











Preview text:
Topic 1 MCQ
1) The primary objective of accounting is to
A) implement strong internal controls.
B) provide useful information to decision makers.
C) prepare financial statements.
D) ensure the profitability of an organization.
2) An accounting information system (AIS) processes ________ to provide users with ________. A) data; information B) data; transactions C) information; data D) data; benefits
3) An accounting information system must be able to perform which of the following tasks? A) collect transaction data B) process transaction data C) provide adequate controls D) all of the above
4) A good example of how an AIS is used to share knowledge within an organization is
A) the use of a corporate database to help staff identify the relevant experts who can
help with a particular client.
B) the use of laptop computers to access a network for messaging worldwide.
C) the monitoring of production equipment to watch for defects.
D) the use of point-of-sale data to determine hot-selling items.
5) A well-designed AIS can improve the decision-making function within the organization.
Which statement below would describe a limitation, rather than a benefit, of an efficient AIS?
A) An AIS reduces uncertainty, and therefore accounting information can provide a basis for
choosing among alternative courses of action.
B) An AIS identifies situations requiring management action.
C) An AIS provides to its users an abundance of information without any filtering or
condensing of such information.
D) An AIS provides information about the results of previous decisions which provides
decision makers with feedback that can be used in future decision making.
6) Inventory information is provided in real time by a firm's accounting information system.
The accuracy of this information is questionable, however, since the production manager
often reports stock outs of components that the system indicates are in stock. Which of the
following characteristics of useful information is absent in the situation described above? A) Relevant B) Reliable C) Timely D) Understandable
7) What does ERP stand for?
A. Enterprise Resource Planning
B. Enterprise Resource Package
C. Electronic Resource Planning D. Resource Package
8) Which of the following statements is NOT a major reason of why accountants of the
twenty-first century must be comfortable with information systems concepts?
A. Computer systems are playing an increasing part in the management and functioning of the organisation
B. Accountants are increasingly exposed to and working with technology and information systems
C. Accountants need to know how computers manage knowledge and its data resources.
D. Accountants need to lead and oversee the design of an accounting information system.
9) An accounting information system can best be defined as:
A. The application of technology to the capturing, storing, sorting and reporting of data.
B. The application of technology to the capturing, storing, sorting and reporting of information.
C. The application of technology to the capturing, verifying, storing, sorting and reporting of
information relating to an organisation’s activities.
D. The application of technology to the capturing, verifying, storing, sorting and
reporting of data relating to an organisation’s activities.
10)An accounting information system is unlikely to help a firm to:
A. determine whether to approve a credit sale
B. decide how much to purchase from suppliers
C. determine the provision for bad debts
D. eliminate financial fraud
Discussion Questions & Problems
purchased, quantity purchased and so on. On
its own this data is not all that useful.
DQ1.1 Describe some inputs, processes However,
and outputs of an accounting
through the application of rules and
information system. (LO1, LO2,
knowledge the data can be made LO3) meaningful, thus
- Inputs: Sales order (record purchase
converting it to information. For example,
requests from customers), purchase data
the collection of data relating to sale may be
(data about purchases initiated with our
summarised into sales by customer of sales
vendors), Receiving data (data about arriving
by product, to provide information about
goods), shipping data (data about goods sent
high spending customers or slow moving
to customers), invoices (received from products vendors)
- Processes: Check data is valid, sort data, manipulate data, posting
DQ1.5 Compare the role of the accountant
- Outputs: Invoice (sent to customer),
today to his or her role before the
cheque (sent to vendor), profit and loss
introduction of computer
report, accounts receivable report technology. How have the
responsibilities and duties changed
DQ1.2 What is the difference between over time? (LO4) data and information? (LO2)
Data are the raw facts relating to or
The discussion of this question can be tied
describing an event. For example, data
into the discussion in question 1.4. What relating to a sale becomes
could include the customer’s name, address,
Evident from the historical discussion of the
salesperson ID, the sale number, sale date,
evolution of the accounting and information items
systems function is that the accountant has
gone from being responsible for both the
accounting function and the information
management function associated with
accounting to just being responsible for the
accounting function. The technically
qualified personnel, who do not necessarily
have accounting skills, have become
responsible for the information storage
function asociated with accounting. In a
sense, the responsibilities of the accountant
have been reduced, since they have lost
direct control of the information storage
function associated with the accounting
discipline. Some may also argue that this
shift has created a greater need for
accountants to be trained not just in the
technical skills of accounting but also in
skills of information management, for example information systems. Topic 2
1) An example of a strategic level decision would be:
A) Determining the quantity of raw materials to purchase
B) Appointing a new line manager responsible for running the delivery department
C) Reconfiguring the production line design to eliminate wasted time due to bottlenecks
D) Deciding whether or not to acquire the remaining shares of a partially owned subsidiary
2) There are two perspectives of organisational design: A) Logical and physical B) Internal and external
C) Functional and business process
D) Scientific and practical
3) An emphasis on business processes is different to a functional perspective of the
organisation because a business process emphasis:
A) Offers highly defined tasks and responsibilities.
B) Gives employees the freedom to do what they want in order to please the customer.
C) Acknowledges cross-functional communication and action is essential to the customer’s needs.
D) Views the customer needs as secondary to those of the functional divisions.
4) A sales person is processing a credit sale. As per company policy, the sales person should
conduct the credit check and forward the result to a supervisor, who would then make a
decision on the creditworthiness of the applicant and send this back to the sales person.
This scenario is more likely to happen in:
A) Functionally based organisation
B) Business process based organisation
C) Both functionally based organisation and business process based organisation
D) Neither functionally based organisation nor business process based organisation
5) Many modern accounting software packages offer separate transaction cycle modules. What is the reason for this?
A) Every organization does not need to implement all of the available transaction cycle modules.
B) Most businesses do not need the revenue cycle module as part of their AIS.
C) The nature of a given transaction cycle is the same irrespective of the type of organization.
D) A properly designed AIS does not use the concept of separate business transaction cycles to process transactions.
6) Which of the following is not a transaction cycle? A) revenue B) expenditure C) human resources
D) general ledger and reporting
7) Which of the following statements is false?
A) Retail stores do not have a production cycle.
B) Financial institutions have installment-loan cycles.
C) A service company does not have an inventory system.
D) Every organization should implement every transaction cycle module.
8) Transaction cycles can be summarized on a high level as "give-get" transactions. An
example of "give-get" in the revenue cycle would be A) give cash, get goods. B) give goods, get cash. C) give cash, get labor. D) give cash, get cash.
9) Which of the following is a primary activity in the value chain? A) infrastructure B) technology C) purchasing D) marketing and sales
10) The transaction cycle that includes the events of hiring employees and paying them is known as the A) revenue cycle. B) expenditure cycle. C) human resources cycle. D) financing cycle.
11) Which of the following is not an example of how an AIS adds value to an organization?
A) All employees at a hospital can access and update patient records from any
computer terminal in the hospital.
B) A customer service representative can find a customer's account data, purchase history,
payment history, and salesperson's name while on the phone with the customer, to resolve issues quickly.
C) Suppliers are able to access sales data directly from the point-of-sale system of a retailer
and deliver inventory automatically when needed.
D) Client tax files are encrypted and made available on the CPA firm's network to any employee with an access code.
12) A typical source document could be A) in some paper form.
B) a computer data entry screen. C) a notepad entry. D) both A and B
13) Which step below is not considered to be part of the data processing cycle? A) data input
B) feedback from external sources C) data storage D) data processing
14) The issuing of a purchase order is part of which transaction cycle? A) the revenue cycle B) the production cycle C) the human resources cycle
D) the expenditure cycle
15) Documents that are sent to customers or suppliers and then sent back to the company in
the course of a business transaction are known as A) turnaround documents. B) source documents. C) source data automation. D) transaction documents.
16) Which of the following is an example of source data automation? A) a utility bill
B) POS (point-of-sale) scanners in retail stores C) a bill of lading D) a subsidiary ledger
17) Pre-numbering of source documents helps to verify that
A) all transactions have been recorded since the numerical sequence serves as a control.
B) source data automation was used to capture data.
C) documents have been used in order.
D) company policies were followed.
18) Business processes can provide an organisation with a competitive advantage. This
competitive advantage is more likely to come from:
A) The design of business processes that are more efficient and effective
B) The design of business processes that are unique or offer something different
C) The design of business processes that are more competitive and flexible
D) The design of business processes that have lower costs of execution
19) The first stage in adopting a business process perspective is that:
A) it should focus on removing middle management
B) it must be represented in the design of the organisation.
C) it should emphasise the flattening of the organisational structure.
D) it must be reflected in the organisation’s latest statements.
20) A process that has been reengineered will have less of a role for specialists because:
A) Specialists are made redundant through the cost-cutting emphasis of BPR.
B) Decisions that require specialists are removed from a process.
C) Generalists are trained and act as specialists through the assistance of decision aids.
D) Jobs are combined and key workers are given decision making responsibility. Discussion Questions 2.7
Describe the differences between the functionally and process-based
organisation. How do these differences affect how the organisation operates? (LO2)
The functionally based organisation is designed around the concepts of a clear division of
tasks, specialisation of labour and tight vertical control and coordination. The functional
based organisation tends to focus more on what gets done – for example each functional
division doing their specific task and specialising on that task. Such an organisational
structure is hierarchically based. The process based organisation focuses more on how things
are done. As a result it looks at how value is delivered to the end customer, emphasising the
interaction between the different business functions, or a horizontal view of the organisation. 2.9
What is the relationship between business processes and ERP systems? (LO5)
Business processes are defined in the text as a series o interlocking activities that work
together, across the organisation, to achieve an organisational goal. The design of the
business process will be influenced strongly by the use of an ERP system. ERP systems
represent a business process perspective that has been captured in organisational software,
with the design philosophy of the ERP system being the support of business processes rather
than a functional perspective. At best, ERP systems can drive the design of a business‘s
rocesses by virtue of the fact that the processes incorporated into the ERP system represent
best practice‘. For organisations adopting ER systems, it is usually recommended that they
change the existing processes to match those encapsulated in the ERP system. Thus ERP
systems can have a strong influence on the design of business processes 2.14
List and describe, through the use of examples, the principles of BPR. (LO7) Principle Description Combine jobs and let
The role of the employee is now across the process, rather workers make decisions
than just one particular task. Potentially they can be
involved from start to finish within the process. Create a single reference
This helps customer satisfaction, giving the customer a point for customers
single reference point regardless of the nature of their
enquiry. Some Australian banks are tending towards this
approach, with client managers allocated customers, in
preference to the traditional functional approach, for
example loans manager, accounts manager and so on Perform steps in a natural
If activities can be performed simultaneously then allow order and at their logical
that to happen, and avoid the passing of work around to location
different locations if possible Allow processes to vary
Not all cases are homogenous. As a result allow variation in
the execution of processes to cater for different circumstances Reduce the impediment of
Controls, while an important part of an organisation, can controls and reconciliations
slow down processes. BPR questions the value of controls –
for example hierarchies and reconciliations – and calls for
non-value adding controls to be removed Topic 3 MCQ
1) Which of the following is not true about program flowcharts?
A) Program flowcharts are a high-level overview of all business processes.
B) Program flowcharts document the processing logic of computer programs.
C) A program flowchart will exist for every computer process symbol on a system flowchart.
D) Program flowcharts increase computer programmer productivity.
2) Data flow diagrams depict
A) processes, but not who is performing the processes.
B) processes, but not the data that flows between processes.
C) who is performing processes, but not how they perform the process.
D) who is performing processes, but not the data that flows between processes.
3) Graphical representations of information are often supplemented by A) product specifications. B) narrative descriptions. C) logic charts.
D) oral descriptions from management.
4) When preparing a document flowchart, the names of organizational departments or job functions should appear in the A) column headings. B) right-hand margin.
C) written narrative accompanying the flowchart. D) title of the flowchart. 5) A data flow diagram
A) is a graphical description of the source and destination of data that shows how data
flow within an organization.
B) is a graphical description of the flow of documents and information between departments or areas of responsibility.
C) is a graphical description of the relationship among the input, processing, and output in an information system.
D) is a graphical description of the sequence of logical operations that a computer performs as it executes a program.
6) In preparing a DFD, when data are transformed through a process, the symbol used should be A) a circle. B) an arrow. C) a square. D) two horizontal lines.
7) In general, a data destination will be shown by A) an arrow pointing away. B) an arrow pointing in.
C) arrows pointing both ways.
D) no arrows, only two horizontal lines.
8) In a data flow diagram of the customer payment process, "update receivables" will appear above or in A) a square. B) a circle. C) two horizontal lines. D) none of the above
9) In a data flow diagram of the customer payment process, "Customer" will appear above or in A) a square. B) a circle. C) two horizontal lines. D) none of the above
10) In a data flow diagram of the customer payment process, "Customer payment" will appear above or in A) a square. B) a circle. C) two horizontal lines. D) an arrow.
11) A DFD created at the highest-level or summary view is referred to as a A) process diagram. B) overview diagram. C) content diagram. D) context diagram.
12) Chan has been hired as an assistant to the internal auditor. He has been asked to
thoroughly document the existing accounting information system in preparation for
making recommendations for improvements. He decides to begin by meeting with the
information technology staff in order to develop an understanding of the overall operation
of the AIS, including data entry, storage, and output. The documentation tool that he
should employ for this purpose is a A) data flow diagram. B) document flowchart. C) system flowchart. D) program flowchart.
13) An employee receives a paycheck prepared in the payroll process. Which one of the
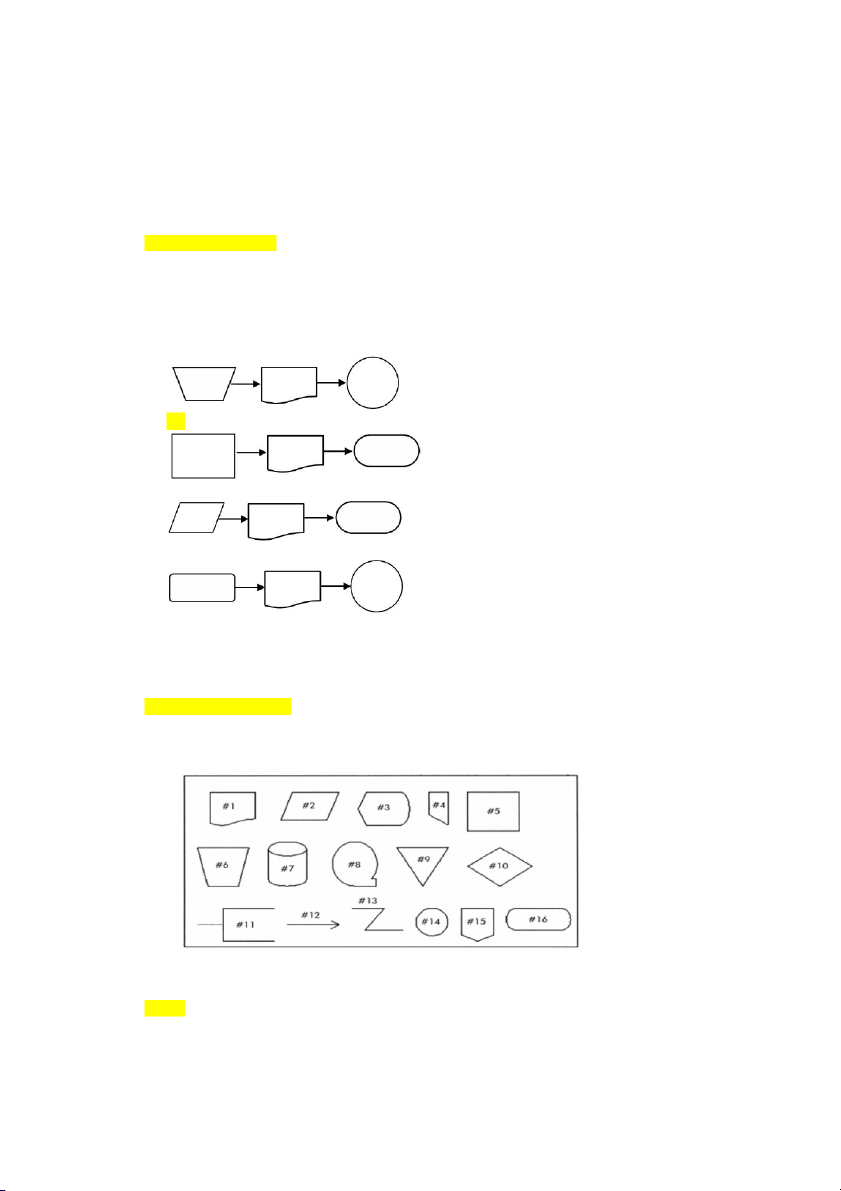
following diagrams represents this activity? A) B) C) D)
14) A flowchart that depicts the relationships among the input, processing, and output of an AIS is
A) an internal control flowchart. B) a document flowchart. C) a system flowchart. D) a program flowchart.
Use the chart below to answer questions 15 to 20 regarding flow chart symbols.
15) Which symbol would be used in a flowchart to represent a manual process? A) #5 B) #6 C) #10 D) #11 Discussion Question 6.3
Describe the information that can be obtained from each of these forms of systems documentation: (a) Process map (b) Context diagram (c) Physical data flow diagram (d) Logical data flow diagram (e) Systems flowchart (LO2, LO3, LO4)
a. The PROCESS MAP is a simple graphical representation of a system, detailing
the activities that occur, the entities that perform the activities, the relationship
between different activities and entities, and any decisions that occur as part of the process.
b. The CONTEXT DIAGRAM provides a representation of the system of interest and
the external entities that interact with it, by either providing inputs or receiving
outputs. It is an overview of the system of interest‘s interaction with the external entities.
c. The LOGICAL DATA FLOW DIAGRAM takes the context diagram and expands it,
to tell us what sequence of activities or processes occur within the system of interest
and the data flows between these activities / processes.It is concerned with the logical
perspective –the tasks that get performed –and not the people, places and things
that are required in order to perform them.
d. The PHYSICAL DATA FLOW DIAGRAM takes the context diagram and expands it,
to tell us the people, places and things that are involvedin the system of interest,
as well as the data flows that occur between these physical entities.
e. The SYSTEMS FLOWCHART provides us with both a logical and physical
perspective of the system, depicting the entities involved and the processes they
perform. In addition, we get details about how the processes are performed
(for examplea computer process versus a manual process). To this extent it
represents a combination of the physical and logical data flow diagrams, but with more detail added. Topic 4 MCQ
1) To accomplish the objectives set forth in the expenditure cycle, a number of key
management decisions must be addressed. Which of the decisions below is not ordinarily
found as part of the expenditure cycle?
A) How can cash payments to vendors be managed to maximize cash flow?
B) What is the optimal level of inventory and supplies to carry on hand?
C) Where should inventories and supplies be held?
D) What are the optimal prices for each product or service? - Revenue Cycle
2) Comparing quantities on a vendor invoice 8 to quantities on the receiving report 8 would
not prevent or detect which of the following situations?
A) Receiving and accepting inventory not ordered
B) Theft of inventory by receiving department employees
C) Update of wrong inventory items due to data entry error
D) Order for an excessive quantity of inventory
3) Which of the following would be the effect least
ive control to prevent paying the same vendor invoice twice?
A) Allow only the accounts payable department to authorize payment for vendor
invoices and allow only the cash disbursements department to cut and mail checks to vendors.
B) Only pay from original invoices.
C) Cancel each document in the voucher package once the check is prepared and mailed.
D) Only pay vendor invoices that have been matched and reconciled to a purchase order and a receiving report.
4) When goods are being ordered from a vendor, which electronic files are either read or updated?
A) inventory, vendors, and accounts payable
B) vendors and accounts payable
C) open purchase orders and accounts payable
D) inventory, vendors, and open purchase orders
5) One of the major responsibilities of the receiving department is
A) deciding if the delivery should be accepted.
B) verifying any purchase discounts for the delivery.
C) deciding on the location where the delivery will be stored until used.
D) updating inventory subsidiary ledgers.
6) Which of the following is generally not shown on a receiving report? A) price of the items B) quantity of the items C) purchase order number D) counted and inspected by
7) The management at Amazon, an Internet-based wholesaler, is considering a new
inventory control system. The current system is inadequate because it results in stockouts
that interrupt production and excess stocks of some materials that result in markdowns
and high carrying costs. The new system, which will focus on forecasting demand for Sad Clown's products, will employ
A) a just-in-time inventory system.
B) the economic order quantity. C) a reorder point.
D) materials requirements planning.
8) Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) includes several variables that must be taken into
consideration when calculating the optimal order size. One variable, the costs associated
with holding inventory, is referred to as A) ordering costs. B) carrying costs. C) the reorder point. D) stockout costs.
9) What aspect below best characterizes a Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory system?
A) frequent deliveries of smaller quantities of items to the work centers
B) frequent deliveries of large quantities to be held at the work centers
C) less frequent deliveries of large quantities of goods to central receiving
D) infrequent bulk deliveries of items directly to work centers
10) What is a key feature of materials requirements planning (MRP)?
A) minimize or entirely eliminate carrying and stockout costs
B) reduce required inventory levels by scheduling production rather than estimating needs
C) determine the optimal reorder point
D) determine the optimal order size
11) When goods are being ordered from a vendor, which electronic files are either read or updated?
A) inventory, vendors, and accounts payable
B) vendors and accounts payable
C) open purchase orders and accounts payable
D) inventory, vendors, and open purchase orders
12) The inventory management approach that attempts to minimize, if not eliminate, carrying and stockout costs is
A) materials requirements planning. B) economic order quantity. C) just-in-time inventory.
D) evaluated receipt settlement.
13) A(n) ________ system posts an approved invoice to the vendor account and stores it in an
open invoice file until payment is made by check. A) Non-voucher B) voucher C) cycle
D) evaluated receipt settlement
14) A disbursement voucher contains
A) a list of outstanding invoices.
B) the net payment amount after deducting applicable discounts and allowances.
C) the general ledger accounts to be debited.
D) All of the above are correct.
15) A voucher package should include
A) a purchase requisition, vendor invoice, and receiving report.
B) a purchase order, vendor invoice, and receiving report., PV
C) a purchase requisition, purchase order, and receiving report.
D) a bill of lading and vendor invoice.
16) What is the best control to mitigate the threat of paying prices that are too high for goods ordered?
A) require the receiving department to verify the existence of a valid purchase order
B) use only approved suppliers and solicit competitive bids
C) only pay invoices that are supported by the original voucher package
D) use bar-code technology to eliminate data entry errors
17) One of the threats associated with the process and activity of receiving and storing goods is A) errors in counting. B) kickbacks.
C) requests for unnecessary items. D) errors in vendor invoices.
18) What is the best way to prevent the acceptance of unordered goods?
A) Order only from approved vendors.
B) Match the packing slip/delivery note to a purchase order before accepting delivery.
C) Enforce an appropriate conflict of interest policy in place.
D) Require specific authorization from the purchasing manager before accepting any goods.
19) Double-checking the accuracy of an invoice is a control that can help to neutralize a
threat in the expenditure cycle. What activity would specifically be associated with this control? A) ordering goods
B) receiving and storing goods
C) paying for goods and services
D) requesting goods be ordered
20) Which control would best prevent payments made to fictitious vendors?
A) Allow payments only to approved vendors.
B) Restrict access to any payment or approval documents.
C) Have an independent bank reconciliation.
D) Make sure all documents are in order before approving payments.




