










Preview text:
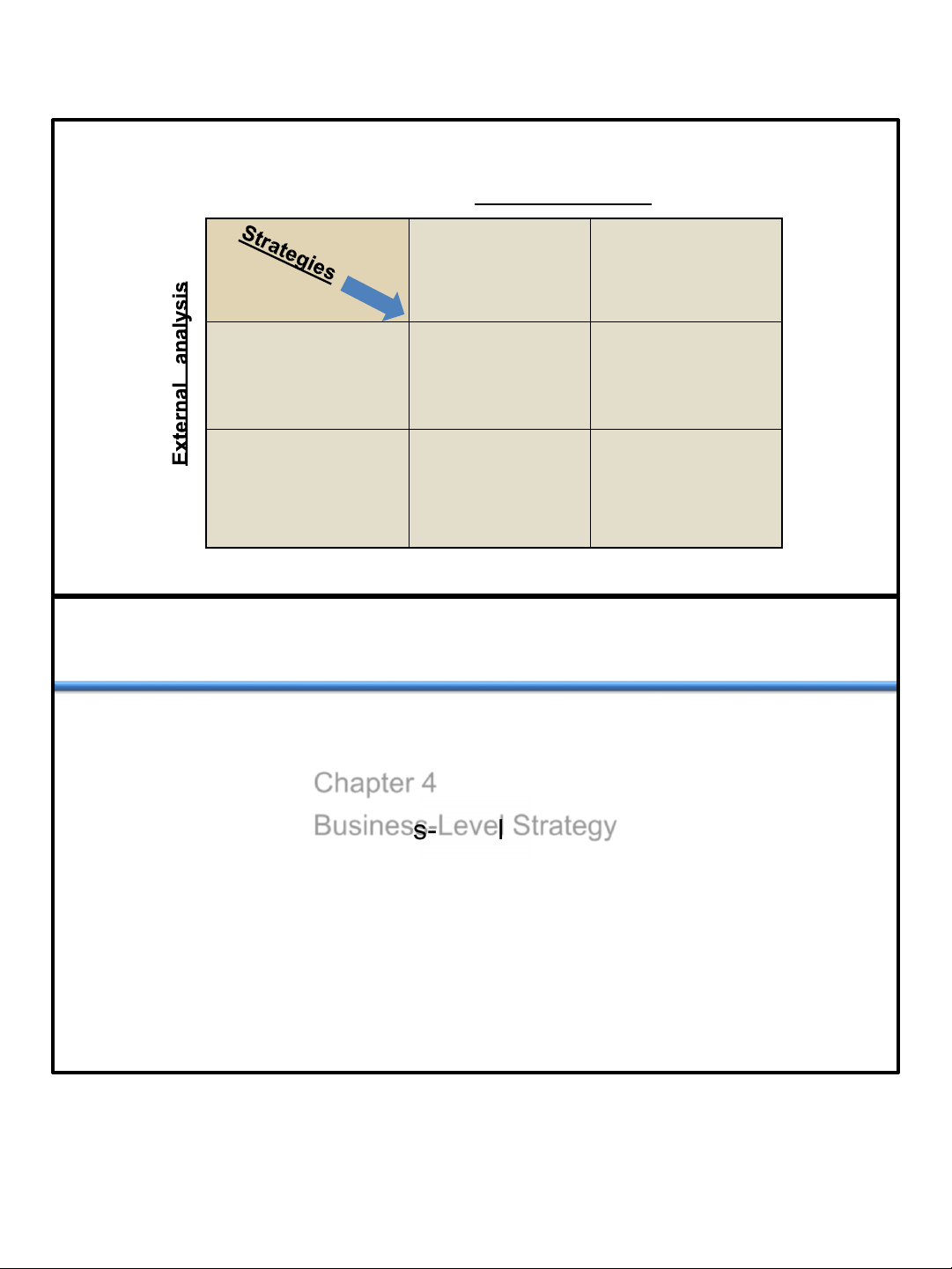
lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 Strategic Management 1 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 SWOT Matrix Internal analysis
Strengths – S
Weaknesses – W List Strengths List Weaknesses
Opportunities – O
S-O Strategies
W-O Strategies
Use strengths to take
Overcoming weaknesses List Opportunities advantage of
by taking advantage of opportunities opportunities
Threats – T
S-T Strategies
W-T Strategies
Use strengths to avoid Minimize weaknesses and List Threats threats avoid threats Ch 6 -2 Chapter 4 Business - Level Strategy 2 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 Learning Objectives
Studying this chapter should provide you with the strategic who ma , na wh ge at m , ent
knowledge needed to: and how.
1. Define business-level strategy.
2. Discuss the relationship between customers and business-level strategies in terms of
3. Explain the differences among business-level strategies.
4. Use the five forces of competition model to explain how above-average returns can be
earned through each business-level strategy.
5. Describe the risks of using each of the business-level strategies.
© 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use. 4–4
© 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or
service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use. 3 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 4 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 Business - Level Strategy
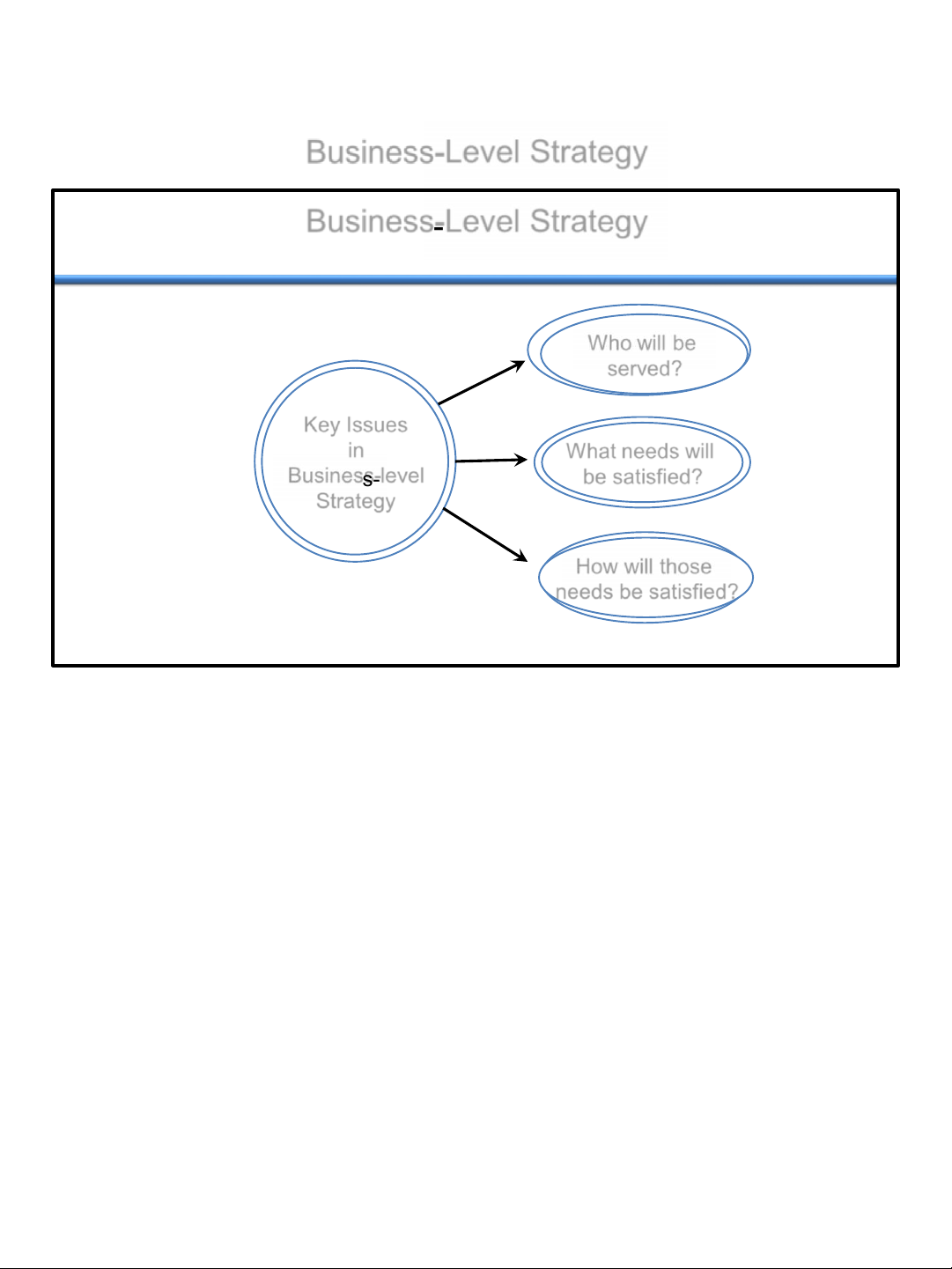
Customers : Their Relationship
with Business-Level Strategies Who will be served? Key Issues in What needs will Business - level be satisfied? Strategy How will those needs be satisfied? 4 –6
© 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or
service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use. 5 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 Business - Level Strategy
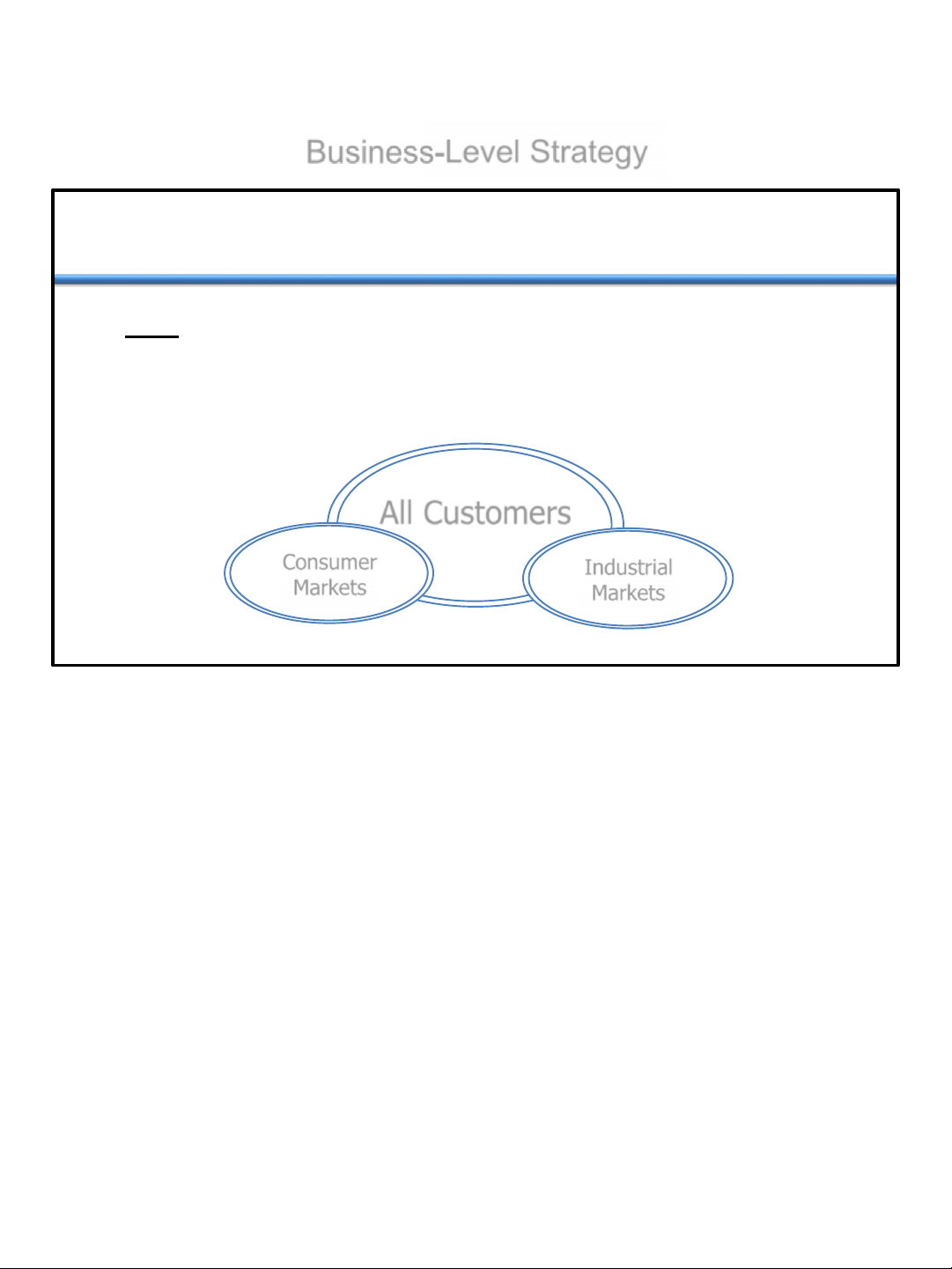
• Who : Determining the Customers to Serve • Market segmentation
– A process used to cluster people with similar needs into individual and identifiable groups. All Customers Consumer Industrial Markets Markets 4 –7
© 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or
service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use. 6 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 Business-Level Strategy Market Segmentation • Consumer Markets • Industrial Markets – Demographic factors – End-use segments – Socioeconomic factors – Product segments
– Geographic factors – Geographic segments – Psychological factors – Common buying factor – Consumption patterns
segments – Perceptual factors – Customer size segments 4–8
© 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or
service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use. 7 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 Business-Level Strategy
What: Determining Which Customer Needs to Satisfy • Customer needs ?
– Good price (lower or lowest price)
– High quality (higher or highest quality) – Better services • Quick delivery • Maintaining after sale • Other supports – Other benefit utilities...
© 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain
product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use. 4–9 8 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 Business-Level Strategy
How: Determining Core Competencies Necessary to Satisfy Customer Needs • Firms must decide:
– Who to serve, what customer needs to meet, and how
to use core competencies to implement value creating
strategies that satisfy target customers’ needs.
• Only firms with capacity to continuously improve, innovate and
upgrade their competencies can expect to meet and/or exceed
customer expectations across time... 4–10
© 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or
service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use. 9 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 Business-Level Strategy
How: Determining Core Competencies Necessary to Satisfy Customer Needs • Firms must decide:
– ......how to use core competencies to implement
value creating strategies that satisfy target customers’ needs.
• Only firms with capacity to continuously improve,
innovate and upgrade their competencies can expect to
meet and/or exceed customer expectations across time....
© 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain
product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use. 4–11 Business - Level Strategy
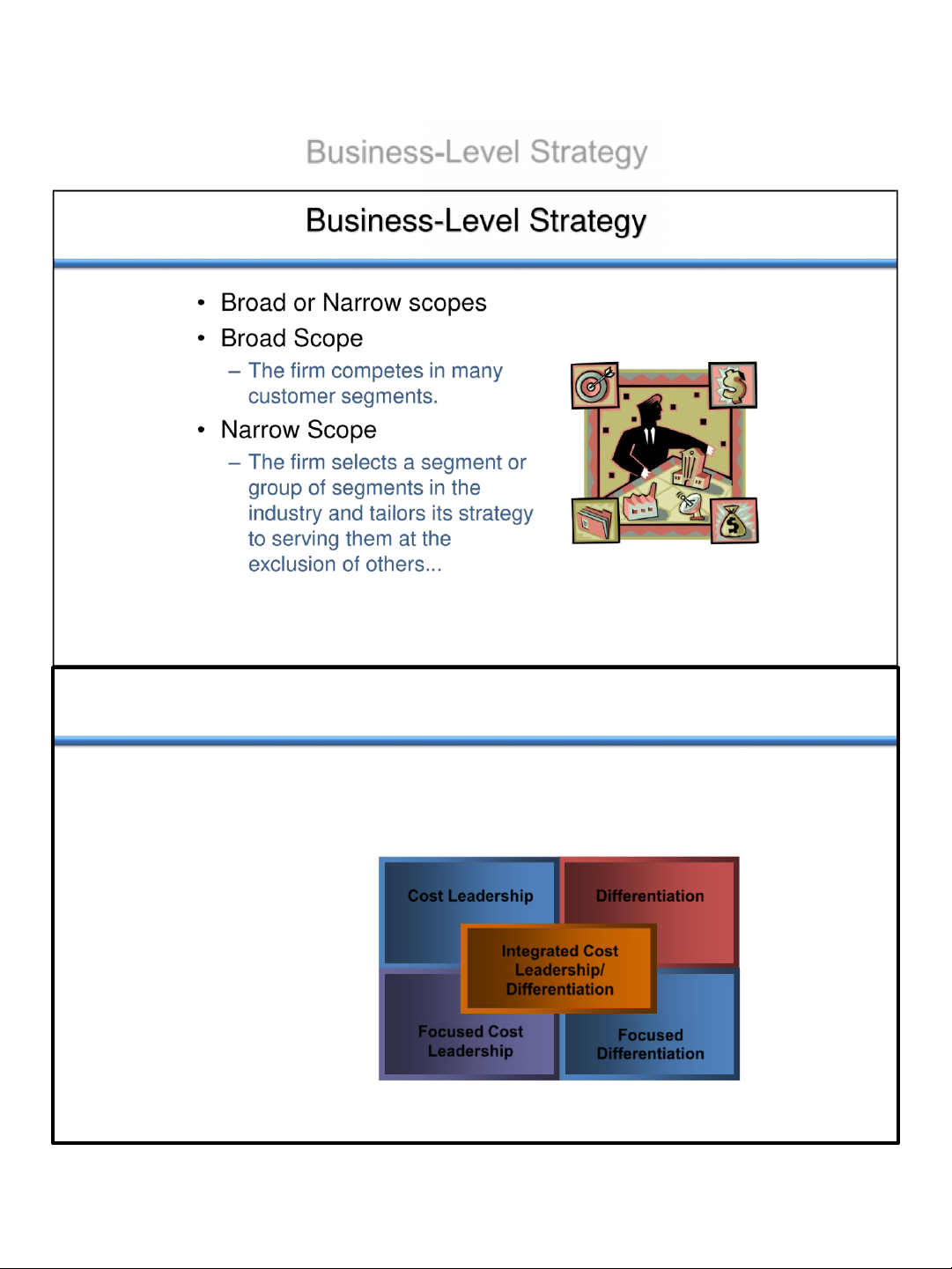
Based on Competitive Advantage Considerations • Which strategy? – Lower cost: – Differentiated: • Which market? – Broad scope markets? – Narrow scope Market 10 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 Business-Level Strategy
• Lower cost: Achieving lower overall costs than rivals
– Performing activities differently (reducing process costs)
• Differentiated: Possessing the capability to differentiate the firm’s
product or service and command a premium price
– Performing different (more highly valued) activities... 11 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 Business - Level Strategy
Basis for Customer Value Lowest Cost Distinctiveness Cost Leadership Differentiation Broad Target
Integra t ed Cost Target
Lead e rship/ Market
Differe ntiation Narrow Focused Cost Focused Target Leadership Differentiation 12 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 Cost Leadership Strategy How?
• An integrated set of actions taken to produce goods or
services with features that are acceptable to customers
at the lowest cost, relative to that of competitors. • Product Characteristics –
Relatively standardized (commoditized) products –
Features broadly acceptable to many customers – Lowest competitive price... 4–16 Cost Leadership Strategy Actions needed:
• Cost saving actions required by this strategy: –
Building efficient scale facilities –
Tightly controlling production costs and overhead –
Minimizing costs of sales, R&D and service –
Building efficient manufacturing facilities –
Monitoring costs of activities provided by outsiders – Simplifying production processes...
© 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain
product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use. 4–17 13 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 Cost Leadership Strategy
How to Obtain a Cost Advantage Determine Reconfigure and control Value Chain Cost Drivers if needed
▪ Alter production process ▪ New raw material
▪ Change in automation
▪ Forward integration
▪ New distribution channel
▪ Backward integration
▪ New advertising media
▪ Change location relative
▪ Direct sales in place of
to suppliers or buyers... indirect sales... 14 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021
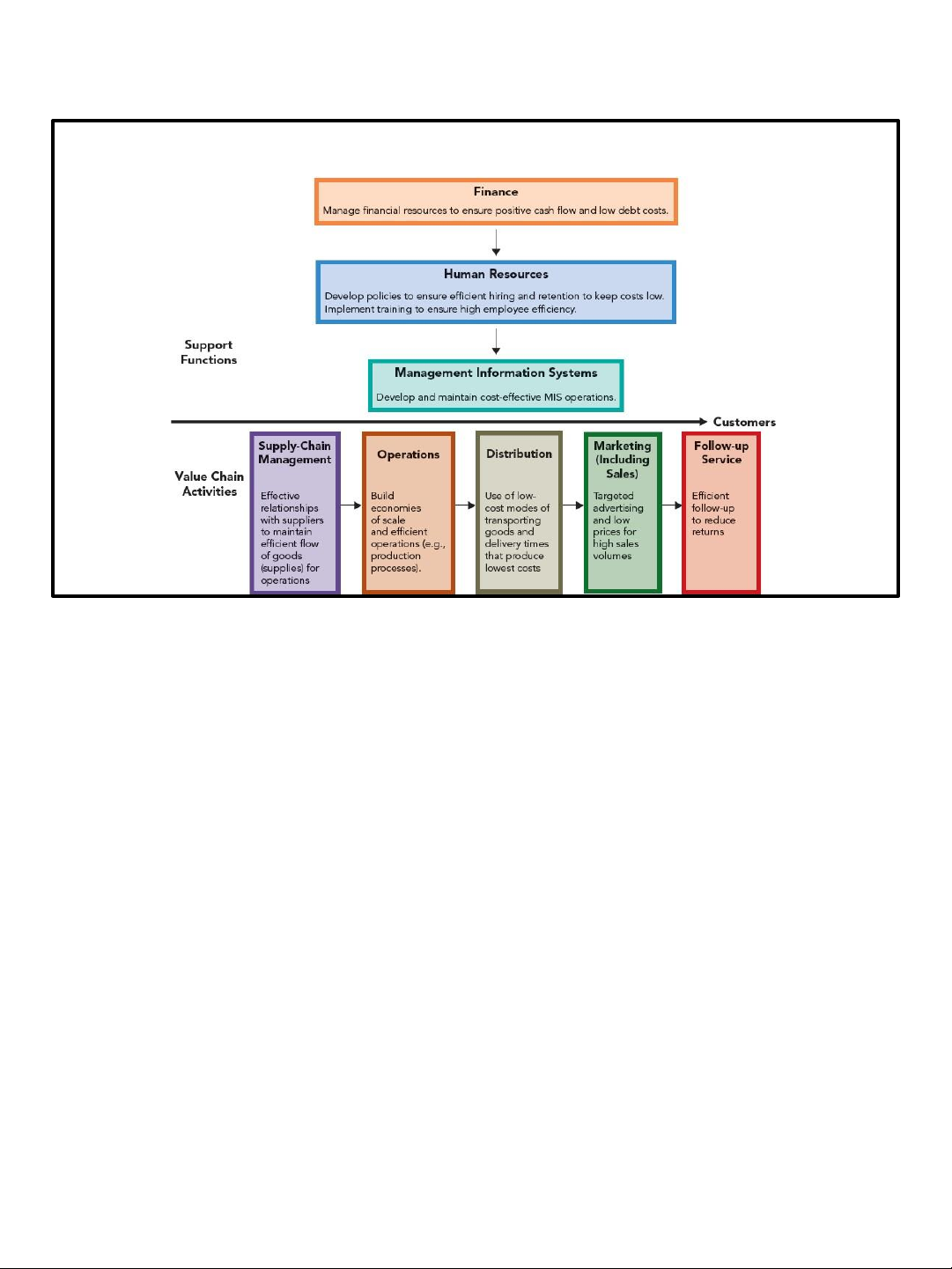
Cost Leadership Strategy
Figure 4.2 Examples of Value-Creating Activities Associated with the Cost Leadership Strategy
©2015CengageLearning.Allrightsreserved.Maynotbecopied,scanned,orduplicated,inwholeorinpart,exceptforuseaspermittedinalicensedistributedwithacertain
productorserviceorotherwiseonapassword-protectedwebsiteforclassroomuse. 4 –19 15 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021
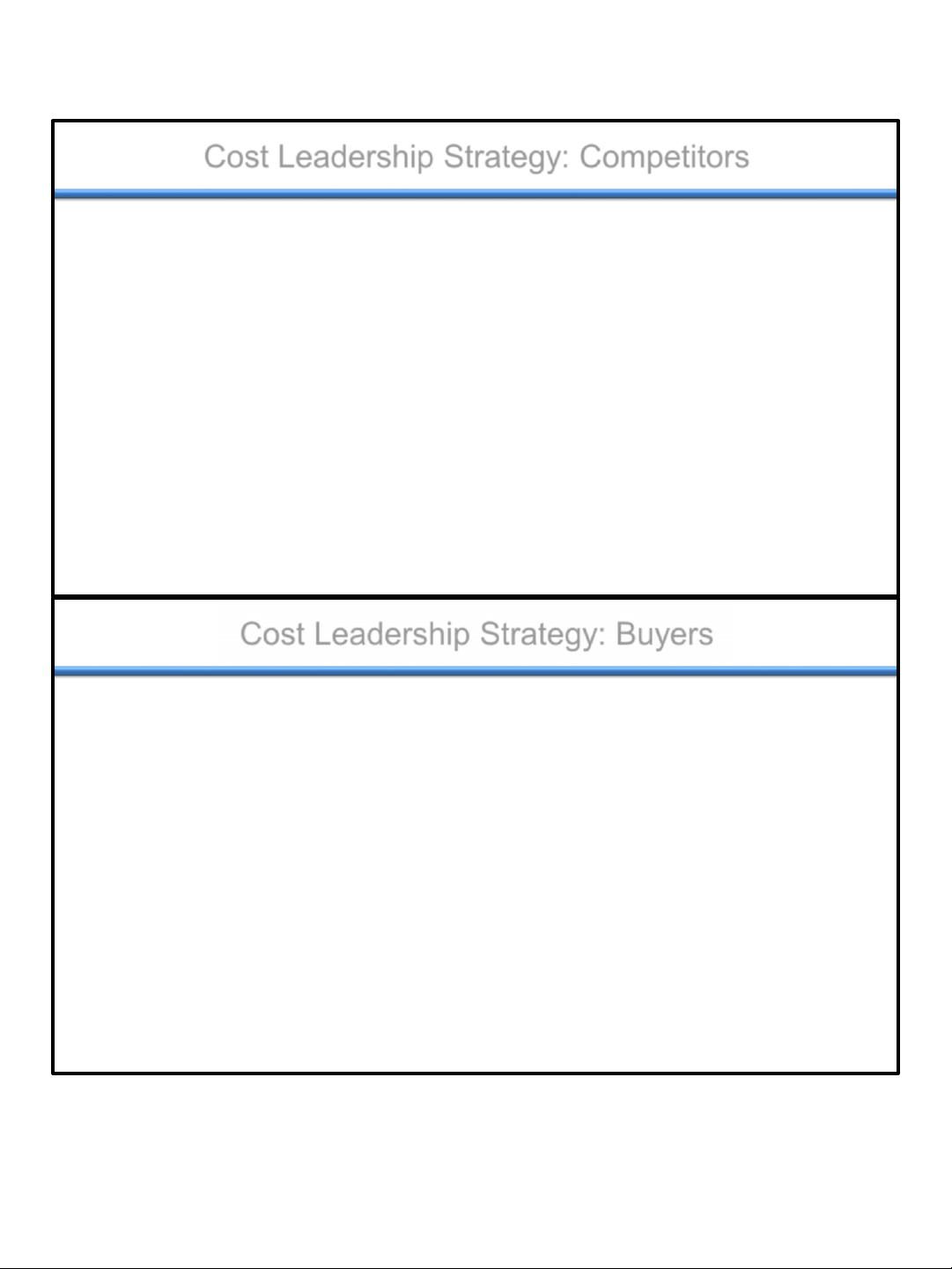
Cost Leadership Strategy: Competitors
Rivalry with Existing Competitors
• Due to cost leader’s advantageous position:
– Rivals hesitate to compete on basis of price.
– Lack of price competition leads to greater profits...
Cost Leadership Strategy: Buyers
Bargaining Power of Buyers
• Can mitigate buyers’ power by:
– Driving prices far below competitors,
causing them to exit, thus shifting power
with buyers (customers) back to the firm... 16 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021
Cost Leadership Strategy: Suppliers
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
• Can mitigate suppliers’ power by:
– Being able to absorb cost increases due to low cost position.
– Being able to make very large purchases, reducing
chance of supplier using power...
Cost Leadership Strategy: New Entrants
The Threat of Potential Entrants
• Can frighten off new entrants due to:
– Their need to enter on a large scale in order to be cost competitive.
– The time it takes to move down the industry learning curve... 17 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021
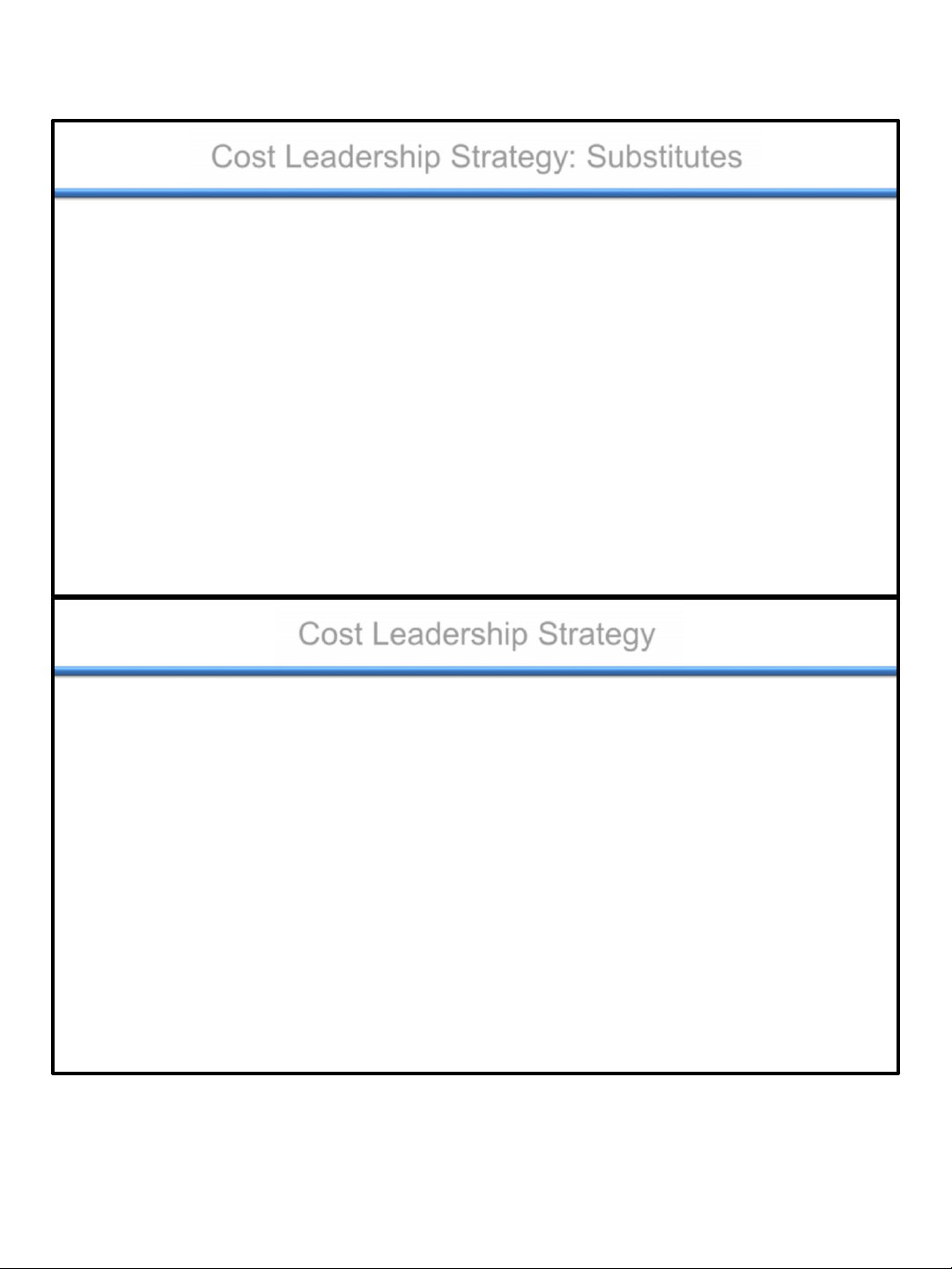
Cost Leadership Strategy: Substitutes
Product Substitutes
• Cost leader is well positioned to:
– Lower prices in order to maintain its value position.
– Make investments to add features unavailable in substitutes.
– Buy intellectual property and patents developed by potential substitutes... Cost Leadership Strategy • Competitive Risks
– Processes used to produce and distribute good or service may become
obsolete due to competitors’ innovations.
– Too much focus on cost reductions may occur at expense of customers’
perceptions of differentiation.
– Competitors, using their own core competencies, may successfully imitate
the cost leader’s strategy .... 18 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 Differentiation Strategy
• An integrated set of actions taken to produce goods or services
( at an acceptable cost) that customers perceive as being different
in ways that are important to them.
– Focus is on nonstandardized products
– Appropriate when customers value differentiated features more than they value low cost... Differentiation Strategy
How to Obtain a Differentiation Advantage Control Cost Reconfigure Drivers if Value Chain needed to maximize
▪ Lower buyers’ costs
▪ Raise performance of product or service
▪ Create sustainability through:
▪ Customer perceptions of uniqueness
▪ Customer reluctance to switch to non-
unique product or service... 19 lOMoAR cPSD| 46560390 11/3/2021 Differentiation Strategy
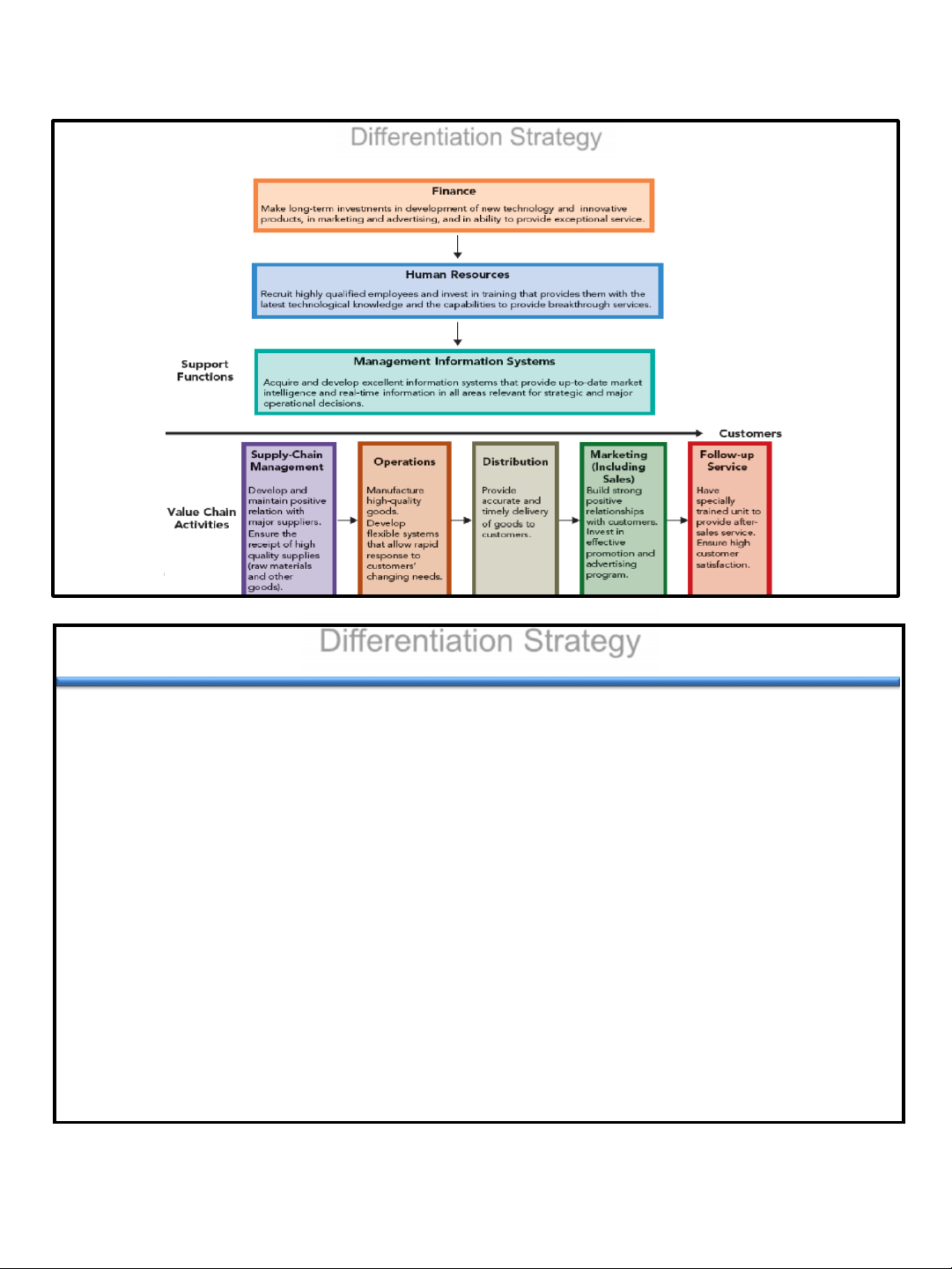
Value chain-Creating Activities Associated with the Differentiation Strategy
©2015CengageLearning.Allrightsreserved.Maynotbecopied,scanned,orduplicated,inwholeorinpart,exceptforuseaspermittedinalicensedistributedwithacertain
productorserviceorotherwiseonapassword-protectedwebsiteforclassroomuse. 4 –28 Differentiation Strategy
Value-Creating Activities and Differentiation
• Highly developed MIS • High quality replacement • parts Emphasis on quality • Worker compensation for • Superior handling of creativity/productivity incoming raw materials • Use of subjective
• Attractive products performance measures • Rapid response to • customer specifications Basic research capability • Technology • Order-processing • procedures High quality raw materials • 20



