







Preview text:
EXAM IN ENGLISH FOR BUSINESS 2
TIME ALLOCATED: 60 MINUTES
SECTION 1: LANGUAGE KNOWLEDGE (40 MARKS)
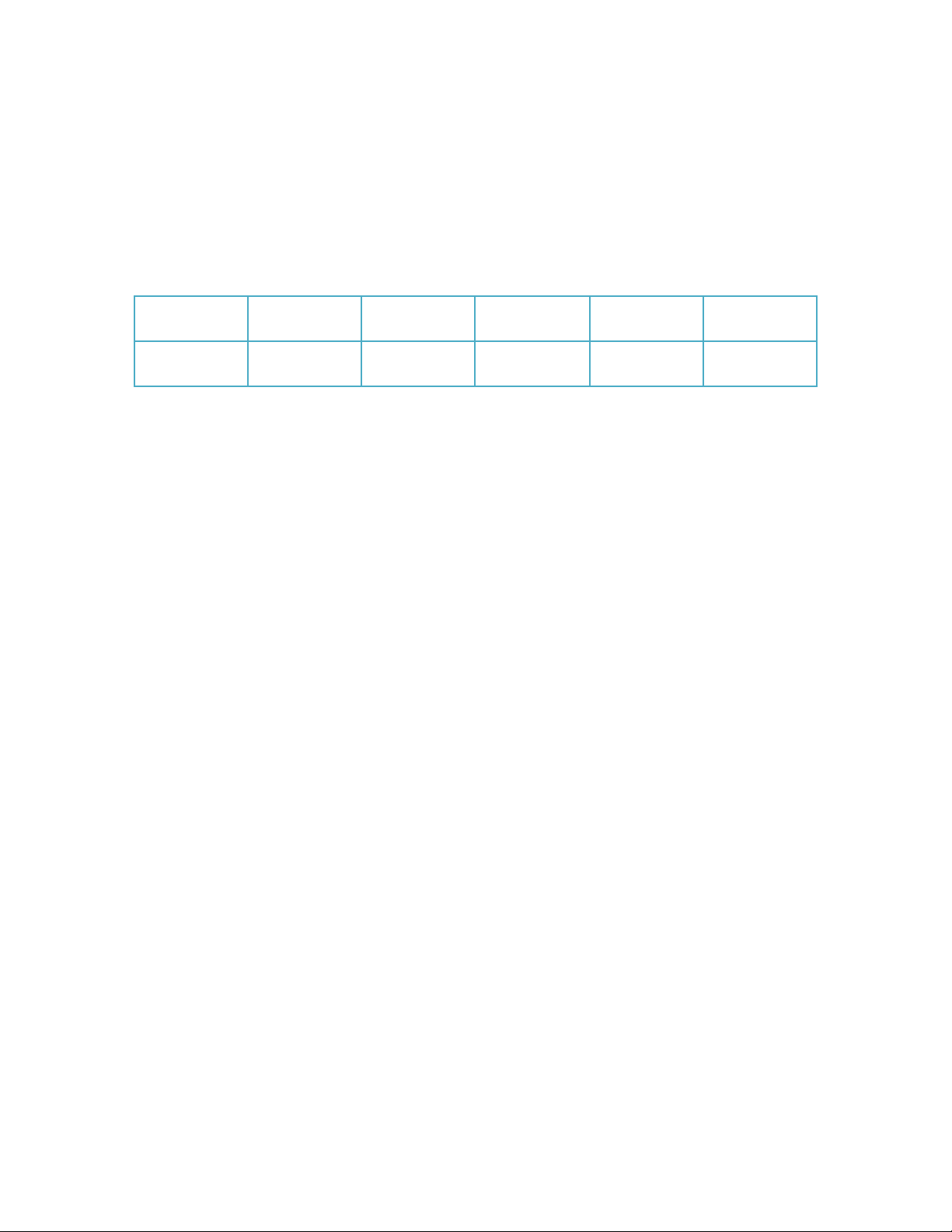
I. Choose one word from the box for each blank. (10 marks) principal primary human exchange focuses stakes downturns depends tolerance funding financial debt
Funding Company Activities
Securing adequate (1) _________ is a cornerstone of any company’s success. It
provides the (2) __________ resources necessary to invest in growth, hire talent,
develop new products, and weather economic (3) __________. There are several (4)
_________ sources of funding for companies: equity, debt, and grants. Equity
financing involves selling ownership (5) stakes in the company to investors, who
provide capital in (6) __________ for a return on investment. (7) ________ financing
entails borrowing money from lenders, such as banks or investors, with the promise to
repay the (8) __________ and interest within a specified timeframe. Grants, typically
awarded by governments or foundations, offer non-repayable funds for specific
projects or purposes. The choice of funding method (9) _________ on various factors,
including the company’s stage of development, risk (10) _________, and financial goals.
II. Choose the best answer. (30 marks)
11. …………… is a type of production where large quantities of identical products are
produced using an assembly line. A. Mass customization B. Unit production C. Customized production D. Mass production
12. The investor expects a high …………… from the venture capital fund. A. securities investment B. hedge fund C. return on investment D. mutual fund
13. A/an …………… reports a company’s financial position and lists the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. A. income statement B. balance sheet C. cash flow statement
D. statement of retained earnings
14. The company’s …………… has increased significantly due to process improvements and reduced defects. A. production yield B. resources allocation C. sustainable technology D. business administration
15. Reducing …………… is crucial to mitigating climate change and protecting the environment. A. green initiatives B. pressure groups C. federal tax D. industrial emissions
16. The couple obtained a/an …………… to purchase their new home. A. financial backer B. stock market C. interest rate D. mortgage loan
17. The company has adopted …………… principles to eliminate waste and improve overall efficiency. A. management style B. performance measurement C. lean manufacturing D. empowerment process
18. The government plans to …………… the telecommunications industry to encourage
competition and lower prices for consumers. A. capitalize B. deregulate C. embed D. downgrade
19. The wealthy individual invested a portion of their portfolio in a/an …………… to diversify their risk. A. level playing field B. hedge fund C. debt capital D. interest payment
20. The company must …………… with all relevant environmental regulations and standards. A. coordinate B. remediate C. replenish D. comply
21. All products must meet the exact …………… outlined in the design documents. A. administration B. specifications C. customization D. outputs
22. By investing in research and development, the company hopes to gain a/an …………….
over its rivals in the market. A. standardized norm B. acquisition opportunity C. competitive edge D. non-exclusive contract
23. The company’s ……………include accounts payable, long-term debt, and accrued expenses. A. Liabilities B. retained earnings C. inventory management D. equity ownership
24. A …………… is a process where tasks are performed sequentially in a specific order. A. production bottleneck B. line efficiency C. strategic vision D. linear workflow
25. The government has set a/an …………… for air pollution levels to ensure public health and safety. A. opposition B. threshold C. balance D. backpacker
26. The company has implemented efficient processes to reduce …………… and deliver products to customers faster. A. capacity planning B. inventory management C. lead time D. production scheduling
27. After a significant loss, the company decided to …………… its operations, laying off
some employees and focusing on its core products. A. cater B. decentralize C. retrain D. restructure
28. …………… is an accounting practice that exploits loopholes in accounting standards to
portray a better financial picture of a company than reality. A. Creative accounting B. Tax accounting C. Managerial accounting D. Forensic accounting
29. The …………… of people in developed countries has increased significantly over the
past century due to advancements in healthcare and living conditions. A. life expectancy B. potential consequence C. compromise deal D. consumer spending
30. The company aims to provide …………… services to its customers by offering
personalized solutions and exceptional customer support. A. raw material B. value-added C. machine maintenance D. unit production
SECTION 2: LANGUAGE USE (60 MARKS) I. Reading (20 marks) NO MORE EASY MONEY
Adapted from Jonathan Moules
Ambitious entrepreneurs are prepared to go the distance to get financial backing for
their bright ideas. Sanchita Saha, founder of City Socialising, a website to help people
make new friends after relocating, travelled all the way to southern France.
This was not as pleasant an experience as it might seem. Once there, she spent months
pitching to hundreds of potential investors to no avail, only to get a lucky break at the end.
First, she looked into ‘angel’ networking clubs, which provide entrepreneurs with
access to large numbers of wealthy individuals interested in investing in early-stage
ventures. However, she turned down a number of these for reasons of cost: they were
charging £1,500 ($2,488) just to submit a business plan.
Eventually, she settled on London Business Angels (LBA), through which she could
pitch to roughly 100 ‘angels’. Through LBA, Saha discovered a third scheme called
the European Border Investment Programme, which was running its own event in Nice.
Although it was a risk, she booked herself on a flight and found herself pitching to
another couple of hundred investors from across the European Union. Among those
were a couple of Finnish investors who, together with five wealthy individuals at
LBA, agreed to back Saha’s business with a combined investment of £300,000.
Raising equity finance through venture capital funds is possible, but it is taking about
twice as long as before the recession struck, according to Simon Cook, Chief
Executive of venture capital firm DFJ Esprit, which has invested in some of Europe’s
most successful technology start-ups. In the past, both FeedBurner, the web-feed
management system, and Skype, the Internet telephony service, have received backing from Cook’s firm.
Access to finance remains difficult for all sorts of companies, whether they are
looking for rich individuals to take equity stakes, debt or venture capital.
Read the text and choose the best answer for each question.
1. What was the problem with some of the ‘angel’ networking clubs?
A. It is difficult to submit a business plan.
B. They provide entrepreneurs with access to large numbers of wealthy individuals.
C. They turned down a lot of business plans. D. They cost a lot to join.
2. Why did Sanchita Saha choose to use London Business Angels?
A. It was the cheapest option available.
B. It offered access to a large number of potential investors.
C. It was recommended by a friend.
D. It had a good reputation for helping startups.
3. What was the final outcome of Sanchita Saha’s efforts to raise funding?
A. She was unsuccessful in securing any investment.
B. She raised £1,500 from angel investors.
C. She raised £300,000 from a combination of investors.
D. She raised £300,000 from venture capital funds.
4. According to Simon Cook, what is the current situation regarding venture capital funding?
A. It is easier to obtain venture capital funding now than before the recession.
B. It is taking longer to obtain venture capital funding now than before the recession.
C. There is no change in the availability of venture capital funding.
D. Venture capital funding is only available for the most promising startups.
Decide if each of the following statements is True (T), False (F), or Not Given (NG).
5. Sanchita Saha was able to raise funding through angel investors.
6. London Business Angels charged Sanchita Saha more than £1,500 to submit her business plan. Free
7. FeedBurner and Skype were both backed by DFJ Esprit.
8. Because of the recession, access to finance is easier for companies that are seeking government grants.
Find an appropriate word from the text to complete each of the following sentences.
You may need to CHANGE THE WORD FORM to make it grammatically correct.
9. The company’s financial …………….. included a group of wealthy individuals and venture capital firms.
10. Venture capital firms often invest in companies by taking equity ……………… in exchange for funding. II. Writing (20 marks)
Write a report about A&C Corporation’s performance in the third quarter of 2024 with
the information provided in the box below. The report should have the title, the
introduction, the body, and the conclusion.
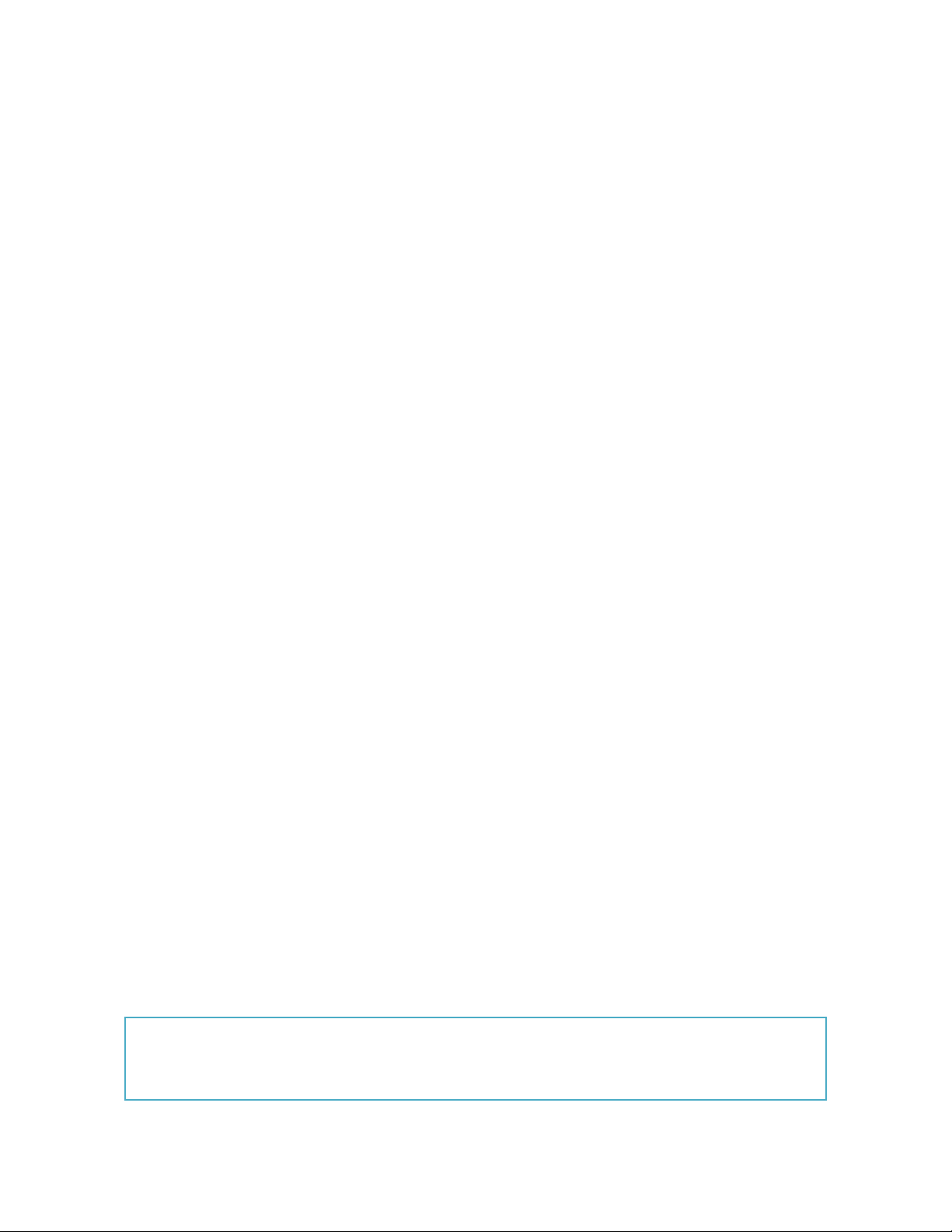
Introduction: company performance in the third quarter of 2024
Revenue: $5.5 million
Costs: $4.3 million, including $20,000 on the marketing campaign
Net profit: $1.2 million
Debts: accounts payable of $80,000; loans payable of $120,000 Taxes: $4,000
Problem: a 5% decrease in sales
Reasons: economic downturn; failure of the marketing strategy
Solutions: cost-cutting measures; digital marketing
III. Listening (20 marks)
Part 1: Listen to the recording and choose the correct answer.
1. The term ‘Lean’ was first coined by …………… . A. Toyota B. Henry Ford
C. The National Institute of Standards and Technology D. The Lean Network
2. Which of the following is NOT one of the Eight Wastes in Lean? A. Underutilization B. Overproduction C. Excess Inventory D. Quality Control
3. The concept of ‘just-in-time’ production is related to which of the Eight Wastes? A. Waiting B. Transportation C. Excess Inventory D. Defects
4. What is the purpose of Value Stream Mapping?
A. To identify non-value-added steps in a process B. To improve company value
C. To reduce transportation costs
D. To increase production speed
5. Which of the following is NOT a common cause of underutilized people? A. Poor workflow B. Inadequate training C. Overproduction D. High employee turnover
Part 2: Listen to the recording and complete the summary below. Write ONE
WORD ONLY for each answer.
Lean management is based on four (1) …………… .
Pull: customer (2) …………… pulls goods or services through the manufacturing
process, minimizing overproduction (3) …………… and ultimately working (4) …………… .
One piece flow: focusing on one single piece at a time (5) ……………
work-in-progress process interruptions, lead and (6) …………… time while
increasing quality and flexibility.
Tact: how fast you need to (7) …………… a product to meet customer demand.
Tact allows us to balance work content achieve a (8) …………… flow and respond
flexibly to changes in the marketplace.
Zero defects: A lean company doesn’t pass on defects. Mistakes from (9)
…………… steps must be fixed before going on, combined with the robust
continuous (10) …………… process.




