


Preview text:
8. MORPHEMES
A. Definition of Morpheme
A morpheme is a short segment of language that meets three criteria:
1. It is a word or a part of a word that has meaning. (là từ hoặc một phần của từ, mà có nghĩa)
2. It cannot be divided into smaller meaningful parts without violation
of its meaning or without meaningless remainder. (Nó không thể
được chia thành các phần có ý nghĩa nhỏ hơn mà không vi phạm ý nghĩa
của nó hoặc không có phần dư vô nghĩa)
3. It recurs in differing verbal environments (vocabulary) with a
relatively stable meaning. (Nó lặp lại trong các môi trường lời nói khác
nhau với ý nghĩa tương đối ổn định)
B. Free and Bound Morphemes
1. A free morpheme can be uttered alone without meaning.
- Cách diễn đạt khác: The morpheme that can stand alone as a single
word (as a meaningful unit) is cal ed free morpheme.
2. A bound morpheme cannot be uttered alone with meaning.
- Cách diễn đạt khác: + A bound morpheme cannot be uttered in isolation.
+ Segments that cannot stand alone and occurs with another root/stem
are cal ed Bound Morphemes.
- Bound morphemes are also called affixes (prefixes, suffixes and infixes) in English.
- Two bound morpheme cannot occur together but it is necessary for a
bound morpheme to occur with a root/stem.
- Bound bases in English are from Latin and Greek. VD:
▪ Opened: (Open + ed) = root + suffix
▪ Reopen: (Re + open) = prefix + root
▪ Men: (Man + plural) = root + infix (infix makes a change inside a root word) C. Bases
1. A base morpheme is the part of a word that has the PRINCIPLE meaning.
2. Base are very numerous, most of them are free morphemes; but some are bound. E. Affixes
– An affix is a bound morpheme that occurs before or within or after a base.
– 3 kinds: prefixes, infixes, suffixes
+ Prefixes are those bound morphemes that occur before a base (VD:
import, reconsider). Prefixes are commonly single.
+ Infixes are bound morphemes that have been inserted within a word.
+ Suffixes are bound morphemes that occur after a base. Suffixes may pile
up to the number of three or four.
F. Inflectional Suffixes (hình vị biến tố)
- Create a new form of the same word. (Tạo một dạng mới của cùng một từ)
1. They do not change the part of speech.
2. They come last in a word when they are present.
3. They go with al stems of a given part of speech.
4. They do not pile up; only one ends a word.
G. Derivational Suffixes (hình vị phái sinh)
- Create a new word, change the meaning. (Tạo một từ mới, thay đổi nghĩa)
1. The words with which derivational suffixes combine is an arbitrary matter.
2. In many cases, but not all, a derivational suffix changes the part of
speech of the word to which it is added.
K. Immediate Constituents (IC division)
1. A word, a phrase or a sentence is usual y composed of different layers of structure.
2. IC division cut is the way to describe the layers of a word, a
phrase or a clause to identify how many parts it consists of.
3. How to cut the constituents of a word?
The 1st cut is between an inflectional suffix (hình vị biến tố hậu
tố) and the rest of the word. (VD: learn/s; want/ed)
At each cut, one of the IC’s should be, if possible, a free form. (VD: in/dependent)
The cut must ensure the meaning of the whole word. (VD:
re/strain; sing/er; short/en) 9. WORDS
B. Simple and Complex Words (S; Cx)
1. Simple words consist of a single free morpheme. (VD: long, slay)
2. Complex words contain, as their immediate constituents (ICs), either
two bound forms or a bound and a free form) C. Compound Words (Cd)
1. Free forms, usually two, as their immediate constituents.
2. Compound words resemble grammatical structures in that they imply.
3. Compound words can be distinguished from grammatical structures
(Gs) in three ways (p122,123 – không biết tóm tắt sao).
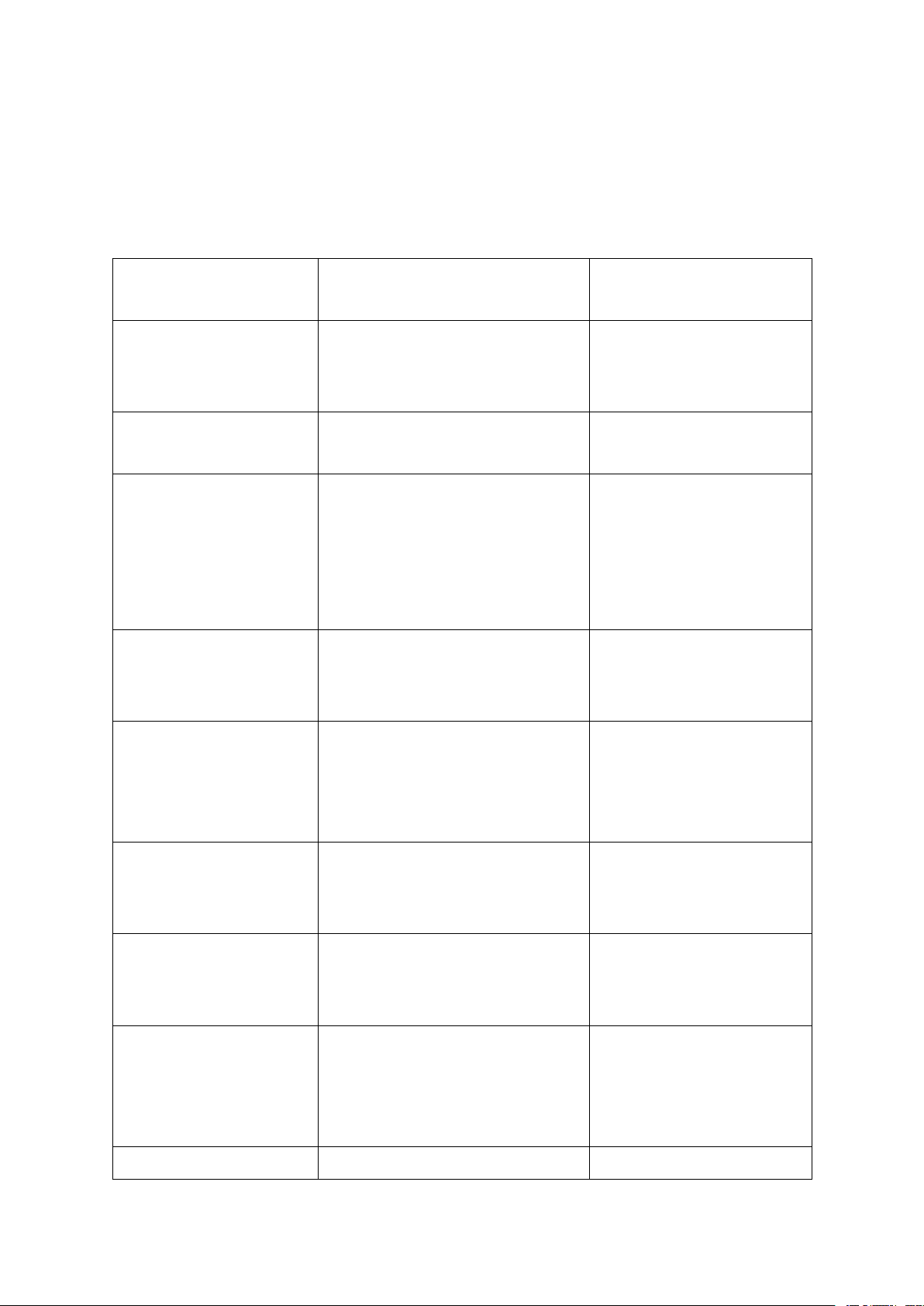
10. PROCESSES OF WORD FORMATION
The joining of two or more words
VD: breakfast, skydive, high A. Compounding into a single word school,… The forming of new words by
VD: disadvise, emplane, re- B. Derivation
combining derivational affixes or ask, teleplay,….
bound bases with existing words
VD: Kodak, nylon, dingbat, C. Invention New word are totally invented goof, blurb The formation of words whose VD: hiss, peewee sound suggests their meaning.
VD: roar (of a waterfall), D. Echoism (sự tạo The meaning is usually sound. clang (of a bell) thành tiếng vang) The meaning may also be the VD: bobwhite
creature that produces the sound.
Cutting off the beginning or the end VD: lab, exam, gym, prom,
E. Clipping (cắt bớt)
of the word, or both, leaving the part math,… for stand to the whole. VD:
A word is formed from the initials or MP (military police), NATO
F. Acronyms (viết tắt)
beginning segments of a succession (North Atlantic Treaty of words. Organization,. )
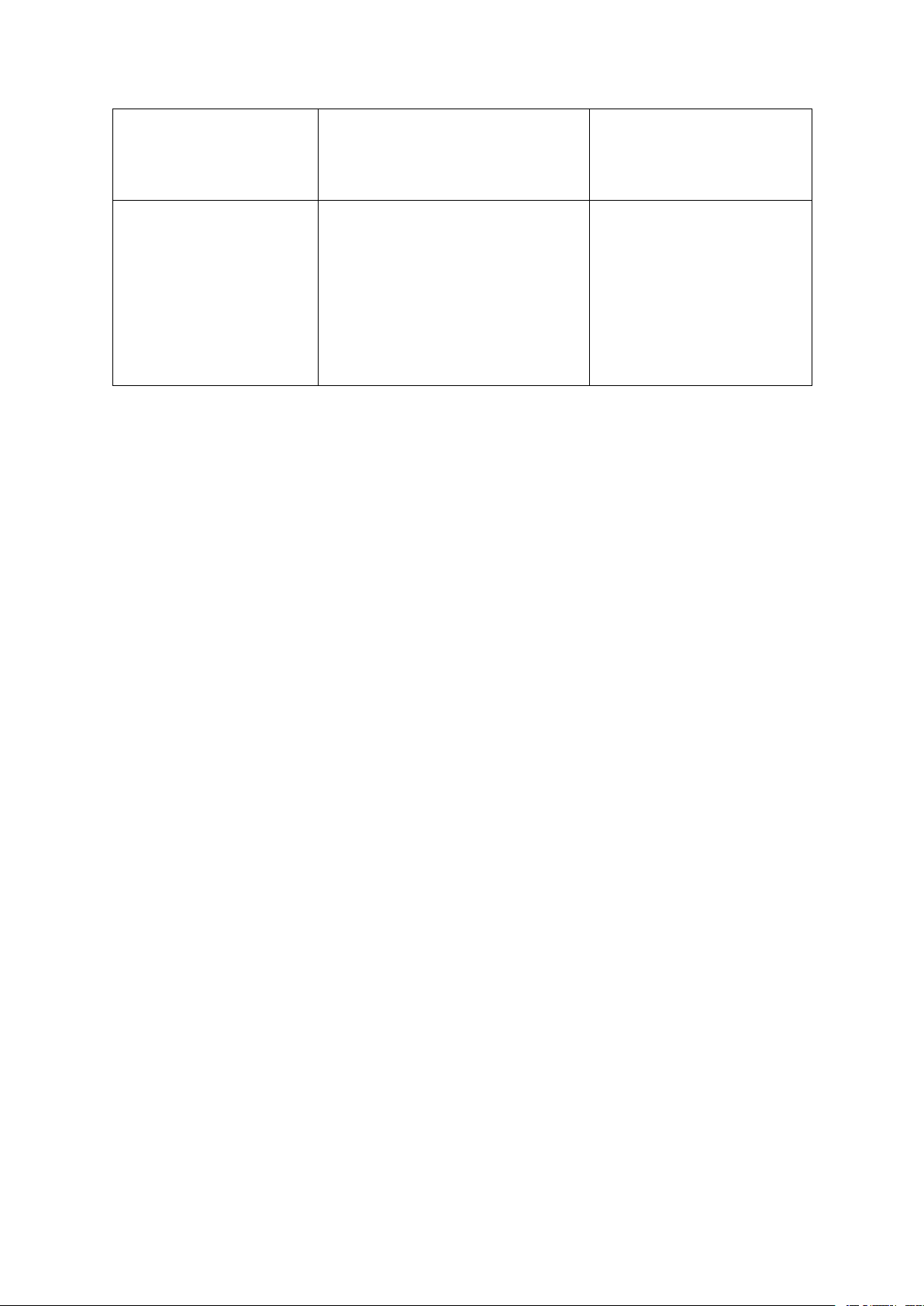
The fusion of two words into one, VD:
G. Blending (pha trộn)
usually the first part of one word
gasohol = gasoline + alcohol with the last part of another.
motel= motor + hotel VD: H. Back-formation
The formation of a word from one
housekeep – housekeeper (đuôi 1 từ cũ) that looks like it derivation.
baby-sit – baby-sitter
Such a process – changing a word, in VD: I. Folk Etymology
part or in whole, to make it more female = femelle
(từ nguyên dân gian) under-standable and more like helpmate = help meet familiar words. J. Antonomasia
The formation of a common noun, a VD: Cashmere Kashmir
(tên 1 người hoặc nơi
verb, or an adj form the name of a (India) chốn từ mới) person or place. Jeans Genoa fustian
The process of forming a new word
VD: pooh-pooh, tiptop,…
by doubling a morpheme, usually
K. Reduplication (điệp
with a change of vowel or initial từ) consonant. Twin-words (p135)
Document Outline
- 8.MORPHEMES
- A.Definition of Morpheme
- B.Free and Bound Morphemes
- C.Bases
- E. Affixes
- F. Inflectional Suffixes (hình vị biến tố)
- G. Derivational Suffixes (hình vị phái sinh)
- K. Immediate Constituents (IC division)
- 9.WORDS
- B. Simple and Complex Words (S; Cx)
- C. Compound Words (Cd)




