Trắc nghiệm Mạng máy tính | Trường Đại học Khoa học Tự nhiên, Đại học Quốc gia HCM
Trắc nghiệm Mạng máy tính | Trường Đại học Khoa học Tự nhiên, Đại học Quốc gia HCM được sưu tầm và soạn thảo dưới dạng file PDF để gửi tới các bạn sinh viên cùng tham khảo, ôn tập đầy đủ kiến thức, chuẩn bị cho các buổi học thật tốt. Mời bạn đọc đón xem!
Môn: Mạng máy tính (CSC)
Trường: Trường Đại học Khoa học tự nhiên, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh
Thông tin:
Tác giả:





Preview text:
CHAPTER 1 – REVIEW CHAPTER 1
1.How manny layers does the TCP/IP model have? => 4
2. How manny layers does the OSI model have? =>7
3.From the bottom, what is the fourth layer of the OSI model? => Transport
4.from the bottom, what is the fist layer of the TCP/NC model? => Network Access
5.In the OSI model, can the Network layer interact directly with the Data Link layer? (e.g, sending data, getting data) => No
6. which organization owns this logo?
=> Internet Engineering Task Force
7. wWhat is the maximum size of a TCP/IP packet in default? =>512 Bytes
8. What is the information of 1, 2, 3, and 4?
=> 1: TCP header; 2: IP header; 3: Frame header; 4: Frame trailer
9. What does this sentence describe?
"It is the overall effective transmission rate, taking into account things like transmission overhead,
protocol inefficiencies, and perhaps even competing for traffic." => throughput
10. What does this sentence describe?
"It is the amount of usable data delivered to the receiving application." => Goodput
11. About the Propagation delay, when the interface sends a packet on a 2000 km cable with a
propagation speed of 200 m/µsec (= 200 km/ms, about 2/3 the speed of light), the first bit will not
arrive at the destination until X ms later. What is the value of X? =>10
12. The basic of "Forwarding table" is the pair of: =>
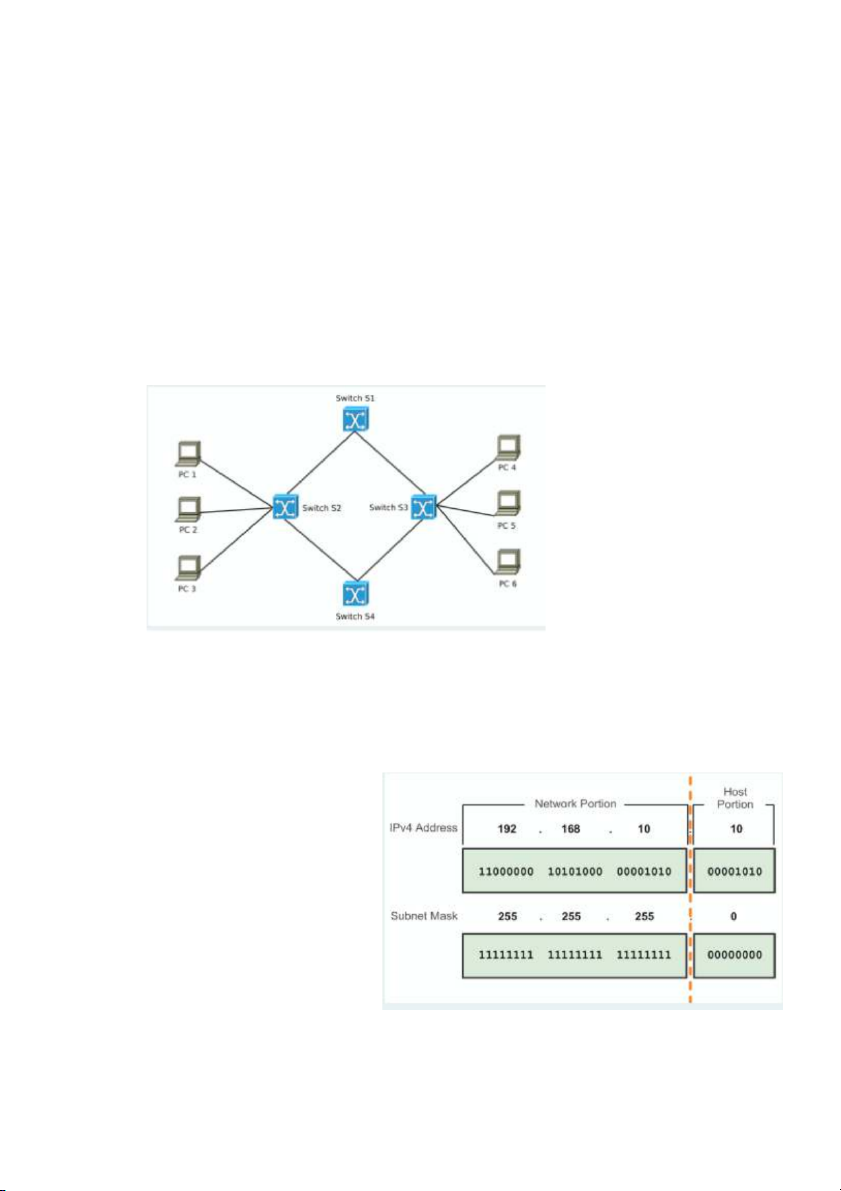
13. What is the type of this network? => Loop
14. What does "802.11" mention? => Wi-Fi standard
15. Which company produced the connection card, which has the MAC address of "18-60-24-85- 0F-22"? => Hewlett Packard
16. What is the IP network address in this figure? => 192.168.10.0
17. The IP layer handles the packet as: => Connectionless
18. The transport layer handles the packet as: => Connection-Oriented
CHAPTER 1 – Q2 – IP FOEWARDING
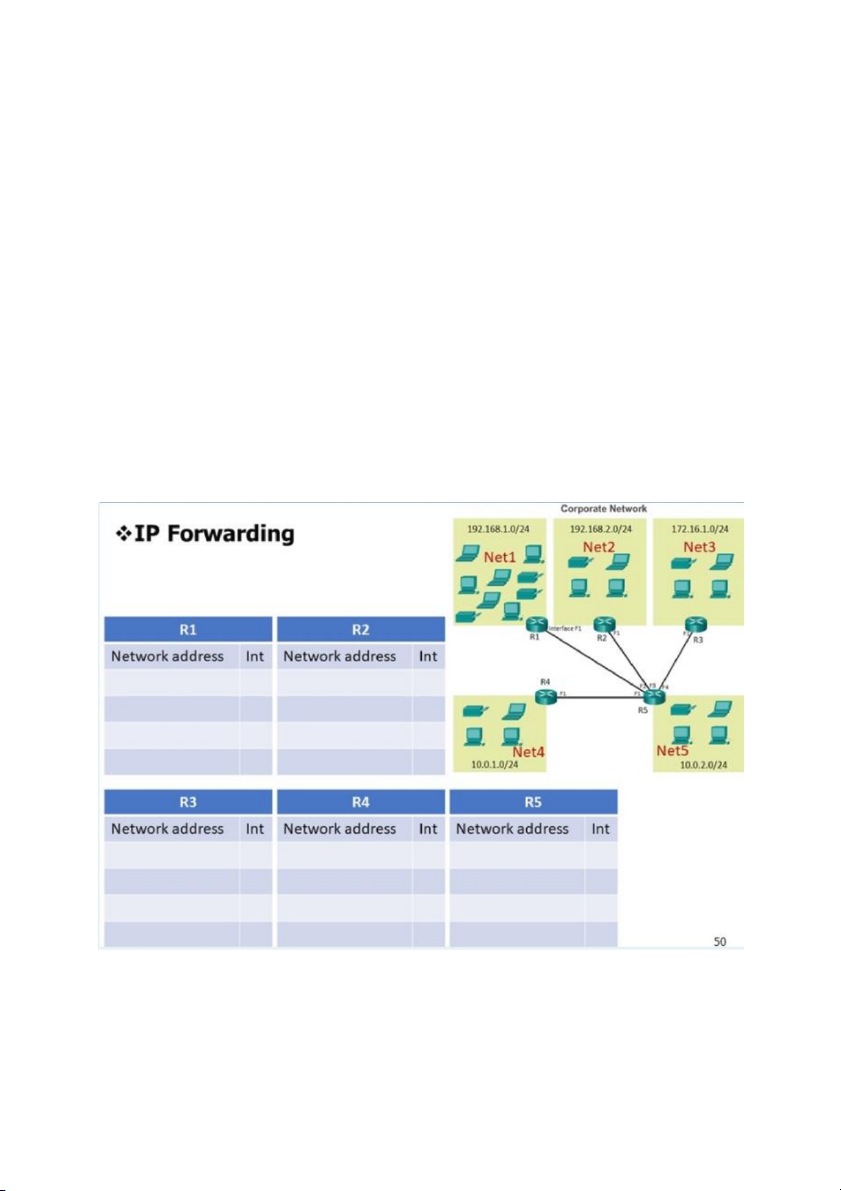
1. Finish the R1's forwarding table. (slide 50) Please answer with format:
/Mask>:,/Mask>:,...,/:Note:
a. The entries need to be in the order of the network name (Net1, Net2,...,Net5)
b. Do not add SPACE to the answer.
Ex: 192.168.1.0/24:F1,192.168.2.0/24:F2,192.168.3.0/24:F3 =>
192.168.2.0/24:F1,172.16.1.0/24:F1,10.0.1.0/24:F1,10.0.2.0/24:F1
2. Finish the R2's forwarding table.
=> 192.168.1.0/24:F1,172.16.1.0/24:F1,10.0.1.0/24:F1,10.0.2.0/24:F1
3. Finish the R3's forwarding table
=> 192.168.1.0/24:F1,192.168.2.0/24:F1,10.0.1.0/24:F1,10.0.2.0/24:F1
4. Finish the R4's forwarding table
=> 192.168.1.0/24:F1,192.168.2.0/24:F1,172.16.1.0/24:F1,10.0.2.0/24:F1
5. Finish the R5's forwarding table
=> 192.168.1.0/24:F2,192.168.2.0/24:F3,172.16.1.0/24:F4,10.0.1.0/24:F1 CHAPTER 4 Q1 FRAGMENTATION
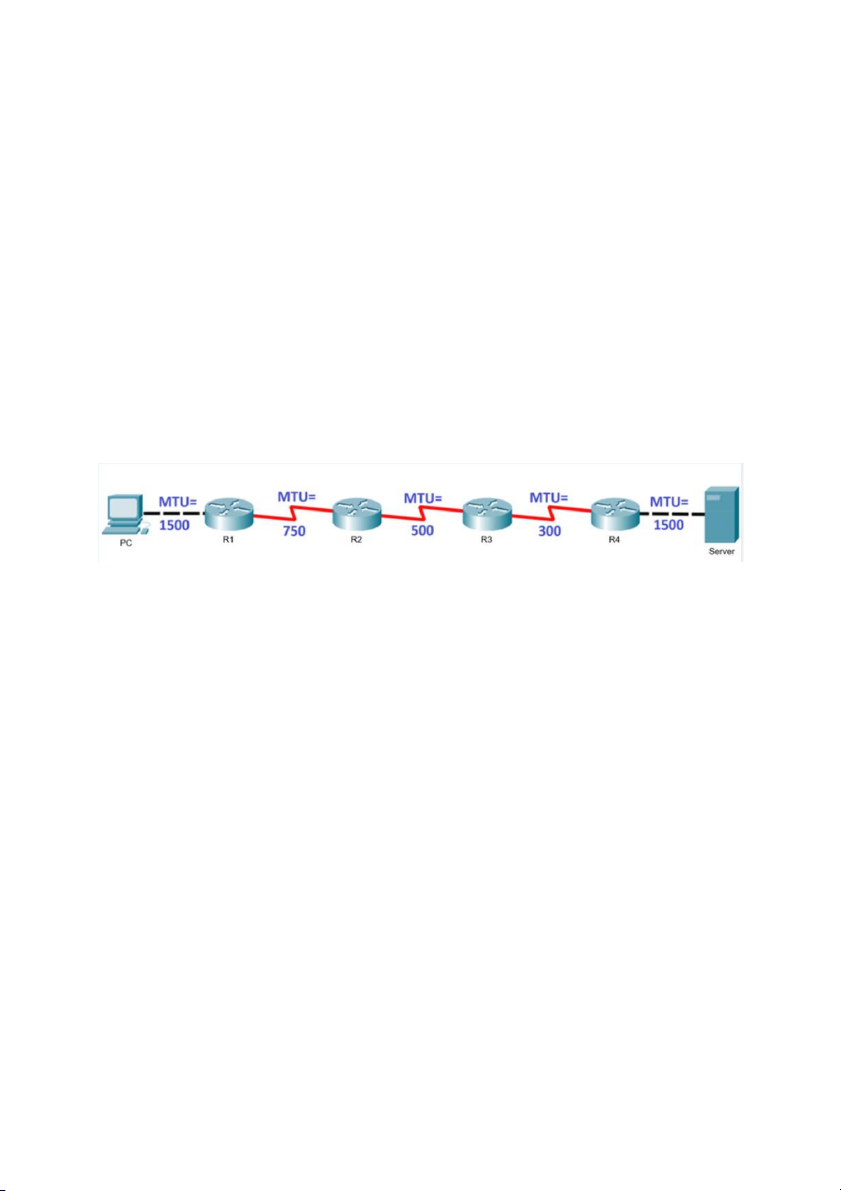
1. PC sends to Server an IPv4 packet with the size of 1500 Bytes.
The MTU of the links is configured as the Figure.
What is the size of the original payload? => 1480
2. At R1, how many fragments will be sent (to R2)? => 3
3. At R2, how many fragments will be sent (to R3)? => 5
4. At R3, how many fragments will be sent (to R4)? => 7
5. At R1, what is the value of the FragOffset of the fragments? Note:
- Enter the answer with the format of ....,...,...,....
- Please do not add any space to the answer. - Ex: 0,500,1000 => 0,91,182 ; 0,728,1456
6. At R2, what is the value of the FragOffset of the fragments? Note:
- Enter the answer with the format of ....,...,...,....
- Please do not add any space to the answer. - Ex: 0,500,1000 => 0,60,91,151,182 0,480,728,1208,1456
7. At R2, what is the value of the FragOffset of the fragments? Note:
- Enter the answer with the format of ....,...,...,....
- Please do not add any space to the answer. - Ex: 0,500,1000 => 0,60,91,151,182 0,480,728,1208,1456
8. At R3, what is the value of the FragOffset of the fragments? Note:
- Enter the answer with the format of ....,...,...,....
- Please do not add any space to the answer. - Ex: 0,500,1000 => 0,35,60,91,126,151,182 0,280,480,728,1008,1208,1456
9. At R4, what is the value of the FragOffset of the fragments? => 0,35,60,91,126,151,182 0,280,480,728,1008,1208,1456
10. At R1, what is the value of the MoreFragment of the fragments? => 1,1,0
11. At R2, what is the value of the MoreFragment of the fragments? => 1,1,1,1,0
12. At R3, what is the value of the MoreFragment of the fragments? => 1,1,1,1,1,1,0
13. At R4, what is the value of the MoreFragment of the fragments? => 1,1,1,1,1,1,0 IP SUBNET
Give you the IP network 172.16.0.0/16.
Let dividing it into 32 subnets having the same number of hosts.
1. How many useable IP addresses (can assign to the device) in each subnet? => 2046 2. What is the 15th subnet? => 172.16.112.0/21
3. What is the broadcast address of subnet 20? => 172.16.159.255
4. What is the first useable IP address of subnet 25? => 172.16.192.1 IP SUBNETING 2
We have the network address of 172.16.0.0/16.
Divide the network address into several subnets and each subnet reserves to 1000 hosts.
1. How many subnets are there? => 64 2. What is the 50th subnet? => 172.16.196.0/22
3. What is the first configurable IP address of the subnet 15? => 172.16.56.1
4. What is the broadcast address of the subnet 7? => 172.16.27.255 ADVANCED IP SUBNETING
We have the network topology below.
The request for the number of host of each network following: - Subnet 1: 2000 hosts - Subnet 2: 100 hosts - Subnet 3: 500 hosts - Subnet 4: 1000 hosts - Subnet 5: 2 hosts - Subnet 6: 2 hosts
Use the VLSM method to divide the IP network of 172.16.0.0 to achieve the above request. 1.
Enter the IP network address of the Subnet 1 as the answer => 172.16.0.0/21
2. Enter the IP network address of the Subnet 2 as the answer: => 172.16.14.0/25
3. Enter the IP network address of the Subnet 3 as the answer: => 172.16.12.0/23
4. Enter the IP network address of the Subnet 4 as the answer: => 172.16.8.0/22
5. Enter the IP network address of the Subnet 5 as the answer: => 172.16.14.128/30
6. Enter the IP network address of the Subnet 6 as the answer: => 172.16.14.132/30
7. Enter the IP broadcast address of the Subnet 1 as the answer: => 172.16.7.255
8. Enter the IP broadcast address of the Subnet 2 as the answer: => 172.16.14.127
9. Enter the IP broadcast address of the Subnet 3 as the answer: => 172.16.13.255
CHAPTER 4 – REVIEW CHAPTER 4B
1. What is the IPv4 loopback address? => 127.0.0.0
2. A non-router host with multiple non-loopback network interfaces is often called: => Multihomed
3. What protocol does the host use to look up the LAN address (e.g., MAC address)? => ARP
4. When a client wants to get a new IP address from the DHCP server, what is the last packet that
the client sends to the DHCP server? => DHCPREQUEST
5. There are ten (10) tandemly arranged routers among the Source (called host A) and the Sink
(called host B). If the host A uses the "tracert" command to print the route to host B, what is the
largest value that TTL can reach? => 11
6. As an administrator, you have to divide the network address 172.16.0.0/16 to 5 subnets with the requirement: - Subnet 1 needs 100 hosts - Subnet 2 needs 500 hosts - Subnet 3 needs 50 hosts - Subnet 4 needs 2 hosts - Subnet 5 needs 2 hosts
Add the text to the answer with the format of "+++4>+" (No space allowed)
=> 172.16.2.0/25+172.16.0.0/23+172.16.2.128/26+172.16.2.192/30+172.16.2.196/30
7. Continue the Q.6, what is the 25-th IP address of the 3-rd subnet? => 172.16.2.153
CHAPTER 5 – Q1 EUI – 64
1. "72-61-39-D2-99-BE" is the:
=> Modification address (Locally use)
2. "18-60-24-85-0F-22" is the:
=> Burned-in-address (Universal use)
3. What is the type of the MAC address of "01-00-5E-40-07-07"? => Multicast
4. What is the type of the MAC address of "FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF"? => Broadcast
5. Convert "00-1A-7D-DA-71-15" to Ipv6 Interface Identifier using EUI-64 method. => 02-1A-7D-FF-FE-DA-71-15
CHAPTER 5 – REVIEWING CHAPTER 5 1. How many bit for IPv6? => 128
2. How many bytes for the default IPv6 header? => 40
3. Does IPv6 have a header checksum? => NO
4. Shorten the IPv6 following below:
1843:0F01:0000:0022:0000:0000:0000:00FA => 1843:F01:0:22::FA
5. Convert the MAC address to IPv6 host prefix (64 bits) using EUI-64. FC:99:47:75:CE:E0 => FE99:47FF:FE75:CEE0
6. [Multiple choices] What parameters will be used in the secure hashing method to specify the
IPv6 interface identification? => Net_Iface => IPv6 address prefix
=> Host-specific secret key
7. The IPv6 network prefix will be contained in message:
=> Router Advertisement
8. How IPv6 host can ask for the MAC address of the specific IPv6 address? => Neighbor Solicitation
9. Can IPv6 subnet with the network prefix larger than 64 bit? => YES
10. Which host address assignment option to ask for all IPv6 information from IPv6 DHCP? => Option