












































Preview text:
UNIT 1: IDENTIF I
Y NG KEY WORDS & LISTENING FOR SYNONYMS
/ PARAPHRASES & DISTRACTORS A. IDENTIFYING KEY WORDS
What do you do in the listening exam before you listen? You read the questions. And
as you read the questions you underline the key words. So what are key words? What are key words?
Key words are names, numbers, negatives, and other important informa ion t words like verbs
and nouns. They are words and phr ses that s a e m most important in e ea h que c stion. Examples
Question: For the speaker, what is the most impressive aspe t of a solar eclipse? c
A. It’s a supernatural phenomenon. B. It is extrem ly beauti e ful.
C. It is fascinating scientifically.
What words would you underline here? Many people would choose “eclipse” as it i s an unusual word and it is a oun n
and that might seem like a good starting point. If you thought
that, however, you might be making a bad mistake. Transript:
If we look through history, the solar e lipse c
has always had a profound effe t c on mankind. If we think for a mom nt
e what i tmeans to have the sun blotted out: the source of life eradicated.
In ancient times, people were unaware of its natural cause and were profoundly impressed and believ d
e i tmust be supernatural. Today most people know that it i s caused by the moon passing betwe n
e the sun and the earth and are more impressed by its beauty. SPEAKING AS
AN ASTRONOMER, I FIND it scientifically fascinating. The key words als i o nclude “for the s e p aker” and “mo t
s impressive”. And the best answer is C.
Why is it important to identify key words?
- Key words give clues to the context and may help predict what the li t s ening passage is about. - If you sel c
e t the key word in advance, it will help you focus bec use the answer is often a near
or even next to the key word. How ver e , they don’t al a
w ys tell what the answer is. This m ans e
that if you hear the word “e lipse” you know tha c
t the answer will be coming soon.
- Underlining them helps you to focus your attention on what is most important as you listen. Tips
- Don’t just concentrate on key words: read the whole question and listen for the meaning, not words. - Many mistakes are m de a in listening by not re ll a y re din a
g the question. If you only focus on
key words, you are likely to word ma ch. t
You see a word in the question and you hear a word
on the cassette and you assume that that must be the right answer. The listening test i s not always that e s a y: the t st
e is to see if you have understood the m aning, e not if you c n a hear
individual words. If you made a mistake with the previous task, i tmay be bec use a you did not
focus on the m aning of the que e
stion, but just looked at words.
- Only use key words to let you know when to listen. And don’t just listen for key words, be
ready for synonym and paraphrase s s as well. 1 Exercise 1
1.1. Read the questions underlining the key words. 1. Whe e c r
an you get extra infor ation abou m t the program? A. by t lephone e B. on the website C. by emai l
2. Looking at the survey r sults, John w e as surprised that A. so many te nagers got on we e l with their parents. l
B. so few te nagers were happy at home. e C. so many t e
e nagers wanted to participate in the survey.
3. The age of people most likely to be involved in car ac ident is c A. 18-19. B. 20-25. C. 65+.
1.2. Listen and circle the corr ct answ e er.
1.3. Work in pairs. Discuss whether you underlined all the nec ssary e key words and how they helped you de ided the co c r ect answ r er. Exercise 2:
Work in pairs or groups and discuss the following questions.
1. At what age are people in your country considered to be adults?
2. What are the advantages to reaching adulthood?
3. How about the disadvantages?
2.1. Read the questions and underline the key words. Then lis en t and choose the best answer A, B, or C. 1. Ac ording to the speak c e , what do today’ r s young adult n s e d to learn? e A higher-level work skills B how to support a family
C how to combine work and study
2. The speaker cl ims that early a a dults today do not have A a mature attitude. B social skills. C financial fre dom. e 3. The speaker compar s e the probl ms e fac d e by today’s young adult s to those faced in A their grandparents’ time. B the e rl a y 20th c ntur e y.
C their parents’ younger days. 4. One r ason given f e or the change in socia tre l
nds is that young people today
A mature at a later date than in the past. B do not want to a cept adult c responsibilities.
C require more time to get a w ll-paid job. e 2
5. What was the difficulty fac d by the researchers at the e start of this study?
A The concept of adulthood has never be n c e l arly de e fined.
B Many social changes did not occur until recently.
C Much of the older data had be n lost or de e stroyed.
2.2. Listen and choose the best answe s to each r question. Vocabulary
benchmark: criterion, point of reference for comparison
touchstone: experimentation, trial
census: counting and surveying of the population for offi ial purposes c
6. In the 1900s, which two of the following factors (A-E) were used as a benchmark of r aching adulthood? e A Getting m rried a B Purchasing a house C Gr dua a tion from school D Having children E St rting a a first job
7. Which three of the following rese rch a
methods (A-F) were used to c rr a y out the study? A Analyzing old video footage B Talking to people in person
C Studying historical writings D Assessing lab s or force tatistics E Che king of c fic al data from over 100 i years ago
F Conducting a survey across a r nge a of ages Discussion
Can the two factors used as a benchmark to det rmi e
ne a person’s adulthood in Vietnam? Are
there any other factors that can be used in Vietnam? B. LISTENING FOR SYNON M Y S & PARAPHRASES Exercise 1
1.1. Look at this multiple-choice question and underline the keywords. Think about the question that i
s being asked. The recording and the question may use different words to talk
about the same thing, that is, they may use synonyms or paraphrase. Before you listen, re d a
through the options and think of diff rent e
ways of expressing the same information. This way
you will recognize the corre t c answer when you he r
a it. Work with a partner. Look at option
A. Are there other ways of saying “12.00”? Think about what you may hear on the recording.
What about “1.45” and “2.15”? Now listen to the re ording and answer the que c stion. 1. The theft occurred A around 12.00 B betwe n 1.45 and 2.00 e C betwe n 2.00 and 2.15 e
1.2. Look at this short-answer question and underline the key words.
2. How long was the woman away from her vehicle?
Can you think of any synonyms or paraphrases for “vehicle”?
Now listen to the recording and answer the question. 3
1.3. Look at question 3. Think about the keywords and synonyms. Then listen to the re ording c and answer the question.
3. The woman suspects her briefcase may have been stolen by A a motorist B a cyclist C a pedestrian Exercise 2 Listen to several differ nt e
recordings and answer the questions by circling the corre t c
options. Pick out any synonyms or paraphrases of the keywords that you hear.
2.1. Listen to a police offi er giv c
ing information about a crime. 1. The burgl ry took p a lace at
A a museum. B the county hall. C a local shop. 2. The burgl ry took p a lace at
A on Sunday night. B on Thursday C at the weekend. evening. 3. The clock is
A one of a pair. B very valuable hall. C the work of an unknown worker.
4. In the painting of Sir John Foxton, he is
A standing by a horse. B standing by a house. C riding a horse. 5. How did the burgl rs ge a t in? A Through the windoww B By the front door. C The police don’t know.
2.2. Listen to two students discussing the details of a presentation.
1. The total number of crimes in the greater London area i s A going up. B going down. C staying about the same. 2. The number of robberies i s A going up. B going down. C staying about the same. 3. The number of burgl r a ies is A going up. B going down. C staying about the same.
4. Of al reported crime, vehicle crime l s ac ount for c A a quarter. B a half . C the majority. Exercise 3 Listen to some extra t c
s and answer the questions by choosing the correct answer. Li ten s again
and write the synonym or paraphrases s
you hear for the underlined words and phrases. Then
explain why the other possible answer are incorrect. 4 Synonyms/paraphrase Reason the other options are incorrec t
1. What do they decide to organize 1. first? A a place to stay A accommodation/hotel B their airfares B C c r hire a C
2. What change will they make in the 2. garden? A improve the shade A B remove plants B C add a water feature C
3. What do the students agree they need 3. to do with their project ? A do more research A B make some cuts B C add some visual effects C
4. The scientists are studying 4. A how snow form in dif s ferent A conditions. B the effe t that snow ha c s on our B climate. C the effe t dif c ferent clouds have C on snow. Exercise 4
Look at the question and list of possible answers. Before you listen, underline the key ideas you need to li ten for s .
What TWO disadvantages of the new mobile phone does the speaker mention? A
It isn’t very user-friendly. B It is very expensive.
C It can’t take photographs.
D It has a short battery life. E It is quite big.
Listen and put options A-E in the order they are mentioned. Don’t answer the question yet.
Remember, the ideas will be paraphrased, so you may not he r a the sam e words you see in the options. A
It isn’t very user-friendly. B It is very expensive. C It can’t take photographs. D It has a short battery life. E It is quite big. Listen again and put a tick (
√ ) or a cross (×) next to ea h
c option A-E depending on whether
or not it matches the information in the recording. Which TWO options are correct? 5 Exercise 5 Listen to the re ording c
and answer the questions by circling the corre t c options. Pick
out any synonyms or paraphrases of the keywords that you hear.
1. Cranley Hill Primary School first opened A 1830 B 1899. C 1983.
2. There are fewer pupils in the school now than in the past because A there are not enough B students have C the loc l population a teachers. transport problems. has declined. 3. The he d te a a h
c er is proud that the school is provided with energy from A wind power from B coal from the local C el ctricity supplied e their own turbine. mines. by nearby villages. 4. The he d te a a h
c er believes that primary pupils should study problems which A are regional r ther a B c n be solved a C may have no cle r a than global. locally. answer.
5. The children meals at school are unusual because A they include food B they are provided by C the children are grown by the local people. involved in cooking children. the food.
C. IDENTIFYING / LISTENING FOR DISTRACTORS
For most questions in the listening paper, you will he r
a two or more potential answers to each
question, but only one wil be correct. l The incorrect answ rs are e c lled distractors. a Distractors are the incorre t
c answers to a question. Identifying distractors helps you to choose
the corre t answer and shows you have understood the listening tex c t. Exercise 1:
1.1. Listen to extracts from each Section of the Listening pape . r Answer the questions in
the table below. Write ONE WORD AND/OR A NUMBER. Questi ns o Distractors 1 What date will they leave? ……………. 2 What day wil the tour vi l si a t farm? ……………. 3
The students decide to do a proje t about c ……………. 4 Problems: • Poor we ther a
• A lack of ……………. 6 1.2. Listen to the ex racts t
again. Write down each possibl e answer and c oss r out the
incorrect ones. Write the dis ractors in the table. t Exercise 2:
2.1. Listen to the conversation betwe n
e two students about a music festival and answer questions 1-3.
Question 1: Circle TWO letters A-G.
1. Which TWO of the following types of music will be performed at the festival? A heavy me al t E folk music B rock music F country & western C jazz G dance music D opera
Questions 2-3: Circle the corr ct lett e ers A-D. 2. When does the festival begin? A 1st May B 9th May C 12th May D 16th May 3.
How long does the festival last? A a weekend B a week C ten days D two weeks
2.2. Make a list of the distractors you heard. 7
UNIT 2: LISTENING FOR MAIN IDEAS What Are Main Ideas? Main ide s
a are overal l information of the whole listening passage, which tell s the
listener the focus of the conversation or monologue. Necessary skills: ! Identifying main ideas:
- Understanding the overal topic or basic idea of a l l cture or a conversation e
- Understanding the speaker’s general purpose in giving a lecture or having a conversation
- Inferring the speaker’s purpose or main idea when it is not directly stated ! Understanding organization:
- Understanding why the spe ker mentions a certain exa a mple or pie e of information c
- Re ognizing how a particular sta c te ent conn m ect to t s he whole passage - Realizing the spe ke
a r’s intention or purpose in an aside - a rem rk a unrelated to the
main subje t of a conversation c
- Re ognizing a change in topic c Example questions: ! Main ideas:
- What are the speakers mainly discussing?
- Why does the man go to see his professor?
- What is the talk mainly about?
- What is the discussion mainly about?
- What aspe t of ………….. does the professor ma c inly discuss? ! Organization:
- Why does the prof ssor mention …? e
- How does the prof ssor describe………? e
- In what order does the student tel his pro l f ssor about …….? e
- How does the prof ssor emphasize her point about…..? e Strategies:
! Pay attention to expressions that indicate the topic: - Today’s talk is on ….
- Today/Now we’re going to talk about / discuss …..
! In a conversation, listen for cues that will indicat a e spe ker a ’s main purpose - How can I help? / - What do you need? - Can you help me with …? ! Li ten for ke s
y words that are emphasized or repe ted. a ! Ke p in mind t e
hat two or more major ideas together may define the overall topic. 8
Exercise 1: Listen and answer each question.
1. What is the main topic of the ta k? l
A. A conflict betwe n industries e
B. Choosing a major with good job potential
C. Applying for a job as a chemist D. How to de lare one’ c s major
2. What are the student and the professor ma nly d i iscussing?
A. How the student can improve her grades B. The m ximum c a r dits the student e c n a regi ter for s
C. How part-time jobs affect the student’s grades
D. The number of credits the student should take
3. What problem does the woman have?
A. She did not bring her wallet.
B. She is upset that she ne ds identifi e c tion photo. a
C. Her driver’s license i no longer valid. s
D. She c me to the bank as it wa a s closing. 4. What is the conve sation m r a nly abou i t ?
A. Why the man wants to major in linguistic s
B. Why the woman plans to le ve for South a America after graduation
C. Why the woman is not going to worry about the job se rch an a y more
D. Why the man cannot find a dec nt job a e fter graduation
5. Why does the woman talk to the man?
A. To ask about the presentation last we k e
B. To ask the man to help her complet a project e
C. To tell him that her computer is not working
D. To show that she can make the computer-simulated models
6. What is the man’s probl m? e
A. He does not have a library card now.
B. He does not know how to use the sc nner a .
C. He c nnot borrow books with his a c rds now a . D. His cash card do s not e work in the library. Exercise 2
2.1. Listen and choose the best answer. 1. What is the conve sation m r a nly abou i t ?
A. Dilemmas in choosing the next step after graduation
B. Problems of studying computers in university
C. The type of degree employers look for in job applic nts a
D. Worries about getting a job after graduation
2. Ac ording to the woman, what do the employer c s want to know? A. if someone c n a m ke a d a eci ion we s l l
B. if someone is very interested in their field
C. if someone can do the work assigned to them
D. if someone has a graduate degree or not 9
2.2. Listen again and compl te the notes. e
Graduate in ……………………. Choice 1: to work
- employers look at ……………………. After graduation
- can work with ………………. see software engineering process etc.
Choice 2: ……………………. - advanced theory in field
- Master’s degree in ……………………. years
Woman’s major: ……………………. Exercise 3
3.1. Listen and choose the best answer.
1. What are the student and professor ma nly talking abou i t ?
A. The rising costs of graduate school
B. The information about scholarships
C. The de dline for scholarship appli a c tions a
D. The perc ntage of students with scholarships e 2. Ac ording to the professor c
, from whom can the student acquire a scholarship?
A. The national government, or private businesses
B. The university’s student union
C. The professor’s physics graduate course D. The office of regi trar s
3.2. Listen again and compl te the notes. e
……………………. starts next fall
Tuition problem " apply for …………………….!
Type 1: ……………………. based on grades Who provides scholarships? 1. national gov. & states
2. …………………….: more funds available 1 < 2
Type 2: ……………………. based on financial need
apply when? …………………….
more info in ……………………. Exercise 4
4.1. Listen to part of a talk by John, an Australian paleontologist (a scientist who studies
dinosaurs and fossils). To help practise ke ping e
track of the talk, put the phrases below in the o der you hear them. r 10
- The very first field trip I went on
- It's an anc stor of the modern e Australian wombat
- I found a funny-looking piece of rock
- An old prof ssor studying dried-up dinosaur bones e
- I immediat ly changed courses e
- I had to do a compulsory unit on extinction
4.2. Which of the following desc ibes the main topic of the talk? r a. Important le t c ures John’s has given
b. Describing the process that led to John's curr nt role e c. Explaining how anci nt e Australian animal be s came extinct 4.3. Look at the sum ary m below and write qu stions e r lated e to the information mi sing s from each gap. Summary
John was interested in the 1. ……………………. so took an ecology course at
university. The course included a section on 2. ……………………. and an
interesting lecture caused him to quickly change his degree.
John says working in paleontology can be difficult and he describes the conditions
as 3. …………………….. However, the discovery of a 4. …………………….
from an ancient animal made him realize he had made the right choice.
E.g. 1. What was John interested in? / Why did John take an ecology course?
Listen to the talk again and compl te e the sum ary m with ON E WORD ONLY. Check your answe s, payin r g attention to your spelling. Exercise 5
5.1. You are going to hear a lecture about family structures. What kind of
information is needed to complete the sentences 1 -4?
Example: Nowadays, the elderly are less lik ly e to rely + on + noun.
• 'on': The verb ‘rel y’ is usuall y followed b y the dependent preposition 'on'.
• a noun: This sentence has a subject and a verb. To complete the sentence we
need an object. This needs to be a noun because the verb ‘rely on’ is followed by
an object. There may be a possessive adjective in front of the noun (e.g. ‘their siblings’) or an art c i le ( .g e . ‘the government).
1. The ……………………. family structure has changed greatly in the last fifty years.
2. Strong family structures used to be necessary due …………………….
3. People often ……………………. the we lth of their parents. a
4. More than ……………………. children have no siblings nowadays. 11 5.2. N w o list n
e and complete the sentences usi g n NO MORE THAN T RE H E WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER. Exercise 6 You will hear a l cture e about sports. Lis en t
carefully and fill in each blank with NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS.
People al ays say that sports help them not only to have a happy life, but also keep them w
(1) ……………………. and (2) …………………….. This i s bec use a sports make them (3)
……………………. and (4) ……………………. with their friends. Sports take (5)
……………………. of forms :(6) ……………………., (7) ……………………. and hunting
and (8) …………………….. Sports are (9) …………………….. If you want to know about
what others' favourite sports are, you should find what kind of weather they have. Generally
speaking, people in hot areas like (10) …………………….while people in cold c pla es prefer
(11) ……………………. or (12…………………….. Some sports, including (13)
……………………., boxing and (14) ……………………., are called (15)
………………….while other sports, such as (16) …………………., are ca led l (17) ………………….. Exercise 7
You will hear a radio program e m in which the speake s r discuss the importance of
looking after old people in winter. Lis en t to the di l
a ogue and fill in each blank with NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS.
Mr. Hastings, a (1) ……………………. from the Social Servic s eDepartment, came to a radio progr mm a e to discuss the mportanc i
e of looking after (2) ……………………. in winter. First
of all, he told the listeners there were (3) ……………………. reasons for them to (4)
……………………. on elderly people during the cold winter. Then he explained what they
should do to help the old. For example, they should (5) ……………………. the old person's
body, make sure that the one room where the old person lives i
s (6) …………………….
make sure if the old person could have a (7) ……………………. meal. Finally, he mentioned
the government and other local (8) ……………………. alre d
a y involved in this kind of work.
He wished the listeners could help the old to contact with the (9) ……………………. to get some help for them. 12 UNIT 3: LISTENING FOR DETAILS What are details?
Details are specific information of the topic. Detai lquestions often require learners to c tch a specific information. Necessary skills:
! Taking notes of major points and important details of a lecture or conversation ! Li tening s
for signal words expressions that identify details, such as the following:
for example, the reason is, on the other hand, I would say ……………….
! El minating incorrect answer choices i
! Identifying a statement that is not mentioned Example questions: ! Ac ording c
to ………………., what is ………………. ?
! Which of the following is true, according to the lecture?
! What does the spe ker say about ……………….? a
! What correction does the spe ker make betw a
e n …………… and ……………….? e
! What does the prof ssor sugge e st the students to do? Strategies:
! Since answers to questions are generally found in order in the listening passage, it
is helpful to take notes in the order of what you hear.
! Detail questions do not require inference. Choose what speakers a tually say c . ! In a ecture, l
detai l questions are about informa i t on rela ed t to the following: new
facts, description, definitions of term /concepts/ s ideas, re sons, a results, and examples. ! Incorre t choi c c s ma e y repe t some of the a
speakers’ words but do not reflect corre t c
information from the l cture or conversation. e 13 Exercise 1
Complete the form below. Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER for each answer. ROOM BOOKING Name:
(1) Duncan ………………… … Telephone number: 5762 23821 Date of arrival: (2) ………………… …
Date of departure: 23rd September Room type: Twin room Cost: (3) £………………… … Payment method: (4) ………………… … Exercise 2
Listen to a phone call betwe n a mother and e
her daughter. Answer each question with
NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS according to what you hear from the conversation.
1. What's the time of the year now?
…………………………………………….
2. What happened during the trip for Jane from her home to the vacation spot?
…………………………………………….
3. What did Jane do on Sunday?
……………………………………………. 4. How long is her vacation?
……………………………………………. 5. When will she come ba k hom c e ?
…………………………………………….
6. What had happened when she lied down on the bea h the other day c ?
……………………………………………. 7. Why isn't John fe ling ver e y well?
……………………………………………. Exercise 3
Now listen to the recording and answer the questions. Write NO MORE THAN FOUR WORDS.
1. What is the most common crime in the UK?
…………………………………………………………………………………….
2. What two forms of theft does the polic woman mention? e
…………………………………………………………………………………….
3. Why are people in more danger when they are abroad?
…………………………………………………………………………………….
4. What should people l ave in the hotel? e
…………………………………………………………………………………….
5. What kind of mobile is popular with thieves?
……………………………………………………………………………………. 14 Exercise 4
Listen to the interviews betwe n a Student Counsellor and two students. Complete the e
notes. Use NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS for each answer. Interview 1 Name: Linda Richmond Course:
1. ……………………………….. Where living:
2. ………………………………..
Membership of student societies/clubs:
3. ……………………………….. Comments on facilities : Quite good Suggestions for improvements:
4. ……………………………….. Other leisure activities :
5. ……………………………….. Interview 2 Name:
6. ……………………………….. Course: Marine Biology Where living: 5 kilometres away
Membership of student societies/clubs:
7. ……………………………….. Comments on facilities :
8. ……………………………….. Suggestions for improvements:
9. ……………………………….. Other leisure activities :
10. ……………………………….. Exercise 5
Listen to the talk about m n and ap e
es, and then compl te each sente e nce with NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS.
1. Men and apes differ little in their ……………………………………………..
2. Both men and apes have ………………………………………. instead of claws or hooves.
3. Like apes, men have no ……………………………………………..
4. Both apes and men differ from other animals in having ………………………….………… 5. Apes c n make and use a
simple tools. Only m n, however a
, c n …………………………….. a
6. It is possible that a chimpanzee has struck a match on a ma chbox and made t fire, but only
man ……………………………………………. 15
Exercise 6: Listen and answer each question.
1. Who is going to organiz the f e ield trip? A. Andy B. George C. Martha D. Joe 2. Whe e d r
id the student hear about the movie scheduled to be shown tomor ow n r ight ? A. In Germany
B. At the TV station’s website
C. From the campus radio station
D. From someone at the School of Broadcasting 3. Whe e c r
an the man find the rec nt information? e A. In history clas s B. In the periodicals section C. In the reference section D. In encyclopedias
4. Why is the woman reluctant to take summer classes?
A. Chemistry is not offered at her university
B. She wants to take a long vac tion a
C. She thinks the credits c n be transfer a r d e
D. She thinks they would be too expensive
5. Ac ording to the man, how is the com c puteri ed system f z as er than wr t it ng i information down? A. It c n conn a
ect to other universities’ libraries.
B. It can print out the information on the printer. C. It uses the c rd a cata og’ l s fast searching system. D. It is s ea ier to learn than the c rd a cata og s l ystem.
6. What type of instrum nt player is the band looking for? e A. Flute B. Clarinet C. Trumpet D. Saxophone Exercise 7
Listen and choose the best answer.
1. What is the woman’s problem?
A. She does not know how to use the internet. B. She cannot regi ter for a c s hemistry class.
C. She is the last person on the waiting list.
D. She made a mistake using the waiting list. 16 2. Ac ording to the man, how c c an the woman che k c if she got into the class? Tick in the corre t box c Yes No Notification by mail fro m the university
Access the school’s internet website
Talk to the professor every day Call the regi tration of s fice
Exercise 8: Listen and choose the best answer. 1. What is the conve sation m r a nly abou i t ? A. How the dormitory i opera s ted
B. How resident assistants c n solve a problem s
C. How to win an argument with your roommate
D. How to solve the problems of living with roommate s 2. Ac ording to the conv c
ersation, what is the proble with the woman’ m s roommate?
Tick in the corre t box for each c phra e. s Yes No
Unwilling to cle n up the room a Listens to loud music Studies in the dormitory
Talks too much with the r sident a e ssistant
3. What does the man think about his new roomma e? t
A. He is unhappy with the new roommate.
B. He gets along well with the new roommate.
C. He thinks the new roommate is too tidy.
D. He thinks that the new roommate is too noisy. Exercise 9
Below is a summary of the conve sation between r Andr w and S e amantha. Compl te the e
summary by writing ONE suitable word in each of the numbered spaces.
As a solicitor, Samantha advises people about their (1) …………………… in m n a y different
topic areas. One of the most interesting are s a for overse s a students i
s (2) ……………… laws.
People are often surprised to find that you are not allowed to bring (3) ……………... into
Australia because in many countries customs regulations pay littl e attention to this matt r e . They atta h
c more importance to (4) …………………… and (5) ………………… . …
However, in Australia, you can't even take (6) …………………… from one to another. It
doesn’t matter whether you are travelling by (7) …………………… or by (8)
……………………. There are (9) ……………………. to remind you not to bring in any fruit.
This is bec use of the need to prot a e t (10) … c … … … …………against pests. 17
UNIT 4: GUESSING AND PREDICTING Why do we ne d to de e v lop gue e ssing and predicting skills?
You are given only a short time to look at the questions before the listening passage
begins. However, to score well in the listening test , you ne d
e to develop the ability to think ahead. The more effe tivel c y you c n pr a
edict, the quicker your mind will form the correct w rd o
associations to make with the topic, and the better you wil lbe able to work out the meaning of what you he r a . The secret to incre s
a ing your listening skills is to better predict what you might hear. Necessary skills: ! Predicting possible answers
! Predicting what the speaker might mention based on the questions given
! Inferring what is likely to happen from what the spe ker says a
! Drawing a conclusion based on the main idea and what the spe ker says a Example questions:
! What will the man/woman/ speaker probably do?
! How will the man and woman look for the information the man ne ds? e
! What will the prof ssor discuss next? e
! What will the man most likely do? Strategies:
! Making assumptions about what you are going to hear by finding the answers to:
Who? What? When? Where? And Why?
! Pay attention to the last part of the conversation. For example, if a speaker agrees with other spe ker a
’s suggestion at the end, the spe ker a will probably do what is suggested” ! Li ten s
for such expressions as following: “I’d better …”, “I will…”, “then…”, “I
think I can…”, “we’ll discuss…”, “we’ll talk more about…” ! Pay attention to tim
e expressions, such as tomorrow, this ev ning, e and ne t x time/ wee / seme k ster 18 Exercise 1
Look at the note completion task below. What type of information must you listen out for? Example: Bus departs at …. Type of information needed
What time does the bus depart? a time 1. The man w nts to study a … at university 2. Louis Pasteur was born in … (2 possible answers) 3.
Cost of concession tickets $ … 4. Address …. Stre t e 5. Reason for delay … 6.
New Yorkers consume …gallons of water ea h day c . 7. Date of arrival … 8.
The problem of longitude plagued the
early navigators for years because the lacked the ability to … 9. Type of car … 10.
Spring rolls are made from … Exercise 2
Look at the task below. What do you think the context of the listening will be? Pr dict e
the type of information ne ded for each spa e c .
e Then listen and complete the notes. Architecture 21 conference Type of information needed Conference dates 1……………. Conference venues 2……………. Reservations phone no. 3……………. Cost $300 for 3 days Student r te $150 for 3 a days 4……………. or Contact person 5……………. Must act fast! Closing date for talks 6……………. Send outline to include 7……………. Maximum length 8……………. Also send 9……………. Email addres s
10…………..@uniconf.edu.au 19 Exercise 3
Read the notes and write what kind of word complet s e each space grammatically: a noun, a ve b
r or a quantity/amount? Think of words r lated e
to the topic of 'lightning and safety' that could comple s te the note .
Lightning Safety: Presentation Plan
Part 1: Planning for lightning - Important to be prepared
- Go inside before it (1) …………….. Part 2: If inside
- Stay away from water, doors, windows, and telephones
- Turn off (2) …………….. Part 3: If outside
- Avoid trees, open spaces, and metal objects
- If the lightning comes near you (3) …………….. and cover your ears Part 4: If someone gets hit
- Get help from a (4) …………….. - Call an ambulance
- Don't worry: (5) …………….. of lightning victims survive!
You are going to hear two students talking about a project. Listen and compl te e the
notes above. Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NU BER M for each answe . r Exercise 4
Read through the table carefully and answer these questions.
a. In which order will you he r the information? a
b. Which answers can you predict? old Value Card new SuperValue Card Points Standard number Double points Free credit period One month (6) ……....... months Interest rate 18.5% (7) ……....... % Cardholder shopping (8) per month ……....... Two per month evenings Free del ve i ry within Benefits Free delivery within 50 miles (9) ……....... miles Fee Nil (10) £…….......
Listen to the recording and complete the gaps in the table. Write NO MORE THAN
TWO WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER for each answe . r 20 Exercise 5
Questions 1-4: Complete the form below. Write NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS
AND/OR A NUMBER for each answer. City Bus Tour Booking Form Number of passengers: 2 Passenger name(s):
Susan Field and James ( ……………………………….. 1)
Contact telephone number: 07988 (2) ……………………………….. Hotel:
(3) ……………………………….. Bus tour time:
(4) ………………………………..pm Bus tour date : 14th August
Questions 5-6: Choose the corre t letter c A, B or C.
5. Why does a ticket for the museum cost £10?
A. The money is needed to fix parts of the buildin . g B. The colle tion of Latin c Americ n art is unique. a
C. It is the only art museum in Europe.
6. The tourist office assistant suggests going to the next town for a good r staurant e because A. they overlook the sea. B. the restaur nts are bigger a .
C. there are more restaurants to choose from.
Questions 7-10: Match the r staurants with their des e c iptions. r Write ONE lett r e A-E next to questions 7-10. 7. The Belleview 8. The Lighthouse Café 9. Harvey's 10. Stone croft House
A. It is visited by famous people who work in entertainment.
B. This restaurant has recently been bought by a new f mil a y.
C. One family has managed the restaurant for over 100 years.
D. It is expensive but serves high quality food. E. It has be n d e e orated in a modern style. c 21 Exercise 6 Question 1 Questions 2 - 5 Choose TWO letters A- F.
Complete the notes below. Write NO MORE THAN
What were the TWO main problems with the first THREE WORDS for each answer. part of Eliot's essay? Captive breeding A. insufficient research Introduction
- a 2______________of captive breeding B. lack of organisation C. lack of concrete examples
Advantages of captive breeding programmes
- allow preservation of species from extinction D. narrow focus
- could give new function for 3_______ in future
- allow reintroduction of species into wild
E. inclusion of irrelevant material
F. insufficient supporting evidence
Disadvantages of captive breeding programmes
- captive breeding is 4 ______________
- psychological effects of captivity
- danger of 5______________for captive animals
- poor success in reintroduction to wild
6.1. Read through questions 1-5 and answer these questions.
1. Why is Eliot having this tutorial?
2. What is the specific topic that Eliot has be n studying? e
3. What do the notes in questions 2-5 tell you about this topic and what do you know
yourself? (E.g. Why is it nec ssary? e Where might i take pla t c ?) e
6.2 Listen to the first part of the re ording and answer c questions 1-5. - Che k how man c y answers you have to choose. - Li ten for s
words that signal key information. Exercise 7:
7.1. The questions and options can give you a lot of information about what you will
hear. Read multiple-choice questions 1-4 and answer questions a—d. a. How m ny a
speakers do you think you will he r? a b. Who has to do assignments? c. Which ac demic subjec a ts is someone studying? d. What ar a of that subj e e t are c they focusing on? 22 1. Wh
ere are the speakers having this discuss on? i A. a library B. a student flat C. a l cture e theatre
2. How has Chloe spent the morning? A. drinking coffee B. training C. studying
3. Ac ording to Bill, what does the exp c erim nt e show?
A. Quantities of w ter are hard to measure. a
B. Children under five make m ny mi a stakes.
C. Clear thinking is difficult for small children.
4. Bill's assignment is about the stages in a child's A. emotional development. B. mental development. C. social development.
Listen to the recording and answer Questions 1-4 above, choosing the cor ect answer r A, B, or C.
7.2. The paragraph below is taken from a summary completion task. a. Which spe ker does it con a c ntrate on? e
b. What aspe t of her studies does it discuss? c
Chloe started the psychology course in the (5) ……....... year. Previously she studied law. She
enjoyed studying the (6) ……....... branch of that subject.
The worst thing was having to remember lots of (7) ……....... She found (8) ……....... especially
technical. She did not enjoy spending her time reading about (9) ……....... in the library. The part
of the psychology course she likes best is experimental psychology, because it involves (10) ……....... activities. Listen to the se ond c r cordin e g and compl te the su e m ary m . Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS for each answe . r 23
UNIT 5: LISTENING AND MAKING INFERENCES What is making inferences? Making inferences m a
e ns to draw conclusions about information that is not stated
directly by using information that you already know or that is stated dire tl c y. Making
inferences while listening can help deepen your understanding of what you he r a . Necessary skills:
! Guessing the implied m aning of a se e ntence or phrase
! Making a generalization from what is said
!Drawing a conclusion based on the main points of a lecture or a conversation
! Re ognizing how intonation or c
stress indicate implied information or opinions s
! Inferring what is likely to happen from what a spe ker sa a ys Example questions:
! What does the prof ssor imply about ? e
! What can be inferred about ?
! What will the prof ssor like to discuss next? e
! What will the student probably do next? Strategies:
! Try to guess the implied m aning e of the given informati n o . The correct answer i s not directly stated. Example:
Read the listening tapescript below of a student talking about m eting his professor for e the
first time and de ide whether his first impre c
ssion was positive or negative.
When I first met my professor, he shook my hand firmly and then asked me
questions about myself. He was very polite. He also was relaxed and se med e
interested in what I was saying.
Even though the student does not state dire tl
c y that his first impression of his prof ssor e
was positive, you c n infer or conclude that he did from the information he does state di a re tl c y. He shook my hand firmly. He ask d que e stions.
He was relaxed and seemed interested. ! Pay attenti n o to clues expr s e sed by ce tai r n words, word stres , s intonat on, i or pa e c of what is sai . d The sam e sen e
t nce can express different mean ng i s when said in different ways. Example:
Oh, you’ve never heard of that. (I m ay ne d to e expl in more than I thought) a
Oh, you’ve never heard of that? (I’m surprised that you’v e never heard of that)
! Pay attention to the last part of a conversat o
i n. For example, if a speaker agrees wi h t the
other speaker’s suggestion at the end, we can infer that the speaker will do what is suggested.
! Use logic and think about how key points rela e. t Example:
When a student says, “I ne d to e
study more for my biology class, but my schedule is so
tight”, we can guess that “tight schedule” m ans e
the speaker doesn’t have enough
time to study for his biology class.
! Do not choose choices that are too general or vague. 24 Exercise 1
1.1. Listen and answer each question.
1. What does the professor imply?
A. Insurance companies base their rates on risk assessments.
B. The students should not have brought their cars to the city. C. The students re lly don’ a t ne d to e worry about their cars.
D. Insurance companies prefer to insure drivers in the suburbs. 2. What can be inferr d abou e t conduct ng interview i s?
A. The students already have the skills to conduct the interviews.
B. Many m nagers are not skilled at conducting interviews. a
C. A good interviewer will not ask too many questions.
D. The secret to a good interview is to make the applic nt do most of the work. a
1.2. Listen again and fill in the blanks. Dictation 1:
One of the most important skill
s that an insurance company ne ds e to have i s the ability to do
(1)……….. (2) ……….. (3) ……….. (4) ………... An insurance company i s (5) ………..
(6) ……….. (7……….. (8) ……….. that they wil lmake more money in insurance payments
than they will pay out (9) ……….. (10) ……….. (11) ……….. , right? Wel lfor that to work, they ne d
e to know what the chances are that something will (12) ……….. (13) ……….. and
that …uh… they’ll have to pay an insurance claim. Let’s look at (14) ……….. (15) ………..
(16) ……….. (17) ………...
For those of you who moved here (18) ……….. (19) ……….. (20) ……….., you’ve probably noticed that your c r a insurance i
s much higher in the city, right? That’s bec use a the city is
considered (21) ……….. (22) ……….. (23) ……….. (24) ……….....uh statistic lly…and a
I’m not trying to scare you or anything…but (25) ……….. you have a higher chance of
having your car stolen, (26) ……….. …what ver…here than y e ou do in the suburbs. Dictation 2:
One of the most important duties (1) ……….. (2) ……….. (3) ……….. is hiring. This we k e
we’re going to talk about conducting (4) ……….. (5) ……….. (6) ……….. . Now a lot
of you are probably thinking that this i s the e s
a y part… the people you interview (7) ………..
(8) ……….. (9) ……….. al l the work, right? And (10) ……….. (11) ……….. (12)
……….. you’re like a lot of the office managers out there now. But (13) ……….. (14) ……….. i
s a skill that has to be developed…it’s not just asking questions. You ne d e to ask
(15) ……….. (16) ……….. (17) ………...
The first step (18) ……….. (19) ……….. to give an interview is to think of what is needed for
the job (20)……….. (21) ……….. (22) ………... I’m not talking about things (23) ………..
(24) ……….....I mean what will the person have to do in the job. Once you (25) ……….. (26)
……….. (27) ……….. of everything they have to do, you ne d
e (28) ……….. (29) ……….. (30) ……….. . 25 Exercise 2
2.1. Listen and answer each question.
1. What does the professor imply?
A. Affirmative a tion is a controversial subj c ect.
B. Debates will be held on a diff rent day of c e lass .
C. The student’s opinions are not his major concern.
D. It is his legal responsibility to tea h the student c s about affirmative a tion. c
2. What will the students probably do to prepare for the exam? A. Attend more study l bs a
B. Get more books on micro and macro economics
C. Study the integration of micro and macro economics
D. Attend the lecture by Gordon Croft
2.2. Listen again and fill in the blanks. Dictation 1: Today’s topic i
s (1) ……….. (2) ……….., and before we start I just want to remind you that
we’re only discussing (3) ……….. (4) ……….. (5) ……….. i tcreates for employers…uh, I know that m n
a y of you probably have strong fe li
e ngs on this subject… but I really don’t want
(6) ……….. (7) ……….. (8) ……….. (9) ……….. (10) ……….. about affirmative action today, OK? Good. Now affirmative a tion c plac s
e a minimum on the number (11) ……….. (12) ……….. a
company must hire, and that’s usually determined as percentage (13) ……….. (14) ………..
(15) ……….. (16) ……….. of the company. But affirmative a tion c c n a place further
responsibilities (17) ……….. (18) ………... For instanc ,
e an employer may be (19) ………..
(20) ……….. (21) ……….. a certain number of minority employees…to, you know, make
sure that the company doesn’t just ke p
e them (22……….. (23) ……….. (24) ……….. (25)
………... Or the company may need (26) ……….. (27) ……….. (28) ……….. (29) ……….. l adership e
position with a minority … maybe a member (30) ……….. (31) ………..
(32) ……….. or something. Dictation 2:
As you know, (1) ……….. (2) ………… is next we k. Now e
in you labs you’ve be n given (3) e
…………. (4) ……….. to help you study, so you should be wel prepared, but I’m going (5) l
………… (6) ……….. (7) ……….. (8) ……….. (9) ……….. anyway to discuss what will
be on the exam. The, uh…major focus will be on m croeconomics (10) ……….. (1 a 1)
………... You ne d to know the major idea e
s we’ve discussed (12) ……….. (13) ……….....
Oh, incidentally, Gordon Croft i sgoing to be (14) ……….. (15) ……….. (16) ………..on
campus next week. He’s one of the l ading e
experts (17) ……….. (18) ……….. (19) ……….. of micro and ma ro c
economics. Now that won’t specific ll
a y be on your exam, but his lecture
may help (20) ……….. (21) ……….. (22) ……….. for you. Anyway just thought I’d offer
that up to you. So study up, make sure you (23) ……….. (24) ……….. (25) ……….. (26)
……….. in your study packet, and uh, if you have time, you might drop (27) ……….. (28) ……….. (29) ……….. . 26 Exercise 3
Listen and choose the best answers. 1. Ac ording to the c ta k, wh l at is clas consc s iousness? A. Satisfied wage e rners in f a a tories c
B. An awareness of the common condition of workers
C. The ides of protec ing laboring children t
D. Support for a labor movement
2. Listen again to part of the lectur . eThen answer the question. What can be inferr d abou e
t wage earne s joining the labor move r ment?
A. They did not want the m chines to take over their jobs. a
B. They were bored and wanted to join the movement for fun.
C. They hoped to find a solution to the endless toil of work.
D. They had to learn how to use the ma hines fro c m the labor movement.
3. Why does the professor mention power machines?
A. To list a few re sons why farmers had a hard time operating the m a a hines c
B. To point out when workers finally had better working conditions
C. To end the talk about labor movements and working conditions
D. To explain why there was a majority of factory workers. Exercise 4
1. Why does the student visit the advisor?
A. He needs to find which major will give him a high paying job. B. He ne ds to ge e
t information on a r port by the e c reer a c nter e .
C. He ne ds advice on choosing a e major. D. H ’
e s having some problems with his parents. 2. Ac ording to the advisor c
, what did the report by the car er center e show?
A. Certain majors had a better chance to get jobs.
B. There is no major that is guaranteed to lead to high paying jobs.
C. More practical majors were more likely to get high paying jobs. D. Th re is a strong conn e e tion be c t een major w s and future earnings.
3. What will the student probably do next?
A. Write a report for the c reer a c nter e B. Ask the care r e c nter to help him choose a e m jor a
C. Try to get a copy of the report for his parents
D. Read the report before choosing a major
4. What does the advisor mean when she says this “…”?
A. She thinks this report is probably available to anyone who’s interested.
B. She doesn’t understand why they are ke ping this report s e ecret.
C. She thinks it’s unlikely they will give the student a copy of the report. D. She re ll
a y doesn’t know if he c n get a copy of the a r port or not. e 27
Exercise 5: Listen and choose the best answer.
Listen and choose the best answers.
1. What is the talk ma nly abou i t ? A. Principles of marketing
B. The importance of customer service
C. Improving advertising skills
D. Advertising through customer service
2. What does the professor say is the main r ason for losing cu e rrent customers?
A. Better offers from competition B. Customers la k f c e lings of lo e yalty
C. F ilure to ask for customer opinions a D. Word of mouth adverti ing s 3. Ac ording to the professor c
, what can be the main result of good custom r service? e
A. Lower spending on advertising B. Higher profits
C. Increased customer referral s
D. More uses for marketing strategie s
4. Why does the professor say this: “…”?
A. To conclude a se tion of the c lecture
B. To emphasize the importance of a point
C. To encourage students to ask questions D. To che k the students’ c understanding
5. Listen again to part of the lectur . eThen answer the question.
What does the professor mean when he says this: “…”?
A. New customers will always be the most important aspe t of a busine c ss. B. It is difficult to c pture a
m ny new customers with advertising. a
C. Old customers are more valuable than new customers.
D. Customers are al ays ready to es w c pe if they are not trea a ted well. 28
UNIT 6: LISTENING FOR THE SPEAKER’S OPINIONS/ ATTITUDES In any part of the Li teni s
ng test , you may have to answer questions on the spe kers’ a feelings or views. You ne d e to recognize voc bular a y rel ted a
to feelings and expressions that introduce an opinion.
What is Speaker’s attitude?
Speaker’s attitude/opinion i
s his/her feelings or emotions on what is discussed. Generally, these fe lings/ e
attitudes are not expressed dire tl
c y, but through intonation or tone of voice.
How can you tell opinions from facts? An opinion is a point of view; i t diff rs
e from a fact in that it c nnot a be proved true.
Some people make their opinions sound like facts, but usually when people give a verbal
opinion, they use phrases such as “I believe …”, “I think…”, “In my opinion, …”, “To my point of view….”. Commonly asked questions:
! Which of the following best describes the professor’s opinion?
! What is the professor’s opinion of …………..?
! What is the student’s attitude toward …………..?
! What is the woman’s initial attitude toward the student’s request?
! What is the student’s attitude toward the suggestion of …………..?
! How sure is the man that woman c n …………..? a Strategies:
! Pay attention to the adjectives and verbs rela ed t
to feelings. These may help you
recognize words or phrases that indicate the speaker’s fe ling or op e inion. Example:
A: The course Chemistry 204 was very helpful.
B: Yeah. I really enjoyed the classes with Professor Jones. ! Guess the spe k
a er’s attitude by the tone of voic ,
e intonation, and the sentence stress that s the pea e
ker uses to show his or her f eling or opinion. Example: (With surprise) You lik d it? e (The spe ker does not agr a e .) e Or (Happily) You lik d it! e (The spe ker is pleased.) a
! Consider the degree of certainty in what a spe ker says. a Example:
You want to know when it was discov red? Hm e m, let me think. Probably around 1600.
(The spe ker is not sure of the information.) a 29 Exercise 1
Match words/ phrases 1 – 7 with their synonyms a – g. 1. worried a. dubious 2. enthusiastic b. hesitant 3. afraid c. annoyed 4. confused d. conc rned e 5. irritated e. sc red a 6. reluctant f. puzzled 7. doubtful g. eager
Can you think of other adjectives expressing peopl ’ e s fe l e ings? Exercise 2
Listen to some people talking and de ide c how ea h
c one feels. Write the adjectives in the “feeling” column. Listen a se ond c tim
e and write down the words that the spe ker a uses to show how he or she feels.
Listen a third time and notice how they use intonation to help get the mes age s across. Speaker Feeling Words used 1 2 3 4 5 6 Exercise 3:
3.1. Listen to Amanda and Walid discussing smoking. Put a tick by the speaker who has
the strongest feelings about the topic and write down the words that th y u e se to describe their fe l e ings. Speaker Tick Words used Amanda Walid
3.2. Listen again and compl te the se e ntenc . e
Walid doesn’t like being with smokers when he i … s A. e ting. B. wa a lking. C. socializing. 30 Exercise 4:
4.1. Take 30 seconds to underline any key wor s in the question below d , including those
that focus on feelings or views.
1. The students think that their project is A. unoriginal. B. uninteresting. C. unusual.
2. What does Hiba say about her teenage life?
A. It was like most other people’s. B. Some of i was disappoint t ing. C. She didn’t enjoy it. 3. Alm d sugge e sts that they writ about e A. something they did alone. B. a signific nt event. a C. an unhappy time.
4. How did Almed’s father fe l about his ide e a ? A. He thought it was crazy.
B. He realized it was useless. C. He believed it was right. 5. How does Hiba fe l abou e t Amed’s cha lenge? l A. ple sed. a B. envious. C. unconc rned. e
4.2. Listen to a conve sation betw r e n two stu e d n
e ts and answer the questions above. Exercise 5
5.1. Listening to eight ex racts. t What does each speaker show?
a. strong agre ment: ……………………….. e b. neither complet agr e e ment nor comple e
te disagre ment: ………………………… e
c. complete disagreement: …………………………..
5.2. Listen again and compl te the extracts. e
1. Well, I……………………………………………
2. I think that’s a ……………………………………………
3. Well, I’m……………………………………………about that.
4. I think you’re……………………………………………
5. Hmm, that’s a bit……………………………………………
6. I think that’s……………………………………………
7. That seems……………………………………………to me.
8. I have to admit I don’t like the…………………………………………… 31 Exercise 6
6.1. Listen to a young woman talking about the topic of marri ge. a She discusses three
different views on marriage. Complete the table as you listen. View Words used Other people’s In favour of marriage views Her parents’ views Her own views 6.2. Answer the question.
How does the speaker feel about mar iage? r
A. She thinks she will get married soon.
B. She is uncertain whether she will ever marry.
C. She fears that her parents will for e he c r to marry. Exercise 7:
7.1. Listen and answer each question.
1. How does the professor fe l abou e t MRI te hnology? c
A. It is too dangerous to be used in medicine.
B. It should use less powerful magnets.
C. It is dangerous because of the l c a k of training.
D. It is perfectly safe as long as people aren’t careless .
2. What is the student’s attitude toward the design of sma ler l el ctronics? e A.
He doesn’t understand how it rela es
t to the idea that form follows function. B.
He thinks the professor’s ideas don’t apply to electronics.
C. He thinks that it is changing the way people think about product design.
D. He thinks that sometimes it goes against the idea that form should follow function.
3. Listen again to part of the lecture. Then answer the question.
What is the professor’s opinion of solar system?
A. He thinks that its theory is overly optimistic.
B. It is the best option for a replac ment for coa e l and oil.
C. He is disappointed that it is not used more in re lity a .
D. He thinks its theory ne ds to e
be developed more before it c n a be used. 32
7.2. Listen again and fill in the blanks. MRI t chnology e is e s
s ential (1) ……….. (2) ……….. (3) ……….. It uh, i t allows us
to take extremely (4) ……….. (5) ………..of the body…far more detailed than those of say X-rays.
Now, uh MRIs work basically (6) ……….. (7) ……….. (8) ……….. (9) ………... Now when I said the magnet
s are powerful, I mean it... so powerful they c n a be dangerous. All me al t has
to be removed (10) ……….. (11) ……….. (12) ……….., belt buckles, change in their
pockets…anything, it’s al l(13) ………. (14) ……….. (15) ……….. before the patient enters the MRI room.
But MRI technology (16) ……….. (17) ……….. (18) ……….. so fast that not al lthe nurses and t chnicians e
who work with i tare (19) ……….. (20) ………... Sometimes (21) ………..
(22) ……….. (23) ……….. of meta …uh let’ l
s say the patient has a me al pin in their le t g (24)
……….. (25) ……….... sometimes that kind of stuff i
s overlooked, and well if you got a piece of m tal e
(26) ……….. (27) ……….. (28) ……….. and you’re near a re ll a y powerful magnet… . 33
UNIT 7: FOLLOWING SIGNPOST WORDS AND TAKING NOTES A. FOLLOWING SIGNP ST O WORDS What are sign post words?
As with writing, speakers make use of special words to help introduce ideas and to provide a
framework for what they are saying, especially in formal speech, such as lectures or talks. We ca e
n think of these words as signpost words b cause they direct our listening.
How important are sign post words? Sign post words c n
a point us towards the next idea, and what kind of information this may be.
Good public speakers and l cturers e
illustrate stages of their talk through the use of signpost
words. Being able to identify and following these words will help you understand formal spoken English.
Also, in the listening test, each section i s considered separat l
e y, and you are not told when the next question in a se ti
c on comes. When the passage i
s being played, you should be aware of
the content of the next question. If you do not think ahe d
a to the next question and you miss
an answer, you might be unable to ke p
e up with the tape. You could stil lbe waiting for an answer that has alre d a y be n
e given. One way to help you recognize when the questions
change is to listen for the m rker a
words/phrases or signpost words. Signpost words help to predict what dire tion c a conversation or talk i
s going in. Once you recognize that the topic has changed, it i
s time to move on to the next question even if you have not completed the previous one. Types of sign post words:
Below are some possible “dire tions” that the signpost words c c n take a you in.
a. Leading towards a comparison
b. Leading towards a contrast or opposite
c. Introducing an example of what was said earlier d. Suggesting c use and ef a fe t or re c sul t
e. Providing additional information
f. Setting out the stages of the talk 34 Exercise 1
Read sentences 1-10 and identify the signpost words and the direction (a-f on the previous
page) that the words are taking you in. Then try to t
comple e the unfinished statements above by cre tin a g an ending which makes
sense in each c se, using the signpost words in the a text to help you. Exercise 2
Look at the words and phrases below and decide what kind of information might follow, e.g. a
contradiction, an example, an additional piece of information. Complete each of the speec t
h bubbles with the mos appropriate word or phrase.
Then listen to Extract 1 and check your answers. 35 Exercise 3 You are going to li ten to a l s e ture in three sections. c B fore e e
a h section, spend half a minute c
reading the questions and underlining the key words.
Look at questions 1-6 and listen to the first se tion. c Questions 1-2
Which of the following areas does the lecturer say she will cover? Circle TWO answers. A Global inequalities B
Poverty in the developing world C The history of globalization D
The key arguments for and against globalization E Trade and e onomics c F The World Tr de Or a ganization Questions 3-5
Complete the following sentenc s using e
NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS OR A NUMBER. 3. Many people fe l g
e lobalization is about the e onomy or ………… c
4. An example is the export of Japanese …………
5. Globalization began approximat l e y ………… ago. 36 Question 6
Which of these is NOT mentioned as important to the development of globalization? A the telephone B the f x a C the postal service D air travel Questions 7-9
Complete the following notes using NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS.
Anti-globalization groups – e.g. Greenpeace and Friends of the
Earth. These are 7………….. organizations. They feel
globalization causes global warming, and depletion of oil, gas, 8…………..and sea life.
Many businesses in developed nations are against globalization
because of competition from 9 ………….. Questions 10-12
Complete the table using ONE OR TWO WORDS OR A NUMBER. Organization Establi hed s Number of member Roles states WTO (10) ………. 123 Prevents members favouring home industries IMF 1946 (11) ………… Provides temporary financia l help UN 1946 Promotes shared values between UN and the (12) ……….
Throughout the lecture, the lecturer uses i
certa n words and phrases to signal, or signpost, key
stages in the lecture. Recognizing these c n
a help you understand and follow her argument.
Look at these “signposts” and divide them into categories.
Introduction: …………………
Sequencing: …………………
Changing topic: …………………
Concluding/Summarizing: ………………… 37 A Turning now to … G
I will start by considering …
B Now let us look a little at … H So, we’ve seen that … C Lastly, … I
I’d now like to move on to …
D In the first part of today’s lecture… J Secondly, I will explain … E I would like to … K So, let’s begin with F Having looked at … L Finally, I intend to … Listen to the whole l cture e
again and number the signposts in the order in which you hear them. Exercise 4
You will hear the following signaling phrases during the first part of the lectur . e
Number them in the order which you expe t to hear them. c Order Phrases ………
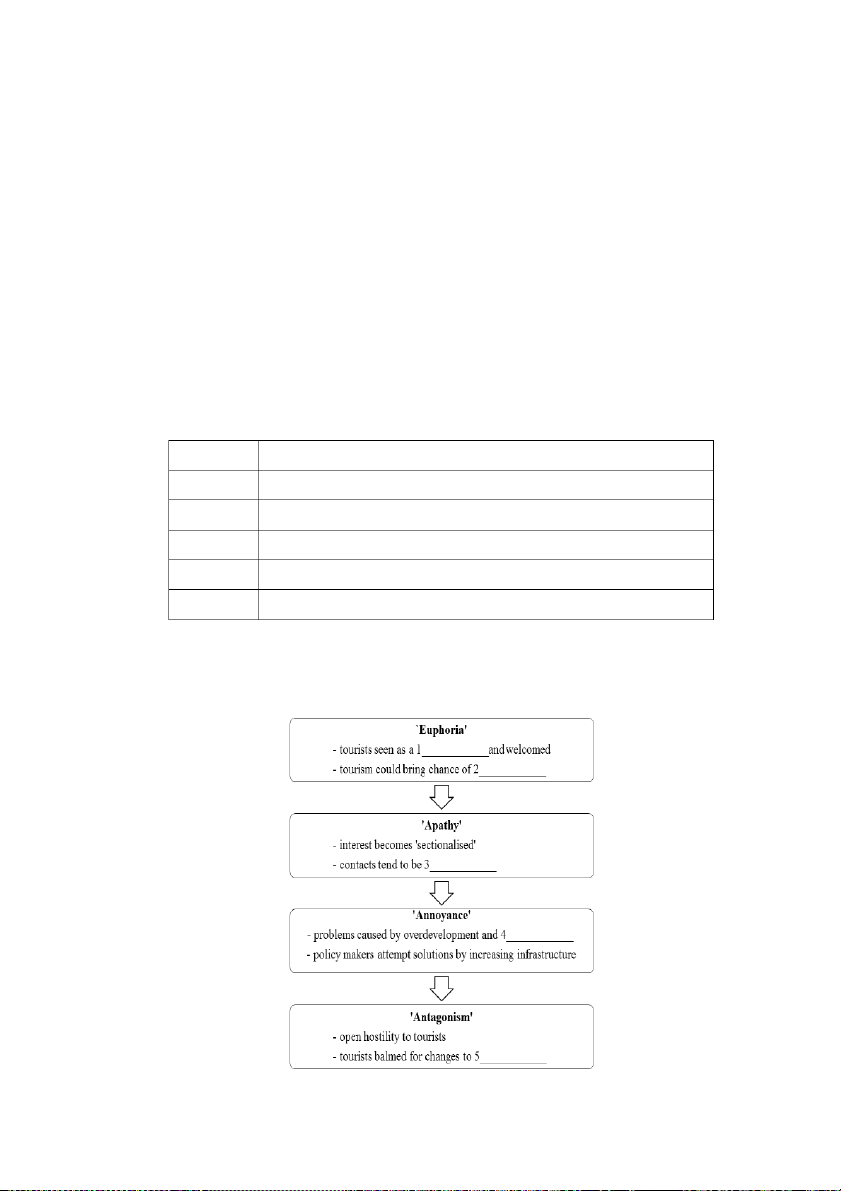
As tourist development begins to increase … ……… Doxey identifies four stages. ………
If development continues to increase … ……… He c lls the first s a tage … ………
… in the final stage of the model … Now listen to the re ording c and compl te e
the task below. Doxey's 'Irridex ' model of tourism. 38 B. TAKING NOTES What is Note-taking?
Note-taking is writing down information while you are listening or reading. When you take
notes, you will organize the information into major points and minor points. You will also
record information that you c n refer to when you answer que a stions. When note-taking:
! Use the organization of a lecture: introduction, body (point-to-point or
comparison/ contrast) and summary. Then, you c n a e sil a y c tegorize a the l cture e for your notes.
! Pay specia lattention to the introduction to get an idea of the topic and the organization of the le ture. c You c n
a use this information as a road map to listen more effectively. The
summary by the spe ker is criti a
c l when checking for missed information. a ! Think ahe d.
a Anticipate what the spe ker might say nex a t.
! Do not try to write everything down. It may le d
a to distraction or confusion about the focus of the lecture.
! Try to take notes in your own words. It will help you summarize the le ture c la er t .
Helpful techniques for note-taking:
! Note the organization of the passage, whether i tuses contrast, compari on, s etc. It ay m be
effective to use a column (just a vertic l a line betwe n e two c te a gories) to group information.
! Create topic headings and indent subtopics. ! Li ten s
for cues such as transitional words, repetition of certain phrases, changes in voice, or number of points.
! Use abbreviations and symbols for commonly occurring words and names. It will incre se a your note-taking spe d. e
! Group rel ted ideas with bracke a t and arrows s
! Make your notes neat and legible enough for your own re din a g. Do not be
concerned about how they look to others.
! Develop your own system and your own abbreviations. You c n even crea a te abbreviations
with your native l nguage if it is more ef a fective. 39
USING SYMBOLS AND ABBREVIATIONS
When you are taking notes, you do not have time to write down everything the spe ker a says.
Therefore, you must note as much information as possible in the fewest words. Ea h c person
can develop his or her own symbols and abbreviations. Exercise 1 To save m
ti e and get down more information when you listen, it is helpful to abbreviate words. It i
s helpful to abbreviate them in a way that will allow you to remember what the full
form is. Another person’s abbreviation may not help you to remember. Practice abbreviating
the following terms in a way that you will know what each abbreviation stands for a few days or a few weeks lat r
e . Look at the examples to see how some t rms have been abbreviated. e Example:
- historical look at work: hist lk at wk - statistics: stats TERM ABBREVIATION a. agriculture
b. mining, manufacturing, and construction c. service industries d. wages and sal r a ies e. average per capita income f. health insurance g. working conditions h. increased productivity i. stock market j. labor unions Follow-up: With a partner, t ke a turns covering up the l ft
e column. Looking at the right column, practice
saying the terms that your abbreviations stand for. Your partner will che k your c ac urac c y. Exercise 2
Work in pairs and work out the meaning(s) of the symbols and the full form of the abbreviations below. 40 Symbol Meaning Symbol Meaning = ‘ ≠ ‘’ > + < _ % € => $ <= £ <≠ / Abbreviation Meaning e.g. cf. etc. imp. i.e. poss. w/ w/o pop. c. / ca. Add. Exercise 3
Listen and take notes on the following sentences, which contain information taken from several l ctu e
res for which you could use some of the symbols and abbreviations above. Try to
take down content words, abbreviat
e as many of these content words as possible, and use your
notetaking symbols and abbreviations. You will hear each item TWICE. Example: You hear: “The dem nd a for oil has incre sed a
greatly in the past 100 years and so the price has also risen.” Your notes: demand for oil in past 100 yrs => price 41
(Items 1-3 are from a lecture on population)
1. ................................................................................................................................
2. ................................................................................................................................
3. ................................................................................................................................
(Items 4-5 are from a lecture on immigration)
4. ................................................................................................................................
5. ................................................................................................................................
(Items 6-7 are from a lecture on American family)
6. ................................................................................................................................
7. ................................................................................................................................
Compare you notes with your classmates’. Follow-up: Re onstruc c
t the full message of what you heard from your notes. Look ba k
c at your notes and see if there were plac s
e that you missed where you could have
used a symbol or a short abbreviation to save time. Exercise 4
Listen and take down the subtopics mentioned in the introduction of a lecture.
Subtopic 1: …………………………………………………………………….
Subtopic 2: …………………………………………………………………….
Subtopic 3: ……………………………………………………………………. Exercise 5
Listen and fill in the mi sing word s s. PILOTS
Many people ………………………………………... But not m ny a people know how to
……………………………….. Pilots know how to ……………………………………. They
………………………………… to become a pilot. Pilots are ………………………………… in the plane.
Before ………………………………, pilots ………………………… of the plane. They must
make sure that ………………………………………............ Pilots train for
…………………………………………. This is why everyone listens to them in
……………………………. Pilots are the ………………………………. They must not
……………………………………., so they e t a food that i
s ………………………………….
Do you want to be ome a pilot one day? c LONG-LINE FISHING
Fishing c n be …………………………………………. But long-line fishing can be a
…………………………………………. In …………………………………………, a boat
travels ………………………………. Storms are always …………………………………
When a storm comes, there is no …………………………………………….. The long-line
fishermen must …………………………………………and hope for the best.
The fish that ………………………………………………….are also very dangerous. They
catch swordfish. …………………………………………... They have a
…………………………………. If a swordfish …………………………, it c n a
……………………………………or even kill him. There is no hospital or doctor to help
……………………………. Long-line fishermen must al ay
w s ……………………………. 42 CELLPHONE USING MANNER
Cell phones …………………………………………………………………. Most people
cannot think about ….......……………………………………………………………………
But we must …………………………………………. when using cel phone l s.
We………………………………………when …………………………………………….. It
is very ……………………………………… that …………………………………. We should
either …………………………………… ………………………………………, or
…………………………………………and not ……………………………………………….
We should ……………………………the phone in …………………………………. Nobody
likes ……………………… while ………………………………………….. In for ign e
countries, people …………………………………………………... if they -
………………………………………… in shows.
Follow-up: Works in pairs. Read to each other what you have t ken down. a 43 TEST PRACTICE
Introduction to VSTEP Listening test format
Each VSTEP candidate takes four test modules, one in each of the four language skills:
listening, speaking, reading and writing.
The listening module takes around 40 minutes, including transferring time. There are three
sections with 35 multiple-choice questions. The questions should be answered on the basis of
what is stated or implied by the speakers in the recording. The recording will be played ONCE only.
* Section 1: The candidate will hear EIGHT short announcements or instructions. There is one
question for each announcement or instruction.
* Section 2: The candidate will hear THREE conversations. There are four questions for each conversation.
* Section 3: The candidate will hear three talks or lectures. There are five questions for each talk or lecture.
There will be time for the candidate to read the instructions and questions and chance to
check the work. Answers can be marked / ticked on the Question Paper as candidates listen. At
the end of the test, the candidate will be given 7 minutes to transfer the answers to an answer sheet. Test taking strategies Before you listen:
! Read the question and options before each section of the recording begins, and try to
imagine the situation and language.
! Identify what question is being asked and try to predict possible answers
! Look through the options and say each item silently. Thinking about pronunciation will
make it easier to identify the answers when you hear them.
! Underline key words in the questions and options. Sometimes the key words are those
that make the difference in meaning between options.
! Think of synonyms and paraphrases of the key words. As you listen:
! Listen carefully for keywords. Use the key words to follow the speaker; otherwise, it will be more likely to get lost.
! Expect the trick! More than one choice may be mentioned, so be careful. Don’t choose
an option as soon as you hear it on the recording. You may hear information relating two
or more options, but only one option will be correct.
! If you're not sure, make a good guess, which is based on key words and phrases you
have heard, then move on to the next question. If you miss a question, don’t waste time
thinking about it. Move on so you don’t miss the next question. 44
! Don't check your answers to the previous section; use the pauses to read ahead preparing
for the next set of questions.
! If you don't have time to read everything, don't worry. Prepare as many questions as you
can, then do your best on the others.
! Keep track of the time. You have a few seconds to read each section before you listen.
You will however have 7 minutes at the end to put your answers on the answer sheet.
! Keep listening all the time, looking only at the questions that relate to the part being played.
! Be alert for synonyms and paraphrases of key words as well as specific information, e.g., dates or numbers.
! Try hard to concentrate on what you are listening to. This can be done by focusing on
the key words underlined in the questions and options. Otherwise, it would be more likely to lose. 45 TEST 1 Part 1: Questions 1 - 8
Directions: In this part, you will hear EIGHT announc ments e or instructions. r The e is one
question for each announc ment e
or instruction. For each question, choose the right answer A,
B, C or D. Then, on the answer sheet, find the number of the question and fil in l the space that
correspond to the letter of the answer that you have c hosen.
1. How many years of accounting experienc are e required? A. 3 C. 30 B. 15 D. 35
2. What type of personnel is Comsat looking for? A. Chemical ngineers e B. Computer designers C. Electric l engin a e rs e D. Communications personnel
3. Who would find this position attractive? A. A r cent college graduate e B. An experienc d corpora e te exe utive c
C. A public utility technician D. A novelist 4. Whe e is the speak r er? A. On television B. At an office party C. At a wedding D. At a birthday party
5. Why should people stay in their seats? A. To avoid the traffic B. To free the ai le s C. To meet the captain D. To serve themselves
6. What happened to Millic nt Pre e ndergood? A. She was fired. B. She passed out. C. She retired. D. She took annual le ve. a
7. Whe e has the caller reached? r A. An answering machine B. A f x li a ne C. A telephone company D. An office
8. Which event was NOT mentioned? A. A painting class B. A le ture on artist c s of the e rly 20 a th c ntur e y C. A foreign film series D. A creative writing class 46 Part 2: Questions 9 – 20
Directions: In this part, you will hear THRE E conversations. The r conve sation wil l not be
repeated. There are four questions for each conversation. For each question, choose the correct answer A, B, C or D.
Questions 9-12: Listen to a conve sation between a student and a counselor r .
9. Why does the woman visit the counselor?
A. To conduct a mock interview B. To r ceive advice on job e possibilitie s
C. To get information on graduation
D. To create a list of companies.
10. What is one quality the woman is looking for in a career? A. A full-time job B. A tea hin c g position C. A care r e in fine arts D. A chance to advance
11. What can be inferr d about the woman? e
A. She won’t apply for a job at the Youth Center.
B. She has be n having trouble lo e c ting a good job. a
C. She is excited about her upcoming career opportunities.
D. She doesn’t have enough money to go to graduat school e
12. Which of the following is NOT the counselor’s suggestion?
A. Look up companies in the phone book. B. Make and sel her own l artwork.
C. Apply to teach art to kids. D. Schedule a mock interview.
Questions 13 - 16: Listen to a conve sation betw r e n tw e o students, Harry and Andrea.
13. What is Harry’s problem?
A. He doesn’t want to sel his thing l s. B. He ne ds to d e e id
c e what to do with his possessions.
C. He wants to take everything to England. D. He has to resit his exam.
14. Which of the items below does Harry want to sell? A. His computer B. His plant C. His fridge D. His TV 15. Whe e r is Har y going to adv r e tise h r is books for sale? A. In the University bookshop B. In the student newspaper
C. In the economics department D. In a charity shop 47 16. Andr a thi e
nks it is unlikely students wil buy the l furniture because
A. They’re al doing the same thing. l B. They live at home.
C. It’s the summer vacation.
D. They don’t have much money.
Questions 17 - 20: Listen to a conve sation r betwe n
e two students about buying a used car.
17. What happened to Sam’s car? A. It was replac d b e y another one. B. It broke down. C. It was stolen. D. It was sold.
18. Why does Jan ne d a car now e ?
A. She lives too far from the university.
B. She spends too much time on the bus.
C. She would fe l safer at night with a car e . D. She hates walking. 19. What does Sam recommend? A. Che k the service r c e ords c B. Avoid buying an old car
C. Get a mechanical inspection
D. Get a che p car to save mone a y
20. How are they travelling to the seller’s house? A. By motorcycle B. On foot C. By bus D. By train Part 3: Questions 21 – 35
Directions: In this part, you will hear THREE t l a ks or lectures. The t lks a or l ctures e will not
be repeated. There are five questions for each t lk
a or lecture. For each question, choose the correct answer A, B, C or D.
Questions 21 - 25: Listen to an information announcem nt for passengers on a ship. e
21. At approximately what time will the ship arrive? A. At 7 a.m. B. At 8 a.m. C. At 9 a.m. D. At 12 a.m.
22. Which of these can childr n h e ave in the restaurant? A. A children’s menu B. Earlier mealtimes C. A children’s party D. A toy shop 48
23. What are available at a reduc d pr e ice? A. Souvenirs of the ship B. First-class c bin a C. Tr in t a icket s D. Meals in the restaurant
24. Which of these is situated in the lounge? A. A computer B. A coffee machine C. A television D. A bar
25. What special event will happen during the voyage? A. A f shion show a B. A concert C. A competition D. A magic show
Questions 26 - 30: Listen to a l cture about e t a e in the UK.
26. When did the first coffee house offer tea? A. In 1760 B. In 1716 C. In 1706 D. In 1786
27. Who was the owner of Tom’s Coffee House? A. Lloyds B. The Golden Lion C. An insurance company D. Thomas Twining
28. What was on the sign of the tea shop owned by Twining? A. The Golden Lion B. The Strand C. The Tea Shop D. Twining 29. Which item is NOT on a compr hensive 18 e th century tea-tray? A. Glasses and spoons B. A te pot and stand a
C. A sugar bowl and a milk jug D. Cups and sauc rs e
30. Whe e was tea kept by the m r istr ss of the house? e A. In basins B. In metal kettles C. In locked wooden commodes D. In locked caddies 49
Questions 31 - 35: Listen to a talk about the Wom n’ e s Conference.
31. How many me tings are going to be he e
ld from August to September in Beijing? A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 5 32. When wil the Non-gov l e n
r mental Organiz tion Forum on a Women be held?
A. From August 13th to September 8th, 1995
B. From August 30th to September 8th, 1995
C. From September 4th to September 15th, 1995
D. From September 4th to September 16th, 1995 33. Whe e was the r Thir d World Confer nce on e Wom n h e eld? A. In Beijing B. In Mexico City C. In Copenhagen D. In Nairobi
34. How many people are expected to attend the Fourth World Conference on Women? A. 30,000 B. 184 C. About 6,000 D. About 60,000
35. How many years has it taken to prepare for the Fourth World Confer nce e in Beijing? A. 13 years B. 10 years C. 5 years D. 3 years 50 TEST 2 Part 1: Questions 1 - 8
Directions: In this part, you will hear EIGHT announc ment e or instruction. r The e is one
question for each announc ment e
or instruction. For each question, choose the correct answer
A, B, C or D. Then, on the answer she t
e , find the number of the question and fill in the space
that correspond to the letter of the answer that you have chosen.
1. Who does the caller wish to speak to? A. A salesperson B. A te hnician c C. An editor D. A printer
2. What is the announcem nt about? e A. A newspaper B. A r dio a show C. Television D. A debat e 3. How much of a r du
e ction is the e every half hour? r A. 10% C. 45% B. 20% D. 50% 4. Whe e doe r s Super Sunday take place? A. In shelters B. In poor are s a C. Across the country D. In an unf miliar place a
5. What will be pur hased with the money? c A. More grain B. Replac ment parts e C. Medicines D. Food
6. What would incr ase the value of the e yen? A. A lower savings rat e B. Higher tr de a tariffs abroad C. F wer consumer loans e D. High economic growth
7. What conce ns the embassies of the tw r o countries? A. Defense B. Commerce C. Educ tion a D. Spa e c 8. When wil the problem abate? l A. By today B. By tomorrow C. In two we ks e D. In ten years 51 Part 2: Questions 9 – 20
Directions: In this part, you will hear THRE
E conversations. The conversation wil l not be
repeated. There are four questions for each conversation. For each question, choose the correct answer A, B, C or D.
Questions 9-12: Listen to a phone call betwe n e Anna and her friend, Peter.
9. Which animal is Anna being asked to look after? A. Rabbits B. Cats C. Birds D. Dogs
10. What does Peter want Anna to do?
A. To look after a pregnant animal B. To buy box of cat food C. To fe d the bab e y animal s
D. To w sh the animals every day a
11. How many babies did one of the animals have last time? A. 2 C. 5 B. 4 D. 6 12. When Peter m ntioned e that one of the animals i
s going to be delivering soon, Anna was A. happy. B. worried. C. sad. D. angry.
Questions 13 - 16: Listen to a conve sation betw r e n e Mike and Tom. 13. Mike often talks about
A. his difficulties at his house. B. finding a place to live. C. the parties he went to. D. his friend’s house.
14. Mike wants to move, but he wants to live A. alone. B. in a quiet plac . e C. ne r a the school. D. with his parents.
15. How many people live in Tom’s house beside Tom? A. 2 C. 4 B. 3 D. 5
16. The expenses which Tom and his housemates share do not include A. food B. rent C. light D. heating 52
Questions 17 - 20: Listen to a job interview. 17. M s. Jane Smith is r A. a counselor. B. a journalist. C. a l cturer e . D. a personnel manager. 18. Peter has had hi p s r sent job e A. since 2002. B. for more than three years. C. for three months. D. since 2003.
19. The r ason he wants a new job is e A. for a change. B. to earn more money. C. to get a promotion. D. to have a new challenge.
20. The thing he likes most about his pr sent job e is A. the responsibility. B. good salary. C. his colleagues. D. working conditions. Part 3: Questions 21 – 35
Directions: In this part, you will hear THREE t lks a
or lectures. The talks or l ctures e will not
be repeated. There are five questions for each t lk a or l cture. e For each question, choose the correct answer A, B, C or D.
Questions 21 - 25: Listen to a talk on oc an spil e ls.
21. The plastic toys we e washed of r f the ship A. in Alaska. B. in the Pacific Oce n. a C. in the Ar tic c Oce n. a D. in the Bering Sea.
22. How long did it take the first ducks to ar ive at the beach? r A. About two we ks e B. About two months C. About ten months D. About twelve months
23. Who we e most excited by the plastic toys? r A. The reporters B. The tourists C. The children D. The oceanographers 53 24. Whe e exactly w r e e the f r irst toys picked up? A. The North Pole B. The Ar tic Ocean c C. The North Atlantic D. Alaska
25. Which of the items below spilled out into the wat r e in the 1990 ocean spill? A. Shoes B. Women clothes C. Toys D. Furniture
Questions 26 - 30: Listen to a discussion in a geography class.
26. What is the discussion mainly about?
A. The similarities betwe n the Himala e yas and Appala hians c
B. Definition and process of continental colli ion s
C. Description of the proc ss that formed the e Himalayas
D. An explanation of how volc nic mountains are f a ormed
27. What is the proc ss of orogeny? e
A. How volcano action forms mountain.
B. How young mountains start to form.
C. Why mountains get smaller over time.
D. When plates collide to form mountain.
28. Why does the professor talk about the Appalachian mountain?
A. To compare their formation to that of the Himalayas
B. To explain why younger mountains are often taller
C. To describe the complex process of orogeny
D. To suggest that they are older than they appe r a
29. What can be inferr d about old mo e untain ranges? A. They were once much tall r e .
B. They have more folds than the Himalayas.
C. They were produced by orogeny.
D. They have not experienced erosion.
30. Why are the Himalayas folded?
A. They experience much volcanic action.
B. India and Asia continue to collide.
C. The mountains are younger than most.
D. They have not undergone erosion. 54
Questions 31 - 35: Listen to a l cture e in a biology class.
31. What is the l cture mainly about? e
A. How people survived the plague B. Pl gue out a bre ks throughout the age a s
C. The consequence of plague in England
D. The true origin of the plague
32. What dire tly caused the plague c in human? A. Rat s B. Ba teria c C. Fl as e D. A virus
33. What is the main topic of the lectur ? e A. The impa t p c lague had on Europe B. The effe t of a c genetic mutation
C. The process of how people got sick from plague
D. An explanation of why plague is so de dl a y
34. How do scientists know that some 14th c ntury European e s possessed delta 32?
A. By interviewing plague survivors
B. By looking through old re ords c
C. By testing their descendants D. By examining a mutation
35. How did the g ne protect some survivors from the plague? e
A. By signaling the immune system to destroy i t
B. By removing the plague from the body
C. By preventing i tfrom coming into cells D. By atta king c and killing the disease 55 TEST 3 PART 1: Questions 1- 8
Directions: In this part, you will hear EIGHT short announcements or instructions. r The e is
one question for each announc ment e
or instruction. For each question, choose the right
answer A, B, C or D. Then on the answer sheet, find the number of the question and fill in the
space that corresponds to the letter of the answer that you have chosen.
Question 1.Who is the audienc for this annou e ncement? A. Tr in travelers a B. Bus riders C. Airline customers D. Subway travelers
Question 2. Whe e is this talk taking place? r A. In a college clas room s B. At a business me ting e C. On a te evision talk show l D. In a station
Question 3. What type of pe formance is going to take place? r A. A concert C. A catwalk B. A dance D. A play
Question 4. What is the main purpose of the report? A. To summarize the story B. To entertain listeners
C. To update traffic and weather D. To explain information
Question 5. Whe e does the speaker work? r A. At a computer company B. At a newspaper C. At a university D. At a department store
Question 6. When should the listene s te r lephone the NLF?
A. Bet een 9 a.m. and 4 p.m. we w stern time
B. Bet een 8 a.m. and 9 p.m. centra w l time
C. Bet een 8 a.m. and 5 p.m. ea w stern time
D. Bet een 9 a.m. and 5 p.m. we w stern tim e
Question 7. What is the main purpose of announcement? A. To issue a warning B. To w lcome visitors e C. To explain fire zones D. To entertain the audience
Question 8. How many childr n does the contestant have? e A. One B. Two C. Three D. Four 56 Part 2
Directions: In this part, you will hear THRE
E conversations. The conversation wil l not be
repeated. There are four questions for each conversation. For each question, choose the correct answer A, B, C or D.
Questions 9-12: Listen to an interview with Sébastien who started the activity known as ‘free running’.
9. What does Sébastien say about fitness and taking up fr e r e unning?
A. Fi people are keen to do dif t ficult things immediat ly e .
B. People who are not fit don’t le rn very quick a ly.
C. Free running is a good way of getting fit.
D. You have to be fit to take up fr e running. e
10. What does Sébastien say about taking risks?
A. He used to take more risks than he does now.
B. He al ays tries to take the minimum amount of risk. w
C. Some of the things he does involve no risk.
D. He always prefers taking risks.
11. What does Sébastien say about his fear of heights?
A. People don’t believe that he has it.
B. He always has to overcome it. C. It is not as gre t as it u a sed to be.
D. He has it as much as everyone does.
12. What does Sébastien say about whe e f r r e run e ning can be done?
A. People’s opinions on this are changing.
B. His own opinions on this have changed.
C. Some people have the wrong opinion on this.
D. People think that it can take place everywhere.
Questions 13-16: Listen to a conversation betwe n e a student who i s looking for a flat in London and a letting agent. 13. He wants to r nt a flat b e ecause he A. is a student in London.
B. is going to stay in London for the rest of his life. C. c n’ a t afford to buy a flat.
D. is going to travel and stay in London for 2 months. 14. He wants the flat to be A. furnished. B. close to the university. C. in central London. D. close to bus station.
15. The man seems to be pleased that there is
A. a post office a ross the stree c t. B. a pub in the neighborhood. C. an internet café ne rby a . D. a subway station nearby. 57 16. He is ve y intere r sted in the se ond o c ffer because A. the rent is low. B. it’s a detached house.
C. there are already four students in the house.
D. he c n share the room with his friends. a
Question 17-20: Listen to an interview with Sophie Morrison, a translator.
17. Why did Sophie take up translating?
A. She had studied modern languages at university.
B. She sometimes used to do translations for fri nds. e
C. She enjoyed reading text in other language s s.
D. She thought translator would be a good job in future.
18. Which, according to Sophie, are the most difficult things to translate? A. cultural references B. informal expressions
C. scientific and technical words D. medical terms
19. How does she fe l about her daily working hour e s? A. They are al ay w s too long. B. They are quite flexible.
C. They shouldn’t include evenings. D. They vary too much.
20. Sophie believes that in the future
A. translating will al be done by l ma hines. c B. more l nguages will n a e d to be t e r nslated. a
C. translators will have to be better trained.
D. translators need to master in more than one language. Part 3: Questions 21 – 35: In thi s part, you will he r
a THREE talks or lectures. The talks or l ctures e will not be repe ted. a
There are five questions for each talk or l cture. e For ea h c question,
choose the correct answer A, B, C or D.
Questions 21 - 25: Listen to a talk of a professor.
21. What is the main purpose of this talk?
A. to discuss incomplete grades. B. to arrange for makeup exam s
C. to explain course policies and proc dures. e
D. to give an overview of the course content 22. What is the speake ’
r s policy for late assignments?
A. He will allow the students one day after the due dat be e fore marking them down B. He will not acc pt la e t a e ssignments.
C. He will subtract one letter from the grade for each day that the paper is late.
D. He will excuse students who are ill.
23. What is the professor’s attendance policy?
A. He calls the roll before every session.
B. He does not take attendance in class.
C. He has each student che k in after cla c ss D. He uses a se ting char a t to take attendance.
24. What is the procedure for a student to rec ive a grade of incomp e lete?
A. The student must submit a r quest form explaining why the incomplete is n e ecessary. B. The student must cal the sp l e ker to explain. a
C. The student must arrange for the incomplete within one we k of the e final exam.
D. The student must register to take the course again. 58
25. What can we infer about the speaker? A. He is not very organized.
B. He does not like his students.
C. He does not mind if his students cal him a l t
home. D. He does not give many exams.
Questions 26 - 30: Listen to a lecture.
26. What is the main subject of this lecture? A. Heredity B. Environment C. Birth order D. Motivation
27. What should the students know before they hear this lecture?
A. Birth order may influence personality.
B. Heredity and environment play a role in the development of the personality.
C. There is research on birth order at the University of Texas at Arlington.
D. Firstborn children and only children have similar personalities.
28. Which one of the people would probably be the most comfortable interacting with a member of the opposite sex?
A. A man with younger sisters. B. A man with older sisters.
C. A woman with younger sisters.
D. A woman with older sisters.
29. What personality trait will firstborn children probably exhibit? A. Likable B. Ambitious C. Sociable D. Talkative
30. According to the research, what might be the dominant personality trait of the youngest child? A. Charming B. Shy C. Motivated D. Happy
Questions 31 - 35: Listen to a talk.
31. What is the main topic of this talk?
A. The American eagle as a symbol on coins.
B. The history of gold coins in the United States C. The United States Mint.
D. The value to collectors of gold coins.
32. What was the value of the original gold eagle? A. $20.00 B. $15.00 C. $10.00 D. $5.00
33. What was the value of silver to gold in 1792? A. fifteen to one.
B. fifteen and a quarter to one
C. fifteen and three quarters to one D. fifteen to three 59
34. What happened after the law of 1834?
A. The Great Depression occurred.
B. The size of gold coins was reduced.
C. All gold coins were turned in to the government.
D. The collecting of gold was severely reduced.
35. What are the restrictions on collecting gold coins today?
A. Gold coins may be imported without restrictions.
B. Gold coins may be collected but not exported.
C. There are few restrictions on the collection of gold coins.
D. Only certain kinds of gold coins may be purchased and so. 60 REFERENCES
1. Adams, G. & Peck, T. (2002). 101 Useful Hints for IELTS. Nhà xuất bản Tr . ẻ
2. Adams, G. & Peck, T. (2004). 202 Useful Exercises for IELTS. Nhà xuất bản Trẻ.
3. Cullen, P., French, A. & Jakeman V. (2014). The Officia Cambridge l Guide to
IELTS for Academic & General Training. Cambridge University Press. 4. F lla, a
T. & Davies, P. A. (2011). Solutions, Pre-intermediate. Oxford University Press.
5. Hallows, R., Lisboa, M., & Unwin, M. (2006). Ielts Express – Intermediat e Course book. Thomson.
6. Harrison, M. (2008). FCE Test Builder. MacMillan Educ tion. a
7. Jakeman, V., & McDowell, C. (2002). IELTS Practice Tests Plus. Nhà xuất bản Trẻ.
8. Jakeman, V., & McDowell, C. (2003). Insight into IELT Extra S with Answ rs. e Cambridge University Press.
9. Jakeman, V., & McDowell, C. (2004). Insight into IELTS. Cambridge University Press.
10. Jakeman, V., & McDowell, C. (2004). Step up to IELTS. Nhà xuất bản t ng ổ
hợp Thành phố H Chí Minh. ồ
11. Linguaforum (2008). LinguaForum TOEFL iBT i-listening - High intermediat e
course. Nhà xuất bản t ng h ổ ợp Thành ph H ố Chí Minh. ồ
12. Lougheed, L. (2006). Barron's Ielts. Nhà xuất bản Trẻ (First News).
13. Macgillivray, M., Yancey, P., Zeter J. & Malar her c , C. (2009). Mastering
Skills for the TOEFL iBt. Compass Publishing.
14. May, P. (2011). First Certificate Trainer. Cambridge University Press.
15. Myounghee, K. et al. (2014). Ivy Li tening s
Toefl iBT- 15 Actual Tests. Nhà xuất bản t ng h ổ
ợp Thành phố H Chí Minh. ồ
16. Robert, R., Gakonga, J. & Preshous, A. (2004). IELT Found S ation. MacMillan Education.
17. Sharpe, P. J. (2007). Barron Practice Exercise
s for the TOEFL 6th edition. Nhà xuất bản trẻ.
18. Terry, M. & Wilson, J. Focus on Ac demic Skills for IEL a TS. Longman.
19. Zeter, J. & Pederson, M. (2008). Sharpening Skill s for the Toefl iBT- Book 1.
Nhà xuất bản Trẻ (First News). 61


