

Preview text:
COMPARATIVE CHARTS – BAR CHARTS
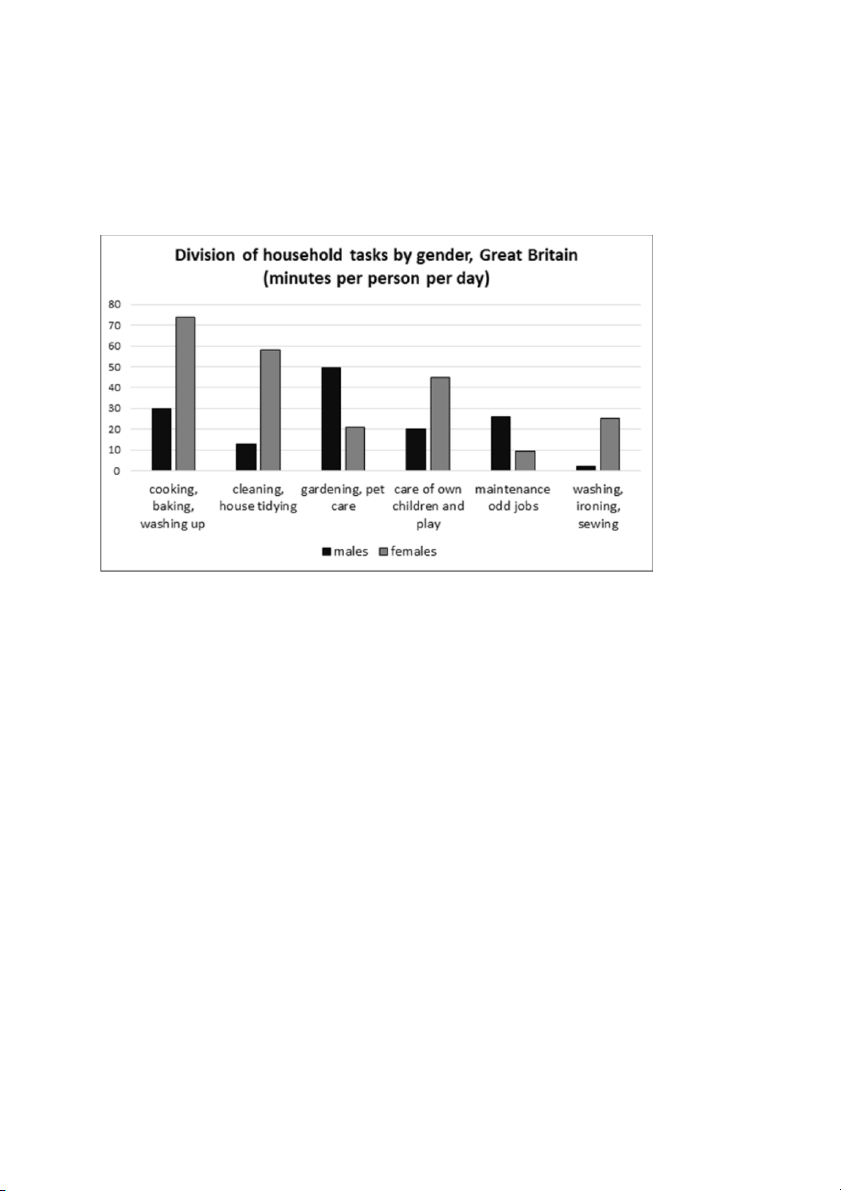
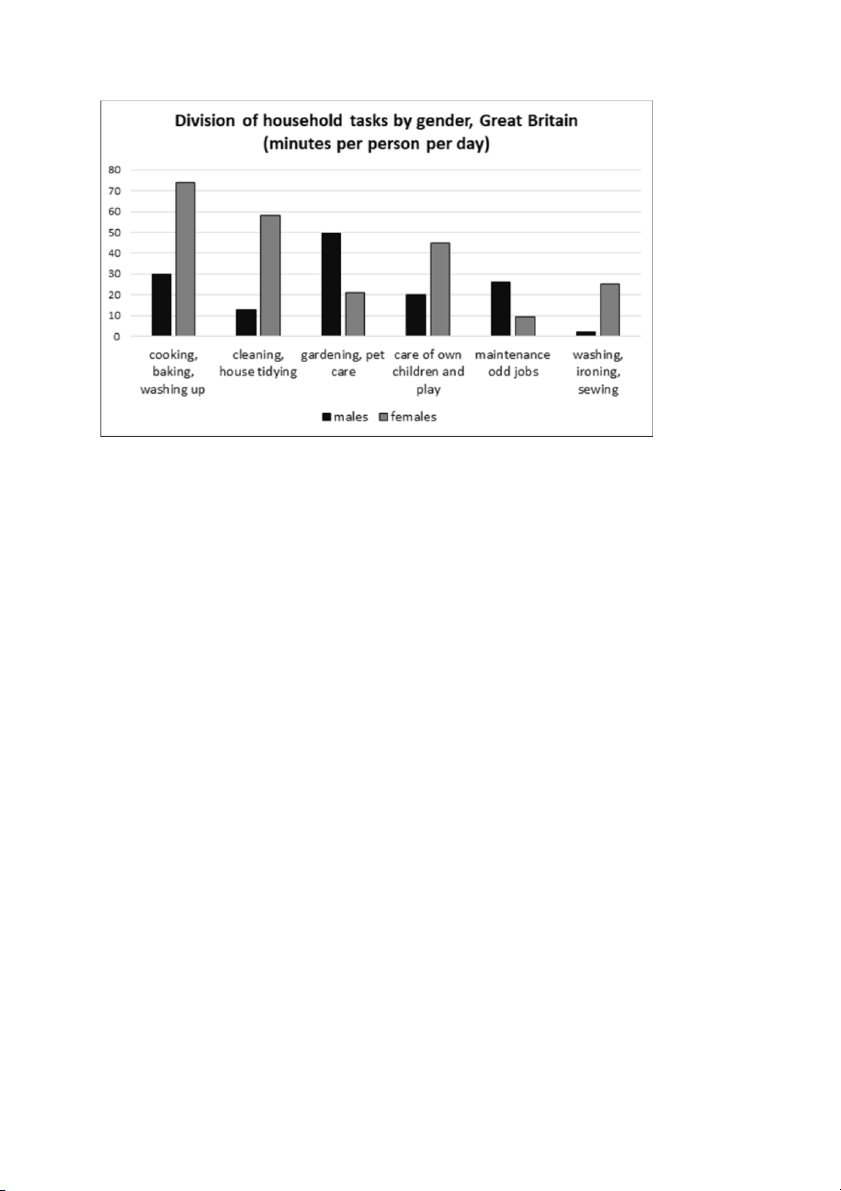
The chart shows the division of household tasks by gender in Great Britain.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make
comparisons where relevant. Time: Trend: Language: REPORT STRUCTURE 1. introduction 2. overview 3. body Conclusion?
Introduction: State what the chart is about
The chart shows the division of household tasks by gender in Great Britain
THE AMOUNT OF TIME / HOW MUCH TIME // MEN AND WOMEN
=> The bar chart describes how much time MEN AND WOMEN SPEND ON SIX
TYPES OF HOUSEHOLD CHORES in Great Britain.
=> The bar chart compares the amount of time MEN AND WOMEN DEDICATE TO
SIX KINDS OF HOUSEHOLD CHORES in Great Britain.
=> The ALLOCATION OF household chores among two sexes in GB, measured in
minutes per day, is illustrated in the bar chart.
Overview: Highlight the main points 1. compare: 2. compare:
Overall, _____________ WHILE ______________
SENTENCE 01: In general, women dedicate more time to household chores than MEN do.
= Overall, women take more household responsibilities than their men counterparts.
= Overall, women are more committed to household chores than men.
SENTENCE 02: Females spend most of their time doing kitchen tasks, WHILE their
male counterparts dedicate the largest amount of time to gardening and pet care.
= WHILE kitchen tasks occupy/take the LARGEST AMOUNT OF TIME of women,
men dedicate most of their time to gardening and pet care.
= WHILE kitchen tasks occupy/take the LARGEST AMOUNT OF TIME of women,
most of men’s time is spent on gardening and pet care. PRACTICE:
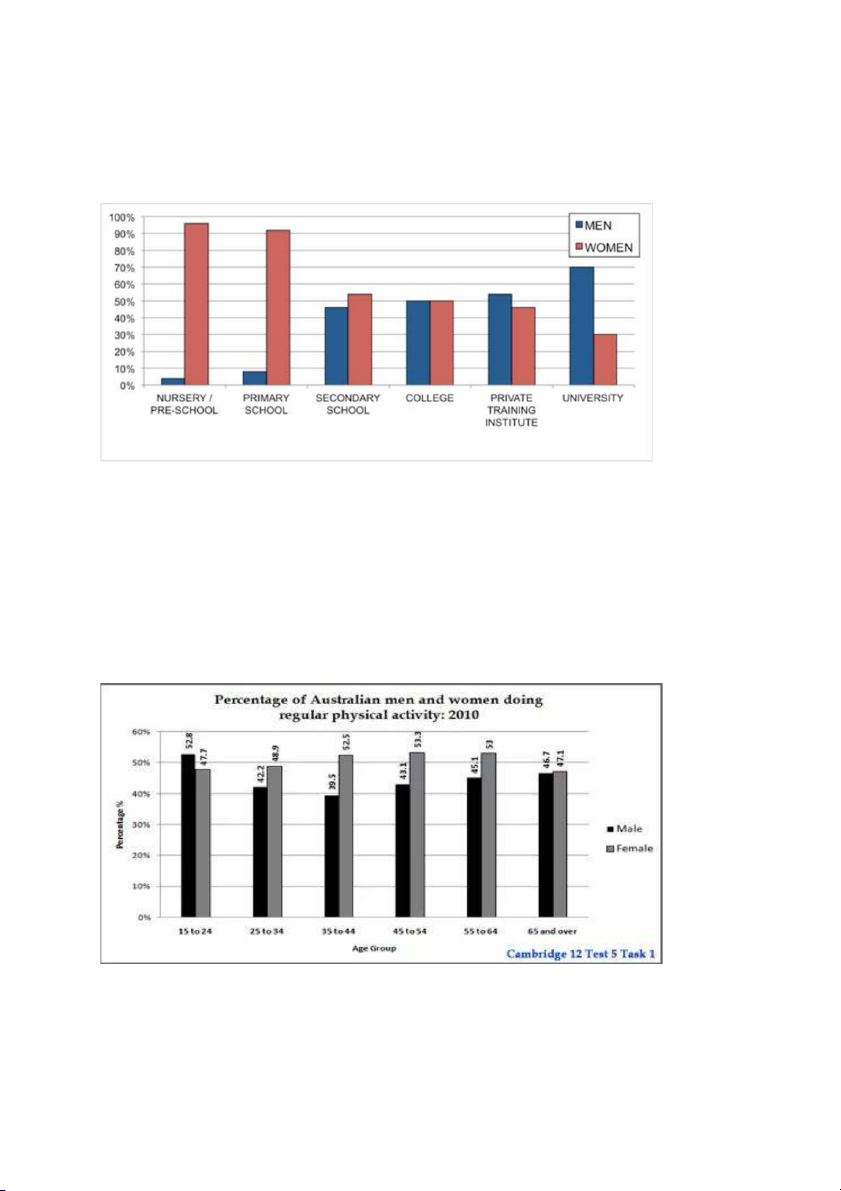
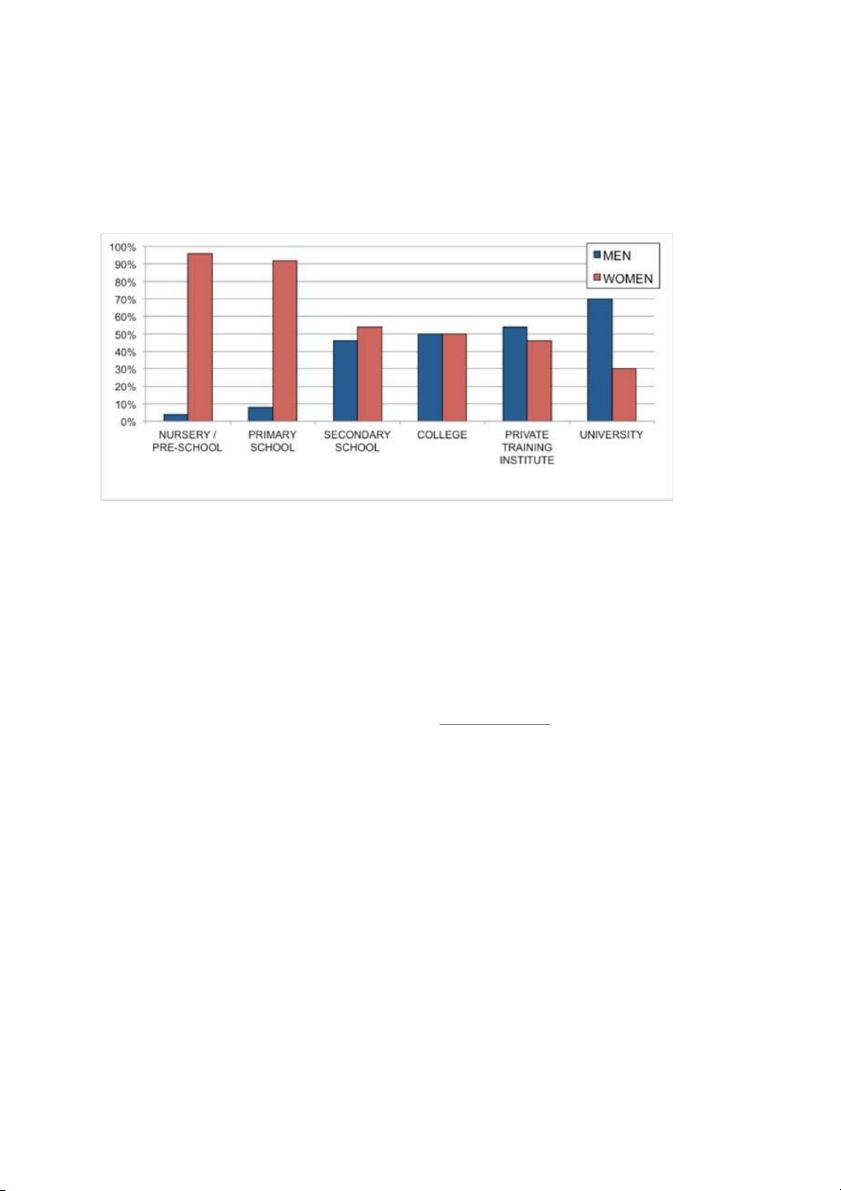
1. The chart shows the percentage of male and female teachers in six different types
of educational setting in the UK in 2010.
The bar chart below shows the percentage of Australian men and women in
different age groups who did regular physical activity in 2010. BODY PARAGRAPHS
TOPIC: The chart shows the percentage of male and female teachers in six different
types of educational setting in the UK in 2010.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant. Body 1: Body 2: PERCENTAGE LANGUAGE
1. NURSERY/PRE-SCHOOL (women: 95% >< men: 5%)
- VERSION 1: Women / accounted for a vast majority (95%) of nursery
teachers, far exceeding the figure for their male counterparts, at 5%.
- VERSION 2: The vast majority of nursery teachers/ were females, at 95%,
compared to a small proportion (5%) for their male counterparts.
=> DESCRIBE WOMEN, FAR EXCEEDING/COMPARED TO/AS OPPOSED TO DESCRIPTION FOR MEN
- VERSION 3 - DÙNG OUTNUMBERED: Female teachers / significantly
outnumbered their male counterparts at the pre-school level, at 95% and 5% respectively.
- VERSION 4: Female teachers in the nursery level, at 95% were dominant ,
as opposed to a small figure (5%) of their male counterparts, marking the biggest gender gap.
- VERSION 5: Nursery schools recruited mainly female teachers rather than
male ones, at 95% and 5% respectively
- VERSION 6: The proportion of female teachers at nursery schools was
significantly higher than THAT OF male ones, at 95% and 5% respectively.
2. UNIVERSITY LEVEL (men: 70% >< women: 30%)
- Men / accounted for far exceeding the fi 70% of university lecturers, gure
for their female counterparts, at 30%.
- 70% of university teachers/ were males, compared to 30% of their female
counterparts = being more than double (ADJ) the figure for their female counterparts, at 30%.
- Male teachers / significantly outnumbered their female counterparts at the
university level, at 70% and 30% respectively. = Male teachers were
dominant in the university level, at 70%, as opposed to 30% of their female counterparts.
- The proportion of male teachers at universities was significantly higher
than THAT OF female ones, at 70% and 30% respectively. = The proportion
of male teachers at universities was MORE THAN DOUBLE THAT OF
female ones, at 70% and 30% respectively.
3. COLLEGE: bằng nhau:
- Colleges equally favoured teachers of both genders.
- Equal proportions of male and female teachers were hired at colleges.
The chart shows the division of household tasks by gender in Great Britain.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make
comparisons where relevant. (Body Paragraph 01)
+ women: an average of about 2.5 hours >< men: 1.5 more hours
+ kitchen tasks such as cooking, baking and washing up:
+ in-house cleaning and childcare: women are more active
+ clothes washing, ironing, sewing: the largest difference (Body Paragraph 02)
+ gardening and pet care: males > female counterparts
+ maintenance jobs: men > women SENTENCE FORMATION BODY 1:
- S1: kitchen tasks: 1st với women, W double M
- S2: cleaning & childcare: data, W are more active than M
- S3: washing, ironing: M spend the smallest amount of time on…., at 2 minutes, compared to…. BODY 2:
- S1: gardening & pet care: 1st với men - 50 mins >< more than double women
- S2: maintenance jobs: M - data >< the smallest với women LANGUAGE
- Women spend twice as much time doing…. as men, data and data, respectively
- Clothes washing and ironing tasks OCCUPY + minutes of women’s daytime.
- The amount of time women devote to washing, ironing and sewing is
significantly higher THE FIGURE FOR MEN…




