













Preview text:
Managing Relationships in Business Markets and Role of Information Communication Technologies
parties of cooperative systems work closely to
buyers and sellers. As a result of high level of
increase the efficiency of operations, there is no
adaptation, this type of relationship is character-
structural commitment through legal bonds.
ized with a high degree of operational linkages
Key Account Management (KAM): KAM and information exchange.
aims to manage relationships with the largest and
Value Creating Networks: Value creating
most important business customers. In KAM, the
networks are considered as important forms of re-
guiding principle is the 80/20 rule. This means
lationship marketing and defined as collaborative
that when 20% of a firm’s customers provides 80%
efforts between two or more firms that bring their
of its business, that 20% deserves special atten-
resources together in order to achieve their mutu-
tion. Firms want to maintain long-term profitable
ally compatible goals that they could not achieve
relationships with the top 20% of customers that
easily alone. In business markets, core capabilities
accounts for 80% of the seller’s total revenue.
of the network member firms come together to
Mutually Adaptive Relationship: In mutually
create superior value for the end consumer.
adaptive relationship there is the high degree of
relationship specific adaptations made by both 88 89 Chapter 5
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets ABSTRACT
Enterprises require focusing on managing relationships in internal markets because internal marketing
activities play a critical role in creating an organizational climate that supports customer relation-
ship management strategies. The main objective of this chapter is to identify requirements for creating
customer-centric culture in organizations. Customer service can cause the success or failure of a com-
pany; hence, the role of internal market in service profit chain cannot be ignored. After explaining the
significance of the service profit chain for the company, the chapter continues with clarifying the role
of customer experience management in creating customer retention. In this chapter, creating customer-
keeping culture, getting 360 degrees of customer insight, using big data and predictive analysis, engag-
ing customers through social media, and managing experience across multi-channels are explained
as requirements for achieving excellence in customer service experience. This chapter ends up with
discussing the characteristics of customer service in the digital era and key business trends about the future of customer service. INTRODUCTION
ence to the customers. Therefore, management of
relationships with the parties that are involved in
The broad perspective of relationship marketing is
the value creation process is critical for the achieve-
not only limited with the management of standard
ment of customer satisfaction and retention.
buyer and seller relationships but also includes
Managing relationships in internal markets also
management of relationships with the parties that
contributes to the value creation because internal
are involved in the value creation process (e.g.
marketing activities play a critical role in creat-
suppliers, internal markets, non-governmental
ing an organizational climate that is compatible
organizations and influence and referral parties).
with the relationship marketing philosophy (Bal-
Attracting, enhancing and maintaining long-term
lantyne, 2000; 2003). Marketing culture, internal
and profitable relationships with customers can be
marketing and business strategy built on customer
possible by delivering superior value and experi-
experience and service are seen as the prerequisite
DOI: 10.4018/978-1-4666-8231-3.ch005
Copyright © 2015, IGI Global. Copying or distributing in print or electronic forms without written permission of IGI Global is prohibited.
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
of implementing relationship marketing (Ben-
Inter-functional cooperation is needed in all
nett & Durkin, 2002). The employee-customer
forms of value creation. Motivated and customer
interaction has an impact on satisfaction with
conscious employee at all levels of the firm can
the customer service; therefore it is important to
be possible by improving the open two way com-
ensure that employees have the traits of customer
munications and coordinating tasks between the
service orientation. The main objective of inter-
front line and support staff. When the various
nal marketing is to hire, train and motivate able
parts of an organization act without cohesion,
employees who want to serve customers well in
this will constrain the performance of employees
order to maintain customer satisfaction (Kotler,
and front line employee (Ballantyne, 2000). Thus
2000). Internal marketing activities include the
firms that want to create high customer value by
creation of a customer oriented internal environ-
adopting relationship marketing strategies must
ment in which all functions of the organization
create an internal environment where all functions
proactively communicate, understand and inform
of the organization proactively communicate,
each other to serve customers effectively (Gilmore
understand and inform each other.
& Carson, 1995). Delivering consistently higher
Bennett and Durkin (2002) highlight that a
quality customer service and achieving a loyal
relational organizational culture requires, spon-
customer base are possible by maintaining a base
taneity, flexibility, creativity and employees
of loyal and stable employees (Sisodia & Wolfe,
who have team, relational and initiative skills.
2000) because findings of the research indicate
Focusing on results, exercising loose control, and
that employee’s job performance is directly tied
being employee oriented, open, parochial, and
to their level of commitment to the organization
pragmatic are considered as the cornerstones of
(Payne & Frow, 2006). At this point, internal
relationship marketing culture (Bennett & Durkin,
marketing is becoming important. Therefore, firms
2002). Relationship marketing culture is expected
must train their employees in order to teach them
to emphasize results over processes because a
how to interact with customers.
process oriented culture is characterized by the
regularity and repetitive nature of the work cycle;
however result oriented cultures are more likely CREATING RELATIONSHIP
to be characterized by initiating behavior and a MARKETING CULTURE IN
dynamic work context that is more compatible INTERNAL MARKETS
with relationship marketing philosophy. Relational
culture much more concerns about people rather
The focus of internal marketing is to get and
than concern about getting the job done. If a culture
retain customer conscious employees (Grönroos,
only interested in the work which people do, in
1990). Organizational culture significantly af-
that culture decision making will become central-
fects employees’ eagerness to serve customers
ized and changes will be imposed by authorities.
(Bellou, 2007). Thus, as Bellou (2007) indicates,
Centralization of decision making creates barrier
it is important to establish a culture that allows
for implementation of relationship marketing.
employee involvement, facilitative management
However, in order to facilitate the relationship
styles, and decentralized decision-making. The
culture, empowerment has to be given to the
organizational culture has to reward customer
employees and the organizational culture should
orientation practices; especially promoting the
be employee oriented rather than job oriented. In
customer service orientation practices among
a relationship culture, employees have to derive
front-line employees is essential.
their identity mainly from association with the
organization and customer base (parochial) rather 90
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
than the nature of their job (professional). As,
ployees can deepen with the help of the employee
Bennett and Durkin (2002) indicate that bankers
centric database. This employee centric database
have seen themselves as belonging to a “banking
facilitates the profiling of the employees, under-
profession”; however intense competition has been
standing the meaning each seeks, knowing the
eroding the view about deriving identity from
barriers each faces and the level of bonding with
the nature of job. In order to survive in a highly
the enterprise. This human resource information
competitive market, they notice that rather than
system helps firms to match right employees with
being in the “banking profession”, they are actu-
appropriate processes, functions and customers
ally operating in the financial services industry, (Gordon, 1998).
in which their primary objective is to provide
Empowerment, as an internal market rela-
high quality service. Parochial dimension of re-
tionship management strategy, contributes to the
lationship culture is also the guiding principle of
creation of relationship marketing culture within
Starbucks. Starbucks has been spending lots of
the organization. Empowerment means giving
efforts to contribute positively to the communities
employees the power, freedom, knowledge and
it serves and the environments in which it oper-
skills to make decisions and perform effectively
ates. Howard Schultz emphasized the Starbucks’
(Daft, 2000; p. 42). Empowerment is also consid- guiding principles as follows:
ered as a motivation tool (Hollander & Offermann,
1990) for task accomplishment because employees
We aren’t in the coffee business, serving people.
improve their own effectiveness by choosing how
We are in the people business, serving coffee
to do task and using their creativity. Companies
that empower their employees increase motiva-
Being parochial and responding primarily to
tion and creativity in return (Conger & Kanungo,
customer needs can be seen as essential for the
1988). Service providers should be empowered
successful creation of relational organizational
to resolve any service failure quickly. As Donald
culture. The communication climate and infor-
Porter from British Airways says that “customers
mation sharing within the company have to be
don’t expect you to be perfect. They do expect you
open. There has to be continuous communication
to fix things when they go wrong” (Brookes, 2013).
within the internal market and as well as with the
Immediate service failure recovery is significant
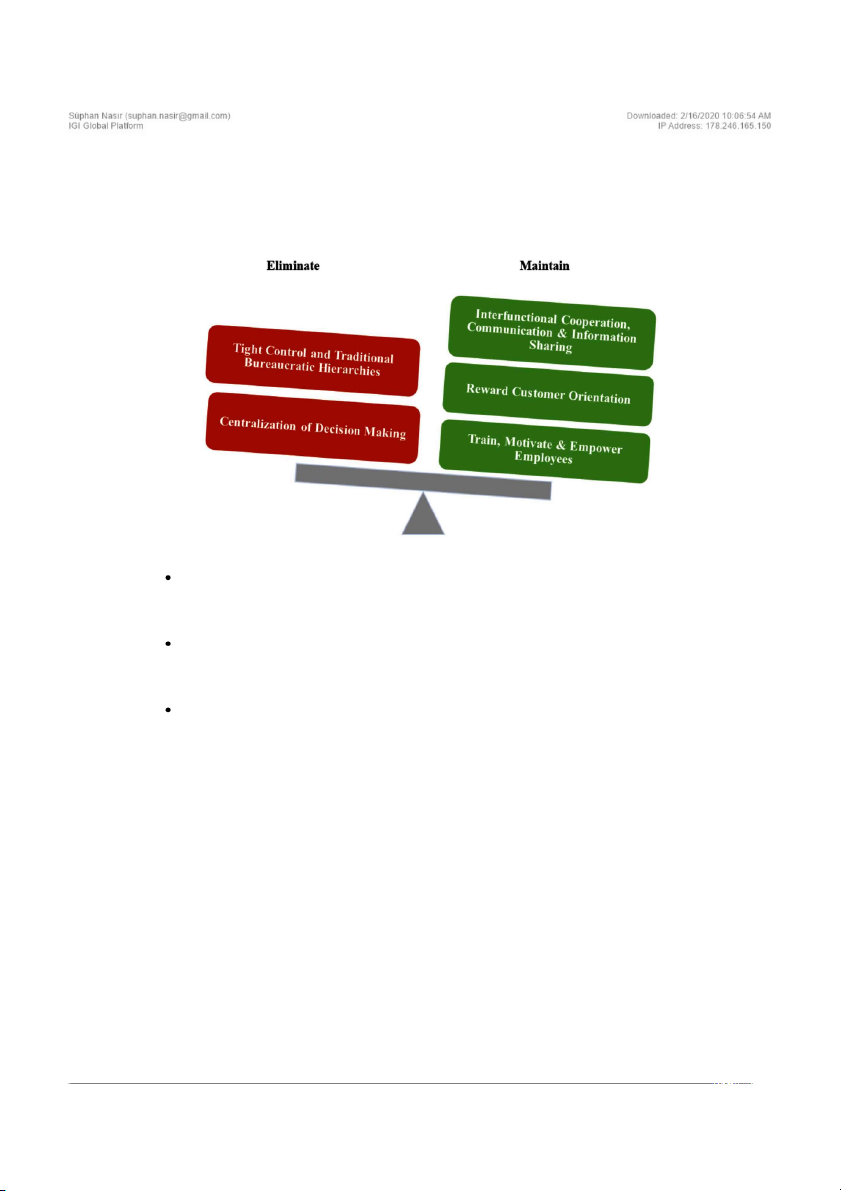
external markets. On the other hand, tight control
for customer retention because 50% of customers
and traditional bureaucratic hierarchies can be
give a company only one week to respond to a
seen as barriers for the relationship marketing
problem before they stop doing business with the
culture. Relationship culture should depend on
company (Harris Interactive, 2011). Companies
employee empowerment. Roles of employees
have been spending billions of dollars for service
have to be defined clearly in order to minimize
improvements in order to solve the problem at
potential conflicts. Furthermore, in a relation-
the first time. If the company is able to solve the
ship culture, organization’s orientation towards
problem of customers at the first time, customer
organizational issues and customers must be much
churn drops down 15% and 20% and it is expected
more pragmatic rather than normative (Bennett
that customers who experience problems and then & Durkin, 2002).
get a solution are actually more loyal to the com-
Companies that adopt relationship marketing
pany than those who never experience a problem
as a key business strategy need to consider their
(Bernoff, 2011). Thus, in order to prevent customer
human resources because relationships with cus-
churn and create customer loyalty, enterprises
tomers will not be enduring until the relationships
have to handle customer complaints and service
with employees deepen. Relationships with em-
failure effectively by empowering their employees. 91
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
Benefits of employee empowerment can be
provide a basis for great word of mouth
summarized as follows (Bowen & Lawler, 2000):
communication and customer retention.
Empowerment of employees provides
Especially empowerment of frontline employ-
quicker responses to customer needs dur-
ees is extremely important because empowering
ing service delivery. Customers want quick
frontline employees is a key component for
responses and want immediate solutions to
breaking the cycle of failure in service delivery
their problems and empowerment may lead
(Schlesinger & Heskett, 1991). Call centers
to spontaneous and creative rule breaking
are also important for the creation of customer
responses to satisfy the needs of customers.
centric organization and delivering outstand-
Empowerment is especially important
ing customer experience. Call centers perform
during the service recovery. Service em-
sales, support, and customer service functions.
ployees have to be empowered to make
Call centers need to handle customer complaints
necessary recovery acts. Empowerment
and fix the problems at the first time in order to
provides quick recovery to the service fail-
create meaningful connections with customers,
ures. Recovering service failures may turn
increase customer loyalty and generate revenue.
dissatisfied customers into a satisfied cus-
Therefore, it is important to reinvent call center
tomer. If the employees do not have power
culture to handle customer problems effectively
and knowledge to recover service failures,
and create outstanding customer experience.
customers will remain dissatisfied.
Figure 1 illustrates requirements of creating re-
With the empowerment, employees feel
lationship marketing culture. Enterprises need to
responsible for their job and find the work
adjust their hiring and training practices, seek out
meaningful. Employees will be more sat-
people who love working in customer service, hire
isfied as their sense of control increases
employees who have problem-solving mentality,
because this will make the work more
train employees to improve their conversation meaningful.
skills (e.g. how to create emotional connection
Customers’ perceptions of service qual-
during the conversation and what to say and how
ity are shaped by the courtesy, empathy
to say it skills), motivate them with meaningful
and responsiveness of service employees.
incentives (e.g. giving titles and perks that make
Employee attitudes are a key part of ser-
employees feel important, providing recognition
vice; thus, if employees feel that they are
and bonuses for great service, creating frontline
empowered they will interact with custom-
career progression plan and developing employee
ers with empathy and this leads to custom-
loyalty programs) and abandon metrics that foster
er satisfaction. Empowered employees can
bad customer experience (e.g. measure and reward
provide better care for the customers.
problem-solving excellence over speed or number
Empowered employees can be a great of calls) (Bodine, 2011).
source of service ideas. If employees are
Briefly, all employees within an organization,
encouraged to tell their opinions about the
not just front-line employees, have to work together
work, this can lead to improved service
for delivering experiences that delight custom-
quality and ideas for new services.
ers. As indicated by Hitachi Consulting (2009)
Empowered employees will provide better
it is critical for every employee to understand
service to the customers and satisfied cus-
the role that they play in delivering experiences
tomers spread their appreciation to other
and enterprises have to create a customer centric
people. Thus, empowered employees may
organization (Hitachi Consulting, 2009) by: 92
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
Figure 1. Creating relationship marketing culture in internal markets
Training employees in order to build the
the success or failure of a company. According to
knowledge, skills, and behaviors that
Harris Interactive Customer Experience Impact
enable employees to serve customers
Report, customer experience is a high priority for successfully,
consumers and 60% of consumers indicate that
Giving the right incentives and rewards to
they are willing to pay more for a better service
employees in order to encourage them to
experience (ClickSoftware, 2011). Since selection,
perform desired behaviors that will lead to
training and motivation of employees can make a
superior customer experience, and
worthwhile difference in delivering better service
Empowering employees and giving them
experience, service firms should attract, develop,
the freedom to make real-time decisions
motivate and retain qualified employees (Berry,
in order to enable them to deliver positive
2000). Internal market needs to be informed about customer experience
the organization’s mission, products, services and
the expectations of its customers. In turn, this
will provide success in the delivery of marketing ROLE OF INTERNAL MARKET
activities to external customers (Gilmore & Car- IN SERVICE PROFIT CHAIN
son, 1995). Unhappy employees mean unhappy
customers, so a company has to treat its staff as it
The concept of internal marketing has been
treats its customers. If a company wants customer
emphasized in the services marketing literature
satisfaction, firstly it has to ensure employee sat-
because the service is a performance product and
isfaction. Management of an organization must
the performer is employee and only when the
carry out internal marketing and provide employee
service provider performs well, the satisfaction
support and reward for good performance because
of external customer increases. Service can cause 93
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
employee relations will affect customer relations
serving customers play a crucial role in creating (Kotler, 2000)
superior customer service experience. Thus, firms
Employee motivation through incentives, re-
have to provide the necessary knowledge about
wards and a compensation system is crucial for
the processes, technologies and customers to the
building stronger relationships with customers
employees. First of all, firms have to identify
and creating customer commitment. However,
relationship marketing skills that are required
enterprises underestimate the importance of the
from employees who participate in delivering
customer experience on customer behavior. The
customer value processes. Then, firms have to
survey results of Forrester’s the state of customer
assess the performance of their employees accord-
experience, indicate that less than one-third of the
ing to these skills and firms have to determine if
companies have employees who share a common
any knowledge gap exists. Finally, firms have to
view of the customer, make decisions that take
develop training programs and technology sup-
the customer into consideration, and reward em-
port to reskill processes where employees require
ployees for improving customer experience (For-
additional knowledge (Gordon, 1998).
rester, 2010). Thus, firms must give importance
Highly satisfied customers means growth and
to internal marketing activities such as training
profitability for the companies. Heskett et al.
and motivating employees. In this way, employees
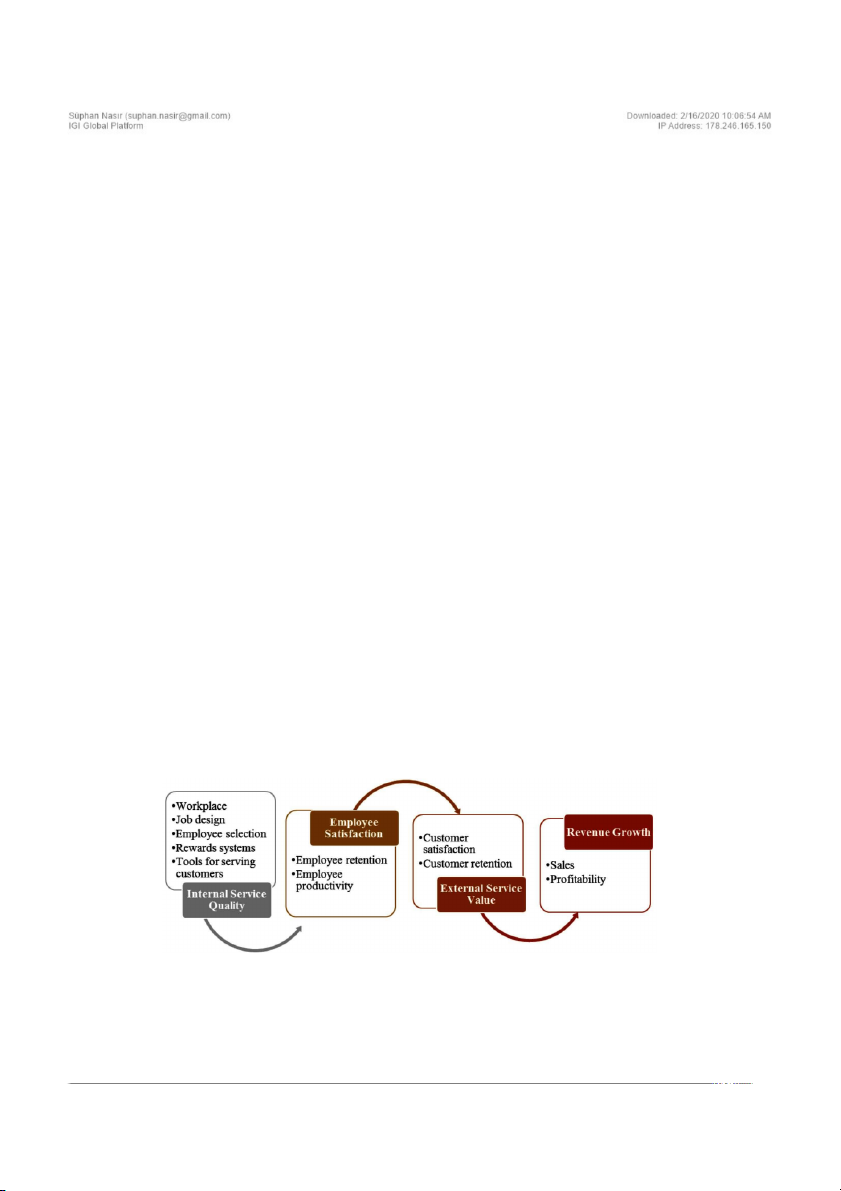
(2008) develop a “service-profit chain” model and
can handle customer relationships professionally.
this model describes the linkages among employee
Internal marketing activities of a firm must also
satisfaction, customer satisfaction, customer re-
include proper monitoring processes that include
tention, sales and profitability. According to the
periodic performance evaluation of employees
service profit chain model, to keep profitability
in order to prevent failures (Parvatiyar & Sheth,
of the company, it is important to manage all the 2000).
links in the company that may affect customer
Employees need mastery of processes, tech-
satisfaction. As can be seen in Figure 2, enhancing
nologies and people with whom they interact in
internal service quality by equipping employees
order to provide superior service and customer
with the skills, power and tools to serve customers
experience. Improving the employees’ knowledge
increases employee satisfaction. If an employee
and providing necessary tools to employees for
is satisfied with his job, employee tends to be Figure 2. Service profit chain
Source: Adapted from Heskett, J. L., Jones, T.O., Loveman, G. W., Sasser, W. E., & Schlesinger, L. A. (2008). Putting the
service-profit chain to work. Harvard Business Review, July-August, 118-129. 94
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
loyal to his job and he will be more productive.
trigger high employee turnover. It is important to
In return this will foster value of external service
keep in mind that employee retention is the key
which leads to increase in customer satisfaction
to customer retention, and as Reichheld (1993)
and retention (Heskett et al., 2008). Quality of
indicates that customer retention can quickly com-
external relationships is so dependent on the
pensate satisfied salaries and other incentives that
quality of internal relationships.
are designed to maintain employee retention. As
Harris Interactive Customer Experience Impact
the employees stay longer with a company, they
Report indicates that 86% of consumers stop doing
are able to serve customers better than new-comer
business with a company because of a bad customer
employees because employees become more famil-
experience and TARP findings reveal the fact that
iar with the business and customers, know what
68% of the customer churn are caused by customer
customers prefer and this enable them to develop
feelings of poor treatment (ClickSoftware, 2011).
trustful relationships with customers. Employees’
It is clear that most customers quit a company due
overall job satisfaction, combined with their ex-
to bad customer service experience. A qualified
perience, helps them serve customers better and
and skilled employee who is committed to deliver-
this leads to customer loyalty. Customers contact
ing customer satisfaction is a valuable asset in an
with the firm through employees, so customers
organization. Employees of an organization can
build a relationship based on trust and expectations
be significant sources of competitive advantage.
with employees, and when the employee leaves
Therefore, employee retention is also an impor-
the firm, the bond is broken (Reichheld, 1993).
tant part of the relationship marketing equation
Employee engagement is considered as one
because employee retention is an antecedent of
of the key CRM implementation elements and
customer retention (Payne, Christopher, Clark,
employees play a significant role within the CRM & Peck, 2000).
processes and implementations. It is impossible
High employee turnover can be seen as a central
to achieve customer-focused organizations and
factor for the cycle of failure in service delivery.
processes without motivated and trained employ-
High employee turnover discourages firms from
ees. Recruiting and selecting the best employees,
investing in hiring, training and other commitment
training and motivating them and providing ef-
building activities, which in turn causes ineffective
fective leadership can be seen as the surest way to
employee performance. Moreover, high employee
enhance employees’ engagement and commitment
turnover negatively affects service quality and
to deliver an outstanding customer experience and
customer retention. As customer churn increases
increase the effectiveness of employee-customer
with the poor service, profitability of the company
interaction (Payne & Frow, 2006).
decreases and this leads to a reduction in the re-
sources of the company to invest in employees’
success (Schlesinger & Heskett, 1991). CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE
To sustain customer loyalty, a company must MANAGEMENT
understand the relationships between customer
retention and the other parts of the business and
Delivering outstanding customer service experi-
align four important aspects of the business: cus-
ence contributes to increase in revenue and profit-
tomers, product/service offering, employees, and
ability of an organization and as well as the entire
measurement systems (Reichheld, 1993). Firms
industry. Through better customer experience,
that cannot understand and quantify the economics
United States airline industry and wireless carriers
of retaining employees, may lose their profitabil-
could earn an additional $8.94 and $14.65 billion
ity because of their human resource policies that
in 2010, respectively (Harris Interactive, 2011). On 95
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
the other hand, enterprises estimate that if firms do
on social networks such as Twitter or Facebook
not offer a positive, consistent and brand relevant
and thousands of their friends and followers see
experience, their potential revenue loss would be
this post (Harris Interactive, 2011).
20% of their annual revenue (Oracle, 2013).
Rising expectation of customers and wide-
A poor service experience leads to customer
spread use of social media by customers to share
frustration and negative perceptions about the
their good and poor experience lead firms to focus
product as well as the company and causes loss of
on delivering exceptional customer experience
customer. SAS Institute Inc. and Peppers & Rogers
(Oracle, 2013). Moreover, companies are defi-
Group (2009) indicate that if enterprises don’t do
nitely making a push to improve their customer
customer experience management, they will go
service experience because Forrester (2010) re-
out of business. Customer experience has to be
port shows that customer experience correlates
the strategic priority of the company, especially
to loyalty. Aberdeen Group (2009) explores the
during the economic downturns. As indicated by
adoption of customer experience management and
Jerry Gregoire from Dell Computer “the customer
the study suggests improving customer retention
experience is the next competitive battleground”
(42%), customer satisfaction (33%) and increas-
(Brookes, 2013). Satisfying customer experience
ing cross-selling and up-selling (32%) as the top
is seen as an opportunity to influence customer
three drivers for companies to invest in customer
acquisition, customer retention, loyalty, and ad- experience management.
vocacy and enable firms to outperform and gain
With the globalization, competition and ad-
competitive advantage. Customer experience
vancements in internet technologies, power has
impacts future buying decisions of customers
shifted from companies to customers. The power
and whether or not they will recommend the firm
shift makes it difficult for companies to sustain
to their friends or family. It is important to note
differentiation based only on price or product.
that customer experience is the way to get more
Forrester’s the state of customer experience report
recommendations. Getting recommendation can
indicates that 90% of firms see customer experi-
be seen as outcome from a good experience.
ence as important and 80% of them consider to
Jeff Bezos, CEO of Amazon.com indicates
use customer experience as a form of differen-
that “If you do build a great experience, customers
tiation (Forrester, 2010). Differentiation through
tell each other about that. Word of mouth is very
outstanding customer service and experience is
powerful” (Zaibak, 2013). On the other hand, poor
much more essential in today’s competitive mar-
experience creates negative word of mouth. Dis-
kets because customers have lots of choices and
satisfied customers can tell their bad experiences
they can easily switch to another brand in case
to other people which can be dangerous for the
of dissatisfaction. Outstanding customer service
future of the firm. White house office of consumer
experience creates differentiation for the company
affairs report indicates that a dissatisfied customer
and allows the company to get competitive ad-
tells the disappointing experience approximately
vantage compared to its competitors. Exceptional
9-15 people. More dramatically 13% of dissatisfied
customer service experience fosters customer
customers tell their dissatisfaction more than 20
satisfaction and satisfied customers tend to stay
people (ClickSoftware, 2011). Harris Interactive
loyal, deepen their interactions, buy more and
(2011) Customer Experience Report supports the
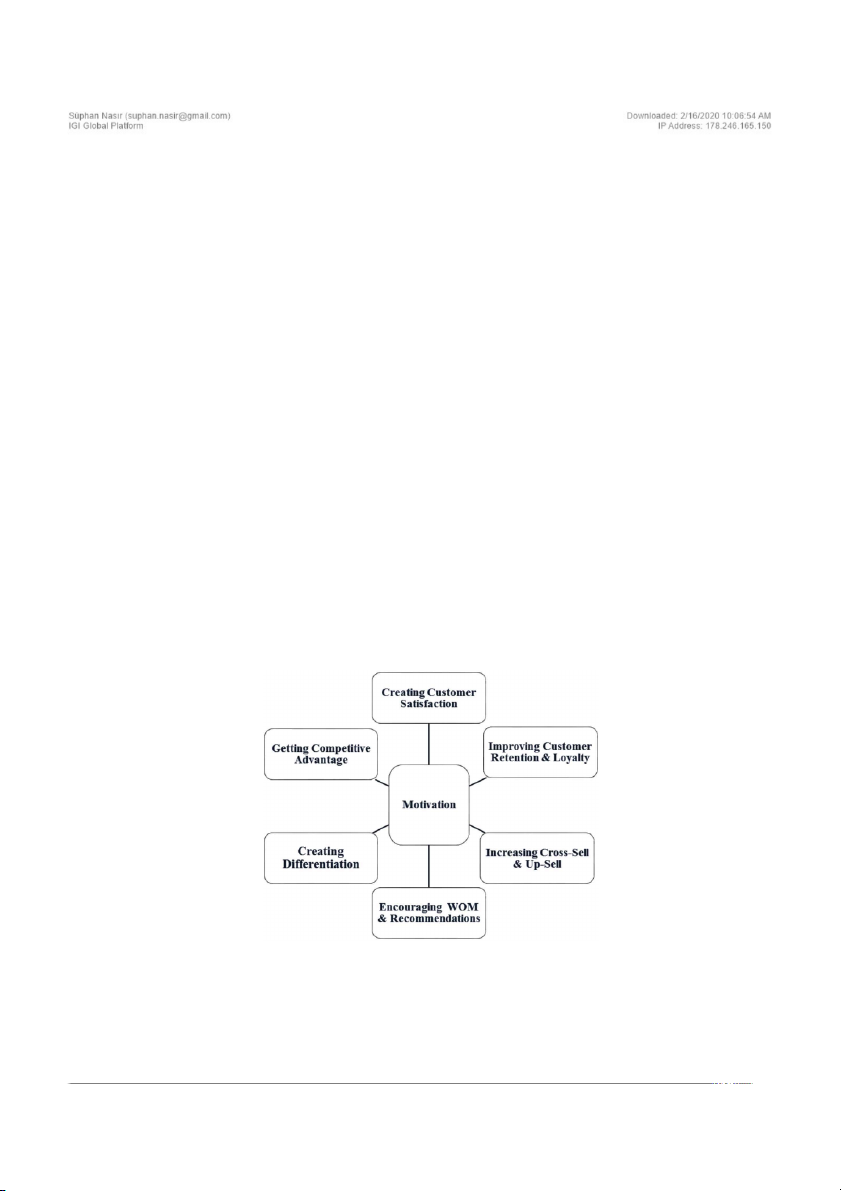
make positive word of mouth. Therefore, as can
fact that negative word of mouth turns into world
be seen in Figure 3, creating customer satisfaction,
of mouth with the use of internet technologies.
improving customer retention and loyalty, increas-
After a poor customer experience 26% of custom-
ing cross-sell and up-sell, encouraging positive
ers post a negative comment about the company
word of mouth, creating differentiation and getting 96
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
competitive advantage may be considered as the
A Lack of a strategy, process, and cooperation
main motivation for the enterprises to focus on
across the organization is seen as the obstacle
improving customer service experience.
to improve the company’s customer experience
In today’s competitive markets, customers are
(Forrester, 2010). Technology, people and pro-
becoming more demanding and revolting. Cus-
cesses of an organization may cause problems
tomers do not tolerance any failure. According the
in delivering outstanding customer experience.
Harris Interactive (2011) Customer Experience
Especially, technology is considered as the big-
Impact Report, 89% of customers quit the company
gest constraint for delivering superior customer
after a negative experience, and that is up from
experience. Limited technology and application
80% in 2007 and 68% in 2006 (Harris Interactive,
infrastructure, difficulty in tracking performance
2007). Customer experience can cause success or
measures and customer feedback, and lack of 360-
failure of a business. Therefore, 97% of executives
degree customer view across all touchpoint may
believe that delivering a superior customer service
create barriers for providing successful customer
experience is critical for their business success. experiences (Oracle, 2013).
Although, customer experience management is
Customer Experience Maturity Monitor report
top of mind for many companies, most companies
indicates that achieving excellence in the design
fail to fulfill even basic practices of customer ex-
and delivery of the customer experience requires
perience management. Forrester report indicates
capabilities and competencies that focus on deep-
that only 53% of companies measure customer
ening customer insight, strengthening customer in-
experience quality consistently, 40% of them track
teractions, and improving marketing performance.
what happens during customer interactions, %34
An enterprise’s customer experience maturity
of companies review customer experience metrics
impacts its likelihood of achieving competitive regularly (Burns, 2013).
advantage. In this report getting customer experi-
Figure 3. Main motivations for enterprises to improve customer service experience 97
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
ence excellence is seen as a journey that starts from
across the entire enterprise. Customer enthusiast
a product-focused business model and ends with a
enterprises have limited capabilities and customer
customer-centric business model that is designed
profiles contain only basic descriptive information,
to develop long-term profitable relationships with
and customer metrics. Customer activist level is
valuable customers. Companies progress in their
the next level of the customer experience maturity
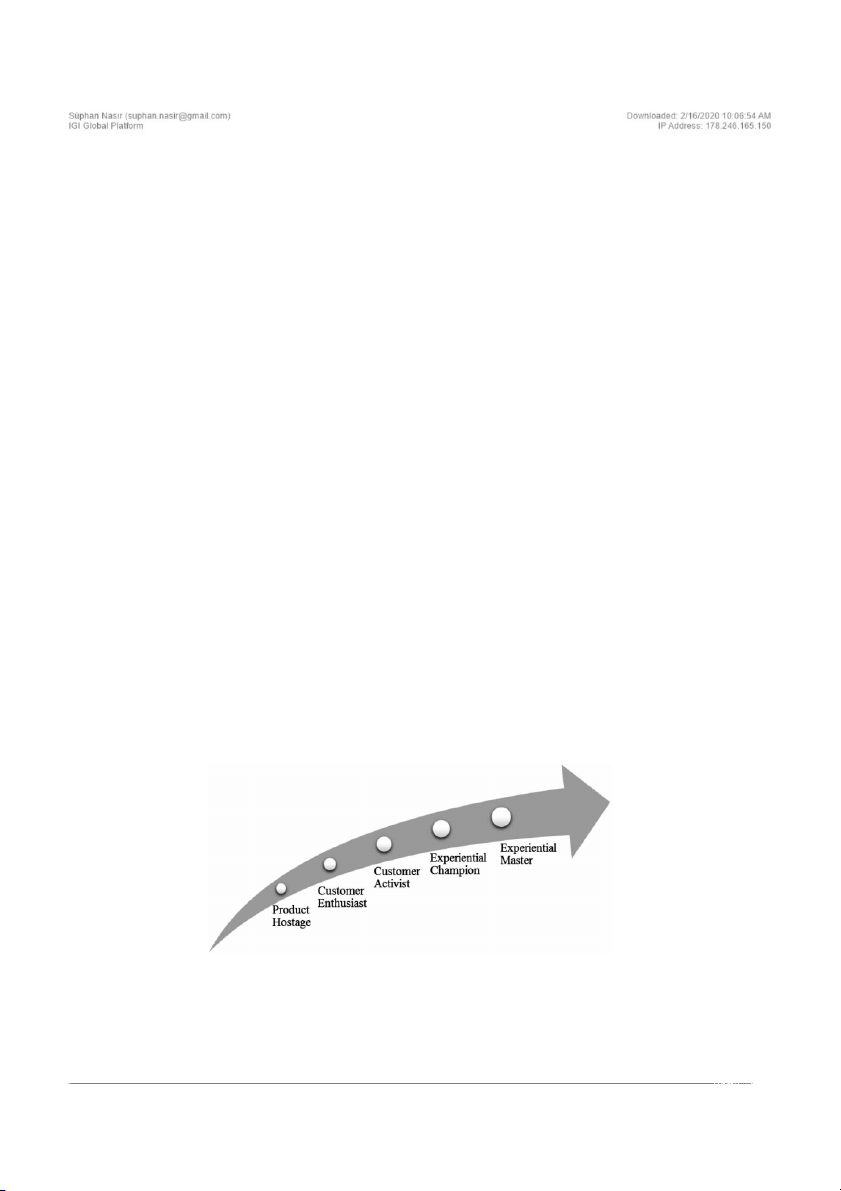
customer experience maturity through five stages,
model. At this stage insights are transformed into
based on how well they perform the encompassing
knowledge across channels. Customer activist en-
insight, interactions and improvement. In this cus-
terprises have the capabilities to link the customer
tomer experience excellence journey, enterprises
data across all touch-points and there is a holistic
progress along a continuum ranging from product
view of the customer across channel interactions
centricity to experiential mastery (see Figure 4).
throughout the enterprise. Enterprise is able to
Enterprises that are at the first level of customer
make analytic investigations to get both descrip-
experience maturity model are primarily product
tive and predictive customer insight. Companies
driven. Enterprises do not have the ability to take
at the fourth level, which is called experiential
action on customer experience strategy because
champion, have mature capability, strong customer
they have no capabilities to take action. Since,
data management processes and sophisticated
customer data is not collected and distributed
customer insight practices. Processes are opti-
across the organization, company is unable to
mized using quantitative techniques. Enterprises
consistently identify customers across touch-
establish customer centric strategy and customer
points and channels, and this lack of customer
insights are robust and predictive. At the fifth
knowledge prohibits the company from efficiently
and last level customer experience is a primary
and effectively treating different customers differ-
source of competitive advantage. Experiential
ently. This level is called product hostage. At the
master enterprises focus on continually improv-
second level, which is called customer enthusiast,
ing process performance; therefore at this stage
companies collect customer data across limited
continuous customer learning and improvement
touch-points and customer data is not prevalent
is automated and optimized. The findings of Cus-
Figure 4. Customer experience maturity model
Source: SAS Institute Inc., & Peppers & Rogers Group (2009). Customer experience maturity monitor: The state of customer
experience capabilities and competencies. Retrieved from http://www.sas.com/en_us/whitepapers/customer-experience-maturity- monitor-103820.html 98
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
tomer Experience Maturity Monitor report reveal
ally led and informed by their customers’ voices.
that most of the enterprises are still at the level 1
Aberdeen’s (2009) study indicates that in order
through 3 on the customer experience maturity
to improve customer satisfaction and customer
continuum. Since they are in the early stages of
experience enterprises have to:
execution of customer experience strategy, there
is a considerable need for improvement. The
Develop customer experience metrics to
findings also indicate that companies that are at
measure customer experience management
the high levels of customer experience maturity performance,
continuum and executing a strong customer experi-
Collect customer feedback across customer
ence strategy are more likely to outperform their touchpoint,
key competitors. Customer experience maturity
Aggregate disparate data to have a more
leads to competitive advantage. (SAS and Peppers holistic view of the customer, & Rogers Group, 2009).
Establish a centralized database that in-
To improve customer experience, companies
cludes a 360 degree view of the customer
have to consider the three “Ds” of customer ex-
and make it accessible to across the com-
perience that are (Allen, Reichheld, Hamilton, &
pany especially marketing, sales and ser- Markey, 2005): vices employees,
Use customer feedback and data to give
Designing the right offers and experiences strategic decisions,
for the right customers (Identify the most
Identify profitable customers and based on
important customers and understand their
their needs and preferences deliver them
needs and what they value. Then, design outstanding experiences, and
a unique proposition to meet their needs).
Make technology investments to enable
Delivering these propositions with an em-
successful customer experience manage-
phasis on cross-functional collaboration
(Treat every customer interaction as a valu-
able resource to get customer insight and
Figure 5. Three D’s of customer experience
create cross-functional teams to deliver a management
compelling experience based on the gath- ered customer insights).
Developing the organizational capabili-
ties to satisfy customers again and again
(Develop an institutional capability to
identify important customers, deliver an
experience tailored to their needs and de-
velop feedback loops. Align company’s
goals, measures, systems and organiza-
tional structure to become a customer-led organization).
Together, with implementing three “Ds” of cus-
tomer experience (see Figure 5), companies may
transform the company into one that is continu- 99
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
ment (e.g., database management, business
Across all channels and touch-points, custom-
intelligence, customer feedback manage-
ers experience the brand. Customers interact face
ment, web experience management, back-
to face with the brand as well as through Web,
front office integration systems, enterprise
call center, phone or email. They experientially resource planning)
evaluate the value of the relationship with the
brand based on their experiences during the
Enterprises may deliver superior customer
interactions and these experiences collectively
service experience by considering 4P’s of cus-
may strengthen relationships if the brand deliv-
tomer service (Leggett, 2012b). Leggett (2012b)
ers superior customer service and experience.
proposes 4P’s of customer service experience as
However, if the brand fails to satisfy customers,
pain, personalization, productivity, and proactiv-
the relationship between the brand and custom-
ity. Enterprises have to provide services without
ers weakens. Enterprises have to consider the
causing pain for the customer. Customers want
customer journey from an emotional perspective
effortless service from the touchpoints and com-
and create great customer experiences by focusing
munication channels. Customers also expect to
on the moments that matter most. Although, it is
receive an accurate, relevant, and complete answer
important to map customer journey for deliver-
to their queries upon first contact with a company.
ing outstanding customer experience, the results
According to the Forrester (2012) report 45% of
of state of customer experience management
US online adults prefer to abandon their online
report demonstrate that only %27 of companies
purchase if they cannot find a quick response
consistently map customer interactions from the
to their queries. Therefore, enterprises have to
customer’s perspective (Burns, 2013). Mapping
provide painless service and enable customers to
the customer journey starts with the identification
start a conversation on one channel and continue
of touchpoint (key moments) and thought points
it on another without having to repeat themselves.
(e.g., customer’s questions and doubts) that may
Personalization is another critical dimension of
have impact on customer experience. Then enter-
outstanding services. Customers are now expect-
prises have to discover tragic (what can go wrong)
ing to receive personalized services based on their
during the customer journey and try to focus on
needs, preferences, and past interaction history
fixing and preventing tragic results and creating
with the company. They do not want a one size
more magic for the customer (GDLN, 2011).
fits all service experience. Enterprises have to
Creating remarkable and amazing moments and
maintain productivity by considering the balance
exceeding customers’ expectations during the in-
between customer satisfaction and cost of service
teraction may lead delighted customers to tell their
experience. While enterprises delivering great
experiences to their friends and which in return
service experience that creates high customer
attract new customers as well as turn customers
satisfaction, it has to be provided at a cost that
into a lifelong customer. Figure 6 illustrates the
makes sense to the business. The last 4 P’s of
requirements for achieving excellence in customer
customer service is proactivity. Customers want
service experience. Creating customer keeping
to feel that the company is considering themselves
culture, establishing 360 degree customer view,
and they expect to receive proactive services and
analyzing big data, engaging customers through
solutions. Customers want to be notified before
social media and management of customer experi-
they expose to a problem. Enterprises have to focus
ence across multi-channels are the requirements
on potential problems that may annoy customers
for achieving excellence in customer service
and these problems have to be addressed before
experience and will be discussed below. they happen (Leggett, 2012b). 100
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
Figure 6. Reqirements for achieving excellence in customer service experience
Creating Customer Keeping Culture
Willingness is important for delivering great
customer service and experience. To work with
Creating customer centric organization and
right employees is the starting point of deliver-
culture is the most important business trends of
ing great service. First of all employees have to
today’s markets. Tjosvold (1993) emphasizes the
be willing to serve. Delivering service requires
importance of creating pull organization that is
some personality traits such as being active, out-
organized around the needs of customers and pulls
going, empathic, friendly, helpful, and gentle etc.
out the resources and staff of the entire organiza-
It is impossible to change someone’s personality.
tion to better serve customers and meet the needs
Therefore, to deliver great customer experience,
of customers. In contrast to the pull organizations,
enterprises have to hire right people who have
traditional push organizations are organized
these personality traits and then firms may teach
around the needs of production, push work from
them about their products, processes and culture.
one functional department to the next and rely
Harris Interactive (2011) Customer Experience
on management from top to bottom. However,
Impact Report indicates that 73% of customers
traditional push organizations can be a barrier to
want to deal with friendly customer service rep-
the creation of customer keeping vision. Creating
resentatives, 55% of customers want to access the
a pull organization, which focuses on creating a
information or help that they need easily, and 36%
customer-keeping vision and listening the voice
of them want personalized experiences.
of the customer, is essential for delivering great
Although, customer-centric culture is seen as
customer service experience. Tjosvold (1993)
key to customer experience management adoption,
states that to achieve customer keeping vision,
most of the companies fail to take steps to foster
teamwork is necessary in the organization. People
a customer-centric culture. The state of customer
in the organization have to work together in a
experience management 2013 report reveals the
structured and customer centric way to increase
fact that only 17% of companies consistently
the value of the customer experience.
screen employee candidates for customer-centric 101
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
values and specific skills needed to deliver the
engage with customers and consider the voice of
customer experience as part of the hiring process.
customers. Identifying the barriers to delivering a
Moreover, only 21% of companies consistently
great experience will help enterprises to improve
train employees to ensure delivery of the organi-
their processes. Enterprises should consider the
zation’s customer experience strategy and 25% of
improving customer experience as an ongoing
companies consistently use informal rewards to
process and continuously work to improve cus-
highlight ideal customer-centric behavior (Burns, tomer service experience.
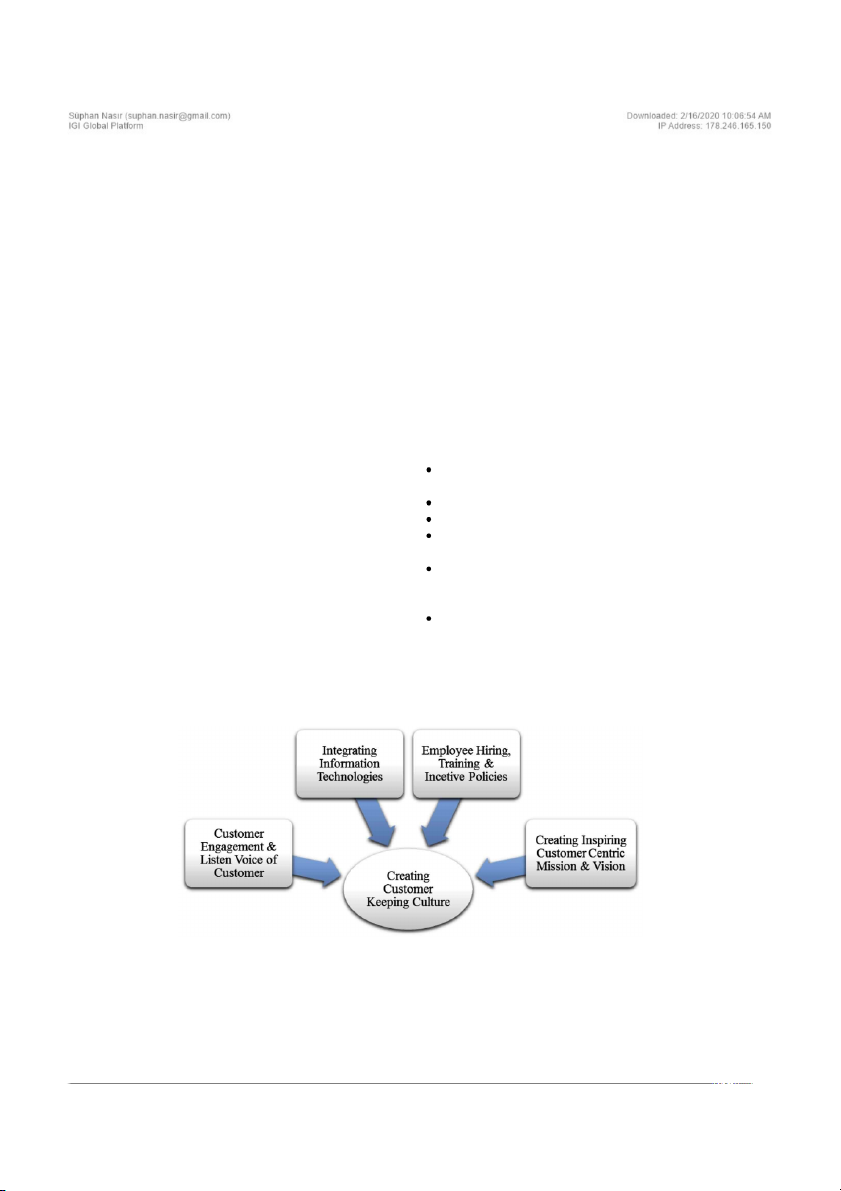
2013). Figure 7 illustrates the requirements for
Employee engagement (employees who are
creating customer keeping culture.
fully committed to the creation of customer
It is important to foster a customer-centric
experience) is considered as one of the core
culture by integrating information technologies in
competencies of an enterprise in delivering great
order to enable frontline employees’ easy access
customer experiences. Employee engagement can
to a complete view of each customer relation-
be sustained by (Temkin Group, 2013b):
ship. With the help of information technologies,
companies are able to provide superior, differenti-
Motivating employees with intrinsic
ated and competitive services across all channels, rewards,
touch point, and interactions in order to keep
Creating a mission that inspires employees,
customers loyal. Enterprises should also ensure
Developing simple service standards,
easy access to information and customer support
Making employee engagement as one of
and create personalized experiences. Enterprises the key metrics,
have to invest in customer relationships and care
Sharing comparative customer experi-
for their customers. As John Russell, President of
ence metrics with employees to evaluate
Harley-Davidson Europe, indicates “the more you performance,
engage with customers the clearer things become
Using employees as customer experience
and the easier it is to determine what you should
evangelists who identify opportunities for
be doing” (Brookes, 2013). In order to create a
improving customer experience based on
customer keeping culture, enterprises have to the voice of the customer,
Figure 7. Creating customer keeping culture 102
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
Encouraging employees to share their in-
on processes that enhance knowledge of and en- sights about customers,
gagement with customers” (Bernoff, 2011). Since,
Training employees for management of
in the age of the customer, the only sustainable key moments (touchpoint),
competitive advantage is considered as knowledge
Empowering employees to create memo-
of and engagement with customers, it is essential rable moments,
to leverage customer insights to personalize cus-
Building teams based on collective respon- tomer service experiences. sibility, and
Enterprises need 360 degree customer view
Encouraging two way communication
in order to enable frontline employees to ac- among employees.
cess right information across various channels
and deliver satisfying services. Since, failing to
Enterprises can foster customer keeping culture
meet customers’ growing expectations causes
in the organization by making customer service
disloyalty and defection, enterprises need to
everybody’s business. This means that every
understand each individual customers as well as
employee in the organization must be responsible
they need to understand customers as a whole
for delivering outstanding customer experience.
because without having a deeper insight about
Customer keeping culture requires a clear vision
customers’ sentiment, trends and changing needs,
and everyone in the organization should carry the
business strategies cannot be successful. Creating
responsibility of this vision. 80% of companies
a 360 degree view of customers enables customer
believe that they deliver a superior experience to
information to be kept in one place and supports
their customers. However, customers believe that
front-line employees in delivering service. 360
only 8% of companies really delivering superior
degree of customer insight can be gathered dur-
experience (Allen et al, 2005). Businesses fall
ing the marketing, sales, and service activities
short on delivering the experiences that customers
through various tools such as data warehouse,
want. Businesses that want to deliver outstand-
ERP, CRM, legacy data, e-Commerce, orders,
ing customer experience need to build a training
invoice, customer requests and complaints, and
program and incentives for employees in order to
through various channels such as email, phone,
encourage them to offer a great experience, update
face to face, web, mail, point of purchase, and
company core values to provide the most appli-
social networks, etc. Supply chains are expected
cable customer experience to all their customers,
to become a source of customer insight. As the
and implement specific technologies to improve
customer data increasingly determines companies’
customer service experience (Oracle, 2013).
future success, supply chain will begin to function
as data chains. Supply chain management today 360-Degree Customer Insight
focuses on getting the right product with the right
quantity at the right time to the place where people
Businesses as well as customers are entering a
want to buy it; but supply chains don’t provide
new era that Forrester calls the age of the cus-
enough information about customers to suppli-
tomer and in this new era customers have been
ers. Next-generation supply chains won’t just get
increasingly becoming powerful and enterprises
product on shelves but will deliver upstream data
have to reinvent themselves to systematically in
about customers to the suppliers. (Bernoff, 2011).
order to understand and serve customers better.
A 360 degree view in the company is necessity
In this new era, it is no longer sufficient to be
to understand what customers really want and in
simply customer-centric. Enterprises have to be
return deliver outstanding customer experience.
customer-obsessed which means that “focusing
Everyone involved in customer touchpoint should 103
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
contribute towards better understanding custom-
through social media channels can lead to up to
ers. Companies that are unresponsive to the real
15% increase in churn rate for existing customers.
voices of target customers cannot tailor their prod-
It is important to spend time to listen to customers
ucts and services to the needs of customers, and
across social channels. Tracking customers across
in order to be responsive to voice of customers,
social channels and listening what they are talk-
companies have to maintain effective customer
ing about the company allow the brand to turn a
feedback loops (Allen et al., 2005). Customer
customer’s negative experience into a positive
feedback contributes to the creation of outstanding
one. Early detection of a problem may prevent
customer experience and value creation process.
a potential disaster. If the company responds to
Taking customer feedback allows companies to
customer complaints on social channels in a proper
know what their customers really want, identify
and personal manner, they may prevent customer
the dissatisfaction of their customers and track how
churn and win its customers back.
customers’ needs are changing. Hence, employees
Listening posts, social networks and blogs can
must be encouraged to report customer concerns.
be used as tools for obtaining feedback as well as
Encouraging the customers to complain is also a
real time insight from customers. Listening social
way to learn about dissatisfaction of customers.
platforms is a significant source of getting feed-
If the customers do not complain, an enterprise
back and real-time insight. Companies have been
cannot know the problem and fix the problem. A
establishing social listening centers to track real-
company should measure customer satisfaction
time insights about their brands in order to find out
continuously and evaluate the results in order to
customer needs that change by the moment, track
improve its services and processes. It is important
competitors’ moves and word of mouth. Listening
to have feedback about customer defections. En-
customer conversations on social platforms can
terprises need to find out why customers defect.
be the early-warning system about the customer
Customer defection can be caused by poor service,
defection or troublesome changes that may happen
price or value. Identifying the defection reasons
(Bernoff, 2011). Harris Interactive (2007) report
enables firm to improve its products, services
argues that to exceed customer expectations, com- and processes.
panies need to know what customer expectations
Social media seen as a key driver for the future
are and take appropriate action. According to the
and customer voice has been becoming louder and
report 9% of consumers continue to do business
noticed with the help of social media. Although
with a company because it cares about customer
81% of enterprises believe that delivering an out-
feedback and takes action to improve service based
standing customer experience requires leveraging
on customer feedback. Therefore, it is important to
the social media effectively; 35% of firms do not
gather customer feedback across communication
have social media for customer service (Oracle,
channels and touchpoint and gathered customer
2013). Enterprises need to integrate social service
feedback have to be operationalized to increase
platform that helps customers in finding answers
the success of the enterprise. Enterprises have
that they can trust and social media has to be
to use customer feedback about their products,
used as a channel to identify customer service
services, and processes in order to improve their
problems. Many customers immediately post
quality of products and services.
their complaints to various social networks about
The results of state of customer experience
a poor customer experience and enterprises have
management report demonstrate that 60% of
to use social networks as problem identification
companies consistently gather customer feedback
and also resolution platform. According to Gartner
about customers’ interactions with the company;
(2012), failure to respond customers’ inquiries
however only 19% of companies consistently share 104
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
what they know about customers with employees
from general to contextualized customer experi-
at all levels of the company, 26% of companies
ences and they have to spend on experience maps
consistently gather input from employees about
for point-in-time relevance and touchpoint specific
their interactions with customers and 31% of com-
behavior analysis. Forrester report highlights the
panies consistently document customer insights to
importance of spending on persona creation, sales
make it easy for employees to understand (Burns,
and service scripts focused on customer value and
2013). Thus, enterprises need to focus not only
post-sales engagement in order to tie the selling
developing and improving customer feedback
effort to the buyer’s process. The report also ad-
loops, but also they consider to disseminate the
vices companies spend less on mass advertising
gathered feedback about the customers across
and reallocate their budgets to support content
the touchpoints and make it easy for employee creation (Cooperstein, 2013).
to access and understand. In addition to sharing
Enterprises require to create a multidimension-
customer insight with employees, an enterprise
al view of the customer to predict next actions of
has to encourage its employees to take feedback
the customer. Since, delivering pleasant customer
from customers and save this input to improve
service experience requires enterprises to under- its processes.
stand the needs and preferences of each customer
Achieving enterprise-level customer insight
and address them in a relevant and timely manner,
begins with data which is accurate, timely and
it is important to combine multi-channel customer
complete across channels. Enterprises need to
data with the enterprise’s internal data to estab-
manage the data in a manner that facilitates re-
lish cross-channel 360 degree customer insight.
porting and analysis. With the accurate, timely
Multidimensional customer data management
and complete data, enterprises give healthy and
platform can be maintained by integration of big
precise decisions and they shape and coordinate
data, predictive analytics, in-memory technologies
their customer interactions (SAS Institute Inc.
and data virtualization. These four key technolo-
and Peppers & Rogers Group, 2009). Although
gies enable enterprises to overcome limitations of
a 360-degree view of the customer can be use-
traditional data management platforms and benefit
ful to track customer history, enterprises need to
from real-time data integration, exploitation of
know more than just historical data about their
new data sources, and faster predictive customer
customers. They need to expand their analysis
insights (Yuhanna & Gualtieri, 2013).
to predict the next step that a customer may take
Empowering agents with multi-channel in-
and use predictive analysis to inform customers
sights improves business performance. Companies
about new products, make cross-selling offers,
that support customer representatives with detailed
serve customers better, and deliver real-time and
multi-channel customer data achieve decrease
more personal engagement (Cooperstein, 2013).
in agent overtime costs (8.9%), decrease in the
Forrester report indicates that enterprises can
average cost per customer contact (6.2%) and
maintain customer engagement by investing in
improve fist contact resolution rate (6.1%) year
real-time data sharing for actionable customer
over year. In addition, companies that extend
intelligence, contextualized customer experiences,
contact center information to non-contact center
tying selling effort to the buyer’s processes, and
staff in order to help them do their jobs better
content-led marketing. To obtain real time data,
achieve more than twice greater year over year
enterprises need to spend more on integrating
increase in annual company revenue compared to
customer data sources, building predictive algo-
companies where there is no information sharing
rithms, and developing multidimensional views of
among contact center and non-contact center staff
customers. Enterprises have to shift their spending (Minkara, 2012). 105
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
Enterprises can maintain customer connect-
Forrester report on competitive strategy in the
edness and deliver outstanding customer service
age of customer states that to become a customer-
experience by finding out what customers want,
obsessed enterprise, enterprises have to transform
helping customers to achieve their goals, measur-
the enterprise from one of slow-moving silos into
ing the value of key customer experience metrics,
an agile evolving organization that is able to adapt
releasing customer insights from unstructured data
quickly to the changing needs of customers. It is
(e.g., open ended comments, call center conversa-
believed that companies that focus on embracing
tions, emails from customers), reviewing trends
business technologies, which enable companies to
and insights from across all customer feedback
improve customer relationships and experience,
channels, using online advisory boards to gather
will be more agile to changes and better positioned
customer feedback, sharing the customer insight
in the future (Cooperstein, 2013). Therefore, it is
within the organization, predicting and preempting
becoming necessary for an enterprise to integrate
obstacles to customer value, developing customer
new technologies to gather, manage and store
journey maps in order to identify gaps and op-
data. With these analytical insights enterprises
portunities of customers’ experience with the
can better anticipate and proactively respond to
enterprise, analyzing the customers’ unhappiness,
the needs of customers (SAS Institute Inc., 2008).
discovering what makes customers loyal, setting
Ensuring data quality and creating a single and
service targets based on customer expectations,
comprehensive view of each customer are also
training employees for the management of key
essential for effective customer data management.
moments, developing simple service standards,
Enterprises that want to deliver excellent cus-
communicating courteously with customer, and
tomer experience through big data analytics need to
listening customers (Temkin, 2013b). Briefly, the
also focus on customer data quality management.
ability of integration of customer feedback and
For delivering outstanding customer experiences,
customer insight throughout the organization is
enterprises need to (Rogers & Gilleland, 2009):
considered as one of the customer experience core
competencies that help an enterprise to deliver
Have information on each customer’s prod-
outstanding customer experiences. uct ownership and usage.
Establish a complete and integrated view Big Data Analytics
of customers’ contact history.
Create a complete and integrated view of
Enterprises deliver poor experience if they do not
each customer across multiple channels
understand customers and the purpose of being
with a view of the entire customer history.
in the business. Understanding what customers
Capture the customers’ expressed needs
want is the first step in creating superior customer
during live customer interaction.
service experiences. Customer insight is a primary
Update customer profiles continuously to
source of competitive advantage and if customer
reflect all customer activity as well as out-
data is managed properly, it can affect the success bound and inbound contact.
of an enterprise. Since the data volumes have been
Make current view of necessary customer
exploding in recent years, enterprises need to man-
information available to all touch-points.
age data effectively. 4 out of 5 companies have
Measure and report customer attitudes and
enough customer data but they do not know how perceptions.
to use it effectively; so it is important to leverage
Monitor changes in customer attitudes or
the right analytical tools (Obrien, 2014).
perceptions in order to proactively identify
and respond potential problems, and 106
Customer Service in Digital Era and Role of Internal Markets
Link customer attitudes and perceptions to
and unstructured data that come from variety of
customer behavior to determine drivers of
sources in order to find out useful information behavior.
for decision making. Analysis of big data allows
enterprises to discover what customers really
Enterprises gather information about their
want, increase their sales and efficiency, close
customers from traditional (e.g. point of sale and
more deals, and improve operations and customer
call centers) and also digital (e.g. online customer
service experience. As can be seen from Box 1,
services) channels in order to understand what
big data technologies allow companies to decrease
customers want and predict what customers can
customer churn. Big data has been changing the
do in the future. The data come from these chan-
way companies manage their relationship with
nels can be unstructured and also multi-structured.
customers and influencing the customer experi-
Big data is the reality of today’s businesses and
ence. Big data is seen as one of the major trends
structured and unstructured data flow in organi-
in delivering great customer experience. Big data
zation on a daily basis. If enterprises manage the
and CRM analytics enable enterprises to find cor-
data well, it can provide powerful insights about
relations, which allow them to identify customer
the customers. Therefore, enterprises are trying to
patterns and based on the knowledge enterprises
find out insights from their data. Since customer
can improve customer engagement by tailoring
insight is the new kind of power, enterprises have
the experience for them (Fonolo, 2013).
to leverage the power of big data in their business
As enterprises realize that customer experience
and extract big knowledge from big data. Since
can be enhanced by predicting behavior of custom-
the big data is defined as high volume (amount
ers, popularity of predictive analytics such as CRM
of data), high velocity (speed of data in and out)
and big data analytics has been increasing. The
and high variety (data kinds and sources) of infor-
ability to predict is an essential element for cre-
mation, it requires new forms of data processing
ating compelling customer experiences, because (Beyer and Laney, 2012).
anticipating customer needs and behaviors allows
Big data analytics helps enterprises to collect,
a company to proactively engage customers with
organize and analyze large amount of structured
customized interactions that are both relevant and
Box 1. T-Mobile USA integrates big data technologies to decrease customer churn
T-Mobile USA integrates big data technologies and this causes decrease in customer churn. Telecom organizations collect massive
amounts of data about their customers and if they have millions of customers, this generates serious big data. However, many of the
telecom companies are unable to manage and use all this big data. T-Mobile USA, which has approximately 33 million customers,
collects massive amounts of data from various channels and puts all data for its use. In order to fully use all of its data, T-Mobile USA
combines subscriber and network data together among multiple databases. It uses several tools to store all the data and analyze it. It
confronts with the customer churn by using a tribal customer model. This model is based on the fact that there are people who have
high influence on others due to their large social network and if one of these customers switches to another telecom provider, it causes
a domino effect and leads others in his or her network to switch. T-Mobile USA calculates the customer life time value for each of these
customers by using multiple databases and this allows T-Mobile USA to determine to most valuable customers. To expect the customer
churn of a customer, T-Mobile USA uses billing, drop call and sentiment analysis. T-Mobile USA combines these different analyses
into an integrated singlenview for customer care. Then it provides this integrated single-view for customer system to agents. This system
enables agents to see key indicators about the customers including the customer lifetime value during the interaction. By using this
system agents can offer customer-specific offers. This management of big data and customized customer-centric approach causes a drop
in monthly customer churn. While the number of lost customers almost 100.000 in the first quarter of 2011, with the big data analysis the
company brings it down to 50.000 lost customers in the second quarter of 2011. With the help of its big data strategy, T-Mobile USA cuts
down its churn rates by 50% in just one quarter.
Source: Big Data Startups (2013). T-Mobile USA cuts downs churn rate by 50% with big data. Retrieved November 23, 2013, from http://
www.bigdata-startups.com/BigData-startup/t-mobile-usa-cuts-downs-churn-rate-with-big-data/ 107




