
















Preview text:
Cơ học lý thuyết Bài tập Hệ lực và Vector
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 1 Tài liệu tham khảo
1. Engineering Mechanics: Statics 7th J. L. Meriam and L. G. Kraige
2. Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics 7th J. L. Meriam and L. G. Kraige
3. Cơ học tập 1: Tĩnh học và động học. Đỗ Sanh
4. Bài tập cơ học tập 1
5. Cơ học tập 2: Động lực học. Đỗ Sanh
6. Bài tập cơ học tập 2
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 2
Đánh giá kết quả học tập 1. Thành phần: 40% - Chuyên cần: Điểm danh: 10 % Bài tập lớn: 10% - Giữa kỳ: 20% 2. Cuối kỳ 60%
Đề thi được sử dụng tài liệu.
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 3 Tĩnh học Nội dung tổng quan: 1. Hệ lực phẳng 2. Hệ lực không gian 3. Cân bằng hệ lực 4. Hệ thanh 5. Lực phân bố đều 6. Ma sát
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 4 Tĩnh học
I. Các khái niệm cơ bản Lực Chất điểm Vật rắn tuyệt đối Hệ quy chiếu Trạng thái cân bằng
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 5
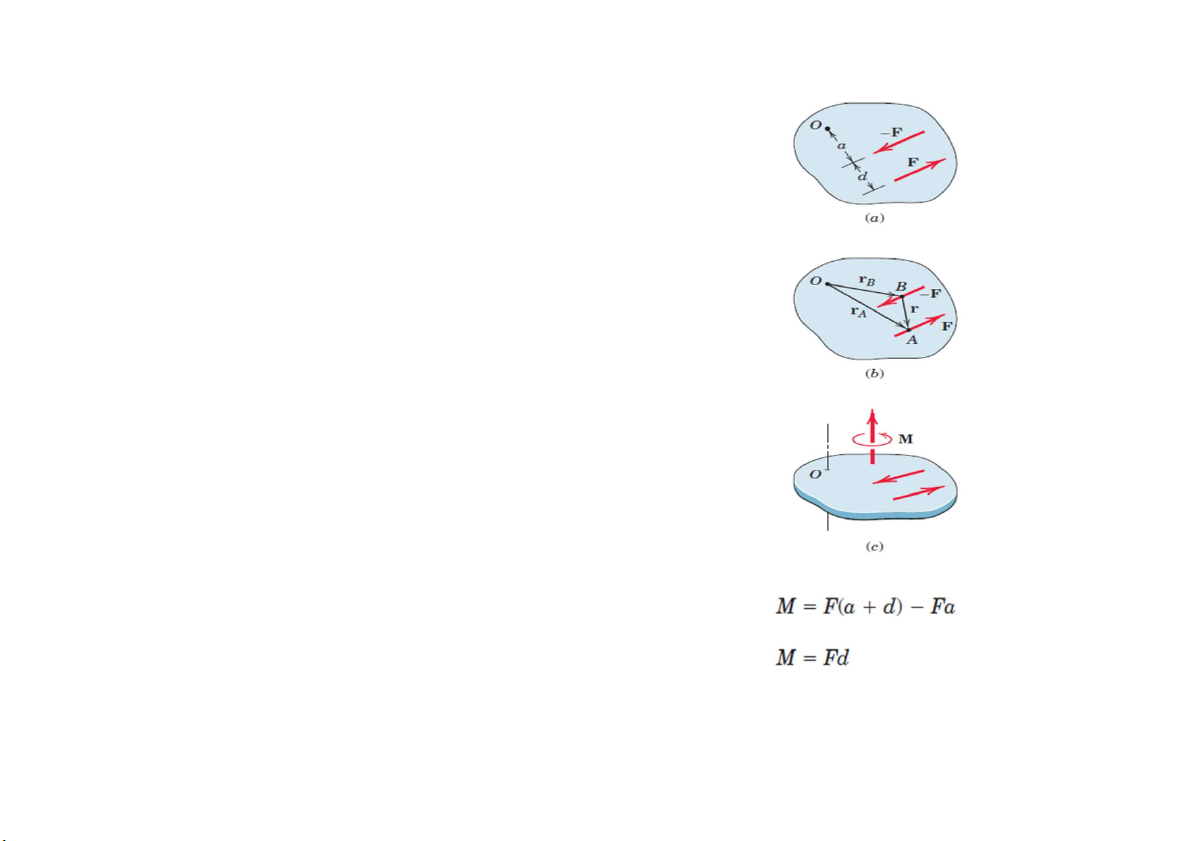
I. Các khái niệm cơ bản Ngẫu lực Hệ lực Hệ lực tương đương Hệ lực cân bằng Hợp lực
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 6
II. Tiên đề tĩnh học 1. Hai lực cân bằng
2. Thêm bớt một hệ lực cân bằng 3. Hợp hai lực
4. Lực tác dụng và phản tác dụng 5. Nguyên lý hoá rắn 6. Giải phóng liên kết
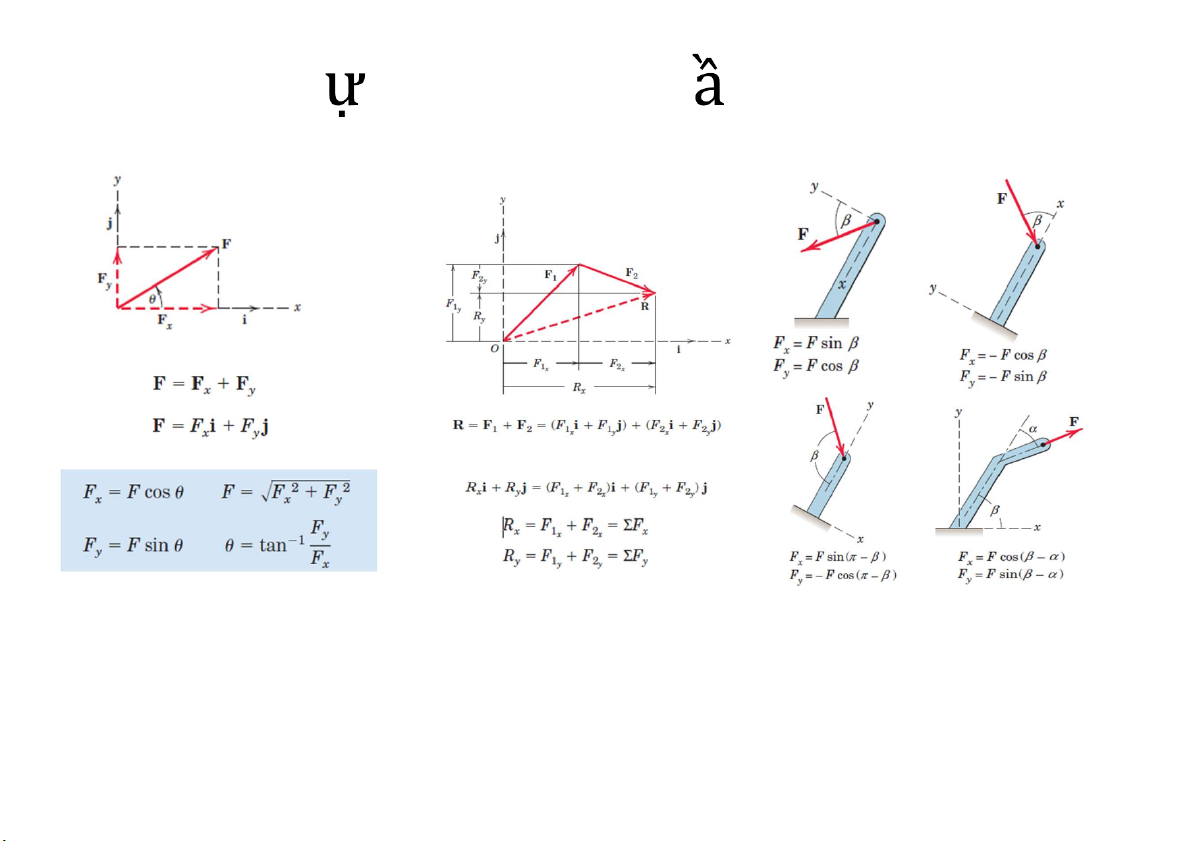
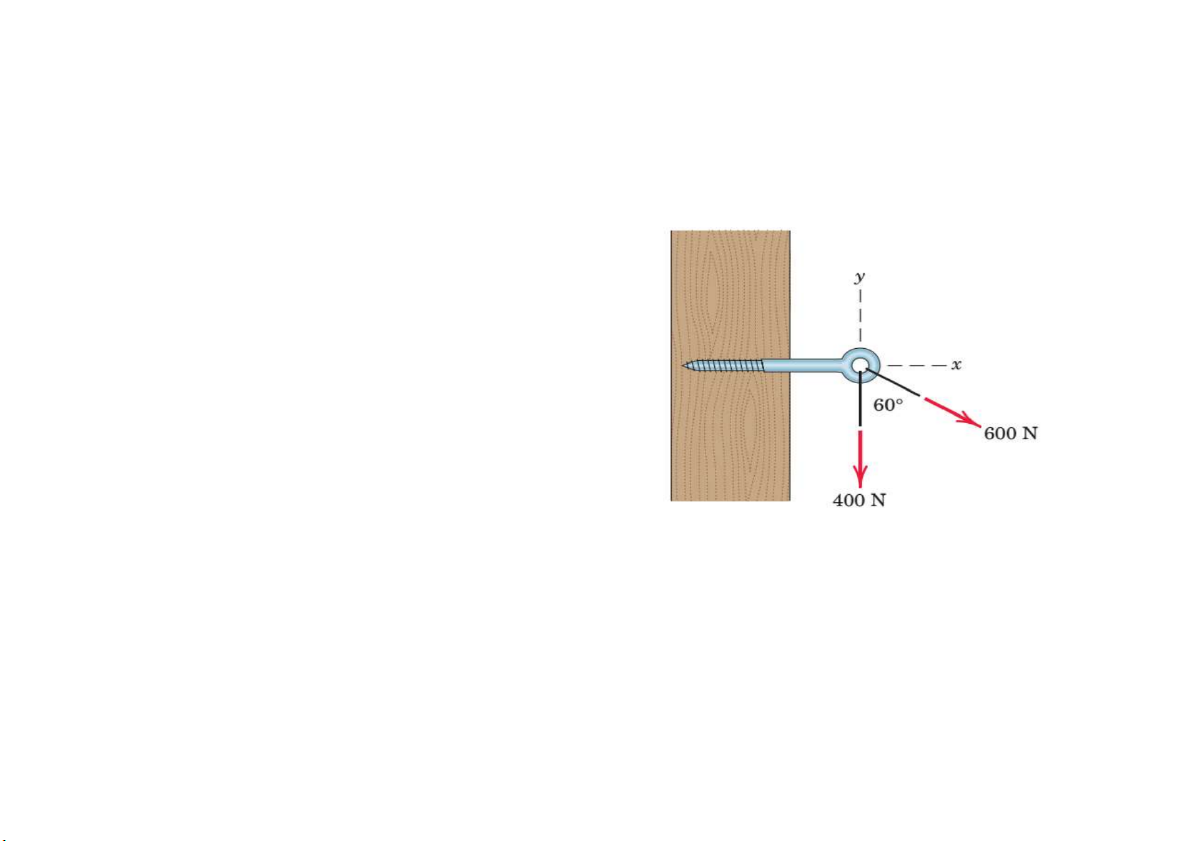
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 7 L c thành ph n 2D Hình chiếu F trên 0x
F.I = (Fxi+Fyj) (i) = Fx + 0 = Fx
i(1,0) |i| = i(1,0)i(1,0) = 1.1+0.0 = 1
J(0,1) i.j = (1,0)(0,1) = 1.0 + 0.1 = 0 IV. Moment 2D R (rx, ry) F (Fx, Fy) I j k Rx ry 0 Rx ry k Fx Fy 0 Fx Fy
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 9
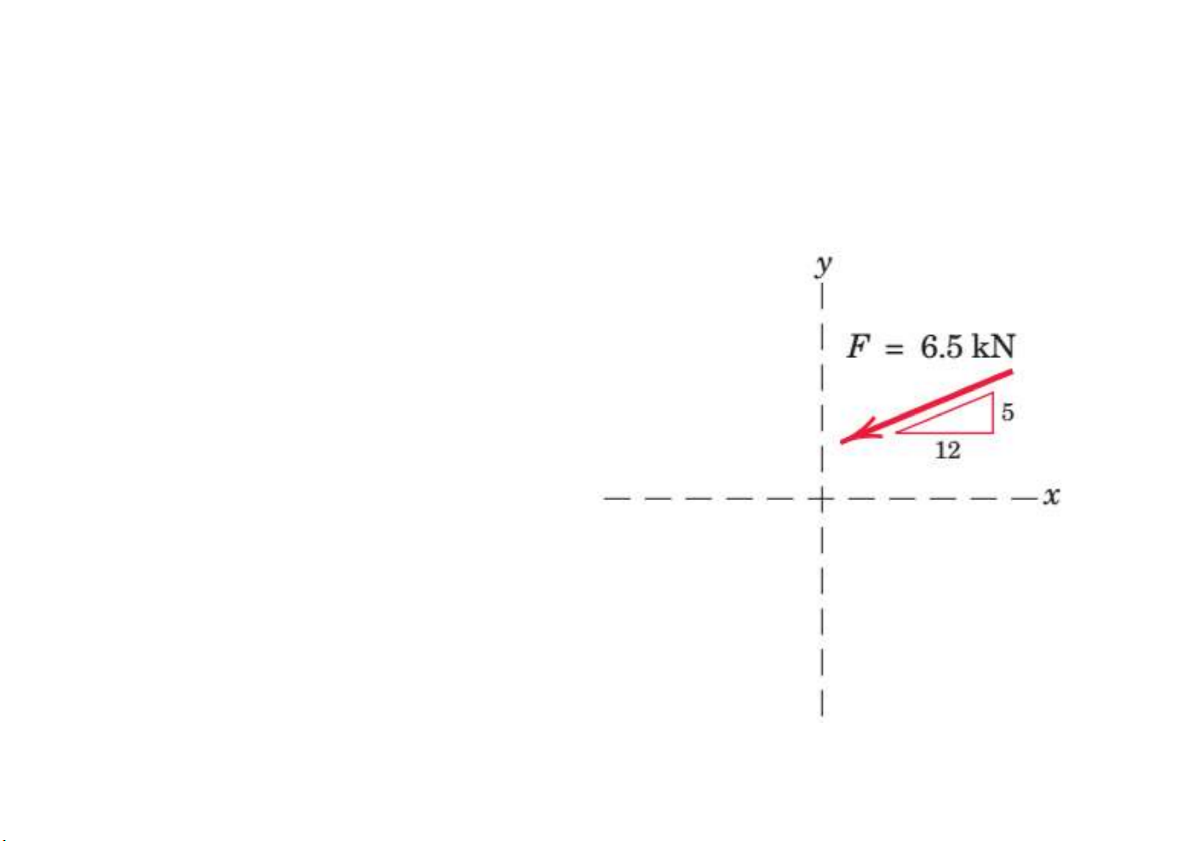
Prob. 1. The slope of the 6.5-kN force F is specified as shown in the
figure. Express F as a vector in terms of the unit vectors i and j. 22.62 F 6i 2.5j kN
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 10
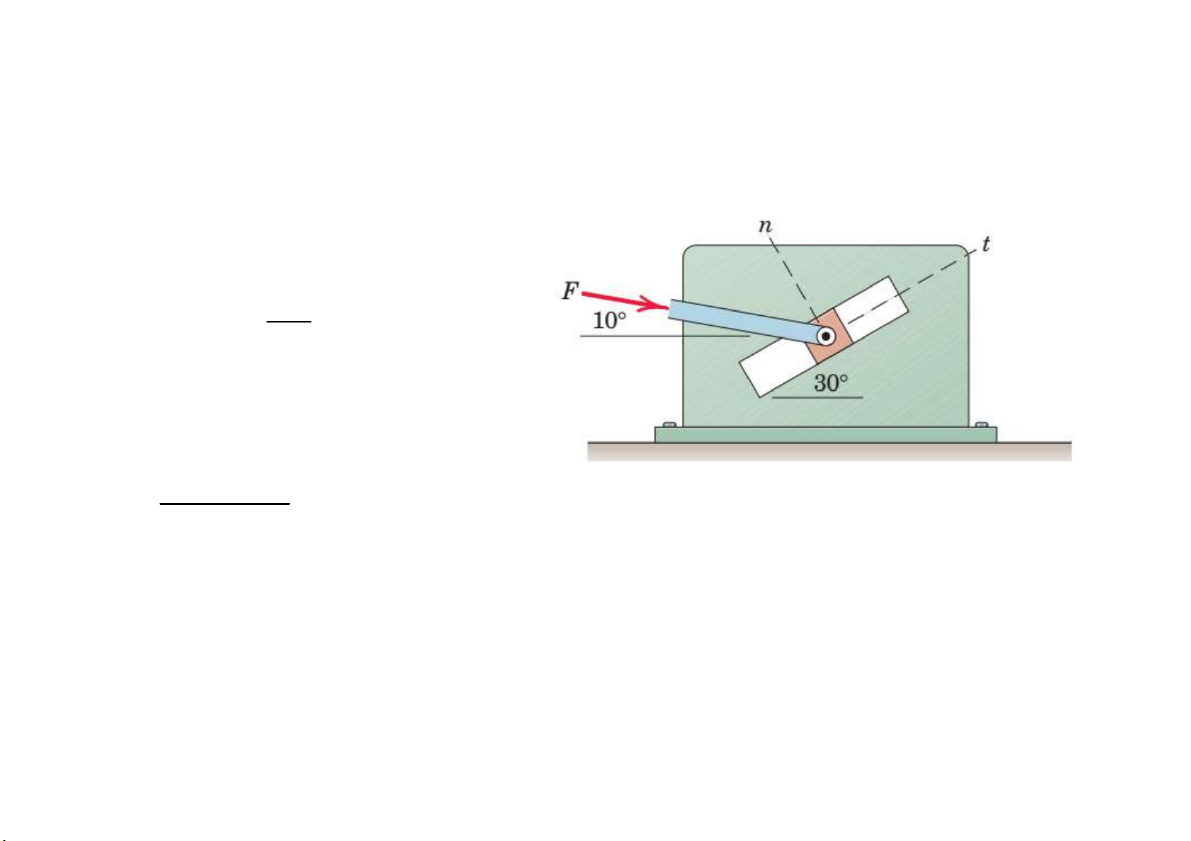
Prob. 2. The t-component of the force F is known to be 75 N.
Determine the n-component and the magnitude of F. F Tan 40 n Ft F F .tan N n t 40 62. 93 Fn F sin 40
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 11
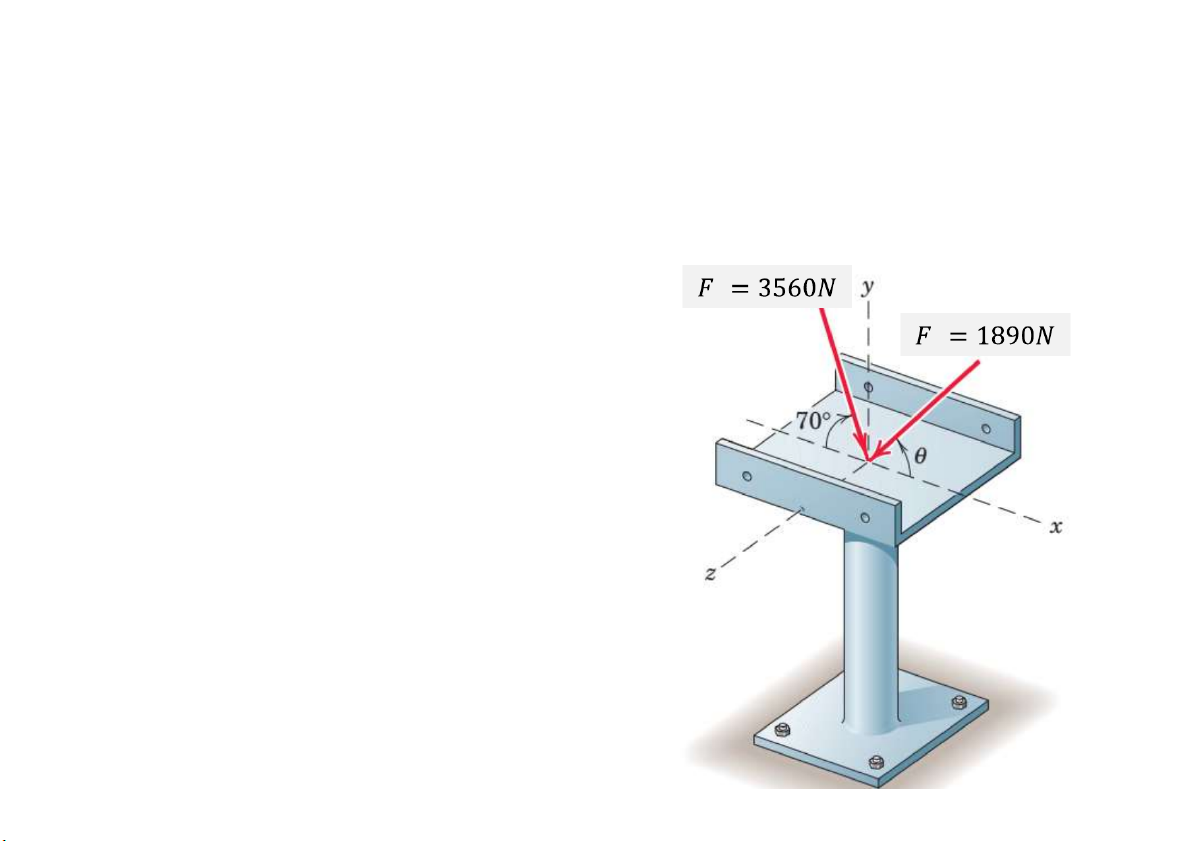
Prob. 3. Two forces are applied to the construction bracket as shown.
a. Determine the angle ɵ which makes the resultant of the two forces vertical.
b. Determine the magnitude R of the resultant. F .cos 70 F cos 2 1 49 92 . R F sin 70 F sin 49. 92 1 2
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force S
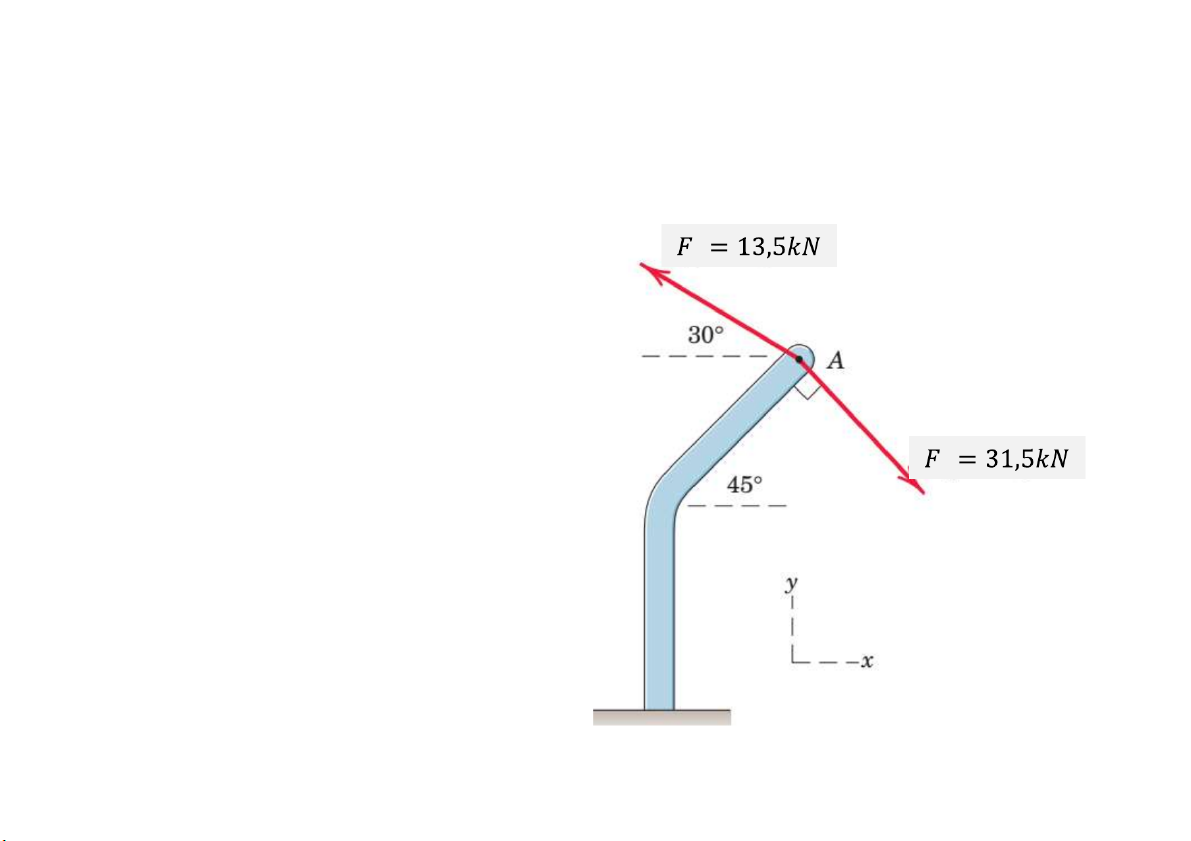
Prob. 4. The two forces shown act at point A of the bent bar.
Determine the resultant R of the two forces. R = 10.5i-15.5j kN
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 13
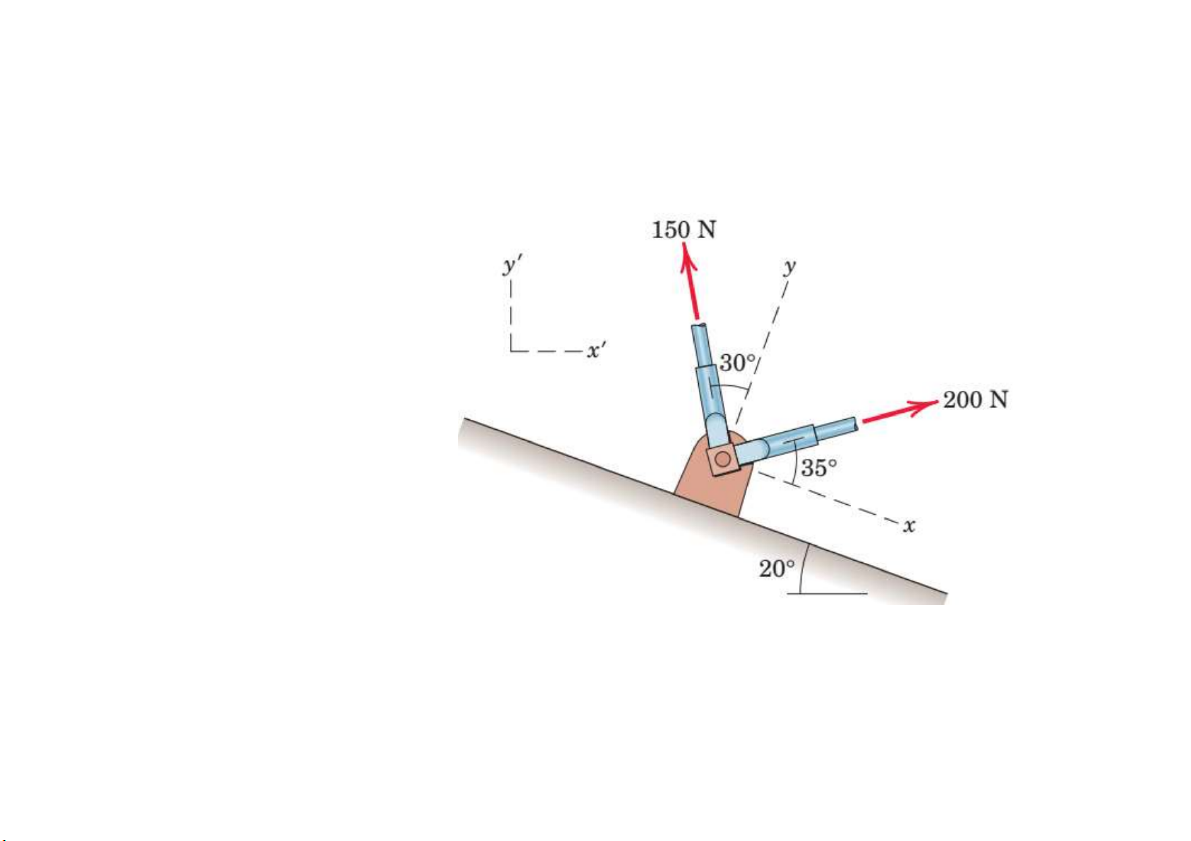
Prob. 5. Determine the resultant R of the two forces applied to the
bracket. Write R in terms of unit vectors along the x- and y-axes and the x’- and y’-axes shown. R=88.8i + 244.6j
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 14
Prob. 6. Determine the resultant R of the two forces shown by (a)
applying the parallelogram rule for vector addition and (b) summing scalar components.
a. R=871. 78N. Góc R vs Oy 36.6 b. R=520i-700j N
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 15
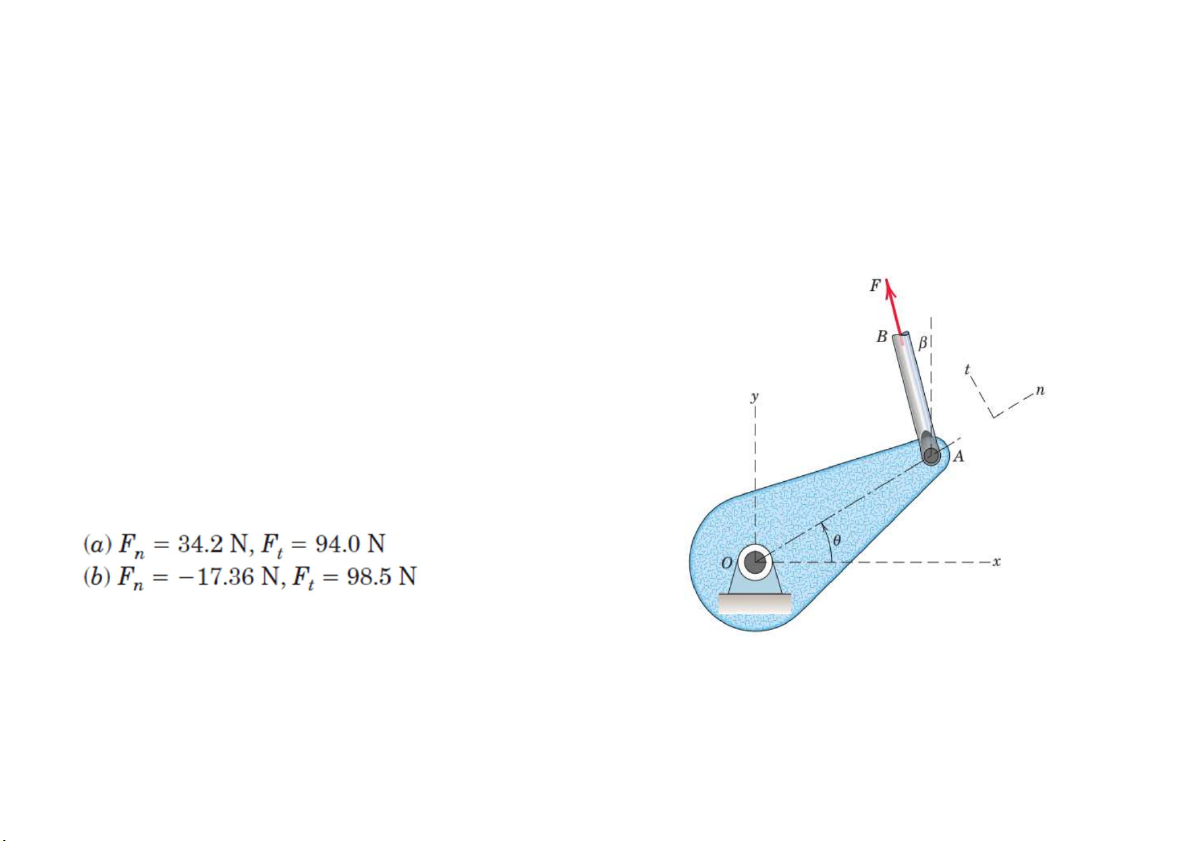
Prob. 7. Determine the n- and t-components of the force F which is exerted
by the rod AB on the crank OA. Evaluate your general expression for F=100N and a) teta= 30, beta= 10 b) Teta=15, beta= 25
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 16
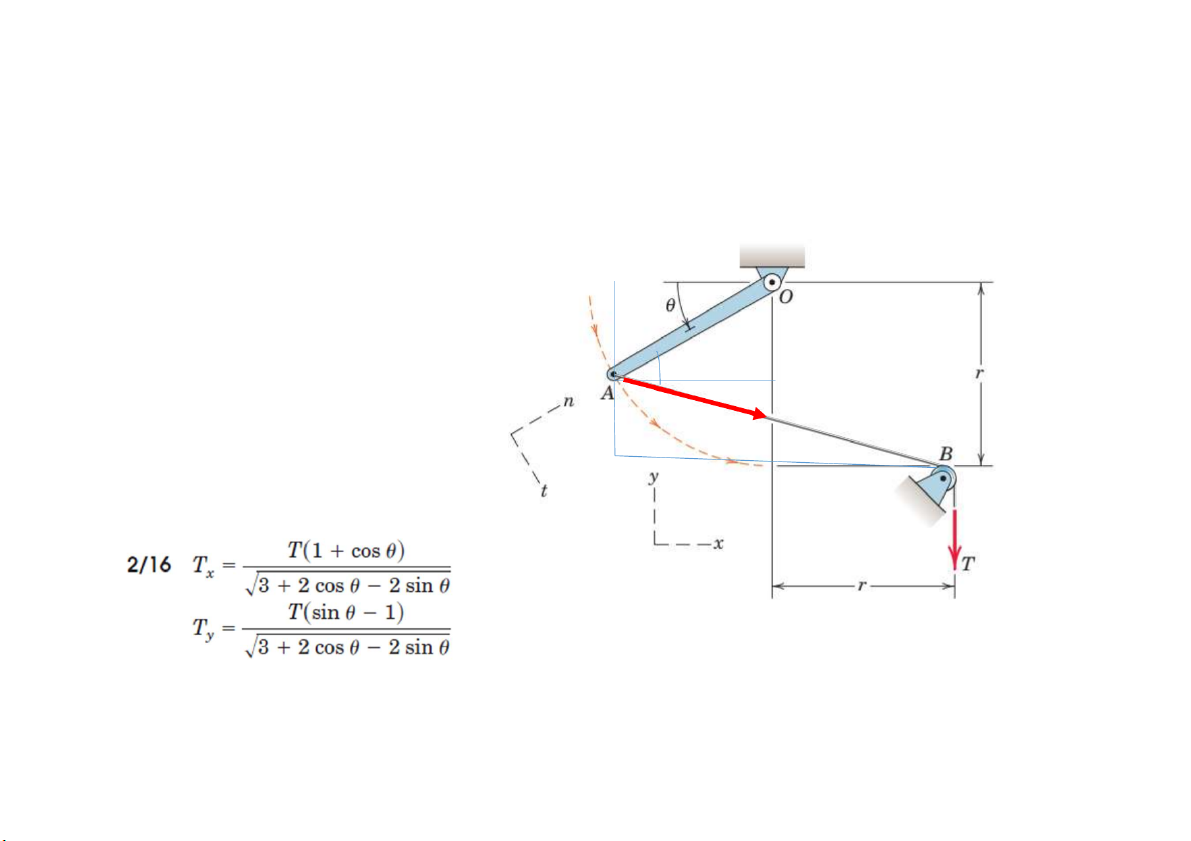
Prob. 8. 1. Determine the x- and y-components of the tension T which is applied to
point A of the bar OA. Neglect the effects of the small pulley at B. Assume that r and theta are known.
2. Determine the t- and n-components of the tension T=100N with teta = 35
Tx=T.cos(Beta). Ty=T.sin(beta). Tt= Tx. sin (teta) Tn= Tx. cos (teta)
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 17
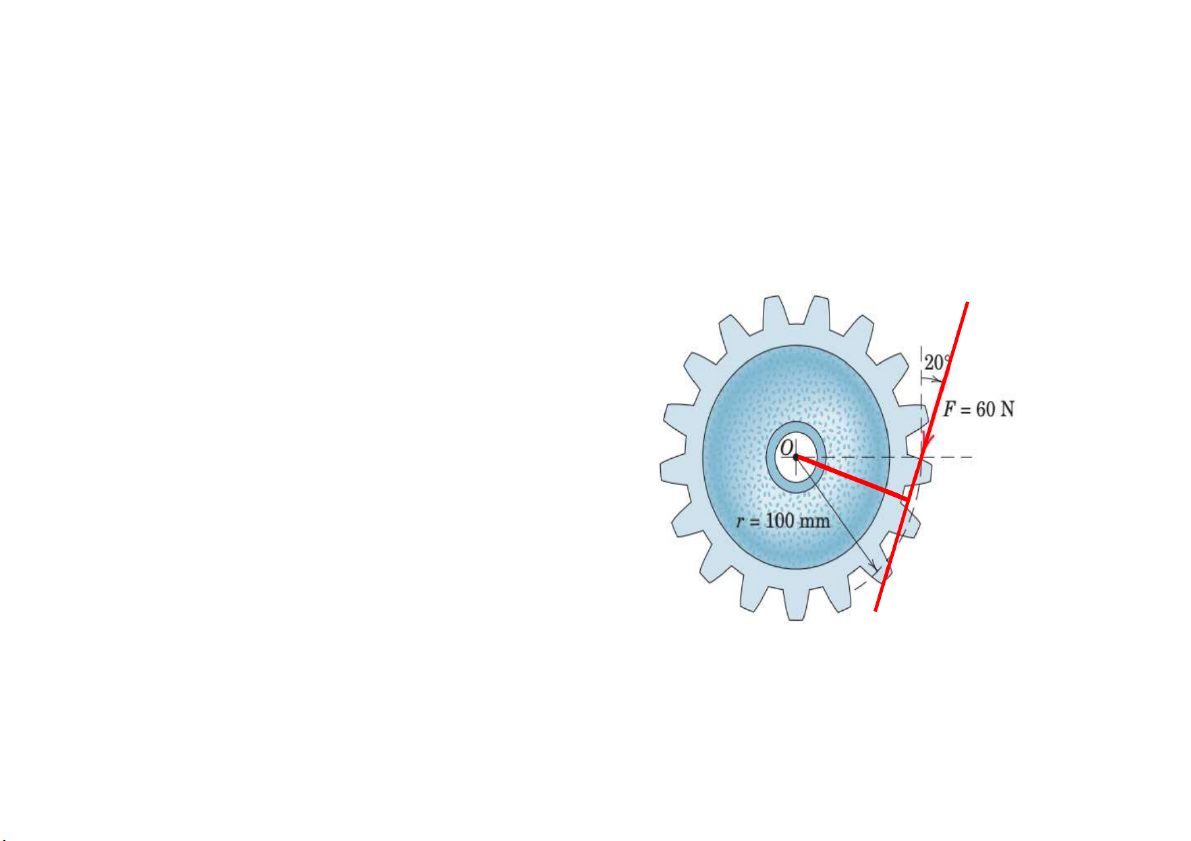
Prob. 9. A force F of magnitude 60 N is applied to the gear.
Determine the moment of F about point O. Mo=-5.64 N.m
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 18
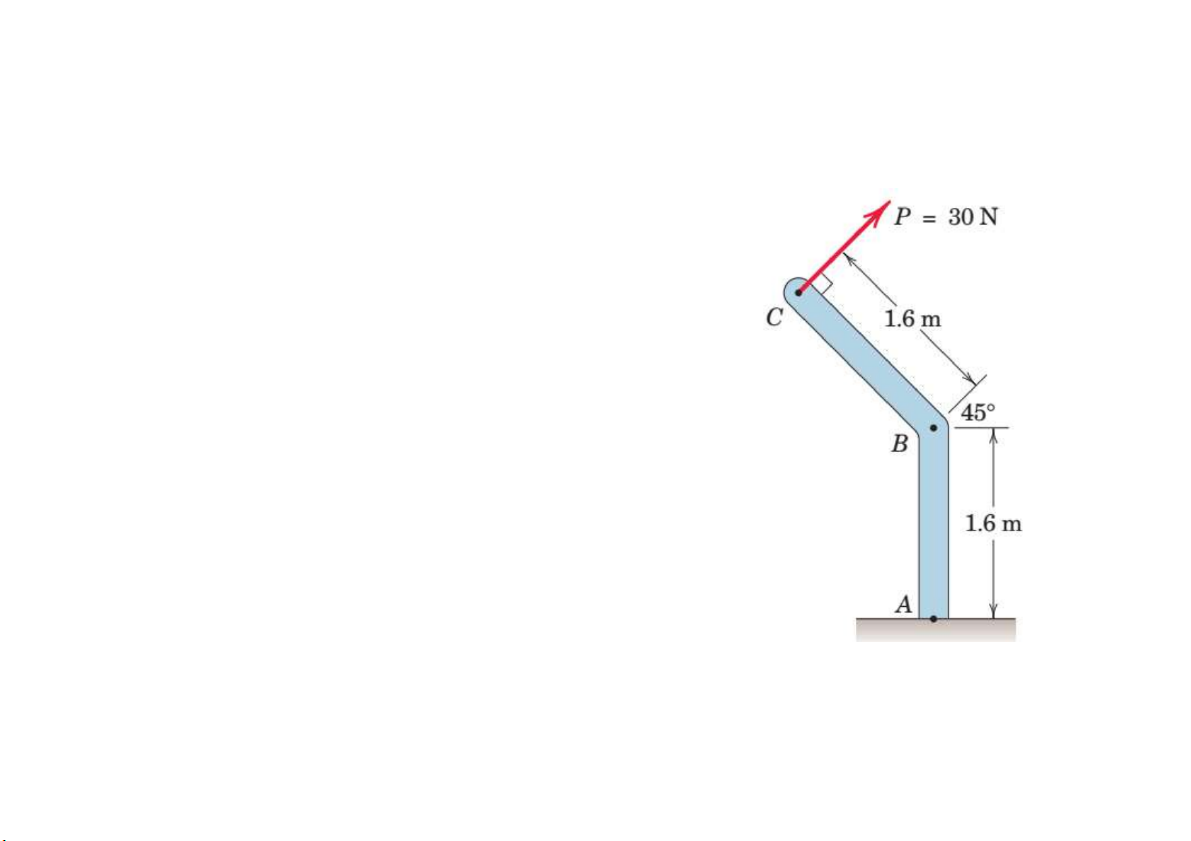
Prob. 10. The 30-N force P is applied perpendicular to the portion
BC of the bent bar. Determine the moment of P about point B and about point A. M P . . Nm . B 16 48 M M Pcos . . . N.m A B 45 16 8194
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 19
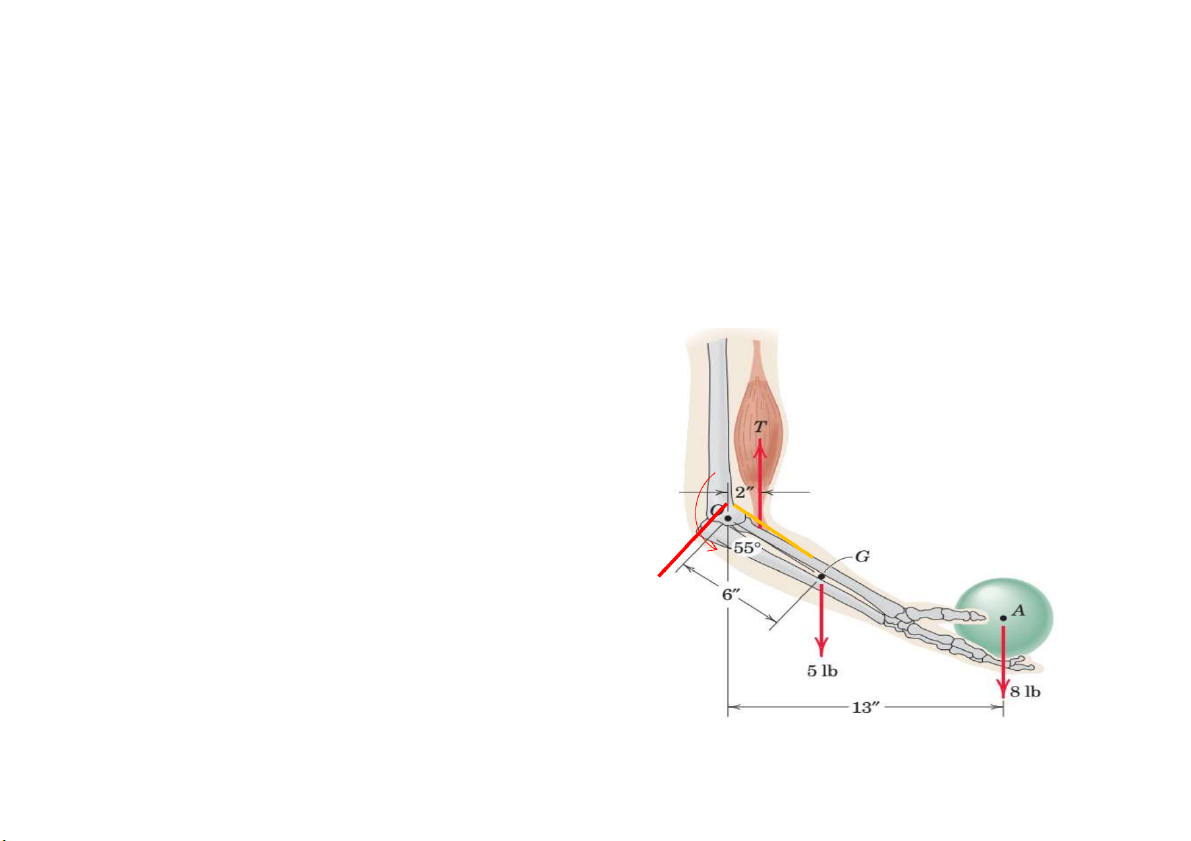
Prob. 11. Elements of the lower arm are shown in the figure. The weight of
the forearm is 5 lb with mass center at G.
1. Determine the combined moment about the elbow pivot O of the
weights of the forearm and the sphere.
2. What must the biceps tension force be so that the overall moment about O is zero? a) Mo = -F.13 – P.cos55.6 b) b) T = Mo/2 P F
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 20
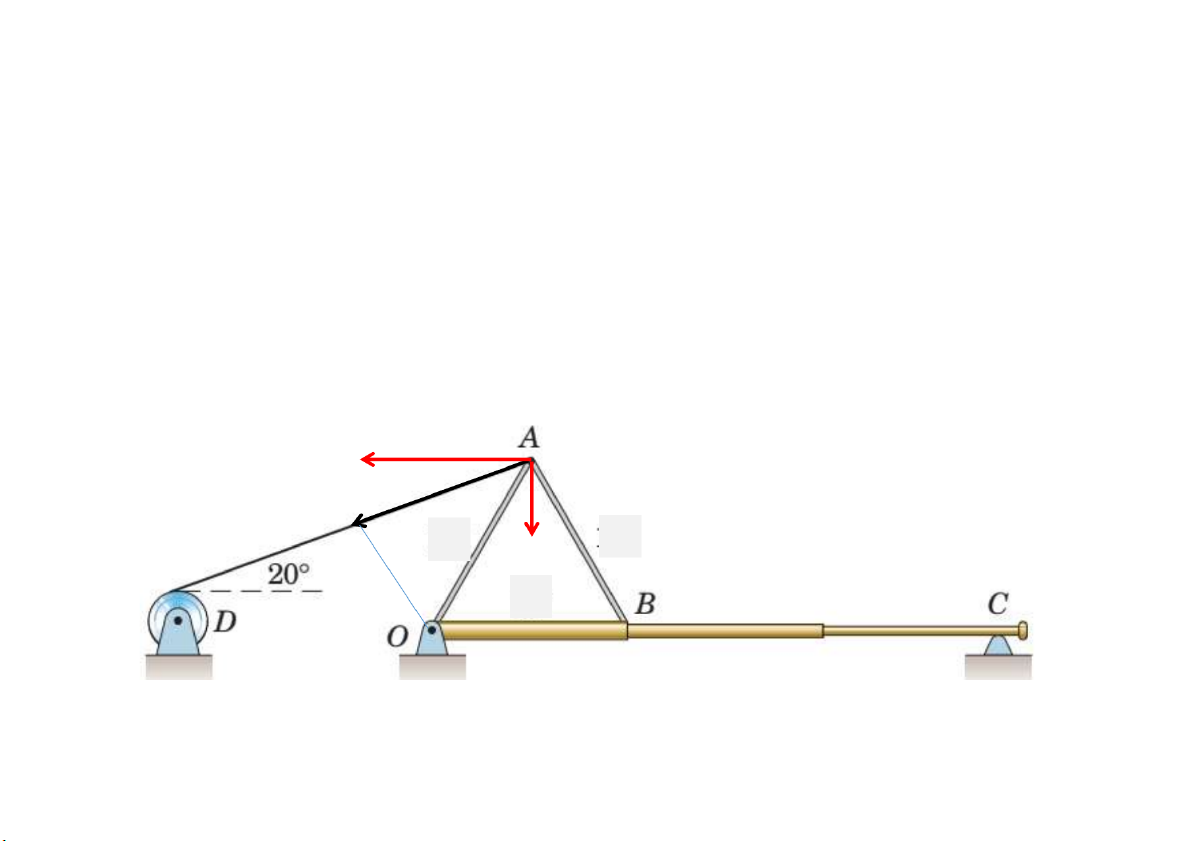
Prob. 12. In order to raise the flagpole OC, a light frame OAB is attached
to the pole and a tension of T=3470N is developed in the hoisting cable by the power winch D.
Calculate the moment of this tension about the hinge point O. D=3sin40 Tx = 3260N Ty = 1186.8 N Mo = 6690N.m 40 3m 3m 3m
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 21
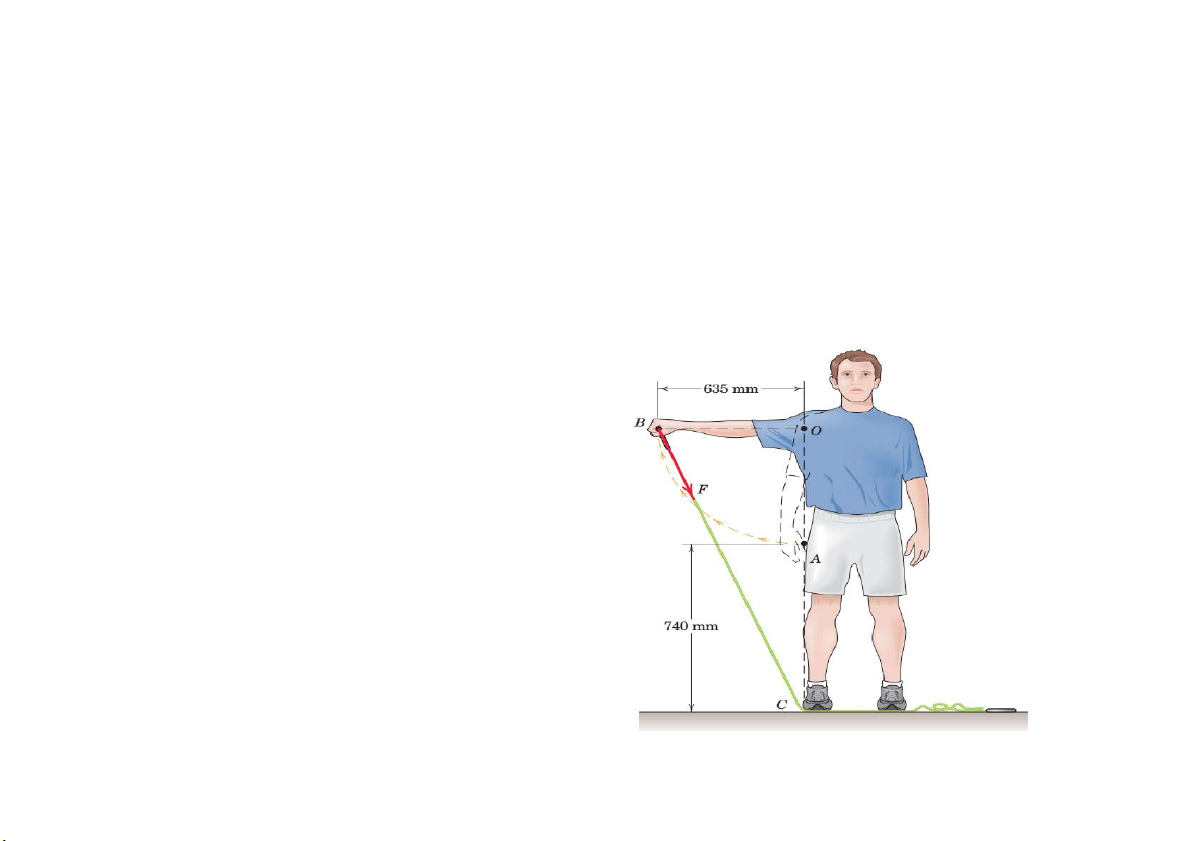
Prob. 13. An exerciser begins with his arm in the relaxed vertical position
OA, at which the elastic band is unstretched. He then rotates his arm to the
horizontal position OB. The elastic modulus of the band is k = 60N/m, That
is, 60 N of force is required to stretch the band each additional meter of
elongation. Determine the moment about O of the force which the band exerts on the hand B. F=k.x=46.44 N Mo=F.cos(a) d=26.68N.m
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 22
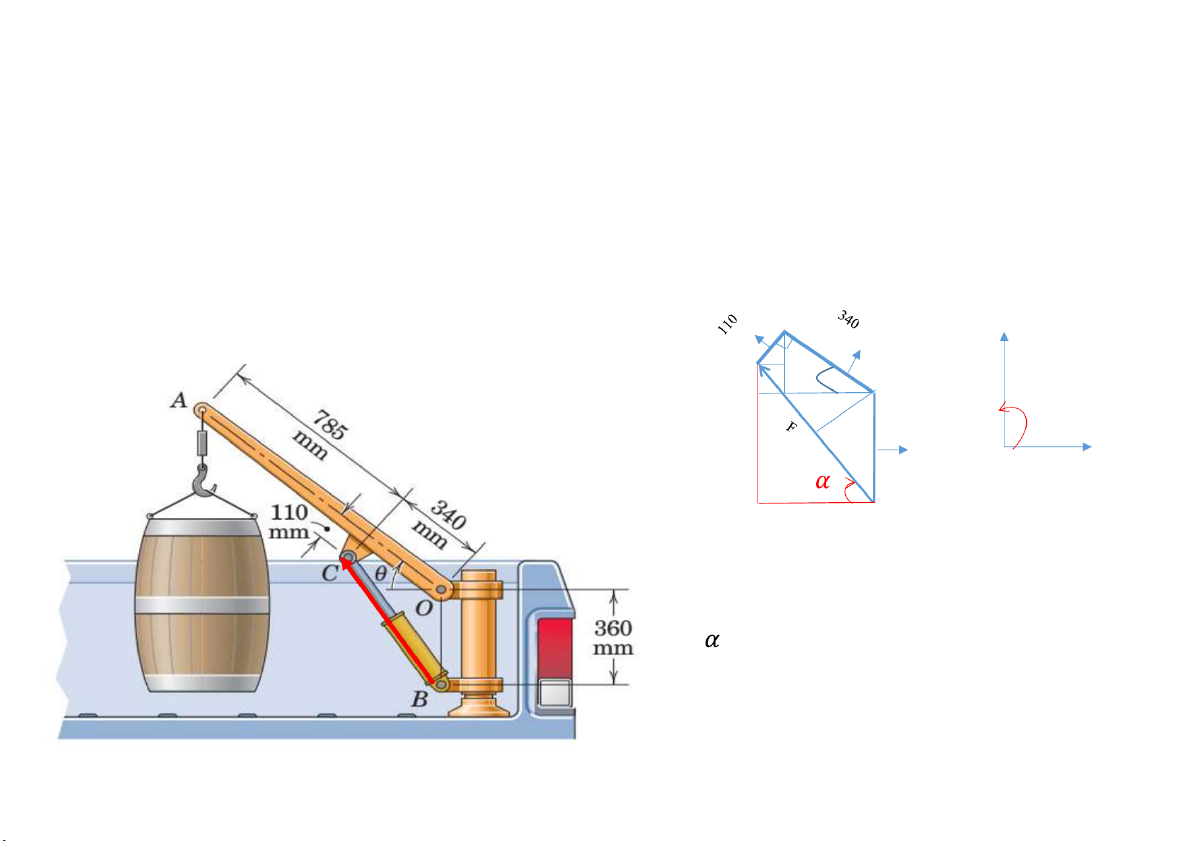
Prob.14. The small crane is mounted along the side of a pickup bed and
facilitates the handling of heavy loads. When the boom elevation angle is the
force in the hydraulic cylinder BC is F=4.5 kN, and this force applied at
point C is in the direction from B to C (the cylinder is in compression).
Determine the moment of this 4.5-kN force about the boom pivot point O. D C ɵ O 360 h O’ B l
h= 360 + 340.sin40 – 110cos40 l = 340cos40 + 110 sin 40 = 56.18
Mo = -F.cos a . 0.360 = 0.902 kN.m
Cách 1. Xác định qua góc tam giác COB
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 23
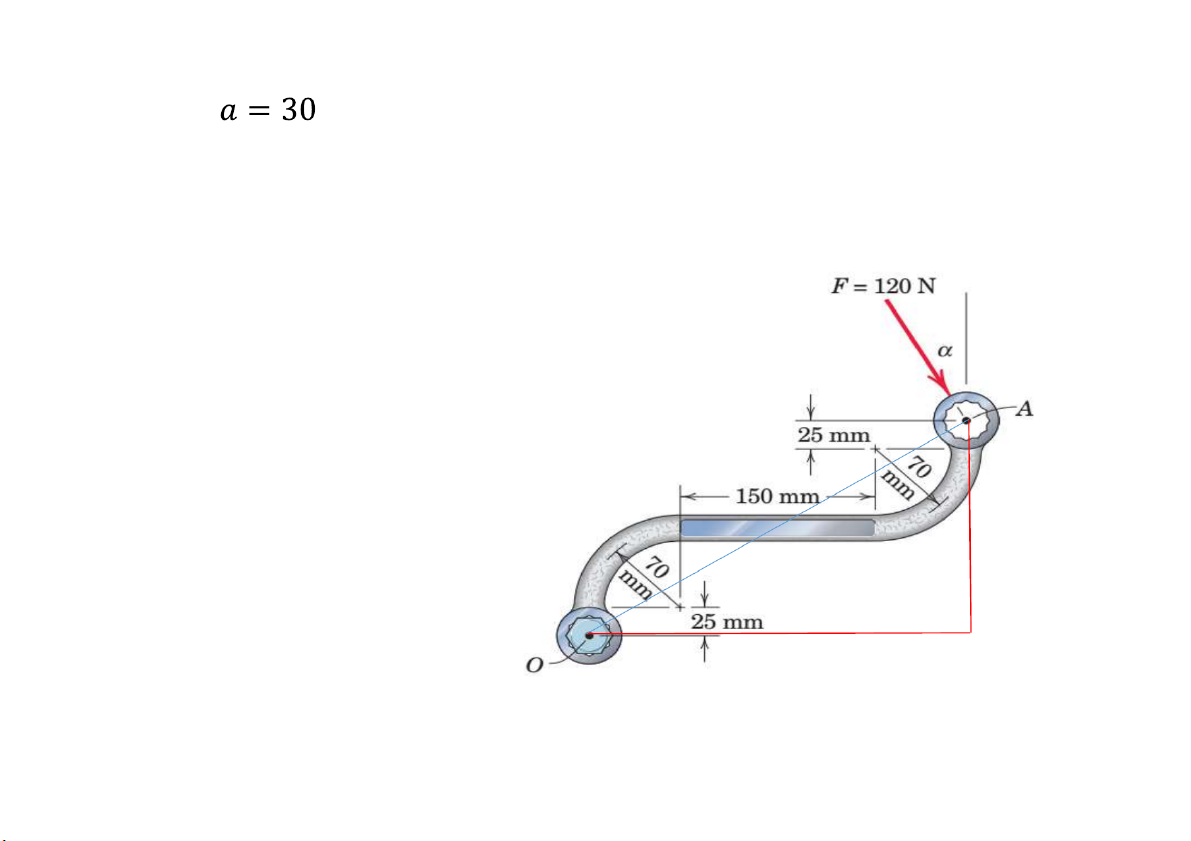
Prob. 15. The F= 120N force is applied as shown to one end of the curved wrench. If
calculate the moment of F about the center O of the bolt.
Determine the value of which would maximize the moment about O; state
the value of this maximum moment. a = 30 Mo = F.cos a . (l) + F.sin(a). (h)= 41.5 N.m
Mo lớn nhất khi: khoảng cách từ O tới
đường tác dụng lực là lớn nhất. Mà
tam giác OAB có AB, OB không đổi. h
Nên Oamax là cạnh huyền của OAB a = arctan(h/l)=33.23 l B Mo = F.OA =41.6 N.m
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 24
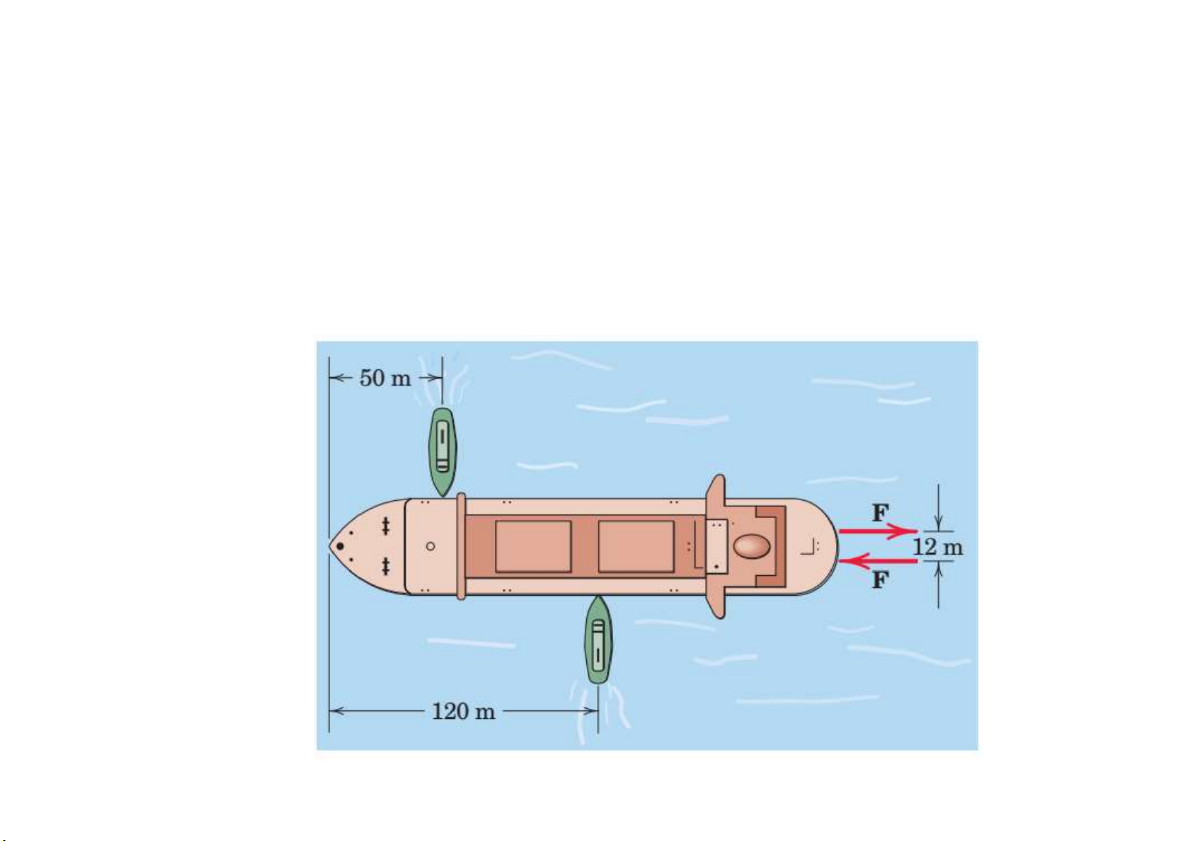
Prob. 16. Each propeller of the twin-screw ship develops a full-speed
thrust of 300 kN. In maneuvering the ship, one propeller is turning full
speed ahead and the other full speed in reverse. What thrust P must each
tug exert on the ship to counteract the effect of the ship’s propellers? -P.50+P.120=F.12 P = 51.43 kN
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 25
Prob.17. During a steady right turn, a person exerts the forces shown on
the steering wheel. Note that each force consists of a tangential
component and a radiallyinward component. Determine the moment
exerted about the steering column at O. Mo = 8.cos30.0.375 = 2.6 N.m Cơ học lý thuy
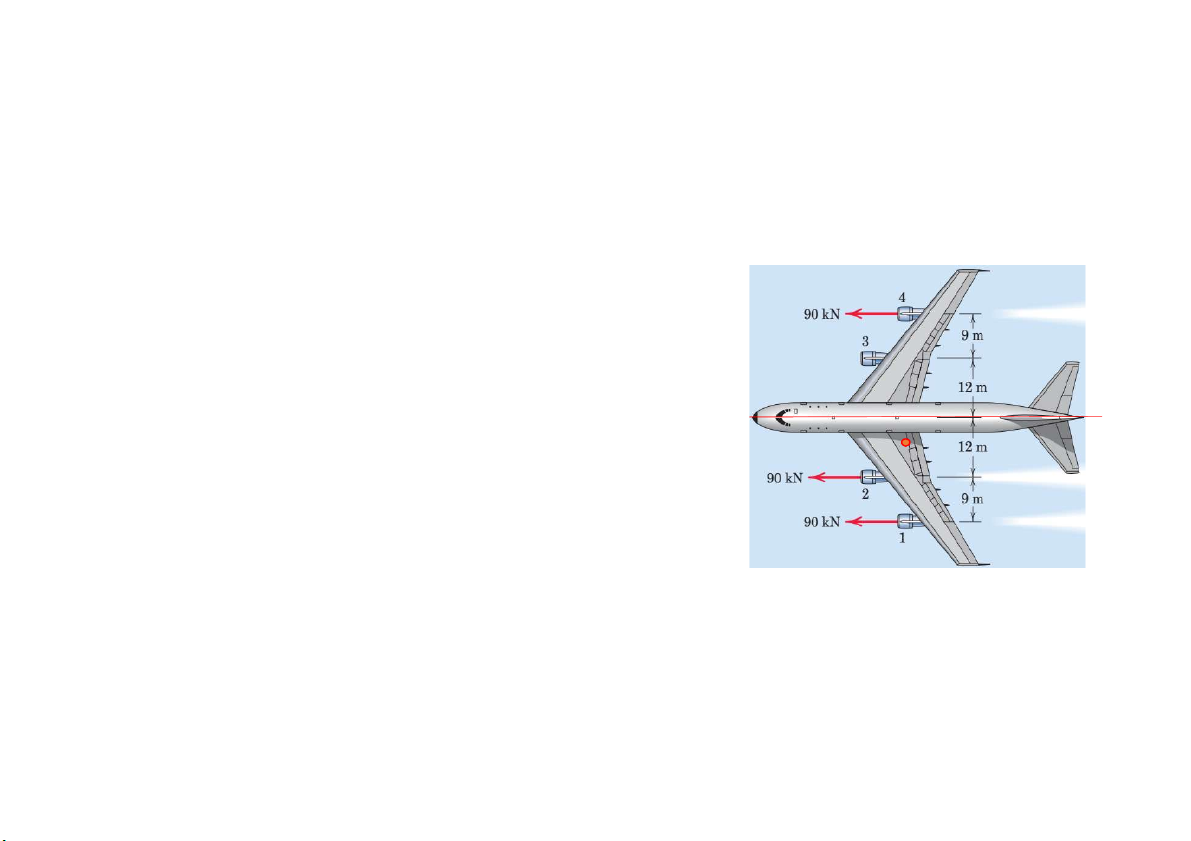
Prob. 18. A commercial airliner with four jet engines, each producing 90 kN
of forward thrust, is in a steady, level cruise when engine number 3 suddenly
fails. Determine and locate the resultant of the three remaining engine thrust
vectors. Treat this as a two dimensional problem.
Khi 4 động cơ hoạt động bình thường thì máy bay chuyển động thẳng F4
đều với lực F=360N đặt tại trục của máy bay. Trong trường hợp này máy bay k bị quay.
Khi có 3 động cơ hoạt động: Để máy bay hoạt động bình thường (chỉ
chuyển động thẳng đều và không bị quay tại trục) thì tổng moment do 3 O
động cơ phải triệt tiêu F2
Giả sử điểm đặt hợp lực F nằm dưới trục O 1 khoảng x (m) . F1 M M 12 4 F 21 x F 12 x F 21 x
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 27
Prob. 19. Determine the x- and y-axis intercepts of the line of action of
the resultant of the three loads applied to the gearset R = -1.641 i – 0.999 j (N) Mo= 1.635 kN.m r x R = Mo (xi + yj) x (Rxi+Ryj) = Mo x= 1.637 m, y = -0.997 m
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 28
Prob. 20. Determine the resultant R of the three forces acting on the
simple truss. Specify the points on the x- and y-axes through which R must pass. R = -15 i – 47,3 j (N) Mo= -352.8 kN.m r x R = Mo (xi + yj) x (Rxi+Ryj) = Mo (-47,3x + 15y)k = -352.8 k (y=0, x= 7,42 m, x=0,y = -23,52m)
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 29
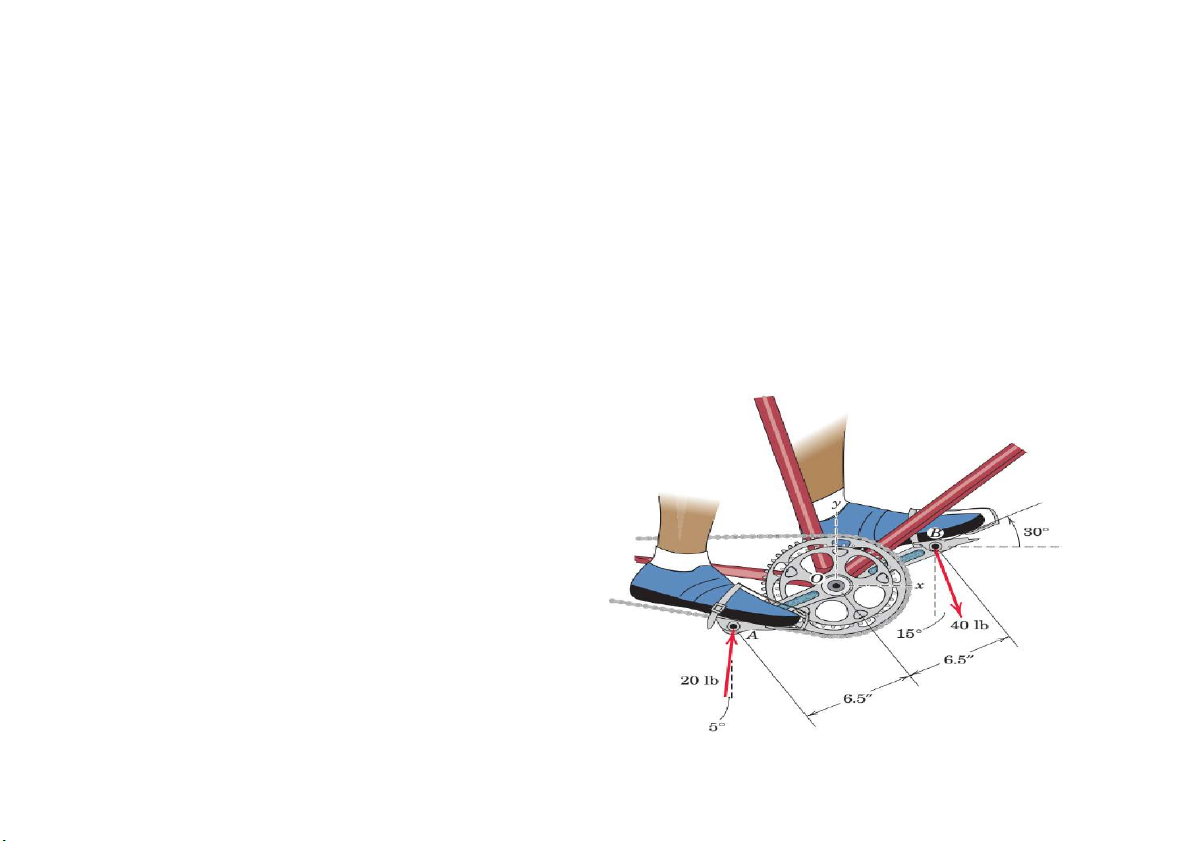
Prob. 21. The pedal-chainwheel unit of a bicycle is shown in the figure. The left foot of the
rider exerts the 40-lb force, while the use of toe clips allows the right foot to exert the nearly
upward 20-lb force. Determine the equivalent force-couple system at point O.
Also, determine the equation of the line of action of the system resultant treated as a single
force R. Treat the problem as two-dimensional. R = 12.10 i – 18.7 j (lb) Mo= -357.6 lb.in r x R = Mo (xi + yj) x (Rxi+Ryj) = Mo (-47,3x + 15y)k = -350.88 k (y=0, x= 7,42 m. X = 0, y = -23,39m)
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 30 Bài toán không gian
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 31
Hệ lực trong không gian
Xác định lực F nếu biết toạ độ 2 điểm trên phương đặt lực
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 32
Hệ lực trong không gian
Xác định lực F nếu biết 2 góc
Tích vô hướng (dot product)
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 33
Hệ lực trong không gian
Tích vô hướng (dot product)
Lực F theo hướng n có vector đơn vị là n. Độ lớn của F là Fn=F.n
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 34
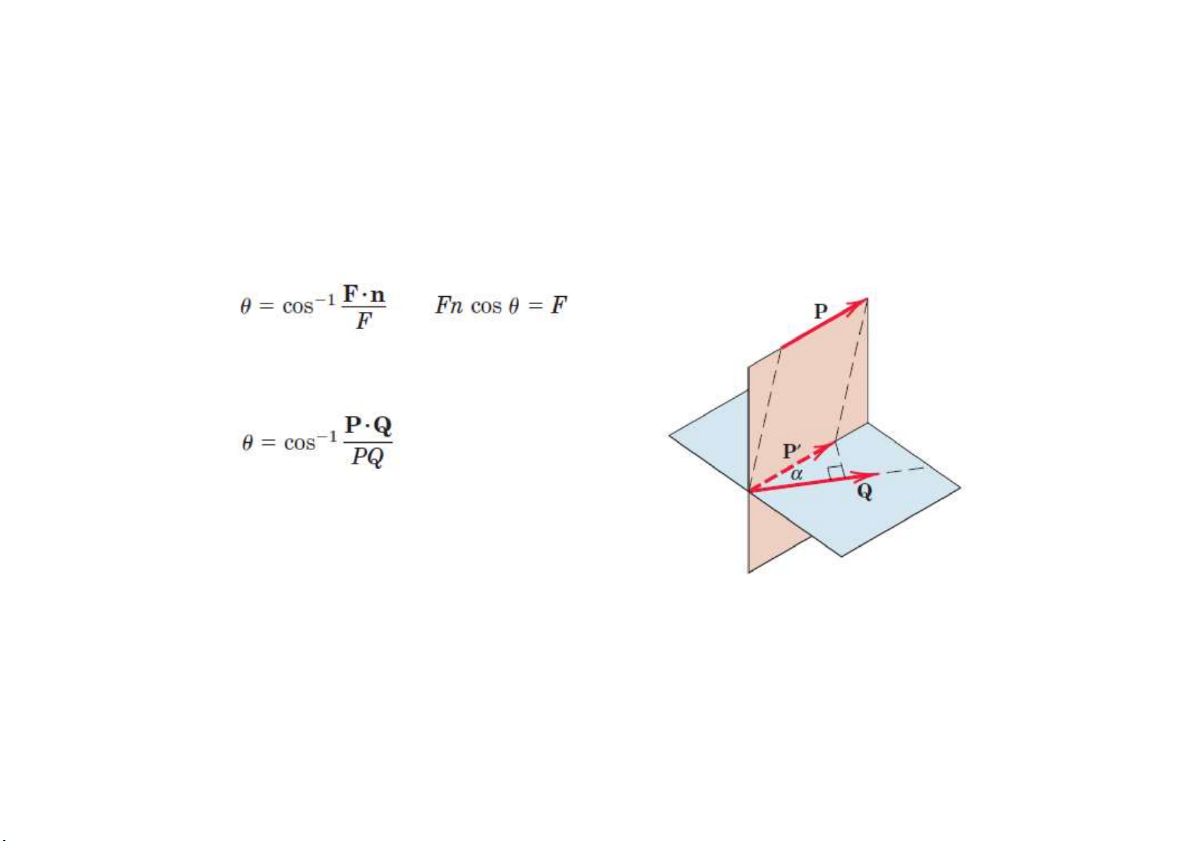
Hệ lực trong không gian Góc giữa 2 vector
Góc giữa lực F và hướng n là Góc giữa lực P và Q là
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 35
Hệ lực trong không gian Ví dụ:
a. Xác định thành phần lực Fx, Fy, Fz
b. Xác định thành phần lực Fxy Góc giữa F và nxy
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 36
Hệ lực trong không gian Ví dụ:
c. Xác định lực FOB là lực của F dọc theo cạnh OB
Xác định vector đơn vị nOB
Độ lớn xác định theo tích vô hướng F và nOB
Thành phần lực FOB trên phương OB
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 37
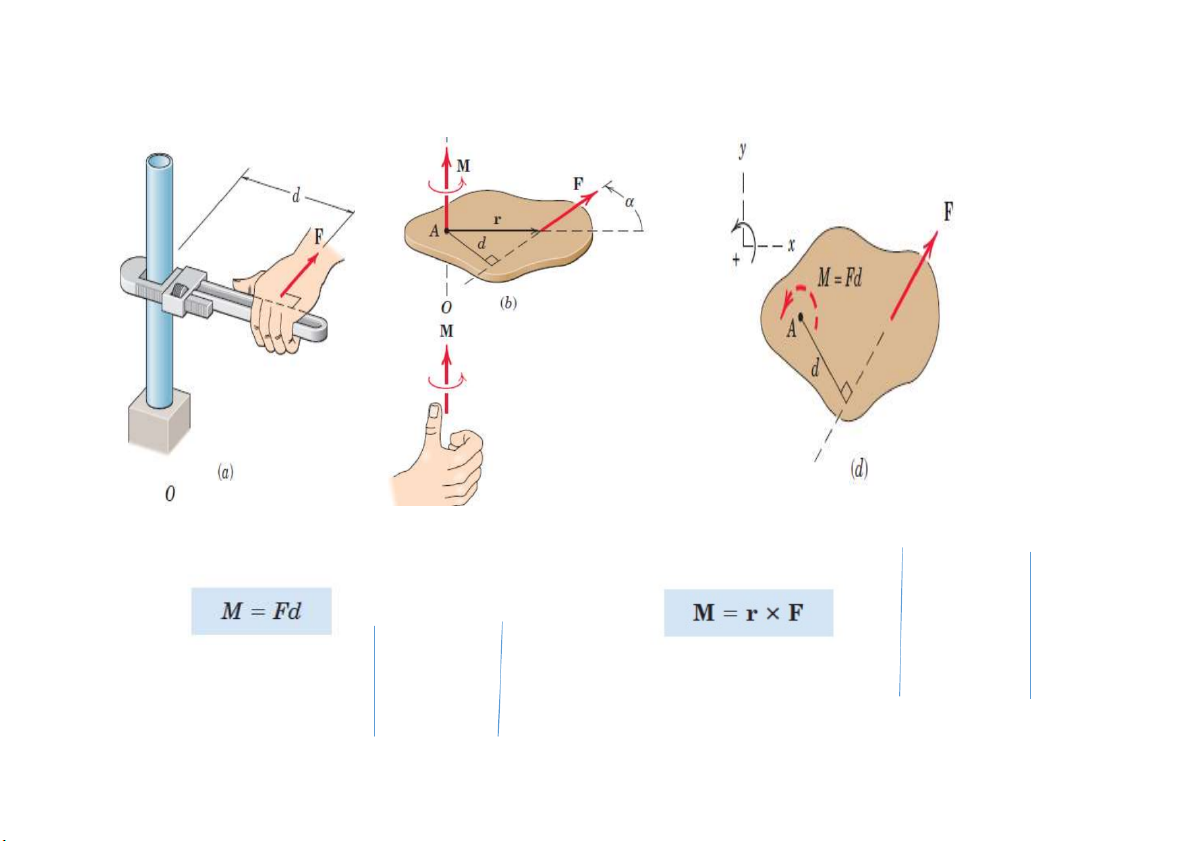
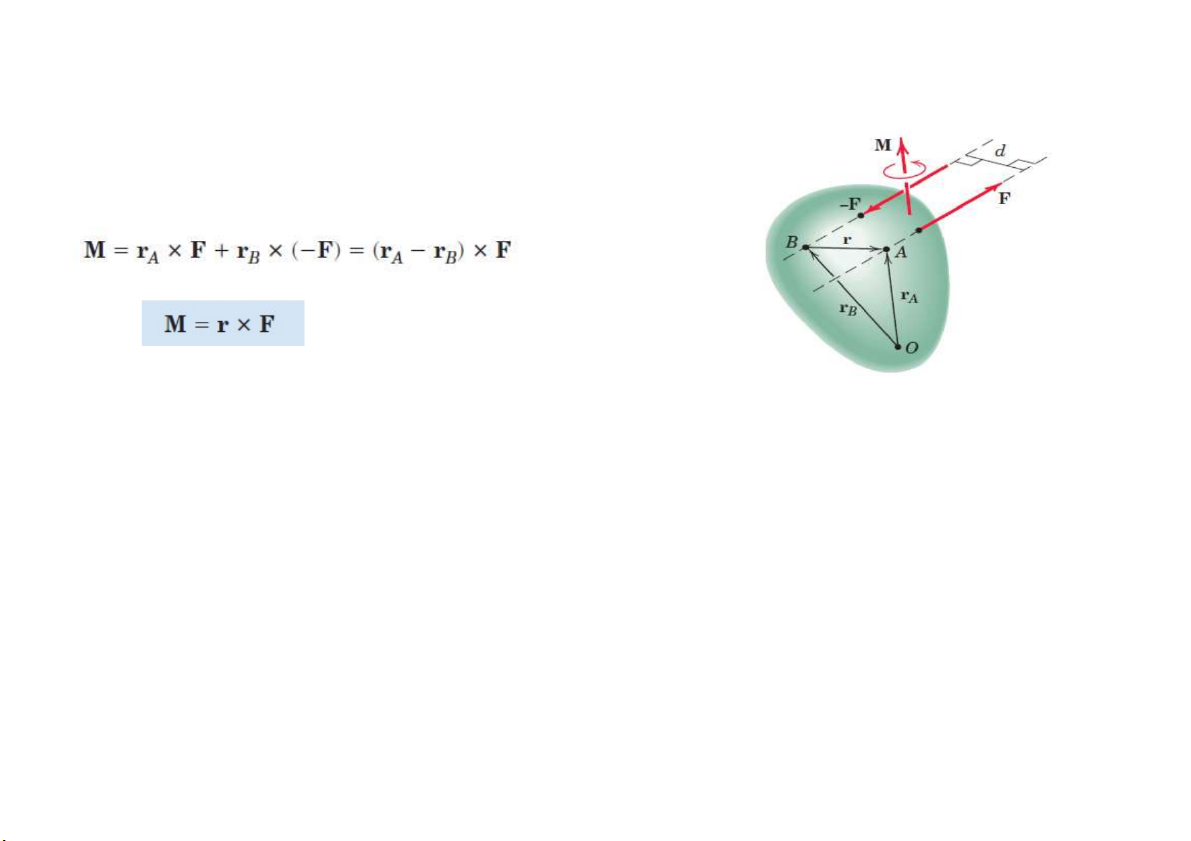
Moment trong không gian
Moment tại O là tích có hướng (cross product) của F và r
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 38
Moment trong không gian
Tính moment của một trục bất kỳ
Định lý Varignon trong không gian
Moment hợp lực của hệ lực đối với một điểm (hay trục) nào đó bằng tổng
moment các lực thành phần của hệ lực đối với cùng điểm (hay trục) đó. (Trường
hợp hệ lực có hợp lực).
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 39
Ngẫu lực trong không gian
Cặp ngẫu lực F tác dụng vào vật rắn với phương tác dụng qua A và B. rB là
khoảng cách từ OB. rA là khoảng cách OA. r là khoảng cách AB.
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 40
Moment trong không gian
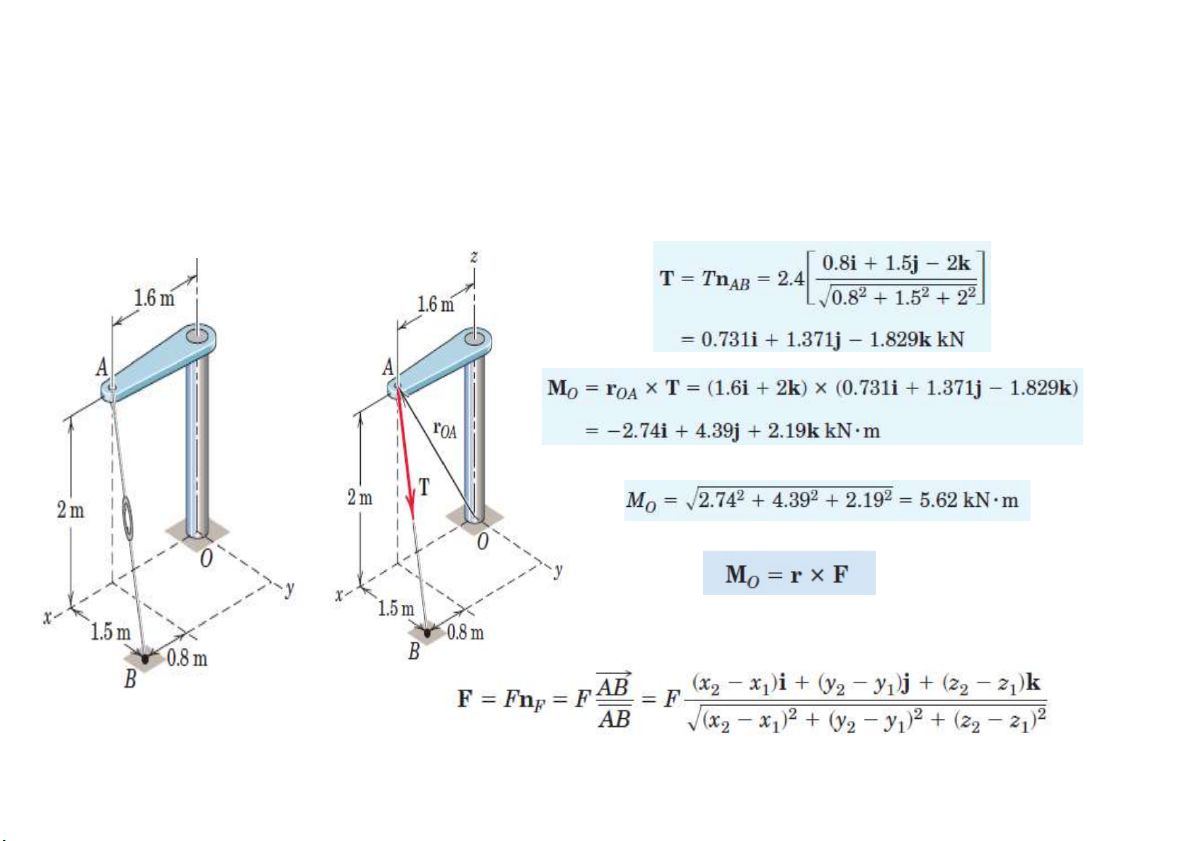
Ví dụ: Một cơ cấu như hình vẽ với đai ốc được gắn vào dây cáp AB có
lực T=2.4 kN. Xác định moment và độ lớn moment tại O do T gây ra A (1.6, 0, 2). B (2.4, 1.5, 0)
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 41
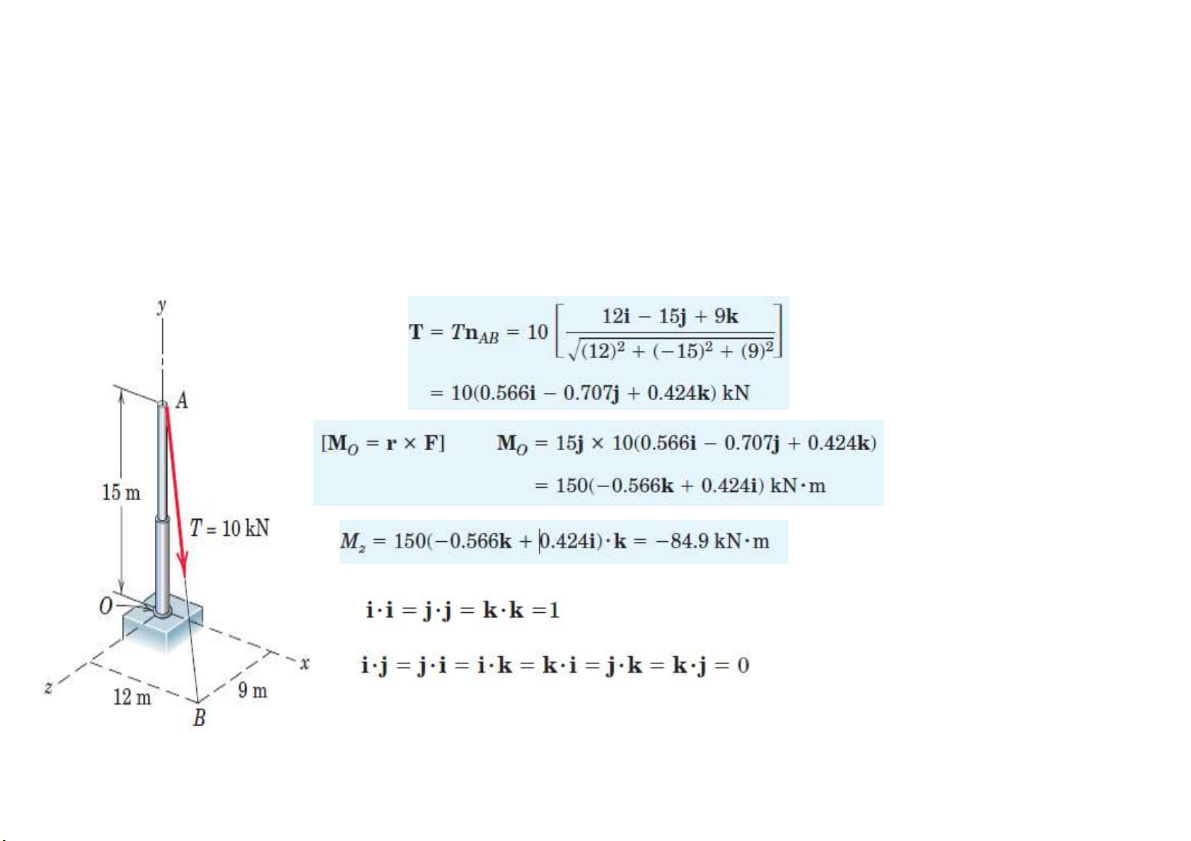
Moment trong không gian
Ví dụ 2: Xác định moment của T=10kN với trục z đi qua O.
Xác định moment của T với trụ z bằng cách xác định lực thành
phần Fz của T với O.
Cơ học lý thuyết - Vector and Force Systems 42