




Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD|5906219 0
Chapter 4, Sec ons 1–2: Informed search algorithms Outline: ♦ Best-first search ♦ A∗ search ♦ Heuris cs Review: Tree search
function Tree-Search(problem,fringe) returns a solu on, or failure
fringe←Insert(Make-Node(Ini al-State[problem]),fringe) loop do if fringe is
empty then return failure node←Remove-Front(fringe) if Goal- Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 1 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90
Test[problem] applied to State(node) succeeds return node
fringe←InsertAll(Expand(node,problem),fringe)
A strategy is defined by picking the order of node expansion Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 2 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 Best- irst search
Idea: use an evalua on func on for each node
– es mate of “desirability” ⇒ Expand most desirable unexpanded node Implementa on:
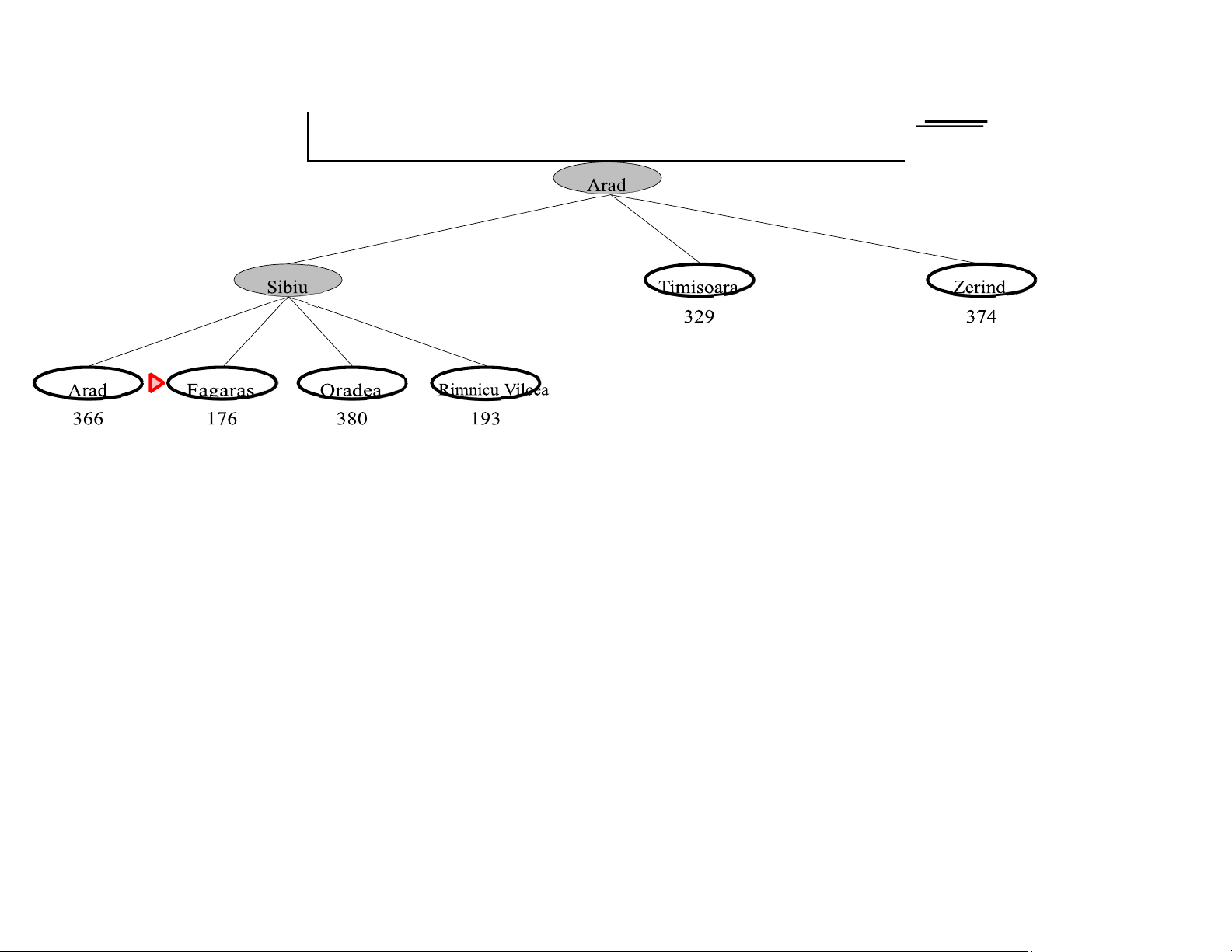
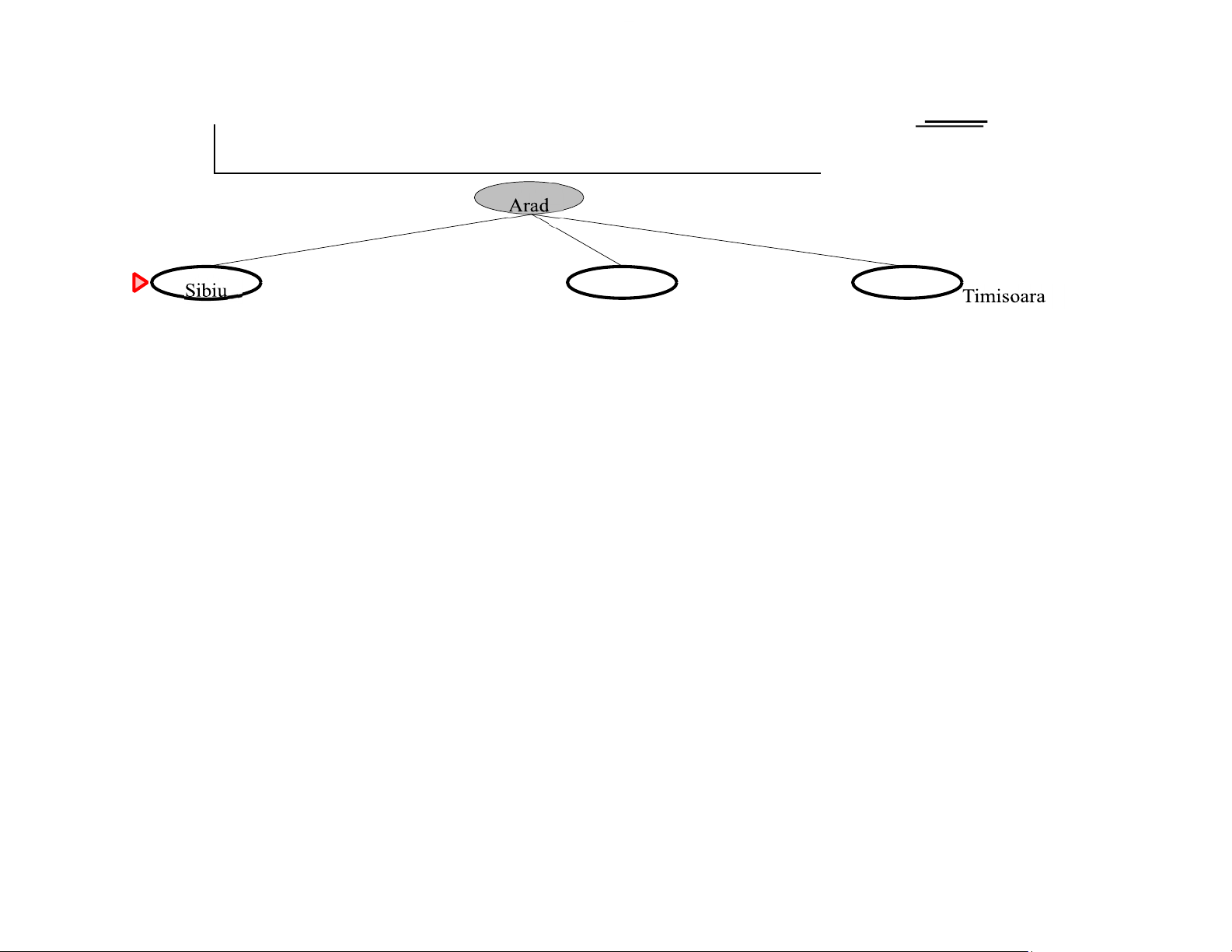
fringe is a queue sorted in decreasing order of desirability Special cases: greedy search A∗ search Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 3 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 Romania with step costs in km Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 4 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 160 242 Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 5 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 161 178 77 151 226 244 241 234 380 98 193 253 329 80 199 374 Greedy search
Evalua on func on h(n) (heuris c)
= es mate of cost from n to the closest goal 6 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 Chapter 4, Sections 1–2
E.g., hSLD(n) = straight-line distance from n to Bucharest Greedy
search expands the node that appears to be closest to goal 7 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 8 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 Greedy search example Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 9 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 Greedy search example Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 10 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 Greedy search example Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 11 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 Greedy search example Properties of greedy search Complete?? Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 12 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 Properties of greedy search
Complete?? No–can get stuck in loops, e.g., with Oradea as goal,
Iasi → Neamt → Iasi → Neamt → Complete in
finite space with repeated-state checking Time?? Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 13 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 Properties of greedy search
Complete?? No–can get stuck in loops, e.g.,
Iasi → Neamt → Iasi → Neamt → Complete in
finite space with repeated-state checking
Time?? O(bm), but a good heuris c can give drama c improvement Space?? Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 14 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 Properties of greedy search
Complete?? No–can get stuck in loops, e.g.,
Iasi → Neamt → Iasi → Neamt → Complete in
finite space with repeated-state checking
Time?? O(bm), but a good heuris c can give drama c improvement
Space?? O(bm)—keeps all nodes in memory Op mal?? Properties of greedy search
Complete?? No–can get stuck in loops, e.g.,
Iasi → Neamt → Iasi → Neamt → Complete in
finite space with repeated-state checking
Time?? O(bm), but a good heuris c can give drama c improvement
Space?? O(bm)—keeps all nodes in memory Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 15 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 Op mal?? No A∗ search
Idea: avoid expanding paths that are already expensive Evalua on func on f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
g(n) = cost so far to reach n h(n) = es mated cost to
goal from n f(n) = es mated total cost of path through n to goal
A∗ search uses an admissible heuris c
i.e., h(n) ≤ h∗(n) where h∗(n) is the true cost from n. (Also require
h(n) ≥ 0, so h(G) = 0 for any goal G.)
E.g., hSLD(n) never overes mates the actual road distance Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 16 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90
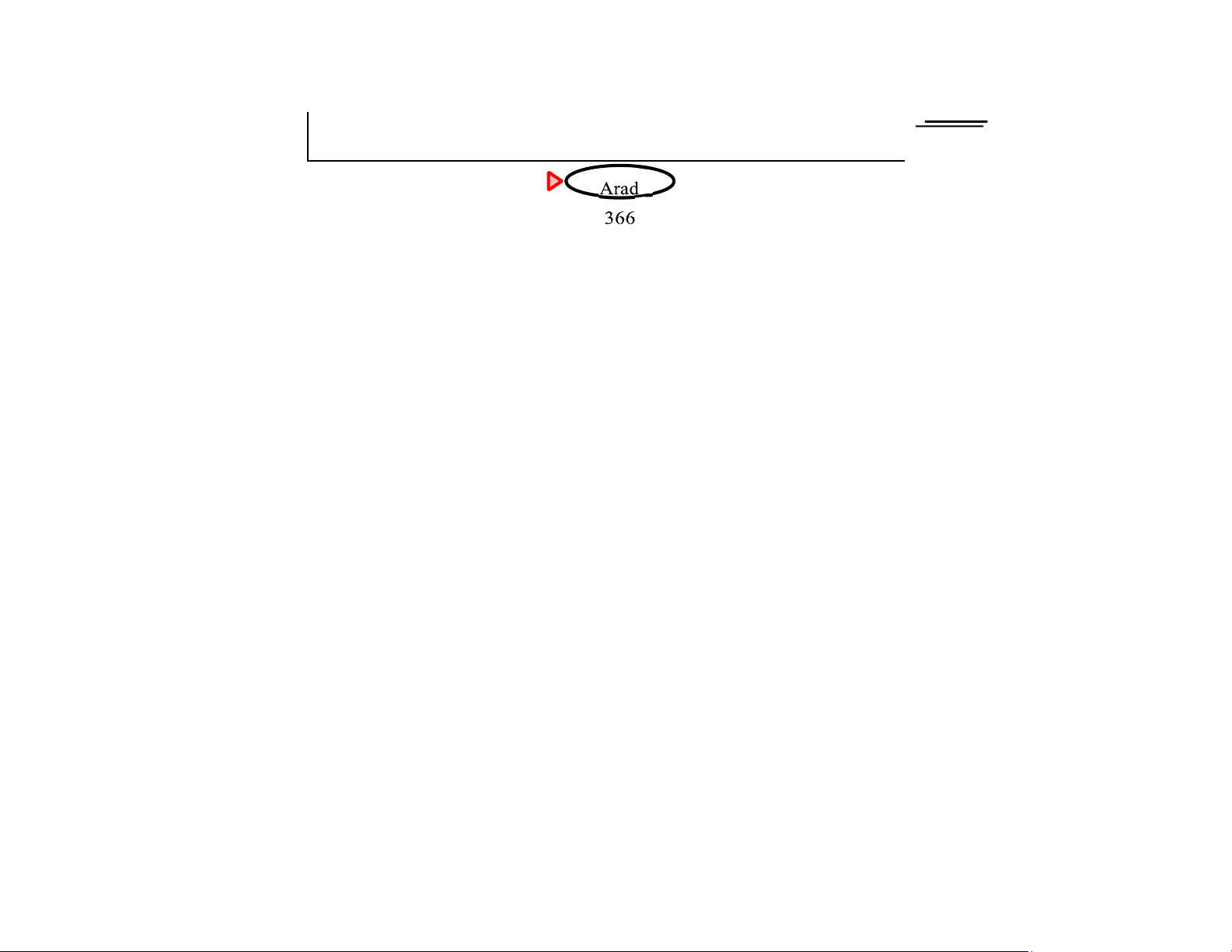
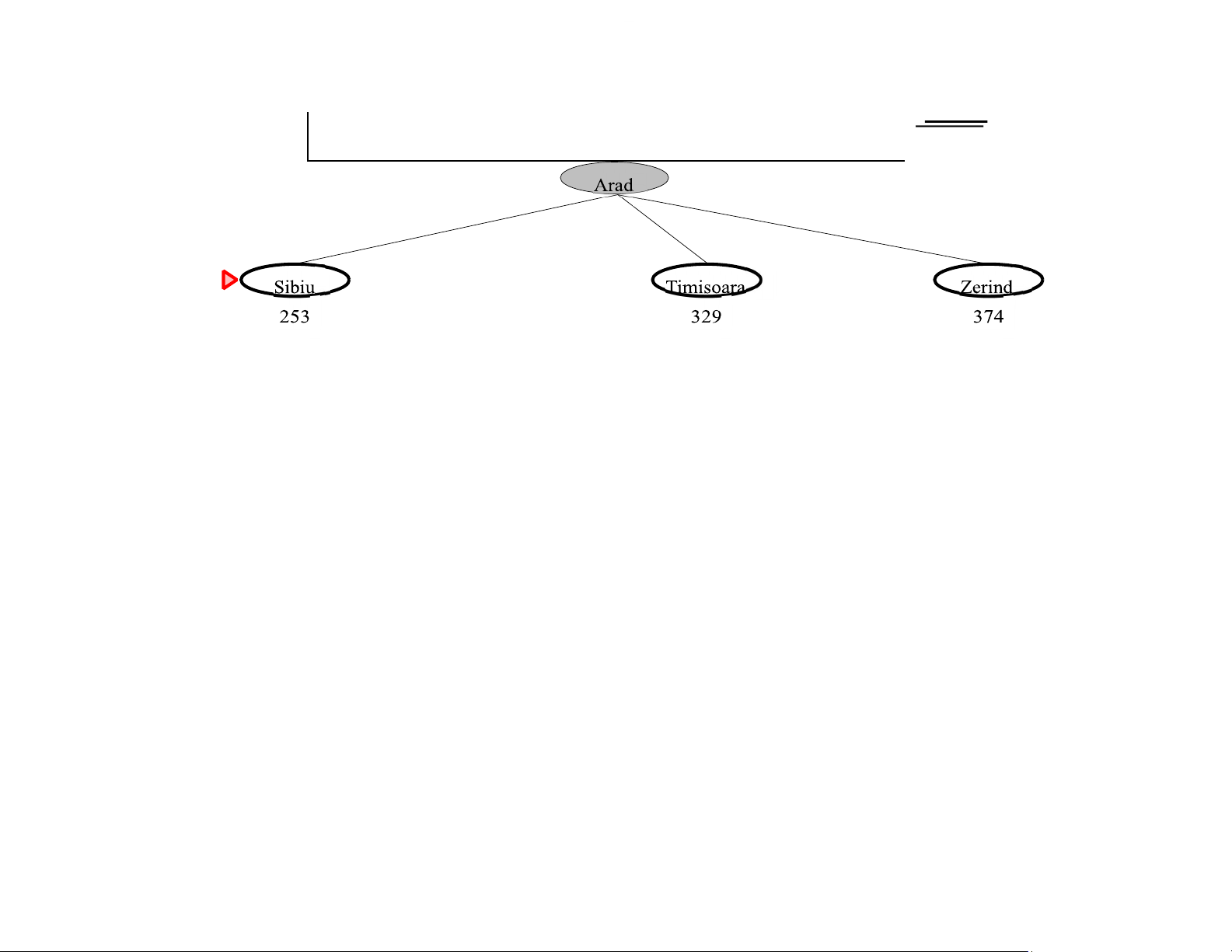
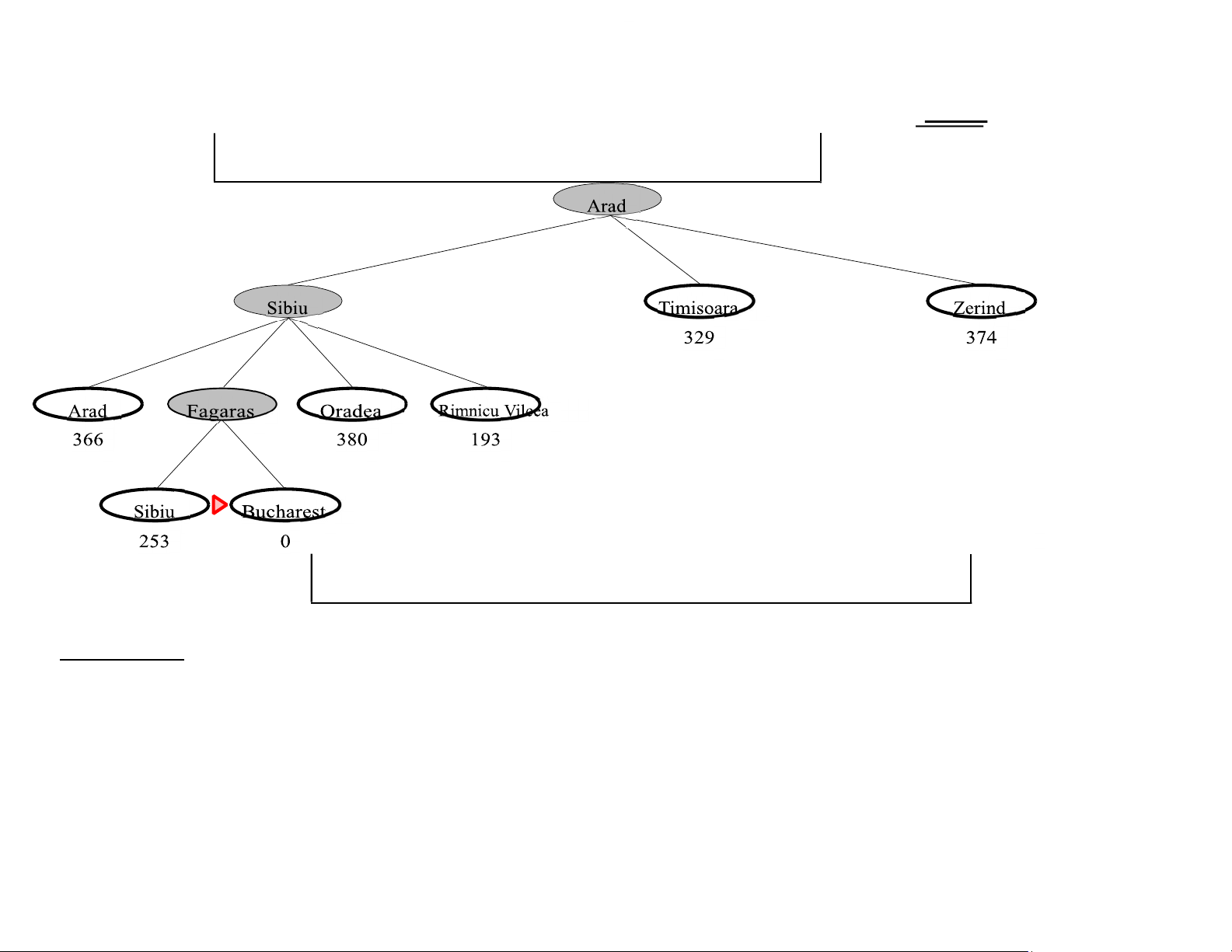
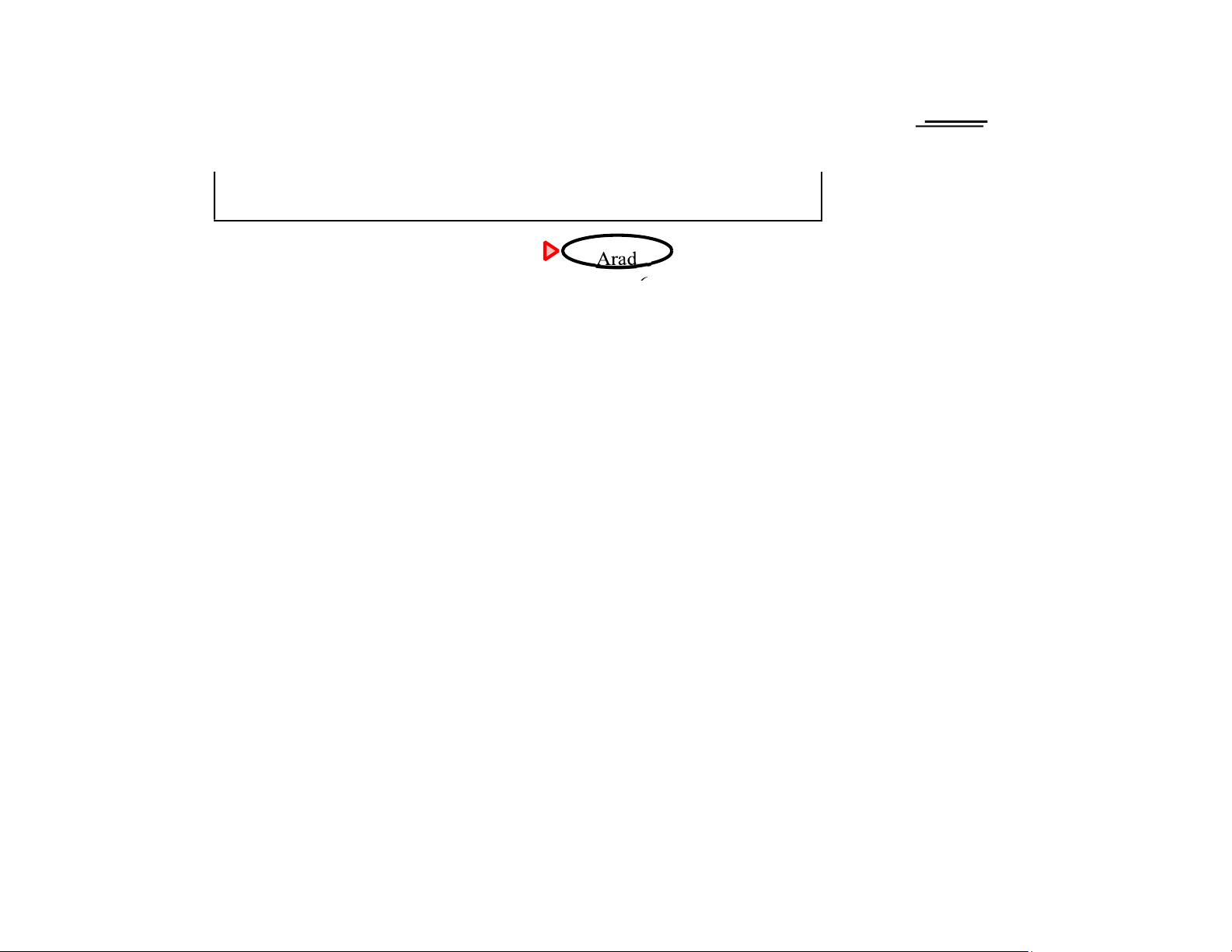
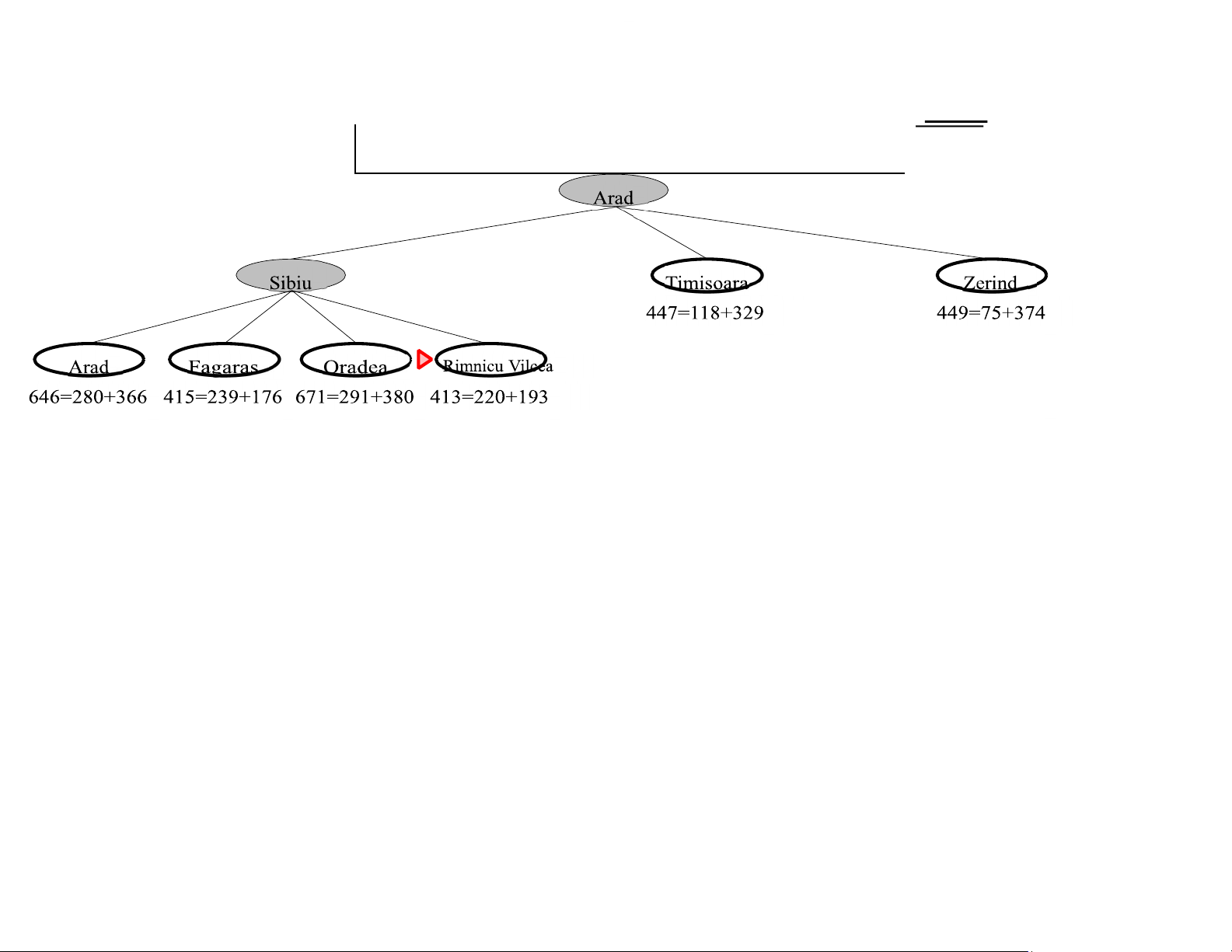
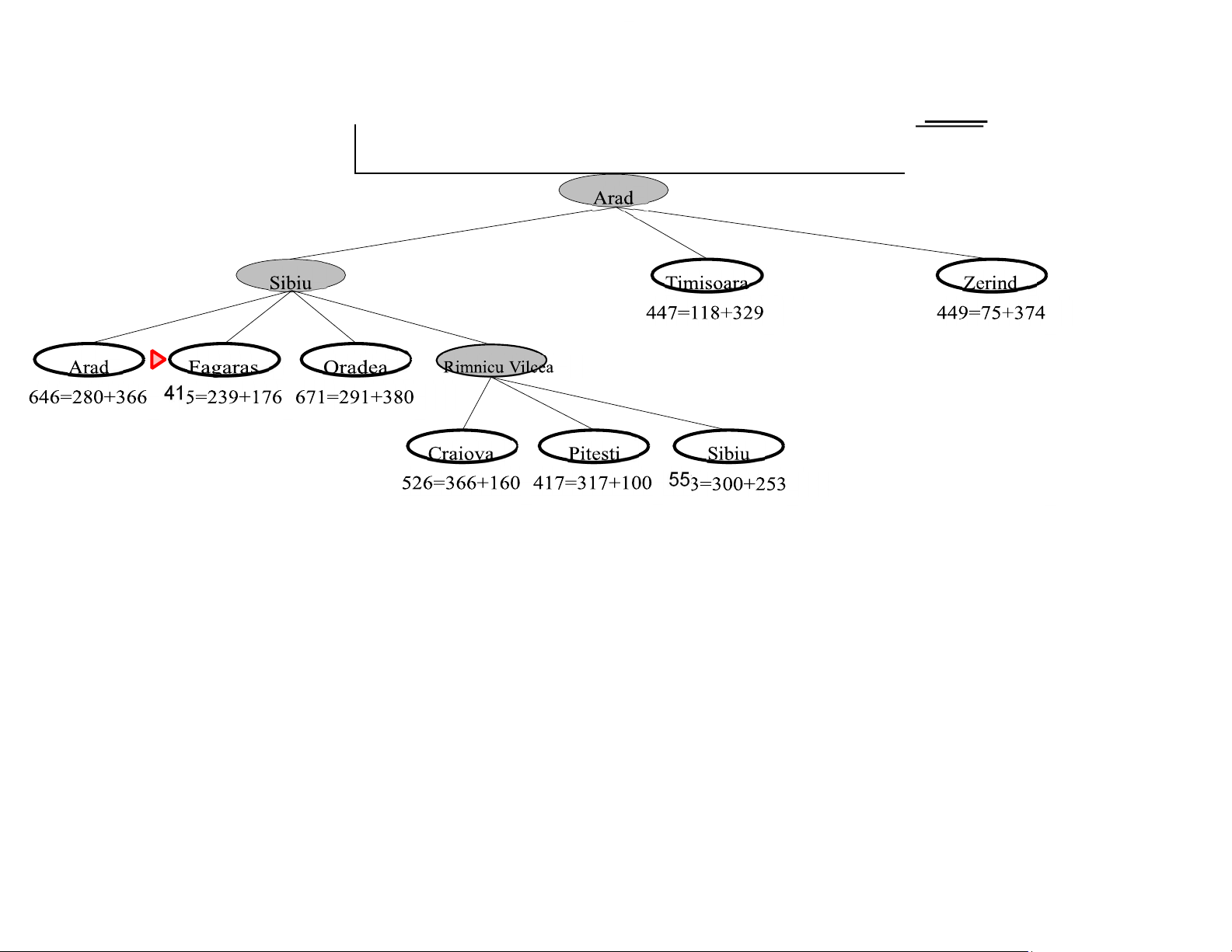
Theorem: A∗ search is op mal A∗ search example 366=0+366 Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 17 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 A∗ search example Zerind 393=140+253 447=118+329 449=75+374 Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 18 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 A∗ search example Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 19 lOMoAR cPSD|590621 90 A∗ search example Chapter 4, Sections 1–2 20