


Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 RTL Coding Guidelines Think Synchronous
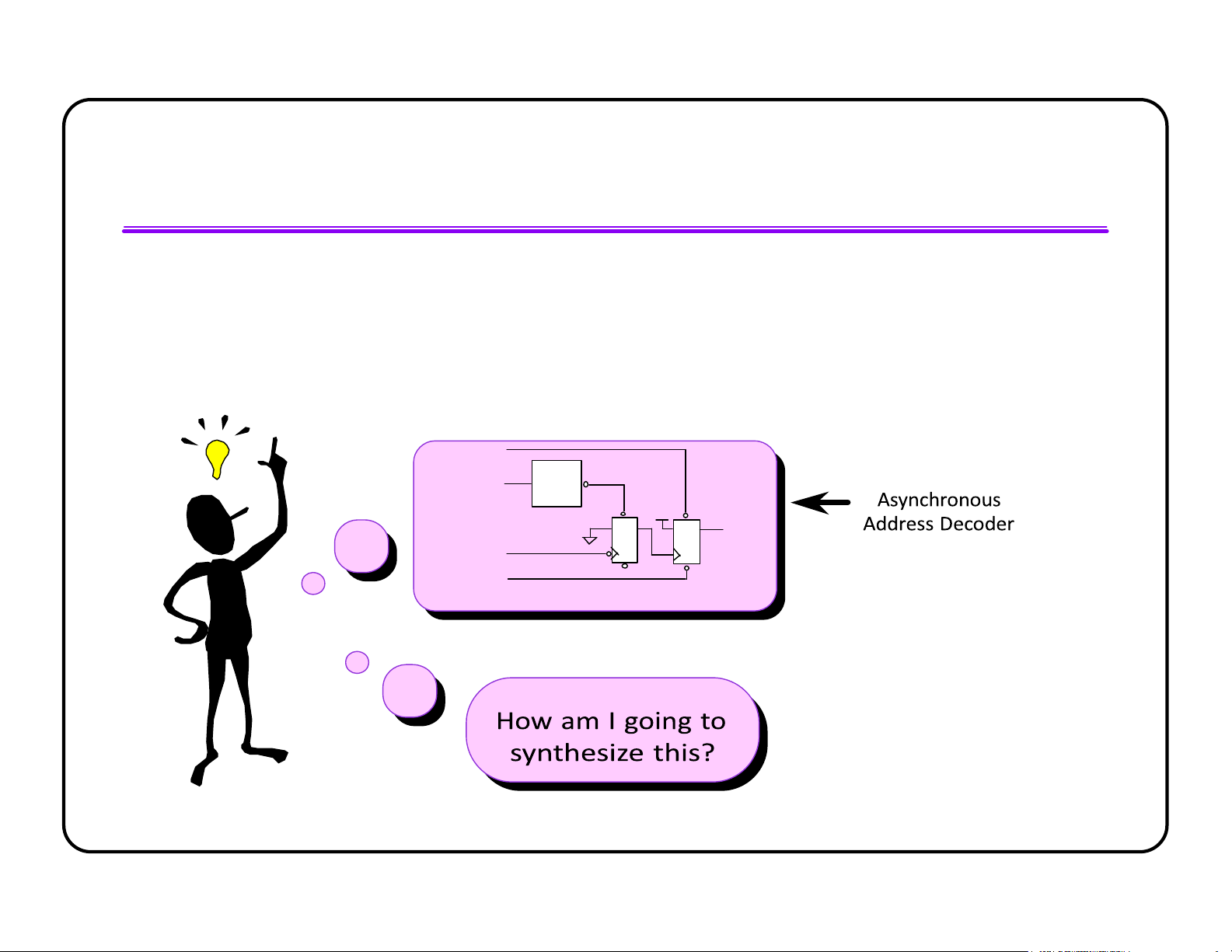
l Synchronous designs run smoothly through synthesis,
simulation and place-and-route l Isolate necessary
Asynchronous logic into separate blocks ACK_SET ADDR ADDR_IN DECODE +5 ACK GND AS ACK_CLR lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 RTL Coding Guidelines Think RTL
l Describe the circuits in terms of its registers and the
combinational logic between them lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 m m o o d d u u l l e e G G I I Z Z M M O O ( ( A A , , C C L L K K , , Z Z ) ) ; ; ... ... GIZMO a a l l w w a a y y s s @ @ ( ( A A ) ) b b e e g g i i n n : : C C O O M M B B O O 1 1 . . . . . . COMBO1 COMBO2 a a l l w w a a y y s s @ @ ( ( p p o o s s e e d d g g e e C C L L K K ) ) . . . . . . a a l l w w a a y y s s @ @ ( ( B B ) ) b b e e g g i i n n : : C C O O M M B B O O 2 2 . . . . . . a a l l w w a a y y s s @ @ ( ( p p o o s s e e d d g g e e C C L L K K ) ) ... ... en en d d m m od od ul ul e; e; RTL Coding Guidelines lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460
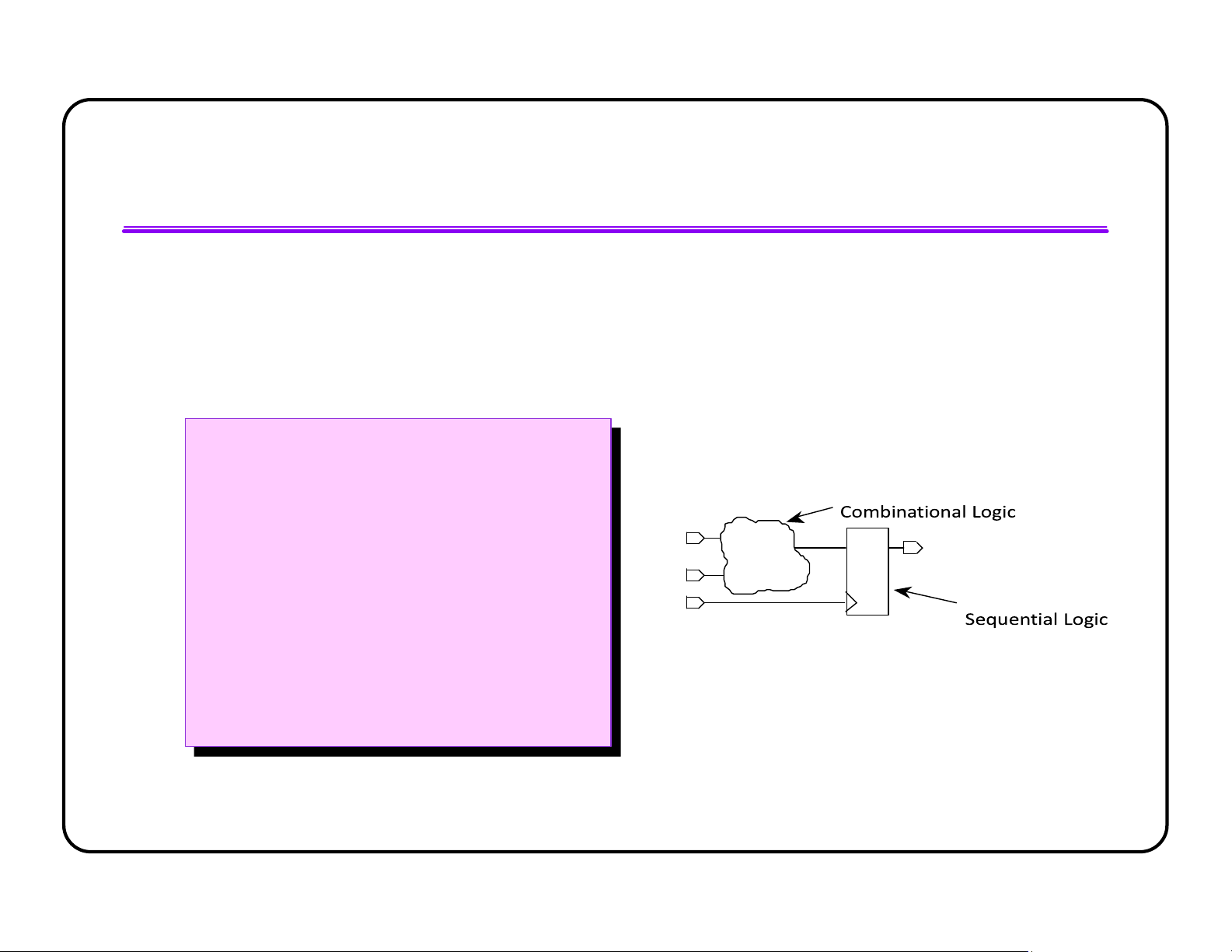
Separate Combinational from Sequential
l Follows RTL coding style l Easy to read and self-documenting
module EXAMPLE (DATA1,DATA2,CLK,Q)
module EXAMPLE (DATA1,DATA2,CLK,Q) input DATA1,DATA2,CLK; input DATA1,DATA2,CLK; output Q; output Q; reg DATA, Q; reg DATA, Q; DATA
always @(DATA1 or DATA2) DATA1 always @(DATA1 or GOBBLEDY Q -GOOK DATA2) begin: COMBO end beg in: COMBO DATA2
DATA <= GOBBLEDYGOOK(DATA1,DATA2);
DATA <= GOBBLEDYGOOK(DATA1,DATA2); end CLK always @(posedge CLK) always @(posedge CLK) begin: SEQUENTIAL begin: SEQUENTIAL Q <= DATA; lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 Q <= DATA; end end endmodule endmodule IF Statements
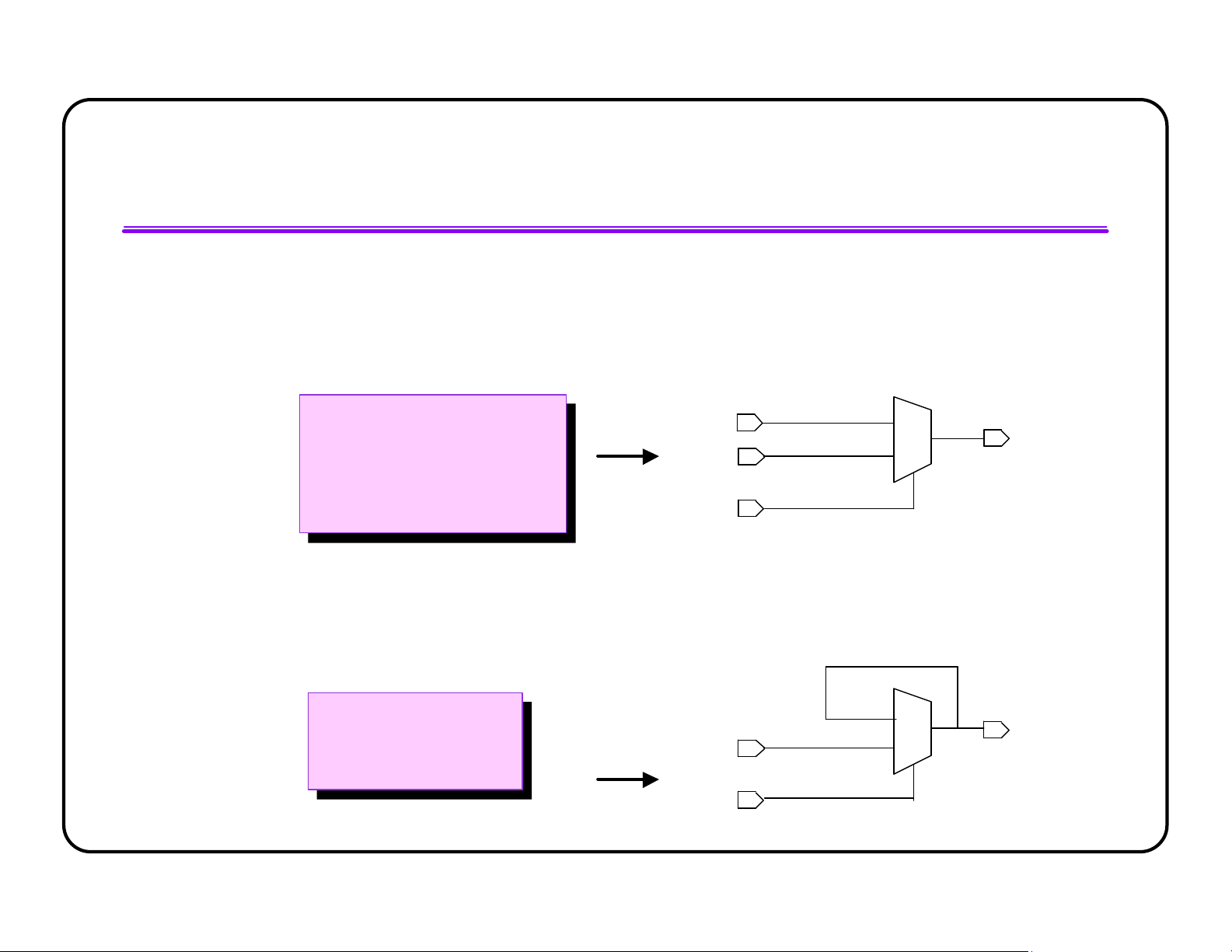
l IF statements infer multiplexer logic a a l l w w a a y y s s @ @ ( ( S S E E L L o o r r A A o o r r B B ) ) B 0 i i f f ( ( S S E E L L ) ) D 1 D <= A; A D <= A; el el s s e e D D < < = = B B ; ; SEL
l Latches are inferred unless all variables are assigned in all branches always @(SEL or A) 0 always @(SEL or A) D 1 if (SEL) if (SEL) A D <= A; D <= A; SEL lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 IF Statements (cont.)
l IF-ELSE-IF statements infer priority-encoded multiplexers D 0
always @(SEL or A or B or C or D) 1
always @(SEL or A or B or C or D) C if (SEL[2] == 1’b1) if (SEL[2] == 1’b1) SEL[0]=‘1’ 0 OUT <= A; 1 OUT <= A;
else if (SEL[1] == 1’b1) SEL else SEL[1]=‘1’ if (SEL[1] == 1’b1) 0 OUT
OUT <= B; else if (SEL[0] == 1 1’b1)OUT <= B; B SEL[2]=‘1’
else if (SEL[0] == 1’b1) OUT <= C; OUT <= C; else else OUT <= D; OUT <= D; A lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 Long delay from D to OUT IF Statements (cont.)
l Remove redundant conditions l Use CASE statements if
conditions are mutually exclusive Don’t OUT <= D; else if (A == B) else if (A == B)
always @(A or B or C or D or OUT <= E; E) OUT <= E;
always @(A or B or C or D or Do E) if (A < B)
always @(A or B or C or D or if (A < B) E) OUT <= C;
always @(A or B or C or D or OUT <= C; else if (A > B) E) else if (A > B) if (A < B) OUT <= D; if (A < B) OUT <= C; lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 OUT <= C; else else if (A > B) OUT <= E; else if (A > B) OUT <= E; OUT <= D; OUT <= D; else CASE Statements Verilog Directives
l full_case indicates that all user-desired cases have been specified
l Do not use default for one-hot encoding
always @(SEL or A or B or C)
always @(SEL or A or B or C) begin begin
case (SEL) //synopsys full_case
case (SEL) //synopsys full_case one hot
3’b001 : OUT <= A;
3’b001 : OUT <= A;
3’b010 : OUT <= B; Does not infer latches
3’b010 : OUT <= B;
3’b100 : OUT <= C;
3’b100 : OUT <= C; endcase lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 endcase end end
always @(SEL or A or B)
always @(SEL or A or B) begin begin case (SEL) case (SEL) Infers latches for OUT
3’b001 : OUT <= A;
33’b010 : OUT <= B;’b001 : OUT <= A; because not all cases
3’b010 : OUT <= B;
33’b100 : OUT <= C;’b100 : OUT <= C; are specified endcase endcase end end CASE Statements Verilog Directives (cont.)
l parallel_case indicates that all cases listed are mutually
exclusive to prevent priority-encoded logic lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460
always @(SEL or A or B or C)
always @(SEL or A or B or C) begin begin
case (SEL) //synopsys parallel_case
case (SEL) //synopsys parallel_case
A : OUT <= 3’b001;
A : OUT <= 3’b001;
B : OUT <= 3’b010; Infers a multiplexer
B : OUT <= 3’b010;
C : OUT <= 3’b100;
C : OUT <= 3’b100; endcase endcase end end CASE Statements “CASE” vs. “IF-ELSE IF”
l Use IF-ELSE for 2-to-1 multiplexers l Use CASE
for n-to-1 multiplexers where n > 2 l Use IF-ELSE IF for priority encoders lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460
l Use CASE with //synopsys parallel_case when conditions are mutually exclusive
l Use CASE with //synopsys full_case when not all conditions are specified
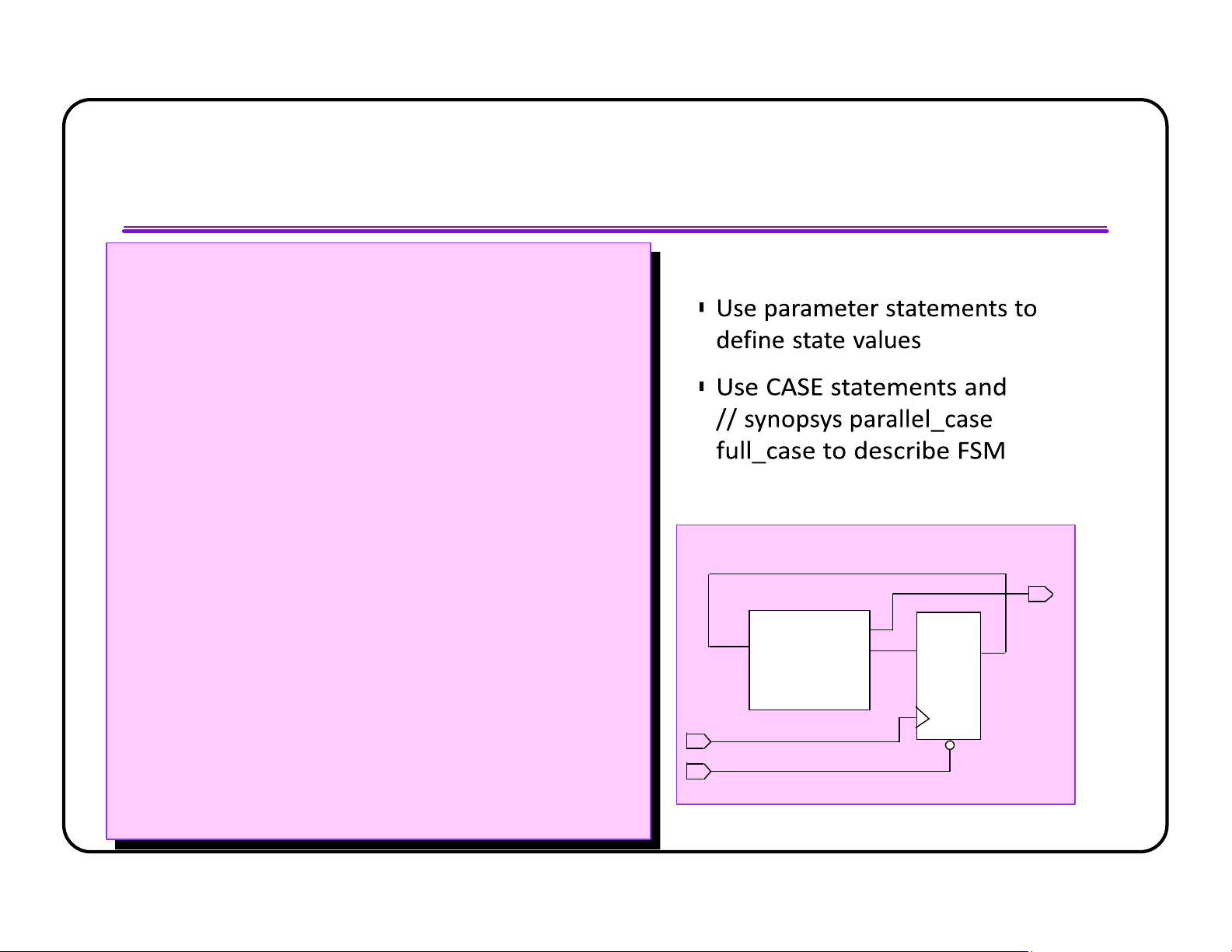
l Use CASE with //synopsys full_case parallel_case for one-hot Finite State Machines (FSMs) CASE Statements FSM Encoding
l Use CASE statements to describe FSMs l Use //synopsys parallel_case
to indicate mutual exclusivity l Use //synopsys full_case when not all
possible states are covered (one-hot) l Do not use default unless recovery state is desired lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 CASE Statements FSM Encoding (cont.)
module EXAMPLE (RESET, CLK, OUT);
module EXAMPLE (RESET, CLK, OUT); input RESET, CLK; input RESET, CLK; output [1:0] OUT; output [1:0] OUT;
parameter IDLE=4’b0001, GO=4’b0010, YIELD=4’b0100,
parameter IDLE=4’b0001, GO=4’b0010, YIELD=4’b0100, STOP=4’b1000; STOP=4’b1000;
reg [3:0] CURRENT_STATE, NEXT_STATE;
reg [3:0] CURRENT_STATE, NEXT_STATE;
always @(CURRENT_STATE)
always @(CURRENT_STATE) begin: COMBO begin: COMBO
case (CURRENT_STATE) // synopsys full_case parallel_case
case (CURRENT_STATE) // synopsys full_case parallel_case
IDLE: begin NEXT_STATE = GO; OUT <= 2’b01; end
IDLE: begin NEXT_STATE = GO; OUT <= 2’b01; end
GO: begin NEXT_STATE = YIELD; OUT <= 2’b11; end
GO: begin NEXT_STATE = YIELD; OUT <= 2’b11; end
YIELD: begin NEXT_STATE = STOP; OUT <= 2’b10; end
YIELD: begin NEXT_STATE = STOP; OUT <= 2’b10; end
STOP: begin NEXT_STATE = IDLE; OUT <= 2’b00; end CURRENT_STATE
STOP: begin NEXT_STATE = IDLE; OUT <= 2’b00; end endcase endcase end end
always @(posedge CLK or negedge RESET)
always @(posedge CLK or negedge RESET) NEXT_STATE STATE begin: SEQUENTIAL begin: SEQUENTIAL AND OUTPUT VECTOR if (~RESET) if (~RESET) DECODING CURRENT_STATE <= IDLE; CURRENT_STATE <= IDLE; else else
CURRENT_STATE <= NEXT_STATE
CURRENT_STATE <= NEXT_STATE end end endmodule endmodule lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 CASE Statements
Watch for Unintentional Latches
l Completely specify all branches for every case and if statement l
Completely specify all outputs for every case and if statement l Use
//synopsys full_case if all desired cases have been specified
What’s wrong with this example?
( Missing Outputs ) ( Missing Case ) a a l l w w a a y y s s @ @ ( ( S S E E L L ) ) b b e e g g i i n n c c a a s s e e ( ( S S E E L L ) ) 2 2 ’
’b00: A <= 1’b1; b00: A <= 1’b1; 2 2 ’b
’b01: A <= 1’b0; 01: A <= 1’b0; 2 2 ’
’b10: B <= 1’b1; b10: B <= 1’b1; e e n n d d c c a a s s e e end end CASE Statements lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 Cascade Chain Inference
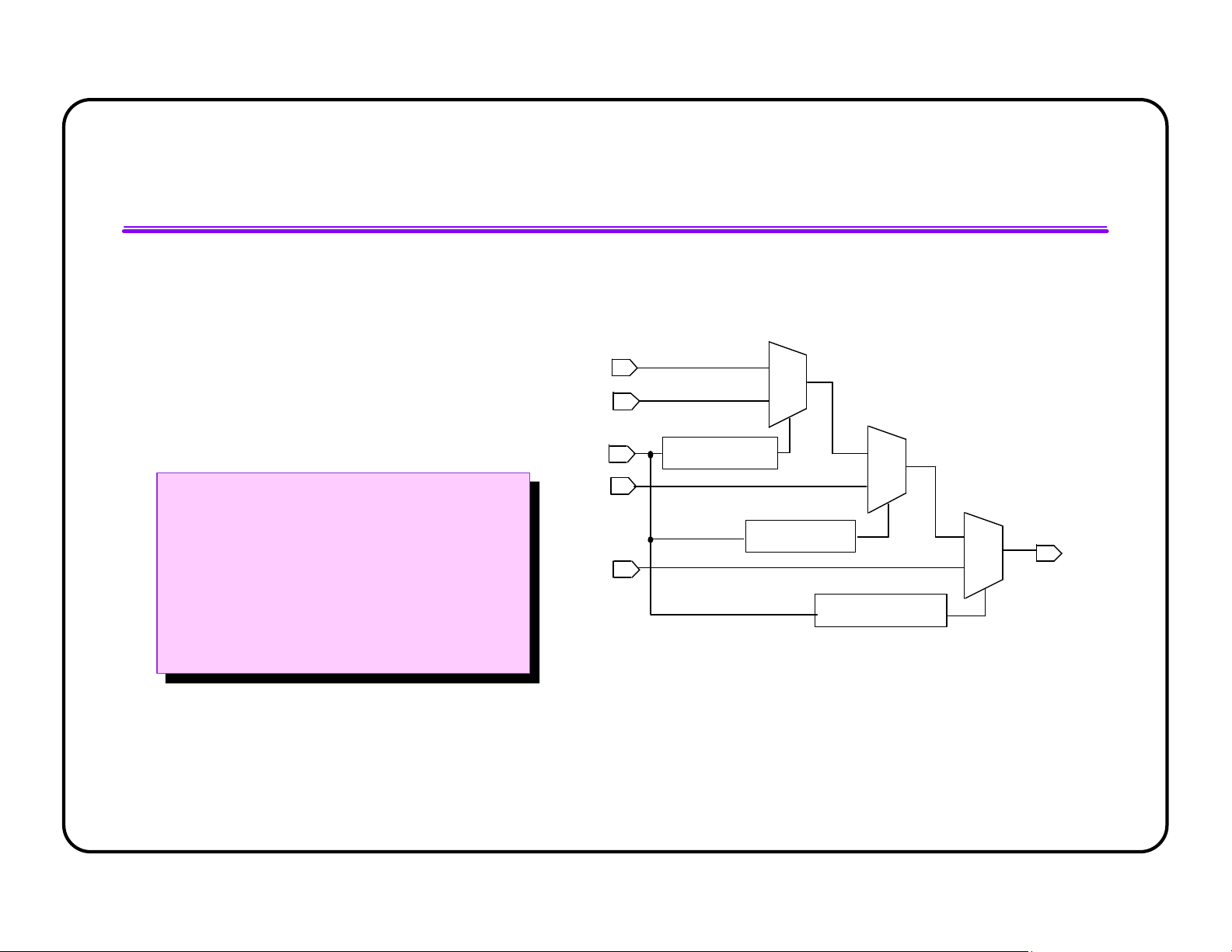
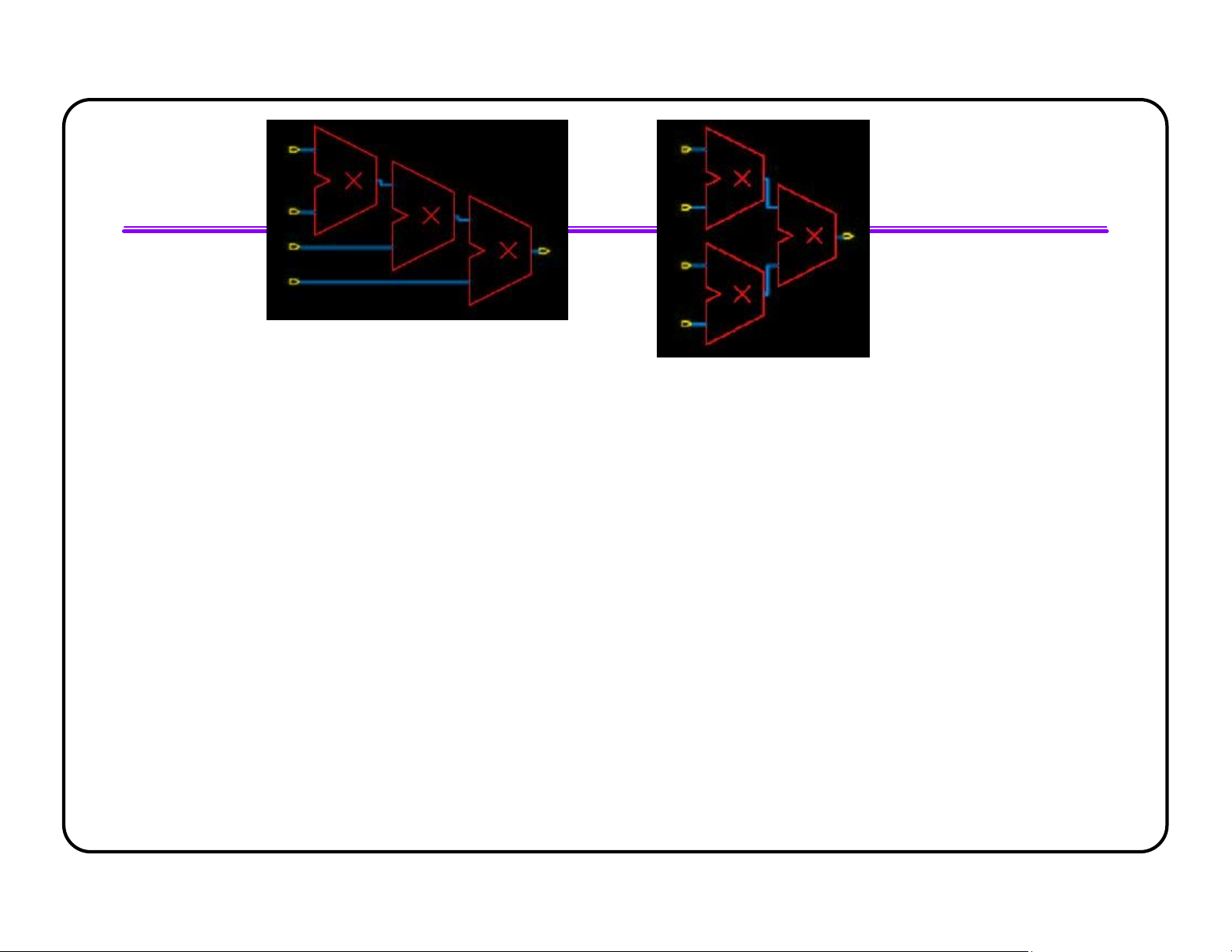
l Using cascade chains improves QoR significantly for multiplexers
l Completely specify all possible cases for cascade chains to be inferred always @(SEL) always @(SEL) begin begin case (SEL) case (SEL) 3’b000: OUT <= A; 3’b000: OUT <= A; 3’b001: OUT <= B; 3’b001: OUT <= B; 3’b010: OUT <= C; 3’b010: OUT <= C; 3’b011: OUT <= D; 3’b011: OUT <= D; 3’b100: OUT <= E; 3’b100: OUT <= E; 3’b101: OUT <= F; 3’b101: OUT <= F; 3’b110: OUT <= G; 3’b110: OUT <= G; lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 3’b111: OUT <= H; 3’b111: OUT <= H; endcase endcase end end Multiplexers
l Use IF or continuous assignment when select is a single-bit signal
always @(SEL or A or B)
always @(SEL or A or B) 0 D
if (SEL) B if (SEL) 1 D <= A; D <= A; A else else D <= B; D <= B;
----------------------- SEL
----------------------assign D = SEL ? A : B;
assign D = SEL ? A : B;
l Use CASE statements when select is a multi-bit bus
always @(SEL or A or B lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460
always @(SEL or A or B or C or D)or C or D) A 00 begin 01 OUT begin 10 case (SEL) B case (SEL) 2’b00 : OUT <= A; 11 2’b00 : OUT <= A; C 2’b01 : OUT <= B; 2 2’b01 : OUT <= B;
22’b10 : OUT <= C;’b10 : OUT <= C; D 2’b11 : OUT <= D;
2’b11 : OUT <= D; endcase endcase end SEL end lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 Operators l Operators inferred from HDL
• Adder, Subtractor, AddSub (+, -), Multiplier (*)
• Comparators (>, >=, <, <=, ==, !=)
• Incrementer, Decrementer, IncDec (+1, -1) l Example
module add (sum, a, b);
module add (sum, a, b); output [15:0] sum; output [15:0] sum; input [15:0] a, b; input [15:0] a, b; Design indicates two adders.
assign sum = a + b + 1’b1;
assign sum = a + b + 1’b1; endmodule endmodule
module add (sum, a, b);
module add (sum, a, b); output [15:0] sum; output [15:0] sum; input [15:0] a, b; input [15:0] a, b; wire temp; wire temp; lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 FE infers one adder with
assign {sum, temp} = {a, 1’b1} + {b, 1’b1};assign {sum, temp} = {a, 1’b1} + {b, 1’b1}; carry chain. endmodule endmodule derations - 94 Operators Operator Sharing
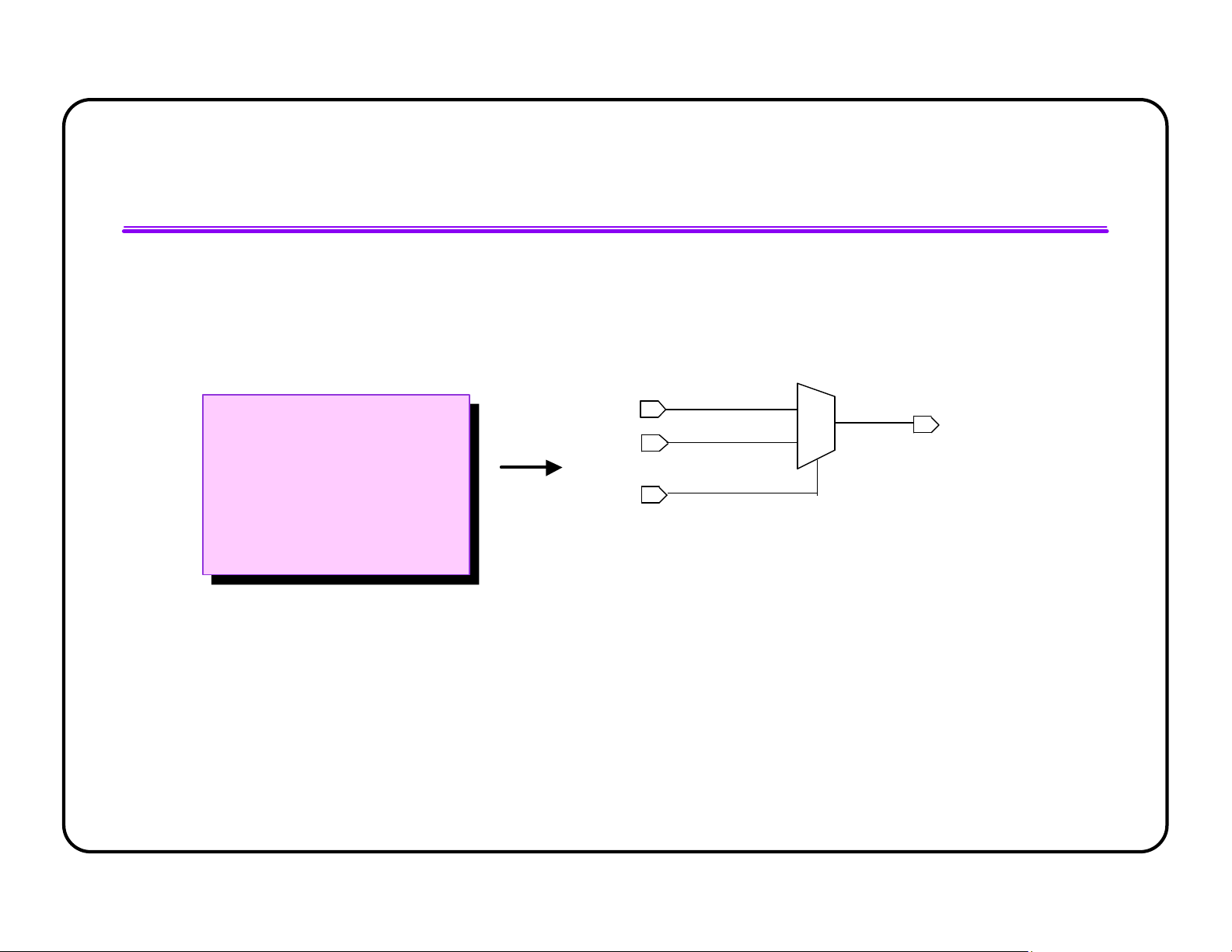
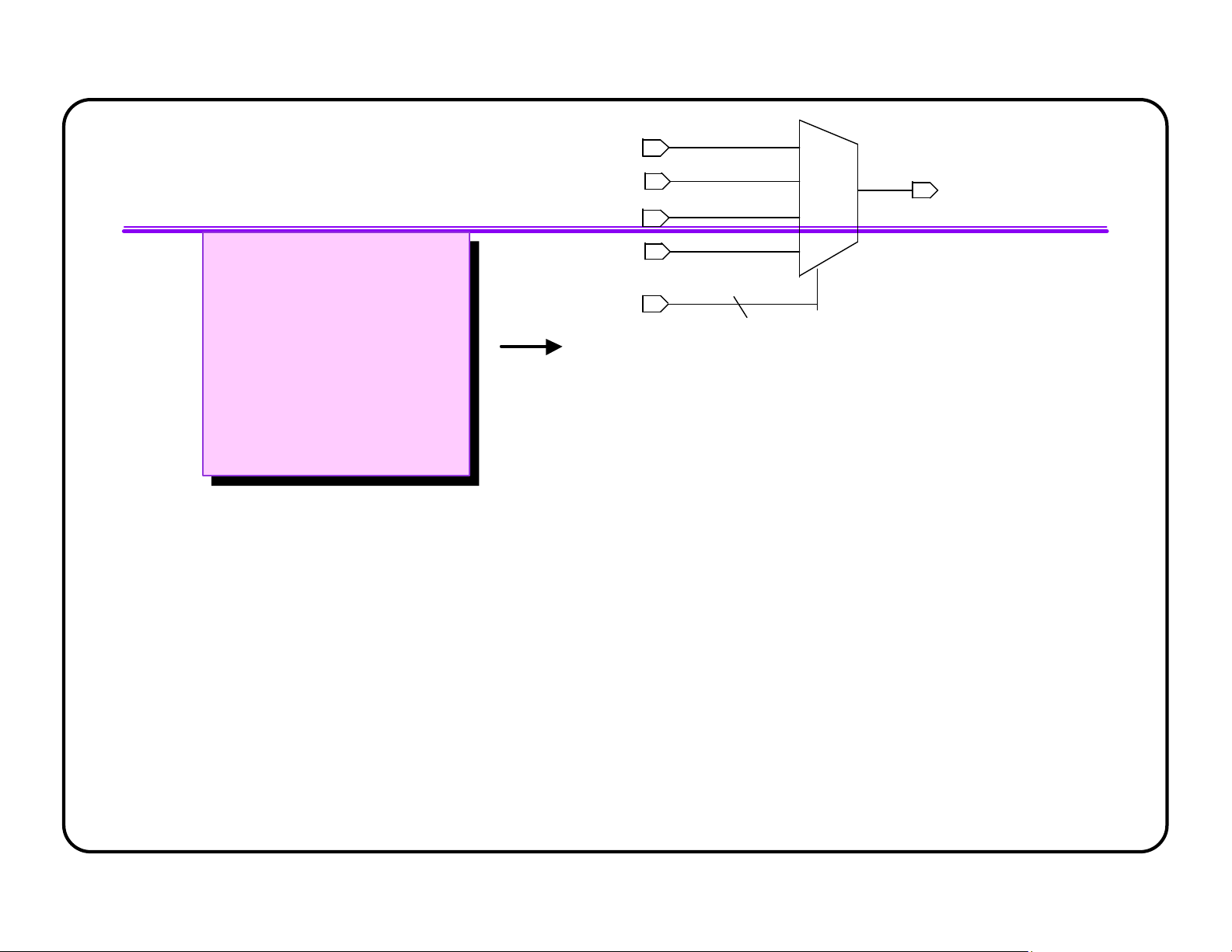
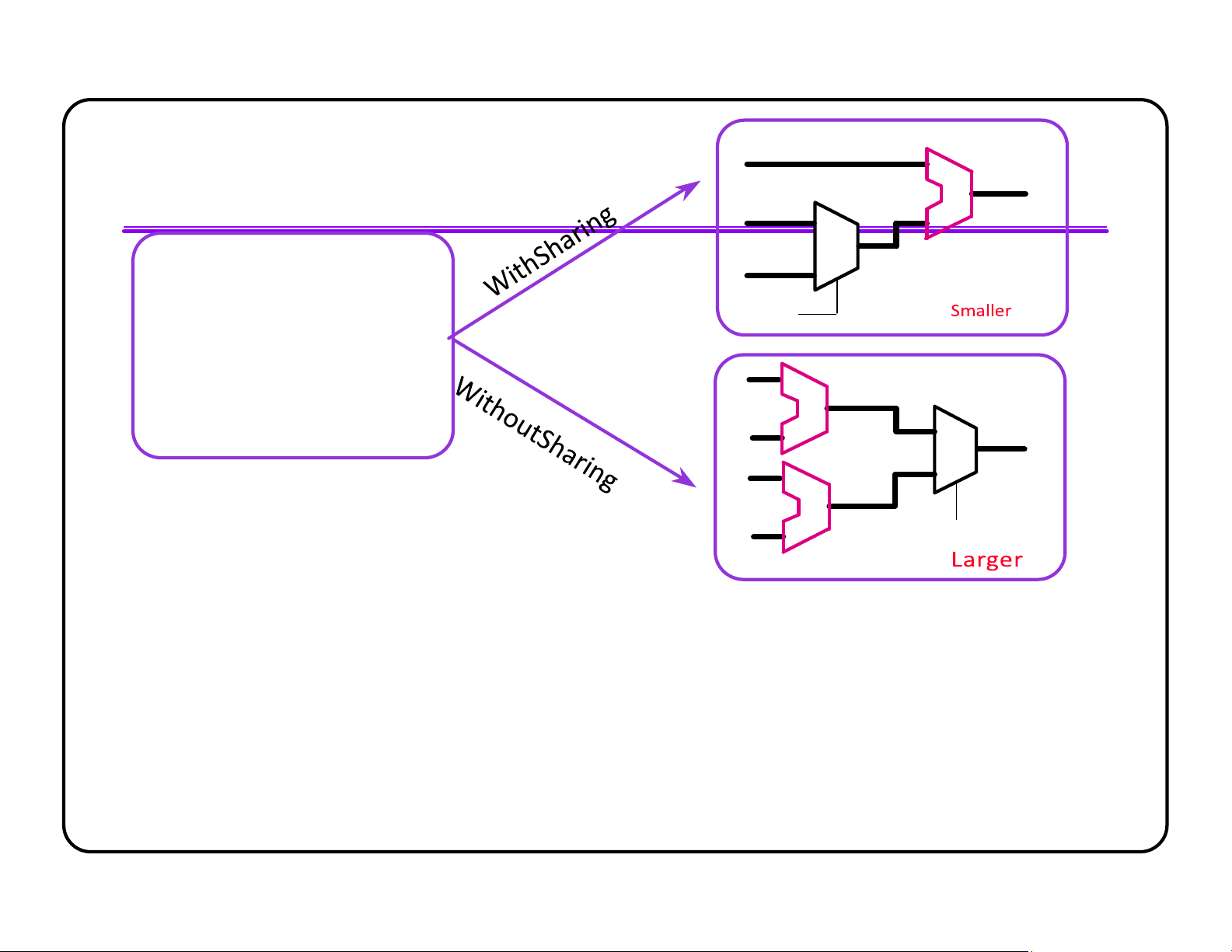
l Operators can be shared within an always block by default l Users can disable sharing lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 A + Z C always @(SEL or A or MUX B or C) B begin SEL if (SEL)
Z = A+B ; else A
Z = A+C ; + end B MUX Z A + SEL C derations - 96 Operators Operator Balancing
l Use parenthesis to guide synthesis lOMoAR cPSD| 58583460 A*B*C*D (A*B)*(C*D) derations - 98



