












Preview text:
Unit 1: Banking business and money
1. What is a commercial bank? Central bank?
• Commercial or retail banks are businesses that trade in money.
• The Central Bank is the foremost monetary institution in a market
economy, often owned by the government; their responsibility is for the national interest.
2. What are some functions of central banks?
Most central banks in the present-day world perform one of the following functions:
(1) they serve as the government’s banker;
(2) they act as the banker of the banking system;
(3) they regulate the monetary system for both domestic and international policy goals;
(4) they issue the nation’s currency.
3. What does the central bank do as a government’s banker?
- As the banker to the government, the central bank collects and disburses
government income, manages the issues and redemption of government
debts, advises the government on all matters pertaining to financial
activities, and makes loans to the government.
4. What does central bank do as a bank’s banker (the banker of the banking system)?
- As the banker to the nation’s banks, the central bank holds and transfers
banks’ deposits, supervises their operations, acts as a lender of last resort,
and provides technical and advisory services.
5. How does the central bank do to regulate the monetary system?
- The central bank uses a variety of direct and indirect controls over the financial institutions.
- The central bank can implement the monetary policy by:
- First, they set a reserve requirement. Reserve requirement is a percentage
of deposits that the central bank sets as the minimum amount of reserves
banks must-have. It plays a central role in how much money banks have
to lend out. By changing the reserve requirement, the government can
increase or decrease the money supply. If the government increases the
reserve requirement, it contracts the money supply, banks have kept more
reserve so they have less money to lend out.
- Second, they use open market operations to buy and sell securities
frommember banks. Open market operations are the government’s buying
and selling government securities. To expand the money supply, the
government buys bonds. To contract the money supply, the government sells bonds.
- Third, they set targets on interest rates they charge their member
banks.The discount rate is the rate of interest that the central bank of a
country charges on the loans that it makes to other banks. An increase in
the discount rate makes it more expensive for banks to borrow from the
government. A decrease in the discount rate makes it less expensive for banks to borrow.
6. How can commercial banks make/ earn profits?
- Banks earn profits based on the difference spread between saving and
lending interest rate when accepting deposit and making loans; between
buying and selling exchange rate when exchanging the national currency
and also make profit from fees and commissions.
7. What is a deposit? Demand deposit? Time deposit?NOW account? Share draft account?
• A deposit is a sum of money that is in a bank account or savings
account. to put something valuable, especially money, in a bank or safe
• Demand deposit (Tiền gửi không kỳ hạn) is an account from which
deposited funds can be withdrawn at any time from the depository
institution. Demand deposit is commonly known as checking account.
• Time deposit (Tiền gửi có kỳ hạn) is an interest-bearing bank deposit
account that has a specified date of maturity, such as a savings
account or certificate of deposit (CD)
• NOW account (Negotiable Order of Withdrawal) (Tài khoản lệnh rút
tiền khả nhượng) is an interest-earning bank account with which a
customer is permitted to write drafts against money held on deposit
• Share draft account (Tài khoản hối phiếu cổ phần) is a version of a
checking account, offered by a credit union instead of a bank.
8. What are functions of commercial banks?
- Commercial bank acts as payment intermediary, credit intermediary and money creation.
The ability of commercial banks to maintain and create demand deposits
by loans and investments influences the supply of money in a nation’s economy. 9.
Name some services provided by commercial banks? How
docommercial banks make a profit?
• They receive and hold deposits, pay money according to customers’
instructions, lend money, offer investment advice, exchange foreign currencies, and so on.
• Banks earn profits based on the difference spread between saving
and lending interest rate when accepting deposits and making loans;
between buying and selling exchange rate when exchange the
national currency and also make profit from fees and commissions. 10.
What does a nation’s money supply include?
The money supply includes coin, currency, and demand deposits
(checking accounts). Commercial banks (NOW accounts) in savings
banks and share drafts in credit unions are now considered to be part of a nation’s money supply. 11.
What are the functions of insurance companies?
The purpose of insurance companies is to allow people to pool their
resources in order to minimize the risk associated with accident, sickness,
death, and other unpredictable circumstances. 12.
What are 4 functions of money?
Money as a Medium of Exchange (the most important function)
o Medium of exchange is anything used for payments for goods and
services and in settlements of debts
o As a Medium of exchange, Money is used to pay for goods or services and settle debts,
Money as a Measure of Value o A measure of value or unit of
account is the unit in which prices are quoted and accounts are kept.
o As a Measure of value, Money measures the value of goods in unit
of account, the unit in which prices are quoted and accounts are kept.
• Store of value o A store of value is anything used to make
purchases in the future o As Store of value, money is used to make purchases in the future.
This function can suffer from inflation.
• Money as a Standard of Deferred Payments o A standard of
deferred payments is unit of account over time o As a Standard of
deferred payments, money is used to pay after you buy sth and is
used to settle the debt in the future. 13.
Does money function as a perfect store of value? Why?
- Money doesn’t function as a perfect store of value
Because money loses its value over time and Inflation is unavoidable 14.
What are the differences between 2 types of money:commodity and token money? Commodity money Token money
Value in use Equal Value in use is much higher (purchasing power) in than
value of material comparison with value Gold, silver Paper note, coin of material Function Medium of Means of payment exchange
14. What is token money? commodity money?
• Commodity Money is a useful goods that serves as a medium of exchange.
• Token money is a means of payment whose value or purchasing
power exceeds the cost of production
15. What is a barter economy?
- Barter economy is the economy in which goods and services are traded
directly without the use of money.
16. How can an insurance company act as a financial intermediary?
receive money/ premium from insured and lend money, invest in securities and real estate. Unit 2: Taxation
1. What is tax? What is taxation?
Tax is compulsory fee that government collects from individuals, organizations
to run government’s program.
Taxation is a term for when a taxing authority, levies a financial obligation on its citizens or residents.
2. What are some main functions of tax?
- Raise government revenue to finance government expenditure: defense, building, infrastructure, …
- As a tool of fiscal policy, tax can regulate the economy, regulate aggregate demand and aggregate supply
- Each type of tax has its own function:
+ customs duty: protect domestic goods
+ excise tax: deterrent on some specific goods
+ individual income tax: redistribute income
+ corporate income tax: encourage capital investment
+ payroll tax: ensure social security
3. What is tax avoidance? Tax evasion?
- Tax avoidance is legal ways/methods to reduce or avoid tax payment.
- Tax evasion is illegal ways/ methods to reduce or avoid tax.
4. What are some ways a company can use to avoid paying tax? Avoid tax on profit? -
Making a tax loss: bring forward capital expenditure so that at the end of
the year all profit is used up -
Tax havens: multinational companies set up their head office in tax havens
5. What are some ways an individual can use to avoid paying tax?
2 forms: deductions and credits -
Perks instead of taxable money (perks: non-financial benefits or
advantages of a job such as lunches, travelling, health insurance) -
Tax shelter: postpone the payment of tax by investing in life insurance policies, pension plans, … -
Tax deductible: subtracting taxable income by doing charity, listing
depantdents, so never pay tax on subtracted money
6. What are some examples of tax evasion?
- Stars have income from advertisements but they do not declare their incometo the tax authority.
- People with part-time jobs do not declare their income
- Companies (small, family-owned) do not declare their activities or
employeeso they do not pay tax or national insurance (payroll tax)
- Companies make false declarations about costs to reduce profits or set upshell companies
7. What is VAT tax? corporate tax? Individual income tax? Capital gains
tax? Capital transfer tax? Excise tax? Customs duties? Tax haven?
Taxdeductible? tax shelter? Laundering money? direct tax? indirect tax?
progressive tax? regressive tax?
- A VAT (Value added tax) is a tax collected at each stage of production,
excluding the already-taxed costs from previous stages.
- Corporate tax is a tax imposed on corporate income
- Individual income tax is a tax paid by people on the money they earn
- Capital gain tax is A tax levied on profits made from the sale of assets
- Capital transfer tax is A tax levied on gifts and inheritances over a certain value
- Excise tax is a tax imposed on specific goods or services at purchase such asfuel, tobacco, alcohol...
- Customs duties is a tax that governments impose on the export and import ofgoods
- Tax haven is a place where people live or invest money in order to pay less
tax than they would in other countries
- Tax-deductible is tax subtracting taxable income by doing charity,
listingdependents, … so never pay tax on subtracted money
- A tax shelter is a vehicle used by individuals or organizations to minimize
ordecrease their taxable incomes by investing in life insurance policies, pension plans, ...
- Laundering money is the illegal process of making large amounts of money
generated by a criminal activity, such as drug trafficking or terrorist funding, ….
- Direct tax is the tax which tax bearer and tax payers are the same.... Direct
taxes include income taxes, property taxes, and taxes on assets.
- Indirect tax is wherein a tax is levied on the seller but paid by the buyer. sales
taxes, customs duties, and excise taxes…
- Progressive tax is a tax that is levied at a higher rate on higher incomes
Ex: Investment income taxes, Tax on interest earned, Rental earnings, Estate tax, Tax credits
- Regressive tax is a tax that is levied at a lower rate on higher income Ex: Taxes
on most consumer goods, sales, gas, and Social Security payroll
8. What is the function of income tax in general?
Income taxes are a source of revenue for governments. They are used to fund
public services, pay government obligations, and provide goods for citizens.
9. How can a criminal organization disguise the origin of money from taxinspectors?
Bypassing money through complex transfers and transactions, or through a
series of businesses, the money is “cleaned” of its illegitimate origin and made
to appear as legitimate business profits.
10. What are the differences between progressive taxes and regressive taxes?
Progressive tax vs regressive tax: -
Definition and give some examples -
Function: (Progressive: redistribution of wealth/ income in society regressive can’t do this) -
A progressive tax imposes a greater percentage of taxation on higher
incomelevels, operating on the theory that high-income earners can afford to pay more.
Ex: Investment income taxes, Tax on interest earned, Rental earnings, Estate tax, Tax credits -
Regressive tax is a tax that is levied at a lower rate on higher income
Ex: Taxes on most consumer goods, sales, gas, and Social Security payroll
Progressive: redistribution of wealth/ income in society- regressive can’t do this
What are the differences between direct taxes and indirect taxes? -
Definition: taxpayer pays the tax directly to tax authority -
Avoid or not: direct tax: use ways to avoid, indirect tax: people do not often use ways to avoid
Unit 3: Accounting and financial statements
1. What is accounting? Why is it necessary for business?
- Accounting is the process of identifying, measuring, recording,
classifying, summarizing, analyzing, interpreting, and communicating
financial transactions and events.
- Accounting is important because it helps a business keep systematic
records to ascertain the financial performance and financial position of an
entity, also helps a business know if it makes a profit or not. Its end
products- financial statements- are the means to report its activities to the public.
2. What are some accounting books? 1. Source document
2. Book of original entry/ Journal 3. Ledger accounts
4. Final accounts/ Financial statement
3. What is a source document? A journal? a ledger? FSs? An account?
• Source document: is the original document that contains the details of a
business transaction, acts as evidence for financial transactions: bank
statements receipts, invoices, bill, confirmation, …
• A journal: is one of the books that records a company's financial
activities for the first time, for example, what they buy and sell.
• Ledger accounts (sổ cái): A ledger is a book that contains all accounts of
a business and used to record the transactions periodically from journals,
• Financial Statements: are written records that convey the business
activities and the financial performance of a company, are end products
of the accounting process, official documents to the public.
• An account: is a recording of similar transactions of the company, record
according to double-entry system.
4. Talk about the accounting process / What are task of an accountant in general?
1. Identify transactions and collect source documents.
2. Record transaction for the first time in a journal
3. Post information from journal to ledger accounts periodically
4. Make a trial balance to make sure that total credits are equal to total debits
5. Use the information in the ledger accounts to make financial statements.
5. What are three common types of accounting information? What dothey
show? Who can be users of these types of accounting information?
3 common types of accounting information are Financial accounting
information, management accounting information, and Tax accounting information.
1. Financial accounting information:
- Shows the information describing the financial resources, obligations at
one point in time, and activities of an economic entity during the year.
- Is used by different groups of users for different purposes.
2. Management accounting information:
- Shows the development and interpretation of accounting information
- Only internal users: managers and employees
3. Tax accounting information:
- Shows the amount of tax individuals/ organizations have to pay. -
Is used by Government (Tax authority), taxpayers.
6. What are three common types of financial statements? What do they show?
1. Balance sheet:
• It shows the financial position of a company on a particular date.
• It lists asset, liabilities and Owner’s equity
2. Income statement:
• It shows how much money a company makes and spends over a period of time.
• It lists total sales, gross profit, cost of goods sold, operating expense, net profit.
3. Cash flow statement:
• It shows cash flow in and out of a company in a period of time.
• Its lists cash flow into 3 categories: Operating activities, Investing
activities, and Financing activities.
7. What is a basic accounting equation?
Assets = Liabilities + Owners' Equity
8. What is asset? liability? Bottom line?
An asset is something that provides a current, future or potential economic
benefit for an individual or other entity.
Liability is all the money that a company will have to pay to someone else in
the future, including taxes, debts, interest and mortgage payments
The bottom line (lợi nhuận) refers to a company's net income, which is
presented at the bottom of the income statement.
What are some examples of source documents?
What does asset include? Liability include? - Accounts receivables - Accounts payables
What purpose do creditors/investors use financial accounting information for?
Creditors such as banks or private creditors use financial accounting
information of the company to decide to lend their money to the company or
not; determine the company’s creditworthiness (tín nhiệm) or to approve any
new credit to the company or not.
Why is financial accounting information called “general purpose accounting information”? -
It is used by different groups of users for different purposes.
Why is tax planning the most difficult task? -
Use ways to avoid tax or minimize tax burden
What are differences between financial accounting and tax accounting? Unit 4: Marketing
1. Selling & Marketing
What is the “selling concept”?
- “Selling concept” suggests that the producers produce goods &
servicesfirst, and then persuade customers to buy them.
What is the “marketing concept”?
- For the marketing concept, the producers have to do market research, then
they produce goods and services to satisfy these needs and wants.
2. What is the difference between traditional marketing (selling) and modern?
Traditional marketing
Modern marketing
- Seller/ producer - centered. Sellers and - Buyers - centered. Sellers and
producers sell and produce what they want producers sell and produce what to sell customers want
- Sellers focus on sales/selling (sales - Sellers/producers focus on market
promotion and distribution). research (customers and competitors),
3. What is market research? Market segmentation? Market opportunities?
- Market research is collecting and analyzing information about the size
of potential market, customer’s needs and reactions to a
product/service and competitors
- Market segmentation is dividing a market into distinct groups of
buyers who have different requirements or buying habits
- Through market research, the company can predict new ones to satisfy
customers, it’s called Market opportunity
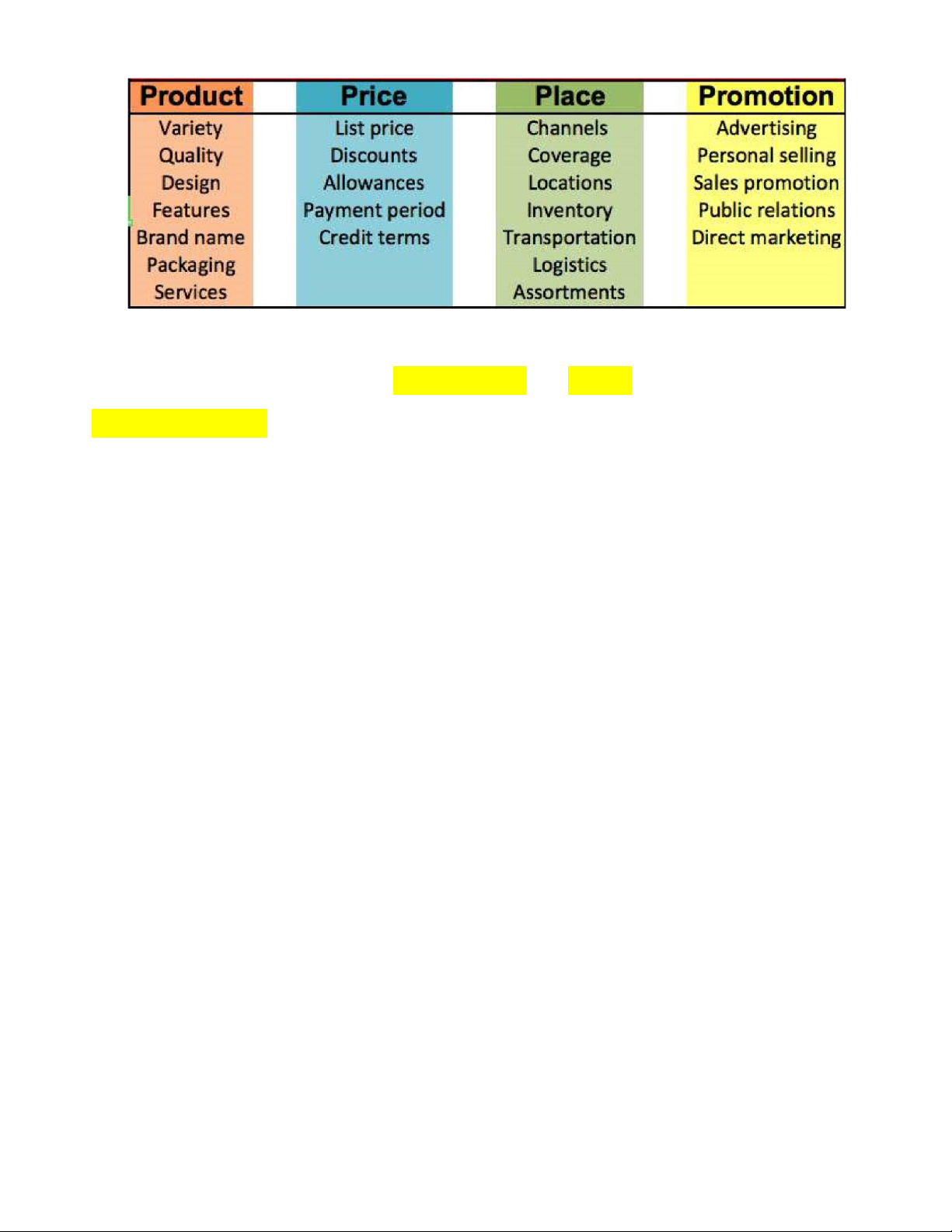
4. What are 4Ps in the marketing mix?
The 4Ps stands for Product, price, place, and promotion
Product include variety, quality, brand name, feature, design, packaging, service
Price inclue listed price, discount, The 4Ps stand for: - Product - Price - Place - Promotion
5. What does market Product include?
Variety, Quality, Design, Features, Brand name, Packaging, Services
6. What does market Price include?
List price, Discounts, Allowances, Payment period, Credit terms
7. What does market Promotion include?
Advertising, Personal selling, Sales promotion, Public relations, Direct marketing
8. What does market Place include?
Channels, Coverage, Locations, Inventory, Transportation, Logistics, Assortments
9. What is marketing mix?
The marketing mix refers to the set of actions, or tactics, that a company uses
to promote its brand or product in the market.
10. What are differences between “selling concept” and
“marketingconcept”?
The selling concept and marketing concept are based on different principles. -
Selling concept means that the producers produce goods and services
first, then they try to sell them, while marketing concept means that the
producers have to do market research first to identify/ determine/ find
out customers’ needs or even create new ones, then they produce goods
and services to satisfy these needs and wants. -
Selling focuses on the needs of the seller and marketing focuses on the needs of the buyer. -
The company’s success relies on its ability to create, deliver and
communicate a better value for its target customers in comparison with its competitors
What are the important roles of market research for a business? -
Know customer’s taste/ wants, especially target customers -
Design a product that meets the customer’s needs -> increase sales -
Design a better product than competitors -> increase competitiveness
in the market -> increase market share. -
Maintain their competitive advantage
Unit 5: International business 1.
What is the reason for development of international trade?
- Each country has its own comparative advantage to produce goods
more efficiently than other countries -> export + climate + location + natural resources + labor 2.
Why do particular countries can produce goods or services
moreefficiently than others?
Particular countries can have different reasons for more efficient
production of goods and services such as their climate, location, labor
forces, natural resources, and other conditions. • climate • location • natural resources • labor 3.
What are 4 factors that result in the efficient production of a country? + Climate + Location + Natural resources + Labor 4.
What does the theory of comparative and absolute advantage
theory indicate? /What does theory of Adam Smith: and David Ricardo indicate?
- Theory of Adam Smith is the theory of absolute advantage, It indicates that
an exporting country focuses only on product or service which it has the
greatest advantage and exports to another country. Supply is limited
(monopoly) price is determined by seller.
• - Theory of David Ricardo is the theory of comparative advantage. It
indicates that an exporting country doesn’t have to be the most efficient
producer, it is only the more efficient producer than importing country
Increase in supply can lead to competitive prices. 5.
What is an International business?
An International business refers to the exchange of goods and services, capital
across national borders and at a global scale 6.
What are some advantages/ benefits of international business to a trading country? - Imports:
+ Provide a variety of product range, high-quality products, access to new items
in the international market, lower price of goods + Make up for the shortage of goods in the domestic market
+ Access to high and new technology to produce goods and reduce
manufacturing costs for domestic producers. - Exports:
+ Expand the markets, diversifying market opportunities
+ Greater production can lead to larger economics of scale and better margins
-> Create jobs for local/domestic employment
+ Gain benefit from trade surplus, raise national wealth and Government budget
revenue, raise the value of national currency… + Create political relationships 7.
What are policies to encourage export?
- Provide marketing information: international trade fair, exhibition
- Establish trade missions: a group of people to look for business
opportunities, sign trade contract with other countries -> find the markets for domestic industries.
- Subsidize exports: dumping (trợ giá): selling on foreign market at the price below the cost of production.
- Tax incentive: tax on exports: 0%, tax credits. 8. What is dumping?
- Dumping is the practice of selling on foreign market at the price below the cost of production. 9.
What are some disadvantages of international trade to a trading country? - Imports:
+ Decline domestic market: reduce the market share of domestic industry
+ Decrease production lead to reduce employment => Harm domestic industry
+ Decrease the value of the national currency. + Depend on other countries -Exports:
+ Raising production makes pollution to be increasingly serious
+ Raising production materials would be exhausted from materials.
+ Administration costs may rise as you may have to deal with export regulations
10. Why do some countries restrict imports?
Because there are some disadvantages of import such as:
+ harming domestic producers, decreasing in domestic employment.
+ decreasing the value of national currency
+ depending on other countries
11. What are 2 common forms of protectionism?
- 2 common forms of protectionism are Tariff and Quota
+ Tariff is the tax on imported goods. It includes Specific tax and ad valorem tax
+ Quota is the restriction on the quantity or value of imported goods over a period of time.
12. What is quota? tariff? Specific tariff? An ad valorem tariff?
- Quota (hạn ngạch) is the restriction on the quantity or value of imported goods over a period of time.
- Tariff is simply taxes placed on imports. 2 types of the tariff are specific
tariff and ad valorem tariff
- A Specific tariff is a certain amount of tax for each unit of the product - An
ad valorem tariff is based on the value of the product
13. What is An ad valorem tax?
- An ad valorem tax is a tax based on the assessed value of an item, such as
real estate or personal property.
14. What is the effect of the tariff, the quota on the market?
- Tariff can raise revenue for the government and increase the price of imported goods.
- Quota can cause a limited supply of goods and increase the price of imported goods.
15. What is Balance of Trade? Balance of payment?
- Balance of Trade (BOT) records export and import activities.
- Balance of Payment is the amount of money that goes in and out of acountry
16. What is Trade deficit? Trade surplus?
- Trade deficit is the amount by which the cost of a country's imports exceeds
the value of its exports for a given period.
- Trade surplus is the amount by which the value of a country's exports
exceeds the cost of its imports for a given period.
17. What is exchange rate?
- An exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency
17. What is a multinational company? A parent company? -
Multinational company is a company that has headquarter in one
countryand branches in other countries -
A parent company is a larger company that owns one or more other companies.
What does CIF/ FOB stand for? CIF stands for cost, insurance, freight and FOB stands for Free on Board
What is embargo? prohibit import and export with another country
What is a government subsidy? Is money given by the government to support
the exporting company or cover the loss of non-profit business.




