







Preview text:
Final Exam Practice Questions
Course: Social Network Analysis, UIT, VNUHCM
(aka. Graph and Network Analysis with Applications)
Lecturer: Dr. Tran Hung Nghiep 2025-09 1. Structure:
A. Multiple-choice question: 50 points, ~25 questions
B. Short-answer question: 50 points, ~5 questions 2. Time: 90 minutes Language: - English for English class.
- Tiếng Việt (English keywords) cho lớp Tiếng Việt. Exam rules:
- This is a semi-open book examination.
- One A4 sheet of notes permitted (both sides al owed).
- Draft papers wil be provided at the exam room.
- Use provided draft papers for long calculations.
- Write the short solutions and final answers directly into this exam paper.
- Only non-programmable calculators are permitted.
Quy định bằng tiếng Việt:
- Đây là bài thi có dùng tài liệu giới hạn.
- Được phép dùng một tờ tài liệu A4 chuẩn bị trước (hai mặt).
- Giấy nháp sẽ được phát tại phòng thi.
- Dùng giấy nháp đã được phát để thực hiện các tính toán dài.
- Viết lời giải ngắn trực tiếp vào chỗ được chừa sẵn trong tài liệu này.
- Chỉ được sử dụng máy tính không có chức năng lập trình. 1/10
SECTION A: Multiple Choice
Mock Questions in English (Tiếng Việt ở dưới):
1. Which network is natural y modeled as a directed graph? A. Facebook friendship B. Road intersections C. Twitter fol ows D. Protein interaction
2. The local clustering coefficient measures A. Node popularity B. Shortest paths
C. How connected a node’s neighbors are D. Community size
3. Girvan-Newman detects communities by removing A. Nodes with high degree
B. Edges with high betweenness C. Random edges D. Weak ties only
4. DeepWalk and node2vec are based on A. Eigen decomposition
B. Random walks plus skip-gram C. Supervised learning D. Threshold models
5. The Linear Threshold model captures A. Random infection B. Social reinforcement C. Random walks D. PageRank
Câu hỏi mẫu bằng Tiếng Việt:
1. Mạng nào sau đây tự nhiên được mô hình hóa dưới dạng đồ thị có hướng (directed graph)?
A. Quan hệ bạn bè Facebook
B. Các giao lộ đường bộ
C. Quan hệ theo dõi Twitter (Twitter fol ows) D. Tương tác protein
2. Hệ số gom cụm cục bộ (local clustering coefficient) đo lường
A. Mức độ phổ biến của nút
B. Đường đi ngắn nhất
C. Mức độ kết nối giữa các láng giềng
D. Kích thước cộng đồng
3. Thuật toán Girvan-Newman phát hiện cộng đồng bằng cách loại bỏ A. Các nút có bậc cao
B. Các cạnh có độ trung gian cao (edge betweenness) C. Các cạnh ngẫu nhiên
D. Chỉ các liên kết yếu
4. DeepWalk và node2vec dựa trên
A. Phân rã riêng (eigendecomposition)
B. Bước ngẫu nhiên kết hợp skip-gram (random walks + skip-gram) C. Học có giám sát D. Mô hình ngưỡng
5. Mô hình Ngưỡng tuyến tính (Linear Threshold model) mô tả A. Lây nhiễm ngẫu nhiên
B. Sự củng cố xã hội (social reinforcement) C. Bước ngẫu nhiên D. PageRank 2/10
SECTION B: Short Answer
Mock Questions in English (Tiếng Việt ở dưới):
I. Graph Representation
Q1. Edge List → Adjacency List → Adjacency Matrix → Draw Graph
Given the undirected graph with edge list:
E = {(1,2), (1,3), (2,4), (3,4), (4,5)} 1. Write the adjacency list.
2. Write the adjacency matrix. 3. Draw the graph clearly.
4. Identify whether the graph contains any triangle.
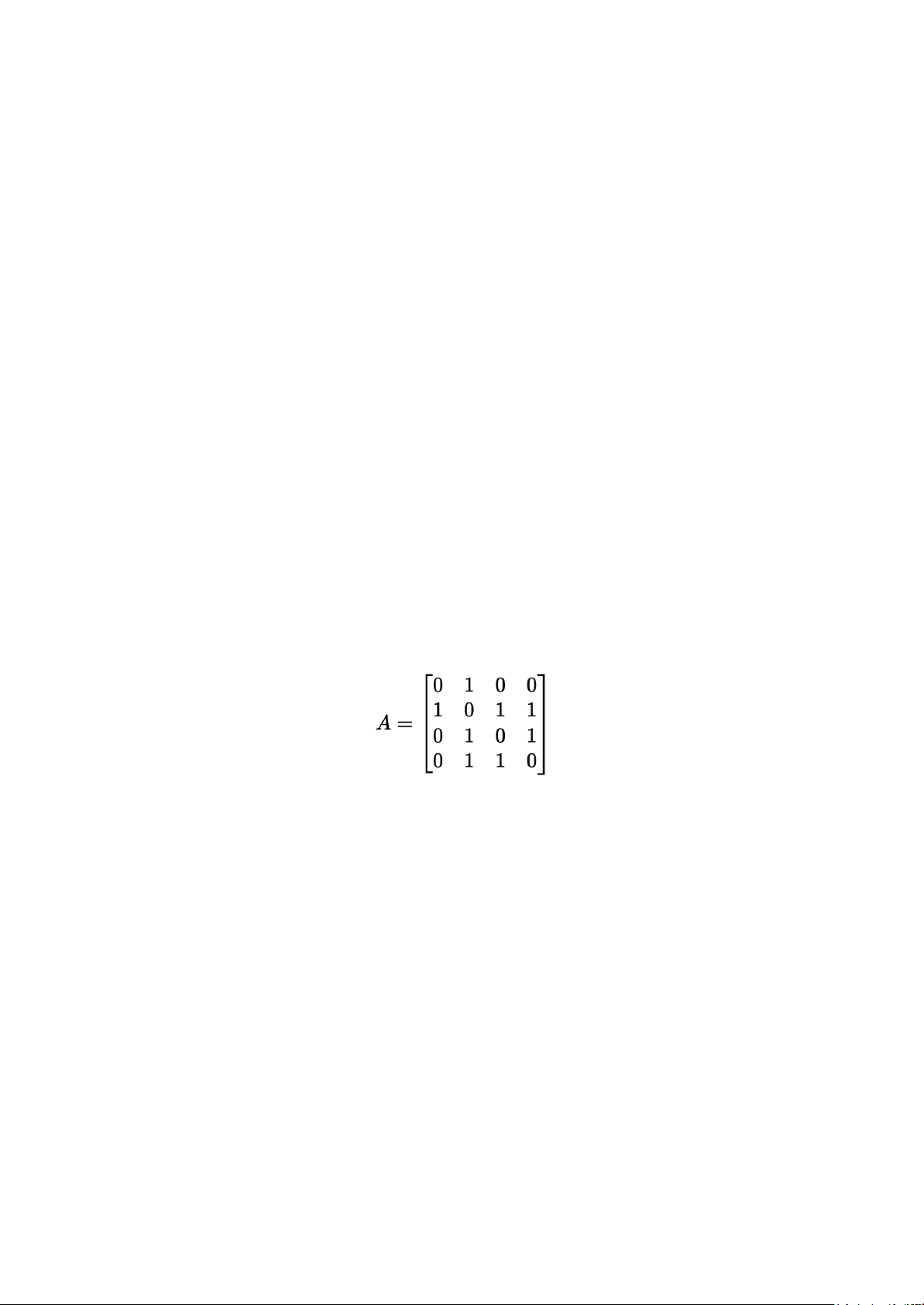
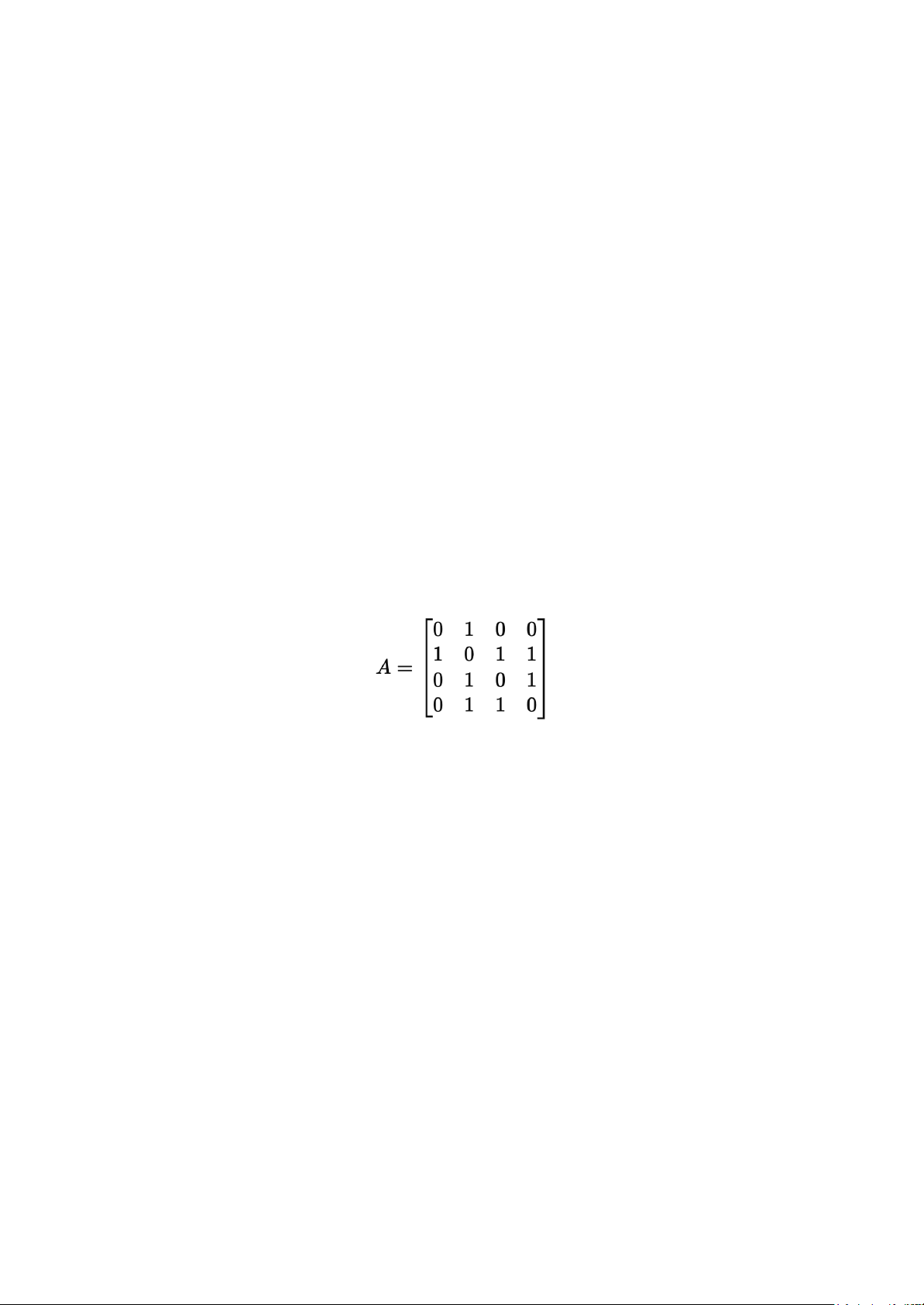
Q2. Adjacency Matrix → Edge List
Given the adjacency matrix (undirected): Nodes are labeled A,B,C,D. 1. Write the edge list. 2. Write the adjacency list.
3. How many edges does the graph have?
Q3. Directed & Weighted Graph Representation
Given the directed weighted edge list:
E = {(A,B,2), (B,C,1), (C,A,3), (C,D,1)}
1. Write the weighted adjacency matrix.
2. Write the adjacency list with weights.
3. Draw the directed graph (show arrows and weights). 3/10
II. Centrality Calculations
Q4. Degree and In/Out-Degree Given the directed graph:
E = {(A,B), (A,C), (B,C), (C,A), (C,D)}
1. Compute in-degree and out-degree of each node.
2. Which node has the highest out-degree?
3. Which node has the highest in-degree?
Q5. Closeness Centrality
Given the graph: A - B - C - D - E
1. Compute the closeness centrality of node D
( use normalized closeness = (n - 1) / ∑(distance to each other node) ).
2. Which node has the highest closeness centrality?
Q6. One Iteration of PageRank
Given a directed graph: A→B, B→C, C→A Assume:
● Initial PageRank: r(0) = (1/3, 1/3, 1/3) ● Damping factor α = 0.8 ● Uniform teleportation
Compute one iteration of PageRank r(1).
III. Clustering & Path Length
Q7. Local Clustering Coefficient
Given the graph with edges: (A,B), (A,C), (B,C), (C,D), (D,E)
1. Compute the local clustering coefficient of node C.
2. Compute the local clustering coefficient of node D. Q8. Triangle Counting
Given the undirected graph: (A,B), (B,C), (C,A), (C,D), (D,E), (E,C)
1. How many triangles are in the graph?
2. Which nodes participate in more than one triangle? 4/10 Q9. Shortest Paths
Given the graph: A - B - C - D, B - E
1. Compute the shortest path distance from A to D.
2. Compute the shortest path distance from E to C.
3. Which node is the most central in terms of shortest paths?
IV. Modularity & Community Detection
Q10. Modularity Calculation
Given the graph with edges: (A,B), (B,C), (C,A), (C,D), (D,E), (E,F), (F,D)
Community assignment: C1 = {A,B,C}, C2 = {D,E,F}
1. Compute the modularity Q using the simplified formula.
2. Does the partition indicate strong community structure?
Q11. Modularity Comparison
Consider two partitions of the same graph in Q10:
● Partition 1: {A,B,C}, {D,E,F} ● Partition 2: {A,B}, {C,D,E,F}
1. Without ful calculation, which partition likely has higher modularity? 2. Explain briefly.
V. Link Prediction & Diffusion
Q12. Local Link Prediction Scores
Given node neighbor sets: Γ(u) = {a,b,c,d}, Γ(v) = {c,d,e} 1. Compute Common Neighbors.
2. Compute Jaccard coefficient.
3. Compute Preferential Attachment score.
Q13. Adamic-Adar vs Resource Allocation Given common neighbors: w1 with degree 2, w2 with degree 10
1. Compute their contribution to Adamic-Adar.
2. Compute their contribution to Resource Al ocation.
3. Which metric penalizes high-degree nodes more? 5/10
Q14. One-Step Independent Cascade
Given the graph: A→B, A→C, B→D ● Active at time t = 0: A
● Activation probability on al edges: p = 0.5
1. Which nodes can become active at t = 1?
2. Which nodes cannot be active at t = 1?
3. Can node D be active at t = 1? Why or why not?
Q15. One-Step Linear Threshold Given the graph: A→C, B→C Weights: wAC = 0.4, wBC = 0.5 Threshold: θC = 0.7
1. If only A is active, does C activate?
2. If both A and B are active, does C activate?
VI. Embeddings & Graph Learning
Q16. Dot Product and Cosine Similarity Given node embeddings: zu = (1,0,2), zv = (-2,1,1) 1. Compute the dot product.
2. Compute the cosine similarity.
3. Based on cosine similarity, are the nodes similar?
Q17. Embedding-Based Link Prediction Given embeddings: zA=(1,1), zB=(2,2), zC=(−1,−1)
1. Which pair is most likely to have a link: (A,B) or (A,C)?
2. Explain using dot product intuition.
Q18. Skip-Gram Pairs from Random Walk
Given a random walk: A→B→C→D Window size = 1.
1. List al (center, context) training pairs used in DeepWalk. 6/10
Câu hỏi mẫu bằng Tiếng Việt:
I. Biểu diễn đồ thị (Graph Representation)
Q1. Danh sách cạnh → Danh sách kề → Ma trận kề → Vẽ đồ thị
(Edge List → Adjacency List → Adjacency Matrix → Draw Graph)
Cho đồ thị vô hướng (undirected graph) với danh sách cạnh (edge list):
E = {(1,2), (1,3), (2,4), (3,4), (4,5)}
a) Viết danh sách kề (adjacency list).
b) Viết ma trận kề (adjacency matrix).
c) Vẽ đồ thị một cách rõ ràng.
d) Xác định xem đồ thị có chứa tam giác (triangle) nào hay không.
Q2. Ma trận kề → Danh sách cạnh
(Adjacency Matrix → Edge List)
Cho ma trận kề (adjacency matrix) của một đồ thị vô hướng:
Các nút được gán nhãn: A, B, C, D.
a) Viết danh sách cạnh (edge list).
b) Viết danh sách kề (adjacency list).
c) Đồ thị có bao nhiêu cạnh (edges)?
Q3. Biểu diễn đồ thị có hướng và có trọng số
(Directed & Weighted Graph Representation)
Cho danh sách cạnh có hướng và có trọng số (directed weighted edge list):
E = {(A,B,2), (B,C,1), (C,A,3), (C,D,1)}
a) Viết ma trận kề có trọng số (weighted adjacency matrix).
b) Viết danh sách kề có trọng số (adjacency list with weights).
c) Vẽ đồ thị có hướng (directed graph), thể hiện rõ mũi tên và trọng số (arrows and weights). 7/10
II. Tính toán độ trung tâm (Centrality Calculations)
Q4. Bậc vào và bậc ra (Degree and In/Out-Degree)
Cho đồ thị có hướng (directed graph):
E = {(A,B), (A,C), (B,C), (C,A), (C,D)}
a) Tính bậc vào (in-degree) và bậc ra (out-degree) của mỗi nút.
b) Nút nào có bậc ra (out-degree) lớn nhất?
c) Nút nào có bậc vào (in-degree) lớn nhất?
Q5. Độ trung tâm gần (Closeness Centrality)
Given the graph: A - B - C - D - E
a) Tính độ trung tâm gần (closeness centrality) của nút D.
( dùng normalized closeness = (n - 1) / ∑(distance to each other node) ).
b) Nút nào có độ trung tâm gần (closeness centrality) cao nhất?
Q6. Một vòng lặp của PageRank (One Iteration of PageRank)
Cho đồ thị có hướng: A→B, B→C, C→A Giả sử:
● PageRank ban đầu: r(0) = (1/3, 1/3, 1/3)
● Hệ số suy giảm (damping factor) α=0.8
● Dịch chuyển đều (uniform teleportation)
Hãy tính một vòng lặp của PageRank, tức r(1).
III. Gom cụm & Độ dài đường đi (Clustering & Path Length)
Q7. Hệ số gom cụm cục bộ (Local Clustering Coefficient)
Cho đồ thị với các cạnh: (A,B), (A,C), (B,C), (C,D), (D,E)
a) Tính hệ số gom cụm cục bộ (local clustering coefficient) của nút C.
b) Tính hệ số gom cụm cục bộ của nút D.
Q8. Đếm tam giác (Triangle Counting)
Cho đồ thị vô hướng: (A,B), (B,C), (C,A), (C,D), (D,E), (E,C)
a) Có bao nhiêu tam giác (triangles) trong đồ thị?
b) Những nút nào tham gia vào nhiều hơn một tam giác? 8/10
Q9. Đường đi ngắn nhất (Shortest Paths) Cho đồ thị: A - B - C - D, B - E
a) Tính khoảng cách đường đi ngắn nhất (shortest path distance) từ A đến D.
b) Tính khoảng cách đường đi ngắn nhất từ E đến C.
c) Nút nào là trung tâm nhất theo tiêu chí đường đi ngắn nhất?
IV. Modularity & Phát hiện cộng đồng
(Modularity & Community Detection)
Q10. Tính modularity (Modularity Calculation)
Cho đồ thị với các cạnh: (A,B), (B,C), (C,A), (C,D), (D,E), (E,F), (F,D)
Phân hoạch cộng đồng: C1 = {A,B,C}, C2 = {D,E,F}
a) Tính modularity Q bằng công thức rút gọn (simplified formula).
b) Phân hoạch này có cho thấy cấu trúc cộng đồng mạnh hay không?
Q11. So sánh modularity (Modularity Comparison)
Xét hai cách phân hoạch của cùng đồ thị ở Câu Q10: ● Phân hoạch 1: {A,B,C}, {D,E,F} ● Phân hoạch 2: {A,B}, {C,D,E,F}
Không cần tính toán đầy đủ, theo bạn phân hoạch nào có modularity cao hơn? Giải thích ngắn gọn.
V. Dự đoán liên kết & Lan truyền (Link Prediction & Diffusion)
Q12. Các chỉ số dự đoán liên kết cục bộ (Local Link Prediction Scores)
Cho các tập láng giềng: Γ(u) = {a,b,c,d}, Γ(v) = {c,d,e}
a) Tính tập láng giềng chung (Common Neighbors).
b) Tính hệ số Jaccard (Jaccard coefficient).
c) Tính điểm ưu tiên kết nối (Preferential Attachment score).
Q13. Adamic-Adar và Resource Allocation Cho 2 láng giềng chung:
w1 có bậc 2, w2 có bậc 10
a) Tính đóng góp (contribution) của mỗi nút vào chỉ số Adamic–Adar.
b) Tính đóng góp của mỗi nút vào chỉ số Resource Al ocation.
c) Chỉ số nào phạt các nút có bậc cao mạnh hơn? 9/10
Q14. Một bước của mô hình Independent Cascade
Cho đồ thị: A→B, A→C, B→D
● Tại thời điểm t = 0: nút A đang hoạt động (active).
● Xác suất kích hoạt trên mọi cạnh: p = 0.5.
a) Những nút nào có thể trở nên hoạt động tại t=1?
b) Những nút nào không thể hoạt động tại t=1?
c) Nút D có thể hoạt động tại t=1 không? Vì sao?
Q15. Một bước của mô hình Linear Threshold Cho đồ thị: A→C, B→C
Trọng số (weights): wAC = 0.4, wBC = 0.5
Ngưỡng (threshold): θC = 0.7
a) Nếu chỉ có A hoạt động, C có được kích hoạt không?
b) Nếu cả A và B đều hoạt động, C có được kích hoạt không?
VI. Biểu diễn nhúng & Học trên đồ thị
(Embeddings & Graph Learning)
Q16. Tích vô hướng (dot product) và cosine similarity
Cho các vector biểu diễn nhúng: zu = (1,0,2), zv = (-2,1,1)
a) Tính tích vô hướng (dot product).
b) Tính độ tương đồng cosine (cosine similarity).
c) Dựa trên cosine similarity, hai nút này có tương đồng (similar) hay không?
Q17. Dự đoán liên kết dựa trên biểu diễn nhúng Cho: zA=(1,1), zB=(2,2), zC=(−1,−1)
a) Cặp nào có khả năng tồn tại liên kết cao hơn: (A,B) hay (A,C)?
b) Giải thích bằng trực giác của tích vô hướng (dot product intuition).
Q18. Các cặp Skip-Gram từ bước ngẫu nhiên (Random Walk)
Cho bước ngẫu nhiên (random walk): A→B→C→D
Kích thước cửa sổ (window size) = 1.
a) Hãy liệt kê tất cả các cặp huấn luyện (center, context) được sử dụng trong DeepWalk. 10/10
Document Outline
- Final Exam Practice Questions
- SECTION A: Multiple Choice
- Mock Questions in English (Tiếng Việt ở dưới):
- Câu hỏi mẫu bằng Tiếng Việt:
- SECTION B: Short Answer
- Mock Questions in English (Tiếng Việt ở dưới):
- I. Graph Representation
- Q1. Edge List → Adjacency List → Adjacency Matrix → Draw Graph
- Q2. Adjacency Matrix → Edge List
- Q3. Directed & Weighted Graph Representation
- II. Centrality Calculations
- Q4. Degree and In/Out-Degree
- Q5. Closeness Centrality
- Q6. One Iteration of PageRank
- III. Clustering & Path Length
- Q7. Local Clustering Coefficient
- Q8. Triangle Counting
- Q9. Shortest Paths
- IV. Modularity & Community Detection
- Q10. Modularity Calculation
- Q11. Modularity Comparison
- V. Link Prediction & Diffusion
- Q12. Local Link Prediction Scores
- Q13. Adamic-Adar vs Resource Allocation
- Q14. One-Step Independent Cascade
- Q15. One-Step Linear Threshold
- VI. Embeddings & Graph Learning
- Q16. Dot Product and Cosine Similarity
- Q17. Embedding-Based Link Prediction
- Q18. Skip-Gram Pairs from Random Walk
- Câu hỏi mẫu bằng Tiếng Việt:
- I. Biểu diễn đồ thị (Graph Representation)
- Q1. Danh sách cạnh → Danh sách kề → Ma trận kề → Vẽ đồ thị(Edge List → Adjacency List → Adjacency Matrix → Draw Graph)
- Q2. Ma trận kề → Danh sách cạnh(Adjacency Matrix → Edge List)
- Q3. Biểu diễn đồ thị có hướng và có trọng số(Directed & Weighted Graph Representation)
- II. Tính toán độ trung tâm (Centrality Calculations)
- Q4. Bậc vào và bậc ra (Degree and In/Out-Degree)
- Q5. Độ trung tâm gần (Closeness Centrality)
- Q6. Một vòng lặp của PageRank (One Iteration of PageRank)
- III. Gom cụm & Độ dài đường đi (Clustering & Path Length)
- Q7. Hệ số gom cụm cục bộ (Local Clustering Coefficient)
- Q8. Đếm tam giác (Triangle Counting)
- Q9. Đường đi ngắn nhất (Shortest Paths)
- IV. Modularity & Phát hiện cộng đồng (Modularity & Community Detection)
- Q10. Tính modularity (Modularity Calculation)
- Q11. So sánh modularity (Modularity Comparison)
- V. Dự đoán liên kết & Lan truyền (Link Prediction & Diffusion)
- Q12. Các chỉ số dự đoán liên kết cục bộ (Local Link Prediction Scores)
- Q13. Adamic-Adar và Resource Allocation
- Q14. Một bước của mô hình Independent Cascade
- Q15. Một bước của mô hình Linear Threshold
- VI. Biểu diễn nhúng & Học trên đồ thị (Embeddings & Graph Learning)
- Q16. Tích vô hướng (dot product) và cosine similarity
- Q17. Dự đoán liên kết dựa trên biểu diễn nhúng
- Q18. Các cặp Skip-Gram từ bước ngẫu nhiên (Random Walk)
- SECTION A: Multiple Choice



