









Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 45903860
THEME 5: ECONOMY 1. U.S. major economic regions and industries
- West: livestock, mining, tourism and high-tech industries in California's "Silicon Valley"
- Midwest: a major farming region and leading producer of industrial goods; contains
the "Corn Belt" (Nebraska to Ohio) and the "Dairy Belt" (Wisconsin, Minnesota. Michigan)
- Northeast: financial center with a large transportation and trade network; was once
the dominant economic area of the nation, but that has shifted in the last 50 years.
- South: historically an agricultural center but in recent decades new industries like
high-tech, automobile, banking, and aerospace have been growing.
2. Five industries driving the U.S. economy a. Healthcare
The Bureau of Labor Statistics expects healthcare jobs to grow at an annualized rate of
18% from 2016 to 2026, much faster than the rate of the rest of the economy. b. Technology
The tech sector is a huge component of the U.S. economy, according to Cyberstates 2019.
Employment in computer and IT is projected to grow 11% from 2019 to 2029, faster than
the average for all occupations. c. Construction
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, construction and extraction occupations are
projected to grow by 4% from 2019 to 2029, which is nearly as fast as the average for all occupations. d. Retail
The retail trade accounts for 5.5% of the nation's GDP, providing 9.6% of total employment
in the U.S., according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. e. Non-durable Manufacturing
Non-durable manufacturing is a predominant pillar in the U.S. with a GDP value-added
that's 4.8% of the national GDP, according to the Federal Reserve.
(Commodities that are defined as having a lifespan of less than three years, such as
gasoline, electricity, and clothing) lOMoAR cPSD| 45903860
3. Revolutionary American Inventions
- The Cotton gin by Eli Whitney and patented in 1794, dramatically reducing the time it took to produce cotton.
- The electric light bulb by Thomas Edison in 1879, enabling manufacturers to work
into the night, which increased productivity
- The telephone by Alexander Graham Bell in 1892, leading to a boon for efficiency,
productivity and profitability
4. Revolutionary Pioneers
- The moving assembly line, by Henry Ford in 1908, reducing the time to produce a car
from 12 hours to less than 3 hours.
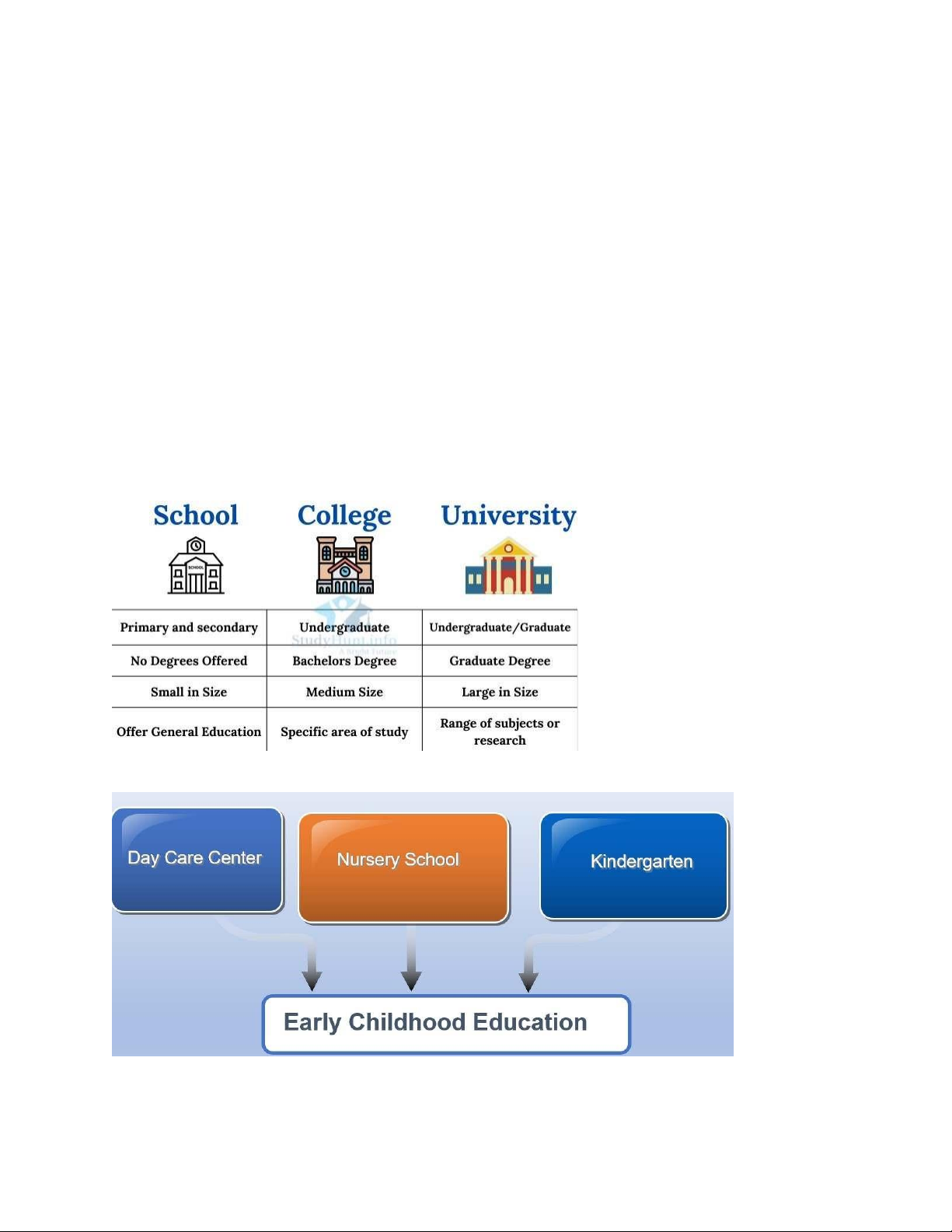
THEME 6: EDUCATION 1. Education system
- Philosophy: American ideal of individual success based on ‘equality of opportunity’
and on ‘working your way to the top’. a. Preschools
- Not free education up to now lOMoAR cPSD| 45903860
- President Joe Biden released his American Families Plan (April 28, 2021),
proposing that provide “free, high-quality, accessible and inclusive preschool” to all
3- and 4-year-olds” (White House statement).
- Kindergarten: Paid service; Child-care center on college campus: Affordable support.
b. Primary and secondary education
- Four basic characteristics of public schools: locally controlled publicly supported by taxes coeducational
free from religious influence
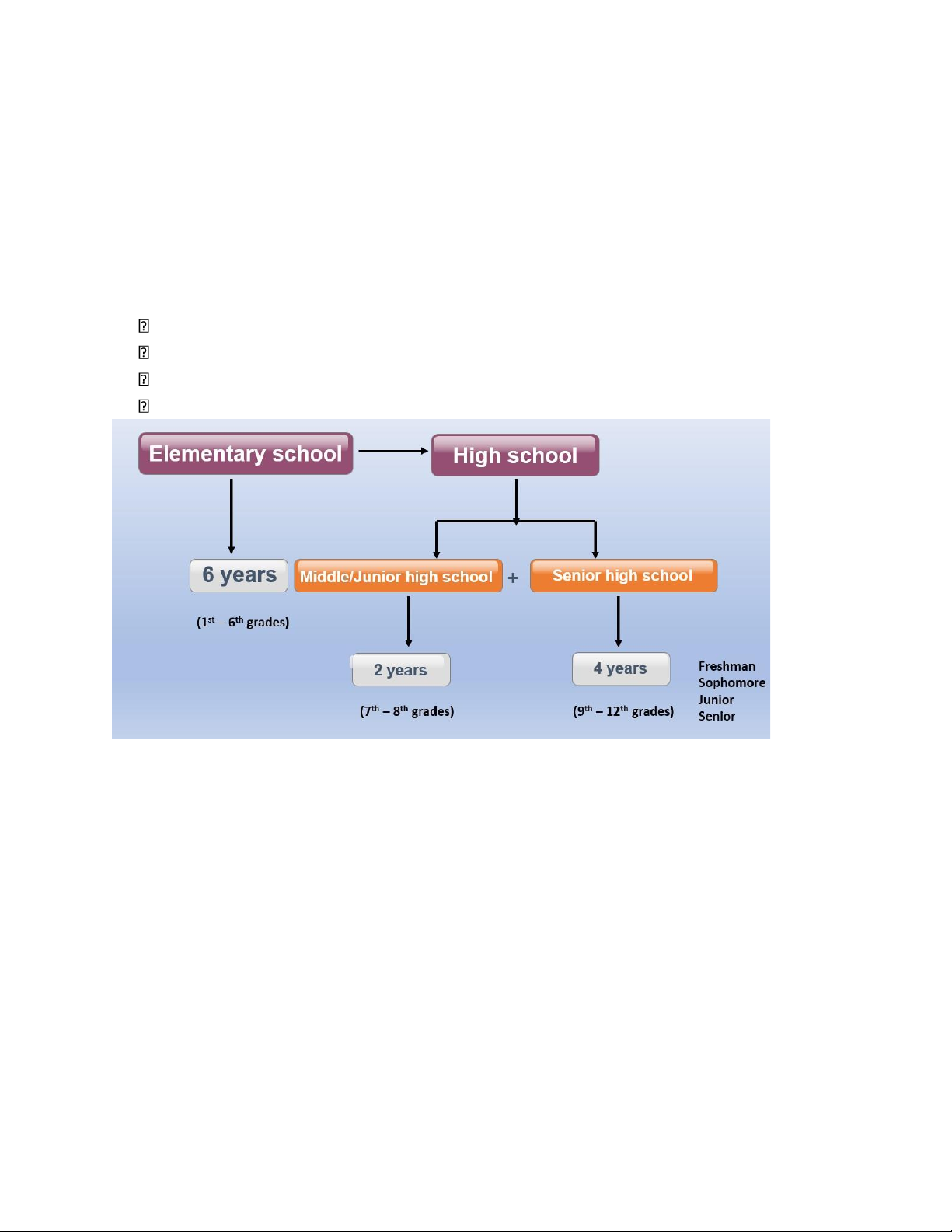
- The American education system requires that students complete 12 years of primary
& secondary (or junior high school & senior high school) education prior to
attending a college or a university.
- This may be accomplished either at public schools (free) or at private schools (paid).
- These 12 years of schooling may also be completed outside the U.S., giving foreign
students the opportunity to pursue the benefits of the American education system &
obtain a quality American education. lOMoAR cPSD| 45903860
c. Post-secondary or higher education
2. Higher education institutions and degrees a. Undergraduate institutions
- Number: More than 4,000 accredited institutions
- Accreditation: quality recognition by national or regional independent accrediting bodies
- State colleges and universities (public universities):
scale: big, each institution consisting of many colleges and/or schools
fund: tax money providing low-cost education
in-state students: lower tuition out-
of-state students: higher tuition
- Private colleges and universities:
scale: smaller, including religious or single-sex institutions
fund: endowments, gifts from alumni, research grants, and tuition fees
- Affirmative Action: A policy promoting the diversity of students of colors/races for
earning a quality degree (with lower admission requirements and financial aids)
b. Community college or junior college
- Two-year academic, vocational, or professional programs
- Nearly always publicly funded by the state, county, or city governments
- Typically much lower tuition than at a 4-year college or university
-> Many students choose accredited community colleges for 2 years to lower the cost of
getting a Bachelor’s degree (credits are transferable to four-year colleges and universities). lOMoAR cPSD| 45903860
c. Liberal arts colleges - Four-year programs
- A wide range of adaptable skills that appeal to many types of employers
- A flexibility to work in many different industries - Degrees: BA, BFA, BS
Bachelor of Arts (BA) for humanities and social sciences
Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA) for creative writing or acting
Bachelor of Science (BS) for business, math, and the sciences
- A strong foundation for graduate study in a Master’s degree or PhD program d. The Ivy League
- Eight private research universities & college - Highly intellectual
- Dominate in the fields of Law, Medicine, Engineering and Business
- Breeding ground for historically significant faces, Noble laureates, corporate giants,
and award-winning professionals - Average tuition: $60,000/yr.
- SAT 1580 or ACT 35: top 25% for most Ivy League schools
- SAT 1450 or ACT 31: bottom 25% - Average GPA: 4.0
e. Diploma mill or Degree mill
- Offers, for a fee, degrees, diplomas, or certificates that requires little or no education or coursework
- Lacks accreditation by a accrediting agency or association not recognized by the U.S. Department of Education
- Tuition paid on a per-degree basis, or discounts for enrolling in multiple degree programs
- Little or no interaction with professors
- Names that are similar to well known reputable universities f. Master’s Degree & Doctoral Degree lOMoAR cPSD| 45903860
- A graduate school degree that typically requires 2 years of full-time graduate school coursework to complete lOMoAR cPSD| 45903860 -
Courses highly focused in a field of study
- Research field for a Doctoral degree is even more focused & specialized than the Master’s degree
- Completion of a Doctoral degree typically takes between 3 & 6 years depending on
research students’ ability, with the thesis resulting from a very long, extensive & original research
3. Admission tests for higher education * Undergraduate & Graduate Admissions
THEME 7: AMERICAN RELIGIONS & HOLIDAYS 1. Understanding Concepts
- Religion: the belief in and worship of a god or gods, or any such system of belief and worship
- Holiday: Originally ‘holy day’, now a day fixed by law or custom on which ordinary
business is suspended in commemoration of some event or in honor of some person
- Celebration: the action of marking one's pleasure at an important event or occasion
by engaging in enjoyable, typically social, activity
- Floating holidays are subject to changed dates every year, unlike fixed holidays which keep the same dates.
2. American religion landscape
- ‘Separation of church and state’: a metaphor interpreted from the first clause in the
Bill of Rights: “Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion.”
- ‘Religious pluralism’ is an attitude or policy regarding the diversity of religious
belief systems co-existing in American society.
According to the U.S. Census, the most common religions in the United States are
Christianity, Judaism, Islam, Buddhism, Hinduism, and unaffiliated religions,
including atheists or agnostics. lOMoAR cPSD| 45903860 - 3. American holidays
American people have three kinds of holiday:
- Shared holidays (international holidays) - Uniquely American holidays - Ethnic holidays Shared holidays
Uniquely American holidays Ethnic holidays Christmas Day Martin Luther King’s Day Native American Powwows Easter’s Day Washington's Birthday Cinco de Mayo New Year's Day Memorial Day Mardi Gras Independence Day St. Patrick's Day Labor Day Hanukkah Veterans’ Day Chinese New Year Columbus Day Thanksgiving Day Arbor Day or Earth Day Flag Day Groundhog Day
a. Shared holidays in the U.S.
Easter (Floating Sunday from March 22- April 25, depending on the first full moon)
- To celebrate Jesus was resurrected from the dead on the third day after his crucifixion
- Eggs are dyed and hidden, and a bunny gives candy to children.
Christmas (Fixed December 25) lOMoAR cPSD| 45903860 -
Christmas season is a time for Americans to spend money and sink in debts.
- Decorating Christmas tree, exchanging gifts, go caroling, eating traditional food. - Christmas traditions:
The sharp leaves symbolize the crown of thorns worn by Jesus during the Crucifixion.
The red berries symbolize the blood of Christ.
New Year’s Day (Fixed January 1):
- Fireworks are displayed and champagne is drunk.
- The ball drop tradition: On one roof at New York Time Square, the ball descends
down a specially designed flagpole, beginning at 11:59:00 p.m. ET, and resting at
midnight to signal the start of the new year.
b. Uniquely American holidays
Thanksgiving (last Thursday in November): The holiday now becomes a celebration of
plentiful food and the warmth of family life.
Independence Day (July 4): The holiday honors the day the U.S. proclaimed its freedom
from Britain with the Declaration of Independence.
Columbus Day (second Monday in October): There are parades in Italian neighborhood.
In some areas, it is a celebration of indigenous peoples, or Italian culture and heritage.
Memorial Day (Last Monday in May):
The holiday originated in the years following the Civil War (1861-1865) and became an
official federal holiday in 1971.
Now the holiday honors those who died in all American wars.
Veterans’ Day (November 11):
Originated as “Armistice Day” on Nov. 11, 1919 to recall the end of World War I.
The holiday now honors all veterans of the U.S. armed forces.
Presidents’ Day (3rd Monday in Feb)
The holiday initially honored George Washington’s birthday (February 22).
It is now combined with Abraham Lincoln’s (February 12). lOMoAR cPSD| 45903860 -
Martin Luther King’s Day (3rd Monday in Jan): The holiday falls on or nearly on King’s
birthday – Jan 15 – in honor of a famous civil rights leader. lOMoAR cPSD| 45903860 Date Official Name January 1 (Fixed) New Year’s Day
January 15–21 (Floating 3rd Monday) Martin Luther King, Jr. Day
February 15–21 (Floating 3rd Monday) Presidents’ Day
May 25–31 (Floating last Monday) Memorial Day July 4 (Fixed) Independence Day lOMoAR cPSD| 45903860
September 1–7 (Floating 1st Monday) Labor Day
Labor Day (1st Monday in Sept): The holiday honors working people.
4. Ten U.S. Federal Holidays
Most of the ten U.S. federal holidays are also state holidays.
A holiday that falls on a weekend is usually observed on the closest weekday (e.g. a
holiday falling on a Saturday is observed on the preceding Friday, while a holiday falling
on a Sunday is observed on the succeeding Monday).
October 8–14 (Floating 2nd Monday) Columbus Day November 11 (Fixed) Veterans Day
November 22–28 (Floating 4th Thursday) Thanksgiving Day December 25 (Fixed) Christmas Day lOMoAR cPSD| 45903860
THEME 8: AMERICAN CORE VALUES




