


Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD| 39099223
INTEGRATED MARKETING COMMUNICATION ESSAY TEST
Lecturer: Doan Thi Thanh Huong Class: MKT1718 Subject: MKT 304
- Name: Nguyen Ngoc Anh
- Student code: HS171171 Hanoi, 30th June 2023
Question 1: What is the Communication and Communication Process? (definition)
Communication is a two-way process in which the message is conveyed between two or more
people in the form of ideas, thoughts, feelings, and views with the goal of generating a common
understanding. Communication is simply the process of communicating intentional information lOMoARcPSD| 39099223
and understanding from one person to another. The name "communication" comes from the
Latin word "Communis," which means "to share." Effective communication occurs when the
message transmitted by the sender is interpreted exactly as intended by the receiver.
The communication process is an interactive and ever-evolving process that initiates
with the sender's conceptualization of ideas. These ideas are then transmitted through a chosen
channel to reach the intended receiver. The receiver, in turn, actively engages with the message
and provides feedback in the form of a responsive message or signal within a predetermined time
frame. This cyclical exchange of information forms the foundation of effective communication,
allowing for the exchange of thoughts, understanding, and the establishment of shared meaning
between individuals or groups.
Question 2: How many stages are there in the Communication Process? What are they?
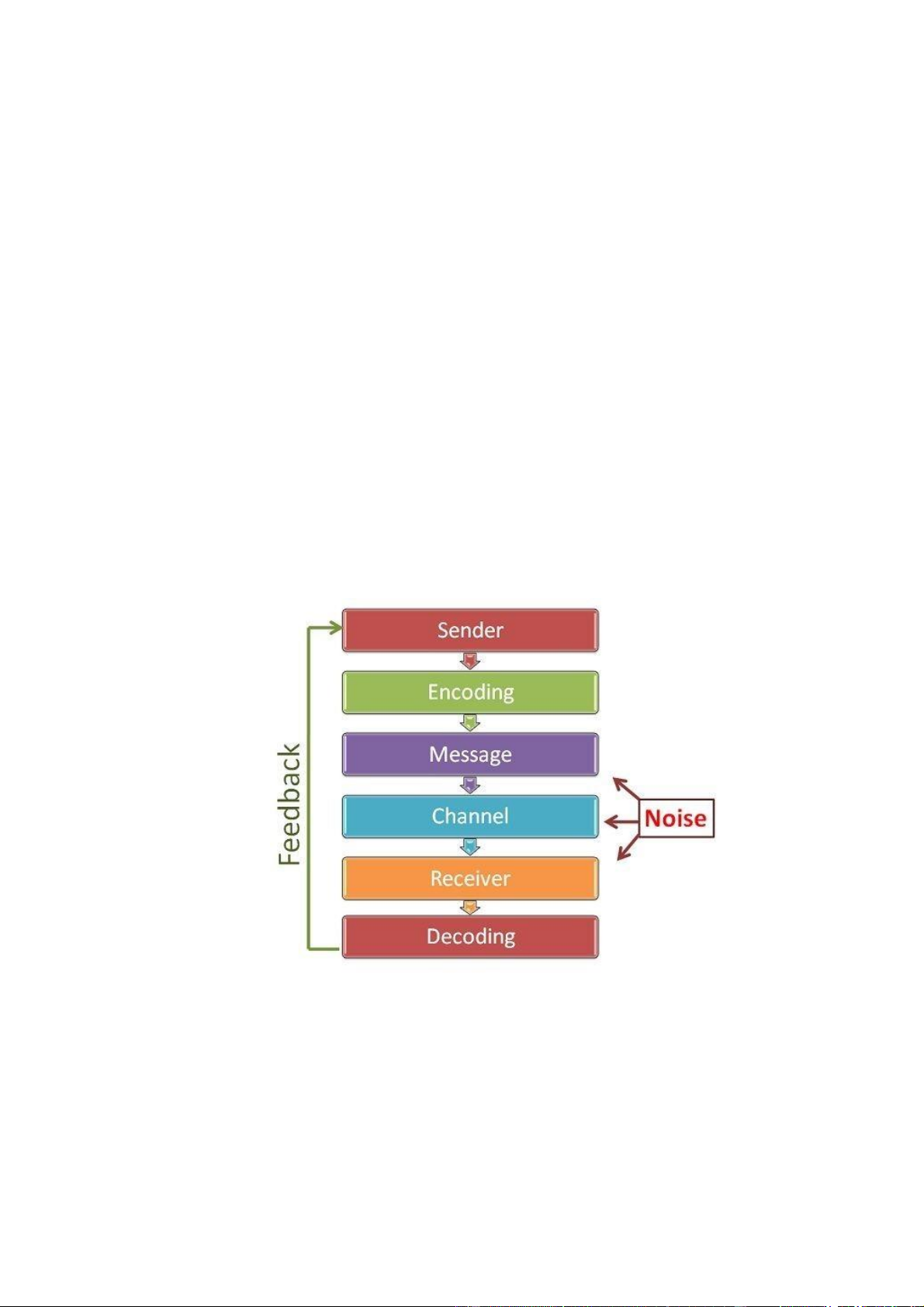
There are seven stages in the Communication process: -
Sender: The sender or communicator begins the discussion and has conceptualized the idea
that he wants to express to others. -
Encoding: The sender begins the encoding process by translating the information into a
message using specific words or nonverbal means such as symbols, signs, body movements, and lOMoARcPSD| 39099223
so on. The sender's knowledge, abilities, perception, background, competencies, and so on all
have a significant influence on the message's success. -
Message: When the encoding is complete, the sender receives the message that he intended
to communicate. The message can be written, spoken, symbolic, or nonverbal, such as body
movements, silence, sighs, noises, and so on, or any other indication that causes a receiver to respond. -
Communication Channel: The Sender selects the medium via which he wishes to
communicate his message to the receiver. It must be properly chosen in order for the message to
be effective and appropriately comprehended by the receiver. The medium used is determined by
the sender's and receiver's interpersonal ties, as well as the urgency of the message being
communicated. Some of the most frequent communication media include oral, virtual, written, sound, gesture, and so on. -
Receiver: The individual for whom the communication is intended or aimed is referred to as
the recipient. He attempts to grasp everything as well as possible so that the communication goal
is met. The receiver's ability to decipher the message is determined by his understanding of the
subject matter, experience, trust, and connection with the sender. -
Decoding: The receiver understands the sender's message and attempts to comprehend it as
well as possible. Effective communication occurs only when the receiver understands the
message exactly as the sender intended. -
Feedback: Feedback is the final stage in the process that confirms the receiver received and
correctly processed the message as intended by the sender. It improves communication
effectiveness by allowing the sender to gauge the effectiveness of his message. The receiver's
response might be vocal or nonverbal.
Question 3: How to make a successful communication? Present briefly with relevant examples. lOMoARcPSD| 39099223
The importance of successful communication lies in understanding the emotions and
intentions behind the information conveyed. In order to effectively communicate, it is necessary
not only to accurately convey a message but also to listen actively and comprehend the full
meaning of what is being said. To achieve successful communication, the following steps can be taken: -
Clearly define communication goals: It is crucial to have a clear understanding of what you
aim to achieve through communication. Ensure that all parties involved are aware of these goals.
For example, a customer support representative clearly communicates the goal of a conversation
with a customer by saying, "My goal is to assist you in resolving the issue you're facing with our
product and ensure your satisfaction." -
Select an appropriate medium: Choose the most suitable communication medium based on
the nature of the message and the individuals or groups involved. Options include face-to-face
communication, email, phone calls, video conferencing, or written communication. For example,
when addressing a customer complaint that requires a detailed explanation or troubleshooting
steps, a customer service representative chooses to engage in a live chat or video call rather than
relying solely on email, allowing for real-time interaction and clarification. -
Create a conducive environment: Ensure that the physical and social environment supports
effective communication. Minimize distractions and interruptions that could hinder the flow of
information. For example, in a retail store, the staff ensures a conducive environment for
communication by maintaining a clean and organized space, minimizing noise, and providing
comfortable seating areas for customers to discuss their needs or concerns with the staff. - Pay
attention to nonverbal cues: Observe body language, facial expressions, and other nonverbal
cues to gain insights into the emotions and reactions of the other person. Nonverbal
communication often conveys additional meaning that can enhance understanding. For example,
a salesperson at a car dealership notices a customer's raised eyebrows and hesitant body language
while discussing a specific feature of a vehicle. Recognizing these nonverbal cues, the lOMoARcPSD| 39099223
salesperson adjusts their explanation and focuses on addressing the customer's concerns to
enhance their understanding and build trust.