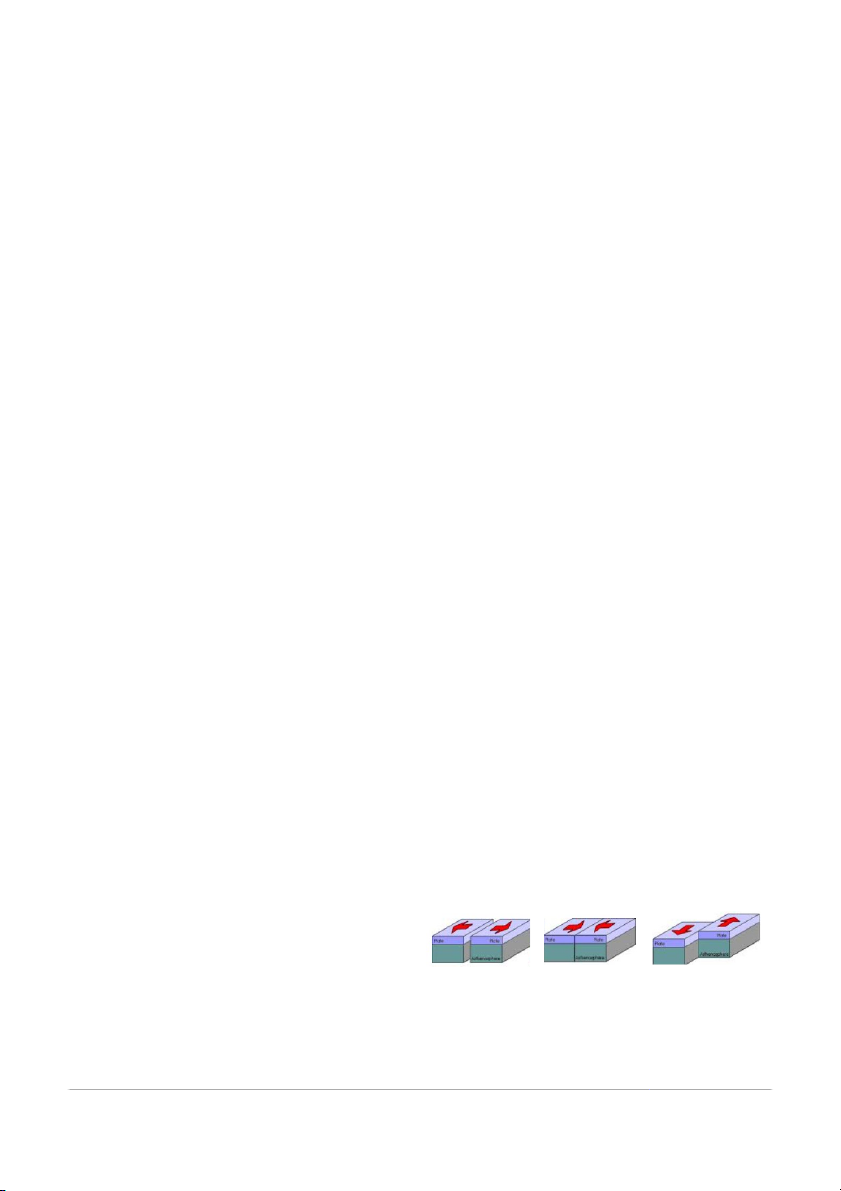
Preview text:
1ST SUMMATIVE TEST-Quarter 1
7. What happens when a continental plate collides with oceanic
Name: _________________________ Section: _____ Score: ____ plate?
A. The oceanic plate stays above the continental plates. GOOD LUCK!
B. The oceanic plate sinks beneath the continental plate.
Part I. TRUE or FALSE. Write TRUE if the statement is correct
C. The continental plate sinks into the mantle.
______ 1. Majority of the earthquake epicenters are situated at
D. The continental plate stays below the oceanic plate. the edges of the continents.
______ 2. Earthquake epicenters, active volcanoes, and mountain
8. How many seismograph stations are needed to locate the
ranges are randomly distributed. epicenter of an earthquake?
______ 3. Volcanoes and earthquakes epicenters are situated in A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 almost same location.
______ 4. Epicenter is a point beneath the earth’s surface where
9. Which of these processes refers to when the ocean floor earthquake originates.
plunges back into Earth’s interior?
______ 5. Asthenosphere is a soft, weak upper portion of the A. Conduction C. Radiation
mantle where the lithospheric plates float and move around. B. Subduction D. Convection
______ 6. At a divergent boundary, new oceanic crust is formed as tectonic plates move apart.
10. Crustal plate A is moving away from crustal plate B. What type
______ 7. Earthquakes are common at transform boundaries due
of plate boundary is described by the motion of the two plates?
to the intense pressure as plates grind against each other. A. Divergent boundary C. Convergent boundary
______ 8. Subduction zones are associated with divergent B. Transform boundary D. none of the above
boundaries where plates slide past each other.
______ 9. Trenches are deep oceanic features associated with
11. Which plate boundary is formed between the Philippine plate
subduction zones at convergent boundaries. and the Eurasian plate?
______ 10. Mid-Ocean Ridges are features found at convergent A. Convergent plate C. Divergent plate
boundaries where two plates collide. B. Transform plate D. Reverse fault Part II. Multiple Choice.
12. In a place known to be along converging plates, all of these can be expected to see, EXCEPT
1. Which of the following statements correctly describe oceanic A. Mountain ranges C. Volcanic islands crust? B. Rift Valley D. Active volcano
A. it is less dense than continental.
B. it is thin and denser than continental.
13. What type of plate undergoes subduction at oceanic-
C. it is thicker than continental crust.
continental convergent plate boundaries and why does it
D. It is thicker and older than continental crust. subduct?
A. Continental plate, it is less dense than oceanic plate.
2. Lithospheric plate are of two types, which is the thickest type?
B. Continental plate, it is denser than oceanic plate. A. Continental plate C. Convergent plate
C. Oceanic plate, it is less dense that continental plate. B. Divergent plate D. Oceanic plate
D. Oceanic plate, it is denser than continental plate
3. An instrument that detects earthquakes.
14. In a transform boundary, what does tectonic plate do? A. Seismograph C. Focus A. Slide past each other C. Collide with one another B. Seismogram D. Fault B. Subduct together D. Move away from one another
4. It is the rigid outermost shell of the Earth which is composed of
15. Convergent boundary is also known as __________
the crust and upper part of the mantle. A. Conservative boundary C. Constructive boundary A. Oceanic plate C. Lithosphere B. Destructive boundary D. Transform boundary B. Continental plate D. Divergent plate
16. If you visit a place in the Pacific known to be along converging
5. How are the earthquakes and volcanoes distributed around the
plates, which of these should you NOT expect to see? world? A. active volcanoes C. rift valleys
A. They are randomly distributed. B. mountain ranges D. volcanic islands
B. They are evenly distributed.
C. They are not randomly distributed.
17. Which is a convergent plate boundary?
D. They are located far from each other. I. II. III.
6. Where does volcanoes and earthquake likely to happen?
A. At the middle of tectonic plates
B. At the edge of tectonic plates C. At the oceanic crust A. I and II only C. III and II only
D. At the outer part of the mantle B. III only D. II. only
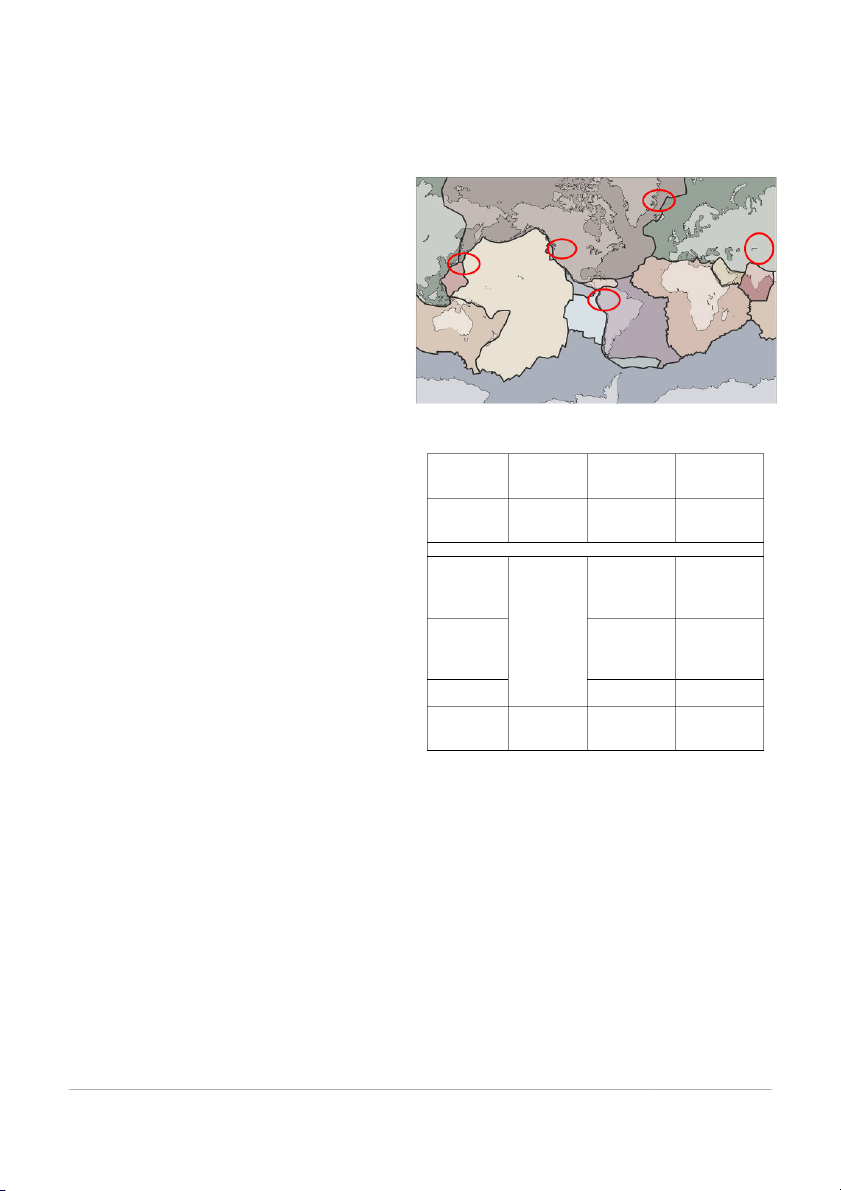
Part III. Map Reading. Study the map of plate boundary. Name the
18. Divergent boundary is best described as
major and minor plates and identify the direction of plate
A. boundary where two plate that are moving apart.
movement/motion by drawing an arrow on some identified areas
B. boundary where two plates slide past each other. marked with circles.
C. boundary where two plates collide with each other.
D. boundary where two plates does not move at all.
19. The following are geologic features that could be formed out
of a plate boundary movement. Which among them is a result of divergent plate boundary? A. island arcs C. oceanic ridges B. Volcanoes D. Mountain ranges
20. A transform plate boundary is best described as
A. boundary where two plate that are moving apart.
B. boundary where two plates slide past each other.
C. boundary where two plates collide with each other.
D. boundary where two plates does not move at all.
21. What is the basis of scientists in dividing earth’s lithosphere into several plates?
A. Formation of mountain ranges C. Earthquakes B. Volcanic eruption D. All of the above
PART IV. Table Completion. Fill out the table with correct data.
Choose your answer/s on the list provided below the table.
22. Which of the following is a result of a diverging plate? A. Himalayas C. Mid-Atlantic Ridge Type of plate Draw the Geologic Geologic B. Mt Mayon D. Philippines boundary Relative Events Features Motion
23. What is formed on the surface of the water if the edge of the 20. 1. 3.
oceanic plate suddenly flicks upward, Divergent 2. 4 A. trench B. tsunami C. volcano D. fault Boundary Convergent Boundary
24. What do you expect to find parallel to a trench? Oceanic- 21. 5. 7. A. hot spot B. Ridge C. Volcanic Arc D. Rift Continental 6. 8. 9.
25. It is a feature/landform produced when two continental plates converge. Oceanic- 10 13. A. volcano C. Mountain range Oceanic 11. 14. B. fault D. volcanic island 12. 15. Continental- 16. 17. Continental 22. 18 19. Transform Boundary Geologic Features: Volcano Rift Valley Oceanic Ridge Island Arc Trench Mountain Range Volcanic Arc Fault Geologic Events: Earthquake Volcanic eruption tsunami
“Success is no accident. It is hard work, perseverance, learning, studying, sacrifice and most of all, love of what you are doing or learning to do.” – Pele




