________________ d. the smallest proportion of = ____________________
9. Complete the main body of the description by filling in the gaps with appropriate expressions. Use two words for each answer.
First of all, we can see that both Japan and Brazil have the (1) ___________ of the workforce in the service
sector (61% and 50% respectively). But while Japan has (2) ___________ people employed in the
agricultural sector with only 7% of the working population, an (3) ___________ of Brazilians work in the
agriculture and industry sectors (25% in each).
In contrast, we can see that (4) ___________ of the Indian workforce, amounting to 61%, is employed in
the agricultural sector, the (5) ___________ of employees work in industry and the remaining 27% are in the service sector. 10. Writing
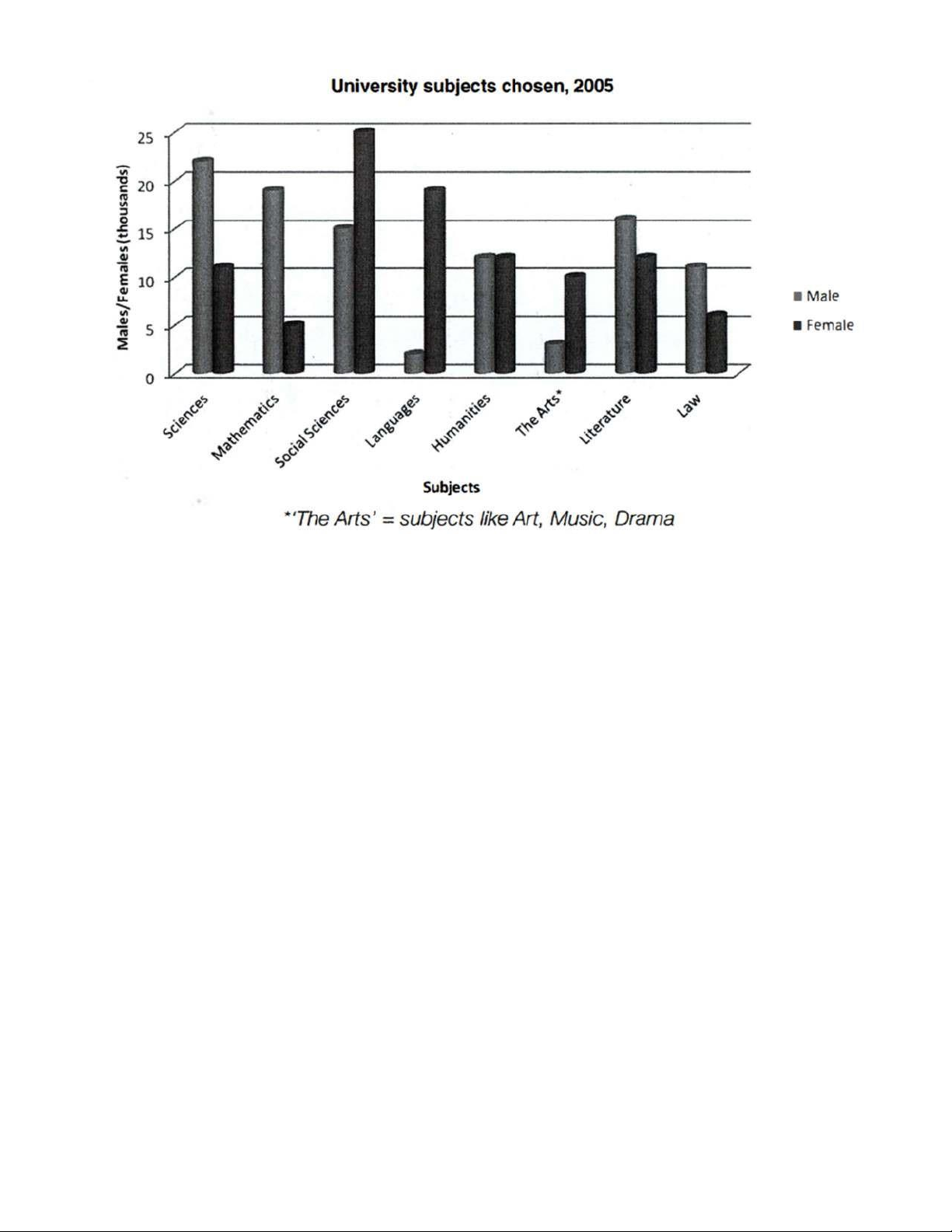
You should spend about 20 minutes on this task.
The bar chart below shows the number of students who chose certain university subjects in 2005.
Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant. Write at least 100 words. lOMoAR cPSD| 45254322
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………