






Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chương 1: Introduction of OB (tr40) => 95% không thi vào
Chương 2: Foundation of individual behavior => Thi nhiều
I. Attitude and Job satisfaction 1.
Hỏi về khái niệm Attitude (tr113), Job satisfaction (tr116), Job involvement (tr116),
Organization commitment (tr116), nhưng mà dù hỏi gì thì vẫn nên nêu lại lý thuyết của attitude. 2.
Hỏi về component of attitude (tr113), có thể bắt nêu vd
+ Cognitive (người đó suy nghĩ, nhận thức như thế nào về vấn đề hiện tại)
+ Affective (người đó cảm thấy như thế nào về vấn đề đó)
+ Behavioral (người đó có xu hướng hành động như thế nào với vấn đề đó -
Một số vd có thể đc nêu ra như sau Ví dụ trong gtrinh
+ Cognitive: My supervisor gave a promotion to a coworker who deserved it less than i did. My supervisor is unfair
+ Affective: I dislike my supervisor!
+ Behavioral: I’m looking for other work; I’ve complained about my supervisor to anyone who
would listen. Một số vd khác
+ A believe that teamwork would help boost the productivity (cognitive) => A feel very excited
when working better in a good team (affective) => He actively participate in discussing,
sharing ideas and supporting the teammates to achieve the common goals (behavioral)
+ B believe that the recognition from the supervisor is important that it motivate him (cognitive)
=> B feels sad and disappointed as the supervisor can’t realise and appreciate him despite
the effective previous project (affective) => The effort he put in the work is decrease and he
refuse to contribute more idea on the work
Hoặc người ta có thể đưa ra 1 tình huống và bắt mình giải thích dựa trên mô hình component
3. Hỏi về Job Satisfaction - What leads to job satisfaction?
=> Nêu lại khái niệm + What cause Job satisfaction (tr121) -
Đưa ra 1 tình huống + Hỏi xem là tình huống đó thì nhân viên có high job satisfaction hay không?
=> Phần này vẫn phải nêu lại khái niệm + Dựa vào những yếu tố dẫn tới Job satisfaction để suy ra
được người đó có satisfied với công việc hay không (tr121) + Đưa ra giải pháp nếu họ chưa có job satisfaction GỢI Ý GIẢI PHÁP - Nếu Job conditions thấp:
+ Improve the work environment: Provide a comfortable, clean, safe, and modern
workspace (e.g., open office designs, relaxation areas).
+ Promote work-life balance: Introduce flexible working policies, such as remote work,
flexible hours, or reduced hours for employees with young children.
+ Enhance communication: Create two-way feedback channels between employees
and management to quickly resolve arising issues. lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420 +
Training and development: Offer professional and soft skil s training programs
so employees feel valued and have opportunities to grow. -
Nếu là vấn đề về personality:
+ Job-personality fit: Ensure task assignments match employees' personality traits
and strengths. For example, introverts may excel in analytical tasks, while extroverts
may thrive in communication-intensive roles.
+ Individual assessment and growth: Use personality assessment tools (e.g., MBTI,
Big Five) to understand employees and build tailored development plans.
+ Supportive environment: Encourage a culture of mutual recognition and build
diverse teams to strengthen cohesion. -
Nếu là vấn đề về pay:
+ Competitive pay structure: Ensure base salaries and bonuses are competitive with
the market, with annual salary increases based on performance.
+ Performance-based rewards: Implement revenue-sharing bonuses, group
incentives, or rewards for innovative contributions.
+ Attractive benefits: Provide health insurance, educational assistance, paid leave,
and additional perks such as childcare support and transportation allowances.
+ Transparency: Develop clear compensation policies so employees understand how
they are evaluated and rewarded. -
Nếu Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) thấp:
+ Strengthen CSR activities: Focus on programs like environmental protection,
community contributions, or education and healthcare support.
+ Encourage employee participation: Organize company-sponsored volunteering
programs and motivate employees to take part.
+ Transparency and communication: Publicly share positive outcomes of CSR
projects to demonstrate the company’s impact.
+ Integrate CSR into daily work: Set sustainable goals in production and business
operations that employees can contribute to achieving.
=> Phần này viết chọn lọc, lọc những ý phù hợp với case study của mình để viết có thể diễn giải dài ra
4. Họ cũng có thể đưa ra một tình huống và hỏi về impact of satisfied hay dissatisfied employees on
the workplace ( When employees do not like their job what wil they do)
=> Hỏi satisfied employees thì tr124, hỏi dissatisfied thì tr126 => thường vào cái dissatisfied nhiều
hơn để họ còn hỏi lan ra cái mô hình tr127, cần nêu rõ đối với mỗi cách responses trong mô hình
có thể gây ra hậu quả gì, câu nào có hậu quả thì ắt sẽ hỏi giải pháp
GỢI Ý HẬU QUẢ VÀ GIẢI PHÁP -
Exit (Leaving the Organization) Consequences:
+ Increased turnover rates, causing instability in the organization.
+ High costs for recruitment and training of replacement staff.
+ Loss of talent, knowledge, and critical experience.
+ Negative impact on team morale, creating anxiety among remaining employees. Solutions:
+ Enhance employee retention:Improve working conditions and benefits policies, Provide
opportunities for career advancement and development.
+ Identify dissatisfaction early: Conduct regular one-on-one meetings to listen to employee
concerns, Use periodic surveys to detect potential risks. lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
+ Implement exit management strategies: Conduct exit interviews to understand the reasons
for leaving and prevent similar issues. - Voice (Speaking Up) Consequences:
+ If heard and acted upon, it can improve the work environment and resolve issues effectively.
+ Strengthens the bond between employees and the organization.
+ If ignored, employees may feel overlooked, leading to frustration and potential y shifting to Exit or Neglect. Solutions:
+ Foster a listening culture: Create transparent feedback channels and encourage employees to share their opinions.
+ Take tangible actions: Ensure feedback is evaluated seriously and responded to promptly,
Implement small changes when feasible to show positive impacts from feedback.
+ Encourage constructive thinking: Train employees to present feedback positively with
concrete solutions rather than merely criticizing.
- Loyalty (Staying Loyal) Consequences:
+ Temporarily maintains stability within the organization, but unresolved issues may turn loyalty into Neglect or Exit.
+ Long-term loyal employees without support may feel overlooked, demotivated, or disil usioned. Solutions:
+ Recognize loyalty: Reward or acknowledge the contributions of patient employees.
+ Provide proactive support: Schedule regular check-ins with loyal employees to understand their feelings. +
Offer growth opportunities: Provide training programs, chal enging projects, or
advancement opportunities to ensure loyal employees feel valued and developed. -
Neglect (Disengaging from Work) Consequences:
+ Decreased productivity, affecting overall organizational performance.
+ Negative attitudes may spread to other colleagues.
+ Increased risk of mistakes, lowering the quality of work. Solutions:
+ Detect early: Monitor employee performance and behavior to identify signs of neglect.
+ Intervene effectively: Conduct private discussions to understand the reasons behind
disengagement and propose suitable solutions.
+ Reignite motivation: Set clear goals and encourage employees to participate in new
projects or training programs to rekindle interest. 5.
Hỏi về Job involvement (MAGIC)
- Có thể hỏi về khái niệm hoặc lấy ví dụ về MAGIC => này cô mình không dạy nên chắc không
vào đâu nhưng mà nếu vào thì gợi ý ví dụ ở dưới lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Anna, a marketing employee at a nonprofit organization. Below is how the five MAGIC elements apply to her work:
+ Meaning: Anna finds great value in her work because the marketing campaign she
implemented raises public awareness about environmental protection and contributes to reducing plastic waste.
+ Autonomy: Anna is given full authority to decide the entire marketing strategy for the
campaign, including budget allocation, selecting communication channels, and developing creative ideas.
+ Growth: During the campaign, Anna learns to use a new data analytics tool to evaluate
marketing effectiveness, improving her skil s and expanding her professional knowledge.
+ Impact: The result of Anna’s campaign is a large number of people pledging to reduce their
use of plastic, bringing about positive change in the community. She clearly sees that her
work has made a real difference.
+ Connection: Anna feels connected to her colleagues as everyone works together, supports
one another, and shares the joy of achieving outstanding results from the campaign. -
Nếu có câu hỏi tình huống thì họ sẽ đưa ra tình huống
Với 1 công việc ABC gì đó, người quản lý có tính cách và cách lãnh đạo như thế này. Bạn là một
thành viên trong tổ chức đó, bạn có cảm thấy mình có job involvement hay không? (này mình sẽ
đánh giá dựa theo mô hình MAGIC kia, cái nào mình có thì mình ghi là mình có, cái nào không thì
mình ghi là không, giải thích ra) thường người ta sẽ bắt mình đưa ra giải pháp
Hoặc sẽ cho trường hợp là một người có high job involvement, sau đó 1 người quản lý mới xuất
hiện hoặc có 1 sự thay đổi nào đó thì người nhân viên kia tự nhiên low job involvement => Mình sẽ
lại phân tích dựa trên MAGIC => đưa ra giải pháp GỢI Ý GIẢI PHÁP Lack of Meaning: lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Problem: Employees may feel that their work is meaningless and doesn't contribute to a
greater purpose, leading to a lack of motivation and commitment. They might become
disengaged or indifferent to their tasks. Solution:
Link the work to a bigger goal: Explain to employees the impact their work has
on the organization or the community.
Recognize contributions regularly: Acknowledge the efforts and achievements of
employees so they can see the meaning in their work. Lack of Autonomy:
Problem: Employees may feel restricted, with no decision-making power, and may not be
trusted to take ownership of their tasks. This can lead to frustration and a lack of creative drive. Solution:
Provide decision-making power: Al ow employees to have autonomy over how
they carry out their tasks, giving them opportunities to experiment and be creative.
Set clear goals: Establish clear objectives, but give employees the flexibility to choose how to achieve them. Lack of Growth:
Problem: Employees have no opportunities to learn new skil s, face chal enges, or develop
professionally, which can lead to boredom and a feeling of being stuck. Solution:
Offer learning and advancement opportunities: Provide training, mentoring, or
chal enging projects that enable employees to develop their skil s.
Set development goals: Encourage employees to set personal growth goals and
support them in achieving these goals. Lack of Impact:
Problem: Employees may feel their work has no clear results or positive impact, leading to
feelings of worthlessness and lack of motivation. Solution:
Clarify the impact of their work: Help employees understand how their work
contributes to the organization or customers' success.
Reward results: Evaluate and reward the outcomes and positive impact of the employees' work. Lack of Connection:
Problem: Employees may feel isolated, with no connection to their col eagues or the
organization, leading to disengagement and higher turnover intentions. Solution:
Create communication opportunities: Encourage team activities and
connections between colleagues to build positive relationships at work. Foster
a supportive environment: Ensure that employees can seek help and support
from colleagues and managers when needed.
6. Organizational commitment: hỏi về khái niệm, components, người ta có thể cho một tình huống
rồi mình sẽ phân tích tình huống đó là loại cam kết nào => nhưng chắc không vào vì cô mình không dạy cái này
+ Affective: cam kết dựa trên tình cảm nhân viên đó có cảm xúc tích cực về tổ chức
+ Continuance: cam kết dựa trên tính toán là nguyện vọng ở lại tổ chức của người lao động
bởi vì họ nhận thức được những chi phí liên quan tới việc rời bỏ tổ chức. lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
+ Normative: cam kết dựa trên chuẩn mực là mong muốn của người lao động ở lại tổ chức
do họ cảm thấy đó là nghĩa vụ của họ. II. Personality and value 1.
Phần personality hầu như không thi, nếu có sẽ chỉ hỏi
What is the MBTI model? (178) 2. Value (189): -
Tình huống: Những người có giá trị khác nhau xong rồi xảy ra xung đột -
International value, Hofstede dimension (194) - ít thi III. Perception - hay thi ●
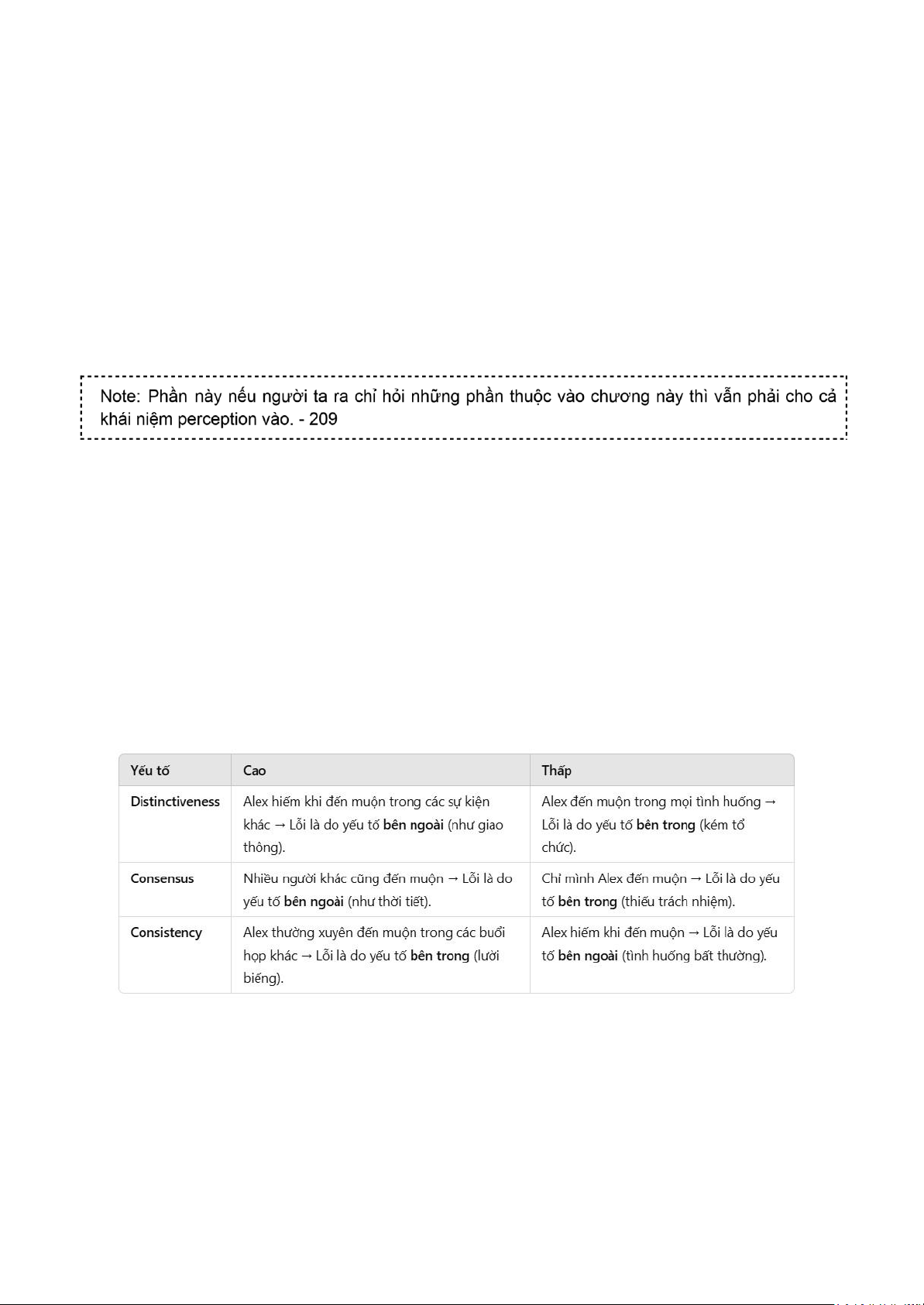
Attribution theory (hay thi nhất) - 211
- Cho tình huống: giải thích theo (3 determining factors:
+ distinctiveness: we want to know whether this behavior is unusual -> yes -> external attribution
+ consensus: if everyone who faces a similar situation responds in the same way, we can say
the behavior shows consensus. If consensus is high -> external +
consistency: more consistent of the behavior -> internal
-> là internal hay external -> Trong TH đó nên làm ntn?
+ Internal y caused behaviors are those an observer believes to be under the personal
behavioral control of another individual. +
Externally caused behavior is what we imagine the situation forced the individual to do.
Ví dụ về 3 yếu tố của Attribution Theory 1. Distinctiveness:
○ Measures whether the person behaves the same way in different situations.
○ Example: Alex is late for today’s meeting. If Alex rarely comes late to other events, this behavior is
considered distinctive (high distinctiveness), and the cause might be an external factor (e.g., traffic).
○ Explanation: High distinctiveness often points to an external cause. 2. Consensus:
○ Measures whether other people in the same situation behave similarly. lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
○ Example: Several others are also late to the meeting. This indicates high consensus, and the cause
is likely external (e.g., a sudden change in the meeting schedule).
○ Explanation: If many others behave similarly, the cause is usually external. 3. Consistency:
○ Measures whether the person behaves the same way in similar situations over time.
○ Example: Alex has been late for several previous meetings. This shows high consistency, and the
cause is likely internal (e.g., lack of discipline).
○ Explanation: High consistency often points to an internal cause. ●
Common shortcuts (không hay thi nếu muốn điểm cao thì nên link tới) -213: : selective
perception, halo effect, contrast effects, stereotyping -> applications of shortcut -tr215
IV. Learning: thường chỉ hỏi khái niệm
Chương 3: DECISION MAKING…: hầu như chỉ vào lý thuyết ●
Rational decision making model:
-> Nêu các bước, diễn giải (chép sách) - tr217 ● Bounced Rationality - ●
Common biases and errors in DM (không thi riêng) - 219 -> sử dụng cái này để giải bài tập
TH cho những lý thuyết khác -> Này để lấy điểm (+) thui. ●
Components model of creativity (3 thành tố): - 229
+ causes (creative potential and creative environment) + creative behavior
+ creative outcomes (innovation)
-> hay hỏi phần lý thuyết, có thể bắt đưa ra ví dụ Nhưng
mình không học phần này nên chắc ko vào đâu
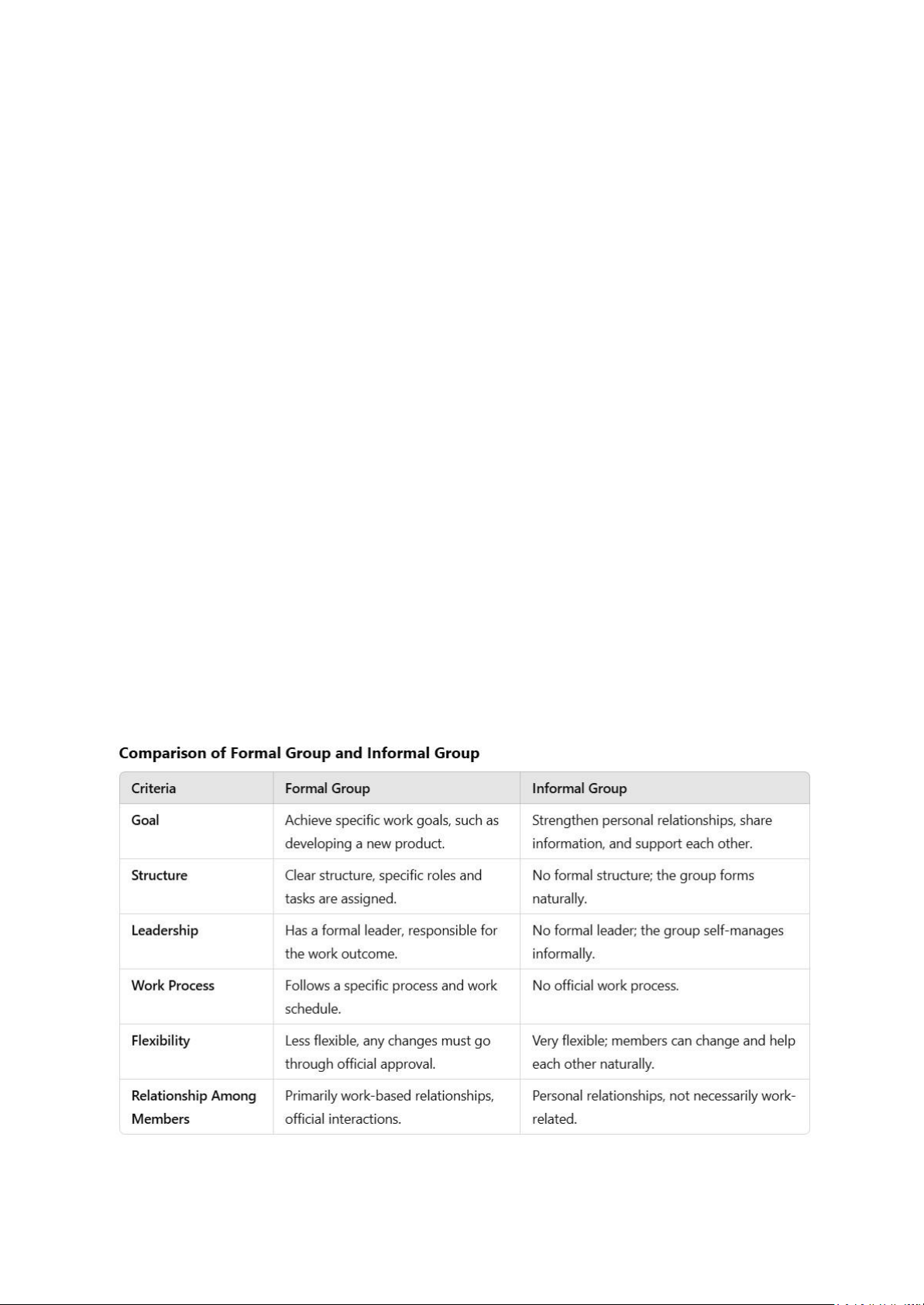
Chương 4: Foundation of Group Behavior 1. Formal group + informal group - Formal group: tr315 - Informal group: tr315 -
Nêu ví dụ liên quan đến workplace: impact positively/ negatively (lấy ví dụ có chiều sâu) GỢI Ý VÍ DỤ Formal Group
A classic example of a formal group is the New Product Development Project Team at XYZ
company. This team is established to research and develop a new product, with the goal of meeting
deadlines and achieving set targets. Structure of the Formal Group:
+ Team Leader: The project manager, responsible for managing progress, assigning tasks, and
reporting to higher management.
+ Team Members: Includes experts from different departments such as marketing, research
and development, finance, and production. Each member has a specific role, such as
market research, product design, financial planning, and overseeing the production process. lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
+ Work Process: Regular meetings are held to track progress, assess results, and adjust plans
as needed. Each member must complete their tasks on time as per the project timeline.
Example of Formal Group Actions:
+ The team organizes weekly meetings to report progress. Members need to adhere to the
group’s guidelines, report their achievements, and present issues that need to be resolved.
+ If there are changes in the plan or additional resources are required, the team proposes and
discusses these adjustments in formal meetings. Informal Group
In XYZ company, apart from the formal project team, there is an informal group made up of
employees from various departments who have a close personal relationship. This group is not
formed to fulfil any specific work duties.
Structure of the Informal Group:
+ Group Leader: There is no formal leader, but there may be a member who is more prominent,
typically someone who is well-liked or approachable.
+ Members: Includes employees from different departments who talk daily, support each other
in both work and personal matters.
+ Work Process: This group does not have any official procedures. The members meet during
breaks to discuss topics unrelated to work, or they assist each other with work problems without formal reporting.
Example of Informal Group Actions:
+ Each morning, the members of the informal group may gather for coffee and share
information about work or personal life issues.
+ During lunch breaks, they might discuss ongoing projects, share difficulties they are facing,
and find ways to support each other without needing approval from leadership. 2.
Giải thích stage of Group Development tr317 -
Lý thuyết (vẽ mô hình + diễn giải) 3. Group properties lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420 - Roles - Norm - Status - Size - Cohesiveness - Diversity
Ví dụ: A cho rằng lđ cần phải… B thì kì vọng lđ phải…. -> 2 người này làm việc có conflict -> sử
dụng lý thuyết về role để giải quyết TH
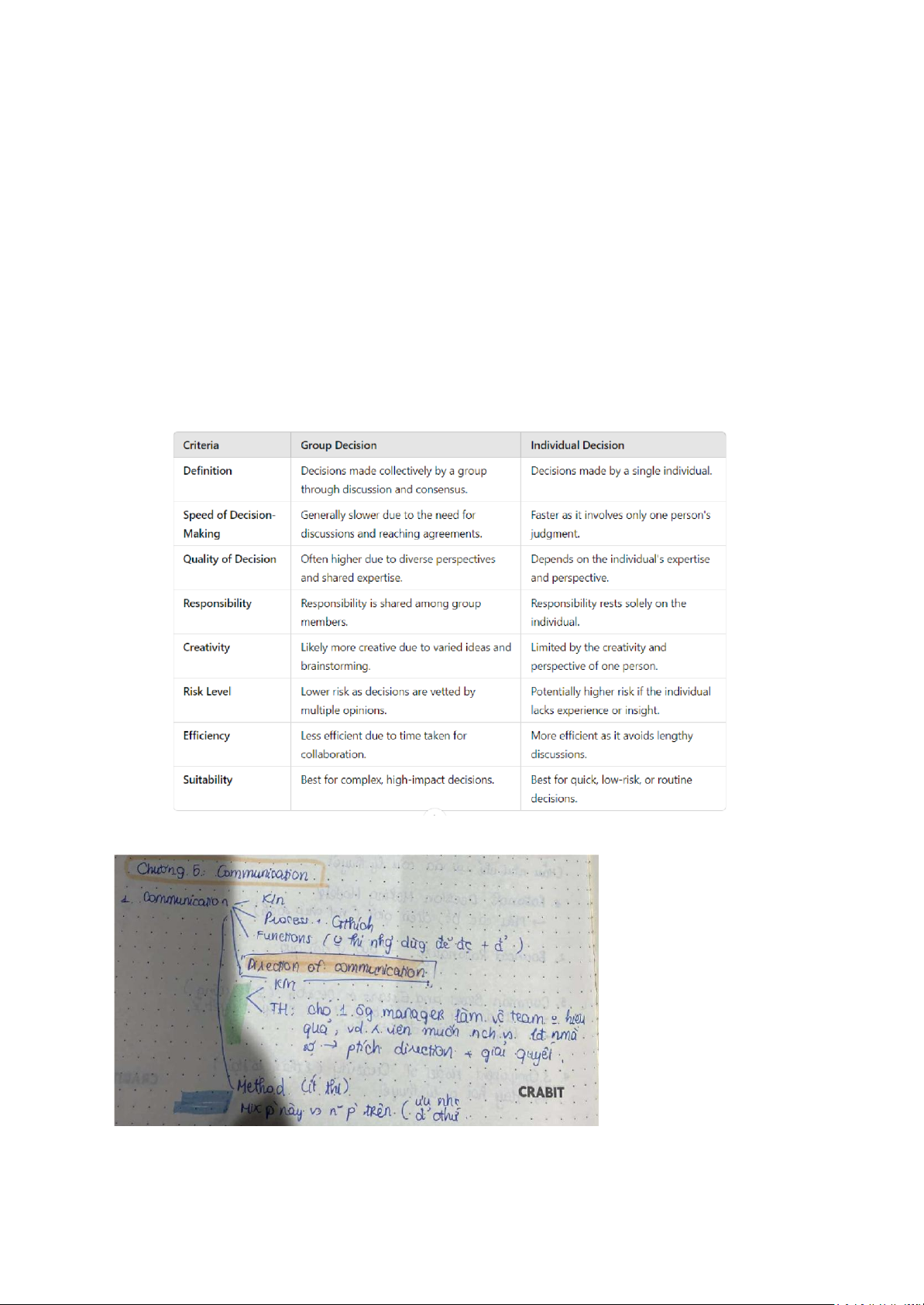
Ví dụ: Người quản lý này tới 1 cty mà họ có 1 cái norm nào đó mà không hiệu quả -> ô tô kê? Group decision: -
hay bắt so sánh group decision và individual decision -
Group decision techniques (thường k thi) -
Barrier to effective communication lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420




