




Preview text:
CHAPTER 11—WATER RESOURCES AND WATER POLLUTION MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Water that is used for crop irrigation in southern California’s Imperial Valley originates as snowmelt in the
a. Sierra Nevada mountain range
b. Tehachapi mountain range of southern California c. Rocky Mountains
d. springs that feed the Colorado River in nearby Arizona e. Cascade Mountain range
2. The Colorado River system can be said to provide water and electricity for
a. one of every ten people in the United States
b. 1% of people in the United States
c. 5% of people in the United States
d. 10 million people in the United States
e. The Colorado River does not provide electricity, but provides water for 10% of the U.S. population
3. Which of the following statements about the Colorado River is not true?
a. 14 major dams and reservoirs have been built along the river
b. the system has experienced severe drought since 1999
c. it provides resources to people in 7 states
d. part of the upper basin originates in the state of Wyoming
e. the river still delivers the same amount of water to the sea in the Gulf of California 4. Lake Powell
a. is a reservoir behind Hoover Dam and is the second largest reservoir in the U.S.
b. is a reservoir behind Hoover Dam and is the largest reservoir in the U.S.
c. is a reservoir behind Glen Canyon Dam and is the largest reservoir in the U.S.
d. is a reservoir behind Glen Canyon Dam and is the second largest reservoir in the U.S.
e. is behind Hoover Dam and Lake Mead is behind Glen Canyon Dam
5. Water covers about ____% of the Earth's surface. a. 51 b. 61 c. 71 d. 81 e. 91
6. A water resource that would be categorized as nonrenewable would be
a. water vapor in the atmosphere b. Precipitation
c. surface water in lakes and streams d. confined aquifers e. Snowpack
7. That portion of surface runoff that we can generally count on as a stable source of freshwater from
year to year is best described as a. surface water b. drainage basin c. reliable runoff d. watershed 225 e. precipitation
8. Ultimately, which of the following is the source of energy that continually drives the hydrologic cycle? a. Gravity
b. energy from the sun and gravity c. Electricity d. geothermal energy e. Wind 9. Virtual water is water
a. that exists only in deep underground aquifers
b. that we hope to be able to draw on in coming years
c. that is not directly consumed but is used to provide us with food and other consumer products
d. that comes as precipitation in desert areas
e. that is predicted to be in runoff from snowfields at high altitudes
10. We can say that the United States has _____________freshwater scarcity stress a. No b. very little or minimal c. Average d. Spotty e. Widespread
11. Worldwide, about 70% of the water withdrawn each year is used for a. industrial processes
b. cooling towers of power plants
c. irrigation of croplands and raising livestock d. domestic use
e. water theme parks in tourist areas
12. In the western United States, as compared to the eastern United States, the major water problem(s) is (are) a. Flooding
b. insufficient water for some urban areas
c. chronic drought and insufficient runoff
d. pollution of rivers, lakes, and groundwater
e. insufficient water for industry
13. Which of the following statements is false?
a. The top of the groundwater zone is the water table.
b. The recharge of aquifers below cities is very efficient because of storm drains.
c. In the zone of saturation, spaces in rock and soil are completely filled with water.
d. Rivers of underground water are sometimes found in caverns in aquifers.
e. More than one of these choices is false.
14. The amount of water needed to produce the amount of beef in one single hamburger (most of which is
used to grow the grain to feed cattle) is approximately
a. the same volume as the hamburger is b. 10 gallons c. 16 gallons d. 10 bathtubs full of water e. 16 bathtubs full of water 226
15. The Ogallala is which of the following?
a. a massive desalination plant in the Middle East
b. the world's largest known aquifer
c. a pumping station drawing fresh water from the Great Lakes for use in the S.W. United States
d. a large body of water in Russia that has almost completely dried up
e. a river in the Middle East that flows into the Mediterranean Sea, and has the potential to become
dried up due to extensive irrigation systems
16. Which of the following is not a way to prevent groundwater depletion? a. waste less water
b. subsidize water conservation c. limit the number of wells
d. do not grow water intensive crops in dry areas
e. tax water pumped from wells near surface waters 17. Large dams and reservoirs
a. reduce danger of flooding upstream
b. disrupt migration and spawning of fish
c. cannot be used for outdoor recreation
d. can be used to provide electric power
e. two of these answers are correct
18. Which of the following statements about the Aral Sea is false?
a. Water has been diverted from the Aral Sea and the two rivers that replenish its water for use in manufacturing.
b. The volume of the Aral Sea has dropped by 90%.
c. The salinity levels have risen dramatically.
d. Most native fish species have disappeared.
e. Salts carried by the wind from the dried up lake basin are negatively impacting local crops.
19. Currently, in the United States, groundwater is being withdrawn ____ times faster than it is being replaced. a. 2 b. 4 c. 8 d. 10 e. 20
20. In 2008, Saudi Arabia announced that it will stop producing wheat by 2016 and will from that point on
import wheat to feed its 29 million people. This decision has been made because
a. its major deep aquifer has been depleted by drawing water for irrigation
b. multiple years of severe droughts have depleted the water table
c. this very rich, oil-financed economy can easily import food rather than grow its own
d. desalinization of sea water around Saudi Arabia has contaminated local freshwater reserves
e. oil seepage from oil fields has contaminated local freshwater reserves
21. Which of the following statements about desalination is true?
a. The common methods of desalination are reverse osmosis and transpiration. b. Desalination is expensive.
c. The removed salt can be dumped back into the ocean with no real concerns.
d. Desalination is the best approach to solving irrigation problems.
e. Desalination is the best method of acquiring clear water for drinking.
22. It is most economically and environmentally sound to focus water resource management on a. increasing the water supply
b. controlling the “mining” of groundwater 227
c. reducing unnecessary waste of water
d. developing desalination plants
e. cloud seeding and towing icebergs to arid regions
23. Saltwater intrusion into freshwater (drinking water) supplies can occur when a. land subsidence occurs
b. snowpack is used as drinking water in areas close to saltwater bodies
c. groundwater is withdrawn near saltwater bodies
d. water is drawn from desert lakes to irrigate crops
e. runoff of agricultural fields drains into wells
24. Conflicts within and between countries over scarce water supplies is expected to be most severe in a.
industrialized, developed countries b. South America c. the United Kingdom
d. the Middle East and part of Asia e. all of these countries
25. In some areas of the Ogallala aquifer, water is being pumped
a. four times faster than it is being replenished
b. at the same rate it is being replenished
c. 10 to 40 times faster than it is being replenished
d. It is not possible to determine this, since the aquifer is so far below ground.
e. The Ogallala is not being pumped at this point in time due to a Federal court decision.
26. Solutions to the increasing problem with water shortages in central and southern California include
a. reducing water waste by improving irrigation efficiency
b. not growing water-thirsty crops in this arid climate
c. raising the historically low cost of water to encourage water conservation
d. educating water users as the value of this precious resource
e. reducing water waste by improving irrigation efficiency, not growing water-thirsty crops in this arid
climate and raising the historically low cost of water to encourage conservation
27. According to the World Resources Institute, what percentage of the water that people use throughout
the world is unnecessarily wasted? a. one-tenth b. one-third c. one-fourth d. one-half e. two-thirds
28. Which of the following is true of flood irrigation?
a. It relies solely on water that falls directly on the crop fields in the form of precipitation.
b. It results in 40% inefficient loss of the water applied.
c. It is the primary form of irrigation used in China.
d. It results in 40% inefficient loss of the water applied and it is the primary form of irrigation used in China.
e. At this time, it is the most efficient way to irrigate, from all of the known methods.
29. Which of the following is the most efficient form of irrigation? a. flood irrigation b. center-pivot irrigation c. low pressure irrigation
d. precision sprinkler irrigation e. micro irrigation
30. According to water resource experts, what are the two main causes of water waste? 228
a. lack of government subsidies for improving the efficiency of water use and ignorance about the amount of water being wasted
b. low cost of water to users and lack of government subsidies for improving the efficiency of water use
c. lack of desire to conserve water and knowledge that there is actually enough water on the planet to supply all uses
d. lack of information about efficient irrigation systems and lack of regulation of water use
e. There is a single main cause of water waste and it is the lack of regulation of water use.
31. The smart card water manager system that is used in ___________has typically reduced water and
electricity use, and has reduced household water bills by about _______% a. Singapore, 10% b. Beijing, 40% c. Singapore, 40% d. Brazil, 10% e. Brazil, 40%
32. According to the United Nations, from 30% to 60% of all water supplied in all of the world’s major
cities in developing countries is a. used for crop irrigation
b. lost through leakage of water mains, pipes, pumps, and valves c. recycled as grey water
d. used for watering landscaping e. polluted
33. Which of the following actions will help to decrease the single greatest use of domestic water in the United States?
a. use a drip system in your garden b. use a low-flow shower head
c. use native plants in your landscaping that do not require a lot of extra water
d. install a water-saving toilet tank
e. use grey water to water your houseplants
34. Benefits of floods include all of the following except
a. provision of productive farmland b. refilling of wetlands c. recharging of groundwater
d. filling up of soil air spaces to prevent oxidation of nutrients e. supporting biodiversity
35. Floodplains usually contain a. highly productive wetlands
b. debris that has been deposited during floods
c. high concentrations of agricultural chemical runoff d. pest insect populations e. nutrient poor soil 36. Floods and droughts are a. strictly natural disasters
b. influenced by human activities
c. decreased by increases in human population
d. independent of human activity
e. always predictable and cyclic
37. Humans increase the likelihood of flooding by all of the following activities except a. building on wetlands 229 b. draining wetlands
c. removing water-absorbing vegetation
d. building a park on a riverbank e. building levees
38. Which of the following human activities is thought to be directly linked to why the damage from
Hurricane Katrina was so devastating to the city of New Orleans?
a. the overdraft of groundwater from the region
b. the implementation of xeriscaping in the region
c. the degradation or removal of coastal wetlands in the region
d. the conversion of forests into land used for agriculture
e. the channelization of streams nearby
39. All of the following are actions that the country of Bangladesh is implementing to adapt to sea level
rises due to climate change except
a. using varieties of rice that can better tolerate flooding
b. shifting to new crops such as maize
c. building small ponds that can collect monsoon rainwater to be used for irrigation during dry periods
d. creating a network of earthen embankments to protect against high tides
e. develop a system of capturing wave action during monsoons to run small, local power plants
40. To reduce flooding risks, an environmentalist is most likely to choose a. floodplain management b. a flood control dam c. channelization of streams d. artificial levees
e. artificial levees combined with channelization of streams
41. All of the following are nonpoint sources of water pollution except a. offshore oil wells b. livestock feedlots c. urban lands d. Croplands e. parking lots
42. Which of the following is a point source of pollution? a. acid deposition b. urban streets c. oil tankers d. suburban lawns e. parking lots
43. Which of the following statements is false?
a. Heat lowers dissolved oxygen in streams and rivers.
b. Organic wastes that can be decomposed by aerobic bacteria reduce the amount of oxygen in the water supply.
c. Toxic chemicals released from industries can result in fish kills.
d. Inorganic nutrients such as fertilizers have no adverse effects on aquatic ecosystems.
e. Sediment can cloud water and reduce photosynthesis.
44. Nitrates and phosphates are examples of a. disease-causing agents b. oxygen-demanding wastes c. organic chemicals d. plant nutrients e. Sediment 230
45. Acids, salts, and metals are examples of a. oxygen-demanding wastes b. organic plant nutrients c. inorganic plant nutrients d. inorganic chemicals e. sediment
46. One class of pollutants that can cause excessive growth of algae is a. radioactive substances b. oxygen-demanding wastes c. plant nutrients d. organic chemicals e. Sediment ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
TOP: 11-5 HOW CAN WE DEAL WITH WATER POLLUTION? BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
47. Which of the following decrease(s) photosynthesis in bodies of water? a. disease-causing organisms b. inorganic plant nutrients
c. sediment such as soil or silt d. heat e. organic chemicals
48. An oxygen sag curve occurs when
a. Fish population numbers sag.
b. Heavy metals that have entered a stream bind oxygen molecules and remove them from the available oxygen supply.
c. The breakdown of biodegradable wastes by bacteria lowers the available oxygen in the water for
organisms with high oxygen requirements.
d. Carbon dioxide values exceed dissolved oxygen values.
e. Oxygen content in the air around a particular body of water becomes slightly lower than normal
49. Which of the following statements is false?
a. Rivers are more vulnerable than lakes to contamination by plant nutrients, oil, toxins, and pesticides.
b. Lakes are more susceptible to pollution because of little water flow.
c. Eutrophication is a natural process and can occur without the influence of humans.
d. Human activities can induce cultural eutrophication.
e. Eutrophication is caused by inputs of nutrients from the surrounding land basin.
50. Which of the following developments of cultural eutrophication would occur last? a. fish kills b. blooms of algae
c. increase in aerobic bacteria
d. increase of plants such as duckweed
e. increase in anaerobic bacteria
51. About ____ of the 100,000 medium to large lakes in the U.S. suffer from cultural eutrophication. a. one-fifth b. one-fourth c. one-third d. one-half e. one-tenth 231
52. Assume you are vacationing by a small lake, where you intend to do some fishing. When you arrive at
this lake, you notice a slight sulfur smell. Which phase of cultural eutrophication does this sulfur smell indicate? a. An algal bloom.
b. Anaerobic bacteria are decomposing the aerobic organisms.
c. Aerobic bacteria are decomposing the algae.
d. Fish have died from lack of oxygen.
e. Insect populations in the lake are dying off. 53. Groundwater
a. has turbulent flows that dilute pollutants
b. has large populations of decomposing bacteria that break down degradable wastes
c. is cold, which slows down decomposition rates
d. may take five to ten years to cleanse itself of wastes e. is quickly renewable
54. _______________________ is the only effective way to protect groundwater. a. pollution prevention
b. community-based local clean up c. bioremediation d. sewage treatment e. stream restoration
55. The practice of suspending rust particles in contaminated water, and then drawing out the rust with
hand-held magnets, has been effective in dealing with a. DDT contaminated water b. arsenic contaminated water c. oil contaminated water
d. heavy metal contaminated water
e. acidified water secondary to acid rain
56. Arsenic is released into drinking water a. from inorganic fertilizers
b. from sewage and animal wastes
c. from food processing facilities
d. when any well is drilled down to the water table e. from mining refuse
57. Which of the following statements about underground contaminants is false?
a. Degradable organic wastes do not decompose as rapidly underground as on the surface.
b. There is little dissolved oxygen to aid in degradation of wastes.
c. Waste products are diluted and dispersed quickly in underground aquifers.
d. It can take hundreds to thousands of years for contaminated groundwater to cleanse itself of degradable wastes.
e. In some coastal areas, groundwater has been contaminated by saltwater intrusion.
58. Which of the following aquatic ecosystems receives the vast majority of the global inputs of pollution? a. estuary b. swiftly flowing stream c. deep-water ocean d. coastal parts of the ocean e. slow-moving river 232
59. Which of the following aquatic ecosystems is most capable of diluting, dispersing, and degrading large
amounts of sewage, sludge, and oil? a. estuary b. swiftly flowing stream c. deep-water ocean d. coastal parts of the ocean e. slow-moving river
60. The majority of the oil pollution of the ocean comes from
a. blowouts (rupture of a borehole of an oil rig in the ocean) b. tanker accidents c. environmental terrorism d. runoff from land
e. normal operation of offshore wells
61. All of the following are true about the discharge trading policy except a. is sponsored by the EPA
b. uses market forces to reduce water pollution
c. allows polluters to pollute at higher levels than they have permits for under certain circumstances
d. purchasing of unused polluting credits from permit holders who are polluting below their allowed levels
e. polluters who pollute at higher levels than they have permits for are immediately closed down
62. Which of the following types of sewage treatment are properly matched?
a. primary--removal of pollutants particular to a given area
b. secondary--removal of oxygen-demanding wastes
c. advanced--removal of suspended solids
d. primary - removal of oxygen-demanding wastes
e. primary and secondary both - removal of pollutants particular to a given area
63. The shift to pollution prevention will most likely be the result of
a. bottom-up political pressure
b. elected officials recognizing the benefits of sustainable living
c. financial benefits of pollution prevention inspiring business leaders
d. community cooperatives promoting the idea
e. top-down politics starting at the White House
64. The main sources of lead, mercury and arsenic water pollutants are a. electric power plants
b. inclined landfills, household chemicals, mining refuse and industrial discharges
c. sewage and inorganic fertilizers
d. runoff from streets and parking lots
e. land erosion from farms that have used chemical insecticides
65. Which of the following statements about drinking bottled water is NOT true?
a. Americans are the world’s largest consumers of bottled water.
b. The movement to boycott bottled water consumption is called back-to-the-tap
c. 86% of the bottles containing bottled water are recycled
d. Some of the bottled water that Americans drink comes from as much as 5,500 miles away.
e. BPA is a chemical in the plastic of water bottles that can leach into the water, especially if the bottle is exposed to the sun. TRUE/FALSE 233
1. Most aquifers are rapidly recharged through precipitation that percolates downward through soil and rock.
ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: COMPREHENSION
2. A large amount of the world's drinking water comes from desalination.
ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
3. We are using freshwater unsustainably by wasting it, polluting it and not charging enough for it.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
4. Some water resources are best categorized as nonrenewable.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
5. Drinking is the biggest use of water worldwide. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
6. Flooding increases with economic and urban development.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: COMPREHENSION
7. Eutrophication is a condition of natural nutrient enrichment of a shallow lake, estuary or slow- moving stream. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
8. Global reduction of grain-fed beef consumption would help to reduce water shortages.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: COMPREHENSION
9. One potential problem associated with global warming is that rising sea levels will cause salt
contamination of coastal area soils.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: COMPREHENSION
10. The creation of dams and reservoirs has decreased the annual reliable runoff available for human use. 234
ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: COMPREHENSION
11. Salt from the region of the Aral Sea is being blown onto the alpine glaciers of the Himalayas,
and is causing them to melt at faster than normal rates.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
12. Federal subsidies are provided to U.S. farmers who reduce water use in irrigation.
ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
13. Drip irrigation systems can increase crop yields by 20–90%.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
14. An oligotrophic lake tends to have relatively high levels of dissolved oxygen.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
15. If we protect more wetlands, that will actually increase the threat of flooding.
ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: COMPREHENSION
16. Use of dams, reservoirs and water transfer projects has disrupted ecosystems.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
17. The shrinkage of the Aral Sea has actually altered the climate of the area around it.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
18. Heat is a type of water pollutant.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KOWLEDGE
19. Atmospheric warming will increase water pollution in areas with increased rainfall and areas with prolonged drought.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: COMPREHENSION
20. Cruise ships are a significant source of pollution of ocean water. 235
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
21. The United States is the world’s largest user of water, and wastes about 50% of all water
drawn from surface and groundwater sources.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
22. Land erosion causes water pollution.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
23. Preventing contamination is the least expensive and most effective way to protect groundwater resources.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: COMPREHENSION
24. Water in a tap in Palm Springs, California, could have originated in northwestern Colorado. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE COMPLETION
1. ____________________ are deep underground sources of freshwater found between the porous
geological layers of sand, gravel, or bedrock. ANS: Aquifers PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
2. When a lot of water is pumped from an aquifer, or when there is a dry spell, the
____________________ sinks lower. ANS: water table
PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
3. ____________________ involves removing dissolved salts from ocean water or from to increase supplies of freshwater. ANS: Desalination 236
PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
4. A flood happens when water in a stream overflows its normal channel and spills into the adjacent area,
called a(n) ____________________. ANS: floodplain
PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
5. One of the most serious overdrafts of groundwater is in the United States in the lower half of the ________________aquifer. ANS: Ogalalla
PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
6. ____________________ is the name given to the natural nutrient enrichment of a shallow lake. ANS: Eutrophication PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
7. Withdrawing massive amounts of groundwater can cause a condition called____________ ______________ ANS: land subsidence
PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
8. ____________________ keep the price of water so low that users do not worry about wasting water. ANS: Subsidies
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
9. About ____________% of the freshwater used in the United States is unnecessarily wasted. ANS: 50 PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
10. Human activities can greatly accelerate the rate at which nutrients and organic substances enter
aquatic ecosystems from their surrounding watersheds in a process called ______________ _______________. 237 ANS: cultural e utrophication
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
11. Spaces in rock and soil called the ____________________ are completely filled with water. ANS: zone of saturation
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
12. The LifeStraw is a portable ____________________that eliminates many bacteria and viruses that are drawn into it. ANS: water filter (lọc)
PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
13. The country with the highest percentage of agricultural land irrigated with drip irrigation is ____________________. ANS: Cyprus PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
14. In the United States and most other developed countries, there has been an increase in the number and
quality of _______________ treatment plants since the 1970’s. ANS: wastewater PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
15. ________________is slower to cleanse itself of contaminants than ____________________
_______________ ________________is.
ANS: Groundwater, flowing surface water
PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
16. Drip irrigation is used on ____________________%of irrigated crop fields in the United States, and
____________________% of irrigated crop fields worldwide. ANS: 4, 1 238
PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE
17. About _________% of the garbage in the huge rotating masses of plastic and other trash in the Pacific Ocean comes from land. ANS: 90 PTS: 1 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: KNOWLEDGE MATCHING
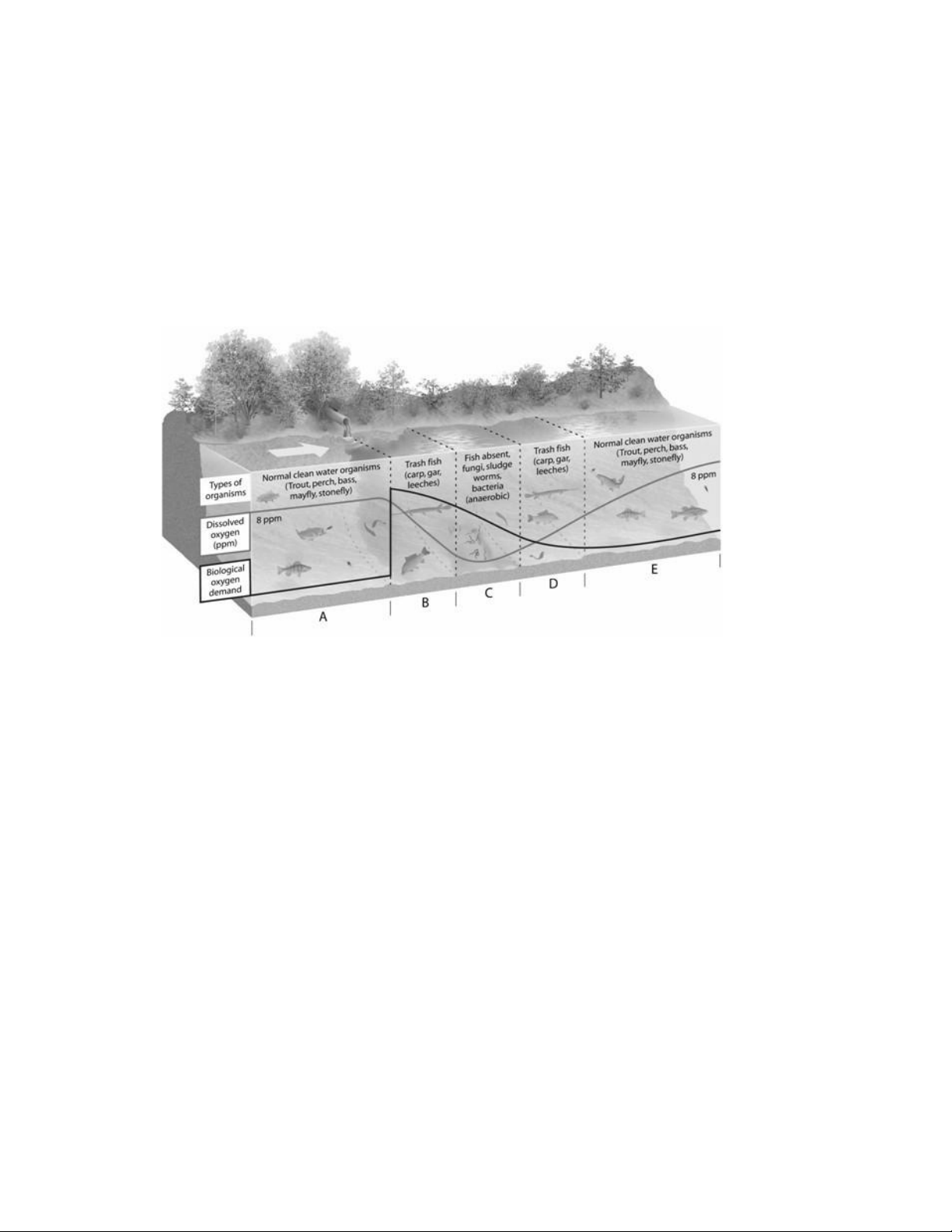
1. On the dilution and decay of degradable wastes figure, choose the zone in which populations of
organisms with high oxygen requirements will most likely be eliminated.
2. On the dilution and decay of degradable wastes figure, choose the zone in which the breakdown of
degradable wastes by bacteria starts to deplete the dissolved oxygen.
3. On the dilution and decay of degradable wastes figure, choose the zone in which the water has
recovered from oxygen-demanding wastes and heat.
4. On the dilution and decay of degradable wastes figure, choose the zone in which the water needs time
and must have an adequate flow rate.
5. On the dilution and decay of degradable wastes figure, choose the zone in which the bacteria have
not started the decay of degradable, oxygen-demanding wastes. 1. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate OBJ: Labeling 2. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate OBJ: Labeling 3. ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate OBJ: Labeling 4. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate OBJ: Labeling 5. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate OBJ: Labeling
BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: COMPREHENSION
Match the items listed below with the appropriate choice 239
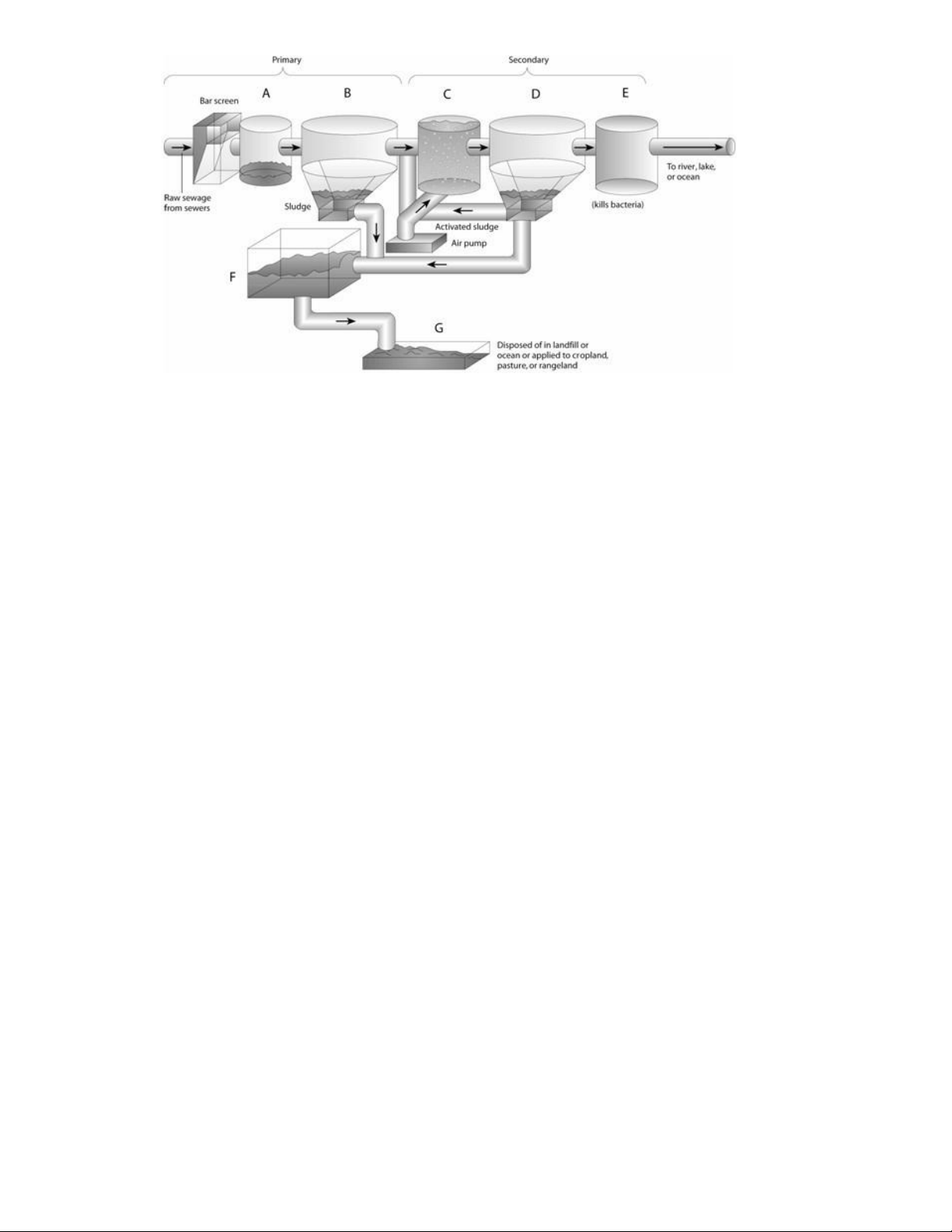
6. On the primary and secondary sewage treatment figure, choose the letter that represents where
bacteria are killed and the water is clean.
7. On the primary and secondary sewage treatment figure, choose the letter that represents where sludge
is dried before being disposed of.
8. On the primary and secondary sewage treatment figure, choose the letter that represents where the water is aerated.
9. On the primary and secondary sewage treatment figure, choose the letter that represents where large
floating objects and solids are removed.
10. On the primary and secondary sewage treatment figure, choose the letter that represents where
activated sludge settles out in the biological process of sewage treatment.
11. On the primary and secondary sewage treatment figure, choose the letter that represents where
suspended solids settle out as sludge in the physical process of sewage treatment.
12. On the primary and secondary sewage treatment figure, choose the letter that represents where all the
sludge is combined before drying. 6. ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate OBJ: Labeling 7. ANS: G PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate OBJ: Labeling 8. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate OBJ: Labeling 9. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate OBJ: Labeling 10. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate OBJ: Labeling 11. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate OBJ: Labeling 12. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate OBJ: Labeling
BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: COMPREHENSION SHORT ANSWER
1. Writer Jacques Leslie, in his Harper’s Magazine article of July 2000, made this statement: “Las Vegas
is America’s city of fantasy, and water, not wealth, is its greatest fantasy of all. Comment on this
statement using information from this chapter. ANS:
Answers may vary but should focus around the comments in the Core Case Study that indicate if it
were not for dams on the Colorado River, the area we know as Las Vegas would be uninhabited desert. PTS: 5 DIF: Difficult OBJ: Critical Thinking 240 BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: ANALYSIS
2. Many of the world’s large rivers flow from one state or province to another, or even through several
others. The Colorado River and Mississippi River are examples of this. In many instances, they flow
from one country to another. Discuss the potential problems that arise from this simple geographical
fact. For example, what potential problem arises if the irrigation water used in Nebraska was polluted
or contaminated as the water moved through South Dakota? ANS:
States, provinces or even countries downstream may suffer the consequences of too many diversions
upstream, or pollution that originates upstream. This situation could lead to lawsuits between states in
a single nation, or legal battles or even wars between nations. The Middle East, for example, is an
area where significant conflicts over water sharing is expected to increase. PTS: 3 DIF: Moderate OBJ: Critical Thinking BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: ANALYSIS
3. List in order, from largest to smallest, the uses of water drawn from groundwater and surface water in
the United States. Also state what the percentages of use are. Include at the end how the drinking
water that is used in your city or town is acquired. ANS:
41% Removing heat from electric power plants 37% Irrigation 13% Public water supplies 5% Industry 4% Raising livestock
End comments will varying depending on whether the student lives in an area with freshwater supplied
directly from a river, or a reservoir, or is drawn from wells. Some students may be unaware of the
source of their drinking water. The point of this question is to make them become aware. PTS: 3 DIF: Easy
BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: COMPREHENSION
4. Hoover Dam was built in the 1930’s on the Colorado River, and at that time was extremely important
as an employment project. The United States was just coming out of the Great Depression and it was
viewed as a life-saver by thousands of people across the country. Now this dam is 80 years old.
Drawing from information in this chapter about aging dams, what is a severe problem that could be expected? ANS:
Aging dams typically fill up with mud and silt within 50 years. PTS: 2 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: ANALYSIS ESSAY 241
1. In a freshwater river or stream, clearly explain what causes an oxygen sag curve and how this can
impact natural populations in that ecosystem. ANS:
If there are high quantities of organic materials added into a body of water, these materials will be
broken down by bacteria. This process can deplete dissolved oxygen in a region of a river, creating an
oxygen sag curve. This can reduce or eliminate populations of organisms with high oxygen
requirements. The depletion of oxygen could also be caused by the addition of thermal pollution.
PTS: 3 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: COMPREHENSION
2. Clearly explain how soil erosion, associated with poor agricultural practices, can lead to a decrease in
dissolved oxygen in bodies of water. ANS:
Poor agricultural practices that result in soil erosion allow for increased levels of silt to enter into
bodies of water. This silt can result in increasing levels of turbidity (cloudiness) in the water column.
This then prevents sunlight from penetrating the depths of the water and limits photosynthesis. In this
way it can result in declining levels of dissolved oxygen in the water. PTS: 4 DIF: Moderate
BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: APPLICATION
3. Explain the advantages and disadvantages of large dams and reservoirs. ANS: Advantages: -provides irrigation water -provides drinking water
-useful for fishing and recreation -produces cheap electricity -reduces downstream flooding Disadvantages
-flood land under the reservoir displaces people and destroys croplands and forests
-large amounts of water are lost from the surface of the reservoir through evaporation 242
-deprives downstream areas of nutrient-rich silt
-risk of failure and devastating downstream floods -
disrupts migration and spawning of fish
PTS: 3 DIF: Easy BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: ANALYSIS
4. List at least five things you are willing to do to help eliminate water waste. As part of your answer
explain why these things are important. ANS:
The answers to the first part of this question will be variable, but will likely come from this list:
-Use water-saving showerheads, toilets, and faucet aerators.
-Take short showers, and shower rather than take baths.
-Repair household water leaks.
-Turn off sink faucets when brushing teeth or shaving.
-Wash only full loads, or use lowest possible load setting for small loads.
-Use grey water for yard and plant watering.
-Wash cars using a bucket of soapy water and spray from hose only to rinse.
-Only use commercial carwashes that recycle water.
-Replace lawn with native plants that use little water.
-Water lawns only in early a.m. or evening.
-Use drip irrigation and mulch for gardens and flowerbeds.
These actions are all important because in the United States about half of water that is drawn from
surface or groundwater for our use is wasted. PTS: 5 DIF: Moderate
BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: EVALUATION
5. Using statistics presented in this chapter, discuss the problem with groundwater contamination in the United States. ANS:
Answers will vary somewhat, but the basic statistics that should be included, at a minimum, are these:
An EPA survey of 26,000 industrial waste ponds and lagoons found that one-third of them had no
liners to prevent toxic wastes from leaking into aquifers. One-third of these sites are within a mile of a
drinking water well. Almost two-thirds of America’s liquid hazardous wastes are injected into the
ground in disposable wells, some of which leak into aquifers used as drinking water sources. 243
By 2008, the EPA had cleaned up about 357,000 of the more than 479,000 underground tanks that
were leaking gasoline, diesel fuel, home heating oil or toxic solvents into groundwater.
PTS: 5 DIF: Moderate BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: APPLICATION
6. A recent Time magazine article discussed the profession of farming in the United States. The theme of
this article was the affluence of some farmers, and the fact that it is a very profitable career to have.
Discuss this fact, now that you are informed on some of the subsidies that traditional agriculture
receive. Keep in mind, also, the value of crop production and farming to our country. Weigh also the
profitability of such careers as being a professional athlete, an actor or actress, a celebrity, a Wall
Street CEO, and include comments on this as part of your answer. ANS:
Answers to this question will vary widely. The point of this question is having the student think about
a reasonable solution to the idea of subsidies for farmers, and yet also consider the value of this
profession to our country. Grading should be based on the quality and clarity of writing and the
presentation of reasonable solutions that are in line with the themes of sustainability. PTS: 5 DIF: Difficult BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: ANALYSIS 244