






Preview text:
TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC BÁCH KHOA
KHOA: ĐIỆN TỬ-VIỄN THÔNG
BỘ MÔN: KỸ THUẬT VIỄN THÔNG ĐỀ THI CUỐI KÌ
Tên học phần: Anh văn chuyên ngành. Mã học phần: Số tín chỉ: 03
Phương pháp đánh giá (*): Trắc nghiệm và Tự luận Thời gian làm bài:75 phút Đề: 01
Họ và tên: …………………………………….MSV: ............................. STT:……
Part 1: Read the following passages and choose the correct answer Passage 1
Telecommunication is defined as the science and technology of communication over a far distance.
The ability to transmit information quickly, accurately, and efficiently has always been one of the
main focuses driving human innovation. From prehistoric man with their fire signal to the fifth-
generation technology providing up to 10 gigabits per second, a never-ending improvement in
telecommunication can be seen together with the development of modern civilization. Here are
some take-aways about the electronic telecommunication history. In 1838, Samuel B. Morse could
send a message by letting electricity run through a wire and holding or releasing a button, which
is called telegraph. In 1876, Alexander Graham Bell discovered how to transmit speech
electrically, and then invented the telephone. In 1893, radio wave was successfully transmitted for
the first time. In 1915, the first long- distance call (coast to coast call) was made by Alexander
Graham Bell and his assistants, making long- distance communication over the country become
real. Together with the conventional telecommunication services based on the telephone and
telegraph systems, data and video communication are being installed and operated thanks to Pulse
Code Modulation (PCM) method, which provided that digital transmission is not only more
economical but also more reliable than its counterpart, analog transmission.
1. Telecommunication means:
a. signal transmitted over the ocean
b. communication through continents c. a & b are correct d. a & b are wrong
2. What drives human innovation?
a. send and receive information rapidly b. run quickly and accurately c. a & b are correct d. a & b are wrong
3. What is 5G bit-rate? a. 10 gigabytes per second b. 10 gigabits per minute c. a & b are correct d. a & b are wrong
4. What does “take-away” in the passage mean? a. main message b. take something away c. a & b are correct d. a & b are wrong 5. PCM is a method to
a. convert signals from analog to digital
b. convert signals from digital to analog c. a & b are correct d. a & b are wrong
6. What is the meaning of “provided that”? a. ensured that b. made sure that c. a & b are correct d. a & b are wrong
7. What is the antonym of “economical”? a. wasteful b. waste c. a & b are correct d. a & b are wrong
8. Who invented the telegraph? a. Alexander Graham Bell b. Samuel B. Morse
c. Samuel B. Morse’s assistants d. a & b are wrong
9. Who invented the telephone? a. Alexander Graham Bell b. Samuel B. Morse
c. Samuel B. Morse’s assistants d. a &b are wrong
10. What happened in 1838?
a. Morse could send a message electrically
b. Morse could transmit electricity
c. Morse could send speech electrically d. a & b are wrong Passage 2:
The resistor is a fundamental electrical component in physical circuits as well as equivalent
circuits. It was the earliest electrical attribute - identified shortly after electrical current was
discovered. All materials exhibit some form of resistance, some are greater than others, eg. copper,
aluminum and gold have low resistance; carbon and tungsten have medium resistance, and then
ceramics, and air have high resistance. The earliest resistors were constructed from metal
substances although, in all fairness, carbon may well have been used in the first resistor
implementation. This substance formed the filament of the first early incandescent light bulb said
to have been invented by Thomas Edison recorded in the USA patent of 1879. Unlike metals,
carbon has a relatively high resistivity and can also be formed into thin films suitable for deposition
on an insulating material such as ceramic. Further, carbon particles can be mixed with insulating
materials (e.g. clay) to further increase its resistivity. Carbon composition resistors were
commonly used in the 1960s and earlier, but are not popular for general use now as other types
have better specifications, such as tolerance, voltage dependence, and stress. In 1960, Felix
Zandman and Sidney J. Stein presented a development of resistor film of very high stability. The
primary resistance element of a foil resistor is a chromium nickel alloy foil several micrometers
thick. Since their introduction in the 1960s, foil resistors have had the best precision and stability of any resistor available.
1. What does resistance mean?
a. The capacity of materials to impede the flow of electric charge
b. The capacity of materials to resist the flow of electric charge c. a and b are correct d. None is correct
2. Which material is a poor conductor? a. Ceramics b. Gold c. Carbon d. None is correct
3. Air is ............... conductive material. a. Low b. High c. Medium d. None is correct
4. Which material makes up the earliest resistor? a. Metal b. Carbon c. Filament d. None is correct
5. Which substance formed the filament of the first early incandescent light bulb? a. Metal b. Carbon c. a and b are correct d. None is correct
6. What does ‘the insulating material’ mean?
a. a material that supports the transmission of heat or sound or electricity
b. a material that reduces the transmission of heat or sound or electricity c. a and b are correct d. None is correct
7. Carbon composition resistors were commonly used in the 1960s and earlier, but are
not in use anymore because of their limitations. a. True b. False
8. What are the limitations of a carbon composition resistor?
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
9. Which is the most stable and precise resistor nowadays?
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
10. What is the main resistance element of foil resistors?
………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………… Passage 3:
Face recognition systems can be used to identify people in photos, video, or in real-time. Face
recognition systems use computer algorithms to pick out specific, distinctive details about a
person’s face. These details, such as distance between the eyes or shape of the chin, are then
converted into a mathematical representation and compared to data on other faces collected in a
face recognition database. Face recognition systems vary in their ability to identify people under
challenging conditions such as poor lighting, low quality image resolution, and suboptimal angle of view.
When it comes to errors, there are two key concepts to understand:
(1) A “false negative” is when the face recognition system fails to match a person’s face to an
image that is, in fact, contained in a database. In other words, the system will erroneously return
an unknown identity in response to a query.
(2) A “false positive” is when the face recognition system does match a person’s face to an image
in a database, but that match is actually incorrect. This is when a police officer submits an image
of “Mai,” but the system erroneously tells the officer that the photo is of “Thảo.”
When researching a face recognition system, it is important to look closely at the “false positive”
rate and the “false negative” rate, since there is almost always a trade-off. For example, if you are
using face recognition to unlock your phone, it is better if the system fails to identify you a few
times (false negative) than it is for the system to misidentify other people as you and to let those
people unlock your phone (false positive).
One of the benefits of facial recognition systems centers on its application in biometrics. It can be
used as a part of identification and access control systems in organizations, as well as personal
devices. The system can also be used to enable automated image recognition capabilities. Through
machine learning and Big Data analytics, social networking sites such as Facebook can recognize
photos of its users and allow automated linking or tagging to individual user profiles. Another
advantage of facial recognition systems involves its application in law enforcement and security
systems. However, facial recognition systems are less reliable and efficient than other biometric
systems such as fingerprints. Factors such as illumination, expression, and image or video quality,
as well as software and hardware capabilities, can affect the performance of the system.
1. What is/are specific, distinctive detail(s) about a person’s face? a. Distance between eyes b. Shape of the chin c. a and b are correct d. None is correct
2. What is/are the challenging condition(s) the face recognition systems need to deal with? a. Poor lighting
b. High quality image resolution c. Optimal angle of view. d. None is correct
3. A “false negative” is
a. When the face recognition system returns a match, but the match is not correct.
b. When the face recognition system fails to match a person’s face to an image which is contained in the database.
c. When the face recognition system can match a query to one image in the database. d. None is correct
4. What is the meaning of “sub-optimal”? a. very good
b. below the highest level or standard c. not optimal d. None is correct
5. Choose ONE correct statement.
a. We can’t use face recognition system to identify people in real-time
b. Face recognition systems use mathematics to extract details of a person’s face.
c. It is better if the system has more false negative than false positive
d. It is important to look closely at one key concept of the recognition error
6. When you use face recognition to unlock your phone, what do you call when the
system allows other people to unlock your phone? a. A false negative b. A false positive c. a and b are correct d. None is correct
7. What is/are the benefit(s) of facial recognition systems?
a. Law enforcement and security systems
b. play as a part of identification and access control systems.
c. Automated linking and tagging d. a, b and c are correct.
8. The synonym of “recognition” is a. Verification b. Authentication c. Identification d. None is correct
9. Give an example of using machine learning and big data analytics in social networking sites.
……………………………………………………………………………………….……..
……………………………………………………………………………………………..
10. Why is face recognition less reliable and efficient than other biometric systems?
a. Because its performance is affected by many factors.
b. Because fingerprint recognition system is developed and improved faster than face recognition system
c. Because its performance isn’t affected by hardware capabilities
d. We don’t need to have constraints on the input image/video of this system.
Part 2: Filling the blank
Photovoltaic Electrical
Semiconductor Panels Grid Systems Solar Conductive Devices
What is …………. (PV) technology and how does it work? PV materials and devices convert
sunlight into ............ ........ energy. A single PV device is known as a cell. These cells are made of
different ................... materials and are often less than the thickness of four human hairs. To boost
the power output of PV cells, they are connected together in chains to form larger units known as
modules or ............ Modules can be used individually, or several can be connected to form arrays.
One or more arrays is then connected to the electrical .................. as part of a complete PV system.
Because of this modular structure, PV systems can be built to meet almost any electric power need, small or large. Part 3: Translation
Translate the following sentences into Vietnamese
1. In a typical telecommunications system, the transmission line can be free space, or various kinds of cable.
……………………………………………………………………………………….……………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2. A band-gap energy is the amount of energy that a valence electron must have in order to jump
from the valence band to the conduction band.
…………………………………………………………………………………….…………….…
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Translate the following sentences into English
1. Trong biểu đồ biểu diễn số ứng viên nam và nữ trong các công việc liên quan đến trí tuệ nhân
tạo, lĩnh vực này được chia thành 6 mảng con: Học máy, xử lý ngôn ngữ tự nhiên, học sâu, robot
học, nhận dạng tiếng nói và thị giác máy tính.
……………………………………………………………………………………….………….…
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
2. Môi trường truyền có thể là không gian tự do, hoặc thông tin được định hướng từ máy phát đến
máy thu thông qua các đường dây truyền dẫn như là cáp quang, cáp đồng, mạch hai dây, mạch bốn dây.
……………………………………………………………………………………….……………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Part 4: Writing Task
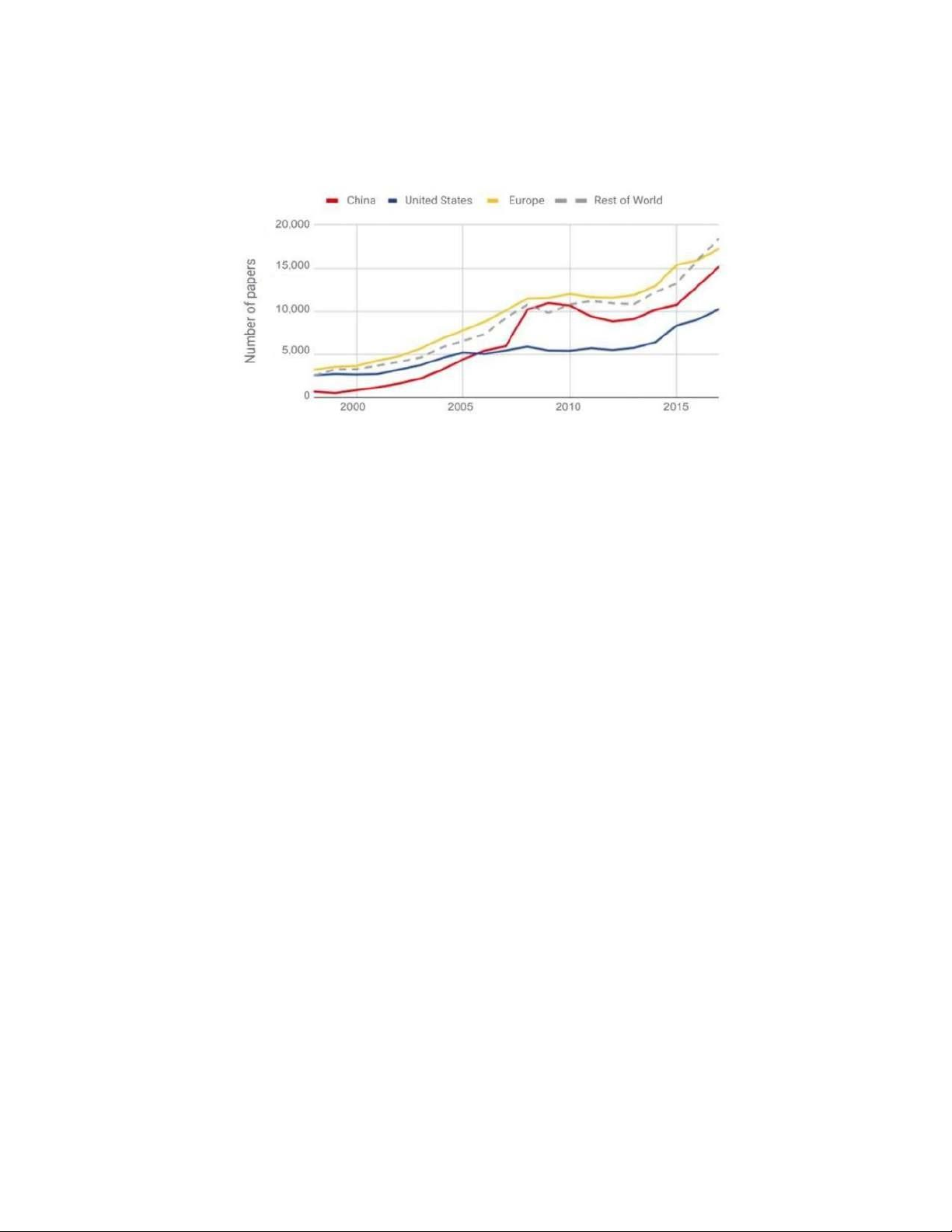
Describe the following graph (at least 150 words and you need to have an opening, an overview, 2 body paragraphs).




