










Preview text:
2/3 (7)
Chapter 3: INTERNATIONAL INVESTMENT
3.1 Concept, causes of formation and development of international investment 3.1.1. Concept
Investment: An investment is the current commitment of money or other resources in the
expectation of reaping future benefits/ you sacrifice sth of value now, expecting to benefit from
that sacrifice later (current sacrifice ←> future benefits)
- In macro-economics and national accounts: expenditure on new capital goods
(goods that are not consumed but instead used in future production). Such investment is
the source of new employment and economic growth. → called development investment
Ex: production of industrial machinery; building factory; building a ship for transportation
- In finance: investment refers to the purchase or ownership of a financial asset with the
expectation of a future return either as income (such as dividends), or as capital gain
(such as a rise in the value of the stock).
Ex: buying shares of an enterprise on a stock market.
- Legal definitions of investment: found in laws and legal agreements, focus on the
issue of property, notwithstanding the productive or financial nature of the investment,
unless specific limitations are made.
→ Broad definitions in international agreement may cover all kinds of asset that
belongs to a foreign enterprise or an individuals
International investment: capital movement across national factors (xem xét tổng thể của TG)
Foreign investment: capital movement across a certain country’s borders. (góc ộ 1 QG)
→ khác ở góc ộ xem xét
Foreign investment of VN: 3,6 (out); 4,5 (in)
3.2 Forms of international investment
3.2.1 Foreign direct investment (FDI)
- Definition (file thay thế)
- (IMF) Direct investment is the category of international investment that
reflects the objective of a resident entity (direct) in one economy
obtaining a lasting interest in a enterprise resident (indirect) in another country
- The resident entity is the direct investor (in home country)
- The enterprise is the direct investment enterprise (in host country - nước nhận ầu tư)
- The lasting interest implies
- The existence of a long-term relationship between the direct investor and the enterprise
- A significant degree of influence by the investor on the management of the enterprise
- (OECD) Foreign direct investment reflects the objective of establishing
a lasting interest by a resident enterprise in one economy (direct investor)
in an enterprise (direct investment enterprise ) that is resident in an
economy other than that of the direct investor. The lasting interest implies the existence of a
long-term relationship between the direct investor and the direct investment
enterprise and a significant degree of influence on the management of the enterprise.
FDI stocks are the total accumulated level of FDI flows are transactions recorded during
direct investment at the end of a given period the reference period (usual y year or quarter). (usually quarter or year). - Types
- Greenfield investment (GI): a company creating a new operation in a foreign country from the ground up (nhà
ầu tư xd 1 cơ sở sx-kd hoàn toàn mới ở nước ngoài)
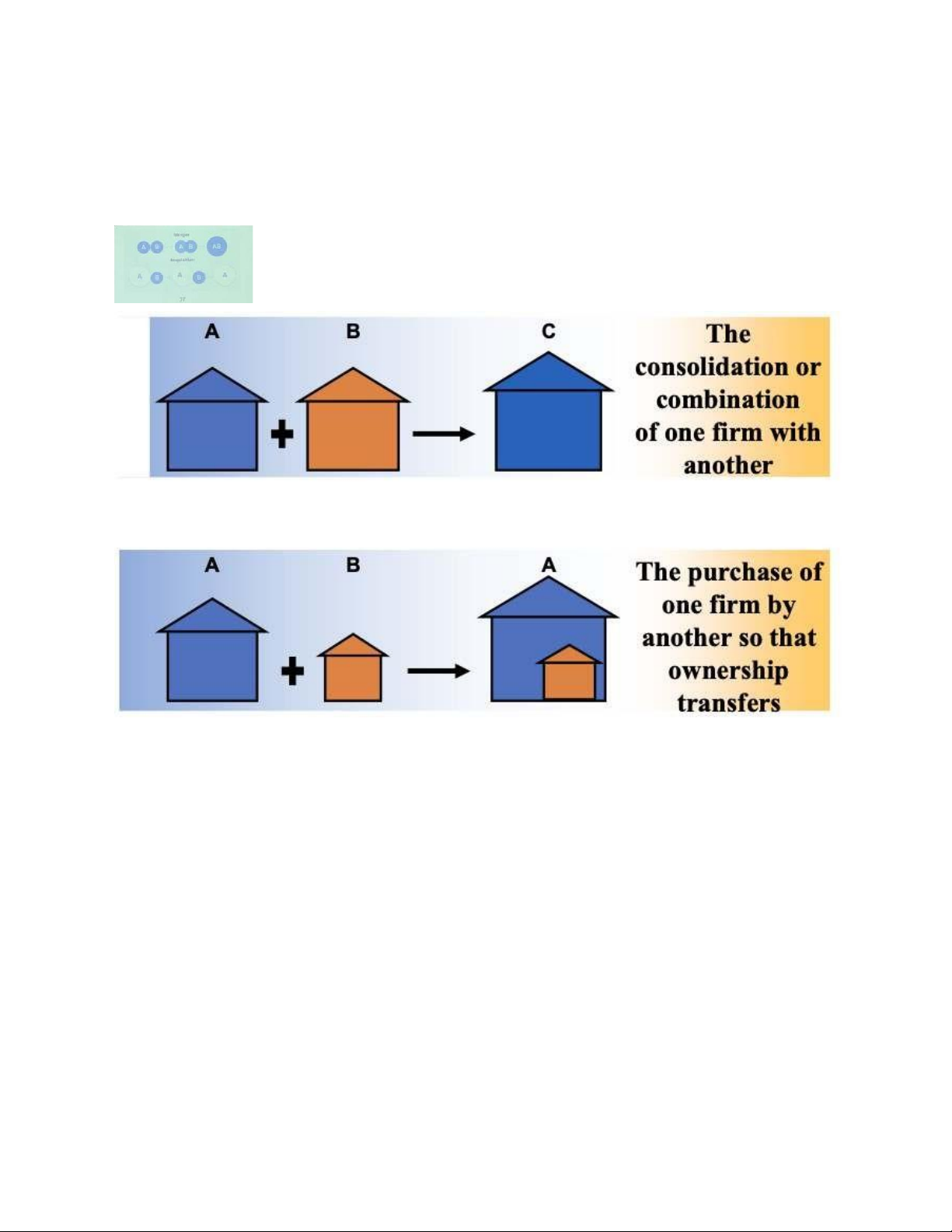
- Merger and Acquisition: the 2nd possible mode of FDI entry is for an investing firm to
merge with or acquire an existing local firm in the host country
→ hình ầu merger/ hình 2 Acquisition - Inward - - Outward - - Components
- Equity capital + retained earnings + Net inter-company loans - Benefit -
South Korea rank 1st in FDI in Vietnam 14/3 (8)
3.2.1 Foreign direct investment (FDI)
- Horizontal M&A: M&A between companies that are in direct competition with each
other in in terms of product lines and markets (1cty mua 1 cty khác trong ngành)
- Vertical M&A: A merger between companies that are along the same supply chain (2
kinds: backward (supply), forward (distributor) Company and supplier Company and distributor
- Conglomerate M&A (các cty h
ko liên quan gì nhau): A merger between
companies in unrelated business activities A: horizontal merger C: vertical merger (2 kinds) B: conglomerate merger
3.2.2. Foreign portfolio investment (Đầu tư chứng khoán) FPI FDI
FPI refers to the investment made in the
FDI pertains to international investment in
financial assets of an enterprise, based in 1
which the investor obtains a lasting interest
country, by the foreign investors
in an enterprise in another country
An investor is inactive An investor is active
Indirect investments in assets are made
Direct investments in assets are made
Investments made are short term in nature
Investments made are long term in nature
FPI are volatile in nature
FDI are stable in nature Practice - Part A 1. Conglomerate 2. Vertical (forward)
3. Greenfield investment (xây cơ sở mới ở nước ngoài) 4. Horizontal 5. Vertical (backward) Part B (nối) Câu 1: (4) Câu 2: Câu 3: (1) (8) Câu 4: (7) Câu 5: (6) Câu 6: (3) Part C: 1. A - 1993 2. A - True 3. 4. B - developing countries 5. 6. 7. -



