




Preview text:
Phan Hữu Thịnh -20CNATMCLC01 Câu hỏi Syntax
Câu 1: The functions of Nominal Clause or Noun Equivalents: [+] subject (S)
That he loves her make me sad (1) What you did is well-done (2)
Where she lives is a secret (3)
- Ở (1) ta thấy “ that he loves her ’’ cũng là mệnh đề phụ trong mệnh đề chính (1)
với chức năng Chủ ngữ [+] Object of Verb
He knows what he should do to improve his English skills.(1)
Could you tell me where i can buy a bag (2)
- ở (1) t thấy mệnh đề phụ là “what...’’ đứng sau động từ “ know” cho nên là tân
ngữ bổ nghĩa thêm cho động từ .Ở (2) cũng tương tự như mệnh đề danh ngữ ở đây
đóng vai trò Object direct còn me là Object indirect đề bổ nghĩa cho động từ “tell” [+] Object of Preposition
I’m interested in what my teacher is speaking (1)
My mom was excited about how i can cook a good dish for her birthday (2)
- Ở (1) mệnh đề phụ danh ngữ bổ ngữ cho giới từ “in” [+] Subject Complement
The topic is what we should do to protect the environment. (1)
What makes me happy is that you pass your exam (2)
-Ở (1) thấy mệnh danh ngữ bổ ngữ cho chủ ngữ “topic” chớ ko phải tân ngữ ( vì is
là verb intransitive nên ko có tân ngữ , chỉ có bổ ngữ) , tương tự (2) mệnh đề danh
ngữ bổ nghĩa cho “what makes me happy”
*** Phân biệt rõ tân ngữ và bổ ngữ : tân ngữ là chịu tác động từ chủ ngữ , còn bổ
ngữ là làm rõ nghĩa hơn cho danh từ . [+] Adjective Complement
She is sad that she cannot speak English. (1)
I was happy when i passed the exam (2)
- Ở (1) ta thấy mệnh đề danh ngữ bổ ngữ để làm rõ lí do cô ấy “sad”
[+] Indirect Object ( person ) and Direct Object ( non-person)
I know when the train will arrive (1)
I will give what i have for her
-Ở (1) thấy được mệnh đề nominal chỉ có 1 tân ngữ thui nên nó là tân ngữ chính ,
direct object ; Ở (2) thì tân ngữ chính làm direct object , còn “her” là direct object .
*** cứ nhớ là khi câu có 1 tân ngữ thì đó direct object , còn 2 tân ngữ trở lên , cái
mô chỉ sự việc là direct , cái mô chỉ người là indirect [+] Subject complement
My command is whatever you wish
- Thấy rõ mệnh đề danh ngữ làm bổ ngữ cho chủ ngữ nghĩa là nó theo sau copula,
the linking ,verb chủ đích là mô tả chủ ngữ của mệnh đề chính đó
***The terms “predicate nominative” and “predicate noun” is also noun clause that
function as Subject complement [+] Apposition
That man , whoever he is , tried to steal some library books
- mệnh đề danh ngữ đóng vai trò đồng vị ngữ
*** hiểu đơn giản là cái apposition có hoặc ko cũng đc , chỉ để làm rõ cái danh từ “
that man” thôi , kiểu trong một câu có 2 vị ngữ cùng làm rõ cho 1 chủ ngữ á mà
một cái vị ngữ chính ( main predicate ) , cái phụ ko cần thiết kia chỉ thêm cho rõ ý gọi là apposition .
Câu 2 : The main function of Adverbial Clause or Adverb Equivalents
Main function is as an Adjunct to “ a related-meaning verb” ( nghĩa là bổ ngu cho
một mệnh đề khác NHƯNG không bắt buộc ) . All Adverbial clauses start with a
subordinating conjunction ( when , as , before ,...)
When i finish studying , i will go abroad
- Nếu chỉ mệnh đề “when i finish studying” thì câu ko rõ nghĩa lí do “i will go abroad”
Cho nên mệnh đề trạng ngữ là mệnh đề phụ , để bổ nghĩa cho mệnh đề chính . hay
còn được gọi là Subordinate clause
When i have a free hour , i’ll clean my house .
I’ll clean my house when i have a free hour I’ll clean my house
- Mặc dù thêm Mệnh đề trạng ngữ để thêm thông tin nhưng khi đọc mệnh đề chính
“ i’ll clean my house” ta vẫn hiểu mà
Adverb Subordinators : Manner , Purpose , Contrast , Condition , Reason ,
Comparison , Result ,Time , Location
*** mọi người cần phân biệt PP và Adverbial clause
I came to church with my four aunts (1)
When i had finished work with my four aunts , i came to church (2)
- Ở (1) “ with my 4 aunts” là cụm giới từ ( Pre Phrase) để bổ sung thêm thông tin
“i came to church” ( Preposition + nominal object )
-Ở (2) thì mệnh đề trạng ngữ cũng chỉ bổ sung thêm thông tin cho mệnh đề chính
NHƯNG là mệnh đề chớ ko phải cụm ( Subordinate “when” + clause )
Câu 3 : The function of Adjective Clause or Adjective Equivalents
- The function is as post-modifier to the preceding noun .Most Adjective Clauses
start with pronoun ( who(ever), which , whatever, whose , when,where and that
(không được nhầm với nominal that ) ) . Adjective Clause chính là Relative clause ( mệnh đề quan hệ )
We set out for the next town where we had planned to stay the night
- Từ “where” chính là thay thế cho “next town” để thêm thông tin là “ we had planned to stay the night” The car t hat hi t me was changing lanes
- Từ “that” là thay thế cho “car” . Nghĩa là mệnh đề tính ngữ ( hay là mệnh đề quan
hệ ) “ that hit me” bổ nghĩa cho “car”
- Nhớ là đứng trước mệnh đề tính ngữ là một danh từ chính được đề cập .
*** Phân biệt Relatives pronoun function giữa Adjective clause và Adverb clause
pronoun của adverbial clause dùng để cung cấp thêm thông tin về ( manner ,place , time,...)
pronoun của adjective clause dùng để bổ nghĩa cho nominal object chính trong câu
Our great-grandparents lived in a time when the environment was less polluted.
- theo Adverbial C thì “when” được dùng bổ sung thêm thông tin cho mệnh đề
chính “ our great-grandparents lived in a time”
- theo Adjective C thì “when” được dùng để bổ nghĩa cho “time”
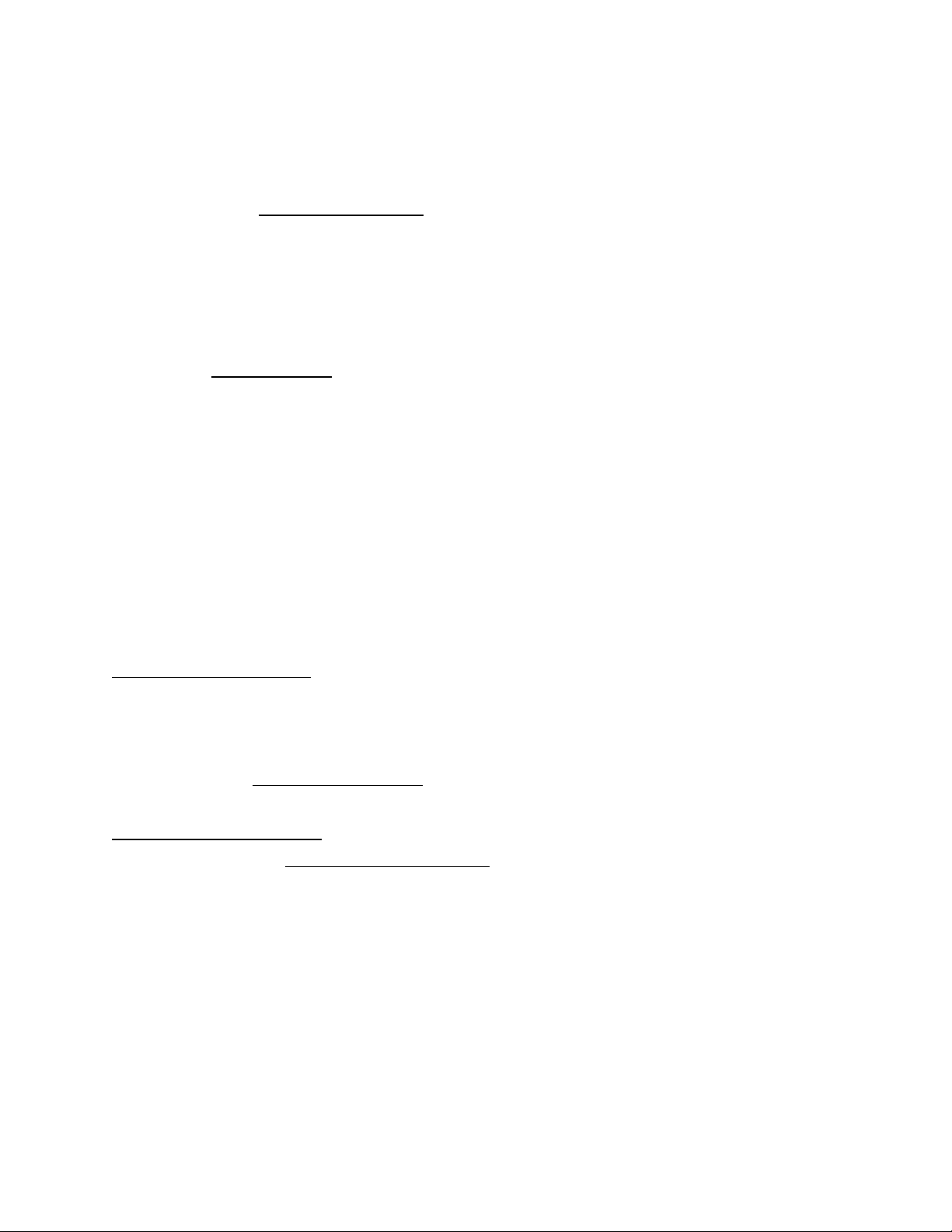
Câu 4 : Difference between Subordinators , Coordinator and Connector ( Conjunct) Subordinator Coordinator Connector Function Subordinators are the Coordinators are the Connectors are the one that can be used to
one that can be used to one that can be used both introduce a link equivalent to show a connection subordinate clause and linguistic units between two link it with a (words,phrases,clause seperated sentences superordinate clause in s or sentences) subornation or sub- coordination Emphasis
De-emphasize the clause Give equal emphasis "Hand off" topic from they are attached to to two similar one main idea to the important clauses next. Semantic - Nominal
- be arranged into 4 groups : and , but , or , so Features - Adjective -Adverbial Join Dependent and Two independent Two or more Independent clauses clauses independent clauses Sentences Complex sentences Compound sentences Compound sentence Position Preceed Following Following Clause Following Clause Clause Clause Initial Initial Initial Initial Medial
Subordinators are place To be most central Final before the clause Often in second clause of co- ordination
Punctuation They are normally Comma , semicolon , Comma , semicolon , placed preceed by no colon , period full stop punctuation Example Because , since, for ,and ,nor, but ,or, moreover ,for
although, while ,if ,until yet, so. ,example, however, in ,when addition, in general, therefore ,thus.
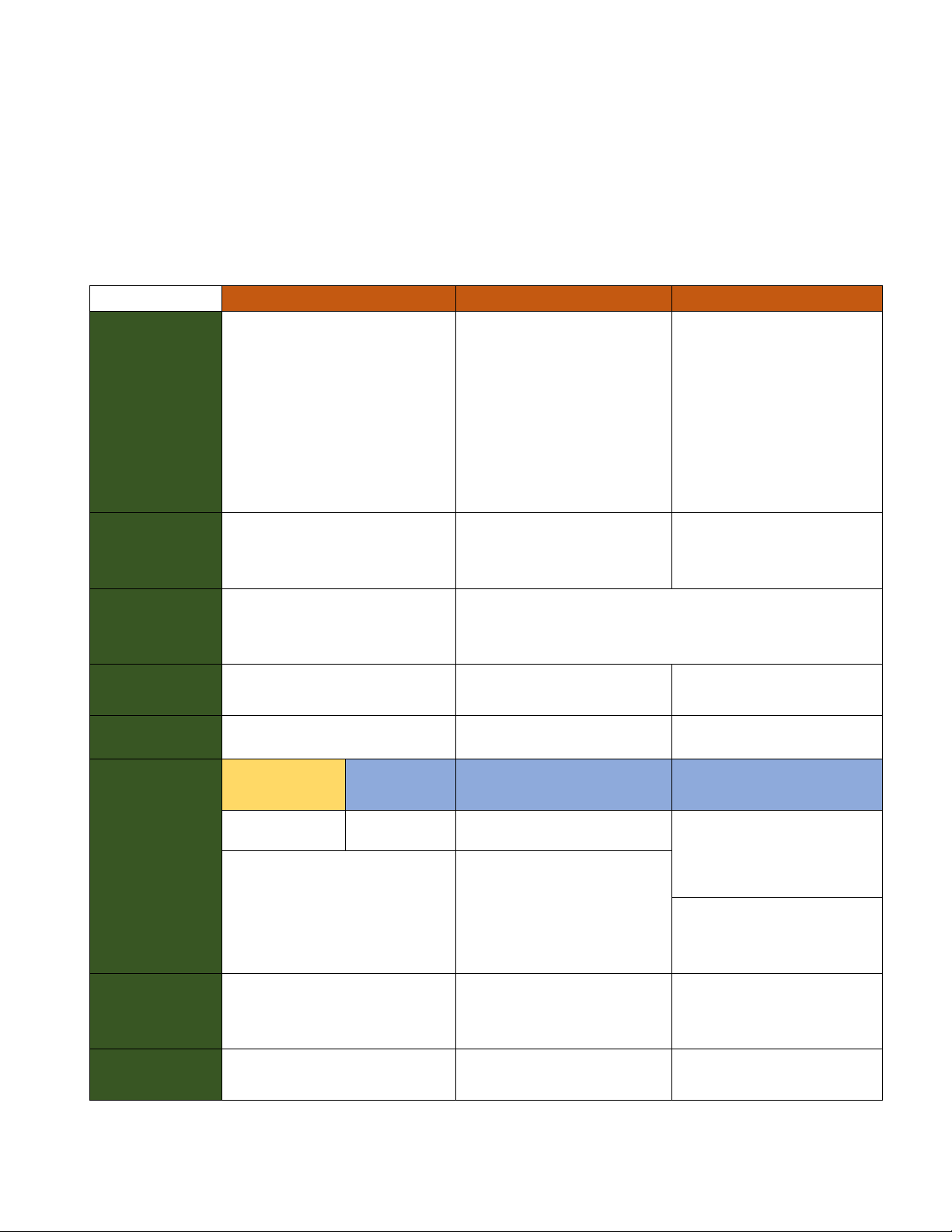
Câu 5 : Difference among Simple sentence (Câu đơn), Subordination
(câu phức), Coordination (Câu ghép), Sub-coordination (Câu Phức-Ghép) Simple Subordination Coordination Sub-Coordination The combination of
The combination of The combination of The combination of only one main clause only one main at least two subordination and plus at least one clause plus at least Independent clauses coordination, the subordinate clause by one subordinate combination at least two mean of Subordinators clause independent clause and as prepositions one or more subordinate clause In spite of Althought I love him but He stayed at home and ( Subordinator) being ( Subordinator) he
( coordinator) he was (coordinator) he watched late for bus , she still was busy , he came cheating on me TV because kept running to the to the party
I love him;Howerver, (subordinator)it was school (conjunct) he was raining and (coordinator) cheating on me his bike was broken ***however có thể dịch chuyển giữa câu và cuối câu , lưu ý dấu câu ~;however,~( medial) ~however~(medial) ~,however. (final)
Câu 6 : The elements / components of structure sentence : SVOCA - subject - verb - object
- predicative ( aka complement )
- adverbial ( aka adjunct ) .
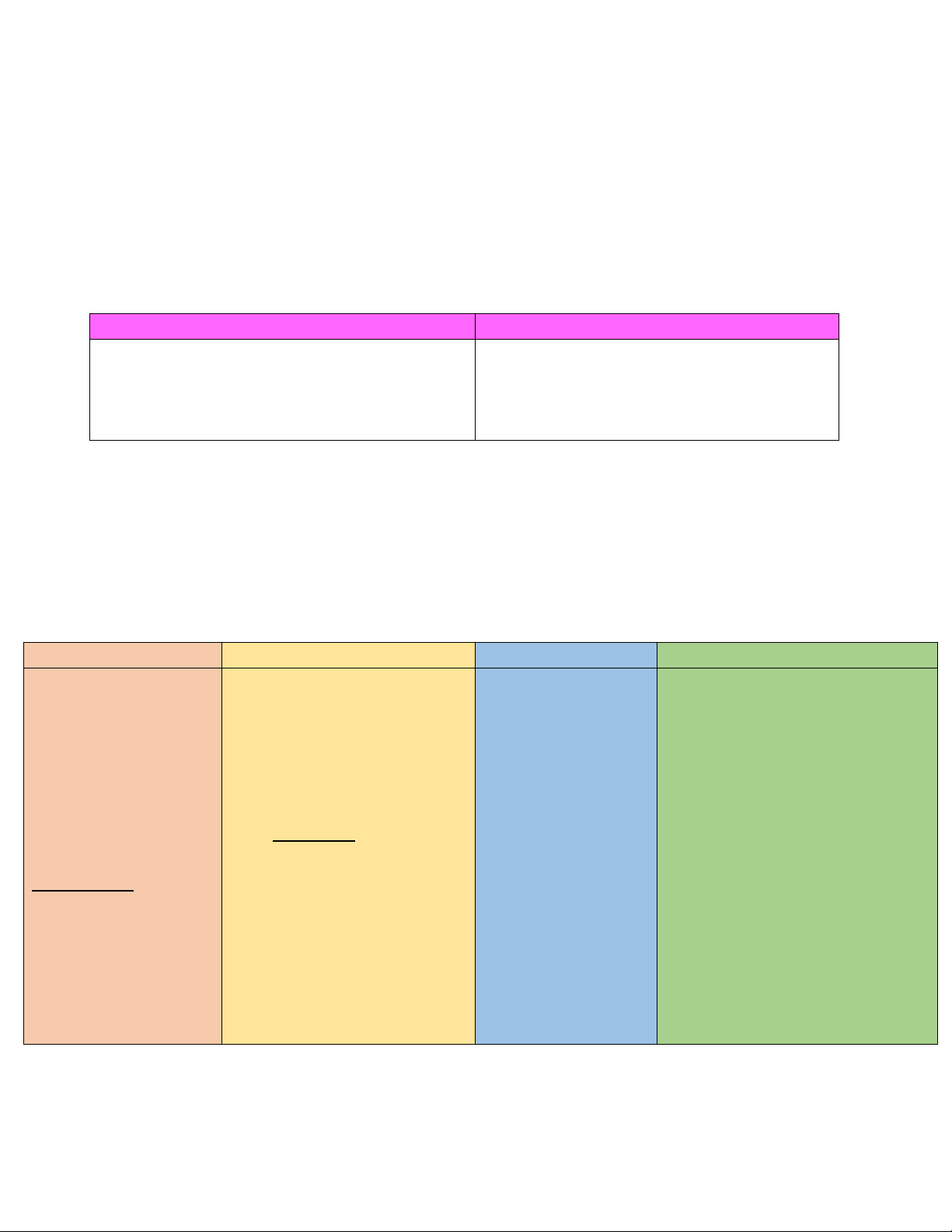
Câu 1 : Difference between internal and external elements in sentence structure : Internal External
-là thành phần nằm trong câu trúc câu
- là thành phần nằm ngoài câu
- cũng chia loại câu như Simple , complex , compound , complex-compound EXAMPLE : Simple Sentence structure :
Internal : S , Vint , Vt , Vi , C , Ad External : An
My sis was received a parcel from the post office S Vptmono Od Ad
Internal : My girl , was received , a parcel , from the post office ( thành phần bên trong )
External : My sis was received a parcel from the post office ( cả câu là external )
Câu 8 : Form of S , V, O , C , A : Subject :
- Simple subject : Pierre puts a lot of garlic in his food
-Complete subjet : That boy puts a lot of garlic in his food
-Compound subject : Pierre and Claudette put a lot of garlic in their food. N
oun ( phrase ) or pronoun : The large car stopped outside our house.
a gerund ( phrase ) :. His constant hammering was annoying
a to-inf :To read is easier than to write
a full that-clause That he had traveled the world was known to everyone
a free relative clause Whatever he did was always of interest.
a direct quotation I love you is often heard these days.
an expletive It is raining.
Verb : transitive, intransitve , intensitive ( đơn )
Object : direct , indirect , complement , preposition
Complement : objects, object complements, adjective complements,
adverbial complements, and subject complements.
Adjunct :adverb phrase , pre phrase and clause
Câu 9 ,10 ,11,12 : Ví dụ verb ( trong sách thầy Thi )
Câu 13 : Differentiate Vtmono and Vtdi:
- Vtmono : có 1 tân ngữ đồng thời là tân ngữ trực tiếp
- Vtdi : có 2 tân ngữ , direct ( non-person ) và indirect ( person )
Câu 14 : Example for pattern / type 1-11
Câu 15 : Example for pattern / type 1-11 having at least 3 externals
Câu2 : Differentiate Vt from Vi as an ordinary verb : V transitive V intensive
-mono : 1 direct object + Cs (AdvP , PP ) - no object + Cs ( Np , Pp , Ap) - di : Oi + Od Od + to/for + Oi - complex : Od + Co
Câu 2 : Identify the Vint , formally :
Verb intransitive : is basically defined that a verb doesn’t have direct object . Có
nghĩa là không có từ nào trong câu cho biết ai hay sự việc đã nhận được hành động
của động từ . Theo sau nội động từ là bổ ngữ cho chủ ngữ ( Cs ) vì thế những từ
hoặc cụm từ đó sẽ trả lời cho câu hỏi “ How ”
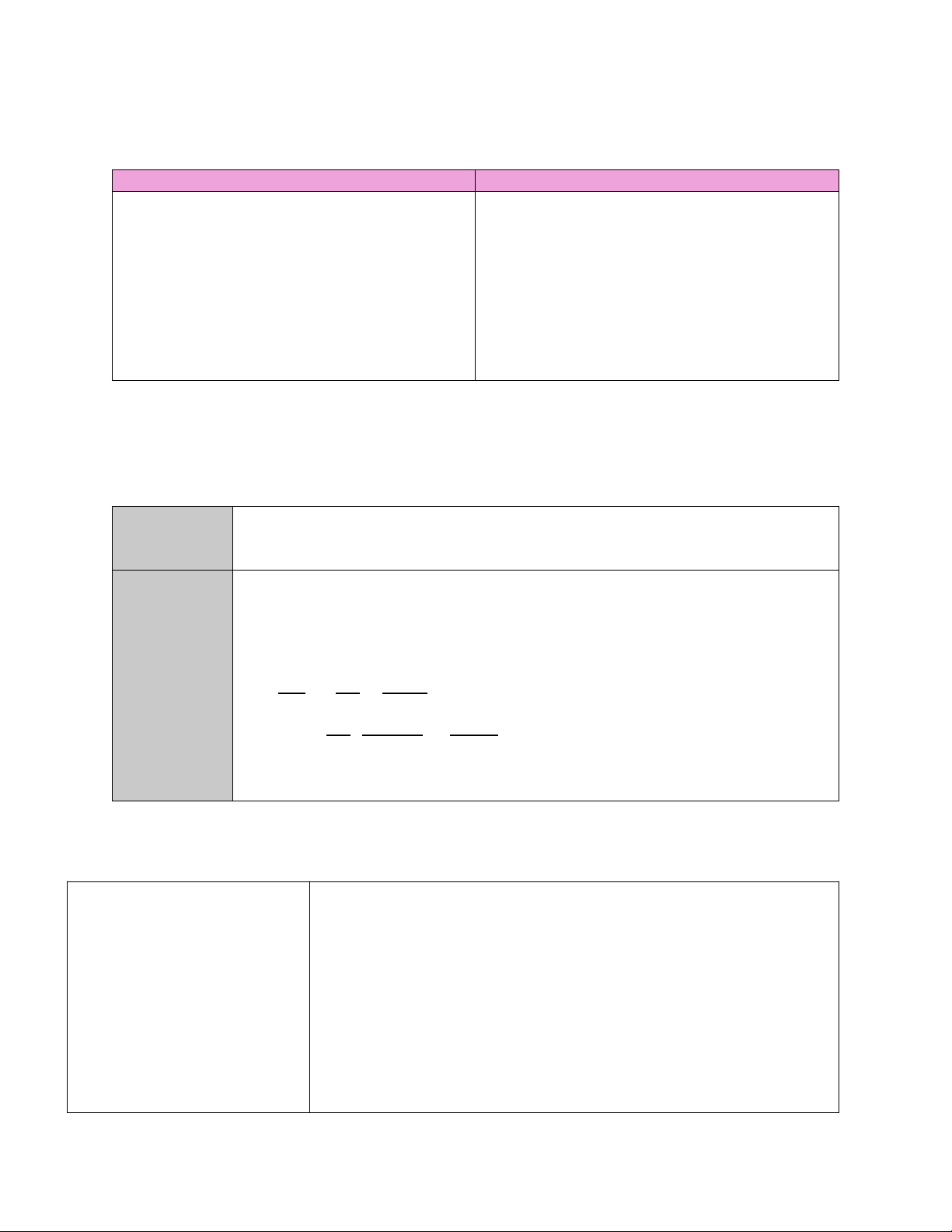
Câu3 : Difference between Adjunct , Disjunct , Filler and Intejection :
Adjunct (sung ngữ) Disjunct (bình ngữ ) Filler ( từ đệm )
Interjection ( thán từ ) -là chức năng như
- cũng là chức năng như - là một từ vô
- là từ diễn tả cảm xúc mạnh , trạng ngữ trạng ngữ nghĩa , để chỉ ra
cường độ . Nó diễn tả cho joy + cho biết thêm
+ cho thấy thái độ của sự phân vân
, sorrow , excitement , pain ,
nhiều thông tin hơn người nói hoặc đánh giá suspence hay do
surprised ,.......và thường kết trong 1 câu
(judge ) về những gì còn
dự hesitation trong thúc bằng “!” + lược bỏ nó , câu lại của câu lời nói ( exclamation mark ) vẫn có ý nghĩa VD: Naturally , i paid for
+ nhiều chức năng VD : Hurrah ! , oh , wow , VD : i put my bag my meal Ouch , oops , Kkk , on the floor
( theo lẽ tự nhiên , tui phải VD : um , er , uh ewwww,....
~ là một adjunct chỉ trả tiền cho bữa ăn của tui ( phân vân ) location thui ) totally ( nhấn mạnh ) i mean ( nhấn ý) right / uh huh ( sự đồng tình ) ĐỀ CƯƠNG SYNTAX
Câu 1 : The syntactic functions of main and subordinate clauses Independent clause Dependent clause
- ( S + V ) Express a complete thought ( can stand
- ( S + V ) Express a incomplete thought , relied alone as a sentence )
on the information from an independent clause
to form a complete , logical thought ( can’t stand
- Independent clause is finte ,meaning contain
on its own to form a sentence )
conjugated verbs as predicates
- Adverbial C , Relative C ( Adj C ) , Noun C.
Câu 2 : The syntactic structure of 11 patterns structures ( done )
11 patterns ( 7 active and 4 passive of simple verb ) ( done ) Complex Verb Definition
Complex verb are verbs that describe the action of the subject “ assigning “ to the
object a certain property or identity Structure
S + Vtcom + Od + Co ( Object complement ) [10] passive : Vptcom + Cs
S + Vtcom + Od + Ao ( Obligatory adverb ) [11] passive : Vptcom + Co
Eg : I find her boring ( her = boring ) Vtcom Od Co
passive : she is fought boring S Vptcom Cs
Transformational / Variant structures Variant /transformational 1/ Wh-question structures - information questions - repeat please questions - elaborate please questions 2/Cleft sentence
-extra position of subject ( real S , formal S { finally } ) or object ( real O ,
formal O { initially , medially , respectively } ) - Use pronoun “IT” 3/Existential sentence
- introductory word ( Wi ) “ THERE” instead of subject ( initially ) 4/Directive sentence
- jussive command , an order or official introduction 5/Exclamatory sentence
- Indicate surprises or wishes by using ‘’WHAT , HOW’’ 6/Inverted sentence
- to add emphasis to statements
- Using inverted coordinator ( Ci ) and coord ( Coo ) 7/Irregular sentence - Elliptical sentence + positive/negative word - Irreagular Wh-question - Formulae - Non-sentence
Câu 3 : Distinguis the Disjunct , Filler and Interjection ( done )
Câu 4 : Application English to Vietnamese traslation ( done )
Câu 5 : Difference between the Obligatory and Optional element [internal and external]. Obligatory Optional
This is determined by the valency
This may or may not be actually of the verb-predicate represented in the sentences
Câu 6 : Learn by heart idioms , phrasal verb . ( done )




