











Preview text:
Lesson 7: Cost Management
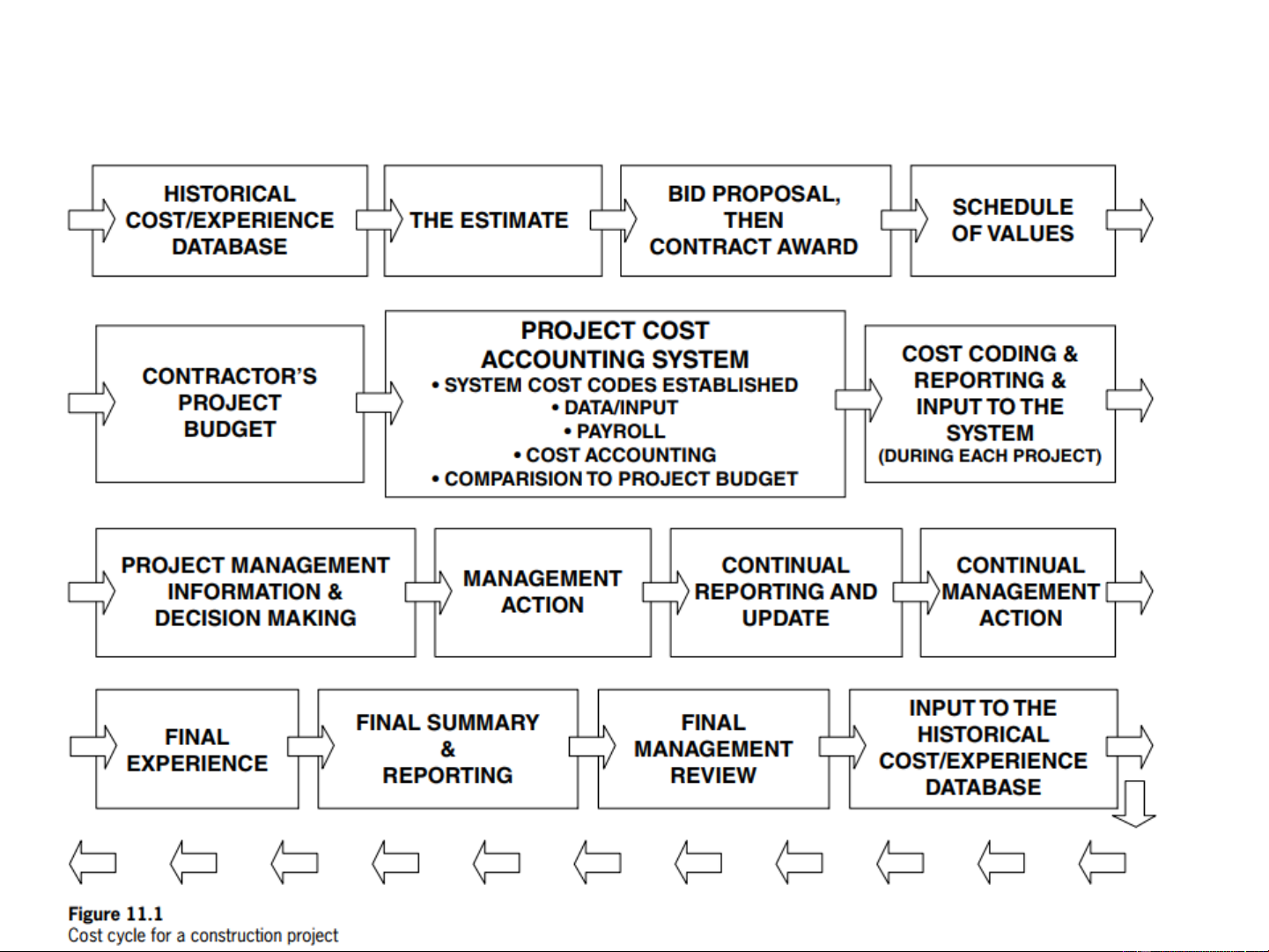
Construction Project Management Lecturer: Nguyen Van Minh Main contents 1. Project cost cycle 2. EVM 2 1. Project cost cyle Project cost life cycle
GĐ chuẩn bị dự án
GĐ thực hiện dự án
GĐ kết thúc dự án Lập BC Lập BC NC khả thi Lập KH lựa Tư vấn Tư vấn đấu Nhà thầu Tư vấn Nghiệm Bảo Khai thác NC tiền (DA<15 tỷ lập chọn nhà thầu thiết kế thầu thi công giám sát thu, bàn hành vận hành, khả thi BCKTKT) XDCT giao bảo trì Thiết kế •Giá dự thầu CĐT lập hồ sơ KT hoặc •Giá đề nghị Thiết kế quyết toán TKBVTC trúng thầu cơ sở trình phê duyệt SƠ BỘ TỔNG MỨC Giá gói thầu TỔNG Giá gói thầu GIÁ HỢP GIÁ GIÁ TRỊ Quy đổi TỔNG ĐẦU TƯ DỰ TOÁN được cập ĐỒNG THANH QUYẾT vốn ĐTXD MỨC ĐẦU nhật TOÁN TOÁN TƯ
CP Bồi thường, hỗ trợ và tái định cư CP Xây dựng (Gxd) CP Xây dựng (Gxd) Suất vốn
Hệ thống định mức và đơn giá xây
dựng theo quy định của Bộ xây dựng CP Thiết bị (Gtb) đầu tư CP Thiết bị (Gtb) CP Quản lý dự án (Gqlda)
CP Quản lý dự án (Gqlda): CP Tư vấn (Gtv) CP Tư vấn (Gtv) CP khác (Gk) CP khác (Gk)
CP Dự phòng (Gdp): Dự phòng KL
CP Dự phòng (Gdp): Dự phòng KL phát sinh (5%) + DP trượt giá
phát sinh (10%) + DP trượt giá 3 1. Project cost cyle 4 2. Earned Value Method (EVM)
What is Earned Value Management (EVM)?
• A method of integrating scope, schedule, and resources, and for measuring project performance.
• It compares the amount of work that was planned with what was
actually earned with what was actually spent to determine if cost
and schedule performance are as planned. 5 2. Earned Value Method (EVM) What is needed for EVM? • A baseline plan
• A project budget (BAC – Budget at Completion) • A project end date
• Tasks are identified & scheduled
• Each task has a budget or effort (resource loaded / weighting) • Actuals tracked 6 2. Earned Value Method (EVM)
To perform EVM, three values need to be determined • Planned Value (PV or BCWS) • Actual Costs (AC or ACWP) • Earned Value (EV or BCWP) 7 2. Earned Value Method (EVM)
Basic concepts of Earned Value Management (EVM)
• Each task in a project earns value as planned work is completed
✓For example (perhaps), if you were paid on this basis, you would earn
$$ at key milestones based on the value of what you have completed (earned value)
• Earned value can be compared to actual cost and budgeted cost to
determine variance and predict future performance 8 2. Earned Value Method (EVM)
• The budgeted cost (e.g., dollars, person-hours, person-days, etc.)
in terms of your baseline plan/budget of the work performed up to a specified point in time
• Also known as Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP)
• Each task in the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is assigned a
BCWP based on its individual cost.
• Project BCWP is total of BCWP for all tasks required to complete the project 9 2. Earned Value Method (EVM) • Planned Value (BCWS)
✓How much work (person-hours) you planned to have accomplished at
a given point in time (this is from the WBS in your plan) • Actual Cost (ACWP)
✓How much work (person-hours) you have actually spent at a given point in time • Earned Value (BCWP)
✓The value (person-hours) in terms of your base budget of what you
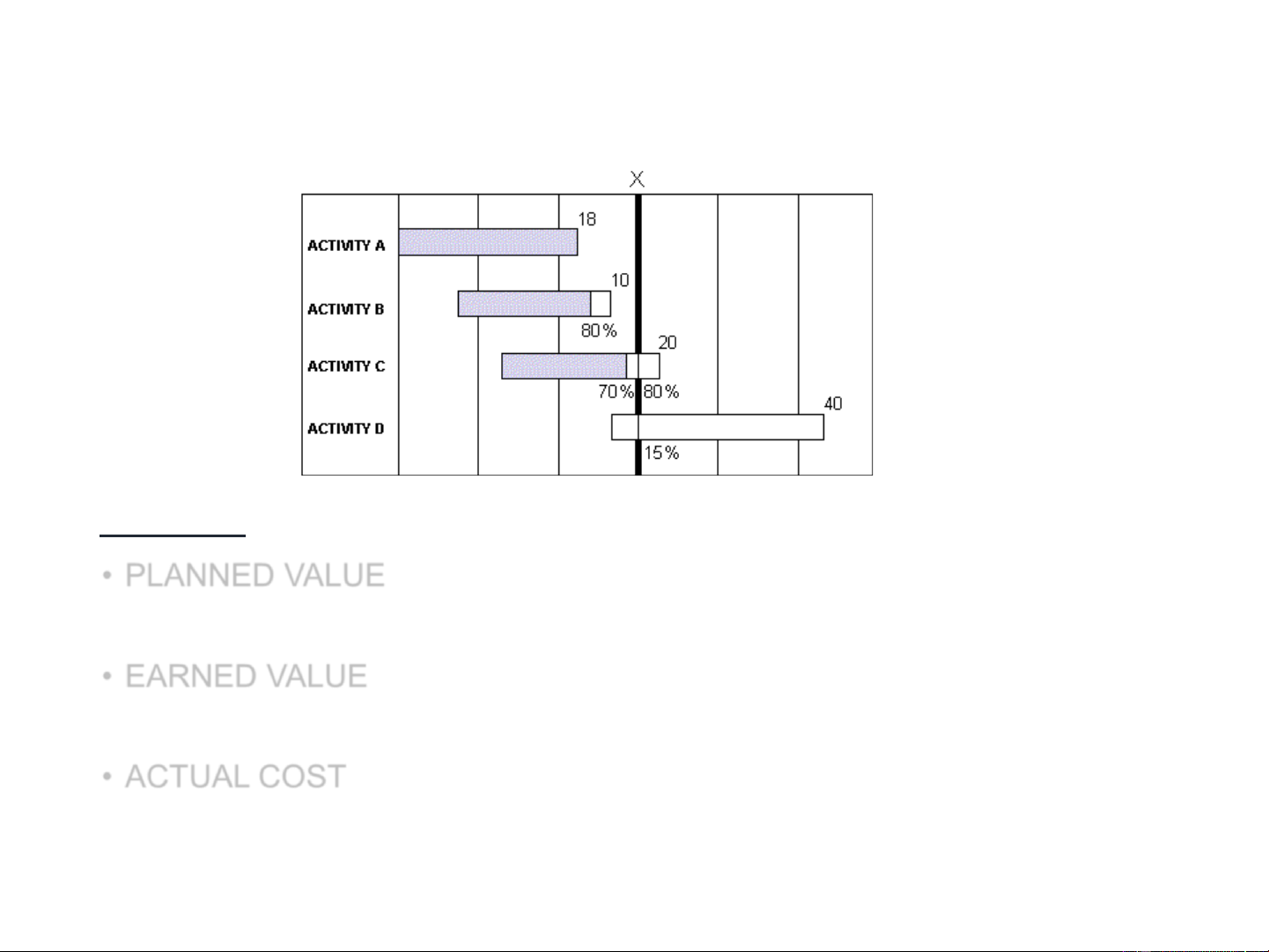
have accomplished at a given point in time (or, % complete X Planned Value) 10 2. Earned Value Method (EVM) On Day X:
• PLANNED VALUE (Budgeted cost of the work scheduled, BCWS) = 18 + 10 + 16 + 6 = 50
• EARNED VALUE (Budgeted cost of the work performed, BCWP) = 18 + 8 + 14 + 0 = 40
• ACTUAL COST (of the work performed , ACWP) =
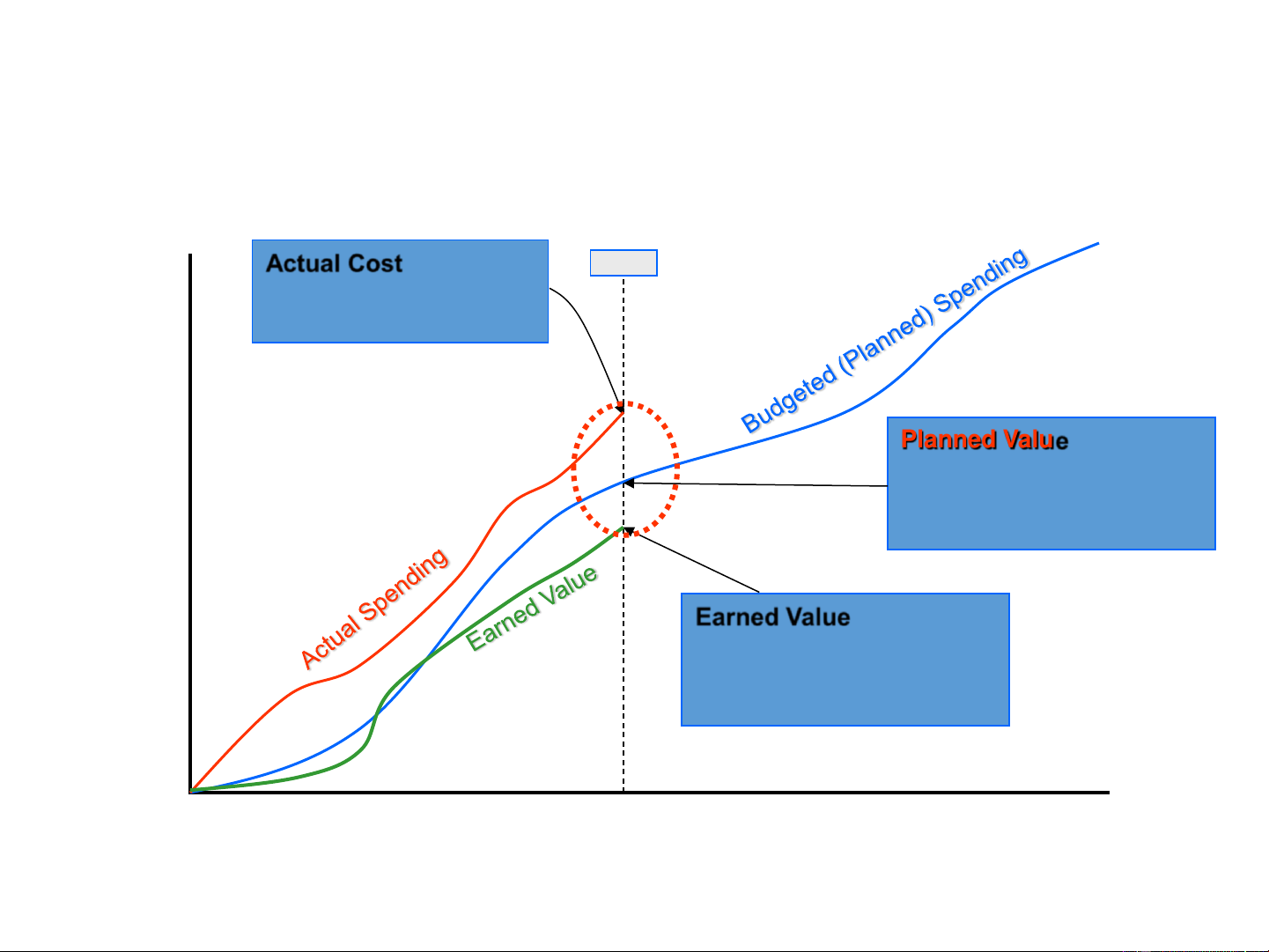
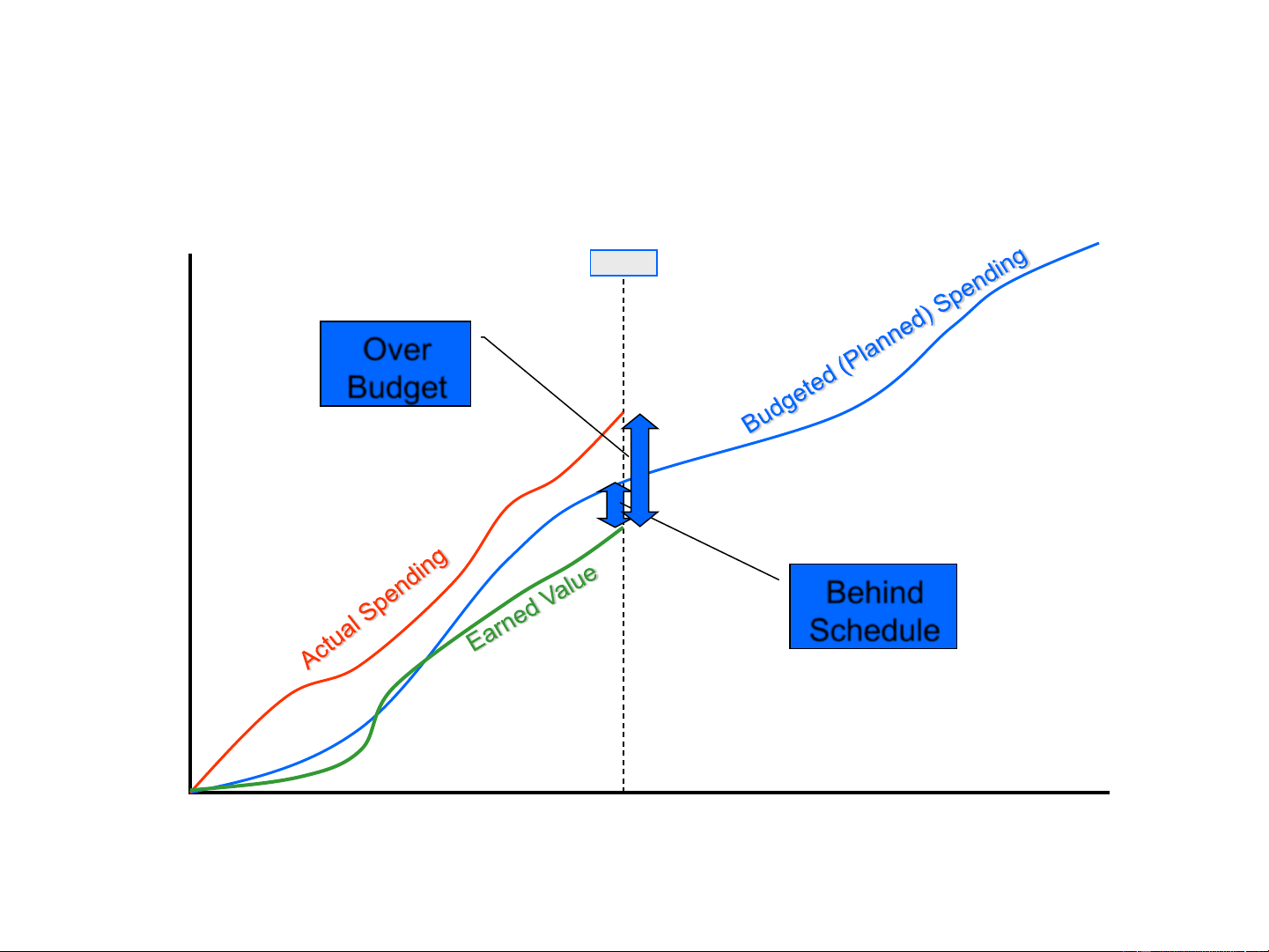
55 (from your project tracking - not evident in above chart) 11 2. Earned Value Method (EVM) Actual Cost: what you Today have actually spent to this point in time. rs) u
Planned Value: what your Ho- plan called for sending on n the tasks planned to be completed by this date. st (Perso
Earned Value: value (cost) Co of what you have accomplished to date, per the base plan. Time (Date) 12 2. Earned Value Method (EVM) Today Over rs) Budget u Ho-n Behind st (Perso Schedule Co Time (Date) 13 2. Earned Value Method (EVM) Terms
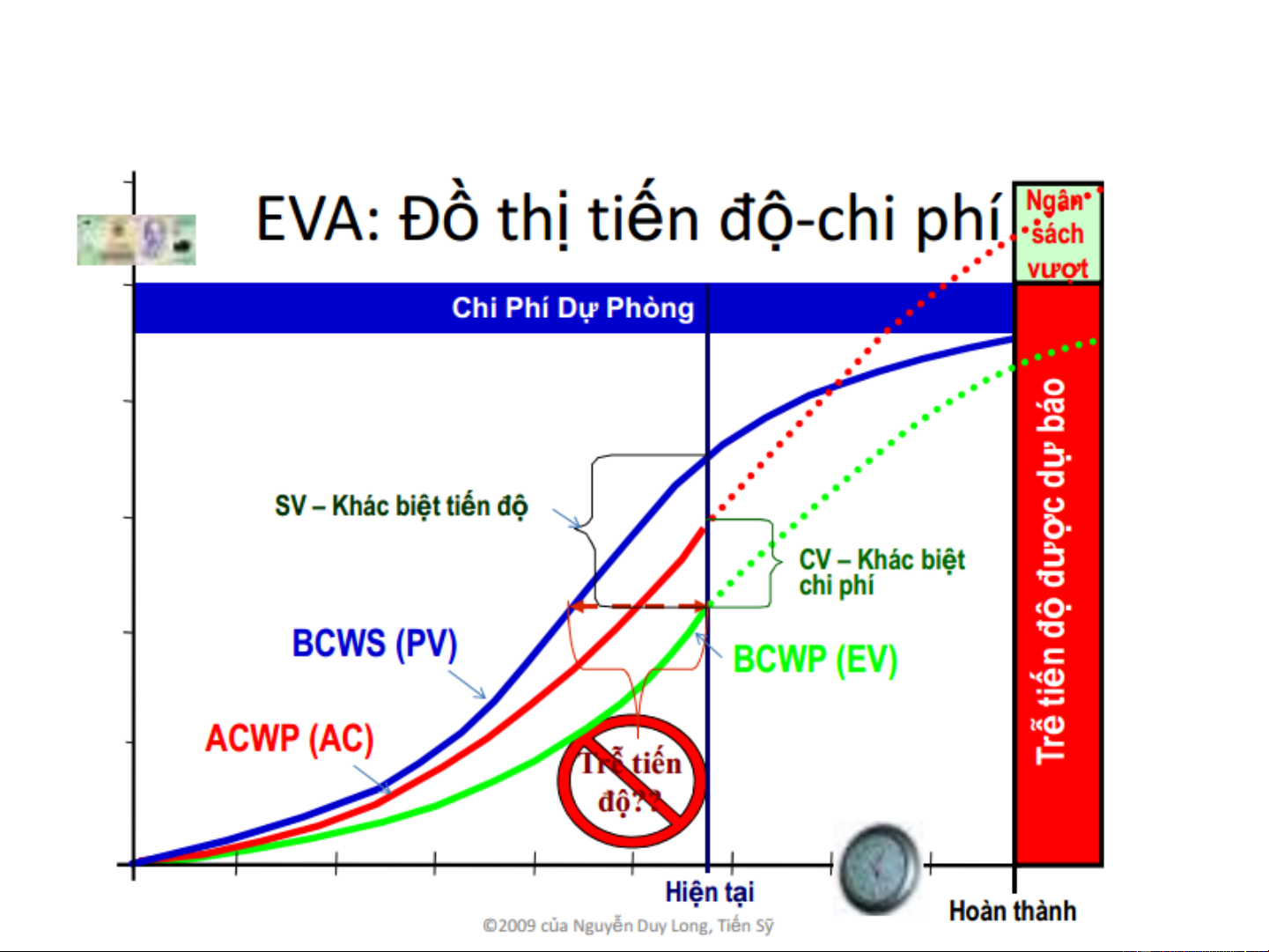
• EV (Earned Value) or BCWP (Budgeted Cost of Work Performed):
This represents the budgeted cost for the work that has been completed to date.
• BCWS (Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled): This is the budgeted
cost for the work that is scheduled to be completed according to the project plan.
• ACWP (Actual Cost of Work Performed): This refers to the actual
costs incurred for the work that has been completed. 14 2. Earned Value Method (EVM)
• STWP (Scheduled Time for Work Performed): The baseline time
allocated for the work to be completed.
• ATWP (Actual Time for Work Performed): The actual time taken to complete the work.
• CV (Cost Variance): Indicates the difference in cost CV = BCWP − ACWP
If CV < 0, it means there is a cost overrun.
• SV (Schedule Variance): Indicates the difference in schedule SV = BCWP − BCWS
If SV < 0, it means the project is behind schedule.
• TV (Time Variance): Indicates the difference in time TV = STWP−ATWP
If TV < 0, it means there is a delay. 15 2. Earned Value Method (EVM)
• Cost Variance % (CV%) CV% = CV / EV
✓Good News: If CV% value is positive, the project is currently under budget by the CV%
✓Bad News: If CV% value is negative, the project is currently over budget by the CV%
• Schedule Variance % (SV%) SV% = SV / PV
Good News: If SV value is positive, the project is currently ahead of schedule by the SV%
Bad News: If SV value is negative, the project is currently behind schedule by the SV% 16 2. Earned Value Method (EVM)
• CPI (Cost Performance Index): CPI = BCWP / ACWP CPI < 1 → Over budget
• SPI (Schedule Performance Index): SPI = BCWP/BCWS SPI < 1 → Behind schedule
• CSI (Cost Schedule Index): CSI = CPI x SPI
The closer CSI is to 1, the greater the chance the project will return to plan. 17 2. Earned Value Method (EVM) 18 2. Earned Value Method (EVM)
• BAC (Budget at Completion) is the total budget allocated for a
project, representing the sum of all planned costs for project activities
• ETC (Estimate To Complete) refers to the estimated cost needed
to finish the remaining work of a project.
• EAC (Estimate At Completion): EAC is the total expected cost to
complete all work represented by the sum of actual costs to date
and the estimate to complete (ETC). 19 2. Earned Value Method (EVM)
Four methods to calculate EAC • Method 1:
If the original plan is no longer suitable: EAC = ACWP + ETC • Method 2:
If the future work is performed as originally planned: EAC = ACWP + BAC – EV EAC = ACWP + BAC – BCWP 20



