















Preview text:
Data W a Ware r house house and and OLAP Week 5 1 Midt i erm dt I • Friday, March 4 • Scope
– Homework assignments 1 – 4 – Open book Team Team Homew o Homew rk o A ssig A n ssig ment n #7 • Read pp. 121 – 139, 146 – 150 of h t e text b ook.
• Do Examples 3.8, 3.10 and Exercise 3.4 (b) and (c). Prepare for the re s re u s l u ts t of the homew o homew rk assignmen t assignmen . t • Due date
– beginning of the lecture on Friday March11th. Top To ic i s
• Definition of data warehouse
• Multidimensional data model
• Data warehouse architecture
• From data warehousing to data mining What is Data W a W re r house? (1) (1)
• A data warehouse is a repository of information
collected from multiple sources, stored under a
unified schema, and that usually resides at a single site
• A data warehouse is a semantically consistent data
store that serves as a physical implementation of a
decision support data model and stores the
information on which an enterprise need to make strategic decisions What is Data W a W re r house? (2) • Dat Da a t w a w rehouses r pr ovide pr on‐ on line analytical analytic
processing (OLAP) tools for the interactive analysis of
multidimensional data of varied granularities, which
facilitate effective data generalization and data mining
• Many other data mining functions, such as
association, classification, prediction, and clustering, can be i t n egr t a d e with OLAP oper ti a ons to h en ance
interactive mining of knowledge at multiple levels of abs ab t s r t a r ction What is Data W a W re r house? (3)
• A decision support database that is maintained
separately from the organization’s operational database
• “A data warehouse is a subject‐oriented, integrated,
time‐variant, and nonvolatile collection of data in
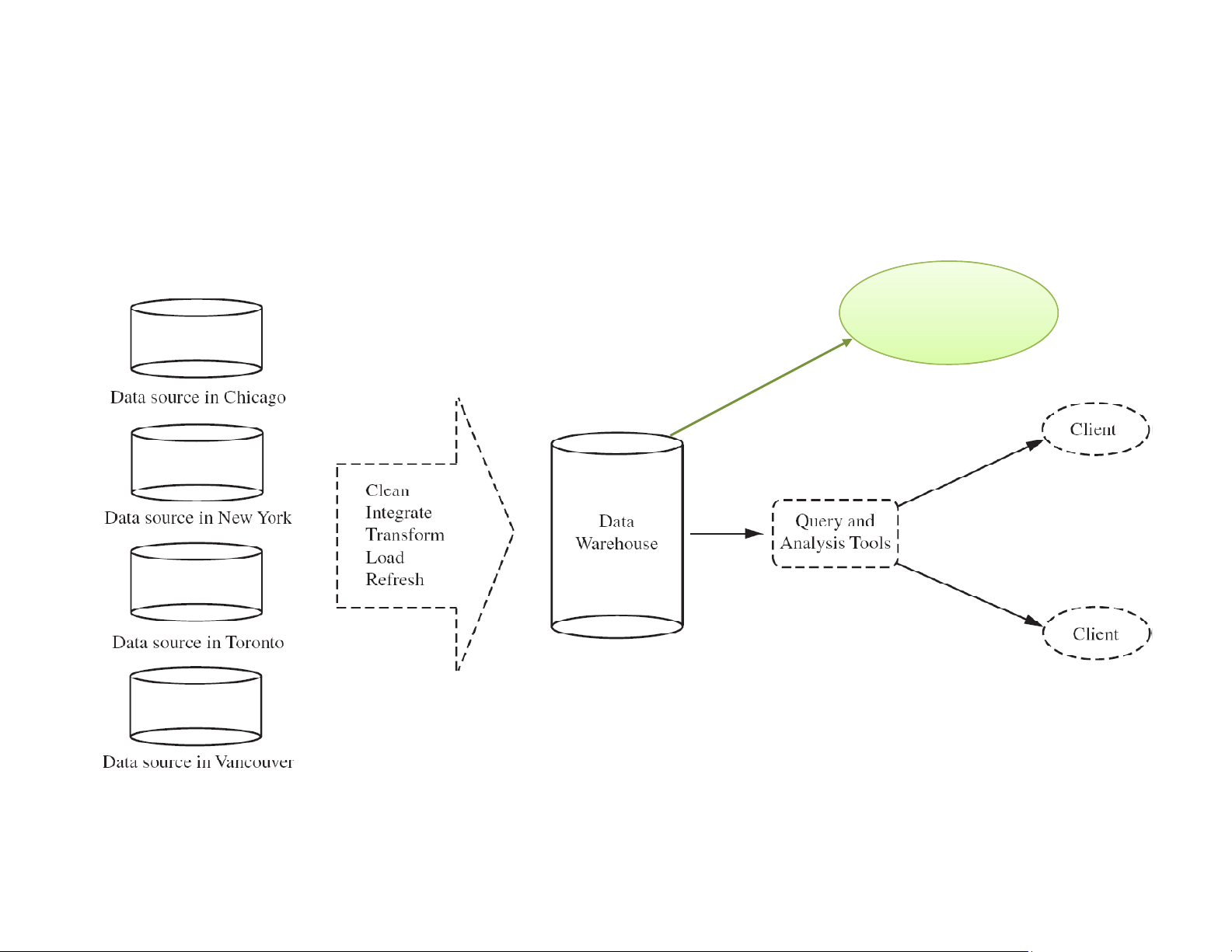
support of management’s decision‐making process [Inm96].”—W. H. Inmon Data Warehouse Framework data mining
Figure 1.7 Typical framework of a data warehouse for AllElectronics 8 Data Warehouse is Subj bject-Oriented
• Organized around major subjects, such as customer, product, sales, etc.
• Focusing on the modeling and analysis of data for
decision makers, not on daily operations or transaction processing
• Provide a simple and concise view around particular
subject issues by excluding data that are not useful in the decision support process Data Warehouse is I t n egr t a ed
• Constructed by integrating multiple, heterogeneous data sources sour
– relational databases, flat files, on‐line transaction records • Dat Da a t cleaning and da t da a t in t in e t gr e a gr t a ion t te t chniques e are ar applied .
– Ensure consistency in naming conventions, encoding
structures, attribute measures, etc. among different data sources
• E.g., Hotel price: currency, tax, breakfast covered, etc. D t a W a ar h e ouse is Time V i ar t an
• The time horizon for the data warehouse is significantly longer
g than that of operational syste y ms
– Operational database: current value data
– Data warehouse data: provide information from a
historical perspective (e.g., past 5‐10 years)
• Every key structure in the data warehouse
– Contains an element of time, explicitly or implicitly D t a W a ar h e ouse is Nonv l o t a il tile
• A physically separate store of data transformed from the operational environment
• Operational update of data does not occur in the data warehouse environment
– Does not require transaction processing, recovery, and concurrency control mechanisms – Requires only t wo oper ti a ons i n d t a a i access ng:
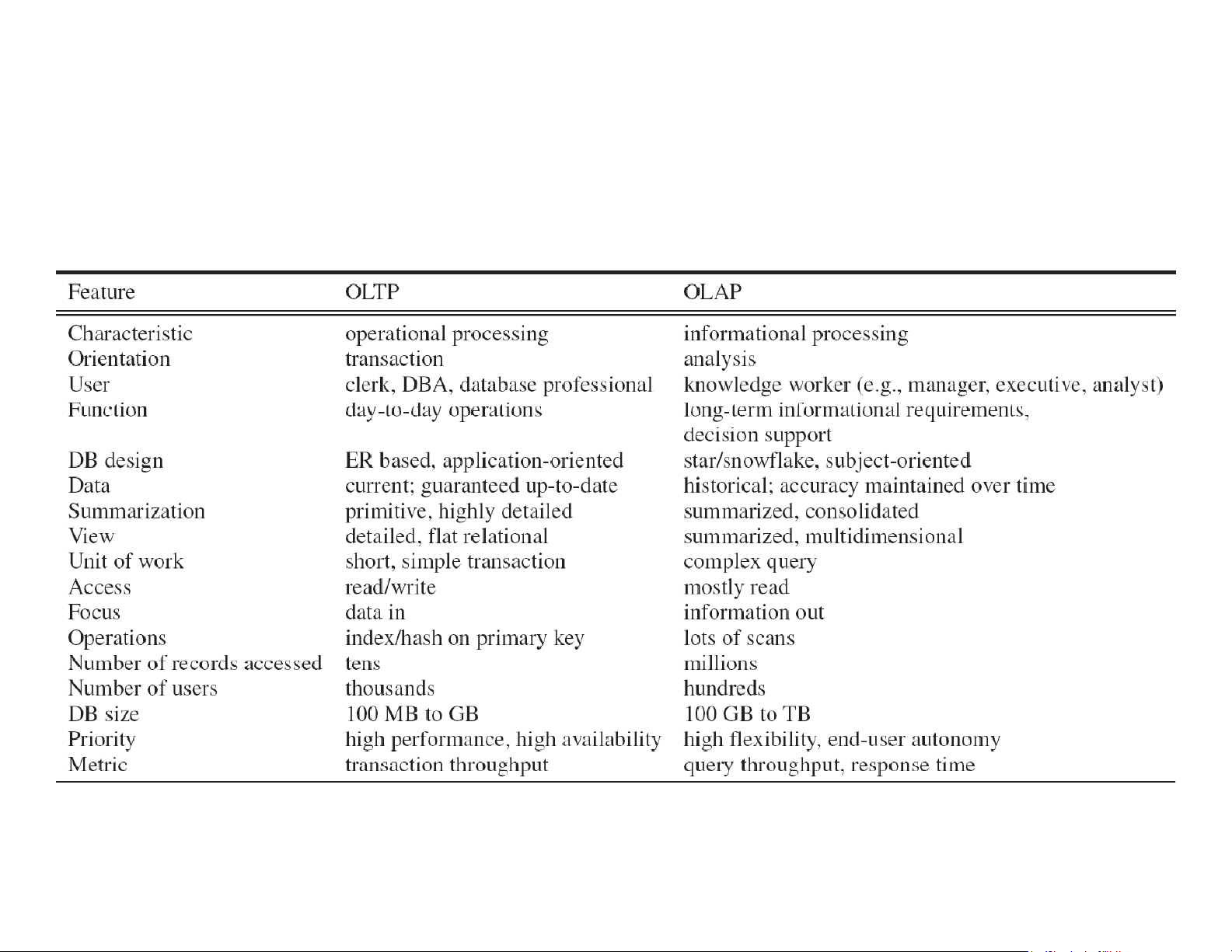
• initial loading of data and access of data OLTP vs OLAP .
Table 3.1 Comparison between OLTP and OLAP 13
Why Separate is Data Warehouse Needed? (1)
• Why not perform on‐line analytical processing directly on operational databases dat inst ins ead t of
spending additional time
and resources to construct a separate data warehouse?
Why Separate is Data Warehouse N d ee d e ? d? ( ) 2 • High g performance for both syste y ms
– DBMS— tuned for OLTP: searching for particular records,
indexing, hashing, concurrency control, recovery
– Warehouse—tuned for OLAP: complex OLAP queries,
multidimensional view, consolidation (summarization and aggreg ti a on) Top To ic i s
• Definition of data warehouse
• Multidimensional data model
• Data warehouse architecture
• From data warehousing to data mining
From Tables and Spreadsheets to Dat C a ubes • A dat da a t w a w rehouse r is based on a multidimensional data model • This model vie w vie s w da t da a t in the for fo m of a da t da a t cube
• A data cube allows data to be modeled and viewed in multiple dimensions
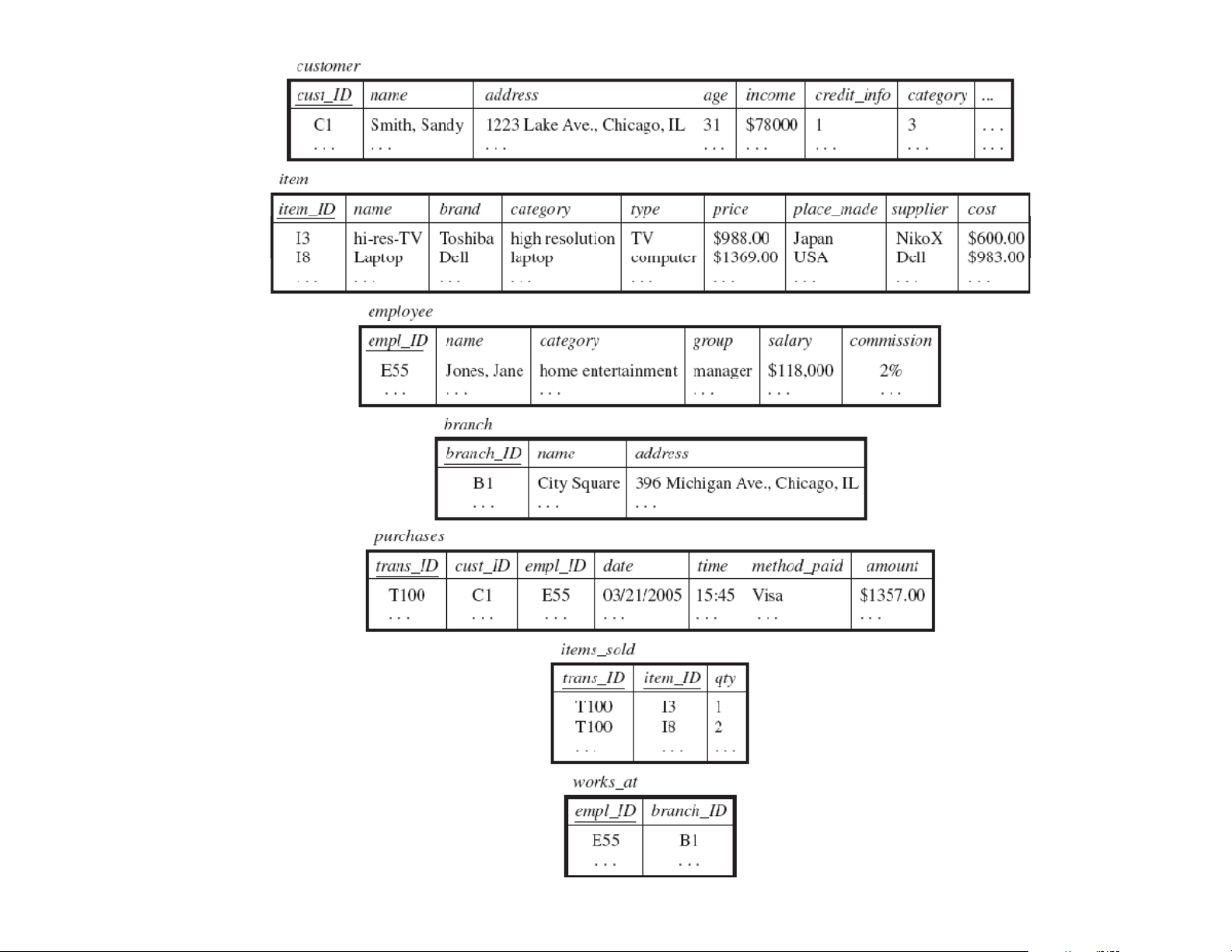
From Tables and Spreadsheets to Data Cub ( es 1) (1) • A da t da a t cube is de fined de by fact c s t and dimensions
– Facts are data which data warehouse focus on • Fact c ta bl b es e co ntain numeric measur es measur (such as
dollars_sold) and keys to each of the related dimension tables
– Dimensions are perspectives with respect to fact
• Dimension tables describe the dimension with
attributes. For example, item (item_name, brand, type), or time(day time(da , w eek w , mont mon h, quart er quart , yea ye r) r fro Fig m ure 1.6. a relati Fr o a nal data gments b o ase for f relations Al lElectroni c s 19 From Tables and Spreadsheets to D Data C Cubes (2) (2) dimensions Facts (numerical measures)
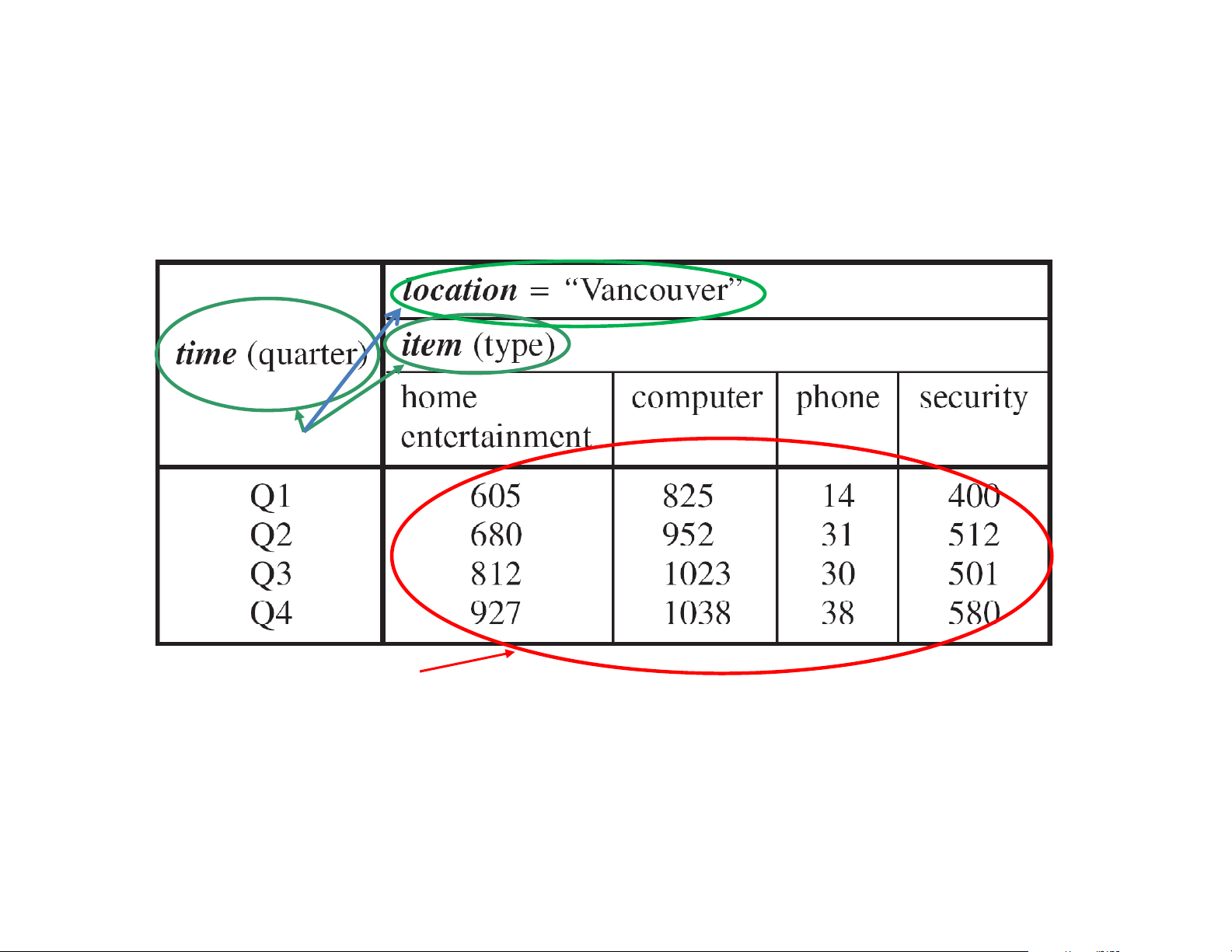
Table 3.2 A 2-D view of sales data for AllElectronics according to the di i mens ons time and it d em , h w ere t the h sal les are f from b branches l located in d i
the city of Vancouver. The measure displayed is dollar_sold (in thousands). 20




