






Preview text:
MBB.IntroProb13.ch05sec3 TRUE/FALSE
1. The Poisson probability distribution is an example of continuous probability distribution. ANS: F PTS: 1
2. The probability distribution of a Poisson random variable provides a good model for data that
represent the number of occurrences of a specified event in a given unit of time or space. ANS: T PTS: 1
3. In a Poisson problem, represents the number of events occurring in a period of time or space x
during which an average of such events can be expected to occur. ANS: T PTS: 1
4. The Poisson probability distribution provides good approximations to binomial probabilities when is lar n ge and is small, preferably with < 7. np ANS: T PTS: 1
5. The Poisson distribution is applied to events for which the probability of occurrence over a
given span of time, space, or distance is large. ANS: F PTS: 1
6. The mean and variance of the Poisson distribution are equal. ANS: T PTS: 1
7. Poisson distribution is appropriate to determine the probability of a given number of defective items in a shipment. ANS: F PTS: 1
8. The Poisson distribution is applied to events for which the probability of occurrence over a
given span of time, space, or distance is very small. ANS: T PTS: 1
9. The mean of a Poisson distribution, where is the average number of successes occurring in a specified interval, is . ANS: F PTS: 1
10. The Poisson probability distribution is an example of a continuous probability distribution. ANS: F PTS: 1
11. The Poisson random variable is the number of successes achieved when a random sample of
size is drawn without replacement from a population of size n N within which M units have
the characteristic that denotes success. ANS: F PTS: 1
12. A Poisson process is the occurrence of a series of events of a given type in a random pattern
over time or space such that (1) the number of occurrences within a specified time or space
can equal any integer between zero and infinity, (2) the number of occurrences within one unit
of time or space is independent of that in any other such (non-overlapping) unit, and (3) the
probability of occurrences is the same in all such units. ANS: T PTS: 1
13. The Poisson parameter is the mean number of occurrences of an event per unit of time or
space during the Poisson process. ANS: T PTS: 1
14. The Poisson probability tables list the probabilities of occurrences in a Poisson process for x
various values of , the mean number of occurrences. ANS: T PTS: 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Which of the following experiments can be modeled by the Poisson distribution?
a. The number of calls received by a switchboard during a given period of time.
b. The number of bacteria per small volume of fluid.
c. The number of customer arrivals at a checkout counter during a given minute.
d. The number of customer arrivals at a checkout counter during a given hour. e. All of these. ANS: E PTS: 1
2. Given a Poisson random variable x, where the average number of times an event occurs in a
certain period of time is 2.5, then P( = 0) is: x a. 2.5 b. 0.0821 c. 1.5811 d. 0.40 e. 1 ANS: B PTS: 1
3. Which probability distribution is appropriate when the events of interest occur randomly,
independently of one another, and rarely? a. Binomial distribution b. Poisson distribution c. Hypergeometric distribution
d. any discrete probability distribution e. all of these ANS: B PTS: 1
4. The mean of a Poisson random variable , where x
is the average number of times that an
event occurs in a certain period of time or space, is: a. b. c. d. +1 e. ANS: A PTS: 1
5. Which of the following cannot generate a Poisson distribution?
a. The number of telephone calls received by a switchboard in a specified time period.
b. The number of customers arriving at a gas station on Christmas day.
c. The number of bacteria found in a cubic yard of soil.
d. The number of children in a family.
e. The number of accidents per day on a certain section of a highway. ANS: D PTS: 1
6. The Poisson random variable is:
a. a continuous random variable with infinitely many possible values
b. a discrete random variable with infinitely many possible values
c. a continuous random variable with finite number of possible values
d. a discrete random variable with finite number of possible values e. all of these ANS: B PTS: 1
7. The standard deviation of a Poisson distribution, for which is the average number of times
that an event occurs in a certain period of time or space, is given by: a. b. c. d. + 1 e. ANS: B PTS: 1
8. Given a Poisson random variable x, where the average number of times an event occurs in a
certain period of time or space is 1.5, then P(x = 2) is: a. 0.2231 b. 0.5020 c. 0.2510 d. 0.1116 e. 0.5 ANS: C PTS: 1
9. The variance of a Poisson distribution, for which is the average number of times that an
event occurs in a certain period of time or space, is given by: a. b. c. d. + 1 ANS: A PTS: 1
10. Which of the following correctly describes a Poisson random variable?
a. It does not generate a binomial either/or outcome because only a single type of
outcome or "event" is occurring during the Poisson process.
b. It is not confined to a fixed number of trials, because its value can equal any
discrete integer between zero and infinity, along a continuum of time or space.
c. It equals the number of occurrences of a specified event within a specified time or space. d. All of these. e. None of these. ANS: D PTS: 1
11. Given that is the Poisson mean or average in a given unit of time or space and t is the total
number of time or space units examined, the expected value of a Poisson random variable equals: a. b. c. d. e. ANS: A PTS: 1
12. In a book, 2 misprints occur per 100 pages. Using the cumulative Poisson probability table
available in your text, we can determine which of the following probabilities in a book of 500 pages?
a. The probability of finding between 5 and 6 misprints equals .099.
b. The probability of finding at least 20 misprints equals .003.
c. The probability of finding at least 24 misprints equals .1234.
d. The probability of finding at least 20 misprints equals 1.
e. The probability of finding at least 24misprints equals 1. ANS: B PTS: 1
13. The number of traffic accidents per day on a certain section of highway is thought to be
Poisson distributed with a mean equal 2.19. Then the standard deviation of number of accidents is: a. 2.19 b. approximately 4.80 c. approximately 1.48 d. 3.14 e. (2.19) 2 ANS: C PTS: 1
14. The number of traffic accidents per day on a certain section of highway is thought to be
Poisson distributed with a mean equal 2.19. Then the probability of no accidents on this
section of highway during one day period is approximately: a. 0.457 b. 0.112 c. 0.318 d. 0.296 e. 0.211 ANS: B PTS: 1
15. The number of traffic accidents per day on a certain section of highway is thought to be
Poisson distributed with a mean equal 2.19. Based on this, how many traffic accidents should
be expected during a week long period? a. 15.33 b. 10.95 c. approximately 10.36 d. approximately 12.21 e. none of these ANS: A PTS: 1
16. If the standard deviation for a Poisson distribution is known to be 3.60, the expected value of that Poisson distribution is: a. 3.60 b. approximately 1.90 c. 8.28 d. 12.96 e. 7.2 ANS: D PTS: 1
17. Which of the following distributions could not be used to describe the exact distribution for a continuous random variable? a. Binomial distribution b. Poisson distribution c. Hypergeometric distribution d. all of these e. none of these ANS: D PTS: 1
18. Which of the following statements is false with respect to a Poisson distribution?
a. The Poisson distribution is an example of a discrete probability distribution.
b. The Poisson distribution is more skewed to the right for smaller values of the parameter .
c. The Poisson distribution is symmetrical when the value of the parameter is close to 5.
d. The mean of the Poisson distribution is equal to the variance. e. All of these. ANS: C PTS: 1 PROBLEM
1. Let the random variable x have the Poisson distribution with mean 3.
What is the probability x will fall in the interval ? ______________ ANS: 0.966 PTS: 1
2. The number of telephone calls coming into a business' switchboard averages 4 calls per
minute. Let be the number of calls received. x Find P( = 0). x ______________
What is the probability there will be at least one call in a given one-minute period? ______________
What is the probability at least one call will be received in a given two-minute period? ______________ ANS: 0.018; 0.982; 0.999676 PTS: 1
3. The quality of computer disks is measured by sending the disks through a certifier which
counts the number of missing pulses. A certain brand of computer disks averages 0.1 missing
pulse per disk. Let the random variable denote the number of missing pulses. x What is the distribution of x? Type of distribution: ______________ Mean of distribution: ______________
Find the probability the next inspected disk will have no missing pulse. ______________
Find the probability the next disk inspected will have more than one missing pulse. ______________
Find the probability neither of the next two disks inspected will contain any missing pulse. ______________ ANS:
Poisson; 0.1; 0.905; 0.005; 0.819 PTS: 1
4. The number of teleport inquiries in a timesharing computer sy x stem averages 0.2 per
millisecond and follows a Poisson distribution.
Find the probability no inquiries are made during the next millisecond. ______________
Find the probability no inquiries are made during the next 3 milliseconds. ______________ ANS: 0.819; 0.549 PTS: 1
5. Rebuilt ignition systems leave an aircraft repair shop at an average rate of 3 per hour. The
assembly line needs four ignition systems in the next hour.
What is the probability they will be available? ______________ ANS: 0.353 PTS: 1
6. Consider an experiment with 25 trials where the probability of success on any trial is 0.01,
and let the random variable be the number of successes among the 25 trials. x
Using the Poisson approximation to the binomial, what are: p(0) = ______________ p(1) = ______________ p(2) = ______________ p(3) = ______________ ANS: 0.779; 0.196; 0.024; 0.002 PTS: 1
7. The probability the 1993-94 flu vaccine immunizes those receiving it is 0.97. If a random
sample of 200 people receive the vaccine, what is the probability the vaccine will be
ineffective on at most 5 people? ______________ ANS: 0.443 PTS: 1
8. A salesperson has found the probability of making a sale on a particular product manufactured
by his or her company is 0.05. If the salesperson contacts 140 potential customers, what is the
probability he or she will sell at least 2 of these products? ______________ ANS: 0.993 PTS: 1
9. A warehouse contains 10 computer printers, 4 of which are defective. A company randomly
selects five of the 10 printers to purchase.
What is the probability all 5 are nondefective? ______________ What is the mean of ? x ______________ What is the variance of ? x ______________ ANS: 0.0238; 3; 0.667 PTS: 1
10. An eight-cylinder automobile engine has two misfiring spark plugs. The mechanic removes all
four plugs from one side of the engine.
What is the probability the two misfiring spark plugs are among those removed? ______________
What is the mean number of misfiring spark plugs? ______________
What is the variance of the number of misfiring spark plugs? ______________ ANS: 0.2184; 1; 0.75 PTS: 1
11. From a group of 10 bank officers, 3 are selected at random to be relocated and supervise new
branch offices. If two of the 10 officers are women and 8 are men, what is the probability
exactly one of the officers to be relocated will be a woman? ______________ ANS: 0.4667 PTS: 1
12. A package of six light bulbs contains 2 defective bulbs. If three bulbs are selected for use, find
the probability none are defective. ______________ ANS: 0.20 PTS: 1
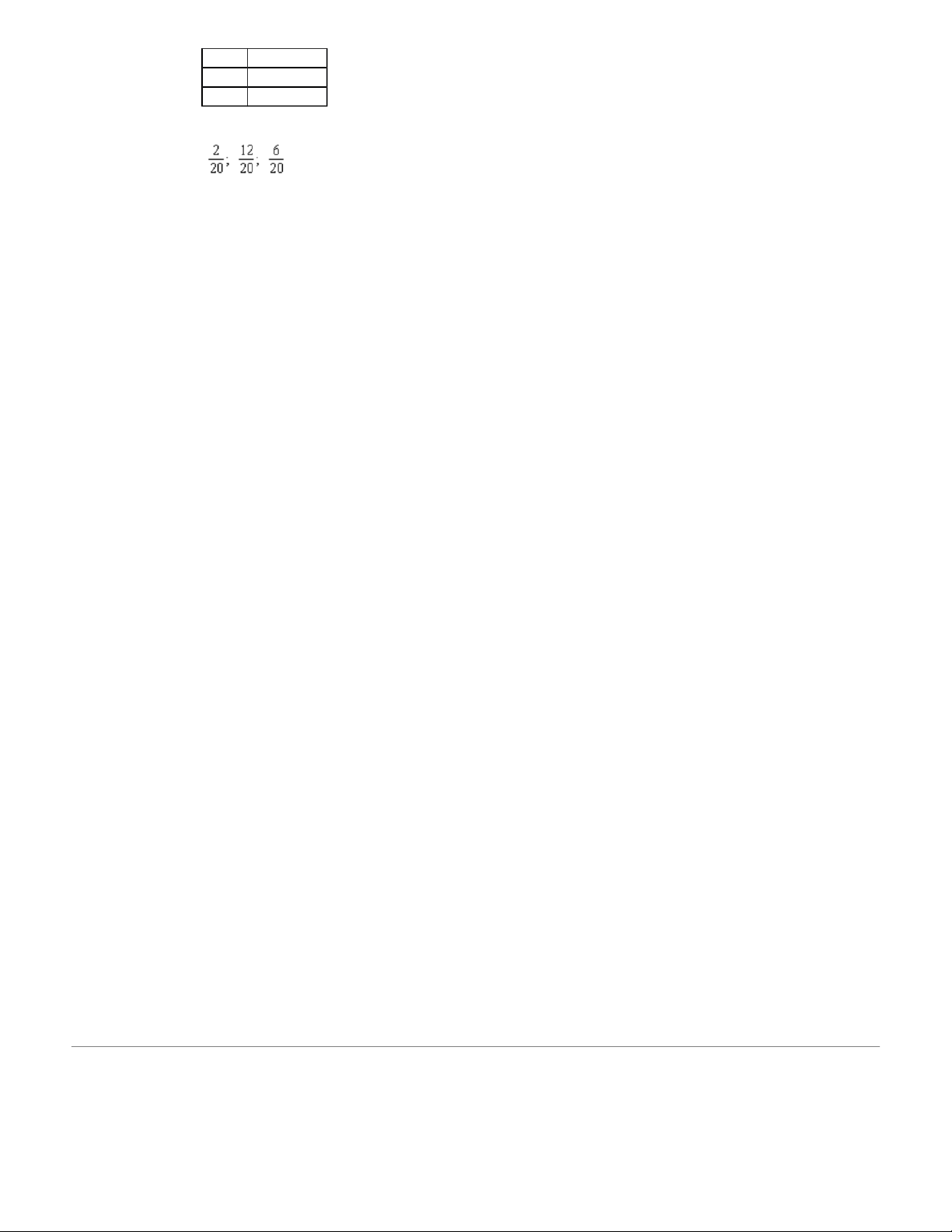
13. Three yellow and two blue pencils are in a drawer. If we randomly select two pencils from the
drawer, find the probability distribution of , the number of yellow pencils selected. x x p(x) 0 _______ 1 _______ 2 _______ ANS: PTS: 1
14. Students arrive at a health center, according to a Poisson distribution, at a rate of 4 every 15
minutes. Let represent number of students arriving in a 15 minute time peri x od.
What is the probability that no more than 3 students arrive in a 15 minute time period? ______________
What is the probability that exactly 5 students arrive in a 15 minute time period? ______________
What is the probability that more than 5 students arrive in a 15-minute time period? ______________
What is the probability that between 4 and 8 students, inclusively, arrive in a 15-minute time period? ______________ ANS: 0.433; 0.156; 0.215; 0.546 PTS: 1
15. The number of people arriving at a bicycle repair shop follows a Poisson distribution with an
average of 5 arrivals per hour. Let represent number of people arriving per hour x .
What is the probability that seven people arrive at the bike repair shop in a one hour period of time? ______________
What is the probability that at most seven people arrive at the bike repair shop in a one hour period of time? ______________
What is the probability that more than seven people arrive at the bike repair shop in a one hour period of time? ______________
What is the probability that between 4 and 9 people, inclusively, arrive at the bike repair shop in a one hour period of time? ______________ ANS: 0.105; 0.867; 0.133; 0.703 PTS: 1
16. It was estimated that 2% of a particular 1997 model minivan had incorrectly installed brake
lines. Suppose 300 minivans of this model are selected at random. Let represent number of x
minivans with incorrectly installed brake lines.
What is the probability that 9 have incorrectly installed brake lines? ______________ ANS: 0.069 PTS: 1
17. The number x of people entering the intensive care unit at a particular hospital on any one day
has a Poisson probability distribution with mean equal to four persons per day.
What is the probability that the number of people entering the intensive care unit on a particular day is two? ______________
What is the probability that the number of people entering the intensive care unit on a
particular day is Less than or equal to two? ______________
Is it likely that will exceed ten? x ______________ Explain.
________________________________________________________ ANS:
0.146525; 0.238103; No; The value x = 10 lies 3.0 standard deviations above the mean. PTS: 1
18. Insulin-dependent diabetes (IDD) is a common chronic disorder of children. This disease
occurs most frequently in persons of northern European descent. Let us assume that an area in
Europe has an incidence of 6 cases per 100,000 per year.
Can the distribution of the number of cases of IDD in this area be approximated by a Poisson distribution? ______________ What is the mean? ______________
What is the probability that the number of cases of IDD in this area is less than or equal to 3 per 100,000? ______________
What is the probability that the number of cases is greater than or equal to 3 but less than or equal to 7 per 100,000? ______________
Would you expect to observe 10 or more cases of IDD per 100,000 in this area in a given year? ______________ Why or why not?
________________________________________________________ ANS:
Yes; 6; 0.151; 0.682; No; The probability of observing 10 or more cases per 100,000 in a year
is 0.084. This is an occurrence which we would not expect to see very often, if in fact mu = 6 PTS: 1
19. It is known that between 8 and 10 a.m. on Saturdays, cars arrive at a toll station in Indiana at a
rate of 60 per hour. Assume that a Poisson process is occurring, and that the random variable x
represents the number of cars arriving at the station between 9:00 and 9:05 a.m.
What is the expected number of cars arriving at the toll station between 9:00 and 9:05 a.m.? ______________
What is the standard deviation of the number of cars arriving at the toll station between 9:00 and 9:05 a.m.? ______________ Find P( = 0). x ______________ Find P( = 2). x ______________ Find P( = 5). x ______________ Find P( = 10). x ______________ ANS:
5; 2.236; 0.0067; 0.0842; 0.1755; 0.0181 PTS: 1




