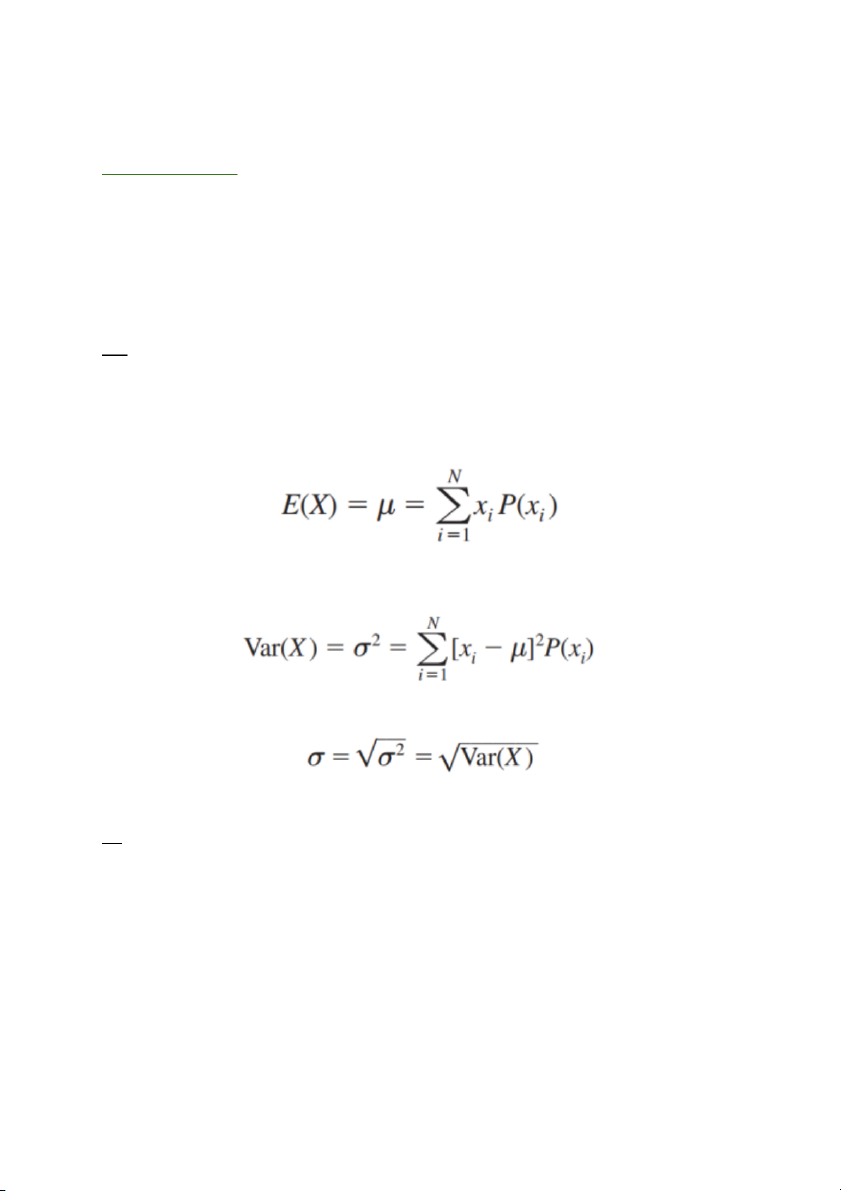


Preview text:
CHAPTER 6: DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION I) KEY CONCEPT
Random variable (Biến ngẫu nhiên) là một biến có giá trị không xác định hoặc một
hàm số gán giá trị cho từng kết quả của một thí nghiệm
+ Discrete random variable (các biến có giá trị cụ thể)
+ Continuous random variable (các biến có giá trị liên tục)
Ở lecture 6 này thì mình chỉ tìm hiểu về Discrete thôi nhé:
Ex: Tung một đồng xu 3 lần. Gọi X là số lần mà số mặt ngửa xuất hiện thì X có thể là
0 (không có mặt ngửa xuất hiện), 1 (mặt ngửa xuất hiện 1 lần duy nhất), 2 (mặt ngửa
xuất hiện 2 lần) và 3 (mặt ngửa xuất hiện trong cả 3 lần)
➔ Công thức tính expected value:
➔ Công thức tính variance of discrete random variable
➔ Công thức tính standard deviation
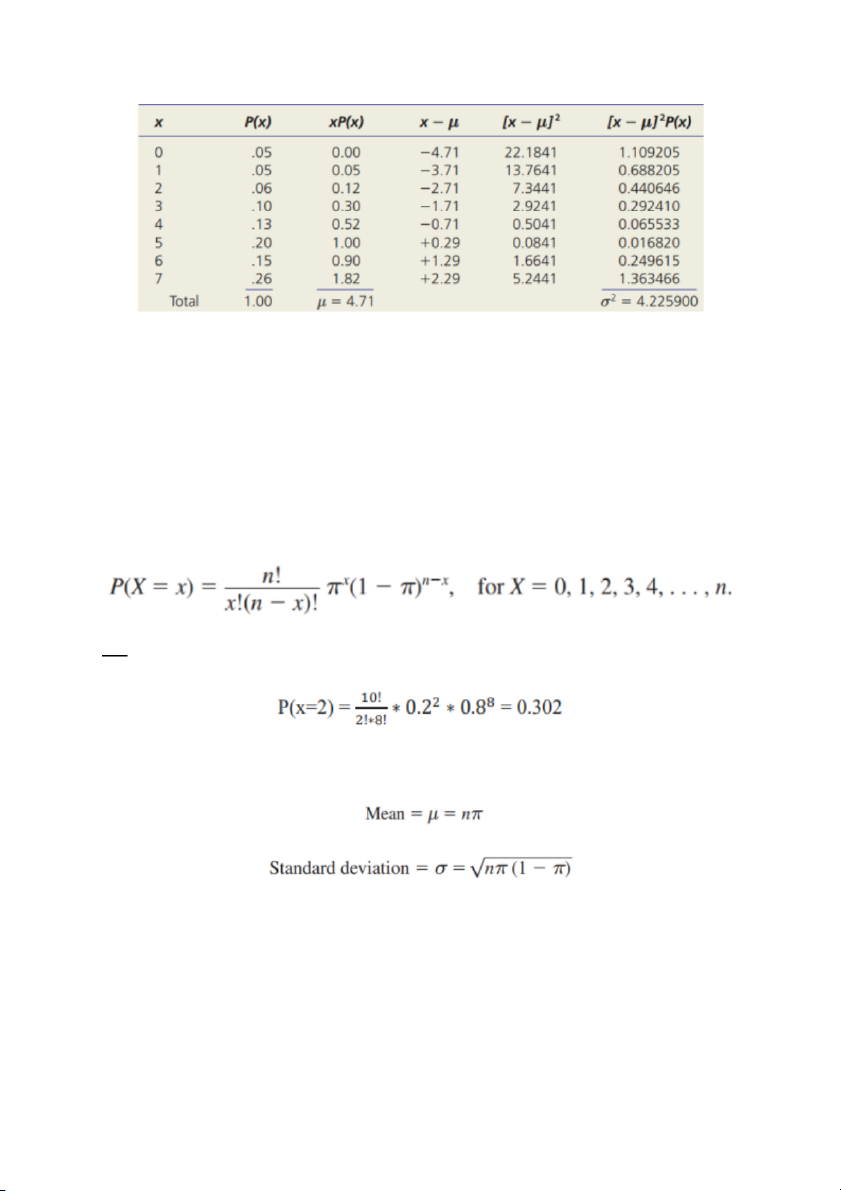
Ex: The Bay Street Inn is a seven-room bed-and-breakfast in the sunny California
coastal city of Santa Theresa. Demand for rooms generally is strong during
February, a prime month for tourists. However, experience shows that demand is
quite variable. The probability distribution of room rentals during
February is shown in Table 6.4 where X = the number of rooms rented (X = 0, 1, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6, 7). The worksheet shows the calculation of E(X) and Var(X).
𝜇 = 0 + 0.05 + 0.12 + 0.3 + 0.52 + 1 + 0.9 + 1.82 = 4.71
Binomial distribution (phân phối nhị thức)
- Phân phối nhị thức là một dạng phân phối rời rạc thường dùng trong thống kê, chỉ
tính đến hai trường hợp, thường được thể hiện là 1 (cho thành công) hoặc 0 (cho thất
bại) trong một số lượng lần thử (nói dễ hiểu hơn thì nôm na nó là như vậy nhé: Phân
phối nhị thức thể hiện xác suất để x thành công trong n phép thử, với xác suất thành
công 𝝅 của mỗi phép thử)
➔ Công thức tính binomial distribution:
Ex: Tỉ lệ suy dinh dưỡng ở trẻ em dưới 5 tuổi là 20%. Nếu chúng ta khám 10 trẻ dưới
5 tuổi, tính xác suất để có 2 em bị suy dinh dưỡng?
➔ Công thức tính mean và standard deviation
Hình dạng của binomial distribution:
Với 𝝅 = 0,5; phân phối sẽ cân đối quanh giá trị trung bình.
Khi 𝝅 > 0,5; phân phối sẽ lệch về bên trái.
Và khi 𝝅 < 0,5 phân phối sẽ lệch về bên phải.
Lưu ý, trong trường hợp P(xP(x
Poisson distribution (phân phối poisson)
- Các biến chỉ có thể nhận các giá trị cụ thể trong một danh sách các số nhất định,
có thể là vô hạn (nói đơn giản thì đếm số lần một sự kiện hiếm xảy ra trong một
khoảng thời gian cố định) ➔ Công thức tính: II) EXERCISE
Question 1: In a certain Kentucky Fried Chicken franchise, half of the customers
typically request “crispy” instead of “original.” (using binomial)
(a) What is the probability that none of the next four customers will request “crispy”? (0.0625)
(b) At least two? (0.6875)
Question 2: The Census Bureau’s Current Population Survey shows 28% of
individuals, ages 25 and older, have completed four years of college (The New York
Times Almanac, 2006). For a sample of 15 individuals, ages 25 and older, answer the following questions
a. What is the probability four will have completed four years of college? (0.2262)
b. What is the probability three or more will have completed four years of college? (0.8355)
Question 3: According to a survey conducted by TD Ameritrade, one out of four
investors have exchange-traded funds in their portfolios (USA Today, January 11,
2007). Consider a sample of 20 investors.
a. Compute the probability that exactly 4 investors have exchange-traded funds in their portfolios. (0.1897)
b. Compute the probability that at least 2 of the investors have exchange-traded
funds in their portfolios. (0.9757)
c. Compute the expected number of investors who have exchange-traded funds in their portfolios. (5)
Question 4: More than 50 million guests stay at bed and breakfasts (B&Bs) each
year. The website for the Bed and Breakfast Inns of North America, which
averages seven visitors per minute, enables many B&Bs to attract guests (Time, September 2001).
a. Compute the probability of no website visitors in a one-minute period. (0.0009)
b. Compute the probability of two or more website visitors in a one-minute period. (0.9927)
c. Compute the probability of one or more website visitors in a 30-second period. (0.9698)
d. Compute the probability of five or more website visitors in a one-minute period. (0.8271)
Question 5: A survey showed that the average commuter spends about 26 minutes
on a one-way door-to-door trip from home to work. In addition, 5% of commuters
reported a one-way commute of more than one hour (Bureau of Transportation
Statistics website, January 12, 2004).
a. If 20 commuters are surveyed on a particular day, what is the probability that
three will report a one way commute of more than one hour? (0.0596)
b. If 20 commuters are surveyed on a particular day, what is the probability that
none will report a one way commute of more than one hour? (0.3585)




