







Preview text:
Unit 7 - VIET NAM AND INTERNATIONAL ORGANISATIONS A. PRONUNCIATION
I. Put a secondary stress and a primary stress for the following words. Some words may not have a secondary stress.
1. community 2. agriculture 3. explanation 4. development
5. competitive 6. destination 7. activity 8. vaccination
9. environment 10. education 11. supermarket 12. particularly
13. independence 14. organisation 15. economic 16. security
17. necessary 18. participation 19. facilitate 20. information
II. Choose the word that has different stress pattern.
1. A. nutritionist B. population C. exhibition D. application
2. A. equality B. professional C. establishment D. difficulty
3. A. disadvantage B. governmental C. economy D. presentation
4. A. possibility B. immediately C. individual D. opportunity
5. A. communication B. disability C. international D. university B. VOCABULARY
I. Complete the sentences with the words in the box.
enter promote aims welcomes committed
created essential respects practical peacekeeping
1. Intergovernmental cooperation is __________ to resolve issues of global importance.
2. Viet Nam participates in __________ activities in a comprehensive and responsible manner.
3. Viet Nam __________ independence, sovereignty, unity, territorial integrity and benefits of all nations.
4. In order to __________ Viet Nam, most foreigners need a visa issued by a Vietnamese Embassy or Consulate.
5. Through open discussion and shared __________ experiences, the workshop provided
valuable lessons for students.
6. Viet Nam has __________ to building and implementing policies and measures to promote international cooperation.
7. The U.S. government helped Viet Nam to __________ job-growth in rural areas through the
adoption of new U.S. technology.
8. Vietnam’s gender equality work has __________ initial positive changes in the awareness and behaviour of the citizens.
9. WHO always __________ innovative ideas, new research that can come up with useful
products for people’s health care.
10. Vietnam National University __________ to develop long term relations with well-known
international universities and organizations.
II. Match the abbreviations with their meanings.
1. UN a. World Trade Organisation 2. WTO b. United Nations
3. WHO c. Asian Development Bank
4. ADB d. Food and Agriculture Organisation
5. FAO e. United Nations Development Programme
6. UNICEF f. Association of Southeast Asian Nations
7. UNDP g. United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund
8. APEC h. World Health Organisation
9. UNESCO i. United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organisation
10. ASEAN j. Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation
III. Choose the best answer to complete the sentences.
1. _______ is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. Trang 1
A. WHO B. UN C. UNESCO D. UNDP
2. Foreign companies in Viet Nam try to make products of higher quality at _______ prices.
A. essential B. practical C. active D. competitive
3. ASEAN is a regional organisation that _______ to promote economic and security cooperation among its members.
A. creates B. aims C. develops D. promotes
4. Like many organisations, USAID supports Vietnam’s transition to a rules-based market
economy more fully aligned to international _______ and standards.
A. businesses B. markets C. organisations D. governments
5. _______ is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing humanitarian and
developmental aid to children worldwide.
A. WTO B. ADB C. UNICEF D. FAO
6. Is it necessary to consider the sustainable and _______ use of natural resources as the key development principle?
A. economical B. industrial C. agricultural D. educational
7. Viet Nam has _______ in multilateral mechanisms and forums at regional and global levels.
A. supported B. protected C. participated D. formed
8. UNICEF works in some of the world’s toughest places, to reach the world’s most vulnerable and _______ children.
A. harmless B. advantaged C. educated D. disadvantaged
9. Is it true that Viet Nam has become a(n) _______ of ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) since January, 1st 1996?
A. member B. supporter C. advisor D. organizer
10. _______ is an intergovernmental forum for economies in the Pacific Rim that promotes free
trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region.
A. UNDP B. APEC C. ADB D. ASEAN
IV. Supply the correct form of the word in the brackets.
1. Member states want to make ASEAN a more credible and _______ international organisation. (respect)
2. _______, Viet Nam is one of the fastest growing economies in the region. (economy)
3. International organizations are optimistic about Vietnam’s economic _______ in the coming years. (grow)
4. Trade agreements make it easier for foreign _______ to set up businesses in Viet Nam. (invest)
5. How many foreign localities and organizations has Ho Chi Minh City increased _______
relationship with? (cooperate)
6. UNDP works in 170 countries and territories to eradicate _______ while protecting the planet. (poor)
7. Viet Nam actively implements _______ to the United Nations on ecosystem restoration. (commit)
8. Is VIETRADE responsible for management, co-ordination and development of trade _______
activities in Viet Nam? (promote)
9. The cooperation between Vietnamese universities and international organisations has opened
up new chances for _______ innovation. (create)
10. UNDP’s programmes support the governments to accelerate _______ of the sustainable development goals. (achieve) C. GRAMMAR
I. Choose the correct answers.
1. The central committee is (most/ the most) powerful decision-making body.
2. Viet Nam was (the second largest/ largest the second) producer of coffee in the world in 2022.
3. Australia is one of (stronger/ the strongest) performing economies in the world. Trang 2
4. Young people were (more likely/ the more likely) to feel optimistic about the future than older people.
5. Viet Nam remains one of the (best/ most) important growth markets in Southeast Asia.
6. A small amount of reliable data is (more useful than/ more than useful) a large volume of questionable data.
7. America is (the most by far popular/ by far the most popular) country for K-12 Vietnamese students.
8. Singapore’s per capita GDP used to be (50 times higher/ higher 50 times) than that of Myanmar and Cambodia.
9. The growth rate this year is expected to be (highest/ higher) than last year.
10. The Asia-Pacific region’s share of protected terrestrial areas is (smaller/ more small) than the global average.
II. Supply the correct comparative or superlative form of the words in the brackets.
Add than where applicable.
1. Viet Nam is one of __________ (vulnerable) countries to climate change.
2. The power relationship amongst producers, processors, traders and consumers is __________ (horizontal) before.
3. One of __________ (bad) pollutants for human health is fine particulate matter.
4. WTO projections show that carbon prices are __________ (efficient) ever when applied globally.
5. Viet Nam now is one of __________ (dynamic) emerging countries in East Asia region.
6. Are the principles of Most-Favoured Nations (MFN) __________ (relaxing) those of the ASEAN?
7. Several countries in Asia-Pacific are __________ (exposed) and vulnerable to natural hazards of all countries.
8. Viet Nam is projected to be one of __________ (fast) growing economies in the world.
9. English is __________ (dominant) foreign language for studying and working in Viet Nam.
10. Is an EAFTA __________ (beneficial) a CEPEA in terms of economic welfare for the global economy?
11. Asia has some of __________ (successful) green cities, such as Hong Kong, Seoul, and Singapore.
12. A decade ago, the average height of Vietnamese children was among __________ (low) group in the world.
13. Vietnamese students are among __________ (good) academic performers in Southeast Asia.
14. ADB has __________ (professional) functions than a bank because it has widened its development activities.
15. Is VUSTA __________ (big) network of non-governmental science and technology organizations in Viet Nam?
16. With more members, it is __________ (difficult) for APEC to reach consensus on what is desirable for the future.
17. Economic growth of Viet Nam had been among __________ (high) in the world in the past decade.
18. Psychological assessments conducted by UNICEF revealed that in most natural disasters,
women are __________ (vulnerable) men.
19. Estimating economic growth in the western is __________ (complicated) that in central Asian countries.
20. A new report of UNICEF suggests the well-being of children living in Canada is __________
(low) those growing up in many other wealthy countries.
III. Choose the best answer to complete the sentences.
1. Water is perhaps _______ resource and is under pressure across Asia.
A. the most fundamental B. most fundamental Trang 3
C. the more fundamental D. more fundamental
2. According to FAO, the price of fresh and healthy food is typically _______ of processed foods.
A. highest B. higher C. higher more than D. higher than that
3. UNICEF states that disability among children is _______ to assess than that among adults.
A. more difficult than B. more difficult
C. more difficult as D. better difficult
4. The most glaring deficits in education investment are in _______ developed countries.
A. the least B. less than C. less more than D. more than
5. Viet Nam has become _______ in the work of international organisations.
A. more active and active B. the more or less active
C. more and more active D. most and most active
6. According to World Bank, plastic waste is _______ abundant type of waste collected in river and coastal sites.
A. the most by far B. the far most C. by far the most D. the far more
7. It is expected that trade and investment exchange between Viet Nam and the EU will become _______ ever.
A. best B. more better than C. the best D. better than
8. They didn’t expect the volunteer project to be _______ it was with the villagers.
A. the most popular B. most popular C. as popular as D. more popular
9. Viet Nam has recorded a growth rate _______ of many other countries in the world.
A. higher much than B. much higher than that
C. higher than much D. higher more than
10. The Non-Aligned Movement is _______ international organisation in the world, after the United Nations.
A. the second largest B. the second larger
C. the largest second D. largest the second
11. The history of AEC can be traced back _______ 1992 when the ASEAN Leaders mandated the creation of the AFTA.
A. as soon as B. as far as C. as far as in D. as soon as before
12. According to WHO, _______ 100 cities in the world, nearly 70 percent are in Asia.
A. as the most polluted B. the most polluted of
C. of the most polluted D. more polluted
13. The WTO and the FAO have development at the heart of their work, but they have quite
different mandates and the links are _______.
A. specific more than B. specific more than that
C. more specific than D. more specific than that
14. Organizations and enterprises had _______ support of vaccines for Viet Nam during the Covid-19 pandemic.
A. as good as B. the better C. the best D. the best of
15. According to UNICEF, the poverty rate for households with disabled children is _______ other households.
A. much higher than that B. much higher than for
C. more higher than for D. higher better than that
16. The IMF forecasts that Vietnam’s GDP growth next year will be _______ Malaysia,
Thailand, and the Philippines.
A. higher than that of B. higher than that
C. a lot higher than D. far higher than that
17. Poverty rates in Cambodia, Indonesia, Nepal, Pakistan, and Viet Nam are about _______ the rates in the 1990s.
A. lower 50 percent than B. lower 50 percent than that Trang 4
C. 50 percent lower than D. 50 percent the lowest of
18. Viet Nam Union of Friendship Organizations has made great efforts to bring _______
possible assistance to foreign NGOs.
A. better than B. the best C. as well as D. as good as
19. The elasticity between poverty and GDP in Indonesia is _______ Brazil.
A. much stronger B. far stronger than
C. a lot stronger than that D. much stronger than that of
20. The South East has _______ health workforce density while the Mekong Delta and Central
Highlands have _______ density.
A. the highest - the lower B. the higher - the lowest
C. the highest - the lowest D. the higher - the lower
IV. Choose the underlined port that needs correcting.
1. Viet Nam is among the nations that has the highest literate population in Southeast Asia. A B C D
2. FAO might lose business to direct contractors if it is not as competitive as it should. A B C D
3. UNDP’s efforts for resource mobilisation during 2019-2022 were not as successful as A B C expecting. D
4. UNICEF was one of the biggest supplier of coronavirus vaccines for Viet Nam during A B C D the Covid-19 pandemic.
5. According to ILO, girls are faring more better than boys and this trend has registered an A B C
overall increase in recent years. D
6. Is digital transformation and digital cooperation the best solutions to implement One ASEAN? A B C D
7. Technology was more influential in setting priorities of knowledge of the consequences A B
of different forms of malnutrition. C D
8. Viet Nam ranked 38th in World Bank’s 2020 Human Capital Index, one of the higher A B C scores in East Asia Pacific. D
9. UNICEF suggests in a study that children in wealthy countries are less optimistic A B
about their future than that in developing nations. C D
10. International communicate is one of the most attractive programmes offered at the A B C
Diplomatic Academy of Viet Nam. D D. SPEAKING
I. Choose the best answer to complete the dialogues.
1. - “Let’s go to Ho Chi Minh city for some years and live it up.” - “ __________ ”
A. No, I’ve never been there.
B. Yes, Ho Chi Minh City is a busy city.
C. I can’t say for sure about Ho Chi Minh City. Trang 5
D. I’m sorry, but I have other plans.
2. - “ __________ ” - “Never mind. Perhaps another time.”
A. Thank you very much for inviting us.
B. That’s very kind of you, but I couldn’t possibly.
C. Would you care to visit us this Sunday?
D. Do you want to go on a tour up to Fansipan?
3. - “Do you feel like doing something completely meaningful today?” - “ __________ ”
A. Yes, I’d love to. B. No, I won’t do meaningless things.
C. I finished lots of things yesterday. D. No, there’s nothing to do today.
4. - “ __________ ” - “Yes, I would be delighted.”
A. You’re not allowed to buy alcohol. You’re under age.
B. Shall I serve the soup or would you like to help yourselves?
C. Would you like to make a donation to our charity appeal?
D. That’s very kind of you to help us correct the notebook entry.
5. - “ __________ ” - “ICRC? I think it’s International Committee of the Red Cross.”
A. What does this acronym stand for?
B. How much do you know about the ICRC?
C. What is the mission of the ICRC?
D. Can you name an international organisation which has a representative in Viet Nam?
II. Complete the conversation with the sentences in the box.
How about other organisations like WHO and ICAO?
You don't know the organisations of which Viet Nam has been a member, do you?
Please help me to navigate their acronym-heavy world. Yes, but that depends.
They are autonomous organizations but linked to the UN through special agreements.
My confusion is the relationship among them.
So can we put UNHCR, UNDP and UNICEF in a group? That's what I mean.
Ha My: Can you do me a favour, Minh An?
Minh An: (1) ______________________________ What’s your problem?
Ha My: Oh, not much of a problem. I’m having a writing assignment about Viet Nam and
international organisations, but I’m confused about the names.
Minh An: (2) ________________________
Ha My: Actually, yes. I know that Viet Nam has already been a member of most of the
biggest organisations in the world, and I can write down the list. (3)
________________________ For example, the UN has several ‘family’
organisations, so how can we know if they belong to each other or have a connection?
Minh An: I think you’re talking about the names like UN, UNDP, UNESCO, UNICEF, etc.
which have the prefix ‘UN’.
Ha My: Yes. (4) ________________________
Minh An: Well, the United Nations and its component parts can be complicated places. The
acronyms we use to call them can be complicated, too.
Ha My: (5) ________________________
Minh An: Some of the names you might already recognize. A number of UN offices,
programmes and funds, such as the Office of the UN High Commissioner for
Refugees (UNHCR), the UN Development Programme (UNDP) and the UN
Children’s Fund (UNICEF) report to the General Assembly or the Economic and
Social Council. (6) ______________________
Ha My: What are autonomous organizations?
Minh An: Autonomous organizations mean they have their own governing bodies, budgets and secretariats. Trang 6
Ha My: (7) ________________________
Minh An: Yes, we can. Together with the United Nations, they are known as the UN family, or the UN system.
Ha My: (8) ________________________
Minh An: The World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Civil Aviation
Organization (ICAO) are autonomous bodies too, but they were created by
intergovernmental agreement. There are also the International Labour Organization
(ILO) and the Universal Postal Union (UPU), which are even older than the UN.
Ha My: That’s interesting to know. Thank you very much for your help. E. READING
I. Read the passage and choose the best answers to fill in the blanks.
UNESCO is the United Nations Educational, (1) __________ and Cultural Organization. It
is an agency of the United Nations.
UNESCO says its purpose, as (2) __________ just after the end of World War II, is “to
build the defences of peace in the minds of men and women”. It does this by helping nations
work (3) __________ , through education for all, science, and culture. This is supposed to help
other nations follow the rule of law and human rights. It also helps promote some (4) __________ in the UN Charter.
UNESCO tries to achieve what it wants to do through six programs: education, natural
sciences, social and human sciences, culture, (5) __________ and information. Some projects
sponsored by UNESCO are literacy, technical, and teacher-training programmes. UNESCO also
decides what will become World Heritage Sites. A World Heritage Site is an important, special,
interesting or beautiful place. (6) __________ a place is a World Heritage Site, the place cannot
be destroyed, as it can give (7) __________ information for the future. The Uluru, for example,
gives a lot of information on the culture of Aborigines. UNESCO is also a (8) __________ of the
United Nations Development Group and works for Millennium Development Goals.
1. A. Environmental B. Informatic C. Scientific D. Technological
2. A. joined B. defined C. started D. created
3. A. hard B. together C. individually D. separately
4. A. dependences B. competitions C. arguments D. freedoms
5. A. communicator B. communicating C. communicative D. communication
6. A. If B. Unless C. While D. Though
7. A. useful B. updated C. effective D. practical
8. A. builder B. founder C. member D. planner
II. Read the passage and choose the best answers to the questions.
ASEAN officially the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, is a political and economic
union of 11 member states in Southeast Asia, which promotes intergovernmental cooperation
and facilitates economic, political, security, military, educational, and sociocultural integration
between its members and countries in the Asia-Pacific. The union has a total area of 4,522,518
km2 and an estimated total population of about 668 million as in 2022.
ASEAN’s primary objective was to accelerate economic growth and through that social
progress and cultural development. A secondary objective was to promote regional peace and
stability based on the rule of law and the principles of the UN Charter. With some of the fastest
growing economies in the world, ASEAN has broadened its objective beyond the economic and
social spheres. In 2003, ASEAN moved along the path similar to the European Union (EU) by
agreeing to establish an ASEAN community that consists of three pillars: the ASEAN Security
Community, the ASEAN Economic Community, and the ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community.
ASEAN regularly engages other countries in the Asia-Pacific region and beyond. A major
partner of UN, SCO, PA, GCC, MERCOSUR, CELAC, and ECO, ASEAN maintains a global
network of alliances and dialogue partners and is considered by many as a global powerhouse,
the central union for cooperation in Asia-Pacific, and a prominent and influential organisation. It Trang 7
is involved in numerous international affairs and hosts diplomatic missions throughout the world.
The organisation’s success has become the driving force of some of the largest trade blocs in
history, including APEC and RCEP.
1. What is the first paragraph mainly about?
A. General introduction of ASEAN
B. ASEAN as a political and economic union
C. ASEAN and countries in Asia-Pacific region
D. The cooperation between ASEAN and countries in Asia-Pacific
2. The objectives of ASEAN are mentioned in _______.
A. the first paragraph B. the second paragraph
C. the third paragraph D. all of the three paragraphs
3. ASEAN community was established in a similar way to _______. A. UN B.APEC C. EU D. RCEP
4. What does the word ‘It’ in the third paragraph refer to?
A. global powerhouse B. organisation C. ASEAN D. Asia-Pacific
5. Which of the following is NOT true according to the third paragraph?
A. ASEAN engages countries in both inside and outside of the Asia-Pacific region.
B. ASEAN has partnerships with UN, SCO, PA, GCC, MERCOSUR, CELAC, and ECO.
C. ASEAN is a regional organisation, but it plays a positive role in the world.
D. ASEAN forces some large organisations to become a partner or cooperate with it. E. WRITING
I. Choose the sentence which has the closest meaning to the original one.
1. Because of poor aftersales services, your reputation got damaged.
A. Your reputation got damaged, so aftersales services are poor.
B. Poor aftersales services made your reputation get damaged.
C. Your reputation got damaged in spite of good aftersales services.
D. However poor the aftersales services were, your reputation didn’t get damaged.
2. We need to improve our product quality so that we can enter global markets.
A. In order to enter global markets, we need to improve our product quality.
B. It’s unnecessary for us to improve our product quality to enter global markets.
C. Thanks to the improvement of our product quality, we can enter global markets.
D. Despite the improvement of our product quality, we still can’t enter global markets.
3. This environmental organisation aims to protect local forests.
A. This environmental organisation protects local forests to achieve its aims.
B. This environmental organisation achieves its aims by protecting local forests.
C. Achieving its goal, this environmental organisation starts to protect local forests.
D. The aim of this environmental organisation is to protect local forests.
4. UNICEF offers disadvantaged teenagers job training and career advice.
A. Disadvantaged teenagers are offered job training and career advice by UNICEF.
B. Disadvantaged teenagers are offered UNICEF by job training and career advice.
C. Job training and career advice are offered by UNICEF and disadvantaged teenagers.
D. UNICEF is offered job training and career advice by disadvantaged teenagers.
5. Viet Nam creates good conditions for both international and local businesses.
A. Viet Nam creates good conditions for either international or local businesses.
B. Viet Nam creates neither good conditions for international nor local businesses.
C. Viet Nam creates good conditions for not only international businesses but also local ones.
D. Viet Nam doesn’t only create good conditions for international and local organisations but also does business.
II. Complete the second sentence so that it has the words in the brackets.
1. South-east Asia is more disparate than Europe in general. (as) Trang 8 Europe isn’t
2. The summit may not be quite as productive as it appears at first glance. (less) The summit may be
3. It’s not the same, but it’s not as bad as I thought it was going to be. (better) It’s not the same, but
4. The United Nations is the largest international organization in the world. (as) No other organizations
5. Are no other solutions to reduce poverty more effective than agricultural production? (most) Is agricultural production ?
6. No other forces for social mobility and globalization are stronger than higher education. (strongest) Higher education
7. Ca Mau and Bac Lieu were the worst affected provinces by climate change. (worse) No other provinces
8. Biogas production from agricultural residues is not as popular as using cow dung. (than) Using cow dung
9. Is the salary in a private institution not as competitive as the salary in a state institution? (more) Is the salary in
10. No other regions enjoy lower dropout rate in primary and secondary education than the Red River Delta. (lowest) The Red River Delta region KEY
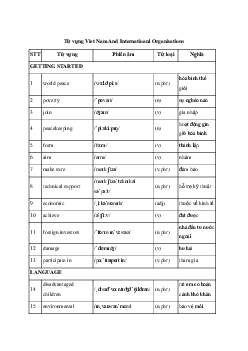
UNIT 7: VIET NAM AND INTERNATIONAL ORGANISATIONS A. PRONUNCIATION
I. 1. com ˈmunity 2. ˈagriculture 3. ˌexplaˈnation 4. deˈvelopment
5. comˈpetitive 6. ˌdestiˈnation 7. acˈtivity 8. ˌvacciˈnation
9. enˈvironment 10. ˌeduˈcation 11. ˈsupermarket 12. parˈticularly
13. ˌindeˈpendence 14. ˌorganiˈsation 15. ˌecoˈnomic 16. seˈcurity
17. ˈnecessary 18. parˌticiˈpation 19. faˈcilitate 20. ˌinforˈmation
II. l. A 2. D 3. C 4. B 5. A B. VOCABULARY
I. 1. essential 2. peacekeeping 3. respects 4. enter 5. practical
6. committed 7. promote 8. created 9. welcomes 10. aims
II. l. b 2. a 3. h 4. c 5. d 6. g 7. e 8. j 9. i 10. f
III. l. A 2. D 3. B 4. B 5. C 6. A 7. C 8. D 9. A 10. B
IV. 1. respectable 2. Economically 3. growth 4. investors 5. cooperative
6. poverty 7. commitment 8. promotion 9. creative 10. achievement C. GRAMMAR
I. 1. the most 2. the second largest 3. the strongest
4. more likely 5. most 6. more useful than
7. by far the most popular 8. 50 times higher 9. higher 10. smaller
II. 1. the most vulnerable 2. more horizontal than 3. the worst
4. more efficient than 5. the most dynamic 6. more relaxing than
7. the most exposed 8. the fastest 9. the most dominant
10. more beneficial than 11. the most successful 12. the lowest
13. the best 14. more professional 15. the biggest
16. more difficult 17. the highest 18. more vulnerable than Trang 9
19. more complicated than 20. lower than
III. l. A 2. D 3. B 4. A 5. C 6. C 7. D 8. C 9. B 10. A
11. B 12. C 13. D 14. C 15. B 16. A 17. C 18. B 19. D 20. C
IV. 1. B (have) 2. D (should be) 3. D (expected)
4. B (suppliers) 5. B (more/ much) 6. A (Are)
7. B (than) 8. C (highest) 9. C (than those)
10. A (International communication) D. SPEAKING
I. 1. D 2. B 3. A 4. C 5. A
II. 1. Yes, but that depends.
2. You don’t know the organisations of which Viet Nam has been a member, do you?
3. My confusion is the relationship among them. 4. That’s what I mean.
5. Please help me to navigate their acronym-heavy world.
6. They are autonomous organizations but linked to the UN through special agreements.
7. So can we put UNHCR, UNDP and UNICEF in a group?
8. How about other organisations like WHO and ICAO? E. READING
I. l. C 2. B 3. B 4. D 5. D 6. A 7. A 8. C
II. l. A 2. B 3. C 4. C 5. D F. WRITING
I. 1. B 2. A 3. D 4. A 5. C
II. 1. Europe isn’t as disparate as South-east Asia in general.
2. The summit may be quite less productive than it appears at first glance.
3. It’s not the same, but it’s better than I thought it was going to be.
4. No other organizations in the world are as large as the United Nations.
5. Is agricultural production the most effective solution to reduce poverty?
6. Higher education is the strongest force for social mobility and globalization.
7. No other provinces were worse affected by climate change than Ca Mau and Bac Lieu.
8. Using cow dung is more popular than biogas production from agricultural residues.
9. Is the salary in a state institution more competitive than that in a private institution?
10. The Red River Delta region enjoys the lowest dropout rate in primary and secondary education. Trang 10