






Preview text:
CHAPTER 15 Distributing Products
The emergence of marketing intermediaries
- Marketing intermediaries: organizations that assist in moving goods and services from
producers to businesses (B2B) and from businesses to consumers (B2C)
- Channel of distribution: a whole set of market of marketing intermediaries, such as
agents, brokers, wholesalers, and retailers, that join together to transport and store goods
in their path (or channel) from producers to consumers
- Agents/brokers: marketing intermediaries who bring buyers and sellers together and
assist in negotiating an exchange but don’t take title to the goods
- Wholesaler: a market intermediary that sell to other organizations
- Retailer: an organization that sells to ultimate consumers
*Why marketing needs intermediaries
-Intermediaries perform certain marketing tasks – such as transporting, storing, selling,
advertising and relationship building – faster and cheaper than most manufacturers could
The utilities created by intermediaries
- Utility: in economics, is the want-satisfying ability, or value, that organizations add to
goods or services by making them more useful or accessible to consumers than they were before *Form utility
-Changing raw materials into useful products *Time utility
-Adding value to the products by making them available when they’re needed *Place utility
-Adding value to the product by having them where people need *Possession utility
-Doing whatever is necessary to transfer ownership from one party to another, including
providing credit, delivery, installation, guarantees, and follow up service *Information utility
-Adding value to products by opening two-way flows of information between marketing participants *Service utility
-Adding value by providing fast, friendly service during and after the sale and by teaching
customers how to best use products overtime
Wholesale intermediaries *Merchant wholesalers
- Merchant wholesalers: independently owned firms that take title to the goods they handle
- Rack jobbers: wholesalers furnish racks or shelves full of merchandise to retailers,
display products, and sell on consignment
- Cash-and-carry wholesalers: wholesalers that serve mostly smaller retailers with a
limited assortment of products
- Drop shippers: wholesalers that solicit orders from retailers and other wholesalers and
have the merchandise shipped directly from a producer to a buyer *Agents and brokers
-They do not carry inventory, provide credit or assumer risks
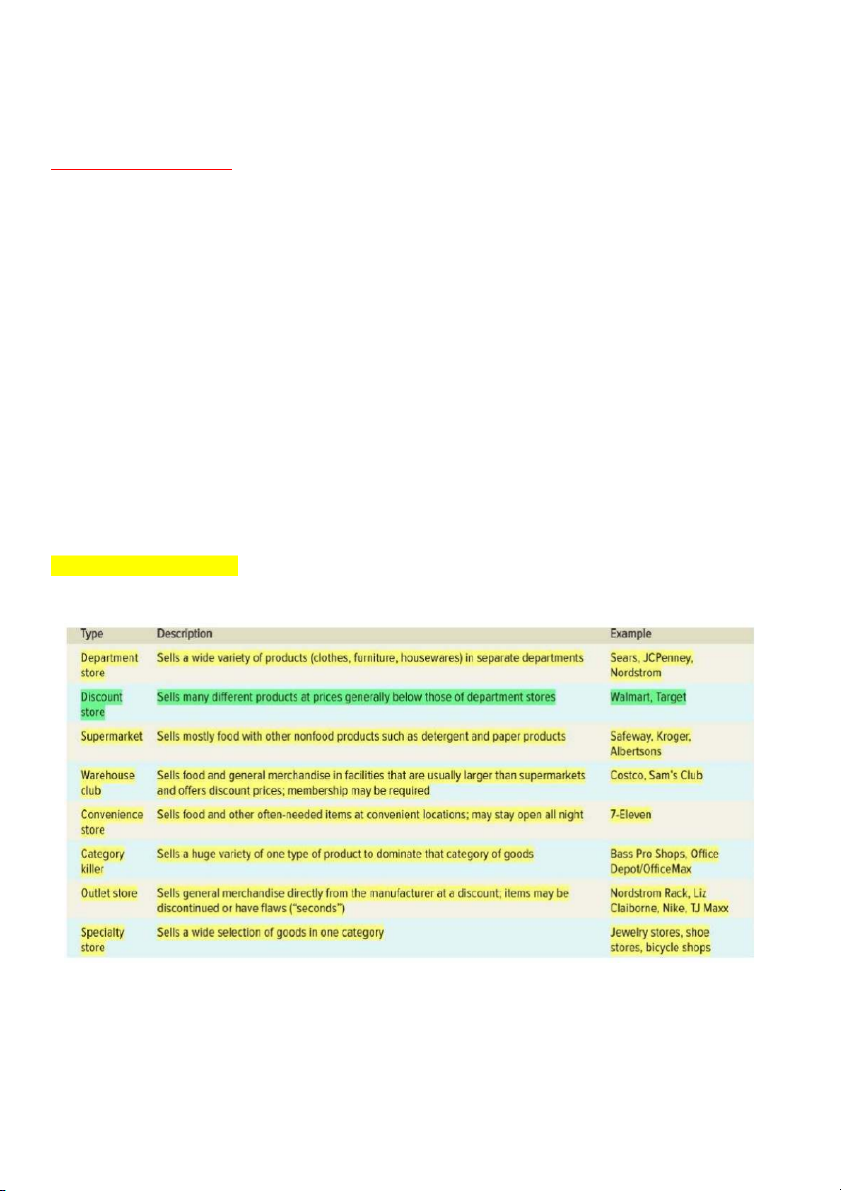
Retail distribution strategy
- Intensive distribution: distribution that put products into as many retail outlets as possible
- Selective distribution: distribution that sends products to only a preferred group of retailers in an area
- Exclusive distribution: Distribution that sends products to only one retail outlet in a given geographic area 16
Using Effective Promotions
Sales promotion: giving buyers incentives
- Sale promotion – the promotional tool that stimulates consumer purchasing and dealer
interest by means of short-term activities.
- Sampling – a promotional tool that letting consumers have a small sample of the product for no charge
Word of mouth and other promotional tools
- Word-of mouth – the promotion tool that people telling other people about products they have purchased
- Viral marketing – the term now used to describe everything from paying customers to
say positive things on the Internet to setting up multilevel selling schemes whereby
consumers get commissions for directing friends to specific websites *Social networking
- One of the greatest advantages of social media platforms is that they offer easier 2 ways
communication between business and customers *Blogging
- Businesses can attract new customers when they coordinate their social media profiles with their blogs *Podcasting
- A means of disturbing multimedia digital files on the Internet for downloading to a portable media player *Email promotions
- Increase brand awareness and update subscribers on various deals or promotions *Mobile marketing -Text messages
Managing the promotion mix: putting it all together Promotional strategies
- Push strategy – promotional strategy in which the producer uses advertising, personal
selling, sales promotion, and all other promotional tools to convince wholesalers and
retailers to stock and sell merchandise
- Pull strategy – heavy advertising and sales promotions efforts are directed toward
consumers so that they’ll request the products from retailers. CH NG 14 ƯƠ Chapter 14
Developing and Pricing Goods and Services
The new-product development process -6 steps
1. Idea generation (based on consumer wants and needs) 2. Product screening 3. Product analysis
4. Development (including building prototypes) 5. Testing
6. Commercialization (bringing the product to the market0
*Generating new-product ideas *Product screening
-A process designed to reduce the number of new product ideas being worked on at any one time *Product analysis
-Making cost estimates and sales forecasts to get a feeling for profitability of new product ideas
*Product development and testing
- Concept testing – taking a product idea to consumers to test their reactions *Commercialization
-Promoting a product to distributors and retailers to get wide distribution, and developing
strong advertising and sales campaigns to generate and maintain interest in the product
among distributors and consumers
*The product life cycle: a theoretical model of what happens to sales and profits for a product
class over time; the 4 stages of the cycle are introduction, growth, maturity, and decline Competitive pricing *Pricing Objectives
1. Achieving a target return on investment or profit 2. Building traffic
3. Achieving greater market share 4. Creating an image
5. Furthering social objectives, both short-run and long-run *Cost-Based Pricing
-Cost-based pricing measures cost of producing a product including materials, labor, and overhead. *Demand-Based Pricing
- Target costing — Designing a product so that it satisfies customers and meets the profit margins desired by the firm.
*Competition-Based Pricing
- Competition-based pricing — A pricing strategy based on what all the other competitors are doing.
- Price leadership — The strategy by which one or more dominant firms set the pricing
practices that all competitors in an industry follow. *Break-even analysis
-The process used to determine profitability at various levels of sales
- Total fixed costs: all the expenses that remain the same no matter how many products are made or sold
- Variable costs: costs that change according to the level of production
*Other Pricing Strategies
-Skimming price strategy — Strategy in which a new product is priced high to make
optimum profit while there’s little competition.
-Penetration strategy — Strategy in which a product is priced low to attract many
customers and discourage competition.
-Everyday low pricing (EDLP) — Setting prices lower than competitors and then not having any special sales.
- High–low pricing strategy — Setting prices that are higher than EDLP stores, but
having many special sales where the prices are lower than competitors.
- Psychological pricing — Pricing goods and services at price points that make the
product appear less expensive than it is. CHAPTER 13 CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP What is marketing?
- Marketing: the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating,
delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large
*The Evolution of Marketing The Production Era
-Early 1900s, general philosophy of business was “Produce as much as you can, because
there is a limitless market for it” The Selling Era
-By the 1920s, business had developed mass-production techniques (such as automobile
assembly lines) -> philosophy turned from producing to selling The Market Concept Era
-Around 1950s, businesses recognized that they needed to be responsive to consumers if
they wanted to get their business ->philosophy called the marketing concept -3 parts
1. A customer orientation – find out what consumers want and provide it
2. A service orientation – same objective: customer satisfaction
3. A profit orientation – focus on goods, services that earn most profit The Customer Relationship Era
-The process of learning as much as possible about customers and doing everything you
can over time to satisfy them - or even exceed their expectations – with goods and services
The Emerging Mobile/On Demand Marketing Era
-Developments such as inexpensive micro transmitters embedded in products will allow
consumers to search by image, voice, or gestures
*Nonprofit Organization and Marketing
-Marketing is a critical part of almost all organizations
-Charities use marketing to raise funds for combating world hunger
-Churches use marketing to attract new members and raise funds
-Politicians use it to get votes
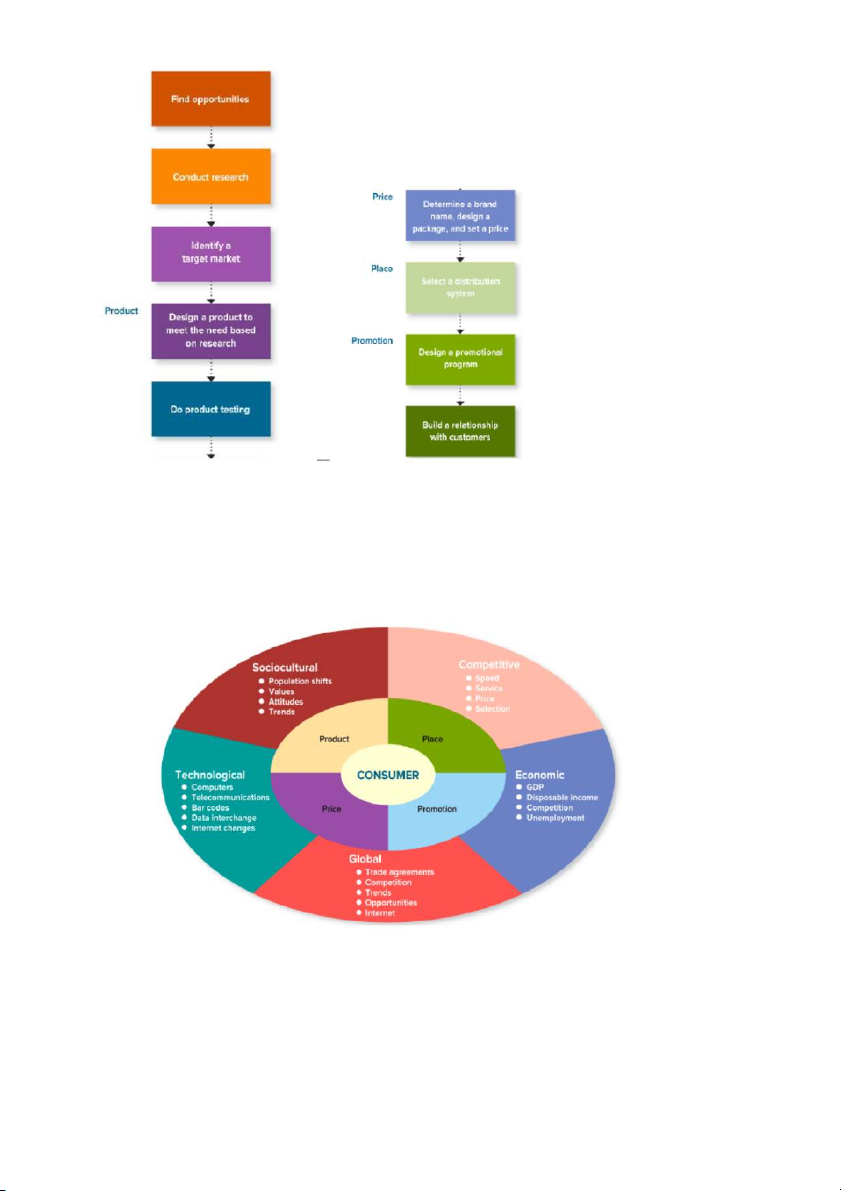
-States use it to attract new businesses and tourists The Marketing Mix
-Marketing teams divided into 4 factors, the ingredients that go into a marketing program
-Managing the controllable parts of the marketing process means
PRODUCT - (1) designing a want satisfying product
PRICE - (2) setting a price for the product
PLACE - (3) putting the product in a place where people will buy it
PROMOTION - (4) promoting the product
-There are 2 major markets in the business
+ Consumer market: all the individuals or households that want goods and services for personal consumption or use
+ Business-to-business (B2B) market: all the individuals and organizations that want
goods and services to use in producing other goods and services or to sell, rent, or supply goods to others 13-5 The consumer market
- Market segmentation: the process of dividing the total market into groups whose
members have similar characteristics
- Target marketing: marketing directing toward those groups (market segments) an
organization decides it can serve profitably
*Segmenting the consumer market
- Geographic segmentation: dividing the market by cities, counties, states, or regions
- Demographic segmentation: dividing the market by age, income, education level, religion, race and occupation
- Psychographic segmentation: dividing the market using the group’s values, attitudes, and interests
- Benefit segmentation: dividing the market by determining which benefits of the product to talk about
- Volume (or usage) segmentation: dividing the market by usage (volume of use)
*Reaching smaller market segment
-Niche marketing: the process of finding small but profitable market segments and
designing or finding products for them
-One-to-one marketing: developing a unique mix of goods and services for each individual customer
*Building marketing relationships
- Mass marketing: developing products and promotions to please large groups of people
- Relationship marketing: marketing strategy with the goal of keeping individual
customers over time by offering them products that exactly meet their requirements
*The consumer decision-making process 1. Problem recognition 2. Information research 3. Evaluate alternatives 4. Purchase decision
-Factor that affect consumer behavior: + Learning + Reference group + Culture + Subculture + Cognitive dissonance




