





Preview text:
REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM - PORTFOLIO MANAGEMENT Part 1. Multiple choices
1. The expected return is determined by: A. Probabilities B. Rates of return on an asset C. Correlations
D. Both the first and second answer
E. The first, second and third answer
2. The risk of a stock in a portfolio can be expressed using the ………. instead of the covariance. A. Correlation coefficient B. Expected return C. Standard deviation D. Coefficient of variance E. Variance
3. Choose all that apply. Asset "A" has an expected return of 6% and a volatility (or standard deviation) of 12%.
Asset "B" has an expected return of 8% and a volatility (or standard deviation) of 20%. The correlation between
assets "A" and "B" is equal to 0.6. Which of the following statements are true?
A. A portfolio that has a 75% allocation in Asset "A" and 25% in Asset "B" has an expected return of 6.5%.
B. A portfolio that has a 75% allocation in Asset "A" and 25% in Asset "B" has a volatility of 14%.
C. A portfolio that has a 75% allocation in Asset "A" and 25% in Asset "B" has a volatility of less than 14%.
D. A portfolio that has a 75% allocation in Asset "A" and 25% in Asset "B" has an expected return of less than 6.5%.
4. Which of the following statements regarding the "efficient frontier" are true? Choose all that apply.
A. The lower part of the efficient frontier is the one investors should focus on since portfolios on the lower part of the
frontier dominate those on the upper part.
B. For a given level of expected return, the portfolio that attains this level of expected return with the lowest
risk must be on the efficient frontier.
C. The efficient frontier can be described as the area that contains all the portfolios with the lowest risk for each level of expected return.
D. The upper part of the efficient frontier is the one investors should focus on since portfolios on the upper
part of the frontier dominate those on the lower part.
5. What happens when we add a risk-free asset to our investable universe? Choose all that apply.
A. We are now able to build a portfolio with zero risk (i.e. certain returns).
B. There is no limit to the effect of diversification anymore.
C. There is one portfolio, the tangency portfolio, which belongs to both efficient frontiers (the one with and the
one without the risk-free asset).
D. The upper and lower parts of the efficient frontier are now two straight lines.
6. You are building a portfolio for a client. You know that this investor cannot perform short sales. What does it imply? Choose all that apply.
A. The constraint this investor faces is typical for retail investors.
B. The fact that the investor cannot perform short sales enhances the possibilities of diversification available to him.
C. The weights (or allocation) to the different assets in this investor's portfolio cannot be negative.
D. The fact that the investor cannot perform short sales adds a constraint to your objective of minimizing the
risk of his portfolio for a given level of expected return.
7. Which of the following statements regarding the impact of age on the investment profile are true?
A. When they retire, some investors get completely out of the stock market.
B. Because stocks tend to offer attractive risk-adjusted returns over the long run, investors with a long investment
horizon are traditionally advised to allocate a large portion of their portfolio to stocks.
C. As long as they are employed, investors tend to gradually reduce their allocation to stocks as they get older.
D. Because stocks tend to offer attractive risk-adjusted returns over the short run, investors with a short investment
horizon are traditionally advised to allocate a large portion of their portfolio to stocks.
8. Which of the following is not true about passive investing?
A. Passive investing is buying a well-diversified portfolio to represent a broad-based
market index without attempting to search out mispriced securities.
B. Holding the market portfolio is efficient, so passive investing is efficient as well.
C. Passive investing cannot be efficient because it involves passive investors.
D. The amount of diversifiable risk in an index fund is near zero.
9. Which of the following statements is not correct?
A. The Capital Allocation Line (CAL) depicts the feasible risk and return combinations available to investors when
the choice of the risky portfolio is made.
B. The slope of the Capital Allocation Line (CAL) is called the Sharpe ratio.
C. The slope of the Capital Allocation Line (CAL) represents the additional return offered by the risky
portfolio beyond the risk-free rate of return per unit of incremental risk.
10. Suppose you are considering adding real estate to your portfolio that currently includes only stocks, bonds, and
cash. Which return characteristic of real estate would affect your portfolio risk?
A. Standard deviation of real estate returns
B. Expected return on real estate
C. Age of the real estate properties
D. Correlation with returns of the other asset classes
11. Which of the following measures is most informative about the average past return of an investment?
A. The arithmetic average return over the period of interest
B. The geometric average return over the period of interest
C. Both arithmetic and geometric average returns over the period of interest
D. The standard deviation of the returns over the period of interest Part 2: Problems
1. During the past five years, you owned two stocks that had the following annual rates of return: Year Stock T Stock B DJIA Index 1 0.19 0.08 0.03 2 0.08 0.03 0.07 3 -0.12 -0.09 -0.02 4 -0.03 0.02 0.01 5 0.15 0.4 0.05
You are required to do the following calculations using the number of observations as 5 shown in column 1 above.
a) Compute the arithmetic means of annual rates of return for each stock and Dow Jones Industrial
Average (DJIA) Index. Which stock is most desirable by this measure? Why? Answer:
b) Compute the standard deviations of the annual rate of return for each stock and Dow Jones Industrial
Average (DJIA) Index. By this measure, which is the desirable stock? Why? Answer:
c) Compute the coefficients of variation for each stock and Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) Index.
By this relative measure of risk, which stock is preferable? Explain. Answer:
d) Compute the geometric means of rate of return for each stock and Dow Jones Industrial Average
(DJIA) Index. Discuss the difference between the arithmetic mean returns and the geometric mean
returns for each stock and Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) Index. Answer:
e) Compute the covariances between the rates of return for the following combinations using calculations
completed in a) and b) above. ● Stock T and Stock B
● Stock T and DJIA Index
● Stock B and DJIA Index.
Are there any benefits in combining the two stocks in a portfolio? Explain. Answer:
f) Compute correlation coefficients between the returns for the same combinations in e) above. Answer:
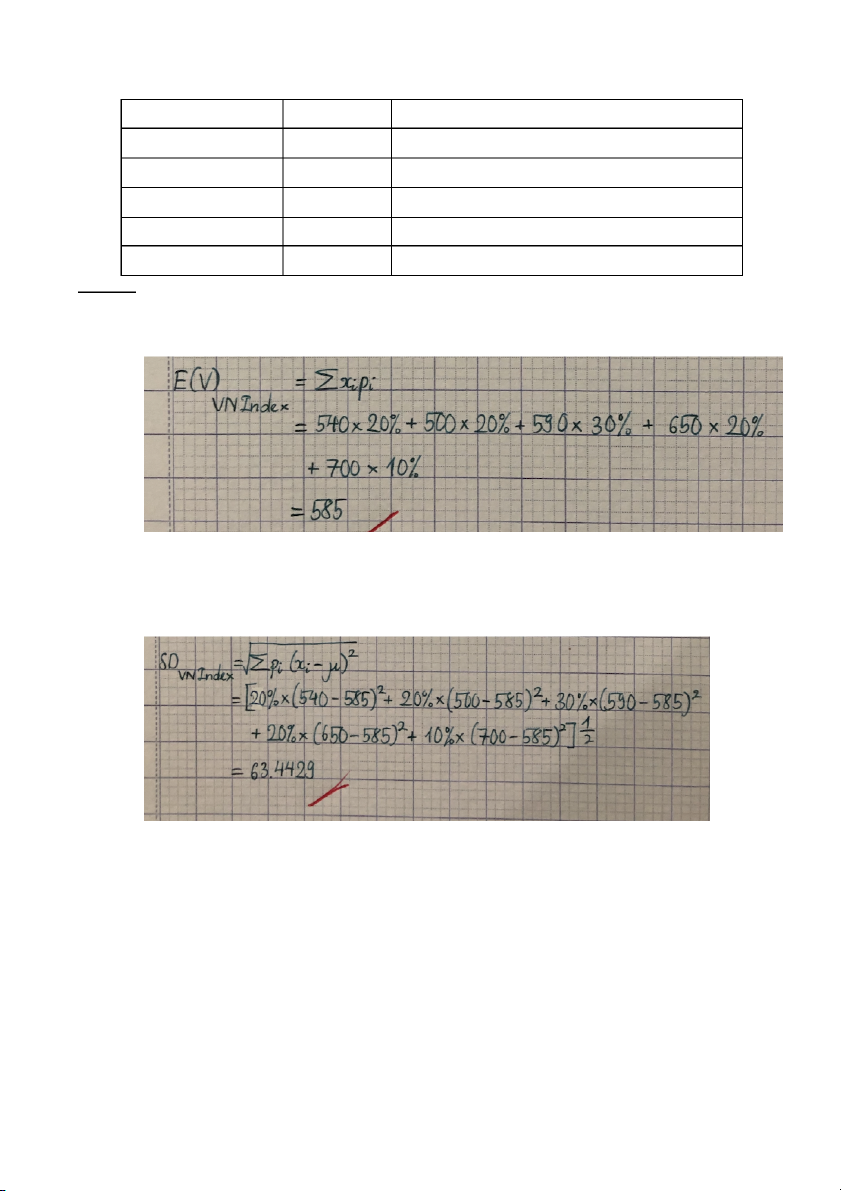
2. Assuming the current VN-Index is 600 points, to forecast this index in the end of the year according to survey
method, our security analysts have the data as below: Vn-Index in 1 year later Probability
the difference between the current and 1 year later 540 20% ? 500 20% ? 590 30% ? 650 20% ? 700 10% ? Calculate: a. Expected VN-Index Ans: b. The risk of Vn-Index Answer:
Part III: Theory Questions
1. Lecture 4: Portfolio Theory and Diversification
2. Lecture 7: Portfolio Performance



