



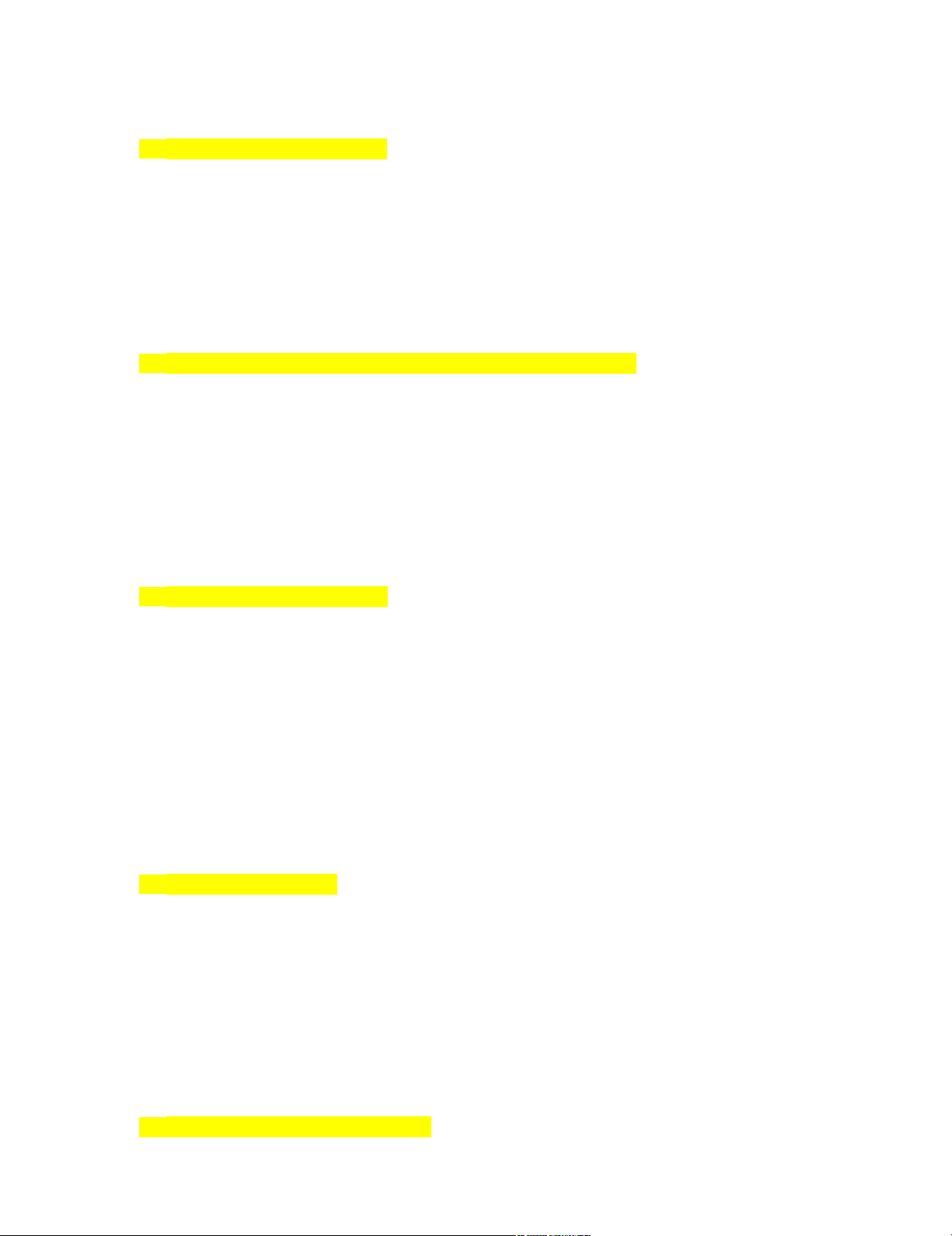





Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD|46958826 lOMoARcPSD|46958826
TUTORIAL 1: INTRODUCTION 10 Principles of economics
and thinking like an economist Coverage: Chapter 1 & Chapter 2 I. Multiple Choice
____ 1. Economics is the study of a. production methods.
b. how society manages its scarce resources.
c. how households decide who performs which tasks.
d. the interaction of business and government.
____ 2. A typical society strives to get the most it can from its scarce resources. At the same time, the society
attempts to distribute the benefits of those resources to the members of the society in a fair manner. In
other words, the society faces a tradeoff between a. guns and butter.
b. efficiency and equality. c. inflation and unemployment. d. work and leisure.
Trade-off: the only way to get more of one good is to get less of the other good
____ 3. High-school athletes who skip college to become professional athletes
a. obviously do not understand the value of a college education.
b. usually do so because they cannot get into college.
c. understand that the opportunity cost of attending college is very high.
d. are not making a rational decision since the marginal benefits of college outweigh the
marginal costs of college for high-school athletes.
The more you produce => The higher the opportunity cost
Opportunity cost = the value of what you have to give up in order to choose something else (often because
option A is chosen over B, where the possible benefit from B is foregone in favor of A) lOMoARcPSD|46958826
____ 4. A construction company has built 50 houses so far this year at a total cost to the company of $8 million.
If the company builds a 51st house, its total cost will increase to $8.18 million. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. For the first 50 houses, the average cost per house was $160,000.
b. The marginal cost of the 51st house, if it is built, will be $180,000.
c. If the company can experience a marginal benefit of $190,000 by building the 51st house,
then the company should build it.
d. All of the above are correct.
Marginal cost = Marginal cost of production is the change in total cost that comes from making
or producing one additional item.
Marginal benefit = the highest amount that a buyer is willing to pay for an extra product
Marginal benefit > Marginal cost
____ 5. The principle that trade can make everyone better off applies to a. individuals. b. families. c. countries. d. All of the above
____ 6. An example of an externality is the impact of
a. bad weather on the income of farmers.
b. the personal income tax on a person's ability to purchase goods and services.
c. pollution from a factory on the health of people in the vicinity of the factory.
d. increases in health care costs on the health of individuals in society.
Externality = Impact of one person’s actions on the well-being of a bystander
____ 7. Which of these activities will most likely result in an external benefit?
a. A college student buys a deck of cards to play solitaire in her dorm room.
b. An elderly woman plants a flower garden on the vacant lot next to her house.
c. An executive purchases a book to read on a business trip.
d. A ten-year-old uses his allowance to buy new Nike shoes.
External benefit = is the benefit gained by an individual or firm as a result of an economic
transaction but where they are not directly involved in the transaction lOMoARcPSD|46958826
____ 8. Which of the following is the most correct statement about the relationship between inflation and unemployment?
a. In the short run, falling inflation is associated with falling unemployment.
b. In the short run, falling inflation is associated with rising unemployment.
c. In the long run, falling inflation is associated with falling unemployment.
d. In the long run, falling inflation is associated with rising unemployment.
(Based on Principle 10: Society faces a short-run trade-off between Inflation and Unemployment. In
short run, many economic policies push inflation and unemployment in opposite directions.)
____ 9. Which of the following statements is (are) correct?
a. Relative to other scientists, economists find it more difficult to generate useful data.
b. Theory and observation are important in economics as well as in other sciences.
c. To obtain data, economists often rely upon the natural experiments offered by history.
d. All of the above are correct.
____ 10. Just like models constructed in other areas of science, economic models
a. incorporate assumptions that contradict reality.
b. incorporate all details of the real world. c. complicate reality.
d. avoid the use of diagrams and equations.
____ 11. Which of these statements about economic models is correct?
a. For economists, economic models provide insights about the world.
b. Economic models are built with assumptions.
c. Economic models are often composed of equations and diagrams.
d. All of the above are correct.
____ 12. Which of the following transactions does not take place in the markets for factors of production in the circular-flow diagram?
a. a landowner leases land to a farmer
b. a farmer hires a teenager to help with harvest lOMoARcPSD|46958826
c. a retired farmer sells his combine to a new farmer
d. a woman buys corn for dinner
circular-flow diagram a visual model of the economy that shows how dollars flow through
markets among households and firms
Markets for factors of production:
Household provide Land, Labour, Capital for Firms, receive Income
Firms provide Wages, Rent, Profit cho Household, receive Factors of production
____ 13. The following table contains some production possibilities for an economy for a given month.
If the production possibilities frontier is bowed outward, then <?= could be Sweaters Gloves 4 300 6 ? 8 100 a. 100. b. 150. c. 200. d. 250.
When a production possibilities frontier is bowed outward, the opportunity cost of producing
an additional unit of a good increases as more of the good is produced.
The more you produce => The higher the opportunity cost
Opportunity cost = the value of what you have to give up in order to choose something else (often because
option A is chosen over B, where the possible benefit from B is foregone in favor of A)
Marginal benefit > Marginal cost ? = x
Produce 4-6 (sweater) = 300 – x (gloves)
Produce 6-8 (sweater) = x - 100 (gloves)
Produce more => Higher Opportunity cost => Higher Marginal cost
(300 – x) < (x – 100) lOMoARcPSD|46958826
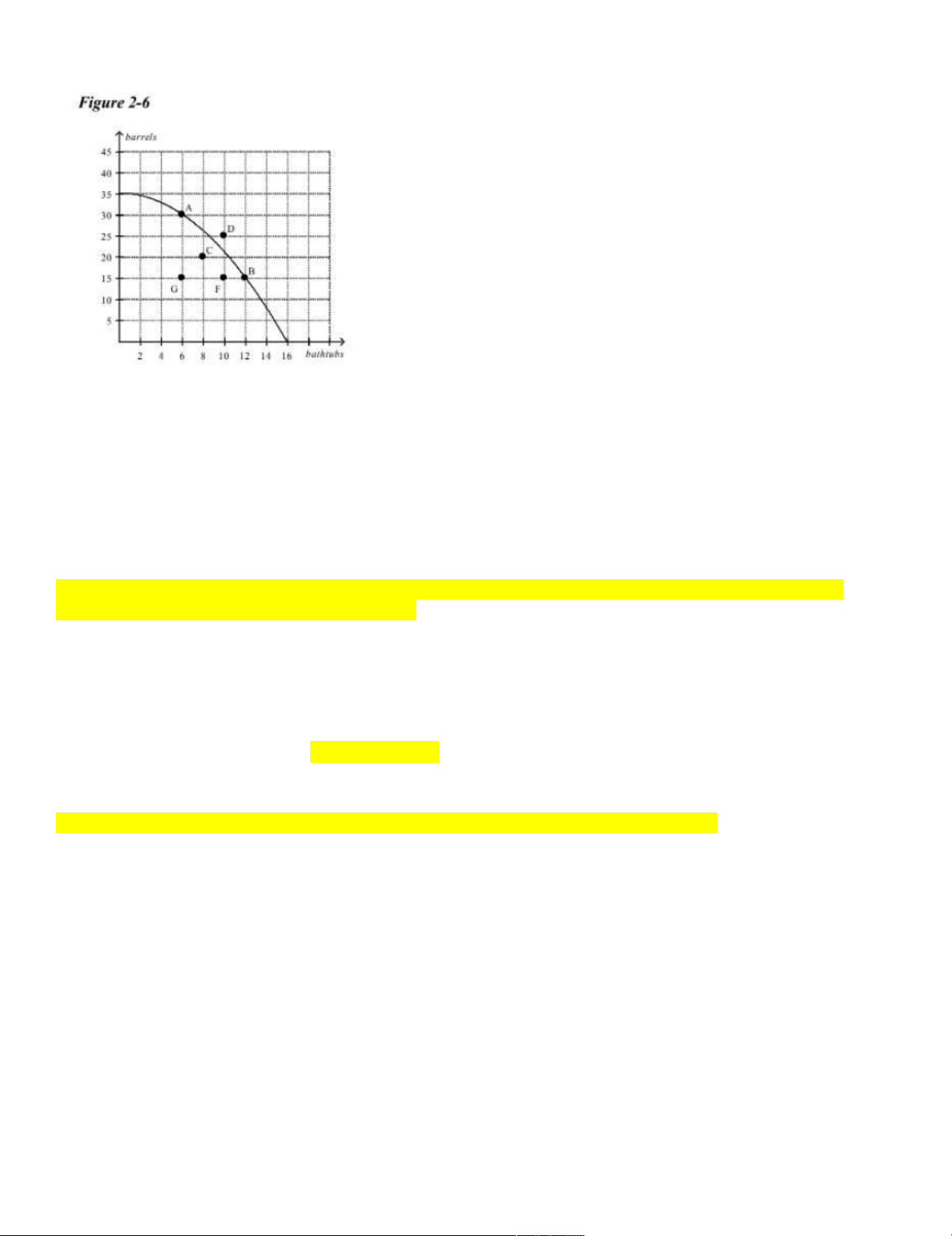
____ 14. Refer to Figure 2-6. This economy has the ability to produce at which point(s)? a. A, B b. A, B, D => on the curve c. A, B, C, F, G d. C, F, G
Because the economy can produce at any point on or inside the production possibilities frontier but
can not produce at points outside the frontier
____ 15. Refer to Figure 2-6. Inefficient production is represented by which point(s)? a. A, B b. C, D, F, G
c. C, F, G => lie inside the PPF, not on the curve d. D
Inefficient production is represented at points inside Production possibility frontier lOMoARcPSD|46958826
The more you produce => The higher the opportunity cost
Opportunity cost = the value of what you have to give up in order to choose something else (often because
option A is chosen over B, where the possible benefit from B is foregone in favor of A)
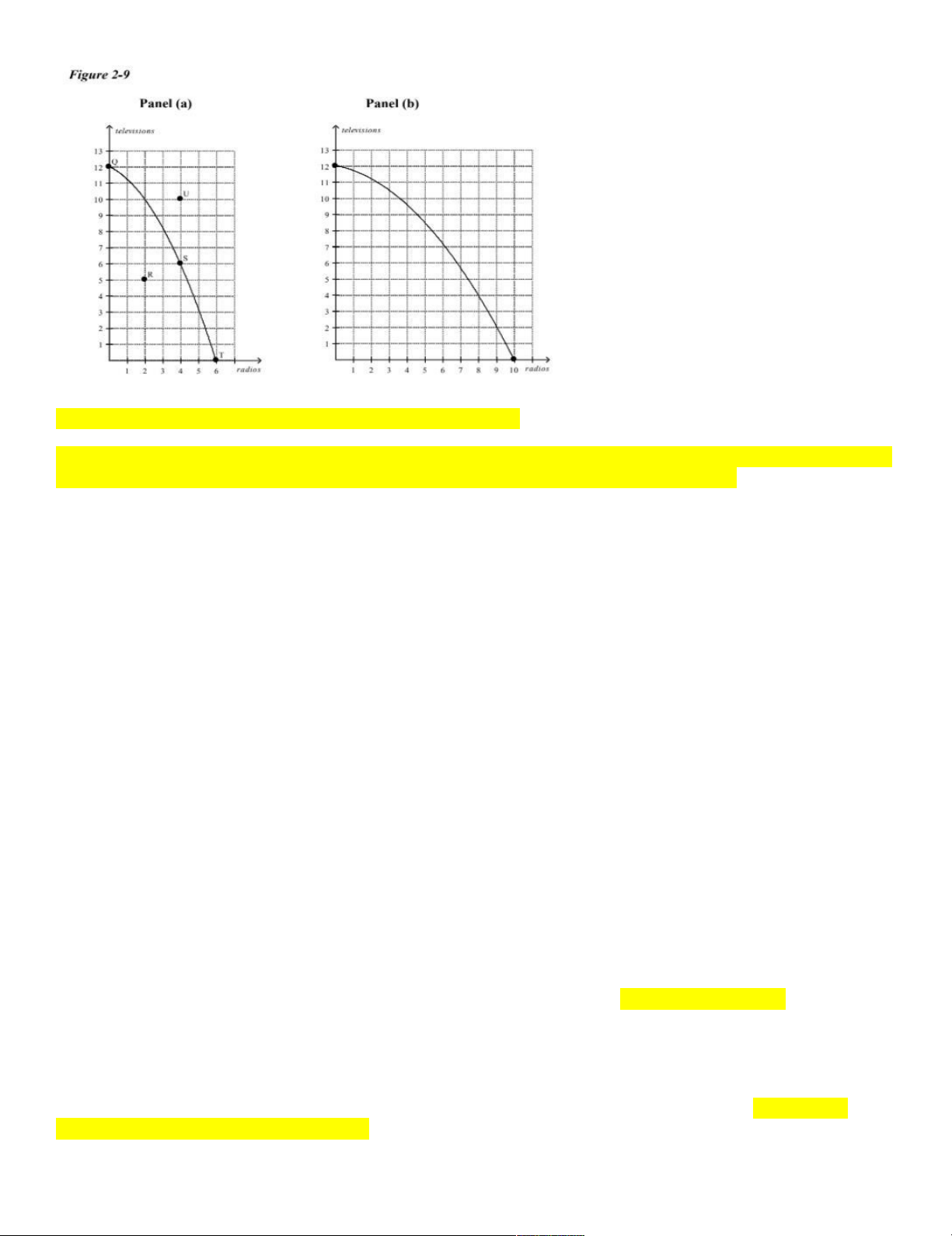
____ 16. Refer to Figure 2-9, Panel (a). The opportunity cost of one television is highest when the economy produces a. 0 televisions. b. 6 televisions. c. 10 televisions. d. 12 televisions.
____ 17. Positive statements are a. prescriptive.
b. claims about how the world should be.
c. claims about how the world is.
d. made by economists speaking as policy advisers.
____ 18. Which of the following is an example of a positive, as opposed to normative (~standard) statement?
a. Income tax rates should not have been cut as they were a few years ago.
b. The quantity of money has grown too slowly in recent years.
c. When the quantity of money grows rapidly, inflation is a predictable consequence. =>Can predict
the consequence of inflation => positive
d. All of the above are positive statements. lOMoARcPSD|46958826
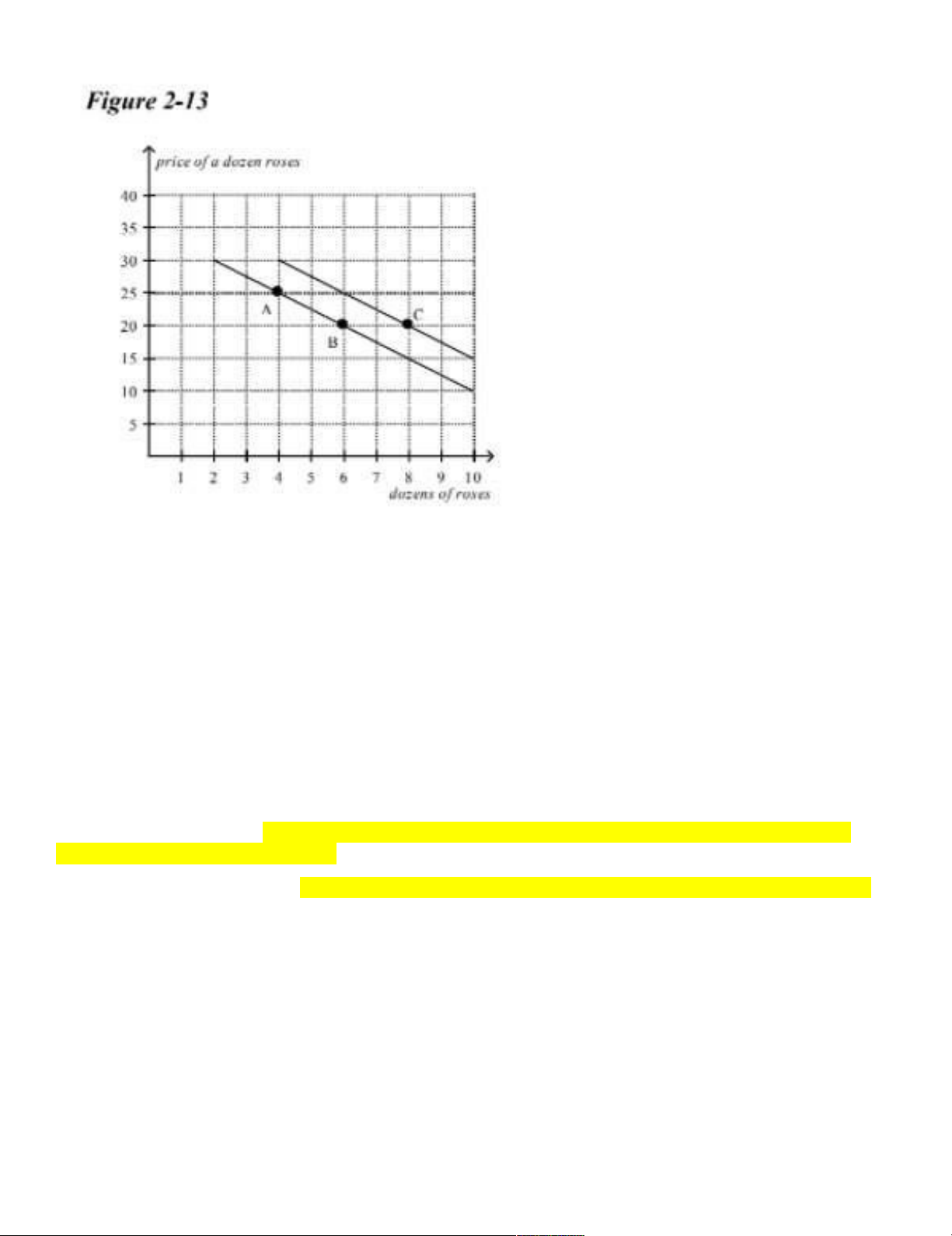
____ 19. Refer to Figure 2-13. The movement from point A to point B is a(n) a. shift of the demand curve.
b. indication of a change in preferences for roses.
c. movement along the demand curve. => because this curve is the Demand curve
d. indication of an increase in income.
____ 20. Refer to Figure 2-13. The movement from point B to point C could have been caused by a. inflation.
b. a change in income. => shift the demand curve. Compared to the movement from point B to point
C, it’s also a shift in demand curve.
c. a change in the price of roses. => change in quantity demanded => movement along the demand curve
d. a change in the cost of producing roses.
II. There is one mistake in each of the following sentences. Find and correct them
1. Economics is the study of how society allocates its unlimited resources. => limited
2. If wages for accountants rose, then accountants’ leisure time would have a lower opportunity cost. => higher
3. A rational decisionmaker takes an action if and only if the marginal cost exceeds the marginal benefit => is less than
4. Efficiency means everyone in the economy should receive an equal share of the goods and lOMoARcPSD|46958826
services produced. => equality
5. The government can potentially improve market outcomes if market inequalities or market
equilibrium exists => market failure
6. Economic models include many details to allow us to see what is truly important. => omit
7. In the circular-flow diagram, firms own the factors of production and use them to produce
goods and services. => buy
8. Refer to Figure 2-14. If this economy uses all its resources in the dishwasher industry, it
produces 35 dishwashers and 75 doghouses. => 0
9. Refer to Figure 2-14. The opportunity cost of moving from point A to point D is 5 dishwashers. => 10
10. Refer to Figure 2-14. The opportunity cost of an additional doghouse decreases as more
doghouses are produced. => increases TUTORIAL 2:
THE MARKET FORCES, SUPPLY AND DEMAND Coverage: Chapter 4 I. Multiple Choice
____ 1. In a competitive market, the quantity of a product produced and the price of the product are determined by a. a single buyer. b. a single seller.
c. one buyer and one seller working together.
d. all buyers and all sellers. (In a competitive market, each buyer knows that there are several sellers from
which to choose, and each seller is aware that his or her product is similar to that offered by other sellers. As
a result, the price and the quantity of a goods are not determined by any single buyer or seller)
____ 2. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
a. Different sellers sell identical products. b. There are many sellers.
c. Sellers must accept the price the market determines.
d. All of the above are characteristics of a perfectly competitive market. lOMoARcPSD|46958826
____ 3. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
a. Sellers set the price of the product. => (Monopoly – the only seller in the market sets the price) b. There are many sellers.
c. Buyers must accept the price the market determines.
d. All of the above are characteristics of a perfectly competitive market.
____ 4. The law of demand states that, other things equal,
a. when the price of a good falls, the demand for the good rises.
b. when the price of a good rises, the quantity demanded of the good rises.
c. when the price of a good rises, the demand for the good falls.
d. when the price of a goods falls, the quantity demanded of the goods rises. => opposite of (the price of
a goods rises, the quantity demanded of the good falls)
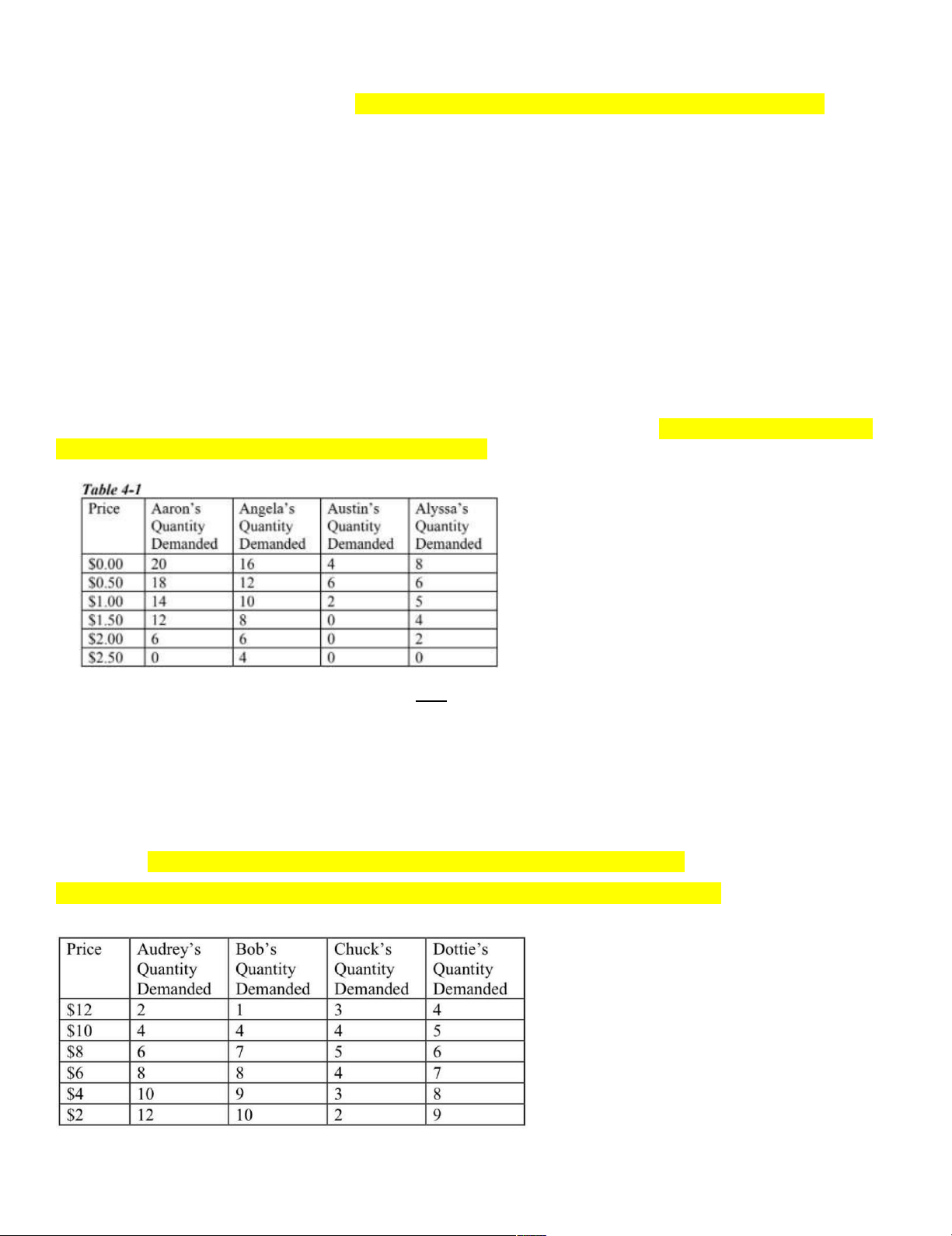
____ 5. Refer to Table 4-1. If these are the only four buyers in the market, then the market quantity demanded at a price of $2 is a. 0 units. b. 3.5 units. c. 6 units.
d. 14 units. => at the price of $2 have 6 of Aaron, 6 of Angela and 2 of Alyssa=>
6+6+2=14 The market quantity demanded = total quantity demanded of individuals
____ 6. Refer to Table 4-2. Whose demand does not obey the law of demand? lOMoARcPSD|46958826 a. Audrey’s b. Bob’s c. Chuck’s d. Dottie’s
the law of demand: Price of a good falls, the quantity demanded of the good rises
____ 7. Which of the following events would cause a movement upward and to the left along the demand curve for olives?
a. The number of buyers of olives decreases. => change in demand => shift the demand curve
b. Consumer income decreases, and olives are a normal good. => change in demand => shift the demand curve
c. The price of pickles decreases, and pickles are a substitute for olives. => price of related good => change in
demand => shift the demand curve
d. The price of olives rises. => the quantity demanded of olives would fall => The demand curve
move upward and to the left
____ 8. You love peanut butter. You hear on the news that 50 percent of the peanut crop in the South has been
wiped out by drought, and that this will cause the price of peanuts to double by the end of the year. As a result,
a. your demand for peanut butter will increase, but not until the end of the year.
b. your demand for peanut butter increases today. (When the price of peanuts to double by the end of the
year => the price of peanuts would rise in the future => the demand for peanut butter increases today)
c. your demand for peanut butter decreases as you look for a substitute good.
d. your demand for peanut butter shifts left today. lOMoARcPSD|46958826
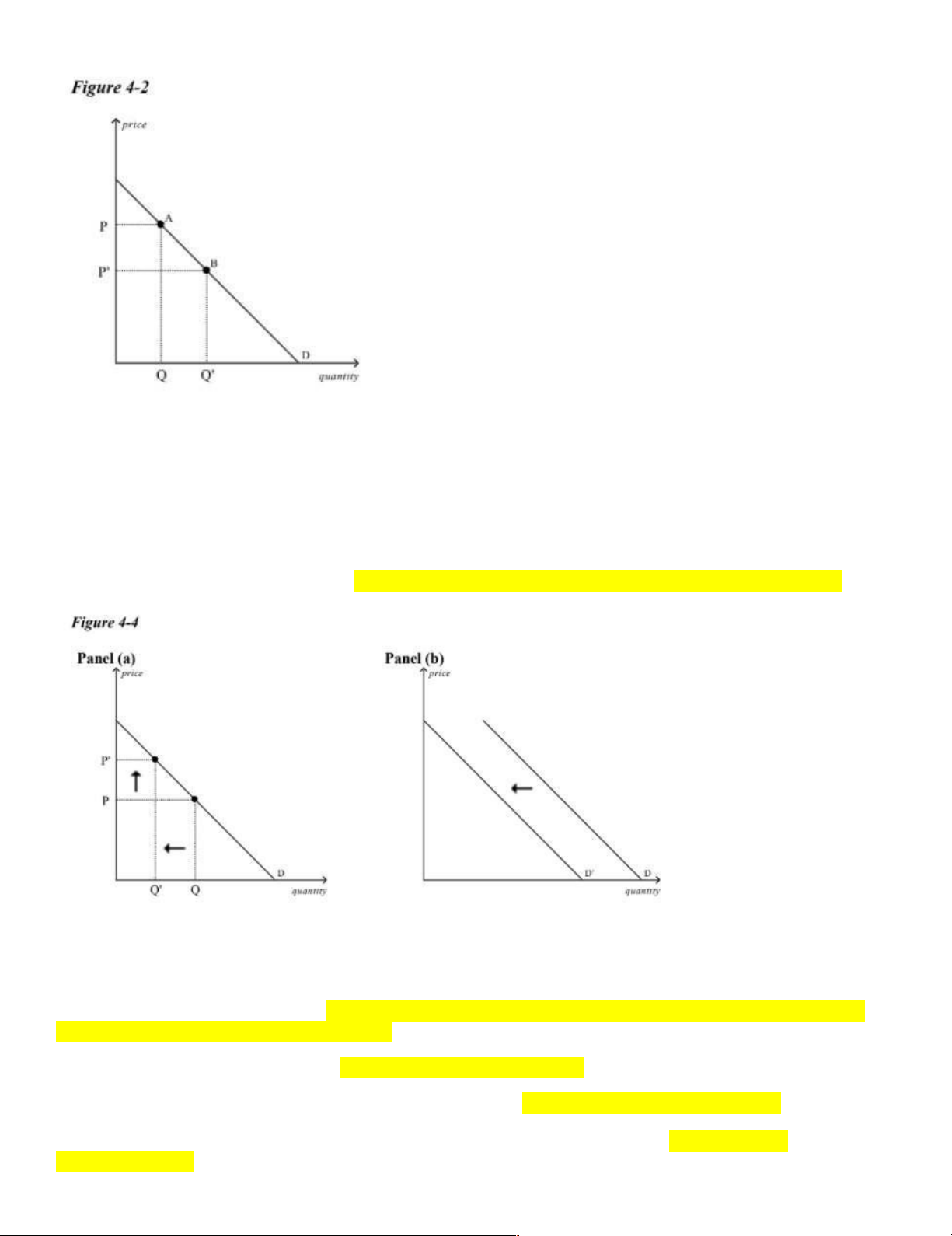
____ 9. Refer to Figure 4-2. The movement from point A to point B on the graph shows a. a decrease in demand. b. an increase in demand.
c. a decrease in quantity demanded.
d. an increase in quantity demanded. => A is Q, B is Q’. Q → Q’ is increase (Q, Q’ on the quantity)
____ 10. Refer to Figure 4-4. The graphs show the demand for cigarettes. In Panel (b), the arrows are consistent
with which of the following events?
a. The price of cigarettes increased. => the quantity demanded of the goods falls => movement along the
demand curve, not shift the demand curve.
b. A tax was placed on cigarettes. => increases in price of cigarettes.
c. The prohibition of cigarette advertisements on television. => directly decrease in demand.
d. Tobacco and marijuana are complements and the price of marijuana decreased. => demand for tobacco increases. lOMoARcPSD|46958826
____ 11. A movement downward and to the left along a supply curve is called a. an increase in supply. b. a decrease in supply.
c. a decrease in quantity supplied.
d. an increase in quantity supplied.
Answer: Because the phrase supply curve shows the change in the quantity supplied. So the answer for question is C.
____ 12. An increase in the price of oranges would lead to
a. an increased supply of oranges.
b. a reduction in the prices of inputs used in orange production.
c. an increased demand for oranges.
d. a movement up and to the right along the supply curve for oranges.
Answer: D is the correct answer for this question because when the price of oranges itself increases, it would lead
to an increase in the quantity supplied of oranges. And when the quantity supplied of oranges increases, the
supply curve will move up and to the right along the supply curve for oranges.
____ 13. What will happen in the rice market now if sellers expect higher rice prices in the near future?
a. The supply of rice will increase.
b. The supply of rice will decrease.
c. The supply of rice will be unaffected.
d. The demand or rice will decrease.
Answer: The answer for this question is B because when sellers expect higher rice prices in the near future, they will
tend to supply less rice. Until the price of rice is as high as they expected, at this point they will sell it for more
profit. Therefore, the current supply of rice will decrease.
____ 14. In a given market, how are the equilibrium price and the market-clearing price related? a. There is no relationship. b. They are the same price.
c. The market-clearing price exceeds the equilibrium price.
d. The equilibrium price exceeds the market-clearing price.
Answer: Because A market-clearing price is the price of a good or service at which quantity supplied is equal to
quantity demanded, also called the equilibrium price. At this price, everyone in the market has been satisfied.
Buyers have bought all they want to buy and sellers have sold all they want to sell.
____ 15. If there is a shortage of farm laborers, we would expect
a. the wage of farm laborers to increase.
b. the wage of farm laborers to decrease. lOMoARcPSD|46958826
c. the price of farm commodities to decrease.
d. a decrease in the demand for substitutes for farm labor.
Answer: A is the answer for this question because when there is a shortage, the quantity demanded for farm workers is
higher than the quantity supplied of farm workers. That is, farms are competing for farm labors to work for them. And
in order for this competition to be highly effective, they are forced to raise wages for farm workers. Table 4-7
The demand schedule below pertains to sandwiches demanded per week. Price Charlie’s Quantity Maxine’s Quantity Quinn’s Demanded Demanded Quantity Demanded $3 3 4 3 $5 1 2 x =2
____ 16. Refer to Table 4-7. Suppose Charlie, Maxine, and Quinn are the only demanders of sandwiches. Also suppose the following: • x = 2
• the current price of a sandwich is $3.00
• the market quantity supplied of sandwiches is 4
• the slope of the supply curve is 2 Then
a. there is currently a shortage of 6 sandwiches and the equilibrium price of a sandwich is less than $3.00.
b. there is currently a shortage of 6 sandwiches and the equilibrium price of a sandwich is $5.00.
c. there is currently a surplus of 6 sandwiches and the equilibrium price of a sandwich is less than $3.00.
d. there is currently a surplus of 6 sandwiches and the equilibrium price of a sandwich is $5.00. Answer:
The current price of a sandwich is $3.00 so at the price, the market quantity demanded of sandwich equals
3+4+3=10. And it is greater than the market quantity supplied of sandwich, which is 4. So the current shortage in this
case equals Qd – Qs = 10 – 4 = 6 Cách 1:
And because there is a shortage in this case, so the Price at shortage is less than the price at equilibrium. So
the equilibrium price of a sandwich must be $5.00. So b is the answer for this question. Cách 2:
When the slope of the supply curve is 2. It means that lOMoARcPSD|46958826 the percentage change in price
the percentage change in Quantity supplied Qs−4 2 = =
➔ Qs (at the price of $5.00) = 5 And the market 5−3
quantity demanded at the price of $5.00 also equals 1+2+2=5. So the equilibrium price of a sandwich is $5.00 Figure 4-11 price 20 S 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 D 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 quantity
____ 17. Refer to Figure 4-11. At a price of $4, which of the following is correct?
a. there is a surplus of 3 units
b. there is a surplus of 6 units
c. there is a shortage of 3 units
d. there is a shortage of 6 units
Answer: We can see that, At the price of $4, the Qs = 2 and Qd = 8. Because the quantity demanded exceeds
the quantity supplied, there is a shortage at this price. And the shortage at this price of $4 equals Qd – Qs = 8 –
2 = 6 units. So D is the answer for this question. Figure 4-13
The diagram below pertains to the supply of paper in university markets. lOMoARcPSD|46958826 price S A y S B x quantity
____ 18. Refer to Figure 4-13. All else equal, the return of college students to campus in the fall would cause a move a. from x to y. b. from y to x. c. from SA to SB. d. from SB to SA.
Answer: The answer for this question is A because all else equal when students return to campus in the
fall, sellers would increase the price of paper to make more profit. And according to the law of supply, the
price of a good rises, the quantity supplied of the good also rises. And when the quantity supplied rises, it
leads to a movement up along a supply curve from x to y.
____ 19. If the supply of a product increases, then we would expect
a. equilibrium price to increase and equilibrium quantity to decrease.
b. equilibrium price to decrease and equilibrium quantity to increase.
c. equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity both to increase.
d. equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity both to decrease. Answer:
When the supply of a product increases, it would lead to a shift in the supply curve to the right. When the
supply curve shifts to the right, it creates a new equilibrium at which the equilibrium price will decrease
and the equilibrium quantity will increase from the original equilibrium. lOMoARcPSD|46958826
____ 20. Which of the following events would unambiguously (chắc chắn) cause a decrease in the equilibrium price of cotton shirts?
a. an increase in the price of wool shirts and a decrease in the price of raw cotton
b. a decrease in the price of wool shirts and a decrease in the price of raw cotton
c. an increase in the price of wool shirts and an increase in the price of raw cotton
d. a decrease in the price of wool shirts and an increase in the price of raw cotton
Answer: Option b. It is because wool shirts and cotton shirts are substitutes, so a decrease in the price of wool shirts
will decrease the demand for cotton shirts. So in order to sell cotton shirts, sellers must reduce the price of this good.
Moreover, the decrease in raw cotton prices will reduce the price of cotton shirts because sellers don’t have to spend too much to make the product. II.
There is one mistake in each of the following sentences. Find and correct them 1.
A movement upward and to the left along a given demand curve is called a decrease in demand. (quantity demanded) 2.
When Mario's income decreases, he buys more pasta. For Mario, pasta is a normal (inferior) good. 3.
Baseballs and baseball bats are substitute (complement) goods. 4.
A decrease in the price of a product and an increase in the number of buyers in the market
affect the demand curve in the same (different) way. (Cái decrease in the price of product chỉ
move down to the right còn increase in the numbers of buyers will shift the demand curve to the right) 5.
Most studies have found that tobacco and marijuana are substitutes (complements) 6.
An increase in the price of ink will shift the supply curve for pens to the right (left) 7.
When a seller expects the price of its product to decrease in the future, the seller's supply curve shifts left (right) now. 8.
Price will rise (fall) to eliminate a surplus. 9.
A decrease in supply will cause an increase in price, which will cause a decrease in demand (quantity demanded). 10.
The actions of buyers and governments (sellers) naturally move markets toward equilibrium. TUTORIAL 3: ELASTICITY
Coverage: Chapter 5 I. Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. lOMoARcPSD|46958826 Table 5-2
The following table shows a portion of the demand schedule for a particular good at various levels of income. Quantity Demanded Quantity Demanded Quantity Demanded Price (Income = $5,000) (Income = $7,500) (Income = $10,000) $24 2 3 4 $20 4 6 8 $16 6 9 12 $12 8 12 16 $8 10 15 20 $4 12 18 24 ____
1. Refer to Table 5-2. Using the midpoint method, when income equals $5,000, what is the price elasticity of demand between $8 and $12? a. 0.56 b. 0.75 c. 1.33 d. 1.80 Āā2ĀĀ
Answer: when applying the midpoint method, we have the equation: | Ā . Āā−ÿ| = ÿ. ÿĀ ÿā2ÿĀ
____ 2. For which of the following ā ÿ−Āÿ Āÿ ÿĀ+ÿā ĀĀ+Āā
The price elasticity of demand = = ā
goods is demand probably most inelastic? a. camcorders b. insulin c. apples
d. devices that remove cores from apples
Answer: The answer for this question is B because insulin is a medicine that is necessary to treat
diabetes. So regardless of the price of insulin, diabetics still have to pay it because there are no good
substitute and if don’t use it, they may die. ____
3. Demand is said to be inelastic if
a. buyers respond substantially to changes in the price of the good.
b. demand shifts only slightly when the price of the good changes.
c. the quantity demanded changes only slightly when the price of the good changes.
d. the price of the good responds only slightly to changes in demand.
Answer: Because when the price of good changes, it affects the quantity demanded. And Demand is
considered inelastic when the elasticity is less than 1, which means the quantity moves proportionately less
than the price. So the quantity demanded changes only slightly when the price of the good changes leads to the inelastic demand. lOMoARcPSD|46958826 ____
4. If demand is price inelastic, then
a. buyers do not respond much to a change in price.
b. buyers respond substantially to a change in price, but the response is very slow.
c. buyers do not alter their quantities demanded much in response to advertising, fads, or general changes in tastes.
d. the demand curve is very flat.
Answer: Because according to theory, the demand is inelastic if the quantity demanded changes only slightly
when the price of the good changes. So when compared to the answer a, the phrase < do not respond much
to a change in price= also means ____
5. Suppose the price of Twinkies decreases from $1.45 to $1.25 and, as a result, the quantity of Twinkies
demanded increases from 2,000 to 2,200. Using the midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand for
Twinkies in the given price range is a. 2.00. b. 1.55. c. 1.00. d. 0.64.
The price elasticity of demand = . 0.64 2,200−2,000 1.45+1.25 2
Answer: When using the midpoint method, we have the equation: 2000+22000 1.25−1. | 2 45 | = ____
6. When demand is perfectly inelastic, the price elasticity of demand
a. is zero, and the demand curve is vertical.
b. is zero, and the demand curve is horizontal.
c. approaches infinity, and the demand curve is vertical.
d. approaches infinity, and the demand curve is horizontal.
Answer: Because according to theory, demand is perfectly inelastic because regardless of the price, the
quantity demanded stays the same. So the demand curve is vertical and the price elasticity of demand
equals zero because there is no change in the quantity demanded. ____
7. In which of these instances is demand said to be perfectly inelastic?
a. An increase in price of 2% causes a decrease in quantity demanded of 2%.
b. A decrease in price of 2% causes an increase in quantity demanded of 0%.
c. A decrease in price of 2% causes a decrease in total revenue of 0%.
d. The demand curve is horizontal.
Answer: The answer for this question is B because in perfectly inelastic demand, the quantity demanded
is constant and equals to zero. And in answer B, we have the equation of price elasticity equals to %
change in the quantity demanded over the percentage change in the price = 0/2=0
➔ So the answer for this question must be B. lOMoARcPSD|46958826
____ 8. Suppose that 50 candy bars are demanded at a particular price. If the price of candy bars rises from that
price by 5 percent, the number of candy bars demanded falls to 48. Using the midpoint approach to
calculate the price elasticity of demand, it follows that the
a. demand for candy bars in this price range is unit elastic.
b. price increase will decrease the total revenue of candy bar sellers.
c. price elasticity of demand for candy bars in this price range is about 1.22.
d. price elasticity of demand for candy bars in this price range is about 0.82.
Answer: Approach the midpoint method, we have:
____ The price elasticity of demand = | 48−50 1
9. If demand is price inelastic, then when price rises, 49 㕥 5% | = 0.82 a. total revenue will fall. b. total revenue will rise.
c. total revenue will remain unchanged.
d. total revenue may rise, fall, or remain unchanged. More information is need to determine the
change in total revenue with certainty.
Answer: When the price is inelastic, it means that the quantity demanded changes only slightly when the
price changes. In this case, an increase in the price leads to a decrease in quantity demanded that is
proportionately smaller, so total revenue increases.
____ 10. The cross-price elasticity of demand can tell us whether goods are a. normal or inferior. b. elastic or inelastic. c. luxuries or necessities. d. complements or substitutes.
Answer: The cross price elasticity of demand measures how much the Qd of the good responds to a
change in the price of another good. So that, when the result of the fomula about the cross-price elasticity
is positive or negative, it shows the good is complements or subtitutes.
____ 11. A key determinant of the price elasticity of supply is the
a. number of close substitutes for the good in question. b. definition of the market. c. length of the time period.
d. extent to which buyers alter their quantities demanded in response to changes in their incomes.
Answer: Because if in the short run, suppliers are unable to completely react to the change in the price. But
in the longer period of time, it’s easier to shift resources among products and adapt to this change
completely, following a change in their relative price.




