








Preview text:
WRITING 6.1
Tổng hợp Composition Diagram IELTS HÒN ĐÁ
The diagram below shows the development of cutting tools in the Stone Age.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
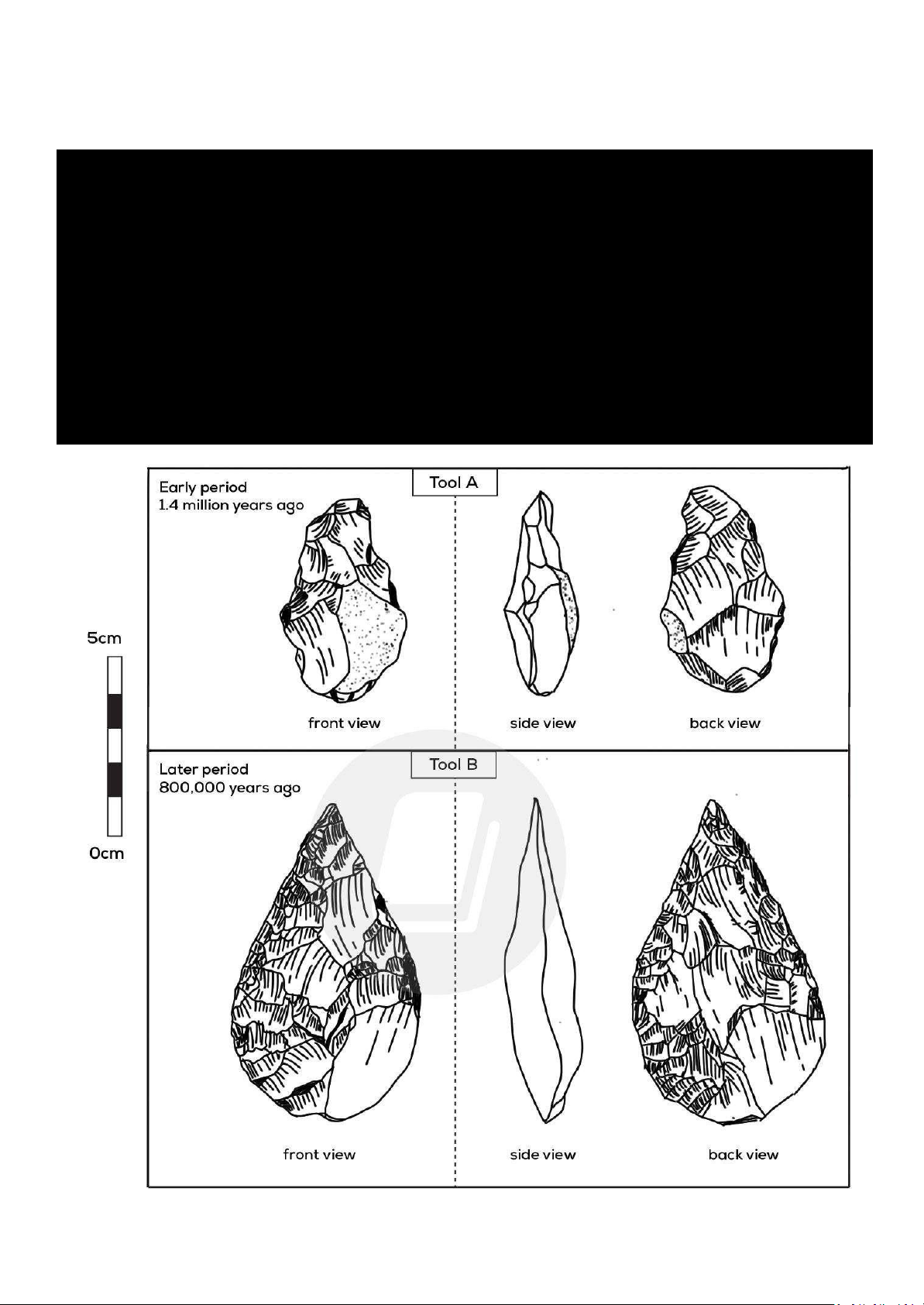
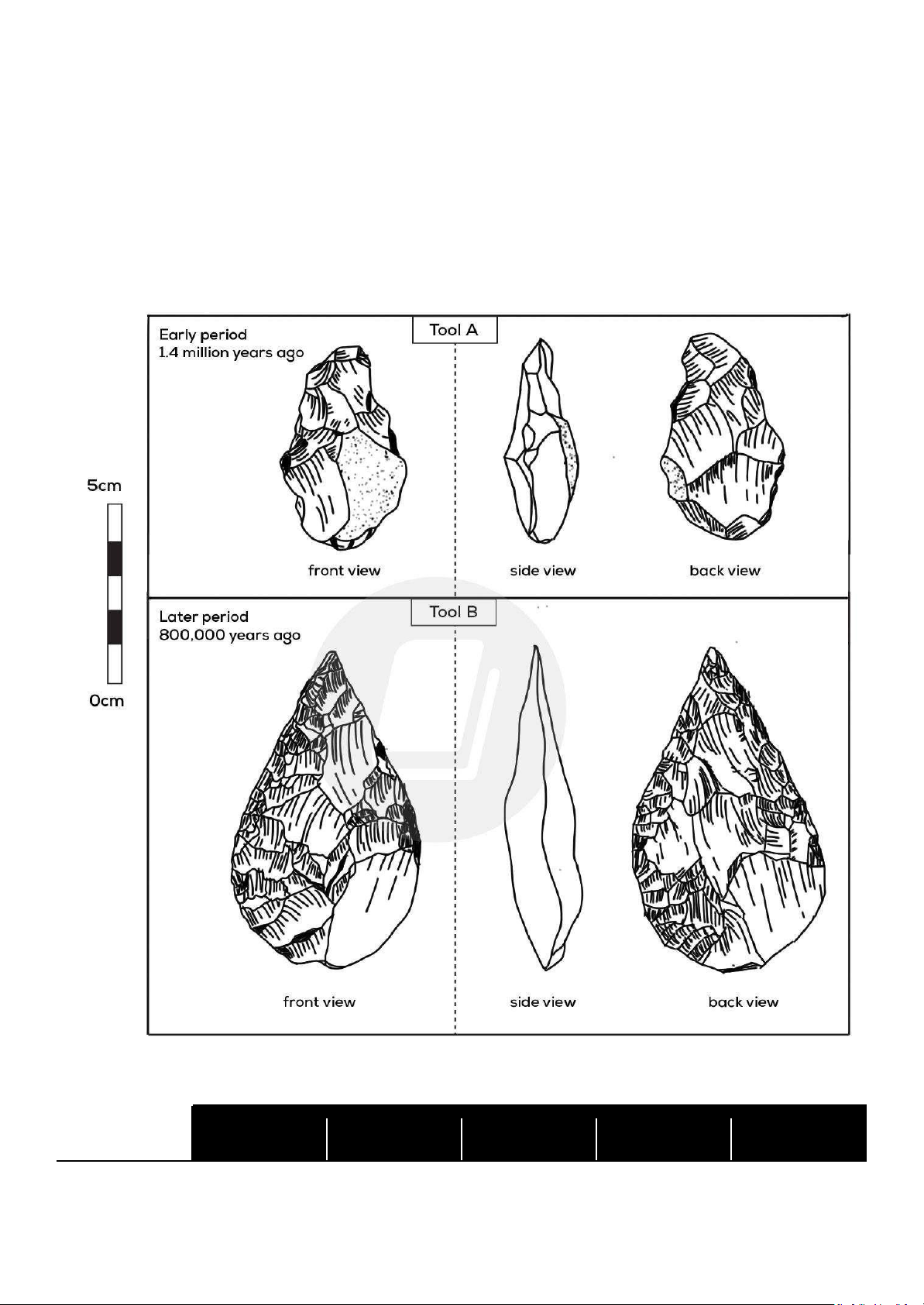
Write at least 150 words. OUTLINE: Period Size Front view Side view Back view thick not 1.4 million years Tool A 5cm high asymmetrical effective at rough ago cutting Tool B 800.000 years ago 7.5 cm high symmetrical tear- thin, sharp smooth drop shaped edge effective at cutting SAMPLE REPORT: Introduction
The diagram provides a comparative analysis of two ancient tools, designated as Tool A and Tool B, focusing on their respective
periods, sizes, and various views (front, side, and back).
Sơ đồ đã cho cung cấp một phân tích so sánh giữa hai công cụ cổ xưa, được gọi là Công cụ A và Công cụ B, t p trung vào
thời kỳ, kích thước và các góc nhìn khác nhau (mặt trước, mặt bên và mặt sau) của chúng. Body 1: Tool A
Tool A dates back to 1.4 million years ago and measures 5 cm in height. Its front view reveals an asymmetrical shape, suggesting a
lack of balance in its design. The side view indicates that it is thick and not effective at cutting, which implies it may have been used
for purposes other than precise cutting tasks. The back view of Tool A is described as rough, further suggesting a rudimentary construction.
Công cụ A có niên đại từ 1,4 triệu năm trước và có chiều cao 5 cm. Mặt trước của nó cho thấy hình dạng không đối xứng,
gợi ý về thiết kế thiếu cân bằng. Góc nhìn từ mặt bên cho thấy nó dày và không hiệu quả trong việc cắt, điều này ngụ ý
rằng nó có thể được sử dụng cho các mục đích khác ngoài việc cắt chính xác.
Mặt sau của Công cụ A được mô tả là thô ráp, càng cho thấy sự chế tạo thô sơ. Body 2: Tool B
On the other hand, Tool B is more recent, dating back to 800,000 years ago, and is larger at 7.5 cm high. It presents a symmetrical,
tear-drop shape in the front view, indicating a more advanced and deliberate design. The side view highlights a thin, sharp edge,
which is effective at cutting, signifying an improvement in functionality over Tool A.
Additionally, the back view of Tool B is smooth, reflecting a more refined manufacturing process.
Ngược lại, Công cụ B có niên đại gần đây hơn, từ 800.000 năm trước, và lớn hơn với chiều cao 7,5 cm. Nó thể hiện hình
dạng giọt nước đối xứng ở mặt trước, cho thấy một thiết kế tiên tiến và có chủ ý hơn. Góc nhìn từ mặt bên nổi b t với một
cạnh mỏng và sắc, hiệu quả trong việc cắt, cho thấy sự cải tiến về chức năng so với Công cụ A. Thêm vào đó, mặt sau của
Công cụ B mịn màng, phản ánh quy trình chế tạo tinh xảo hơn. Overview
In summary, Tool B, being more recent, exhibits significant advancements in design and functionality compared to Tool A. It is
larger, more symmetrical, and more effective at cutting, which points to an evolution in tool-making techniques over time.
Tóm lại, Công cụ B, với niên đại gần đây hơn, thể hiện những tiến bộ đáng kể về thiết kế và chức năng so với Công cụ A.
Nó lớn hơn, đối xứng hơn và hiệu quả hơn trong việc cắt, điều này cho thấy sự phát triển trong kỹ thu t chế tạo công cụ theo thời gian. IELTS CÂY CẦU
The pictures below show three different kinds of bridges.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
Write at least 150 words. OUTLINE: Dimension Location
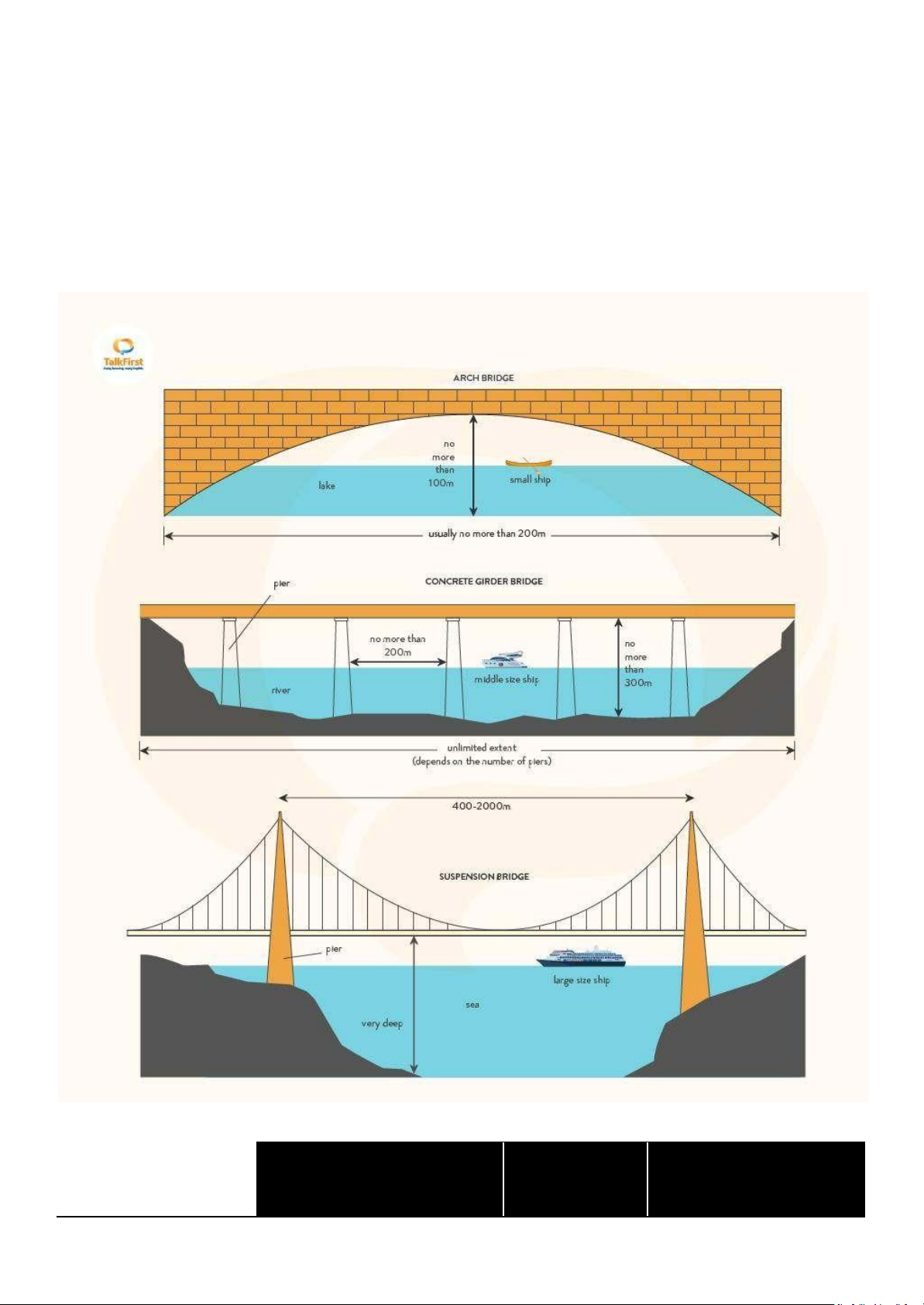
Ship that can pass underneath ● 200m length ● Arch bridge lake small ship only 100m high ● ● unlimited length maximum distance Concrete Girdle Bridge river small + middle size ships between two bridge ● pillars = 200m 300m high Suspension Bridge ● unlimited length ocean
small + middle size + large size ships ● maximum distance between two bridge pillars 400-2000m unlimited high ● SAMPLE REPORT: Introduction
The diagram compares three types of bridges: Arch Bridge, Concrete Girdle Bridge, and Suspension Bridge, focusing on their
dimensions, locations, and the types of ships that can pass underneath them.
Sơ đồ đã cho so sánh ba loại cầu: Cầu Vòm, Cầu Dầm Bê Tông và Cầu Treo, t p trung vào kích thước, vị trí và các loại tàu
có thể đi qua bên dưới chúng.
Body 1: The Arch Bridge
The Arch Bridge has a fixed dimension of 200 meters in length and 100 meters in height. It is typically located over lakes and can
accommodate only small ships passing beneath it.
Cầu Vòm có kích thước cố định là 200 mét chiều dài và 100 mét chiều cao. Nó thường nằm trên các hồ và chỉ có thể cho
phép các tàu nhỏ đi qua bên dưới.
Body 2: The Concrete Girdle Bridge
The Concrete Girdle Bridge features unlimited length and a height of 300 meters. The maximum distance between two bridge
pillars is 200 meters. These bridges are commonly found over rivers and can allow small to middle-sized ships to pass underneath.
Cầu Dầm Bê Tông có chiều dài không giới hạn và chiều cao 300 mét. Khoảng cách tối đa giữa hai trụ cầu là 200 mét. Loại
cầu này thường được xây dựng trên các con sông và có thể cho phép các tàu nhỏ đến tàu cỡ trung đi qua bên dưới.
Body 3: The Suspension Bridge
The Suspension Bridge also has an unlimited length and an unlimited height. The distance between two bridge pillars ranges from
400 to 2000 meters. This type of bridge is typically located over oceans and is capable of allowing ships of all sizes—small, middle-
sized, and large—to pass underneath.
Cầu Treo cũng có chiều dài không giới hạn và chiều cao không giới hạn. Khoảng cách giữa hai trụ cầu dao động từ 400
đến 2000 mét. Loại cầu này thường nằm trên các đại dương và có khả năng cho phép tàu nhỏ, tàu cỡ trung và tàu lớn đi qua bên dưới. Overview
Overall, the diagram highlights the varying dimensions, locations, and capacities of different bridge types in relation to the size of
ships they can accommodate. The Arch Bridge is limited to small ships, the Concrete Girdle Bridge can handle small to middle-sized
ships, and the Suspension Bridge is the most versatile, allowing passage for ships of all sizes.
Tóm lại, sơ đồ này nêu rõ các kích thước, vị trí và khả năng của các loại cầu khác nhau liên quan đến kích thước của các
tàu có thể đi qua bên dưới. Cầu Vòm giới hạn chỉ cho tàu nhỏ, Cầu Dầm Bê Tông có thể xử lý tàu nhỏ đến tàu cỡ trung, và
Cầu Treo là loại đa năng nhất, cho phép các tàu có mọi kích cỡ đi qua. IELTS CON NGỰA
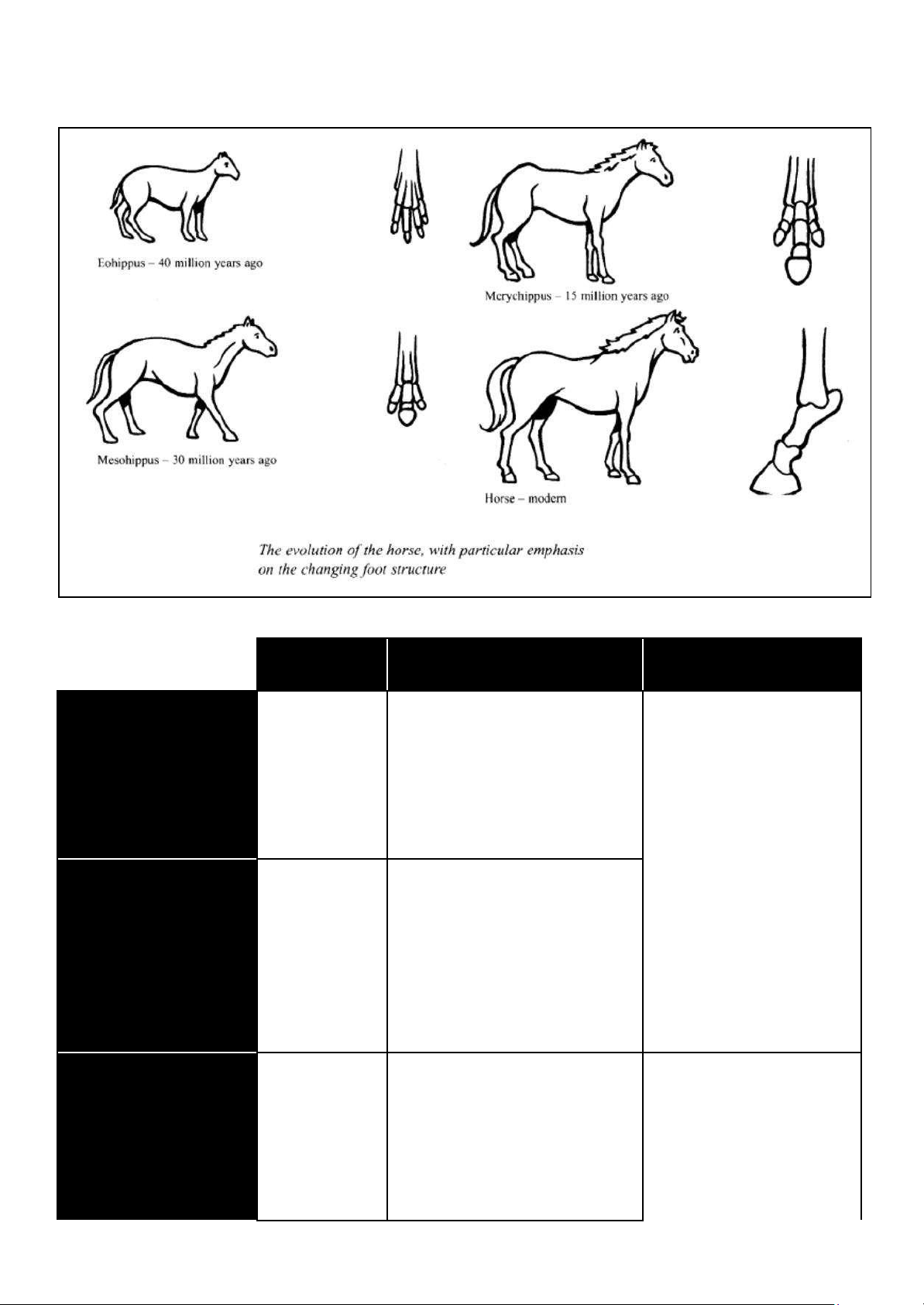
The diagrams below show the development of the horse over a period of 40 million years.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
Write at least 150 words. OUTLINE: Time Foot structure Height + Appearance ● ● five toes 40 million years Eohippus ago four similar toes, one small toe ● quite short ● mane and tail not Mesohippus 30 million years ● three toes developed ago ● middle toe most developed Merychippus 15 million years ● three toes ago ● middle toe much more developed ● tall ● developed mane Modern horse modern days ● only one toe and tail ● developed fully into the hoof of a horse SAMPLE REPORT: Introduction
The diagram outlines the evolution of the horse with a particular emphasis on the changing foot structure, spanning from the
Eohippus 40 million years ago to the modern horse.
Sơ đồ đã cho nêu rõ sự tiến hóa của loài ngựa với sự nhấn mạnh đặc biệt vào cấu trúc bàn chân, từ Eohippus cách đây 40
triệu năm đến ngựa hiện đại.
Body 1: Eohippus and Mesohippus
The Eohippus existed 40 million years ago and had five toes, with four similar toes and one small toe. It was quite short in height,
and both its mane and tail were not developed. Around 30 million years ago, the Mesohippus appeared, which had three toes.
Among these, the middle toe was the most developed. The Mesohippus was taller than the Eohippus, but specific details about its
height and appearance were not provided.
Eohippus tồn tại cách đây 40 triệu năm và có năm ngón chân, với bốn ngón tương tự nhau và một ngón nhỏ. Nó có chiều
cao khá thấp, và cả bờm và đuôi đều chưa phát triển. Khoảng 30 triệu năm trước, Mesohippus xuất hiện, có ba ngón
chân. Trong đó, ngón giữa là phát triển nhất. Mesohippus cao hơn Eohippus, nhưng chi tiết cụ thể về chiều cao và ngoại
hình không được cung cấp.
Body 2: Merychippus and Modern horse
The Merychippus emerged 15 million years ago, also with three toes. However, the middle toe was much more developed
compared to the Mesohippus. The Merychippus was tall and had a developed mane and tail. The modern horse, which exists today,
has only one toe, which has fully developed into the hoof of a horse. This development represents a significant evolutionary change
from its ancestors. The modern horse is characterized by its tall stature and fully developed mane and tail.
Merychippus xuất hiện cách đây 15 triệu năm, cũng với ba ngón chân. Tuy nhiên, ngón giữa phát triển nhiều hơn so với
Mesohippus. Merychippus có chiều cao và có bờm và đuôi đã phát triển. Ngựa hiện đại, tồn tại ngày nay, chỉ có một ngón chân,
đã phát triển hoàn toàn thành móng guốc của ngựa. Sự phát triển này thể hiện sự thay đổi tiến hóa đáng kể từ tổ tiên của nó.
Ngựa hiện đại có đặc điểm là chiều cao lớn và bờm và đuôi phát triển đầy đủ. Introduction
Overall, the diagram shows a clear progression in the evolution of the horse, particularly in terms of foot structure. The
transformation from multiple toes in the Eohippus to a single hoof in the modern horse is accompanied by changes in height and
the development of the mane and tail.
Tóm lại, sơ đồ này cho thấy sự tiến hóa rõ ràng của loài ngựa, đặc biệt là về cấu trúc bàn chân. Sự chuyển đổi từ nhiều
ngón chân ở Eohippus đến một móng guốc ở ngựa hiện đại đi kèm với sự thay đổi về chiều cao và sự phát triển của bờm và đuôi. IELTS KHINH KHÍ CẦU
The picture below shows how a hot balloon works.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
Write at least 150 words. OUTLINE
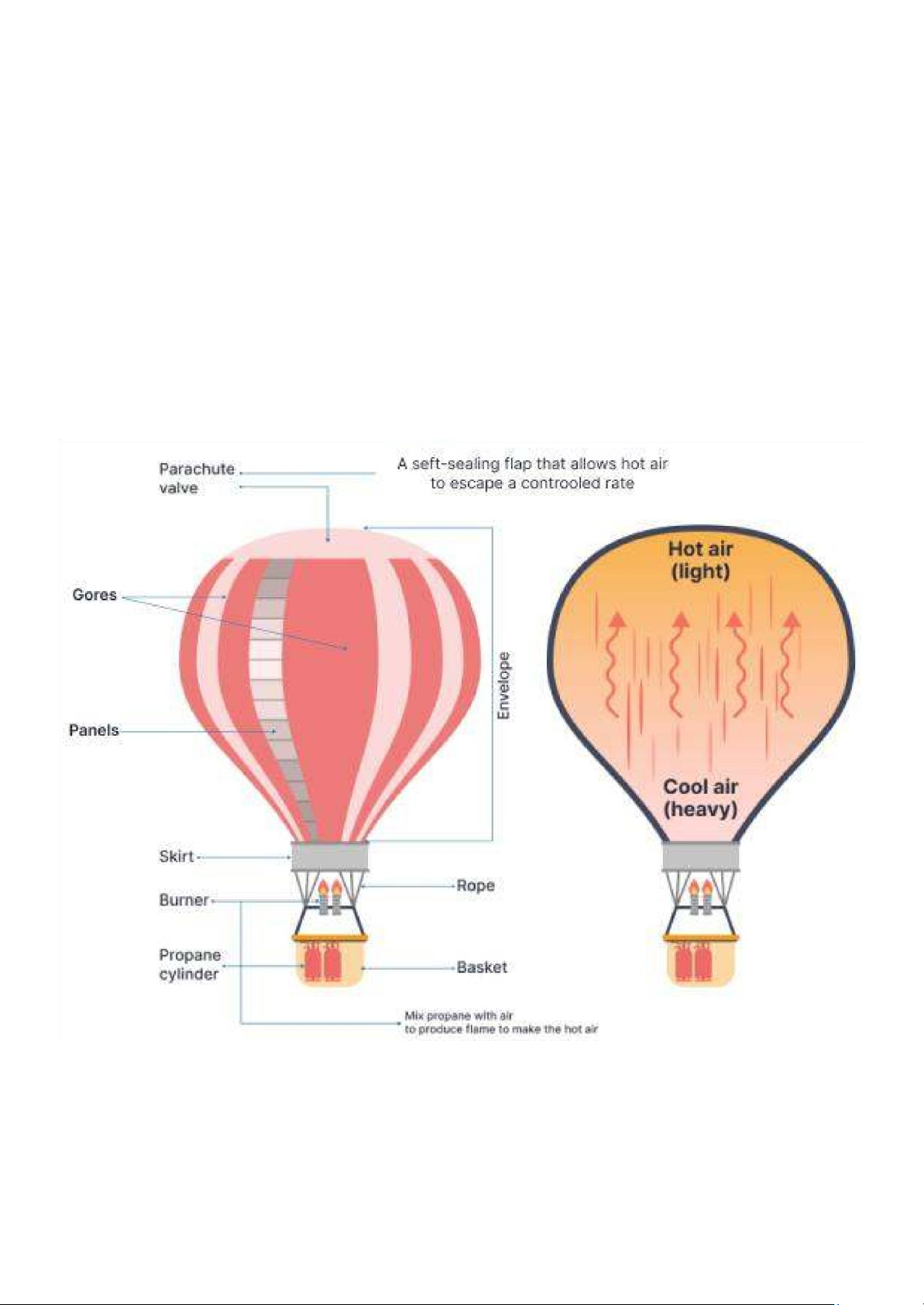
How a Hot Air Balloon is Made: ● Envelope:
○ Parachute valve: A self-sealing flap that allows hot air to escape at a controlled rate.
○ Gores: Sections of fabric that make up the balloon.
○ Panels: Smaller sections within the gores.
○ Skirt: The lower part of the envelope.
● Burner System:
○ Burner: Produces flame to heat the air inside the envelope.
○ Propane cylinder: Supplies propane to the burner.
○ Rope: Likely used to control the burner or other parts of the balloon. ● Basket:
○ Basket: The compartment where passengers stand.
How a Hot Air Balloon Works:
● Heating Mechanism:
○ Propane mixed with air: Creates a flame to heat the air inside the envelope.
● Air Dynamics:
○ Hot air (light): Rises to the top of the envelope.
○ Cool air (heavy): Stays at the bottom of the envelope. SAMPLE REPORT Introduction
The diagram outlines the process of how a hot air balloon is constructed and operates. It details the main components involved in
its assembly and explains the principles behind its functionality.
Sơ đồ này mô tả quá trình chế tạo và hoạt động của khinh khí cầu. Nó nêu rõ các thành phần chính trong quá trình lắp
ráp và giải thích nguyên lý hoạt động của khinh khí cầu. Overview
Overall, the hot air balloon consists of three primary parts: the envelope, the burner system, and the basket. The functioning of
the balloon relies on the heating mechanism provided by the burner system, which enables the balloon to rise and fall by
controlling the temperature of the air inside the envelope.
Nhìn chung, khinh khí cầu gồm ba phần chính: vỏ, hệ thống đốt và giỏ. Hoạt động của khinh khí cầu dựa vào cơ chế đốt
nóng của hệ thống đốt, cho phép khinh khí cầu bay lên và hạ xuống bằng cách điều chỉnh nhiệt độ không khí bên trong vỏ.
Body 1: How a Hot Air Balloon is Made
The construction of a hot air balloon begins with the envelope, which is made up of several sections. The parachute valve, located
at the top, allows for controlled release of hot air. The gores are large fabric sections, subdivided into smaller panels, and the skirt
forms the lower part of the envelope. The burner system includes the burner, which generates a flame to heat the air, and the
propane cylinder, which supplies fuel to the burner. Additionally, a rope is used to control various parts of the balloon. The basket,
where passengers stand, completes the structure.
Việc chế tạo khinh khí cầu bắt đầu với vỏ, được tạo thành từ nhiều phần khác nhau. Van dù, nằm ở phần trên, cho phép
thoát khí nóng một cách có kiểm soát. Các mảng vải lớn được gọi là "gores", chia thành các phần nhỏ hơn gọi là "panels",
và phần dưới của vỏ gọi là “skirt”. Hệ thống đốt gồm có bộ đốt, tạo ra ngọn lửa để đốt nóng không khí, và bình propane
cung cấp nhiên liệu cho bộ đốt. Ngoài ra, dây thừng được sử dụng để kiểm soát các phần khác nhau của khinh khí cầu.
Giỏ, nơi hành khách đứng, hoàn thiện cấu trúc của khinh khí cầu.
Body 2: How a Hot Air Balloon Works
The operation of a hot air balloon relies on the heating mechanism. Propane mixed with air is ignited by the burner, producing a
flame that heats the air inside the envelope. The dynamics of hot air rising and cool air descending within the envelope facilitate
the balloon's ascent and descent. Hot air, being lighter, rises to the top of the envelope, causing the balloon to lift. Conversely,
when the air cools and becomes heavier, it descends, bringing the balloon down.
Hoạt động của khinh khí cầu dựa vào cơ chế đốt nóng. Hỗn hợp propane và không khí được đốt bởi bộ đốt, tạo ra ngọn
lửa để làm nóng không khí bên trong vỏ. Cơ chế động lực học của không khí nóng bay lên và không khí lạnh hạ xuống
trong vỏ cho phép khinh khí cầu bay lên và hạ xuống. Không khí nóng, nhẹ hơn, bay lên đỉnh của vỏ, làm cho khinh khí cầu
bay lên. Ngược lại, khi không khí nguội đi và nặng hơn, nó hạ xuống, kéo khinh khí cầu xuống. IELTS NGỌN SÓNG
The diagrams below show a structure that is used to generate electricity from wave power.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
Write at least 150 words.
Generating Electricity From The Sea SAMPLE REPORT: Introduction:
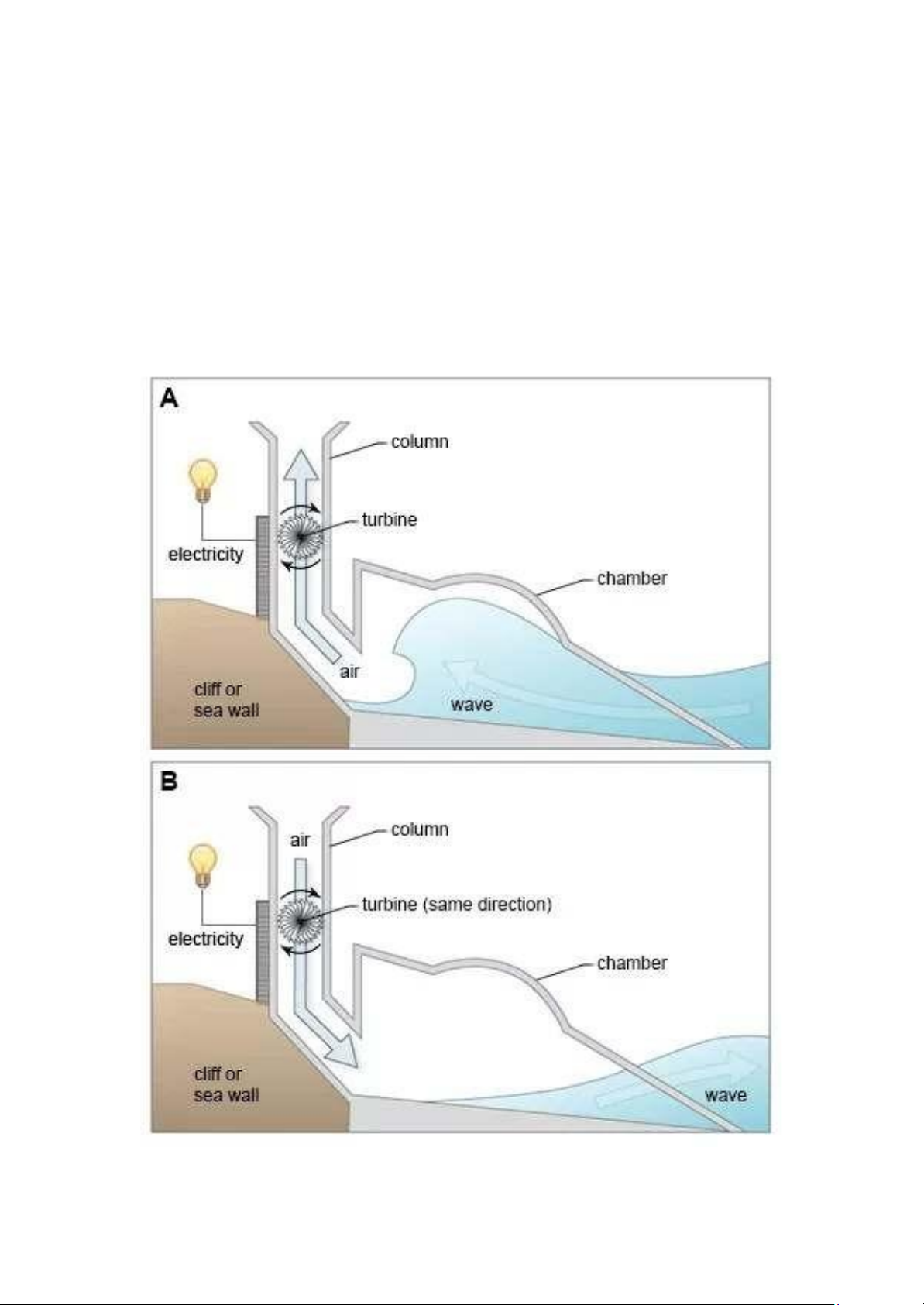
The diagrams illustrate the generation of electricity utilizing wave power through a specially engineered structure.
Các biểu đồ minh họa quá trình tạo điện từ năng lượng sóng thông qua một cấu trúc được thiết kế đặc biệt. Body 1: Structure:
The structure, consisting of a wave chamber and a tall column containing a turbine, is erected on a steeply sloping coastal cliff or
sea wall where it is subject to the movement of the ocean waves.
Cấu trúc này, bao gồm một buồng sóng và một cột cao chứa tua-bin, được xây dựng trên một vách đá hoặc tường biển
dốc nơi nó tiếp xúc với sự chuyển động của sóng biển.
Body 2: The first diagram
The first diagram shows how the incoming wave fills a large chamber and forces the air inside this space up the column and through
the turbine. The pressure of the air rotates the turbine which generates a current of electricity.
Biểu đồ đầu tiên cho thấy cách sóng đến đổ vào một buồng lớn và ép không khí bên trong buồng lên cột và qua tua-bin.
Áp lực của không khí làm quay tua-bin, tạo ra dòng điện.
Body 3: The second diagram
The process does not end there for the structure is able to continue producing power as the sea recedes as can be seen in the
second diagram. As the water now flows away from the structure, it draws air back down the column and downwards through the
turbine in the same direction as the previous upward flow of air. The turbine continues to turn, thus generating even more electricity.
Quá trình không dừng lại ở đó vì cấu trúc này có thể tiếp tục sản xuất điện khi sóng rút đi, như được thấy trong biểu đồ
thứ hai. Khi nước chảy ra khỏi cấu trúc, nó kéo không khí xuống cột và qua tua-bin theo cùng hướng với luồng không khí
trước đó. Tua-bin tiếp tục quay, từ đó tạo ra thêm điện năng. Overview
Overall, the process is continuous, leveraging both the incoming and receding waves to drive the turbine and generate a steady
flow of power. The first diagram details how the rising wave forces air through the turbine, while the second diagram demonstrates
how the falling wave sustains the turbine's movement, ensuring ongoing electricity production.
Tóm lại, quá trình này diễn ra liên tục, t n dụng cả sóng đến và sóng rút để quay tua-bin và tạo ra một dòng điện ổn định.
Biểu đồ đầu tiên chi tiết cách sóng dâng ép không khí qua tua-bin, trong khi biểu đồ thứ hai minh họa cách sóng hạ duy
trì sự chuyển động của tua-bin, đảm bảo việc sản xuất điện liên tục. IELTS LỌC NƯỚC
The diagram below shows a simple system that turn dirty water into clean water.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
Write at least 150 words. SAMPLE REPORT Introduction
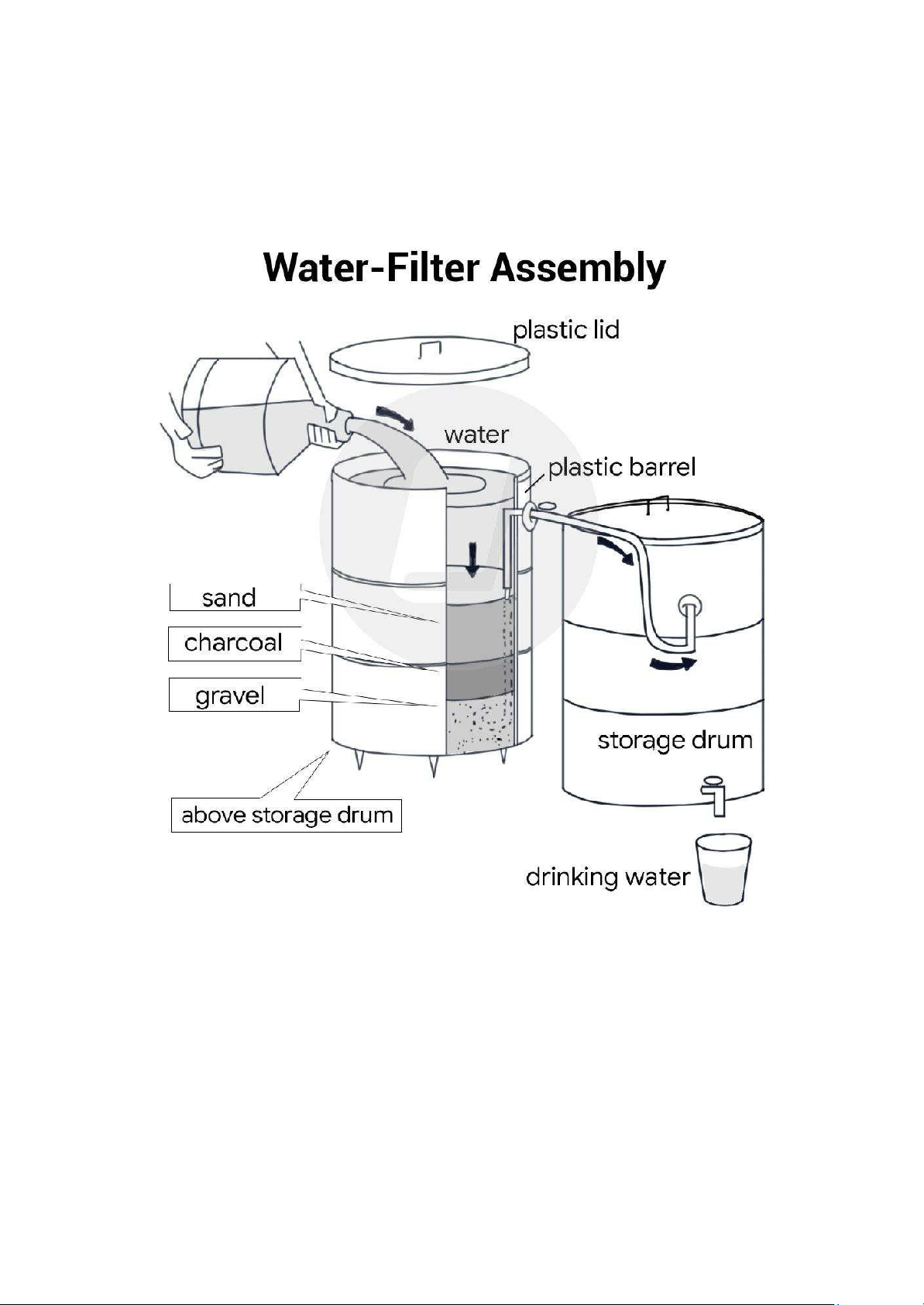
The diagram illustrates a simple method of purifying dirty water in order to make it suitable for consumption.
Biểu đồ minh họa một phương pháp đơn giản để làm sạch nước bẩn, giúp nó trở nên an toàn để sử dụng. Overview
Overall, the system showcases how readily available natural materials and basic equipment can be utilized to produce drinkable
water in just a few straightforward steps.
Về tổng quan, hệ thống này cho thấy cách các v t liệu tự nhiên có sẵn và thiết bị cơ bản có thể được sử dụng để sản xuất
nước uống chỉ trong vài bước đơn giản. Body 1: The structure
Firstly, a storage drum and a plastic barrel are positioned adjacent to each other, with the top of the latter higher than the former.
These two components are connected by a pipe running from the bottom of the barrel into the side of the drum. Subsequently, a
filter is constructed within the barrel by adding layers of sand, charcoal, and gravel. Lastly, a tap is installed at the bottom of the
drum, and another one is placed at the top of the pipe.
Trước tiên, một thùng chứa và một thùng nhựa được đặt cạnh nhau, với đỉnh của thùng nhựa cao hơn thùng chứa. Hai
bộ ph n này được kết nối bằng một ống dẫn từ đáy thùng nhựa vào bên hông của thùng chứa. Sau đó, một bộ lọc được
xây dựng trong thùng nhựa bằng cách thêm các lớp cát, than và sỏi. Cuối cùng, một vòi nước được lắp đặt ở đáy thùng
chứa, và một vòi khác được đặt ở đỉnh của ống dẫn. Body 2: The process
The process commences by lifting the plastic lid of the barrel and pouring impure water into it. The water then passes through the
filter and travels up the pipe into the drum, where it is stored. When the tap in the drum is opened, potable water is released for use.
Quá trình bắt đầu bằng việc mở nắp nhựa của thùng và đổ nước bẩn vào. Nước sau đó đi qua bộ lọc và di chuyển lên ống
dẫn vào thùng chứa, nơi nó được lưu trữ. Khi vòi nước trong thùng chứa được mở, nước uống được giải phóng để sử dụng. IELTS THÁP EIFFEL
The diagrams below give information about the Eiffel Tower in Paris and an outline project to extend it underground.
Write a report for a university lecturer describing the information shown.
You should write at least 150 words. SAMPLE REPORT Introduction
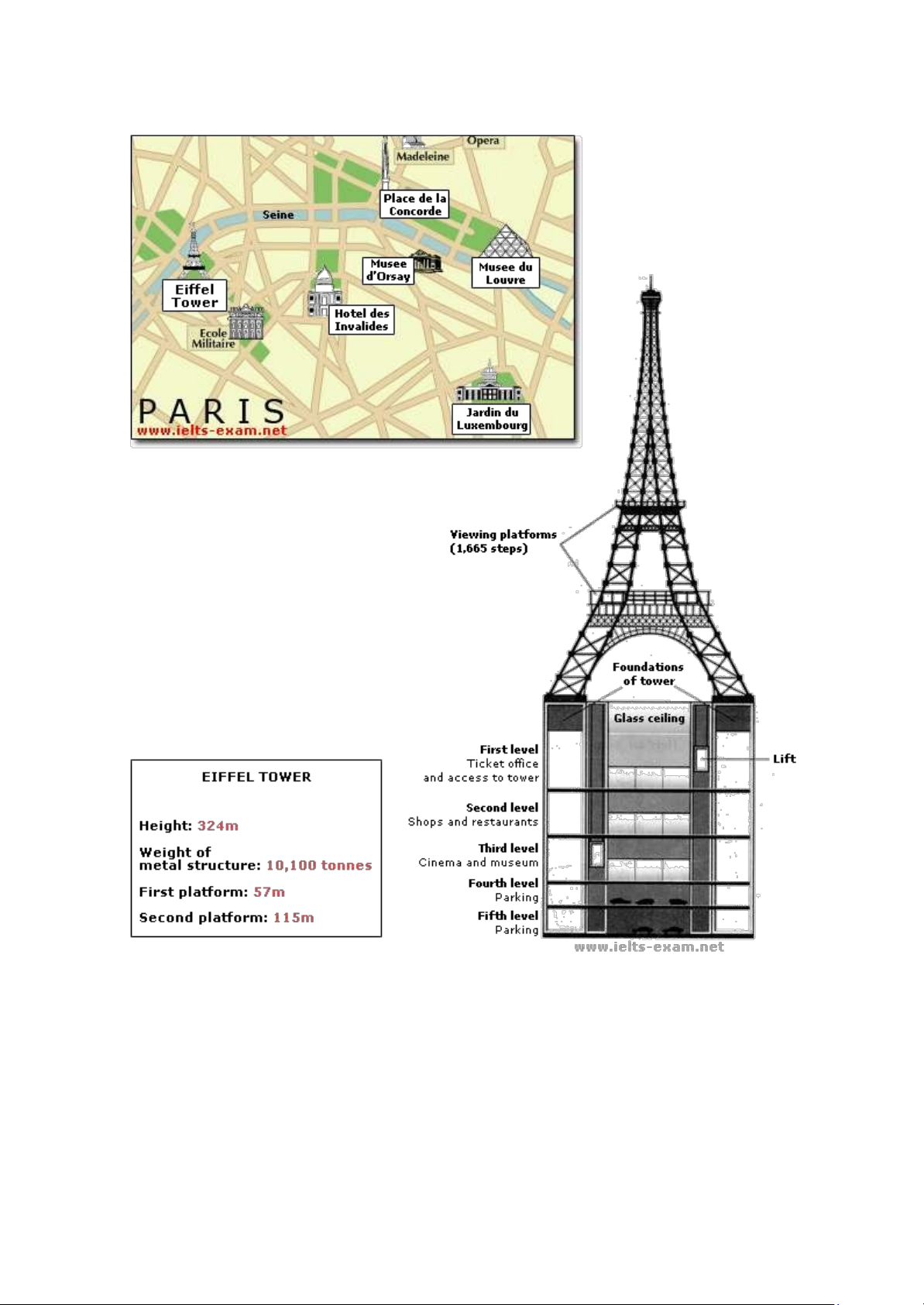
The given map and diagram show the location of Eiffel Tower, which is to be extended with an underground beneath it, and provide
a general information about tower’s parameters.
Bản đồ và sơ đồ đã cho cho thấy vị trí của tháp Eiffel, sẽ được mở rộng với một khu vực ngầm bên dưới, và cung cấp thông
tin tổng quan về các thông số của tháp. Overview
Overall, this report consists of two parts: the structure above the ground and the planned underground extension. The existing
structure of the Eiffel Tower, located between Champ de Mars and the Seine River, is 324 meters tall and includes two viewing
platforms. The planned underground extension will feature five levels with various amenities such as shops, restaurants, and
parking, along with a glass ceiling to enhance the viewing experience.
Tổng thể, bài báo cáo này gồm hai phần: cấu trúc trên mặt đất và phần mở rộng ngầm đang được lên kế hoạch. Cấu trúc
hiện tại của tháp Eiffel, nằm giữa Champ de Mars và sông Seine, cao 324 mét và bao gồm hai tầng quan sát. Phần mở
rộng ngầm dự kiến sẽ có năm tầng với nhiều tiện ích như cửa hàng, nhà hàng và bãi đ u xe, cùng với trần kính để tăng
cường trải nghiệm quan sát.
Body 1: Structure above the ground (currently existing)
The Eiffel Tower, as the map shows, is located between the building of Pare du Champ de Mars and the river Seine. The tower
bases on two huge foundations. Overall height of tower is 324 meters. Being constructed of metal, it weights 10.100 tonnes. There
are two viewing platforms on tower. If measured from the ground, distance to first platform is 57 meters, while second one is 115
meters from the surface of Earth.
Theo bản đồ, tháp Eiffel nằm giữa công viên Champ de Mars và sông Seine. Tháp dựa trên hai nền móng lớn. Chiều cao
tổng thể của tháp là 324 mét. Được xây dựng bằng kim loại, tháp nặng 10.100 tấn. Trên tháp có hai tầng quan sát. Nếu
đo từ mặt đất, khoảng cách đến tầng quan sát đầu tiên là 57 mét, trong khi tầng thứ hai cách mặt đất 115 mét.
Body 2: Structure underground (being planned to be built)
As for underground, which is planned to be built beneath the Eiffel Tower, it is going consist of five floors, two lifts, that will be
used to transfer from one floor to another, and a glass ceiling above the first floor. According to diagram, the first level of
underground will house a ticket office, access to the tower and administration area. Next, second and third levels will incorporate
shops, restaurants, a cinema and a museum as well. The last two levels, will be parking place for various vehicles. And finally, a
ceiling made of glass, is going to be placed on the first floor to play a role of atrium instead of roof. So that visitors are going to feel
better experience viewing the tower itself from underground.
Phần ngầm dự kiến sẽ được xây dựng bên dưới tháp Eiffel, sẽ bao gồm năm tầng, hai thang máy để di chuyển giữa các
tầng, và một trần kính phía trên tầng đầu tiên. Theo sơ đồ, tầng đầu tiên của khu vực ngầm sẽ có phòng bán vé, lối vào
tháp và khu vực hành chính. Tiếp theo, tầng hai và ba sẽ bao gồm các cửa hàng, nhà hàng, rạp chiếu phim và bảo tàng.
Hai tầng cuối cùng sẽ là bãi đ u xe cho các loại phương tiện. Cuối cùng, một trần kính sẽ được đặt trên tầng đầu tiên để
làm nhiệm vụ như một giếng trời thay vì mái nhà, giúp du khách có trải nghiệm quan sát tháp tốt hơn từ dưới mặt đất.
IELTS HỆ THỐNG CUNG CẤP NƯỚC
The following diagram shows how rainwater is reused for domestic purposes.
Write a report for a university lecturer describing the information shown.
You should write at least 150 words. OUTLINE:
Stage 1: Collection and Initial Treatment
● Rainwater is collected in a dam.
● Water from the dam is sent to a water treatment plant.
● Water treatment plant processes the rainwater to produce drinking water.
● Drinking water is supplied to households for consumption.
Stage 2: Household Use and Additional Collection
● Rainwater is also collected from roofs and stored in rainwater tanks adjacent to houses.
● Stored rainwater is used for domestic purposes.
● Stormwater is directed into stormwater treatment systems.
● Treated stormwater flows into nearby waterways.
Stage 3: Wastewater Treatment and Recycling
● Household wastewater is sent to a wastewater treatment plant.
● Wastewater treatment plant recycles the water.
● Excess treated water is released into the river.
● Recycled water is sent back for domestic use. SAMPLE REPORT Introduction
The illustration depicts different steps through which rainwater is collected, processed and released for reuse for domestic consumptions.
Hình ảnh minh họa các bước khác nhau qua đó nước mưa được thu th p, xử lý và tái sử dụng cho các mục đích sinh hoạt. Overview
Overall, rainwater recycling process involves various interrelated phases including the use of the dam, treatment plant, water tank
and the whole process is dependent on rain pour.
Nhìn chung, quy trình tái chế nước mưa bao gồm nhiều giai đoạn liên quan chặt chẽ như sử dụng đ p, nhà máy xử lý nước,
bể chứa nước và toàn bộ quy trình này phụ thuộc vào lượng mưa.
Body 1: Stage 1 - Collection and Initial Treatment
When the rain pours down to earth, a dam is used to collect rainwater and this water is then sent to a water treatment plant in
order to produce drinking water. This water is then released for household consumptions.
Khi mưa rơi xuống đất, một con đ p được sử dụng để thu th p nước mưa và nước này sau đó được gửi đến nhà máy xử lý
nước để sản xuất nước uống. Sau đó, nước này được phân phối để sử dụng trong sinh hoạt gia đình.
Body 2: Stage 2 - Household Use and Additional Collection
The houses have their own rainwater tanks which are placed adjacent to them and used for storing rainwater running from the
roofs. Rainwater stored in tanks is used for domestic purposes as well. Additionally, surface runoff water in the form of stormwater
is preserved and made to flow directly into waterways nearby.
Các ngôi nhà có bể chứa nước mưa riêng được đặt bên cạnh để lưu trữ nước mưa chảy từ mái nhà. Nước mưa được lưu
trữ trong bể cũng được sử dụng cho các mục đích sinh hoạt. Thêm vào đó, nước chảy tràn bề mặt dưới dạng nước mưa
bão được bảo quản và cho chảy trực tiếp vào các đường nước gần đó.


