Preview text:
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Exercises
CHAPTER 4: TORSION (exercises)
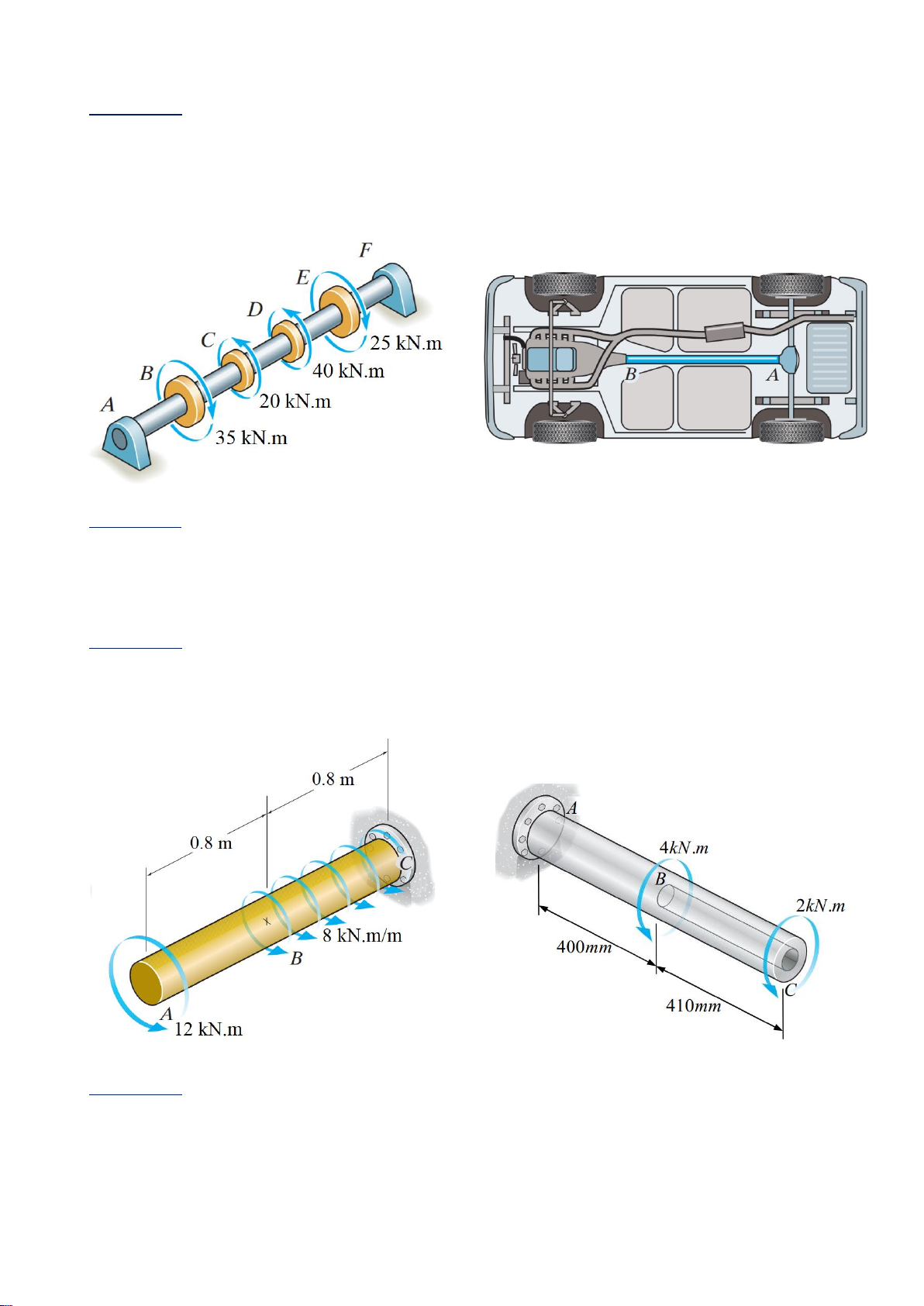
Problem 1: The solid shaft has a diameter of 19mm. If it is subjected to the toques shown:
1. Draw the toque diagram of shaft. (Figure 1)
2. Determine the maximum shear stress developed in BE of the shaft.
3. Determine the angle of twist in between section through A and F.
The bearings at A and F allow free rotation of the shaft. AB = BC = CD = DE = EF = 0.8m Figure 1 Figure 2
Problem 2: The drive shaft AB of an automobile is made of a steel having an allowable shear
stress of 80MPa. If the inner diameter of the shaft is 80mm and the engine delivers 85W to
the shaft when it is turning at 50rev/min. Determine the required thickness of the shaft’s
wall and the angle of twist of the shaft, AB = 1.2m. (Figure 2)
Problem 3: The solid shaft has a diameter of d. If it is subjected to the toques shown:
1. Draw the toque diagram of shaft. (Figure 3)
2. Determine the required diameter d of the shaft, [𝜏] = 90MPa.
3. Determine the angle of twist in section A. Figure 3 Figure 4
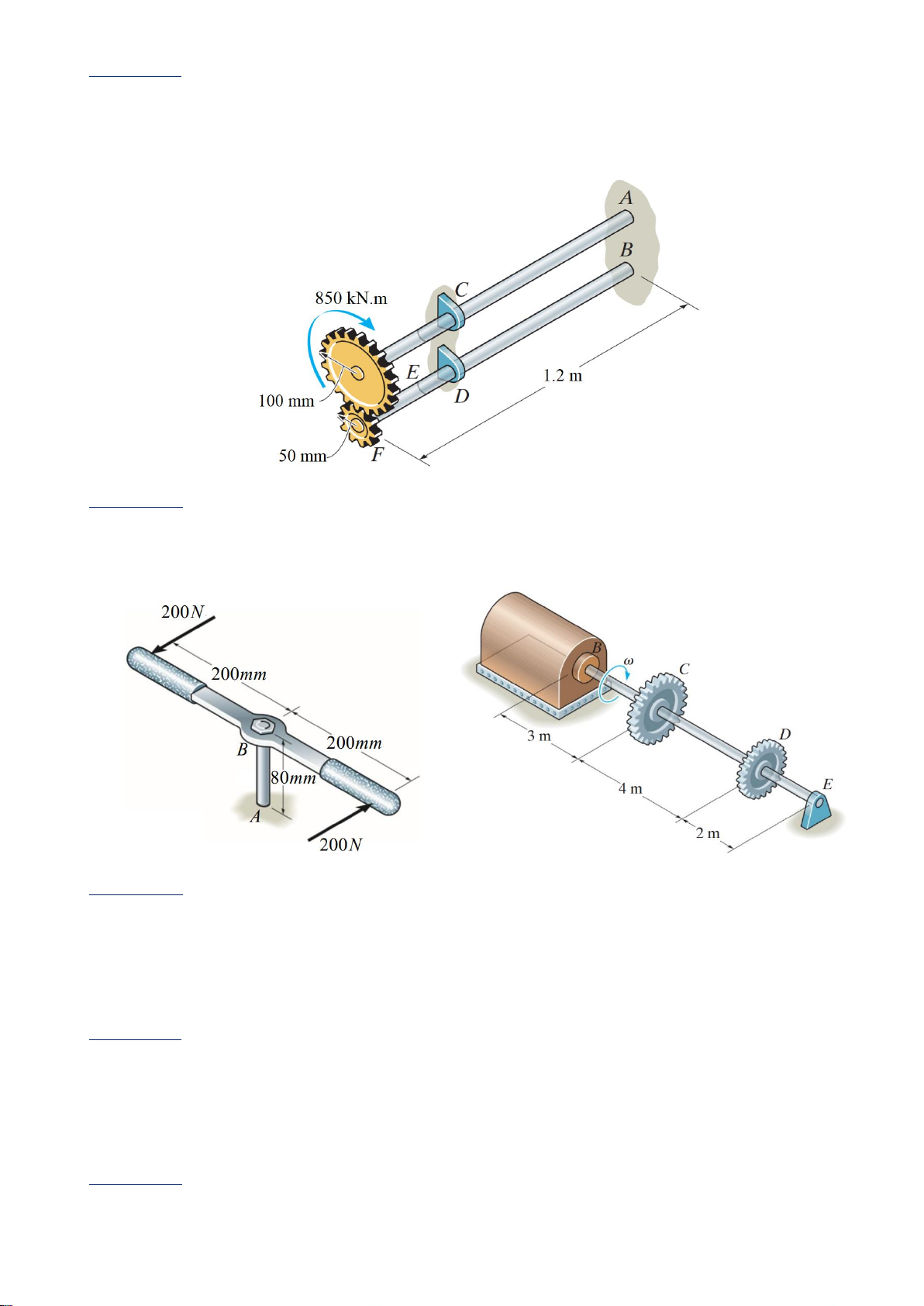
Problem 4: The steel shape consists of AB has a diameter of D, BC has outer diameter of D
and the thickness t. The shape is made from the material having G = 120GPa, [𝜏] = 90MPa.
1. Draw the torque diagram of shaft. (Figure 4)
2. Determine the required diameter D of the shaft if the thickness t = 12mm.
3. Determine the angle of twist of shape.
Ph.D Lieu T. Bich Nguyen Chapter 4. TORSION.
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Exercises
Problem 5: Both of shaft have the same of diameter D, made from the same materials having
the shear modulus elasticity G = 120GPa, [𝜏] = 110MPa.
1. Determine the reaction at the fixed support A, B. (Figure 5)
2. Determine the required diameter D of the shaft.
3. Determine the angle of twist of the gear F. Figure 5
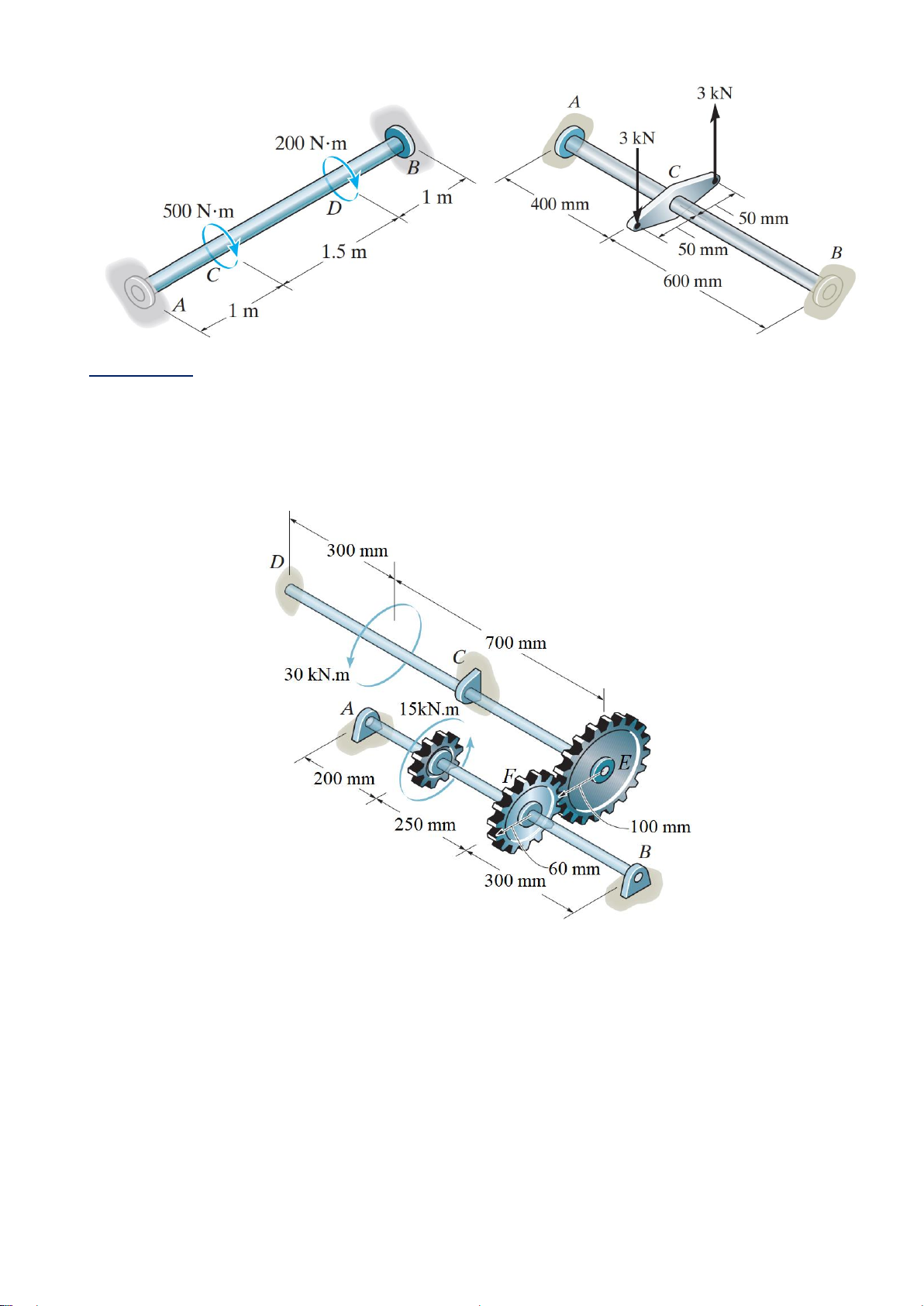
Problem 6: The solid shaft AB has a diameter of d is fixed at A. It is made from the steel
having G = 90GPa, [𝜏] = 60MPa. (Figure 6)
1. Determine the required diameter d of the shaft.
2. Determine the angle of twist of shaft. Figure 6 Figure 7
Problem 7: The turbine develops 180kW of power, which is transmitted to the gears such
that both C and D receive an equal amount. If the rotation of the steel shaft is v = 500
rev/min., the shaft is made of the steel having [𝜏] = 80MPa and has a diameter of D,
determine the required of D of shaft. The journal bearing at E allows the shaft to turn freely about its axis. (Figure 7)
Problem 8: If it is subjected the torques shown and is made of the steel having [𝜏] = 55MPa, G = 90GPa, (Figure 8)
1. Draw the torque diagram of the shaft.
2. Determine the required diameter D of the shaft.
3. Determine the angle of twist at section through point C.
Problem 9: The steel shaft has a diameter of 60mm and is fixed at its ends A and B. If it is
subjected to the couple, determine the maximum shear stress in regions AC and CB of the
shaft. Gst = 85 GPa. (Figure 9)
Ph.D Lieu T. Bich Nguyen Chapter 4. TORSION.
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Exercises Figure 8 Figure 9
Problem 10: The two shafts are made of A-36 steel having [𝜏] = 100MPa, G = 8.103 kN/cm2
and the same diameter of d. They are supported by bearings at A, B, C; which allow free
rotation and the support at D is fixed. (Figure 10)
1. Determine the required diameter d of the shaft.
2. Determine the angle of twist at section through bearing A. Figure 10
Ph.D Lieu T. Bich Nguyen Chapter 4. TORSION.