








Preview text:
International University IU
STATISTICS FOR BUSINESS [IUBA] CHAPTER 04
THE NORM AL DISTRIBUTION
St a nda rd Norma l Distribut ion
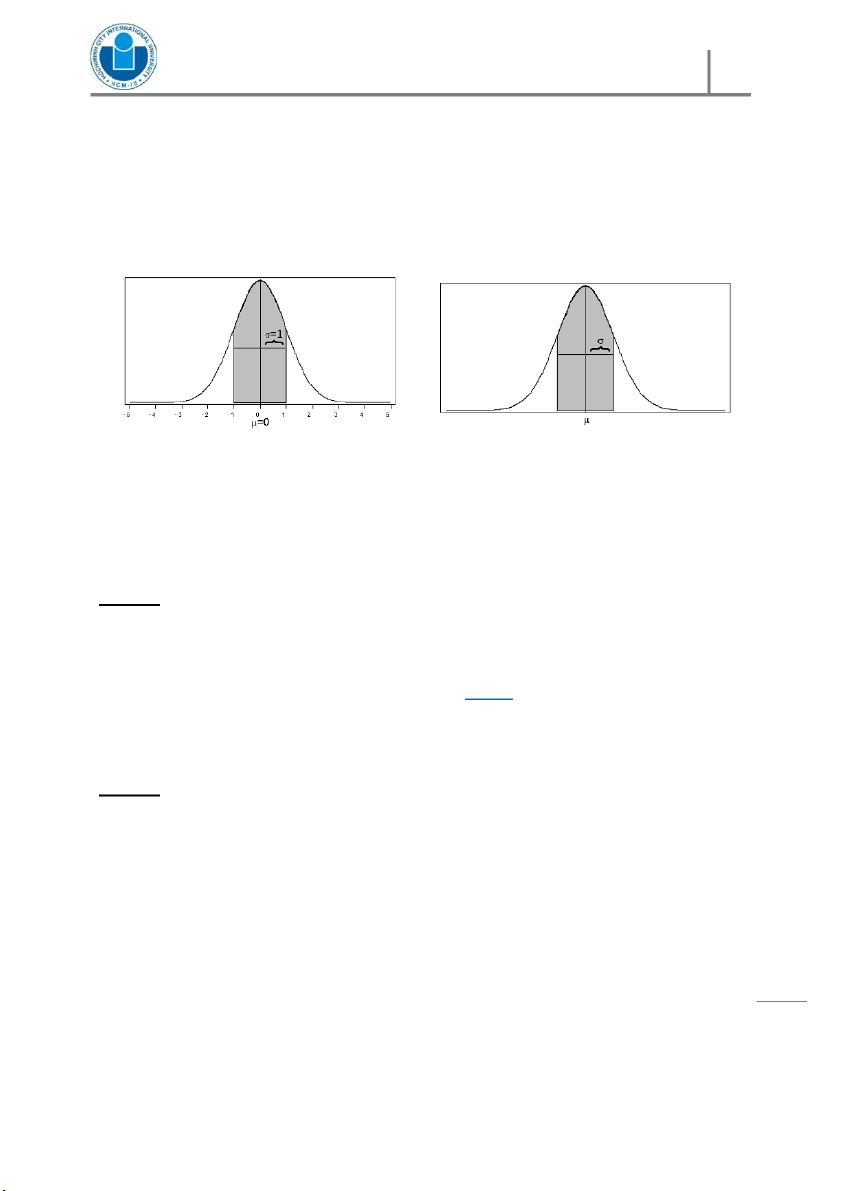
Norma l Dist ribution
~ ( ,)
~ (,) PART I
Finding probabilities of the normal distribution with given values n tio u St ep 01:
Use t he follow in g form ula t o t r ansform t he norm al random var iable , trib
w here ~ (, ) int o t he standard normal random variable , where is l D ~ (0,1). a rm − o = N e h : T 4 r 0 te St ep 02:
Use t he calculat or or Table 2 (Areas of St andard Norm al Dist ribut ion) in ap h
Appendix C t o com put e t he pr obab ilit ies (or ar eas) of t he norm al C
dist r ibu t ion based on t he st andar d nor m al dist ribut ion. s | es sin u r B s fo istic tat S
Powered by statisticsforbusinessiuba.blogspot.com 1
International University IU CALCULATOR INSTRUCTION
St ep No.01: Press M ODE 3: STAT [ AC ]
St ep No.02: Press SHIFT + 1 | [ STAT ] 7: DISTR
Aft er t hat , t he calculat or w ill show you 4 available sym bols.
How ever, w e just pay at t ent ion t o t he first t hree ones. 1 : P ( 2 : Q ( 3 : R (
+ We use [ 1 : P ( ] t o com put e t he pr obabilit y bet w een t he
st andard norm al random variable to −∞, or ( < )
+ We use [ 2 : Q ( ] t o com put e t he probabilit y bet w een t he
st andard norm al random variable to the mean or ( 0 < < ) .
+ We use [ 3 : R ( ] t o com put e t he pr obab ilit y bet w een t he
st andard norm al random variable to + ∞. ( > ) St ep No.03:
Press [ = ] t o get t he result . n tio u trib is l D a rm o N e h : T 4 r 0 te ap h C s | es sin u r B s fo istic tat S
Powered by statisticsforbusinessiuba.blogspot.com 2
International University IU Example | Part 1:
(Case of finding probabilities of the normal distribution with given values) PROBLEM :
A psychologist has devised a st ress t est for dent al pat ient s sit t ing in t he w ait ing room s.
According t o t his t est , t he st ress scores (on a scale of 1 t o 10) f or pat ient s w ait ing for root cana l
t reat m ent s are found t o be approximat ely norm ally dist ribut ed w it h a m ean of 7.59 and a
st andard deviat ion of 0.73.
a. W hat percent age of such pat ient s have a st ress score low er t han 6.0? SOLUTION: = 7.59, = 0.73 .. St ep 01:
( < 6.0) = < = ( < −2.1781) . St ep 02:
M ODE 3 : STAT [ AC ]
SHIFT + 1| [STAT]
7 : DISTR 1 : P (-2.1781) n tio
Then, press [ = ] t o get t he result ( −. ) = . u trib
Sum m ing up, ( < 6.0) = ( < −2.1781) = 0.0147 is l D a
b. W hat is t he probabilit y t hat a random ly select ed root canal pat ient sit t ing in t he w ait ing rm
room has a st ress score bet w een 7.0 and 8.0? o N e SOLUTION: h = 7.59, = 0.73 : T 4 .. St ep 01:
(7.0 < < 8.0) = .. < < r 0 . . te ap
= − 0.8082 < < 0.5616) h C St ep 02:
(There are t hree different met hods of using t he pocket calculator s | es
to solve the problem of calculating the probability betw een tw o sin
given values. You can use only one of three follow ing methods u r B
that depends on your choice, not all of them, since each of them
alw ays provides the same result w ith others) s fo istic tat S
Powered by statisticsforbusinessiuba.blogspot.com 3
International University IU
M ETHODS 01: Using 1 : P (
M ODE 3 : STAT [ AC ]
SHIFT + 1| [STAT] 7 : DISTR 1 : P (0.5616) [ ]
SHIFT + 1| [STAT] 7 : DISTR 1 : P (-0.8082)
Then, press [ = ] t o get t he result
(.) − (−.) = .
M ETHODS 02: Using 3 : R (
M ODE 3 : STAT [ AC ]
SHIFT + 1| [STAT] 7 : DISTR 3 : R (-0.8082) [ ] n
SHIFT + 1| [STAT] 7 : DISTR 3 : R (0.5616) tio u
Then, press [ = ] t o get t he result trib is
(−.) − (.) = . l D a rm o N e
M ETHODS 03: Using 2 : Q ( h : T 4
M ODE 3 : STAT [ AC ] r 0 te
SHIFT + 1| [STAT] 7 : DISTR 2 : Q (-0.8082) ap h C [ + ] s | es
SHIFT + 1| [STAT] 7 : DISTR 2 : Q (0.5616) sin u
Then, press [ = ] t o get t he result r B s fo
(−.) + (.) = . istic tat S
Powered by statisticsforbusinessiuba.blogspot.com 4
International University IU Sum m ing up,
(7.0 < < 8.0) = (−0.8082 < < 0.5616) = 0.5033
c. The psychologist suggest s t hat any pat ient w it h a st ress score of 9.0 or higher should be given
a sedat ive prior t o t reat m ent . W hat percent age of pat ient s w ait ing for root canal t reat m ent s
w ould need a sedat ive if t his suggest ion is accept ed? SOLUTION: = 7.59, = 0.73 . St ep 01:
( ≥ 9.0) = ≥ (. = ( ≥ 1.9315) . St ep 02:
M ODE 3 : STAT [ AC ]
SHIFT + 1| [STAT] 7 : DISTR 3 : R (1.9315)
Then, press [ = ] t o get t he result ( .) = .
Sum m ing up, ( > 9.0) = ( > 1.9315) = 0.0267 n tio u trib is l D a rm o N e h : T 4 r 0 te ap h C s | es sin u r B s fo istic tat S
Powered by statisticsforbusinessiuba.blogspot.com 5
International University IU PART II
Finding the values of X given a probability St ep 01:
The pro babilit y t hat a nor m al r ando m variable w ill be above (below , or
sym m et r ic) it s m ean a cert ain num ber of st andard deviat ions is exact ly
equal t o t he probabilit y t hat t he st andard no rm al r andom var iable w ill be
above (below , or sym m et r ic) it s m ean t he sam e num ber of (it s) st andar d deviat ions.
In part icular, ( > ) = ( > )
( < ) = ( < )
( < < ) = (− < < ) St ep 02: Find TA (Table Area)
(Table Ar ea TA f or a point of t he standard normal distribut ion is t he area n
given in t he st andar d n orm al pr obabilit y t able o f Table 2 in Appendix C tio u
under t he st andar d nor mal cur ve bet w een 0 and point > 0) trib is In part icular, l D a For rm ( > ): o N e
If ( > ) < 0.5, = . − ( > ) h : T 4
If ( > ) > 0.5, = ( > ) − . r 0 te For ( < ) : ap h C
If ( < ) < 0.5, = . − ( < ) s | es
If ( < ) > 0.5, = ( < ) − . sin u r B
For (− < < ) , = ( − < < )/ s fo istic tat S
Powered by statisticsforbusinessiuba.blogspot.com 6
International University IU St ep 03:
Look inside Table 2 (Areas of t he St andar d Norm al Dist r ibut ion) in
Appendix E for t he values of corresponding t o TA. St ep 04:
Use t he f ollow ing form ula t o t r ansf or m t he st andard norm al ran dom
var iable to t he normal random variable = ± In par t icular , For ( > ) :
If ( > ) < 0.5, t he value of “ ” will be positive, or +
If ( > ) > 0.5, the value of “ ” will be negative, or − For ( < ) :
If ( < ) < 0.5, the value of “ ” will be negative, or − n
If ( < ) > 0.5, the value of “ ” will be positive, or + tio u
For (− < < ) , t he values of “ ” will include negative and positive trib is
value, or – and + l D a rm o N e h : T 4 r 0 te ap h C s | es sin u r B s fo istic tat S
Powered by statisticsforbusinessiuba.blogspot.com 7
International University IU Example | Part 2:
(Finding the values of X given a probability) PROBLEM 01:
If X is a norm ally dist ribut ed random variable w it h m ean 120 and st andard deviat ion 44, find a
value x such t hat t he probabilit y t hat X w ill be less t han x is 0.56.
SOLUTION: We have ~ ( 120,44) St ep 01:
W e are looking fo r t he value of t he random var iab le such that
( < ) = .. In order to find it, we look for the value of the
st andard norm al deviat ion such that ( < ) = . . St ep 02:
If t he area t o t he left of is equal to 0.56, the area between 0 and (the Table Area) is equal t o n
= . − . = .. tio u trib is St ep 03:
We lo ok inside Table 2 (Areas of St andard Norm al Dist ribut ion) in l D a
Appendix C for t he value corresponding to = 0.06 and find rm
= 0.15 (actually, = 0.0596, which is close enough to 0.06). o N e h : T 4 St ep 04:
We need t o find t he appr opr iat e value. Here we use the following r 0 equat ion. te ap h
= + = + (.)() = . C s | es sin u r B s fo istic tat S
Powered by statisticsforbusinessiuba.blogspot.com 8
International University IU PROBLEM 02:
For a norm al random variable w it h mean 19,500 and st andard deviat ion 400, find a point of t he
dist ribut ion such t hat t he probabilit y t hat t he random variable w ill exceed t his value is 0.02. SOLUTION: = 19,500, = 400
( > ) = ( > ) = 0.02 = 0.5 − 0.02 = 0.48 = 2.05
Thus, = + = 19,500 + ( 2.05) (400) = 20,320 PROBLEM 03
For ~ ( 32,7) , find two values
, sym met rically lying on each side of t he m ean, and
w it h ( < < ) = 0.99. SOLUTION: = 32, = 7 n tio
( < < ) = (− < < ) = 0.99 u trib = 0.99/ 2 = 0.495 is l D = 2.576 a rm Thus, o
= + (−) = 32 + (−2.576)(7) = 13.968 N e h
= + () = 32 + (2.576)(7) = 50.032 : T 4 r 0 te ap h C s | es sin u r B s fo istic tat S
Powered by statisticsforbusinessiuba.blogspot.com 9
International University IU PART III
The Normal Approximation to the Binomial Distribution
When t he num ber of t rials in a binomial distribution is large ( > 100), t he calculat ion of
probabilit ies becom e dif ficult for t he pocket calculat or. Fort unat ely, t he binom ial dist ribut ion as
increases and therefore we can approximate it as normal distribution. Condit ion:
Norma l Dist ribution as an Approxima t ion t o Binomial Dist ribut ion
Usually, t he norm al dist r ibut ion is used as an approxim at ion t o t he binom ial dist r ibut ion
w hen and ( 1 − ) are bot h greater than 5—that is, w hen
> 5 and( − ) > 5
St ep 1: Com put e and for the binomial distribut ion. n =
= ( − ) tio u
St ep 2: Conver t t he discr et e random var iable int o a cont inu ous rand om var iab le. trib is
Cont inuit y Correct ion Fa ct or l D a
The addit ion of .5 and/ or subt ract ion of .5 from t he value(s) of when t he normal distribution rm o
is used as an approxim at ion t o t he bin om ial dist ribut ion , w here is the number of successes in N e h
trials, is called the continuity correction factor. : T 4
Ther efor e, w hen w e calculat e t he binom ial probabilit y of an int er val, w e should subt ra ct r 0 te
0.5 from t he left limit a nd a dd 0.5 t o t he right limit t o get t he corr esponding nor m al ap h pr obabilit y. C s | In par t icular , es sin u
> ,. r B
< ,. s fo istic
= ,.. tat S
Powered by statisticsforbusinessiuba.blogspot.com 10
International University IU
w here = a normal variable with mean and st andard deviat ion = a given value
St ep 3: Com put e t he required pr obabilit y using t he nor m al dist r ibut ion. Example | Part 3:
(The Normal Approximation to the Binomial Distribution) PROBLEM :
CASIO Viet nam m akes calculat ors. Consum er sat isf act ion is one of t he t op priorit ies of t he
com pany’s m anagem ent . The com pany guarant ees t he refund of m oney or a replacement for
any calculat or t hat m alfunct ions w it hin t w o years from t he dat e of purchase. It is kn own from
past dat a t hat despit e all ef fort s, 5% of t he calculat ors m anufact ured by t his company n
m alfunct ion w it hin a 2-year period. The company recent ly m ailed 500 such calculat ors t o it s tio u cust om ers. trib is
a. Find t he probabilit y t hat exact ly 29 of t he 500 calculat ors w ill be ret urned for refund or l D
replacem ent w it hin a 2-year period. a rm o SOLUTION: N e h
Step 1: Compute and for the binomial distribution. : T 4
= = 500 × 0.05 = 25 r 0 te ap √95 h
= (1 − ) = √500 × 0.05 × 0.95 = ≈ 4.8734 C 2 s |
Step 2: Convert the discrete random variable int o a continuous random variable. es sin u
To m ake t he cont inuit y cor rect ion, w e subt ract 0.5 from 29 and add 0.5 t o 29, w h ich gives t he r B
int erval 28.5 t o 29.5 t o obt ain t he value 29. Thus, ( = 29) for the binomial problem will be s fo
approximat ely equal t o ( 28.5 ≤ ≤ 29.5) for the normal distribution. istic
Step 3: Compute the required probability using the normal distribution. tat S
Powered by statisticsforbusinessiuba.blogspot.com 11
International University IU −
(28.5 ≤ ≤ 29.5) = 28.5 − 25 ≤ √95 ≤ 29.5 − 25 √95 2 2
7√95 ≤ ≤ 9√95 = (0.7182 ≤ ≤ 0.9234) = 0.0584 95 95
Thus, based on t he norm al approxim at ion, t he pr obabilit y t hat exact ly 29 of t he 500 calculat ors
w ill be ret urned for ref und or replacem ent w it hin a 2-year period is approxim at ely 0.0584
b. W hat is t he probabilit y t hat 27 or more of t he 500 calculat ors w ill be ret urned for refund or
replacem ent w it hin a 2-year period? SOLUTION:
Step 1: Compute and for the binomial distribution.
= = 500 × 0.05 = 25 √95 n
= (1 − ) = √500 × 0.05 × 0.95 = ≈ 4.8734 2 tio u
Step 2: Convert the discrete random variable int o a continuous ra ndom variable. trib is
For t he cont inu it y correct ion, w e subt ract 0.5 fr om 27, w hich gives 26.5 t o obt ain t he value 27. l D a
Thus, ( ≥ 27) for the binomial problem will be approximately equal to ( ≥ 26.5) for the rm o norm al dist r ibut ion. N e h
Step 3: Compute the required probability using the normal distribution. : T 4 r 0 − te ( ≥ 26.5) = ap ≥ 26.5 − 25 √95 h C 2 s | es
≥ 3√95 = ( ≥ 0.3078) = 0.3791 sin 95 u r B
Thus, based on t he norm al approxim at ion, t he probabilit y t hat 27 o r m ore of t he 500 s fo
calculat ors w ill be ret urned f or ref und or replacem ent w it hin a 2-year per iod is appr oxim at ely istic 0.3791 tat S
Powered by statisticsforbusinessiuba.blogspot.com 12
International University IU
c. W hat is t he probabilit y t hat 15 t o 22 of t he 500 calculat ors w ill be ret urned for refund or
replacem ent w it hin a 2-year period? SOLUTION:
Step 1: Compute and for the binomial distribution.
= = 500 × 0.05 = 25 √95
= ( 1 − ) = √500 × 0.05 × 0.95 = ≈ 4.8734 2
Step 2: Convert the discrete random variable int o a continuous ra ndom variable.
For t he cont inuit y cor rect ion, w e subt ract 0.5 f rom 15 and add 0.5 t o 22, w hich gives t he
int erval 14.5 t o 22.5 t o obt ain t he int erval 15 t o 22. Thus, ( 15 ≤ ≤ 22) for the binom ial
problem w ill be approxim at ely equal t o (14.5 ≤ ≤ 22.5) for the normal distribution.
Step 3: Compute the required probability using the normal distribution. −
(14.5 ≤ ≤ 22.5) = 14.5 − 25 ≤ √95 ≤ 22.5 − 25 √95 n 2 2 tio u √95 trib
− 21√95 ≤ ≤ −
= (−2.1546 ≤ ≤ −0.5130) = 0.2884 is 95 91 l D a
Thus, based on t he no rm al approxim at ion, t he p robabilit y t hat 15 t o 22 of t he 500 calculat ors rm o
w ill be ret urned for ref und or replacem ent w it hin a 2-year period is approxim at ely 0.2884 N e h : T 4 r 0 te ap h C s | es sin u r B s fo istic tat S
Powered by statisticsforbusinessiuba.blogspot.com 13




