






Preview text:
1. Which of the following is NOT considered to be an objective of budgeting? A. Authorization A. Activities Coordination A. Expansion A. Resources allocation
2. Which of the following is NOT one of the main purposes of a budget? A. To compel planning
A. To inform shareholders of performance
A. To communicate ideas and plans
A. To provide a framework for responsibility accounting
3. Which of the following statements relating to budgets is correct?
A. A budget covers period longer than one year and is used for strategic planning
A. A budget manual will contain instructions governing the preparation of budgets
A. A budget is usually prepared by the shareholders of a company
A. The budget committee is responsible for the preparation of functional budgets
4. Which of the following is NOT considered to be function of the budget committee?
A. Preparing functional budgets A. Timetabling A. Issuing the budget manual
A. Monitoring the budgeting process
5. When preparing a production budget, what does the quantity to be produced equal?
A. Sale quantity + opening inventory of finished goods + closing inventory of finished goods
A. Sales quantity - opening inventory of FGs + closing inventory of FGs
A. Sale quantity - Opening inventory of FGs - closing inventory of FGs
A. Sales quantity + opening inventory of FGs - closing inventory of FGs
6. If a company has no production resource limitations, in which order would the following budgets be prepared? (i) Material usage budget (ii) Sales budget (iii) Material purchase budget
(iv) Finished goods inventory budget (v) Production budget (vi) Material inventory budget A.(ii),(iv),(v),(i),(vi),(iii)
7. In a situation where there are no production resource limitations, which of the
following items of information must be available for the production budget to be completed?
(i) Sales volume form the sales budget
(ii) Material purchases form the purchases budget
(iii) Budgeted change in finished goods inventory
(iv) Standard direct labour cost per unit A. (i), (iii)
8. Which of the following is NOT a functional budget? A. Production budget A. Distribution cost budget A. Selling cost budget A. Cash budget
9. Which of the following is a principal budget factor?
A. The highest value item of cost
B. A factor which limits an organisation’s performance
C. A factor common to all budget centers
D. A factor controllable by the manager of the budget center
10. The following details have been extracted from the receivables collection records of MidoCO
Invoices paid in the month after sale: 60%
Invoices paid in the second month after sale: 25%
Invoice paid in the third month after sale: 12% Bad debts: 3%
Invoices are issued on the last day of each month
Customers paying in the month after sale are entitled to deduct a 2% settlement discount
Credit sales values for August to November are budgeted as follows August September October November $35,000 $40,000 $60,000 $45,000
What is the amount budgeted to be received from credit sales in November? A. 46,260 A. 49,480 A. 50,200 A. 50,530
11. The following details have been extracted from the payables records of Dimo Co:
Invoices paid in the month of purchase: 25%
Invoices paid in the first month after purchase: 70%
Invoices paid in the second month after purchase: 5%
Purchases for September to November are budgeted as follows September: $250,000 October: $300,000 November: $280,000
For suppliers paid in the month of purchase, a settlement discount of 5% is received.
What is the amount budgeted to be paid to suppliers in November? A. $278,500 A. $280,000 A. $289,000 A. $292,500
12. What does a master budget comprise?
A. The budgeted statement of profit or loss
A. The budgeted cash flow, budgeted statement of profit or loss and budgeted
statement of financial position A. The budgeted cash flow
A. The entire set of budgets prepared
13. Nimo Co, is going to prepare a budgeted income statement for the six months ending on 31 December 20X2
Monthly sales are forecasted to be $4,000 for July, $5,500 for each of August and September
and $6,000 per month from October onwards
Selling price is fixed to generate a margin of 30%
Overhead expenses (excluding depreciation) are estimated at $1,000 per month
The company plans to purchase non-current assets on 1 July costing $6,000 , which will be paid
for at the end of September and are expected to have a five-year life (with no residual value)
The budgeted net profit for the six month ending 31 December 20X2 is A. $2,700 A. $3,300 A. $3,600 A. $7,700
14. A company’s master budget contains the following budgeted income statement. $ $ Sales revenue 130,000 Variable material cost 25,000 Variable labour cost 35,000 Variable overhead 15,000 Fixed overhead 40,000 115,000 Budgeted net profit 15,000
The company’s management are planning to change the materials specification. This would
reduce the materials cost per unit by 10%. The reduced product quality would result in a 2%
reduction in the selling price and a 5% fall in the sales volume.
The revised budgeted net profit for the period would be A. $8,530 A. $12,155 A. $14,155 A. $14,625
15. The correlation coefficient between two variables, x and y, is +0,85
The proportion of variation in y that is explained by variation in x is (to two decimal places) A. 0.72 A. 0.85 A. 0.92 A. 1.57
16. There are two variables, a and y. The proportion of variation in y that is explained by variation in x is 0.83 A. 0.69 A. 0.83 A. 0.91 A. 1.52
17. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. The coefficient of determination must always fall between -1 and + 1
A. The correlation coefficient must always fall between 0 and +1
A. A disadvantage of the high-low method of cost estimation is that it does not take into
account the full range of available date
A. A cost estimate produced using the high-low method can be used to reliably predict the cost for any level of activity
18. The following information for advertising and sales has been established over the past six months: Month Sales revenue Advertising expenditure 1 155 3 2 125 2.5 3 200 6 4 175 5.5 5 150 4.5 6 225 6.5
Using the high-low method which of the following is the correct equation for linking advertising and sales from the above date?
A. Sales revenue = 62,500 + (25 x advertising expenditure)
A. Advertising expenditure = -2,500 + (0.04 x sales revenue)
A. Sales revenue = 95,000 + (20 x advertising expenditure)
A. Advertising expenditure = -4,750 + (0,05 x sales revenue)
19. A company has recorded the following date in the two most recent periods total cost of production Volume of production $13,500 $700 $18,300 $1,100
What is the best estimate of the company’s fixed costs per period? A. $13,500 A. $13,200 A. $5,100 A. $4,800
20. The following shows the total overhead costs for given levels of a company’s total output Cost Out put (units) 4,000 1,000 7,000 2,000 10,000 3,000 9,500 4,000
A step up in fixed costs of $500 occurs at an output level of 3,500 units
What would be the variable overhead cost per unit (to the nearest $0,01) using the high - low method A. $1,67 per unit A. $ 1,83 per unit A. $ 2,75 per unit A. $ 3,00 per unit
21. Which of the following are the disadvantages of a bottom-up style of budgeting? (i) Consume more time
(ii) May cause managers to introduce budget slack
(iii) Morale and motivation is improved
(iv) Changes implemented by senior managers may cause dissatisfaction A. (i) and (ii) only A. (ii) and (iii) only A. (i), (ii) and (iv) only
A. (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
22. Which of the following best describes ‘zero-based budgeting’?
A. A method of budgeting whereby all activities are re-evaluated each time a budget is formulated
A. The budget for each period is based on the current year’s results, modified for changes in activity levels
A. The budget is updated in regular increments, by adding the budget for a further
accounting period when the earliest accounting period has expired
A. A budget method where an attempt is made to make expenditure under each cost
heading as close to zero as possible.
23. Which of the following best describes a “top-down) budget?
A. A series of budgets is prepared, from the most optimistic performance down to the most pessimistic
A. Top management prepares a budget with little or no input from operating personnel
A. A budget which is set by delegating authority from top management, allowing
budget holders to participate in setting their own budgets
A. A budget which has been set be scaling down individual expenditure items until the total
budgeted expenditure can be met from available resources Chapter 7
25. Which of the following is the correct formula to calculate working capital?
A. Inventory - Cash - Receivables + Payables
A. Inventory + Cash + Receivables - Payables
A. Receivables + Payables- Inventory - Cash
A. Inventory + Cash + Payables - Receivables
26. The Economic order quantity (EOQ) can be expressed as follows: 2cdh
What does h describe in this formula?
A. The cost of holding one unit of inventory for one period
A. The cost of placing one order
A. The cost of a unit of inventory
A. The customer demand for the item
27. The Economic order quantity (EOQ) can be expressed as follows: 2cdh
What does c describe in this formula?
E. The cost of holding one unit of inventory for one period
E. The cost of placing one order
E. The cost of a unit of inventory
E. The customer demand for the item
28. Biel lLtd. is a manufacturing company which has several thousand types of inventory items.
The company wants to introduce a new inventory control system
Which is the most suitable system for an organization with so many inventory items. A. Re-order level system A. Periodic review system A. ABC system A. Just-in-time system
29. The annual demand for an item of inventory is 2,400 units. The cost of placing an order is
$80 and the cost of holding an item in stock for one year is $15.
What is economic order quantity, to the nearest unit? A. 113 A. 160 A. 12,800 A. 25,600
30. The demand for a product is 13,500 units for a three-month period. Each unit of product has
a purchase price of $15 and ordering costs are $20 per order placed. The annual holding cost of
one unit of product is 10% of its purchase price.
What is the Economic Order Quantity (to the nearest unit)? A. 424 A. 600 A. 848 A. 1,200
31. A company determines its order quantity for a raw material by using the Economic Order Quantity( EOQ) model.
What would be the effect on the EOQ and the total annual holding cost of decrease in the cost
of ordering a batch of raw material?
A. Lower EOQ, Lower Total annual holding cost
A. Higher EOQ, HigherTotal annual holding cost
A. Lower EOQ, Higher Total annual holding cost
A. Higher EOQ, Lower Total annual holding cost
32. A manufacturing company uses 25,000 components at an even rate during a year. Each
order placed with the supplier of the components is for 2,000 components, which is the
economic order quantity.The company holds a buffer inventory of 500 components. The annual
cost of holding one component inventory is $2.
What is the total annual cost of holding inventory of the component? A. $2,000 A. $2,500 A. $3,000 A. $4,000
33. A company wished to minimize its inventory costs. Order costs are $10 per order and
holding costs are $0,10 per unit per month. Fall Co estimates annual demand to be 5,400 units. A. 300 units A. 949 units A. 1,039 units A. 90,000 units
34. For a particular component, the re-oder quantity is 6,000 units and the average inventory Holding is 3,400 units.
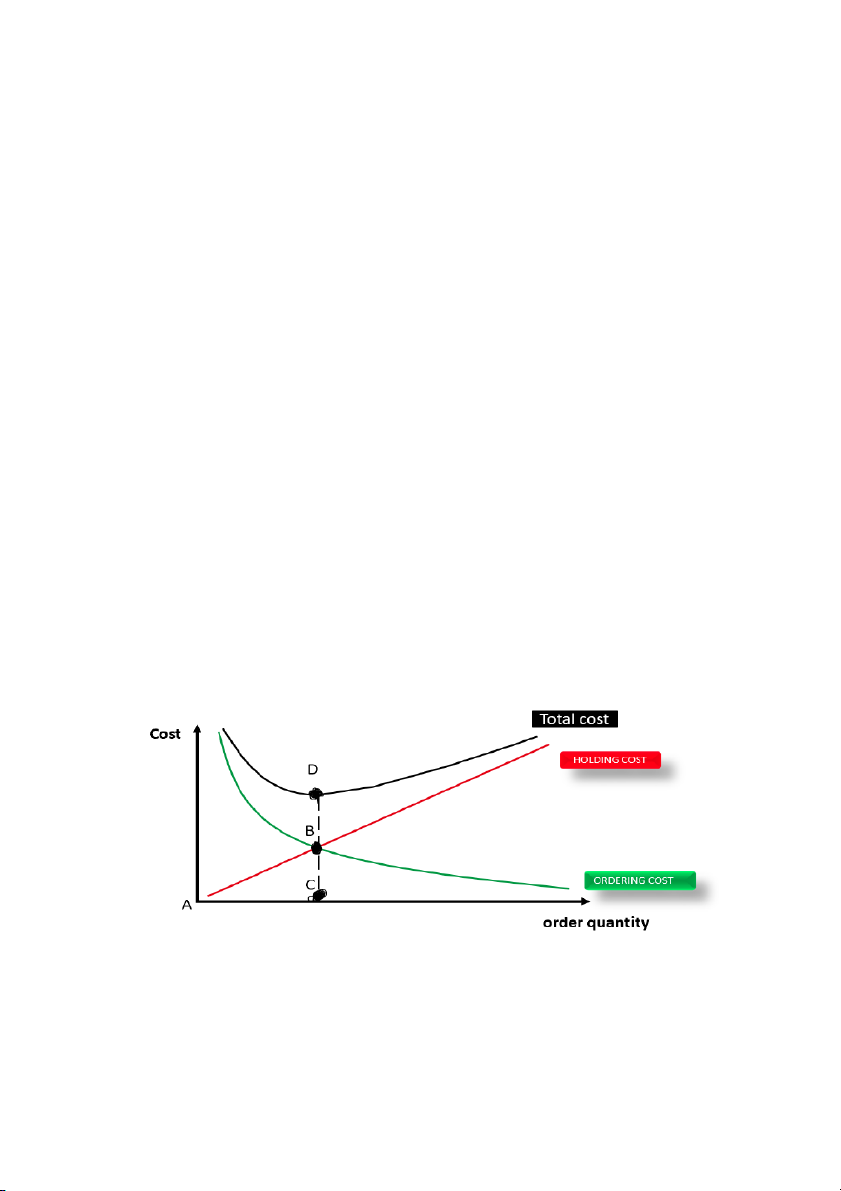
What is the level of safety inventory (in whole units)? A. 400 A. 3,000 A. 3,400 A. 6,400 35.
Where on the graph would you read off the value for the economic order quantity? A. At point A A. At point B A. At point C A. At point D
36. Apart from the actual cost of buying inventory, there are other inventory costs to consider.
Which of the following is an inventory holding cost?
A. Clerical and administrative expenses
A. Opportunity cost of capital tied up
A. Production stoppages due to lack of raw materials
A. The cost of inventory packaging materials
37. Which of the following is correct with regard to inventories?
(i) stock-outs arise when top little inventory is held
(ii) Safety inventories are the level of units maintained in case there is unexpected demand
(iii) A re order level is where an order should be placed whenever inventory falls to this level. A. (i) and (ii) only A. (i) and (iii) only A. (ii) and (iii) only A. (i), (ii), and (iii)
38. Which of the following is/are a reason(s) for holding inventory?
(i) to ensure continuity of production (ii) to reduce ordering costs (iii) for technical reasons
(iv) to take advantage of quantity discounts A. (iii) only A. (i) and (ii) only A. (i),(ii) and (iv) only A. All of the above
39. The key trade-off that lies at the heart of working capital management is that between
A. business stability and solvency A. Debtor and creditors
A. Current assets and current liabilities
A. Liquidity and profitability
40. A company uses the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model to establish reorder quantities.
The following information relates to the forthcoming period: Order cost = $25 per order
Holding costs = 10% of purchase price Annual demand = 20,000 units Purchase price = $40 per units EOQ = 500 units No safety inventory is held
What is the total order cost plus total holding cost? A. $22,000 A. $33,500 A. $802,000 A. $803,000
41. A company determines its order quantity for a raw material by using the Economic Order Quantity( EOQ) model.
What would be the effect on the EOQ and the total annual holding cost of an increase in the
annual cost of holding one unit of the component in inventory?
A. Lower EOQ, Higher Total annual holding cost
A. Higher EOQ, LowerTotal annual holding cost
A. Lower EOQ, No effect on Total annual holding cost
A. Higher EOQ, No effect on Total annual holding cost
42. The purchase price of an inventory item is $42 per unit. In each three-month period usage of
the item is 2,000 units. The annual holding costs associated with one unit 5% of its purchase price. The EOQ is 185 units.
What is the cost of placing an order (to 2 decimal places)? A. $0.02 A. $0.05 A. $4.49 A. $8.98 Bonus �
1. Match the following cost item is corresponding cost categories associated with holding inventory. Cost items Cost categories 1. Emergency reorder costs a. Holding costs 2. Insurance cost b. Reorder costs
3. Clerical and administrative expenses c. Shortage costs 1-c 2-a 3-b
2. Which inventory control system is being described? Descriptions Inventory control systems
1. This system addresses the problem of when to order a. Periodic review
inventory and how much to order system
2. Inventory levels are reviewed at fixed time intervals to fit in b. Perpetual inventory
with production schedules, and variable quantities are ordered methods as appropriate.
3. Production and purchasing are linked closely to sales demand c. Just-in time
on a week to week basis. This means that negligible manufacturing systems
inventories of raw materials and finished goods need to be held
4. this is a system whereby the inventory records are updated d. Economic order
for each receipt and issue of inventory as it occurs quantity system 1-d 2-a 3-c 4-b Chapter 8:
46. Which of the following is NOT an example of budget bias?
1) A production manager overestimates costs when setting the budget so that they will not be
blamed for overspending in the future
II) A sales manager underestimates revenues when setting the budget to guard against poor results.
III) A manager try to ensure that his spending rises to meet his inflated budget.
IV) A manager overestimates revenues when setting the budget in order to make a favourable impression on senior managers. A. None of the above B. I, II and III C. II and III D. All of the above
47. Which of the following is NOT the advantages of decentralisation?
The quality of decisions is likely to improve
Senior managers might easily to contr
ol over detailed day to day operations.
The increased responsibility should motivate managers.
Decisions should be taken more quickly in response to changing conditions.
48. Within a system of responsibility accounting,main types of responsibility centre include of:
Cost centre, revenue centre, profit centre, management centre
Cost centre, profit centre, capital working centre, investment centre
Cost centre, revenue centre, administration centre, debt centre
Cost centre, revenue centre, profit centre, investment centre
49. Division A is a profit centre within PC Ltd. Over which of the following is the manager
of division A likely to have control? (1) Transfer prices
(2) Level of inventory in the division
(3) Discretionary fixed costs incurred in the division
(4) Apportioned head office costs A. (1), (2), (3) and (4) B. (1), (2) and (3) only C. (1) and (2) only D. (1) only
50. Division A is a revenue centre within PC Ltd. Which of the followings that the manager
of division A has NO responsibility for? (1) Transfer prices (2) Trade discount
(3) Investment in working capital
(4) Apportioned fixed costs incurred in the division A. (1), (2), (3) and (4) B. (1), (2) and (3) only
C. (1). (3) and (4) only D. (2) only
51.Gross profit margin might be an appropriate measure for which of following responsibility centres:
A. All types of responsibility centres
B. Only cost centre, profit centre and investment centre
C. Only profit centre and investment centre D. Only profit centre
52. Which of the following is NOT a perspective that is monitored by the balanced
scorecard approach to performance measurement? Financial Customer Innovation and learning Supplier
53. While using Balanced scorecard, which of the following measures could be use under
Innovation and learning perspectives Working capital ratios
The rate of labour turnover Sales revenue Number of clients
54. Which of the following describes a flexible budget?
A budget comprising variable production costs only
A budget which is updated with actual costs and revenues as they occur during the budget period
A budget which shows the costs and revenues at different level of activity
A budget which is prepared using a computer spreadsheet model.
55. What is a budget cost allowance?
A budget of expenditure applicable to a particular function
A budget allowance which is set without permitting the ultimate budget manager the opportunity
to participate in setting the budget
The budgeted cost expected for the actual level of activity achieved during the period
A fixed budget allowance for expenditure which is expected every period, regardless of the level of activity
56. Within decentralised organisations there may be cost centres, investment centres and
profit centres. Which centres have the highest and lowest degree of autonomy respectively?
Investment centres and Cost centres Profit and Cost Centres
Cost Centres and Revenue Centres
All responsibility centres have the same degree of autonomy
57. Which of the following sentences best describes what is necessary for a responsibility
accounting system to be successful?
Each manager should know the criteria used for evaluating his or her own performance.
The details on the performance reports for individual managers should add up to the totals on the report of their superior.
Each employee should receive a separate performance report.
Service department costs should be apportioned to the operating departments that use the service.
58. Which of the followings is NOT the features of effective performance measures?
The measures promote goal congruence.
The measures incorporate only those factors over which the responsibility centre manager has control.
The measures encourage the pursuit of longer term objectives as well as short- term, budget constrained objectives.
The measures might cause demotivation and stress-related conflict between a manager and
the manager's subordinates, superiors or fellow managers.
59. Which of the following items would be excluded in the calculation of controllable divisional profit? Sales to external customers Head office costs Variable divisional expenses
Controllable divisional fixed costs Bonus �: 1. Cost centre A. ROI 2. Revenue centre B. production costs variation 3. Profit centre C. Sales variance 4. Investment centre D. Profit margin 1-B 2-C 3-D 4-A Chapter 9-mcq
64.A company expected to produce 200 units of its product, the Bone, in 20X3. In fact, 260 units were produced.
The standard labour cost per unit was $70 (10 hours at a rate of $7 per hour). The actual labour
cost was $18,600 and the labour force worked 2,200 hours although they were paid for 2,300 hours.
What is the direct labour efficiency variance for the company in 20X3? A. $400 (A) B. $2,100 (F) C. $2.800 (A) D. $2,800 (F)
65. Extracts from a company's records from last period are as follows. Budget Actual Production 1,925 units 2,070 units Variable production overhead $11,550 $14,904 cost Labour hours worked 5,775 8,280
What is the variable production overhead expenditure variance? A. $1,656 (F) B. $2,484 (F) C. $2,484 (A) D. $3.354 (A)
Variable production overhead expenditure variance = Actual variable overhead cost - Budgeted variable overhead cost
Actual variable overhead cost = Actual labour hours worked × Variable overhead cost per labour hour = 8,280 × ($14,904 / 5,775) = $21,504
Budgeted variable overhead cost = Budgeted labour hours worked × Variable overhead cost per labour hour = 5,775 × ($11,550 / 5,775) = $11,55
Variable production overhead expenditure variance = Actual variable overhead cost - Budgeted variable overhead cost = $21,504 - $11,550 = $9,954 (Favourable)
Therefore, the variable production overhead expenditure variance is $9,954 (Favourable), and the
correct answer is: A. $1,656 (F) 8280x 11550/5775-14904
66.Extracts from a company's records from last period are as follows. Budget Actual Production 1,925 units 2,070 units Variable production overhead $11,550 $14,904 cost Labour hours worked 5,775 8,280
What is the variable production overhead efficiency variance? A. $2,070 (A) B. $3,726 (A) C. $4,104 (A) D. $4,140 (A)
(2070x 5775/1925-8280) x11550/5775=4140(A)
67. Which of the following would help to explain a favourable direct labour efficiency variance? i.
Employees were of a lower skill level than specified in the standard ii.
Better quality material was easier to process iii.
Suggestions for improved working methods were implemented during the period A. (i), (ii) and (iii) B. (i) and (ii) only C. (ii) and (iii) only D. (i) and (iii) only
68. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. An adverse direct material cost variance will always be a combination of an adverse material
price variance and an adverse material usage variance.
B. An adverse direct material cost variance will always be a combination of an adverse material
price variance and a favourable material usage variance.
C. An adverse direct material cost variance can be a combination of a favourable material price
variance and a favourable material usage variance.
D. An adverse direct material cost variance can be a combination of a favourable material
price variance and an adverse material usage variance.
69.A company has a budgeted material cost of $125,000 for the production of 25.000 units per
month. Each unit is budgeted to use 2 kg of material. The standard cost of material is $2.50 per kg.
Actual materials in the month cost $136.000 for 27,000 units and $ 53,000 kg were purchased and used.
What was the adverse material price variance? A $1,000 B. $3.500 C $7.500 D. $11,000
27000x2x2.5-136000=1000A
70.A company has a budgeted material cost of $125,000 for the production of 25,000 units per
month. Each unit is budgeted to use 2 kg of material. The standard cost of material is $2.50 per kg.
Actual materials in the month cost $136,000 for 27,000 units and 53.000 kg were purchased and used.
What was the favourable material usage variance? A. $2.500 B. $4,000 C. $7.500 D. $10.000
(27000x2-53000)x2.5=2500F
71. The following information relates to labour costs for the past month: Budget Labour rate $10 per hour Production time 15,000 hours Time per unit 3 hours Production units 5,000 units Actual Wages paid $176,000 Production 5.500 units Total hours worked 14,000 hours There was no idle time.
What were the labour rate and efficiency variances?
A. Rate: $26,000 Adverse: Efficiency: $25.000 Favourable
B. Rate: $26,000 Adverse; Efficiency: $10,000 Favourable
C. Rate: $36,000 Adverse; Efficiency: $2.500 Favourable
D. Rate: $36,000 Adverse; Efficiency: $25.000 Favourable
Labour rate: 14000x10-176000=36000 (A)
Efficiency : (5500x3-14000)x10=25000 F 72. Number of units produced 2.200 2,000 Budget Actual $ $ Direct materials 110,000 110,000 Direct labour 286,000 280,000 Variable overhead 132,000 120,000
The actual number of units produced was 2,000,
What was the total direct materials variance? A. Nil B.$10,000 Adverse C.$10,000 Favourable D. 511,000 Adverse 2000x50-110000=10000A 73. Number of units produced 2.200 2,000 Budget Actual $ $ Direct materials 110,000 110,000 Direct labour 286,000 280,000 Variable overhead 132,000 120,000
The actual number of units produced was 2,000,
What was the total direct labour variance?! A. $6,000 Favourable B. $20,000 Adverse C. $22,000 Favourable D. Nil
=> Budgeted labour cost per unit = $286,000/2,200 units = $130 per unit
Flexed budget direct labour cost for 2,000 units = $130 per unit x 2,000 units = $260,000
Actual direct labour cost for 2,000 units = $280,000
Total direct labour variance = Actual direct labour cost - Flexed budget direct labour cost
Total direct labour variance = $280,000 - $260,000 = $20,000 Adverse
Therefore, the correct answer is option B, $20,000 Adverse. 2000x130-280000=2000A 74. Number of units produced 2.200 2,000 Budget Actual $ $ Direct materials 110,000 110,000 Direct labour 286,000 280,000 Variable overhead 132,000 120,000
The actual number of units produced was 2,000.
What was the total direct variable overheads variance? A Nil B. $12.000 Favourable C. $12,000 Adverse D $11,000 Adverse
Spending variance = Actual variable overhead cost - Budgeted variable overhead cost = $120,000 - $132,000 = $12,000 (Favourable)
Efficiency variance = Budgeted variable overhead cost per unit × (Actual units produced - Budgeted units produced)
= ($132,000 / 2,200 units) × (2,000 units - 2,200 units)
= ($60 per unit) × (-200 units) = $12,000 (Adverse)
Total direct variable overhead variance = Spending variance + Efficiency variance
= $12,000 (Favourable) + $12,000 (Adverse) = $0
Therefore, the correct answer is: A. Nil 2000x(132000:2200)-120000
75. Which of the following situations is most likely to result in a favourable selling price variance?
A. The sales director decided to change from the planned policy of market skimming pricing to
one of market penetration pricing.
B. Fewer customers than expected took advantage of the early payment discounts offered.
C Competitors charged lower prices than expected, therefore selling prices had to be reduced in order to compete effectively.
D. Demand for the product higher than expected and prices could be raised without
adverse effects on sales volumes.
76.A company uses variance analysis to control costs and revenues.
Information concerning sales is as follows:
Budgeted selling price: $15 per unit
Budgeted sales route:10.000 units
Budgeted contribution per unit $5 per unit Actual sales revenue: $151.500 Actual units sold: 9.800 units
What is the sales volume variance? A.$500 Favourable B. $1,000 Favourable C. $1,000 Adverse




