










Preview text:
1 1 Learning Objectives Chapter 1:
Explain the key role of a systems analyst in The World of the business Modern Systems Analyst
Describe the various types of systems an analyst might work on
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing
Explain the importance of technical, people, and World, 3rd Edition business skills for an analyst
Explain why ethical behavior is crucial for a systems analyst’s career
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 2 1 1
Learning Objectives (continued) Overview
Describe the many types of technology an Information Systems analyst needs to understand
Crucial to success of modern business organizations
Describe various job titles and places of
employment where analysis and design work is
Constantly being developed to make business done more competitive
Discuss the analyst’s role in strategic planning
Impact productivity and profits for an organization
Keys to successful systems development
Describe the analyst’s role in a system
Thorough systems analysis and design development project
Understanding what business requires
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 3
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 4 1 1 Overview (continued)
The Analyst as a Business Problem Solver
Systems analysis – what system should do
Has computer technology knowledge and programming expertise
Systems design – how components of
Understands business problems
information system should be physically implemented
Uses logical methods for solving problems Has fundamental curiosity
Systems analyst – uses analysis and design
Wants to make things better
techniques to solve business problems with information technology
Is more of a business problem solver than technical programmer
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 5
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 6 1 1
Analyst’s Approach to Problem Solving
Systems That Solve Business Problems
Research and understand the problem
System – interrelated components functioning together to achieve outcome
Verify that the benefits of solving the problem outweigh the costs
Information systems – collection of interrelated
Define the requirements for solving the problem
components that collect, process, store, and
provide as output information needed to
Develop a set of possible solutions (alternatives) complete tasks
Decide which solution is best, and make a recommendation
Subsystems – part of larger system
Define the details of the chosen solution
Supersystem – larger system contains Implement the solution subsystem
Functional decomposition – dividing system into
Monitor to make sure that you obtain the desired results
smaller subsystems and components
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 7
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 8 1 1
Information Systems and Component
Information Systems and Subsystems Parts
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 9
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 10 1 1
System Boundary vs. Automation Types of Information Systems Boundary
Transaction processing systems (TPS)
Capture and record information about organization’s transactions
Management information systems (MIS)
Take information captured by TPS
Produce reports for planning and control
Executive information systems (EIS)
Monitoring competitive environment and strategic planning
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 11
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 12 1 1
Types of Information Systems (continued)
Types of Information Systems (continued)
Decision support systems (DSS)
Explore impact of available options or decisions (What-if scenarios)
Communication support systems
Facilitate communication internally and with customers and suppliers Office support systems
Help employees create and share documents
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 13
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 14 1 1
Required Skills of the Systems Analyst Technical Knowledge and Skills Analyst uses tools:
An analyst should have fundamental technology knowledge of:
Software productivity packages (MS Office)
Computers / peripheral devices (hardware)
Integrated development environments (IDEs) for programming languages
Communication networks and connectivity
CASE tools / coding, testing, and documentation
Database and database management systems support packages (DBMS)
Analyst understands SDLC phase techniques:
Programming languages (for example: VB.NET or Project planning Java)
Systems analysis, systems design
Operating systems and utilities
Construction, implementation, systems support
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 15
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 16 1 1 Business Knowledge and Skills People Knowledge and Skills Analyst must understand:
Systems analysts need to understand how people:
Business functions performed by organization Think Organizational structure Learn
Organization management techniques React to change Functional work processes Communicate
Systems analysts typically study business administration in college
Work (in a variety of jobs and levels)
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 17
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 18 1 1
People Knowledge and Skills (continued) Integrity and Ethics
Interpersonal and communication skills are
Analyst has access to confidential information crucial to:
such as salary, an organization’s planned
projects, security systems, etc. Obtaining information
Must keep information private Motivating people
Any impropriety can ruin an analyst’s career Getting cooperation
Analyst plans security in systems to protect
Understanding the complexity and workings of an confidential information
organization in order to provide necessary support
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 19
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 20 1 1
Required Skills of the Systems Analyst
The Environment Surrounding the Analyst
Types of Technology Encountered Desktop Networked desktops Client-server Mainframe
Internet, intranet, and extranet
Wireless, PDAs, Cell Phones (mobile workers)
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 21
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 22 1 1
Typical Job Titles and Places of Employment
The Analyst’s Role in Strategic Planning
Job titles of systems analyst vary greatly, but
Special projects affecting executives entail same thing
Business process reengineering – radical
improvements to existing processes
Places of employment vary from small
businesses to large corporations
Strategic planning development process
Information systems strategic planning
Analysts can be internal employees or outside consultants
Application architecture plan (business focus)
Analysts can be developing solutions for internal
Technology architecture plan (infrastructure focus)
business managers or for external clients and
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) integrated customers systems
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 23
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 24 1 1
Components of an information systems
Rocky Mountain Outfitters (RMO) and Its strategic plan
Strategic Information Systems Plan
RMO sports clothing manufacturer and
distributor about to begin customer support system project
First understand: nature of the business,
approach to strategic planning, and objectives for customer support system
RMO systems development project used to
demonstrate analysis and design concepts
Reliable Pharmaceutical Service (RPS) is a
second case study for classroom purposes
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 25
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 26 1 1
Introduction to Rocky Mountain Outfitters
Early RMO Catalog Cover (Spring, 1978) (RMO) business
Began Park City, Utah in 1978 supplying winter
sports clothes to local ski shops
Expanded into direct mail-order sales with small
catalog – as catalog interest increased, opened retail store in Park City
Became large, regional sports clothing distributor
by early 2000’s in Rocky Mountain and Western states
Currently $100 million in annual sales and 600
employees and two retail stores
Mail-order revenue to $60 million, phone-order revenue is $30 million
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 27
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 28 1 1
Current RMO Catalog Cover (Fall 2005) RMO Strategic Issues
Innovational clothing distributor, featured
products on Web site ahead of competitors
Original Web site functions:
Enhance image, request copy of catalog, portal to Outdoor sports Web sites
Enhanced Web site functions:
Add specific product information, weekly specials, and all product offerings
Detailed IS strategic plan Supply chain management
Customer relationship management
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 29
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 30 1 1
RMO’s Organizational Structure RMO Locations
Managed by original (married) owners
John Blankens – President
Liz Blankens – Vice president of merchandising and distribution
William McDougal – Vice president of marketing and sales
JoAnn White – Vice president of finance and systems
Background in finance and accounting
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 31
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 32 1 1
RMO Information Systems Department RMO IS Department Staffing
Mac Preston: Assistant vice-president and chief information officer (CIO)
Recent promotion made after IS strategic plan created
CIO reports to finance and systems VP
CIO is Increasingly important to future of RMO
IS department wil report directly to the CEO … if
CIO can successfully implement new strategic IS plan
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 33
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 34 1 1 Existing RMO Systems
Existing RMO Systems (continued)
Small mainframe-based system RMO informational Website
Supports inventory, mail-order, accounting and
Hosted by Internet service provider (ISP) human resources Merchandising/Distribution
Has dedicated connectivity to distribution and
12 year old mainframe COBOL/CICS, DB2, VSAM mail-order sites application LANs and file servers Mail order
Supports central office functions, distribution
14 year old mainframe COBOL application
centers, and manufacturing centers Phone order
Manufacturing has dial-up capability
Oracle and Visual Basic system built 6 years ago
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 35
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 36 1 1
Existing RMO Systems (continued)
The Information Systems Strategic Plan Retail store systems
Supports RMO strategic objectives
8 Year old point-of-sale and batch inventory
Build more direct customer relationships
package, overnight update with mainframe
Expand marketing beyond Western states Office systems
Plan calls for a series of information system
LAN with office software, Internet, email
development and integration projects over Human resources several years
13 year old mainframe-based payroll and benefits
Project launch: new customer support system to Accounting/Finance
integrate phone orders, mail orders, direct
Mainframe package bought from leading vendor customer orders via Internet
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 37
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 38 1 1
RMO Technology Architecture Plan
RMO Application Architecture Plan
Distribute business applications
Supply chain management (SCM)
Across multiple locations and systems
Product development, product acquisition,
manufacturing, inventory management
Reserve mainframe for Web server, database, and telecommunications
Customer support system (CSS)
Allow incremental and rapid growth in capacity
Integrate order-processing and fulfillment system with SCM
Strategic business processes via Internet
Support customer orders (mail, phone, web)
Supply chain management (SCM)
Strategic information management system
Direct customer ordering via dynamic Web site
Extract and analyze SCM and CSS information for
Customer relationship management (CRM)
strategic and operational decision making and
Web-based intranet for business functions control
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 39
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 40 1 1
RMO Application Architecture Plan Timetable for RMO Application (continued) Architecture Plan Retail store system (RSS)
Replace existing retail store system with system integrated with CSS Accounting/Finance system
Purchase intranet application to maximize
employee access to financial data for planning and control Human resource (HR) system
Purchase intranet application to maximize
employee access to human resource forms,
procedures, and benefits information
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 41
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 42 1 1 The Customer Support System Analyst as a System Developer
RMO core competency is their ability to develop
Part 1: The modern systems analyst and maintain customer loyalty
Supply chain management (SCM) must be
Chapter 1: Nature of the analyst’s work defined before CSS can begin
CSS is a core system supporting customer
Chapter 2: Systems development life cycle relationship management (SDLC)
Systems analysis phase will define system requirements in detail
Chapter 3: How projects are planned and managed
Strategic plan’s stated objectives wil form guidelines as project proceeds
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 43
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 44 1 1
Analyst as a System Developer (continued)
Analyst as a System Developer (continued)
Part 2: Systems analysis tasks
Part 3: Systems design tasks
Chapter 4: Investigating systems requirements
Chapter 9: Overview of systems design and information gathering
Chapter 10: Traditional approach to design
Chapter 5: Modeling system requirements
Chapter 11: Object approach to design
Chapter 6: Traditional approach to requirements
Chapter 12: Object-oriented development
Chapter 7: Object-oriented approach to
Chapter 13: Database design requirements
Chapter 14: User interface design
Chapter 8: Evaluating alternatives for
requirements, environment, and implementation
Chapter 15: System interfaces and controls
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 45
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 46 1 1
Analyst as a System Developer (continued) Summary
Part 4: Implementation and support
Systems analyst solves business problems using
Chapter 16: Making the system operational information systems technology Current Trends
Chapter 17: Spiral model, extreme programming
Problem solving means looking into business
(XP), unified process (UP), prototyping,
problem in great detail, completely component-based development
understanding problem, and choosing best
Chapter 18: Software packages and enterprise solution resource planning (ERP) Appendices:
Information systems development is much more
Project management, planning, interviewing than writing programs
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 47
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 48 1 1 Summary (continued) Summary (continued)
Systems analyst has broad knowledge and
System - collection of interrelated components
that function together to achieve some outcome
variety of skills, including technical, business, and people
Information systems outcome: solution to a
Integrity and ethical behavior are crucial to business problem success for the analyst
Information systems, subsystems, and
Systems analyst encounters a variety of rapidly
components interact with and include hardware, changing technologies
software, inputs, outputs, data, people, and procedures
System analyst works on strategic plans and
then systems development projects
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 49
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 50 2 2 Learning Objectives Chapter 2:
Explain the purpose and various phases of the Approaches to System
systems development life cycle (SDLC) Development
Explain the differences between a model, a tool,
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing a technique, and a methodology World, 3rd Edition
Describe the two overall approaches used to
develop information systems: the traditional
method and the object-oriented method
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 2 2 2
Learning Objectives (continued) Overview
Describe some of the variations of the system
Systems development life cycle (SDLC) development life cycle (SDLC)
Provides overall framework for managing system development process
Describe the key features of current trends in
Two main approaches to SDLC
system development: the spiral model, eXtreme
Traditional approach: structured systems
Programming (XP), the Unified Process (UP), and
development and information engineering Agile Modeling
Object-oriented approach: object technologies
requires different approach to analysis, design, and programming
Explain how automated tools are used in system development
All projects use some variation of SDLC
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 3
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 4 2 2
Phases of the Systems Development
Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Lifecycle (SDLC)
Systems development project
Project planning: initiate, ensure feasibility, plan
Planned undertaking with fixed beginning and end
schedule, obtain approval for project
Produces desired result or product
Analysis: understand business needs and
Can be a large job of thousands of hours of effort processing requirements or a small one month project
Design: define solution system based on
Successful development project:
requirements and analysis decisions
Provides a detailed plan to follow
Implementation: construction, testing, user
Organized, methodical sequence of tasks and
training, and installation of new system activities
Produces reliable, robust, and efficient system
Support: keep system running and improve
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 5
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 6 2 2
Information System Development Phases SDLC and problem-solving
Similar to problem-solving approach
Organization recognizes problem (Project Planning)
Project team investigates, understands problem
and solution requirements (Analysis)
Solution is specified in detail (Design)
System that solves problem built and installed (Implementation)
System used, maintained, and enhanced to
continue to provide intended benefits (Support)
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 7
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 8 2 2 Planning Phase of SDLC Analysis Phase of SDLC
Define business problem and scope
Gather information to learn problem domain
Produce detailed project schedule Define system requirements
Confirm project feasibility
Build prototypes for discovery of requirements
Economic, organizational, technical, resource, and schedule Prioritize requirements
Staff the project (resource management)
Generate and evaluate alternatives
Launch project official announcement
Review recommendations with management
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 9
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 10 2 2 Design Phase of SDLC Implementation Phase of SDLC
Design and integrate the network
Construct software components
Design the application architecture Verify and test Design the user interfaces
Design the system interfaces Convert data
Design and integrate the database
Train users and document the system
Prototype for design details Install the system
Design and integrate system controls
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 11
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 12 2 2 Support Phase of SDLC Scheduling Project Phases Maintain system
Waterfall approach – each phase falls into next phase
Small patches, repairs, and updates
Freeze planning specifications before analysis Enhance system
Freeze analysis specifications before design
Small upgrades or enhancements to expand system capabilities
Once go over the waterfall for each phase, do not go back
Larger enhancements may require separate development project
Overlapping (or concurrent) phases Support users
Waterfall is not realistic, we are not perfect
Help desk and/or support team
Overlaps can be more efficient than waterfall
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 13
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 14 2 2
Scheduling Project Phases (continued)
The waterfall approach to the SDLC
Iteration - Work activities are repeated
Each iteration refines previous result
Approach assumes no one gets it right the first time
There are a series of mini projects for each iteration
Example: Outline, rough draft, edited result
Example: Blueprint, frame, completed house
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 15
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 16 2 2
Overlap of Systems Development
Iterations across life cycle phases Activities
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 17
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 18 2 2 Some Models Used in System Methodologies and Models Development Methodologies
Comprehensive guidelines to follow for completing every SDLC activity
Collection of models, tools, and techniques Models
Representation of an important aspect of real
world, but not same as real thing
Abstraction used to separate out aspect Diagrams and charts
Project planning and budgeting aids
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 19
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 20 2 2 Tools and Techniques
Some Tools Used in System Development Tools
Software support that helps create models or other required project components
Range from simple drawing programs to complex CASE tools Techniques
Collection of guidelines that help analyst complete
system development activity or task
Can be step-by-step instructions or just general advice
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 21
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 22 2 2
Some Techniques Used in System
Relationships Among Components of a Development Methodology
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 23
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 24 2 2
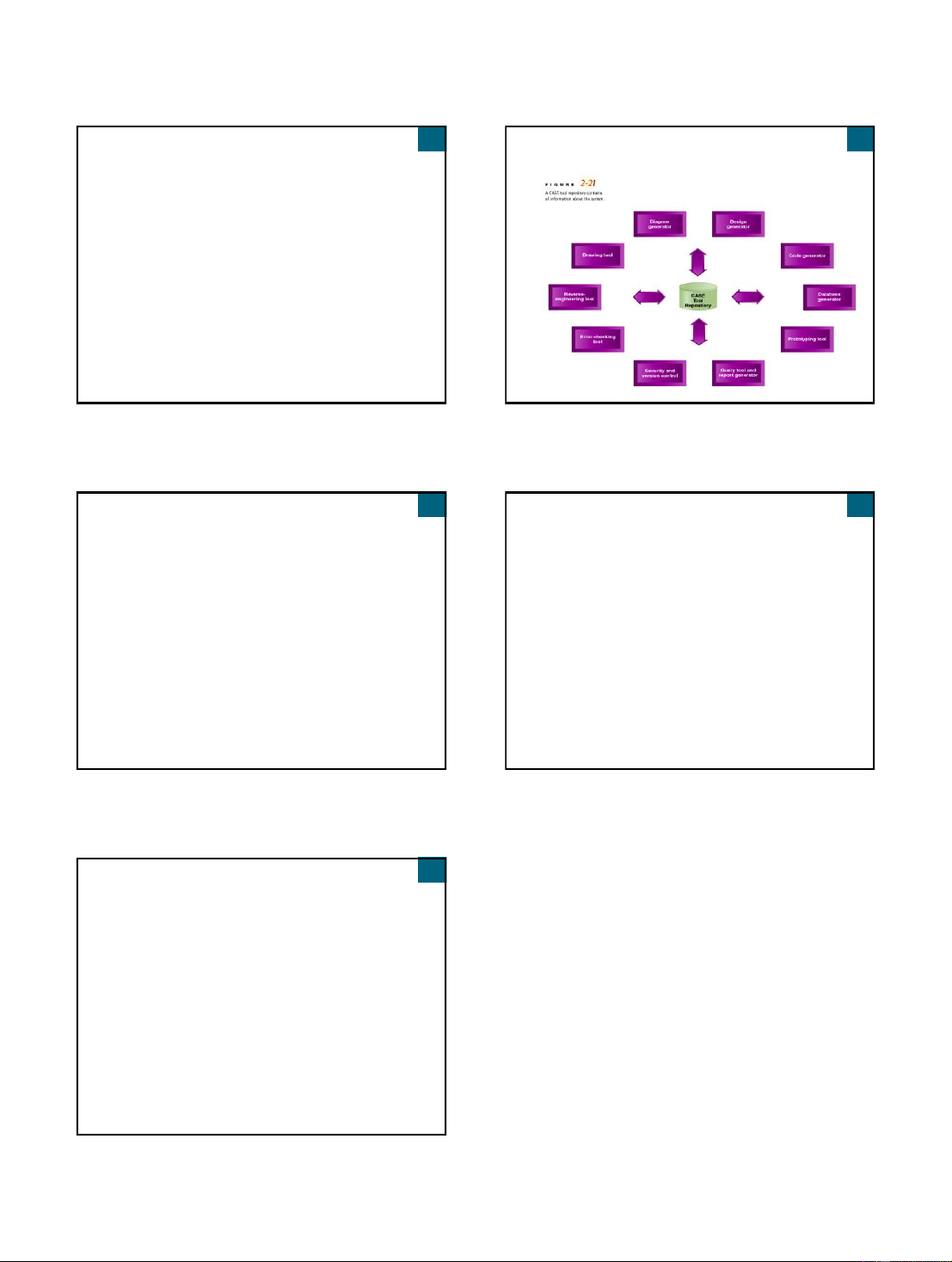
Two Approaches to System Development
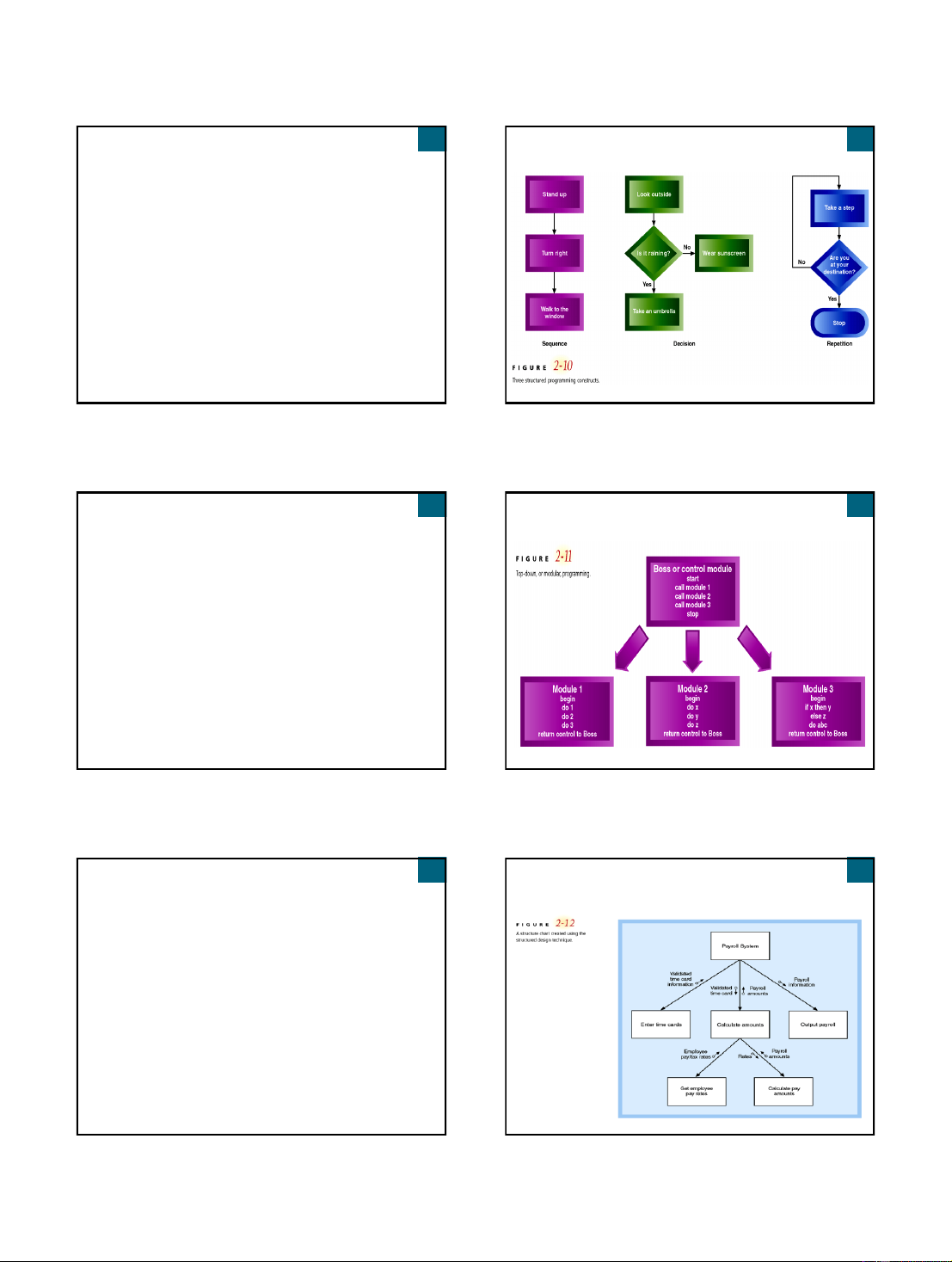
Three Structured Programming Constructs Traditional Approach
Also called structured system development
Structured analysis and design technique (SADT) Structured programming
Improves computer program quality
Allows other programmers to easily read and modify code
Each program module has one beginning and one ending
Three programming constructs (sequence, decision, repetition)
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 25
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 26 2 2 Top-Down Programming
Top-Down or Modular Programming
Divides complex programs into hierarchy of modules
The module at top controls execution by “cal ing” lower level modules Modular programming
Similar to top-down programming
One program calls other programs to work together as single system
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 27
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 28 2 2 Structure Chart Created Using Structured Design Structured Design Technique
Technique developed to provide design guidelines
What set of programs should be
What program should accomplish
How programs should be organized into a hierarchy
Modules are shown with structure chart
Main principle of program modules
Loosely coupled – module is independent of other modules
Highly cohesive – module has one clear task
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 29
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 30 2 2
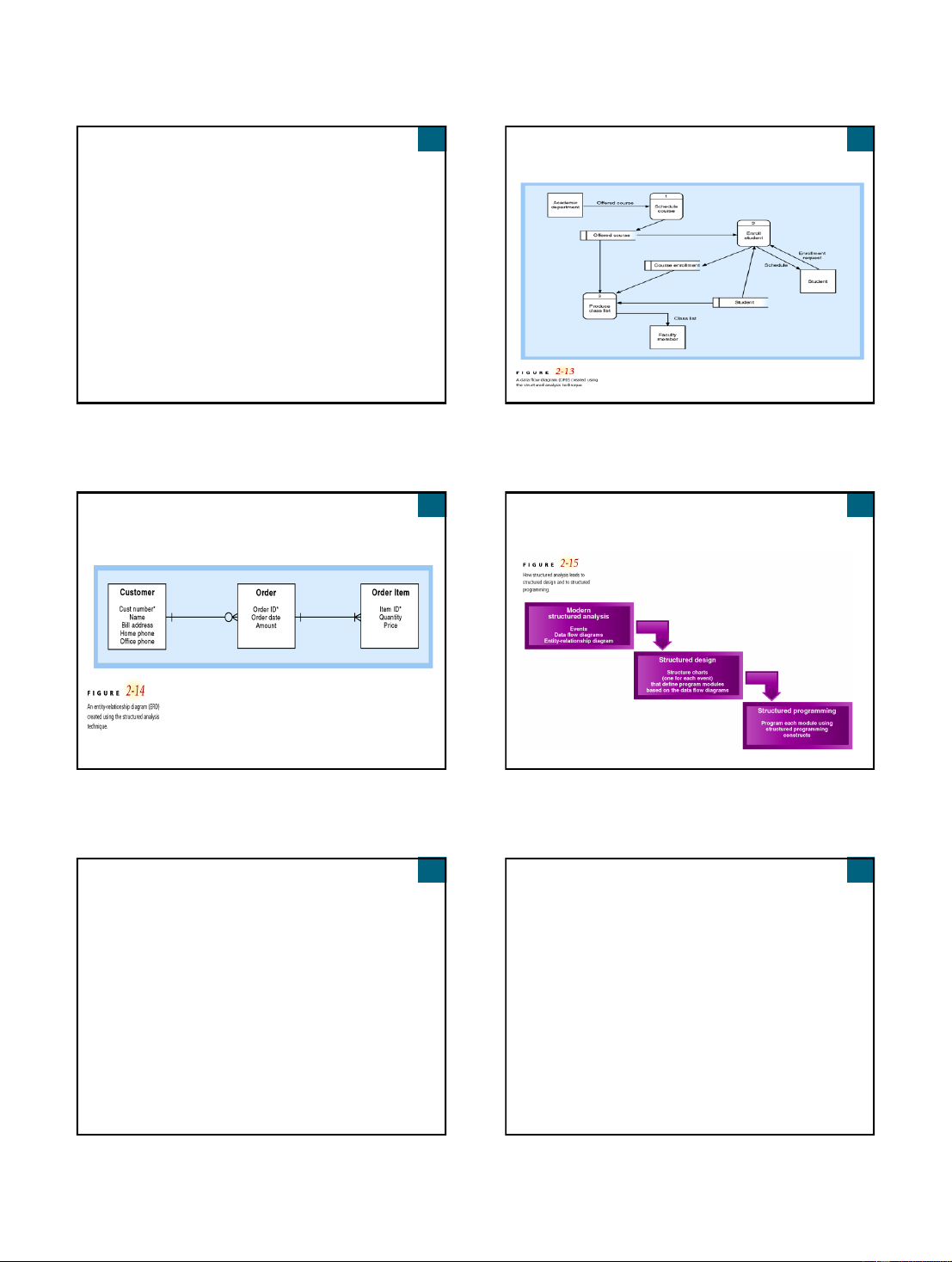
Data Flow Diagram (DFD) created using Structured Analysis Structured Analysis Technique
Define what system needs to do (processing requirements)
Define data system needs to store and use (data requirements) Define inputs and outputs
Define how functions work together to accomplish tasks
Data flow diagrams and entity relationship
diagrams show results of structured analysis
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 31
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 32 2 2
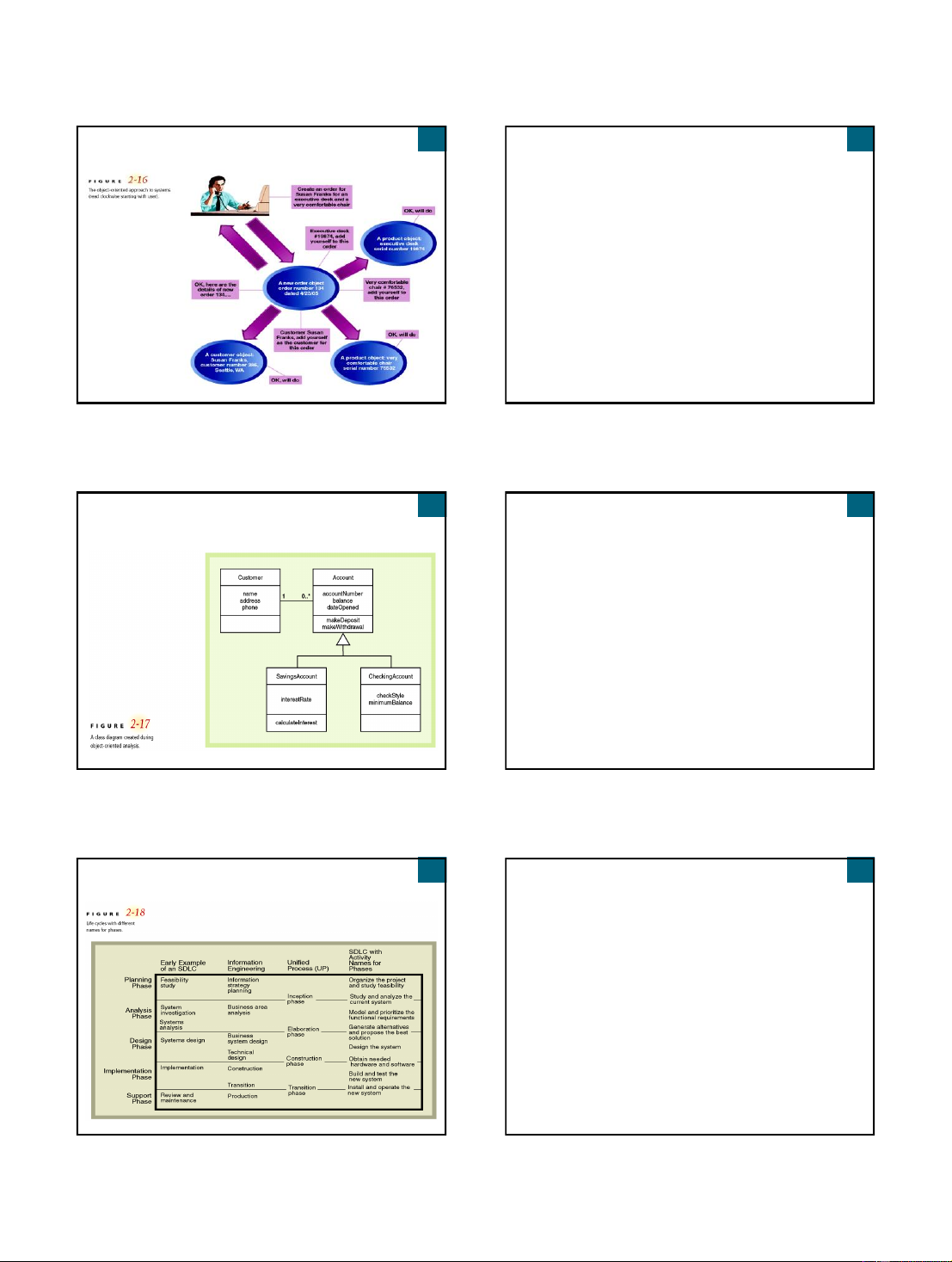
Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) created
Structured Analysis Leads to Structured
using the Structured Analysis technique
Design and Structured Programming
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 33
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 34 2 2 Information Engineering (IE) Object-Oriented Approach
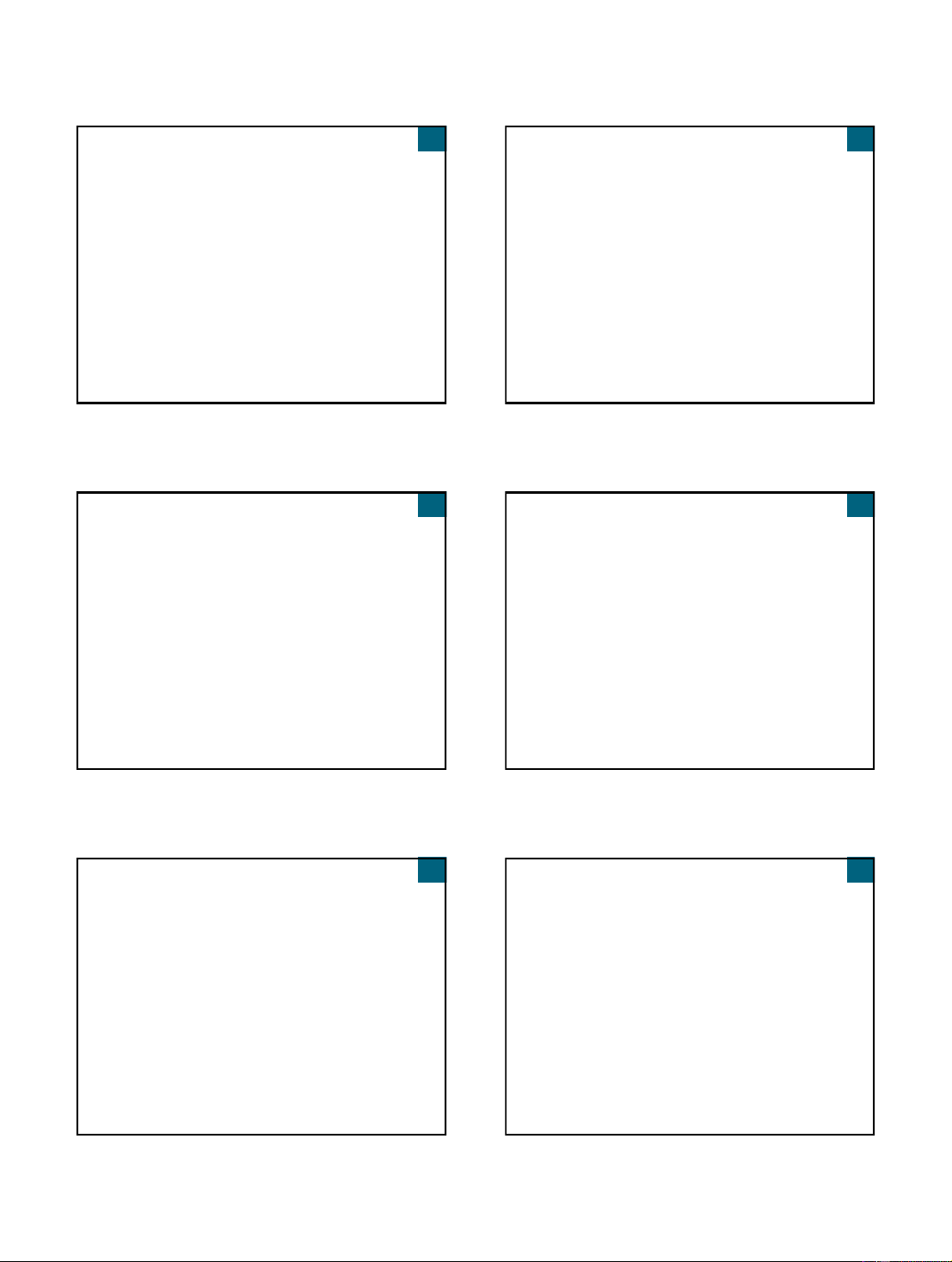
Views information system as collection of
Refinement to structured development
interacting objects that work together to accomplish tasks
Methodology with strategic planning, data
modeling, automated tools focus
Objects - things in computer system that can respond to messages
More rigorous and complete than SADT
No processes, programs, data entities, or files are defined – just objects
Uses process dependency diagram
Object-oriented analysis (OOA)
Industry merged key concepts from structured
Defines types of objects that do work of system
development and information engineering
Shows how objects interact with users to complete
approaches into traditional approach tasks
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 35
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 36 2 2
Object-Oriented Approach to Systems
Object-Oriented Approach (continued)
Object-oriented design (OOD)
Defines object types needed to communicate with people and devices in system
Shows how objects interact to complete tasks
Refines each type of object for implementation
with specific language of environment
Object-oriented programming (OOP)
Writing statements in programming language to
define what each type of object does
Benefits of OOA include naturalness and reuse
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 37
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 38 2 2
Class Diagram Created During OO SDLC Variations Analysis
Many variations of SDLC in practice
No matter which one, tasks are similar
Based on variation of names for phases
SDLC compared to IE compared to UP
Based on emphasis on people
User-centered design, participatory design
Based on speed of development
Rapid application development (RAD) Prototyping
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 39
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 40 2 2
Life Cycles with Different Names for Current Trends in Development Phases Spiral Model Highly iterative approach
Works around the phases (analysis, design,
construction, testing, integration with previous
prototype component) in a spiral until project is complete
Initial planning is to do just enough analysis to build initial prototype
Each iteration in the spiral addresses greatest risk
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 41
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 42 2 2 The Spiral Life Cycle Model Extreme Programming (XP)
Recent, lightweight, development approach to
keep process simple and efficient
Describes system support needed and required
system functionality through informal user stories
Has users describe acceptance tests to demonstrate defined outcomes
Relies on continuous testing and integration,
heavy user involvement, programming done by small teams
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 43
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 44 2 2 The Unified Process (UP)
The Unified Process (UP) (continued)
Object-oriented development approach
Reinforces six best practices Offered by IBM / Rational Develop iteratively Booch, Rumbaugh, Jacobson
Define and manage system requirements
Unified Modeling Language (UML) used primarily for modeling
Use component architectures
UML can be used with any OO methodology Create visual models
UP defines 4 life cycle phases Verify quality
Inception, elaboration, construction, transition Control changes
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 45
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 46 2 2 Agile Modeling Agile Modeling (continued)
Hybrid of XP and UP (Scott Ambler) has more Simplicity:
models than XP, less documents than UP
Interactive and Incremental Modeling: Use simple content Apply right models Depict models simply
Create several models in parallel
Use simplest modeling tools Model in small increments Teamwork: Validation
Get active stakeholder participation Consider testability
Encourage collective ownership
Model with others and display models publicly
Prove model is right with code
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 47
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 48 2 2
CASE Tool Repository Contains all
Tools to Support System Development System Information
Computer-Aided System Engineering (CASE)
Automated tools to improve the speed and quality of system development work
Contains database of information about system called repository
Upper CASE - support for analysis and design
Lower CASE - support for implementation
ICASE - integrated CASE tools
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 49
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 50 2 2 Summary Summary (continued)
Systems development projects are organized
All development approaches use a SDLC to around the SDLC manage the project.
SDLC Phases include project planning, analysis,
Models, techniques, and tools make up a
design, implementation, and support to be
systems development methodology completed for each project
System development methodologies are based
Systems developers learn SDLC based on the
on traditional approach or object-oriented sequential waterfall approach approach
In practice, phases overlap and projects contain
many iterations of analysis, design, and
System development methodology provides implementation activities
guidelines to complete every activity in the SDLC
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 51
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 52 2 Summary (continued)
Original SDLC was waterfall approach
Most SDLC use iteration across phases
Rapid application development (RAD) goal is to speed up development
Current trends include: spiral model, eXtreme
Programming (XP), Unified Process (UP) and Agile Modeling
CASE tools are designed to help analysts complete tasks
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 53 3 3 Learning Objectives Chapter 3:
Explain the elements of project management and The Analyst as a
the responsibilities of a project manager Project Manager
Explain project initiation and the activities in the
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing
project planning phase of the SDLC World, 3rd Edition
Describe how the scope of the new system is determined
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 2 3 3
Learning Objectives (continued) Overview
Fundamental principles of project management
Develop a project schedule using PERT and
Need both technical and management skills Gantt charts
How information system projects initiated
Part of overall strategic plan
Develop a cost/benefit analysis and assess the
Respond to immediate business need
feasibility of a proposed project
Describe project planning phase of SDLC Define scope of project
Discuss how to staff and launch a project
Compare estimated costs and benefits Develop project schedule
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 3
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 4 3 3 Project Management Project Success Factors People
Project management important for success of system development project Organizing 2000 Standish Group Study Directing
Only 28% of system development projects Planned result successful Scheduling
72% of projects cancelled, completed late, over Budgeting
budget, and/or limited in functionality
Management: Getting things done through other
Thus, project requires careful planning, control, people and execution
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 5
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 6 3 3 Reasons for Project Failure Reasons for Project Success
Incomplete or changing requirements
Clear system requirement definitions Limited user involvement
Substantial user involvement Lack of executive support Lack of technical support
Support from upper management Poor project planning
Thorough and detailed project plans Unclear objectives Lack of required resources
Realistic work schedules and milestones
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 7
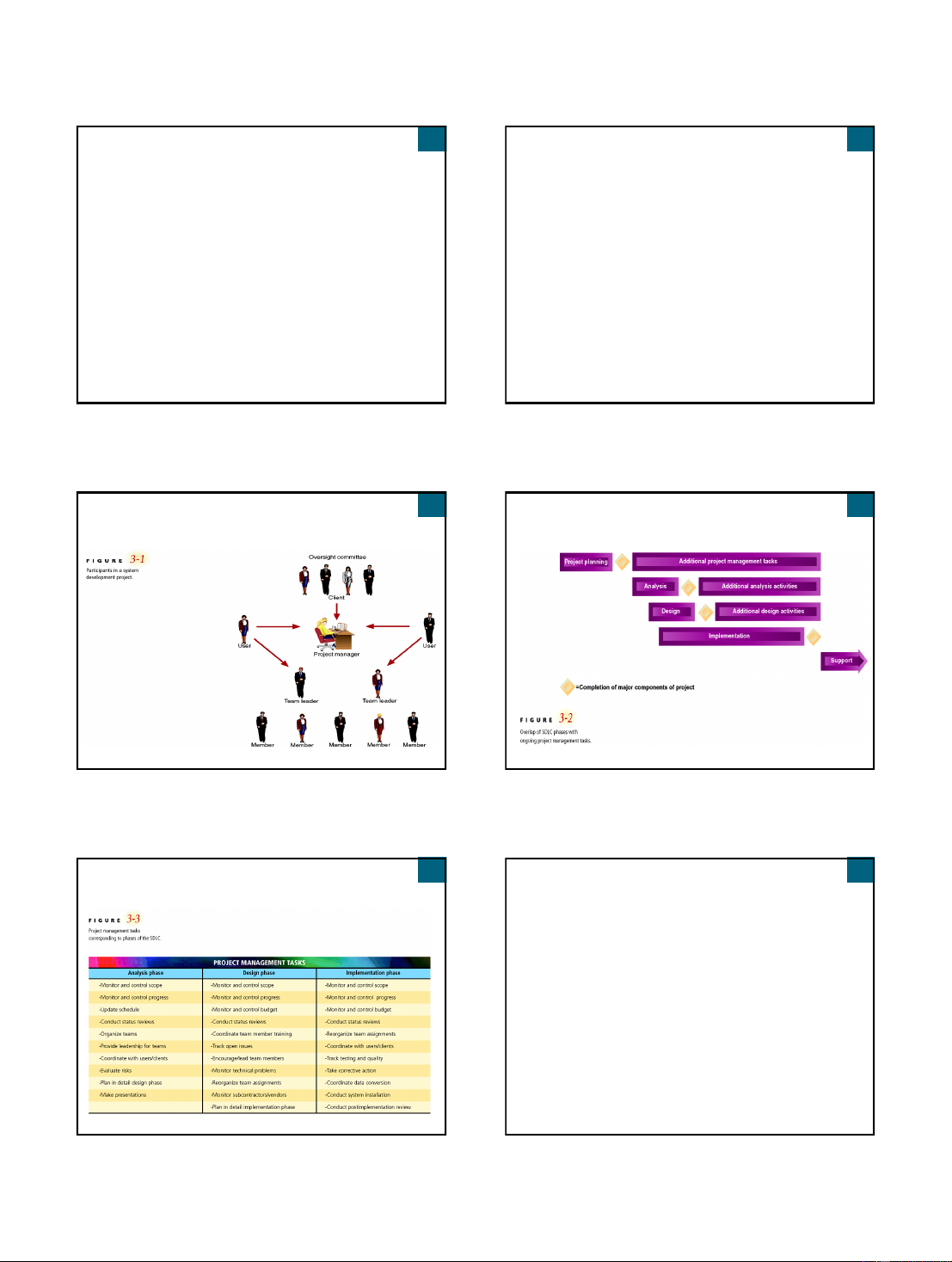
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 8 3 3 Participants in a System
Overlap of SDLC Phases with Ongoing Development Project Project Management Tasks
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 9
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 10 3 3
Project Management Tasks Corresponding
Project Management Body of Knowledge to Phases of the SDLC Scope management
Control functions included in system
Control scope of work done by team Time management
Build detailed schedule of all project tasks
Monitor progress of project against milestones Cost management
Calculate cost/benefit initial analysis Monitor expenses
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 11
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3rd Edition 12