






Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Chap 9
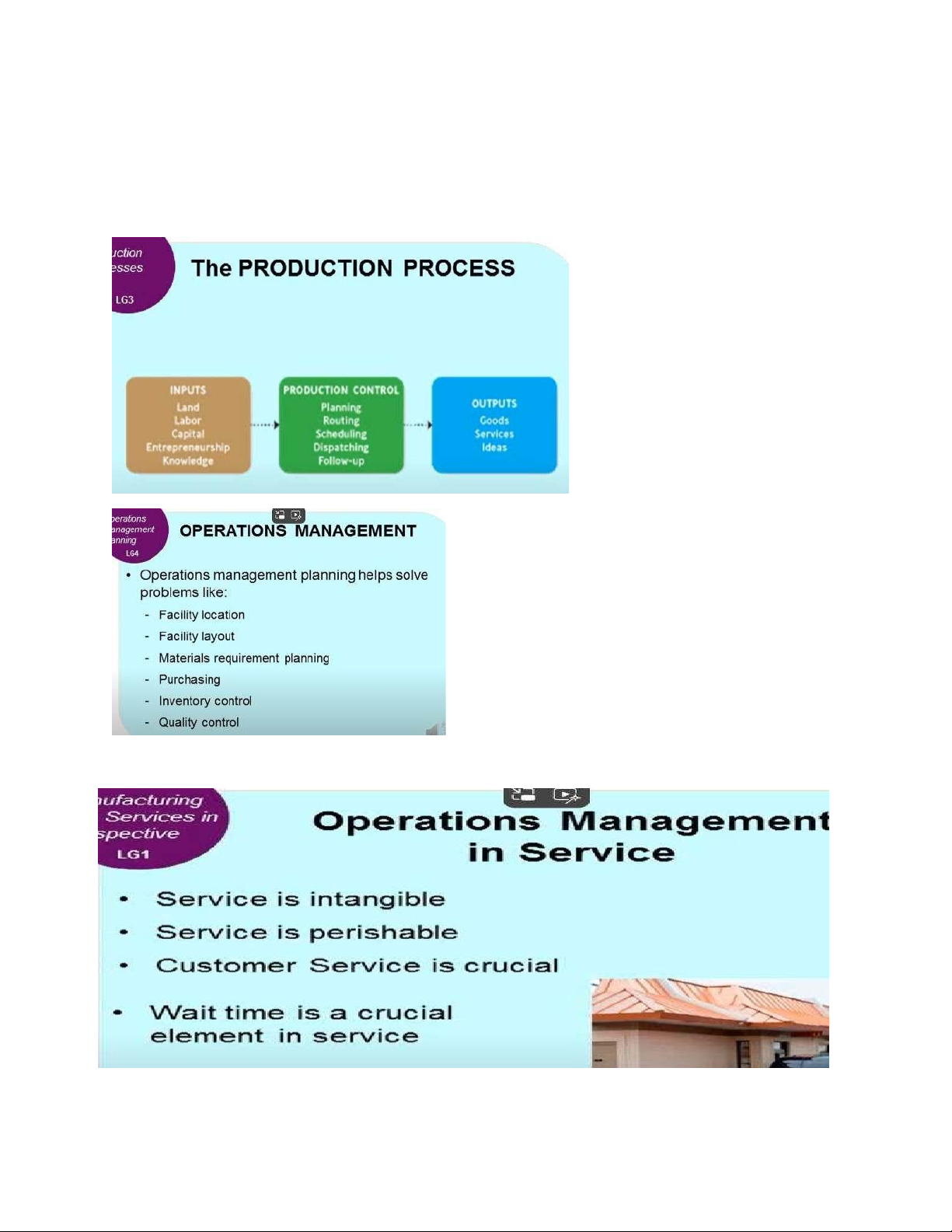
Production : the creation of goods using land, labour, capital, entrepreneurship and knowledge ( the factors of production )
Production management : all the activities managers do to help firms create goods Chap10 lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Extrinsic rewards Intrinsic Rewards
Proposed managers had two different sets of assumptions conceriing workers.
Their attitudes abt motivating workers were tied to these assumptions
Theory X ( workers lazy don’t want to work )
Theory Y ( workers feel excited to work and feel proud to do these stuff
The expectancy theory : the amount of effort employees exert on a specific task depends on
their expectations of the outcome
Equity theory : Employees try to maintain equity between inputs and outputs compared to others in similar positions
Workers often base perception of their outcomes on a specific person or group
Percevied inequities can lead to reduced quality and productivity, absenteeism, even resignation. Chap 13 Marketing - The 4P + Product
A good, servies, or idea that satisfies a consumer’s want or need.
Test marketing – Testing product concepts among potential product users
Brand Name – A word, letter, or a group of words or letters that differentiates one seller’s goods from competitor’s + Price (and ) place . Competitor’s prices . Production costs . Distribution
. High or low price strategies
Middlemen, intermediaries, brokers ( ng trung gian ) are important in place strategies bcs
getting a product to consumers is critical lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 - Promotion
All the techniques sellers use to inform people about their products and motivate them to
purchase those products includes .Advertising .Personal selling .Public relations .Word of mouth .Sales promotions
Consumer Market : all the individuals or household that wants goods and services for
personal use and they have the resources to buy them
B2B : individuals and organizations that buy goods and services to use in production or to
sell, rent, or supply to others. - Marketing to consumers
. The size and diversity of the consumer market forces marketers to decide which groups they want to serve
. Market segmentation : Divides the total market into groups with similar characteristics.
. Target Marketing : Selecting which segments an organization can serve profitably - B2B marketers include : . Manufactures . Wholesalers and retailers
. Hospitals, schools and charities . Government
- Products are often sold and resold several times before reaching final consumers
Ownership and Sales Flow:
1. Raw Material Supplier (Business 1):
o This business sells raw materials or basic components to the next business. lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336
o Example: A supplier sells cotton to a manufacturer. The raw materials are
transferred but not yet in their final form.
2. Manufacturer or Assembler (Business 2):
o The second business receives raw materials and transforms them into a finished or semi-finished product.
o The manufacturer owns the product after production but does not sell it directly to consumers.
o Instead, they sell the finished goods to a third business, such as a wholesaler,
distributor, or retailer.
o Example: The textile manufacturer turns cotton into fabric and then sells it to a wholesaler.
3. Wholesaler/Distributor (Business 3):
o The third business buys finished goods in bulk from the manufacturer.
o They own the products during this stage but typically do not sell directly to
consumers. Instead, they sell to retailers or other businesses that will sell to consumers.
o Example: A wholesaler buys the fabric and sells it in bulk to clothing retailers.
4. Retailer (Business 4):
o Retailers purchase the products from wholesalers or distributors.
o The retailer owns the products and sells them to the final consumer.
o Example: A clothing store buys fabric from the wholesaler, turns it into clothing, and sells it to consumers.
Why Don’t Manufacturers Sell Directly to Consumers?
1. Specialization: Manufacturers focus on production, while wholesalers and retailers focus
on distribution and consumer sales.
2. EfÏciency: By working with third businesses like wholesalers, manufacturers can reach a
wider market, and wholesalers can manage bulk sales efÏciently.
3. Geography: Retailers are often better positioned to sell to local or regional consumers,
while manufacturers may be located far away from where consumers are. lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336
4. Business Model: Manufacturers may not have the infrastructure or resources to sell
directly to consumers, while retailers specialize in marketing and customer service.
Chapter 11 : Humann Resource Management
The process of determing huma resource needs and then recruting, selecting,
developing, motivating, evaluating, compensating and scheduling employees to
achieve organizational goals HRM’s role has grown because of
. Incresed recognition of employees as a resource
. Changes in law that rewrote old workplace practices CIVIL RIGHTS ACT OF1964
Title VII prohibits discrimination in hiring, firing, compensation,apprenticeships, training, terms,
conditions or privileges of employment based on : . Race . Religion . Creed . Sex . Age . National Orgin
Job analysis : a study of what employees do who hold various job titles
Job description : a summary of the objectives of the job, the type of job, the responsibilities and
duties, working conditions and relationship to other jobs.
Job specifications – A summary of the minimum qualifications needed to do a particular job
Recruitment : The set of activities for obtaining the right number of qualified people at the right
time.( INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL SOURCES )
Training and Development : All attempts to improve productivity by increasing an employee’s ability to peform.
Traning focuses on short term skills.
Development focuses on long term abilities.
( Developing the workforce – Orienntation- Traning& DevelopemntAssessment- Turnover) lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336
Compensation : FINANCIAL AND BENEFITS ( insurance, edu, training) Wages& salary Bonuses Profit Sharing Commissions Stock Options
Chapter14 : Developing and Pricing Goods
Convenience and goods and services : products consumers purchase frequently with minimal
effort. These include : Candy, snacks, gas, milk and eggs
Shopping goods and services : products consumers buy only after comparing value, quality,
price, and styles. These include : clothes, shoes, appliances and furniture, childcare, home remodeling
Specialty goods and services : products with unique characteristics and brand identity. These
include : tiffany jewelry, rolex watches, lamborghini
Unsought goods and services : products consumers aren’t aware of or haven’t thought of
buying until they need them ( CAR towing services, funeral services, renter’s insurance )
Industrial goods: products used in the production of other products and sold in the B2B market.
( installations, capital items, accessory equipment, supplies, service)
Product life cycle : A theoretical model of what happens to sales and profits for a product overtime. Product life cycle stages : 1. Introduction 2. Growth 3. Maturity 4. Decline
Competitive pricing( pricing objectives)
1. Achieving a target return on investment or profit 2. Building trafÏc
3. Achieving greater market share lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 4. Creating an image
5. Furthering social objectives both short run and long run
Break-evenanalyse : The break-even point occurs when revenue equals expenses, meaning the
business has neither made a profit nor incurred a loss Total fixed costs Variable costs Chapter 15
Channel of distrubution: A group of marketing intermediaries that joining to tranport and store
goods from producers to consumers
Electronic retailing: selling goods and services to ultimate consumers over the internet.
A clothing brand selling directly to consumers through its online store.
Telemarketing : the sale of goods and services via the telephone.
Sample: A bank calling customers to offer credit cards.
Vending machines dispense convenience goods when consumers deposit suffcient money Direct selling
multilevel marketing uses salespeople who work as independent contractors direct marketing :
any activity that directy links manufacures or intermediaries with ultmate customers A company
like Apple selling products directly through its website or physical Apple Stores. Direct
marketing is a broader concept that encompasses various methods of reaching individual
consumers directly, such as email, mail, or phone.
Chapter 16 Effective promotions lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336



