



Preview text:
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam
HỌC VIỆN HÀNG KHÔNG VIỆT NAM
KHOA KỸ THUẬT HÀNG KHÔNG CHƯƠNG 3
DÒNG CHUYỂN ĐỘNG KHÔNG NHỚT VÀ
KHÔNG NÉN ĐƯỢC QUA BIÊN DẠNG
CÁNH – LÝ THUYẾT CÁNH 2D
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam
CHƯƠNG 2: CÁC KHÁI NIỆM CƠ BẢN
1. Quỹ đạo và lưu tuyến 2. Lưu số 3. Định lý Joukowski
4. Lý thuyết cánh mỏng
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam
1. Quỹ đạo (pathline) và lưu tuyến (streamline)
q Unsteady Motion: If at various points of the flow field quantities
(velocity, density, pressure) associated with the fluid flow change with
time, the motion is said to be unsteady.
q Steady Motion: If at various points of the flow field quantities
(velocity, density, pressure) associated with the fluid flow remain
unchanged with time, the motion is said to be steady.
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam
1. Quỹ đạo (pathline) và lưu tuyến (streamline)
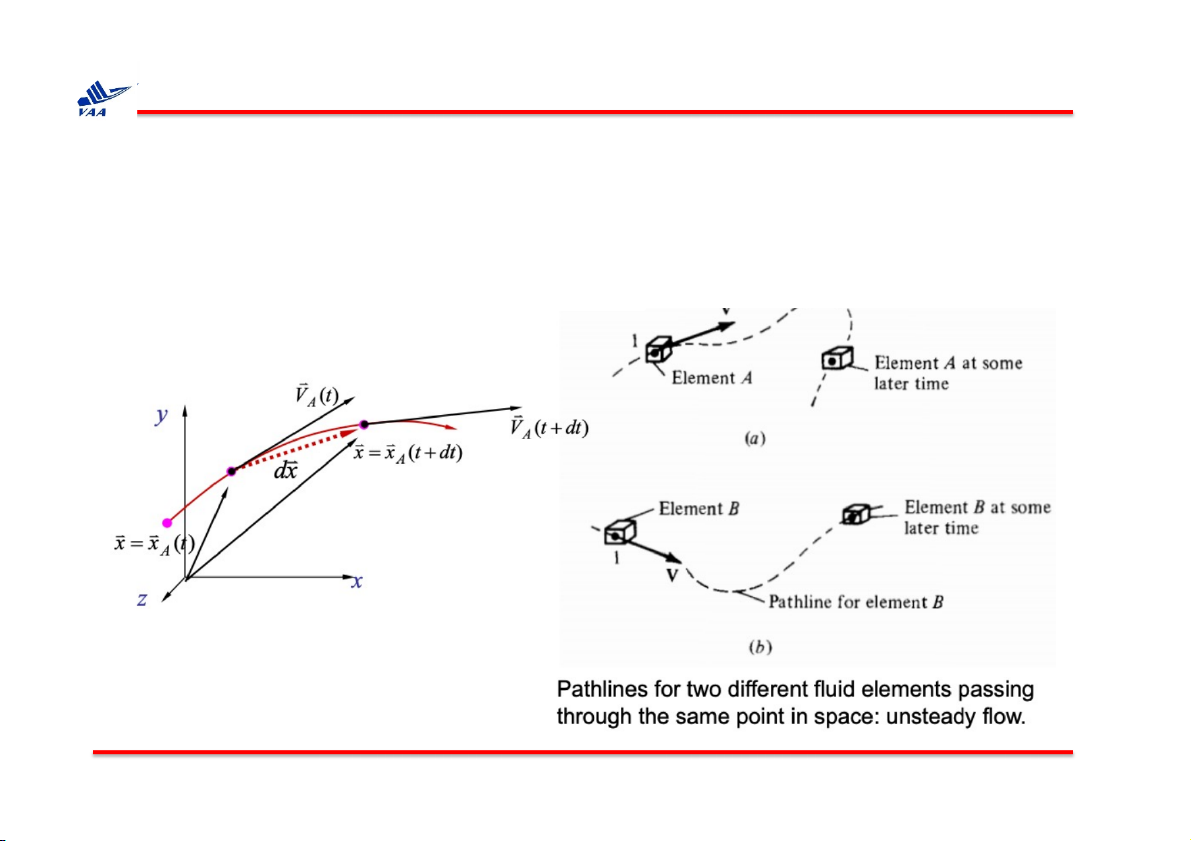
q Pathline: The curve described in space by a moving fluid element is
known as its trajectory or pathline (Đường cong mô tả chuyển động của
1 phần tử trong không gian).
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam
1. Quỹ đạo (pathline) và lưu tuyến (streamline)
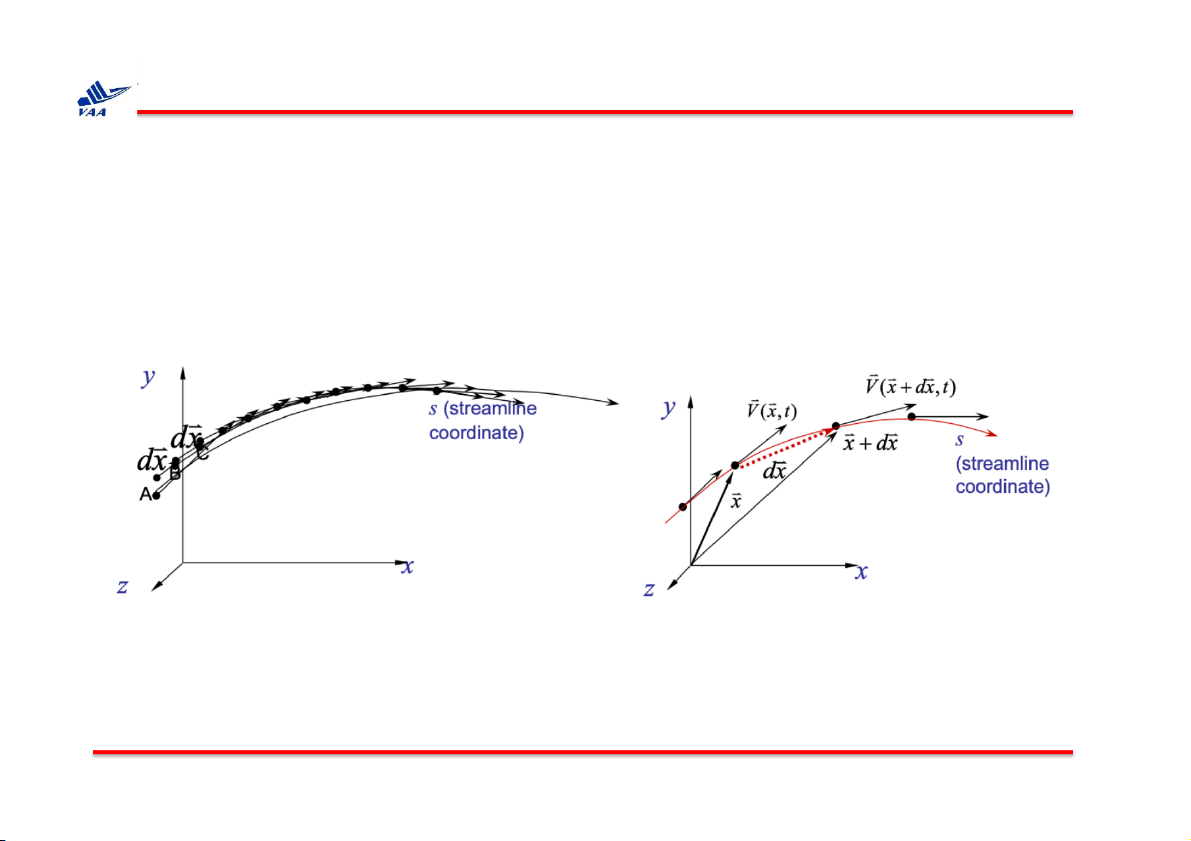
q Streamline: is a curve whose tangent at any point is in the direction of
the velocity vector at that point (Đường cong có tiếp tuyến tại bất kỳ
điểm nào là theo hướng của vector vận tốc tại thời điểm đó).
Note that here dx is the displacement along the streamline.
For steady flow, streamlines and pathlines are the same.
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam
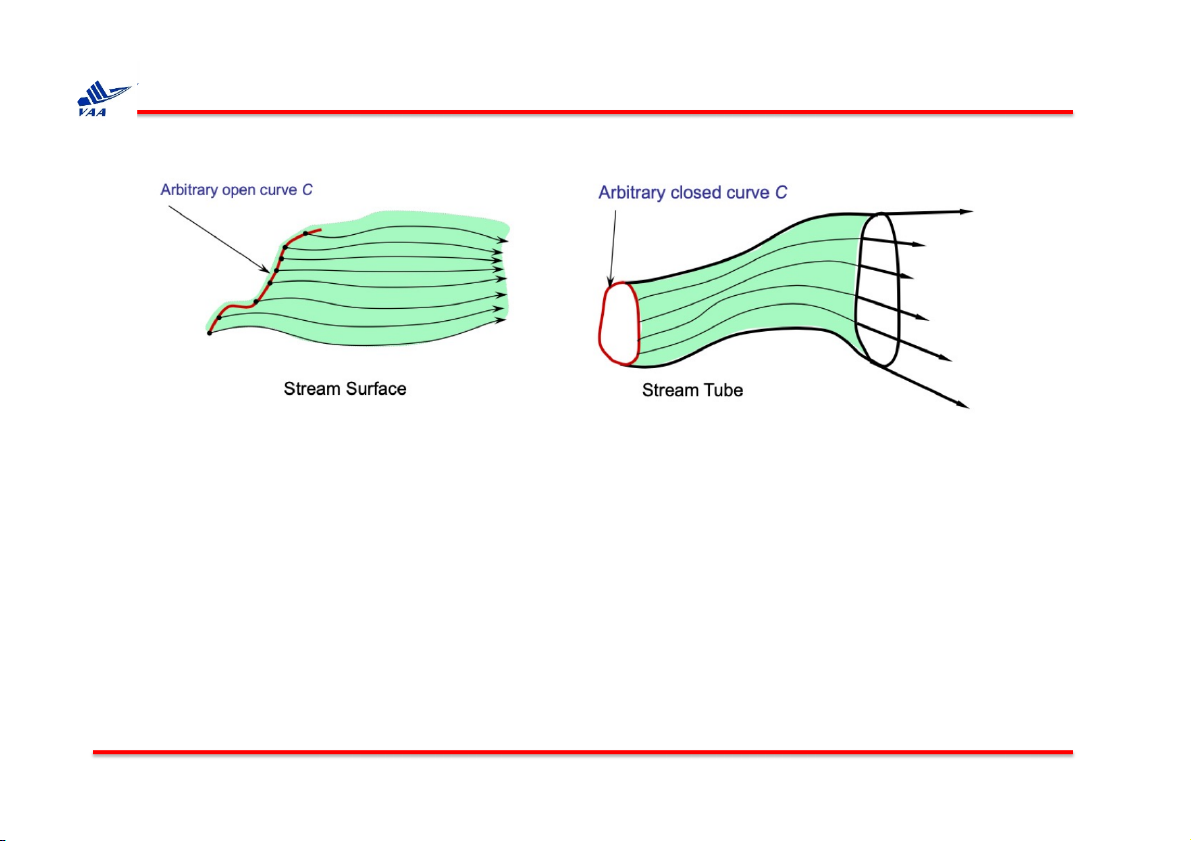
1. Quỹ đạo (pathline) và lưu tuyến (streamline) q Stream Surface
Ø Starting from an arbitrary open curve C.
Ø If we trace out streamlines that start from points on this curve, we have a stream surface that contains C.
q Stream Tube: On the other hand, if we choose a closed curve, we have a stream tube.
Ø From the definition of streamline, no flow can cross a stream tube.
Ø Therefore, a stream tube acts like an imaginary pipe/channel.
Ø Due to this property, stream tube is a useful tool for analysis.
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam
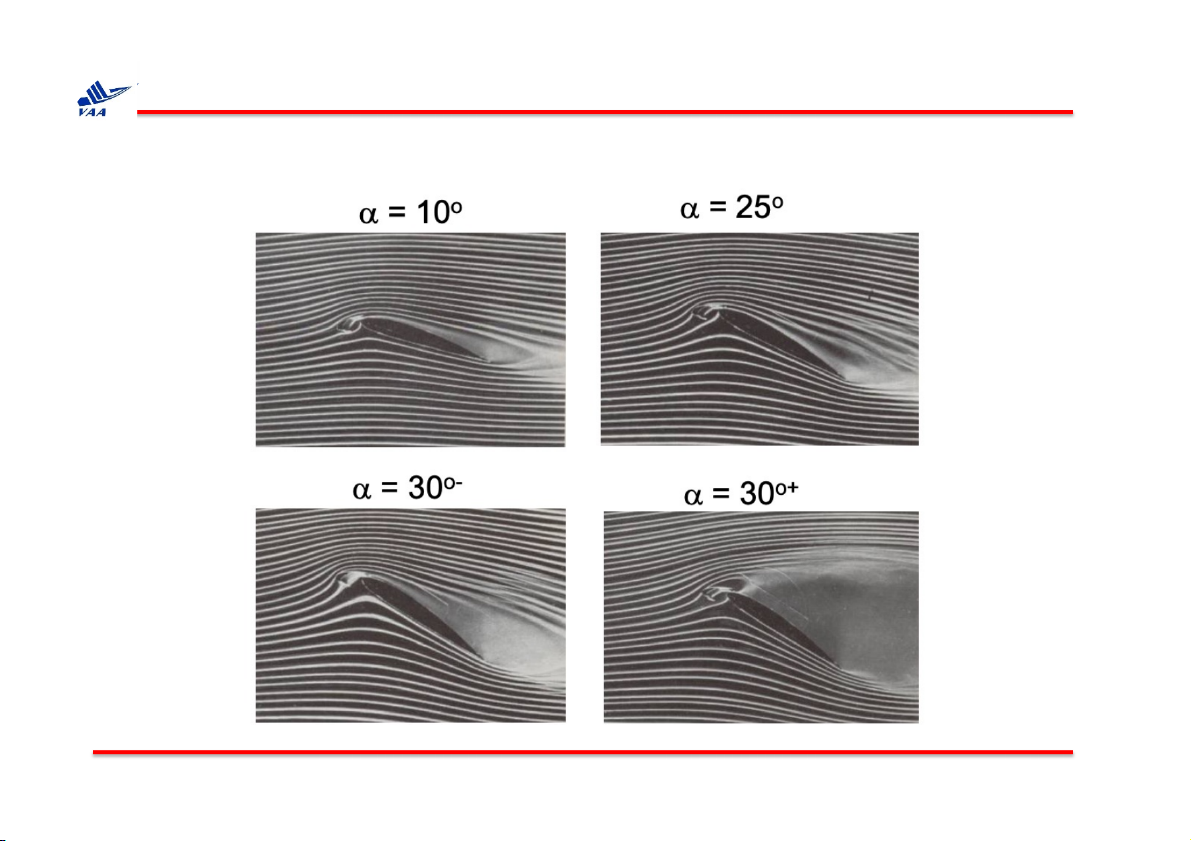
1. Quỹ đạo (pathline) và lưu tuyến (streamline)
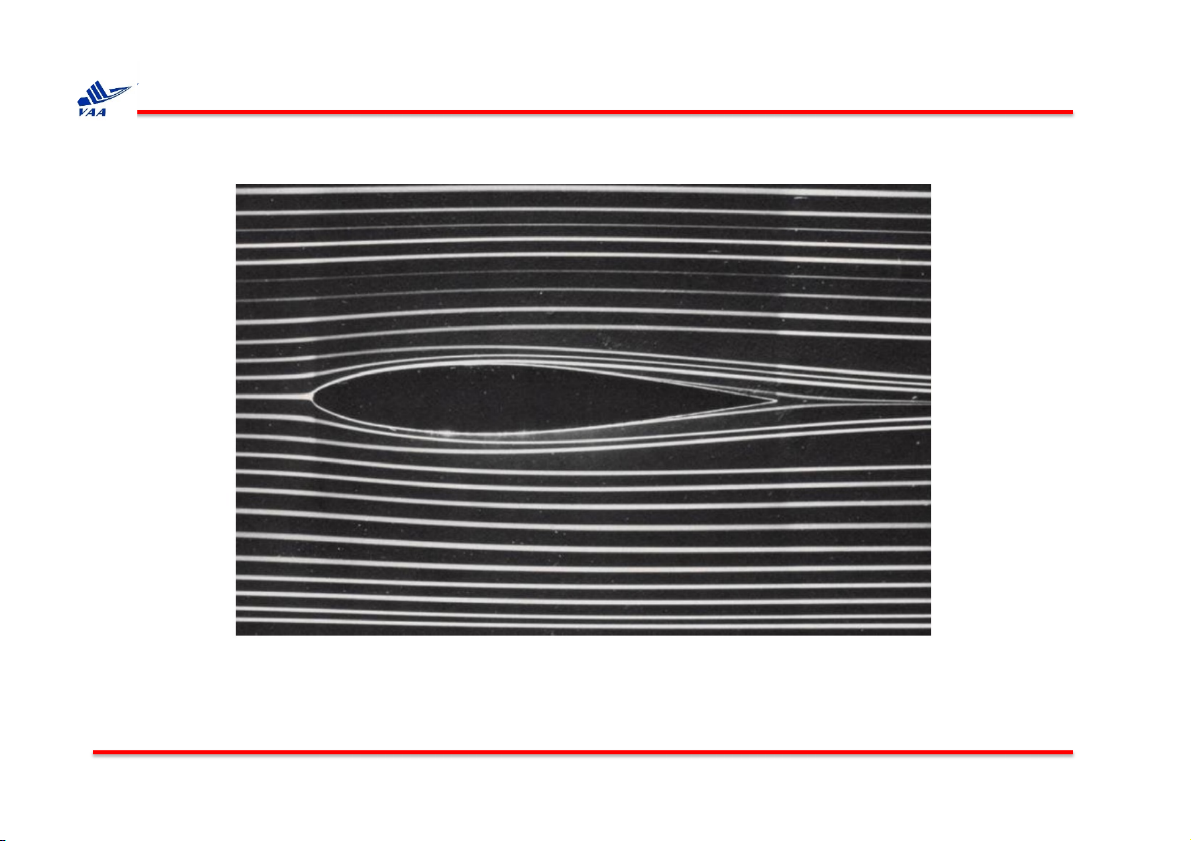
Flow past an airfoil, visualized by dye in water tunnel.
(From Van Dyke, M., 1982, An Album of Fluid Motion, Parabolic Press).
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam
1. Quỹ đạo (pathline) và lưu tuyến (streamline)
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam
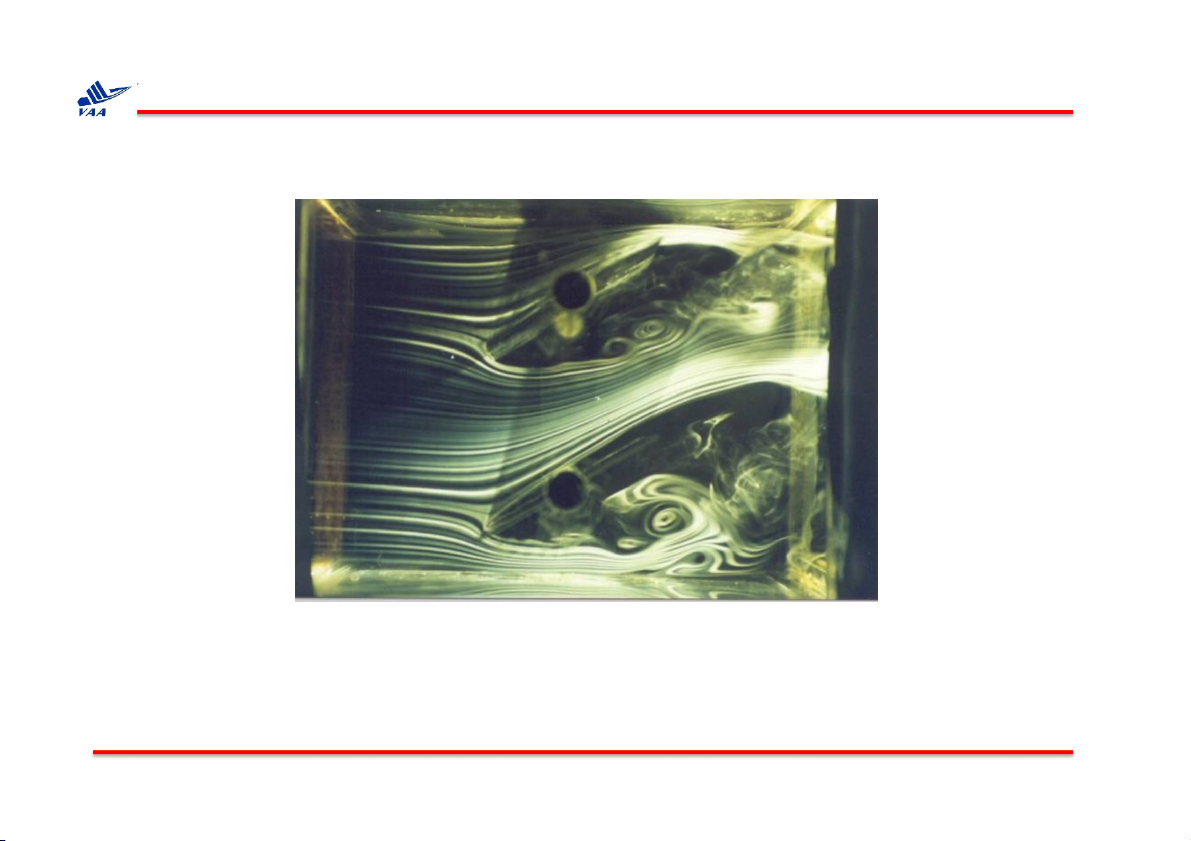
1. Quỹ đạo (pathline) và lưu tuyến (streamline)
Flow past a damper, visualized by smoke-wire.
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam
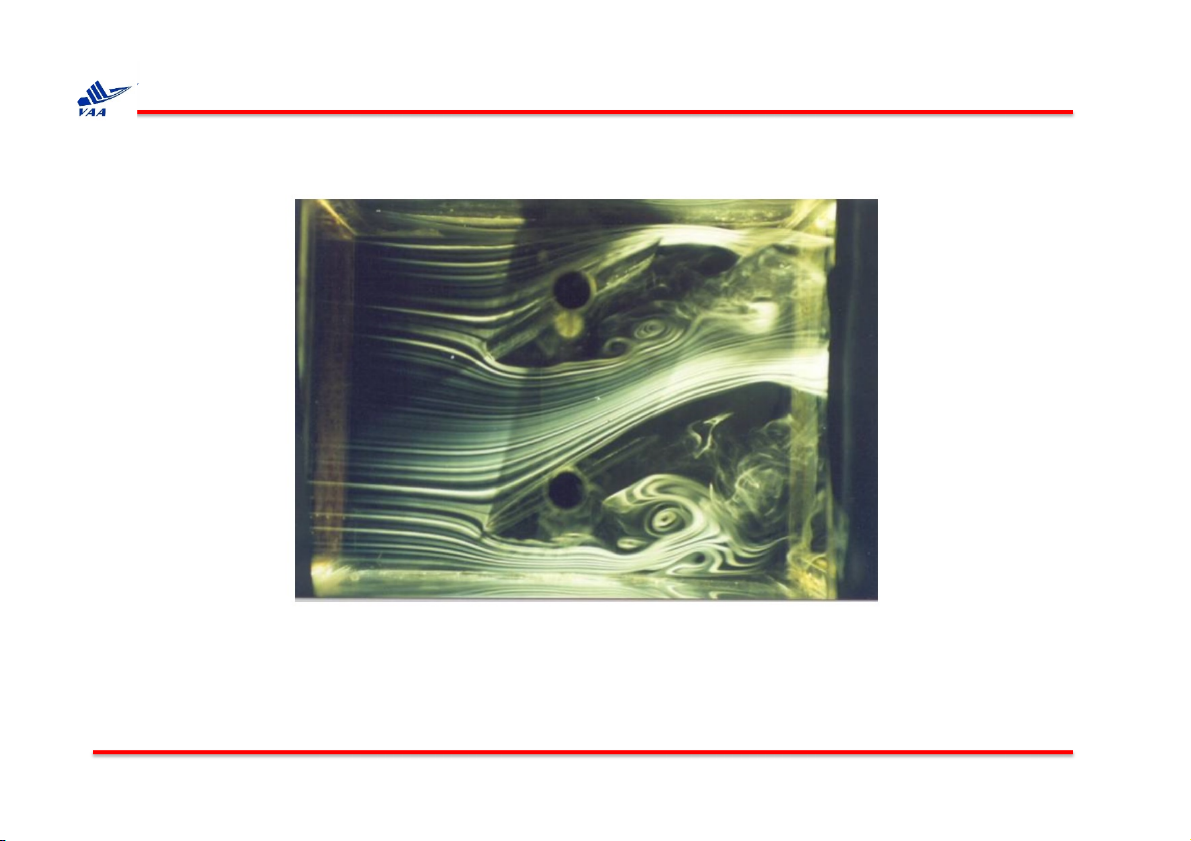
1. Quỹ đạo (pathline) và lưu tuyến (streamline)
Flow past a damper, visualized by smoke-wire.
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam
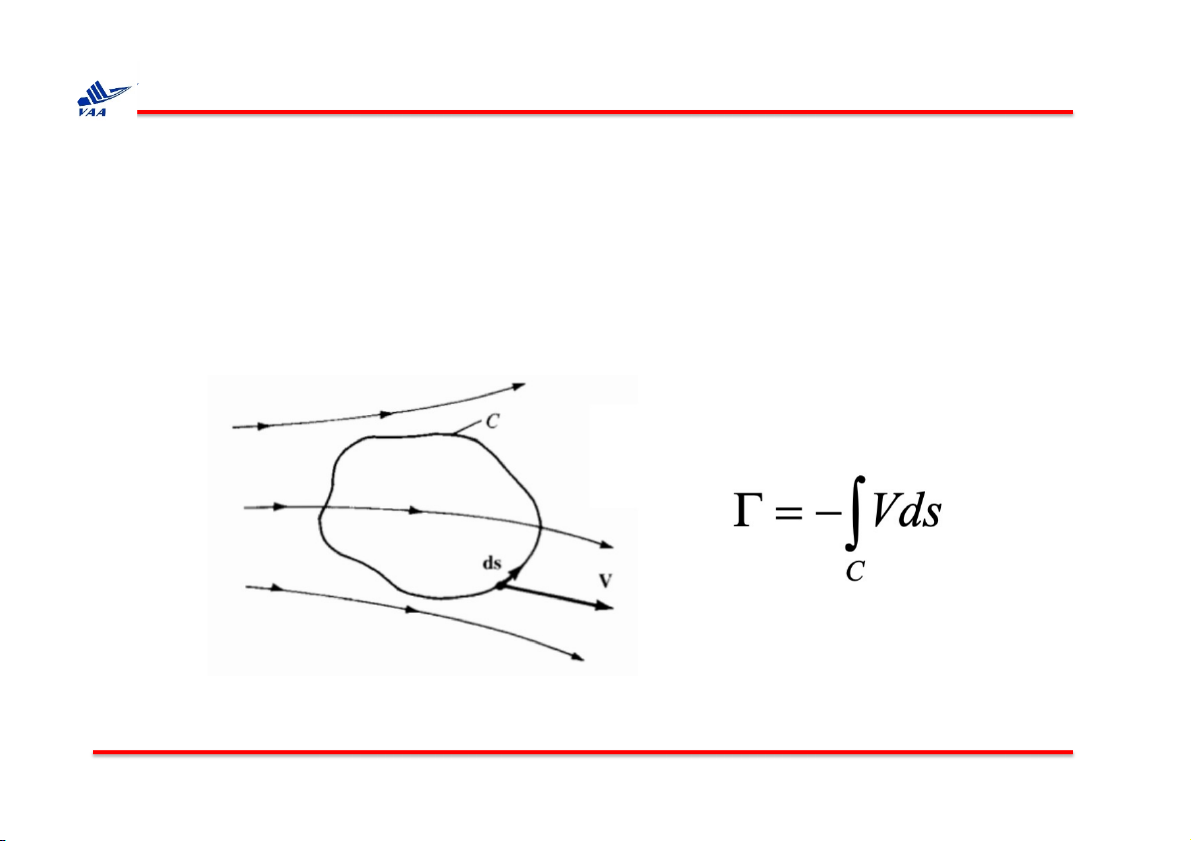
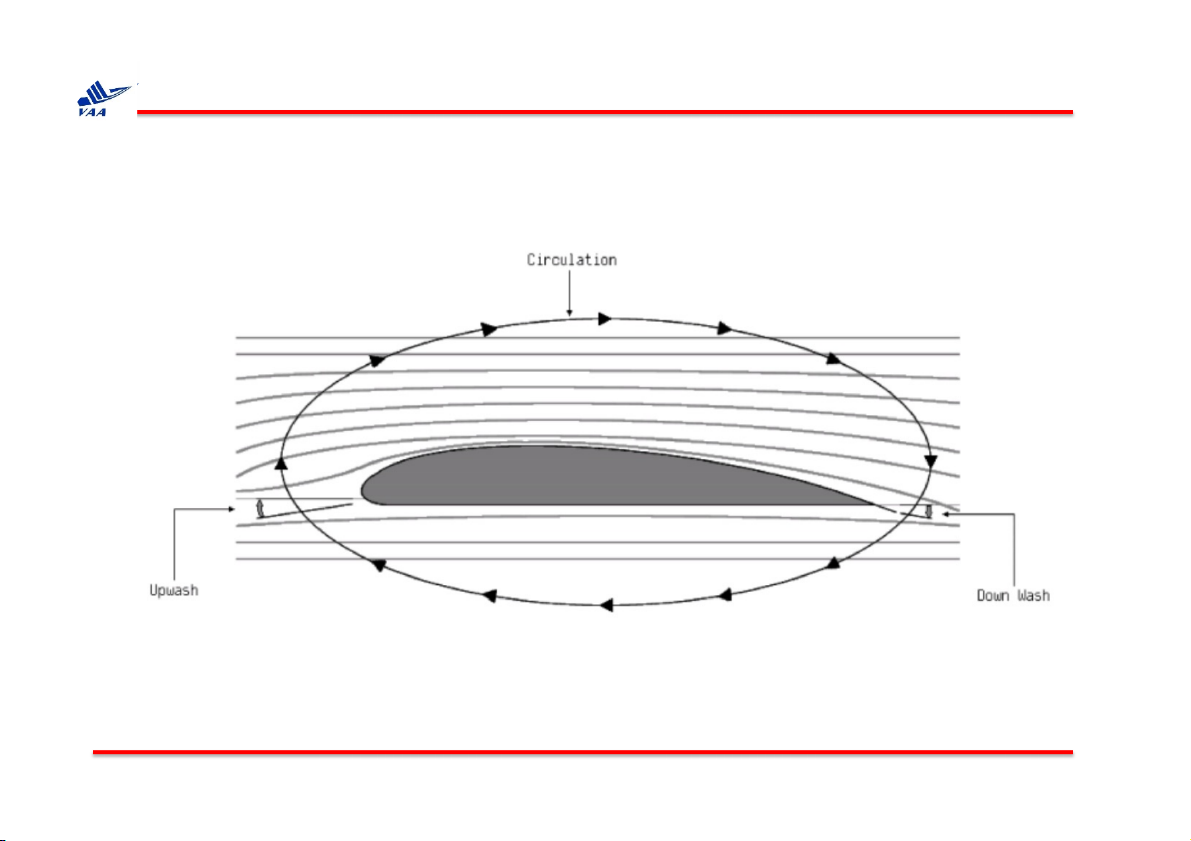
2. Lưu số (circulation)
q Fundamental to the calculation of aerodynamic lift.
Consider a closed curve C in a flow field. Let V and ds be the velocity and
directed line segment, respectively, at a point on C. The circulation, denoted by Г is defined as
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam
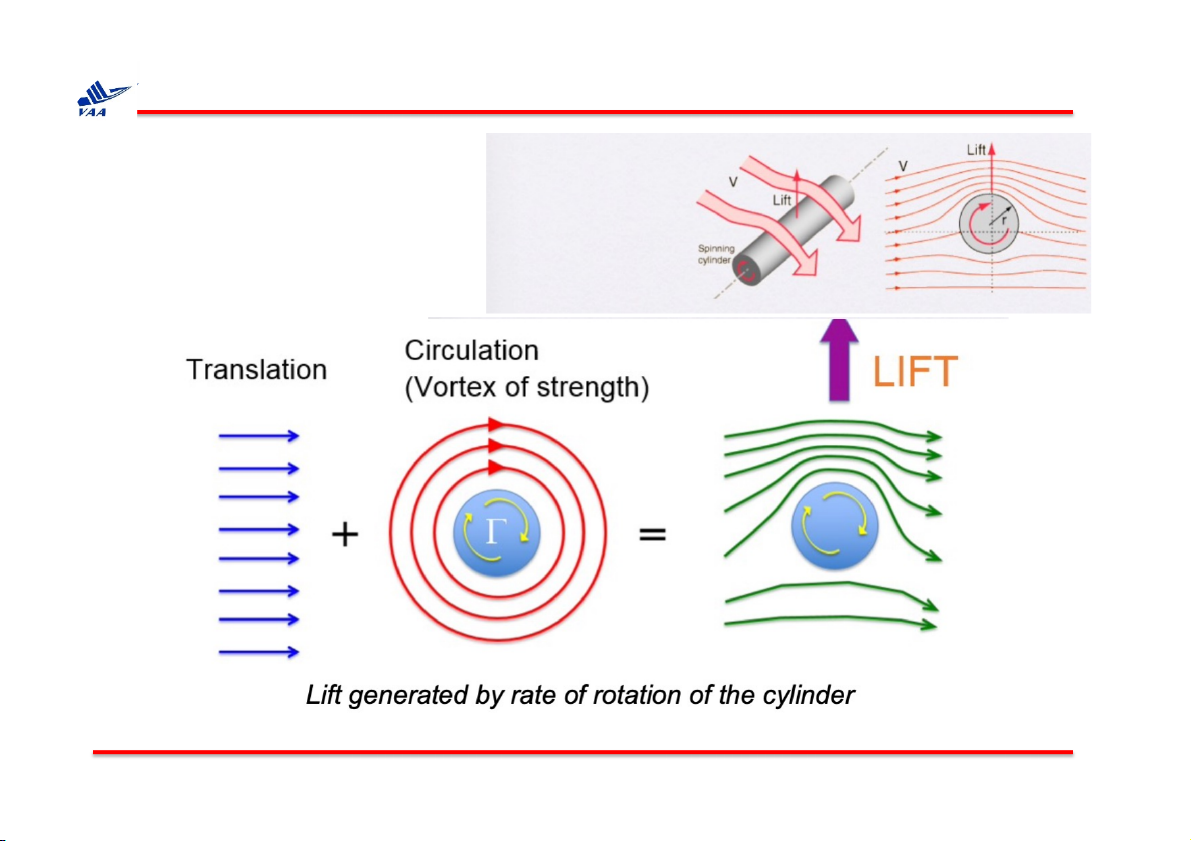
2. Lưu số (circulation) q Magnus Effect
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam
2. Lưu số (circulation) q Magnus Effect
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam 3. Định lý Joukowski
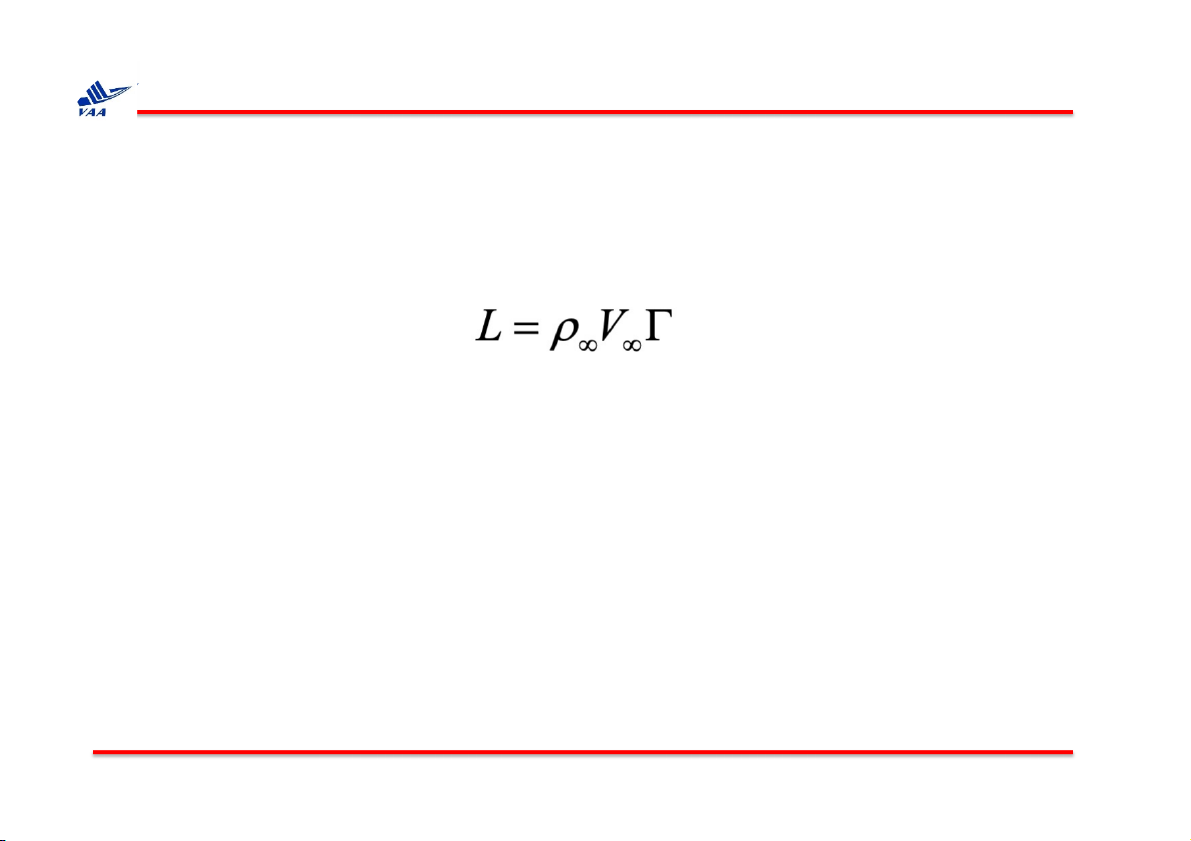
For a closed two-dimensional body of arbitrary shape, the lift per unit span is:
This result underscores the importance of the concept of circulation. The
Kutta-Joukowski theorem states that lift per unit span on a two
dimensional body is directly proportional to the circulation around the body.
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam
3. Định lý Joukowski
q Inviscid flow (Dòng không nhớt)
q Incompressible flow (Dòng không nén được)
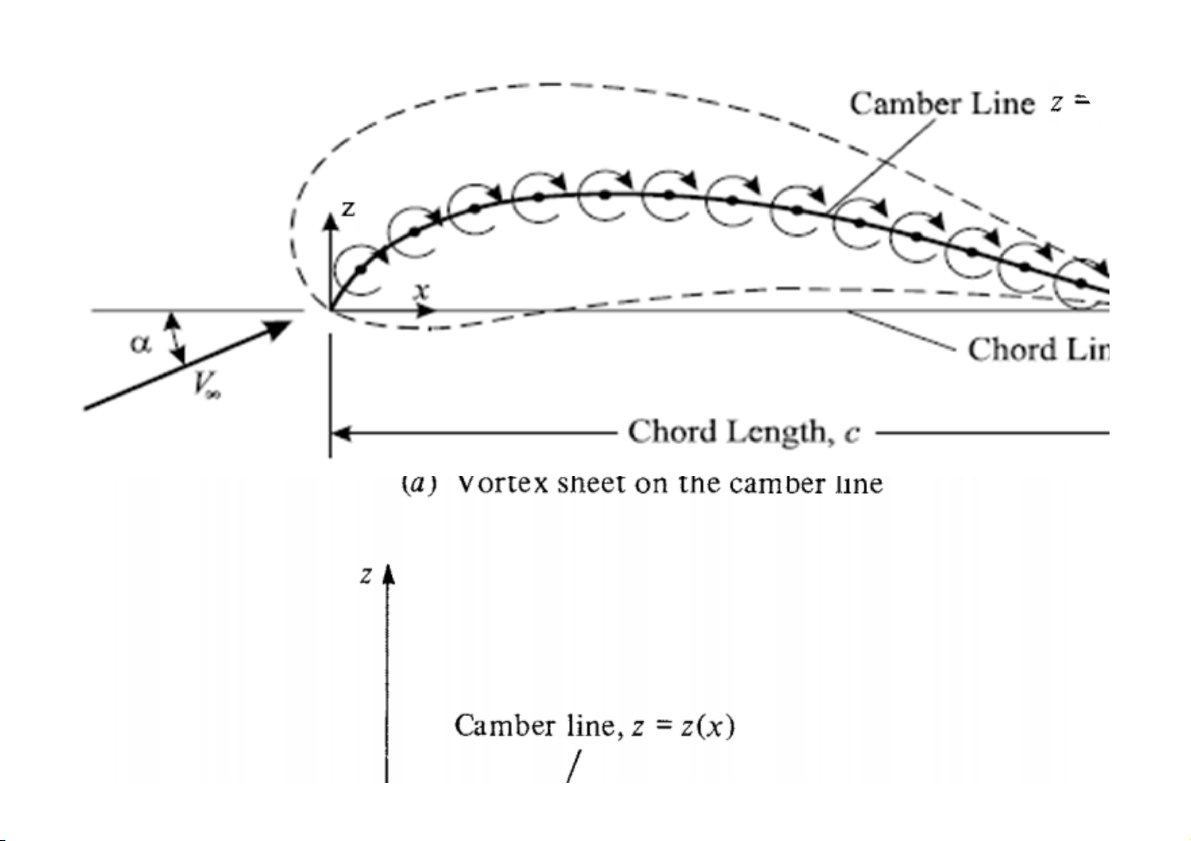
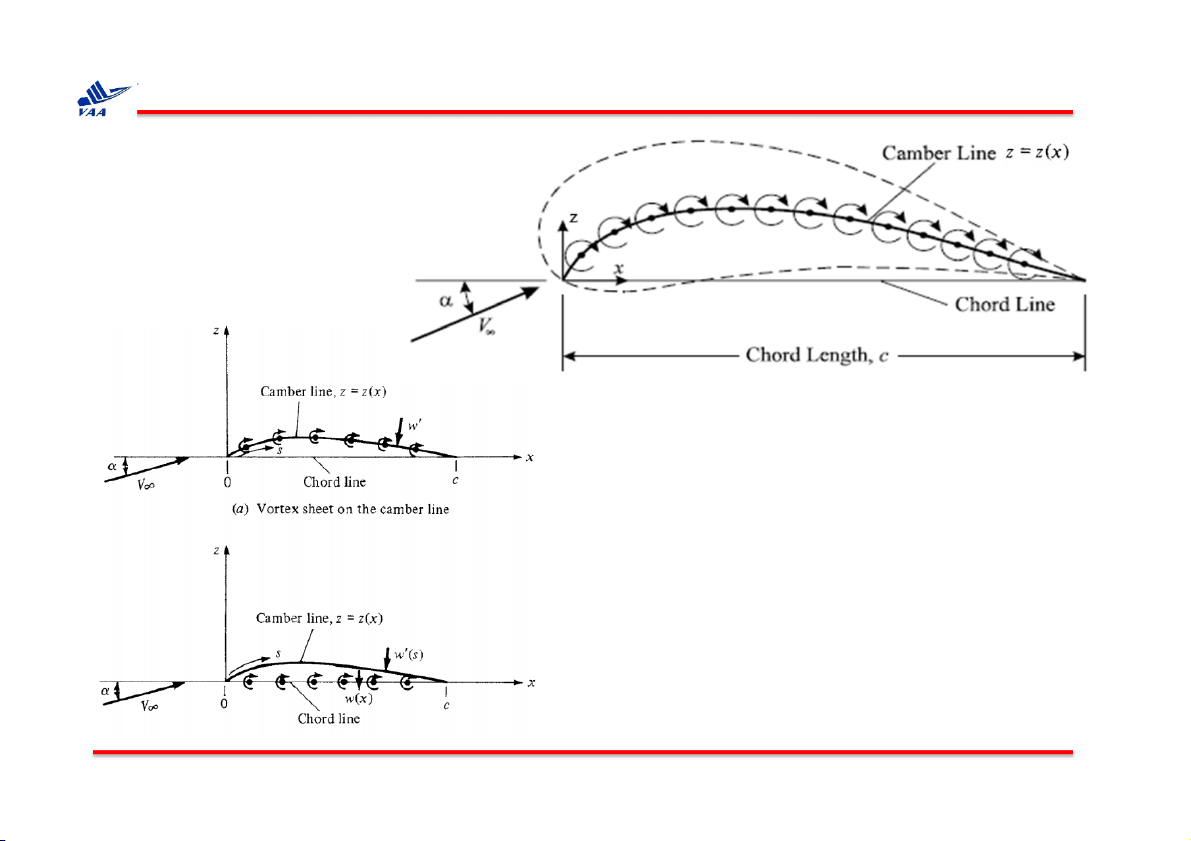
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam 4. Thin airfoil theory Assumptions: • 2-dimensional flow • Inviscid flow • Incompressible flow
• Camber line is a streamline
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam 4. Thin airfoil theory
Ø w’(s): the component of velocity normal to the camber line induced by
the vortex sheet (vận tốc cảm ứ
ng vuông góc với đường camber)
Ø w’(x): the component of velocity normal to the chord line induced by
the vortex sheet(vận tốc cảm ứ
ng vuông góc với dây cung cánh)
Ø α: angle of attack (góc tới)
Ø 𝛾 = 𝛾(𝑠): strengh of vortex (phân bố xoáy)
Ø z = z(x): The shape of the camber line (phương trình đường camber)
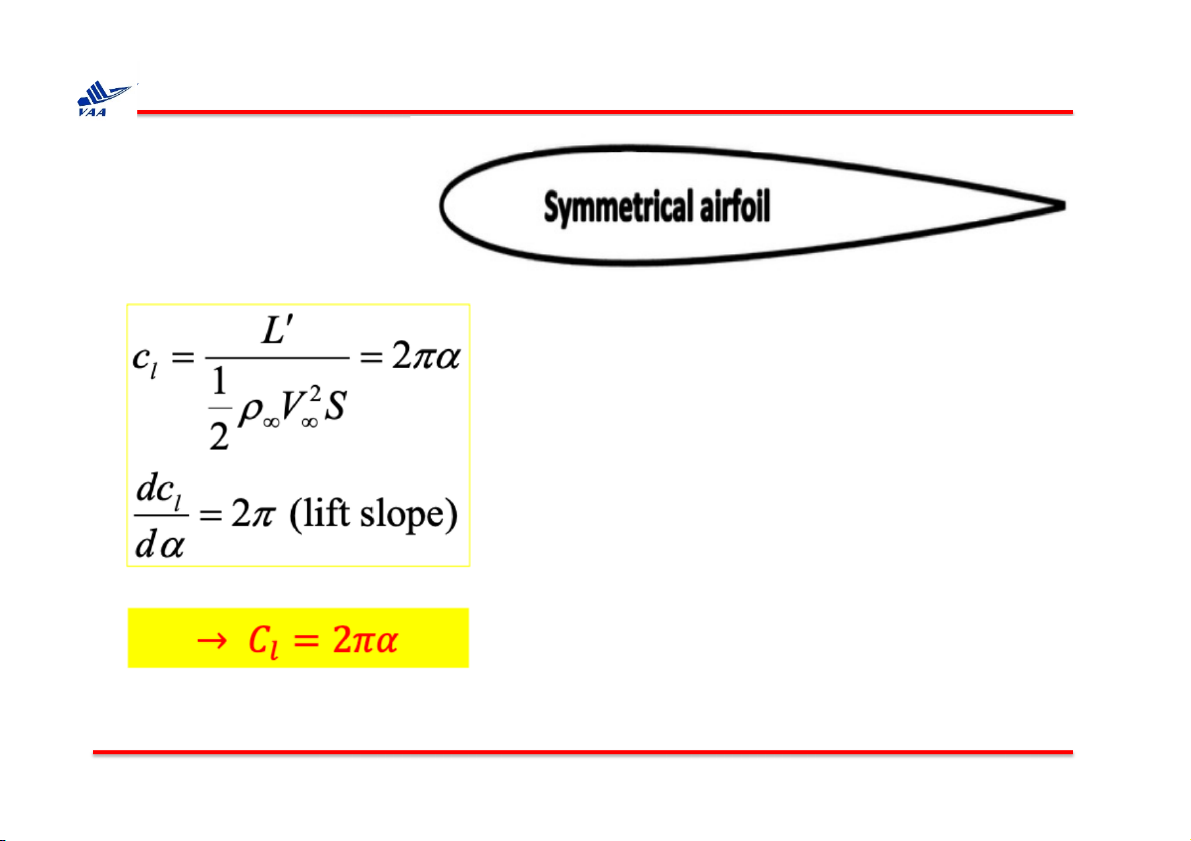
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam 4. Thin airfoil theory q Symmetrical airfoil ⇒ Lift coefficient C is linearly L
proportional to the angle of attac . k
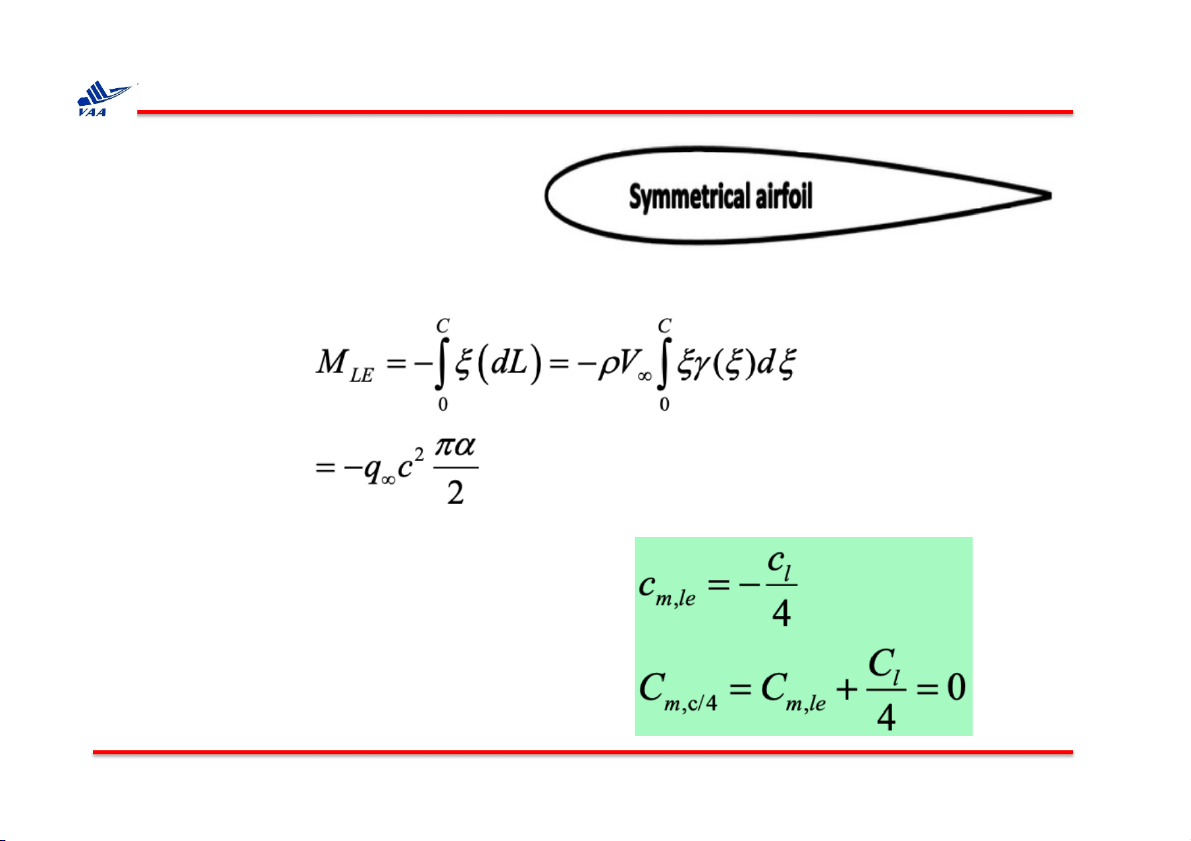
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam 4. Thin airfoil theory q Symmetrical airfoil
The total moment about the leading edge per unit span:
The moment coefficient at leading edge:
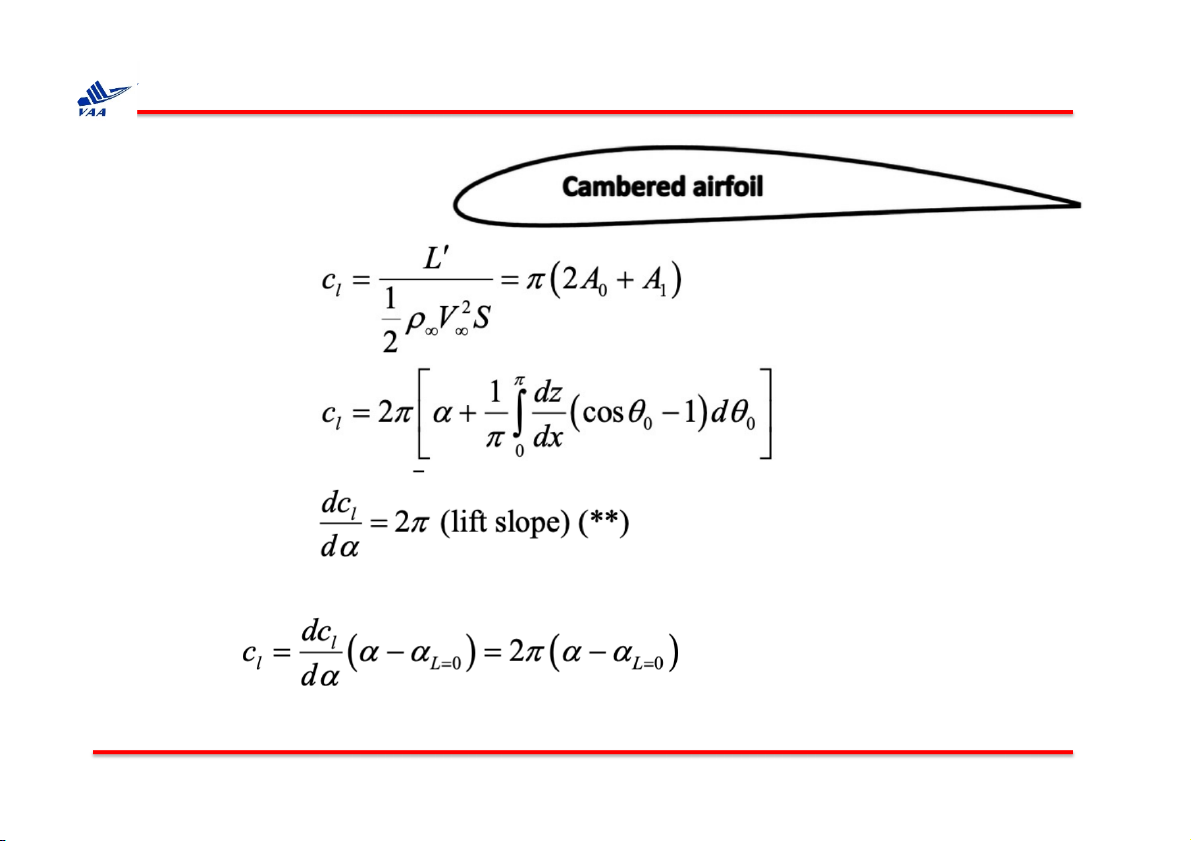
Học viện Hàng không Việt Nam 4. Thin airfoil theory q Cambered airfoil Lift coefficient:
⇒ For any shape of airfoil à General
result of thin airfoil theory. We have:



