





Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
EarthWear’s Revenue process: học kỹ về process revenue, inventory, nhập hàng lưu hàng,… Invidual:
Corporate: how it works? Revenue will be given through customer order. After the customer order
they will check, decide to sell to the customers or not (through credit approval,…). After approval
of the order, they will ship and bill. After they bill, they will record and receive the payment.
Customer order, check credit approval, shipp, bill and record, receive payment. In some cases, we will have the return. 1. Customer order 2. Credit approval form
3. Shipping documents (or open order nếu chưa ship,…)
4. Sale invoices when you bill
5. If record, have to have sales record, cash, account receivable.
6. If you have to return – sales returns and allowances (sẽ có return memorandum). Mà
return thì record vào returns and allowances.
7. Allowance for doubtful account: 1 lần duy nhất vào cuối kỳ Accrual expense/accrual liabiltiies.
Functions in the Revenue process: table 10-2
Phải make sure each major function không bị nắm giữ bởi 1 người, 1 ng chỉ có thể nắm 1,2 cái. Inherent risk, control risk.
Mỗi một procedures sẽ khác nhau với mỗi cái
Control risk muốn biết thì phải đi hỏi chứ không có one applied all. Table 10-5. Table 10- 9.
Substantive analytical procedure: với mỗi account thì phải so sánh với chỉ số gì? Bai 10-24.
1. When we should recognize the revenue?
We have sales contract, price, value of the contract, assure about the value of the contract.
In this case, do we have the contract sign? lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
This means when u audit there is no contract. From the audit evidence there is no sales recorded.
2. When should we record the revenue?
Cháy xưởng – ghi nhận chi phí: nhưng không có con số ước tính chính xác thì không thể ghi nhận : V
3. Không được ghi nhận ngay lúc nhân 48 đô đó, khách hàng xài bao nhiêu thời gian thì ghi
nhận bấy nhiêu tháng Còn 35% thì tính sao?
Đọc phần 5 steps to recognize revenue.
10-25: identify weakness and provide recommendation.
Trong bài thi, cô sẽ cho control system và mình sẽ judge xem control như vậy có tốt hay không?
- Almost no internal control over the fee collection.
- No recording, at least there is somebody do the recording cash receipt daily, and at the
end of the day have to have 1 person to count the petty cash.
- Cross-check: the one recording cannot be the one who hold the cash. 10-26: Audit procedures nao? a. Number 1
Người ta chứng minh account receivable này thuộc về công ty? Thế chấp. Review xem nó
có đem account receivable đó đi thế chấp không. Loan confirmation không chứng minh được điều đó.
b. Number 3 . Check completeness. c. Number 4
d. Number 6. Allowance – uncollectable account. e. Number 5 – confirmation f. Num 2. 10-27. lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
a. What would u do if you sent confirmation but not yet receive response. Cac TH nhan lai confirmation: - Nhan lai va tra lai so dung
- Nhan va tra lai so khac. – coi no co material khong. Neu material ma lech, nguyen nhan
lech (cutoff sai, ben kia tra ma ben minh chua nhan duoc,...) - Nguoi ta khong gui lai:
+ Subsequent receipt check: xem sau ngay ket thuc nien do khach hang co tra tien khong.
Neu sau do thi ngay ket thuc nien do no nợ mình.
+ Check xem chứng từ gốc mua hàng có phát sinh khoản tiền đó không. Thì có phát sinh
nhưng lỡ sau 31/12 nó k trả thì sao.
Highest quality evidence: subsequent payment đáng tin cậy hơn. Vì sao? Vì subsequent
payment, cho mình thấy 31/12 nó nợ mình thì nó mới trả tiền
Nó có trả tiền sau kết thúc niên độ không, 10-30.
Ngày của hóa đơn và ngày thực sự ship đi.
Những cái nào nhầm qua nhầm lại phải điều chỉnh tăng giảm. Table 13-8
The managers may overstate receivables, understates payables,… Based on knowing the
incentives of managers, auditors will test these. Tabel 13-9
LIFO liquidation la gi? Giá tồn trong sổ là giá cũ, vậy có khoản lợi nhuận khổng lồ nếu liquidate tới
sắp hết kho. Lợi nhuận trên báo cáo tài chính bị thổi phồng do LIFO liquidation chứ không phải lợi nhuận thật. Provision for bad debts: 13-33: Manipulate inventory account lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
Sử dụng … giả làm tăng số lượng lên. Cùng sản xuất 10 cái mà giờ là 100, lợi nhuận nhiều hơn.
Thêm time slip vào. Đi giám sát người ta kiểm, nhà máy to không kiểm hết. Cố tình gian dối, chỉ
cho cái chỗ không kiểm soát được.
Kiểm toán viên đã không làm cái test nào để công ty qua mặt. Đó là analytical procedures. Các
công ty competitors, có competitors nên nó bị mất thị trường. Sales không thay đổi được nhưng
inventory và COGS thay đổi được. Tỷ lệ sẽ khác. Nguyên nhân là gì?
Các tài khoản sẽ thay đổi theo pattern khớp nhau
Maintenance, insurance tăng – nó đang mua cho thằng nào, sales hay PPE, thì PPE phải tăng. Vậy
những cái tăng đó có make sense không.
Lúc check xong rồi, TOC, đáng lẽ mọi thứ phải chuẩn hết. Sau đó mới đưa giấy tờ bảo quên, vậy
thì nó control không tốt. Xem phần costing, standard cost các thứ có tốt không.
C. Phát hiện ra thì auditor có trách nhiệm nói với audit comittee không? Phải báo cáo với kiểm
soát nội bộ của công ty về vấn đề cố ý gian lận.
CHAP 14: AUDITING THE FINANCING/INVESTING PROCESS Prepaid expenses and PPE.
Prepaid expenses: assets that provide econmic benefit for less than a year. Prepaid rent, insurance,
1. Inherent risks assessments:
- prepaid insurance would generally be assessed as being low, since these accounts do not
involve any complex or contentious accounting issues.
- Hạch toán/record is below: Record prepaid insurance
Each month allocate 1 million into expense.
2. Control risk assessments:
- Based on the effectiveness of control procedures in the purchasing cycle.
Recommended steps in the purchasing cycle for prepaid insurance:
+ Request of buying insurance (prepaid – of course)
+ Request acceptance and sign the contract + Payment of the expenses + Record into the book lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
IF Internal control is effective: the sign of contract is made by appropriate
authority,payment is compared carefully,… risk of recording Prepaid insurance will decrease. Purchasing Cycle:
1. Xác định nhu cầu (ví dụ: cần mua bảo hiểm, nguyên vật liệu, dịch vụ).
2. Lập yêu cầu mua hàng (purchase requisition).
3. Phê duyệt yêu cầu mua.
4. Tìm nhà cung cấp và lập đơn đặt hàng (purchase order – PO).
5. Nhận hàng hoặc dịch vụ.
6. Ghi nhận và kiểm tra hóa đơn (invoice).
7. Thanh toán cho nhà cung cấp.
8. Ghi nhận kế toán (ghi vào báo cáo tài chính, ví dụ: ghi nhận tài sản trả trước).
- Additional control procedures for prepaid insurance may include the use of an insurance
register which contains a separate record of all insurance policies in force: kiểm tra giấy tờ
insurance còn hạn không, đối chiếu thông tin tránh thiếu sót hoặc ghi nhận sai thời gian.
- The entity should also maintain controls that provide for the systematic allocation of
prepaid insurance to insurance expense. Insurance expense cần được allocate each accounting period.
3. Substantive procedures: các bước kiểm toán chi tiết cho prepaid expenses:
Kiểm tra cái gì của prepaid expense? Balance or transaction? What major assertions?
- Comparing the current year balance in prepaid insurance and insurance expense with the
prior year's balances and ratios after considering any changes in operations: to see the changes
(in/decrease) match with the situations in reality of the entity such as expansion of entity
(more assets higher insurance expense), close (insurance expense decrease)
- Substantive tests of balances for prepaid insurance and insurance expense may be
necessary when the auditor suspects misstatements based on prior years' audits or when
analytical procedures indicate that the account balance may be misstated. - Procedure for auditing:
+ The auditor begins testing of the prepaid insurance account balance by obtaining an
insurance schedule from the client that contains a detailed analysis of the policies
included in the prepaid insurance account (see Exhibit 14-1).
+ The auditor's work then focuses on testing the validity, completeness, ownership,
valuation, and classification audit objectives.
Các mục tiêu kiểm toán được tập trung kiểm tra: lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392 Audit Objective / Meaning Example Audit Assertion Procedure The prepaid Review insurance contracts insurance must to ensure they are issued in
Validity (tính hợp lệ) relate to the company’s name and the entity’s
pertain to current activities. actual operations. Compare the client’s insurance schedule to the All prepaid general ledger and review Completenes s insurance amounts must be whether any insurance (tính đầy đủ) fully recorded. payments were omitted. Audit Meaning Example Audit Objective / Procedure Assertion The company must have Examine policy documents Ownership (quyền ownership or rights to and payment records to sở the prepaid
confirm that the entity is the hữu) benefit. policyholder. Recalculate the remaining The balance must reflect prepaid amount based on
Valuation (định giá) the correct unexpired policy terms and allocation portion at year-end. schedules. lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392 Classification The prepaid portion must be Verify that amortized (phân loại đúng) correctly presented as a portions are classified as current asset; expenses and remaining expired amounts should balances as current assets. be expensed. Audit Objective / Purpose of the Assertion Required Evidence Evidence - Copy of the insurance policy/contracts- Invoice and To confirm that the Validity proof of payment (e.g. bank transaction is real and transfer, relates to the entity. receipt)
- Full list/schedule of all insurance policies- Review of bank statements, expense accounts, or To ensure no prepaid Completenes s disbursement journals amounts are omitted. Audit Required Evidence Purpose of the Objective / Evidence Assertion
- Insurance policy naming the entity as To prove the company the insured party- Ownership owns the prepaid Supporting insurance rights.
correspondence with the insurer lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392 - Amortization To ensure the correct or allocation portion is recorded as Valuation scheduleInsurance policy prepaid (i.e. unexpired) start and end dates- Payment at year-end. amount and terms
- General ledger account details- To verify prepaid Financial statement amounts are recorded Classificatio mappingReview of adjusting as assets and expensed n entries appropriately.
When performing substantive procedures for prepaid expenses (like prepaid insurance), the
primary assertion that auditors test is: ✅ Primary Assertion:
👉 Existence and Valuation (or Accuracy) 🔍 Why?
1. Existence – To ensure that the prepaid expense actually exists at the balance sheet date
(i.e., the company truly has a right to future benefits).
2. Valuation/Accuracy – To verify that the amount is correct, appropriately allocated, and
not overstated. Prepaids must be amortized (expensed) over the period they benefit.
📁 What audit evidence do we need?
Here are the main types of evidence auditors would collect: Evidence Purpose 📄 Insurance
To verify total premium amount, period covered, and contracts /
service dates. agreements
Shows how much of the prepaid has been expensed 📆
Amortization and how much remains. Tests valuation and schedule accuracy.
🧾 Invoices and proofTo confirm the company has actually paid of payment (existence). 🧮
Calculation ofTo verify correct allocation of expense vs. remaining monthly expense prepaid. lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392 📊 Prior
yearTo identify any unusual fluctuations (analytical comparison procedure).
Between general ledger and supporting documents
🗂️ Reconciliations
– ensures completeness and accuracy.
✍️ Example substantive test:
"Recalculate the unexpired portion of prepaid insurance by reviewing the insurance policy,
premium paid, and the effective period, and compare it to the recorded prepaid balance in the general ledger."
4. Potential misstatements: 5. Related accounts
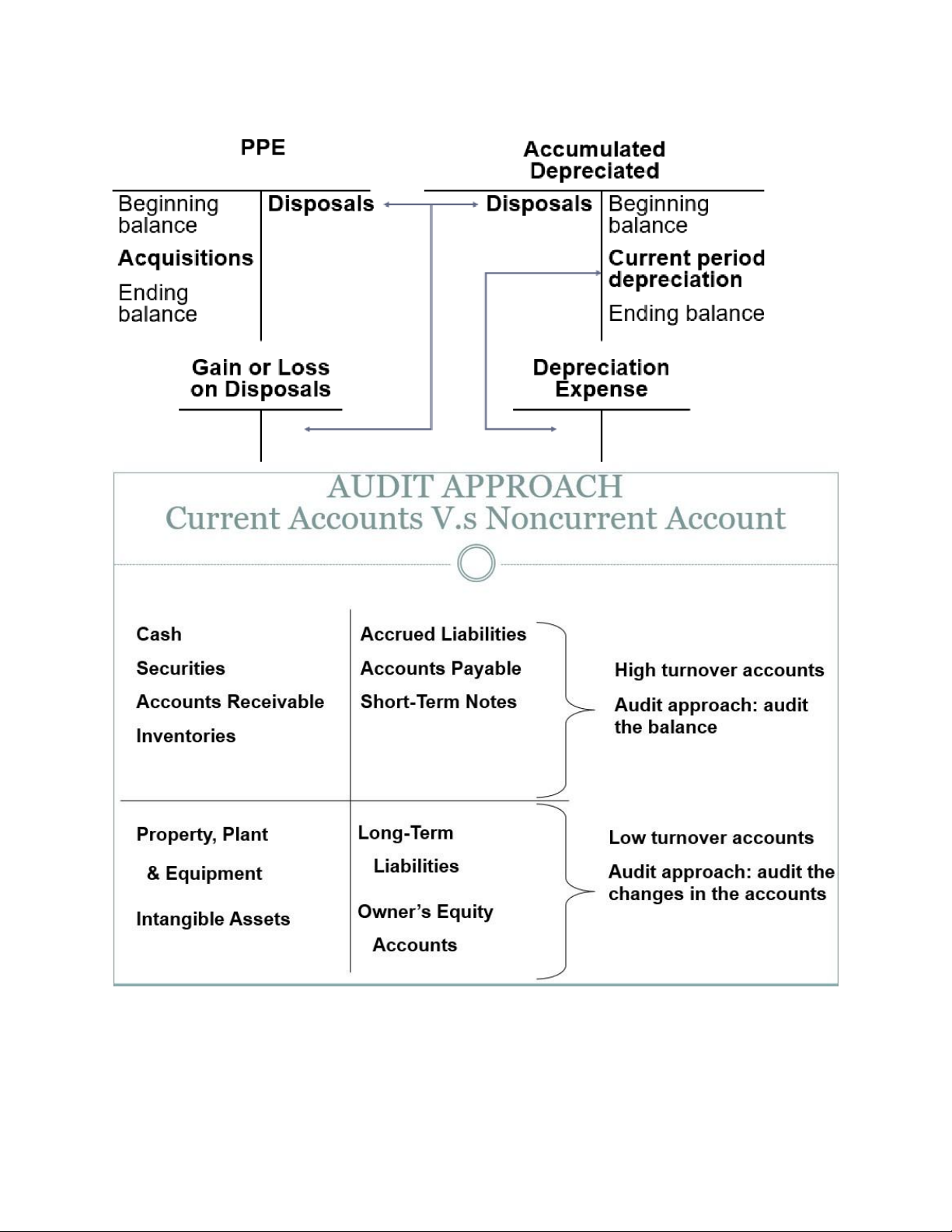
Property, plant and equipments: Tangible assets with a service life of more than one year that
are used in the operation of the business and are not acquired for the purpose of resale Three major subgroups: Land
Buildings, machinery, equipment and land improvements Natural resources
1. Related accounts of PPE: lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
2. How to control PPE?Control Procedure Explanation lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
The company sets a capital budget to plan and 1. Use of a plant
andlimit spending on PPE. This helps ensure only equipment capital budget necessary and
approved assets are acquired and keeps costs under control.
A subsidiary ledger is a detailed record showing information for each individual asset (e.g., 2.
Maintenance of apurchase date, cost, location, depreciation). It subsidiary ledger
supports the general ledger and helps prevent loss, errors, or fraud. 3.
A system ofAll acquisitions, disposals, or transfers of PPE must authorizations be
approved by authorized personnel (e.g., finance manager, CEO). This reduces the risk of Control Procedure Explanation
unauthorized or unnecessary asset purchases.
Regularly compare actual spending on PPE to 4.
Analysis of variancesthe approved budget. If there are large from budgeted
differences, investigate why. This helps identify expenditures
overspending, inefficiencies, or potential fraud. 5.
A statement of policyThe company should have clear rules on what is a distinguishing
betweencapital expenditure (PPE) versus a revenue capital and revenueexpenditure (expense).
This ensures proper expenditures accounting trea
3. Audit document? Giấy tờ làm việc của kiểm toán viên Working papers
- Summary analysis that emphasizes changes during the year under audit
- Analyses of additions and retirements for the current year (các khoản bổ sung và loại bỏ,
vd như tài sản mua thêm hoặc thanh lý)
- Analyses of repairs and maintenance expense accounts - Tests of depreciation
4. Initial audits: kiểm toán lần đầu.
Beginning balances: xác minh số dư đầu kỳ để đảm bảo các báo cáo tài chính năm hiện tại được
lập trên cơ sở đáng tin cậy.
- Substantiated by review of predecessor firm’s working papers
- If not previously audited, a complete historical analysis of property accounts is needed
- Thorough review of all major charges and credits to property accounts lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392 5. PPE Audit steps:
A. Use the understanding of the client and its environment
B. Understanding of internal control
C. Assess the risks of material misstatement
D. Perform further audit procedures—tests of controls.
1. Nature of tests of controls.
2. If necessary, revise the risks of material misstatement based on theresults of tests of
controls. (change the material misstatement if needed)
E. Perform further audit procedures—substantive procedures for property,plant, and equipment.
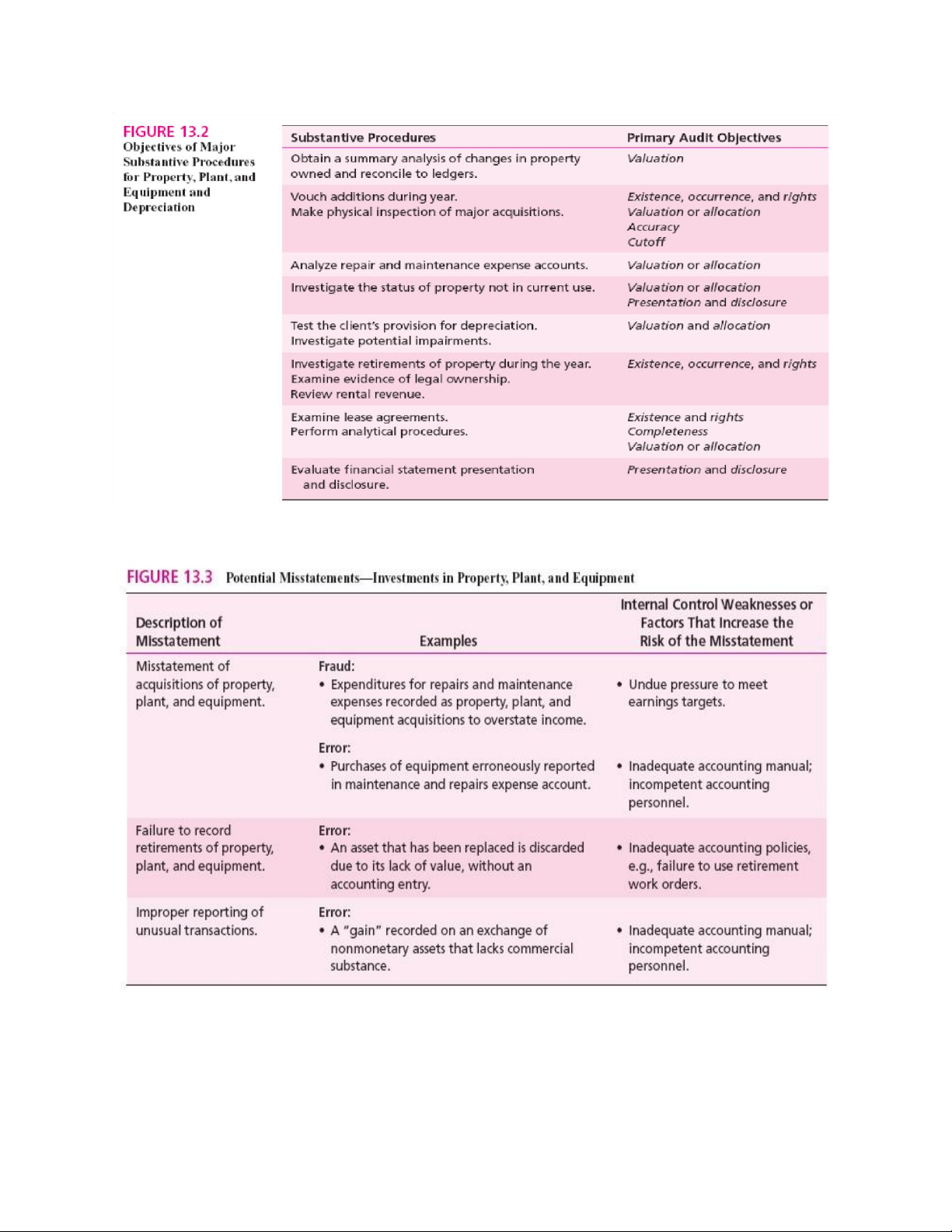
1. Obtain a summary analysis of changes in property owned andreconcile to ledgers.
Thu thập phân tích tổng hợp thay đổi về tài sản và đối chiếu với sổ cái.
2. Vouch additions to property, plant, and equipment during the year.Đối chiếu các
khoản mua sắm tài sản trong năm.
3. Make a physical inspection of major acquisitions of plant andequipment. Kiểm tra
thực tế các tài sản mua lớn trong năm.
4. Analyze repair and maintenance expense accounts.
5. Investigate the status of property, plant, and equipment not incurrent use.
6. Test the client’s provision for depreciation.
7. Investigate potential impairments of property, plant, and equipment.
8. Investigate retirements of property, plant, and equipment during theyear.
9. Examine evidence of legal ownership of property, plant, andequipment.
10. Review rental revenue from land, buildings, and equipment ownedby the client but leased to others.
11. Examine lease agreements on property, plant, and equipmentleased to and from others.
12. Perform analytical procedures for property, plant, and equipment.
13. Evaluate financial statement presentation and disclosure for plantassets and for related revenue and expenses. lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
6. Potential misstatements:
7. Vouch (lần theo từ sổ kế toán đến tài liệu gốc) additions (các khoản bổ sung, mua sắm trong năm): lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
=> Mục tiêu: Đảm bảo các khoản ghi tăng tài sản là có thật, hợp lệ, được phân loại đúng, và không
nhầm lẫn với chi phí sửa chữa hay bảo trì.
(chép cái này, cái bên dưới đọc tham khảo) a.
Review changes in Construction in Progress (CIP); check work orders. b.
Trace transfers from CIP to fixed assets; check proper classification. c.
Vouch PPE additions to invoices/contracts; recalculate totals and check forimproper capitalization. d.
Investigate acquisitions exceeding approved amounts; check for properapproval. e.
Examine unusual debits to PPE not from asset purchases. f.
Ensure full cost of installment purchases is recorded; unpaid parts shownas liabilities. a.
Review changes during the year in construction in progress and examine supporting work
orders, both incomplete and closed. b.
Trace transfers from Construction in Progress account to the propertyaccounts, observing
propriety of classification. Determine that all completed items have been transferred out of the account. c.
On a test basis, vouch purchases of property, plant, and equipment toinvoices, deeds,
contracts, or other supporting documents. Recompute extensions, footings, and treatment of
discounts. Make certain repairs and maintenance expenses were not improperly capitalized.Trên
cơ sở chọn mẫu, đối chiếu việc mua sắm PPE với:
o Hóa đơn, giấy chứng nhận sở hữu, hợp đồng hoặc các tài liệu hỗ trợ khác.
o Tính toán lại (recompute) các phép tính, chiết khấu.
o Đảm bảo chi phí sửa chữa không bị ghi nhận sai thành tài sản cố định. d.
Investigate all instances in which the actual cost of acquisitionssubstantially exceeded
authorized amounts. Determine whether such excess expenditures were analyzed and approved by appropriate officials. e.
Investigate fully any debits to property, plant, and equipment accounts not arising from
acquisition of physical assets. f.
Determine that the total cost of any plant and equipment assets purchasedon the
installment plan is reflected in the asset accounts and that the unpaid installments are set up as liabilities. lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
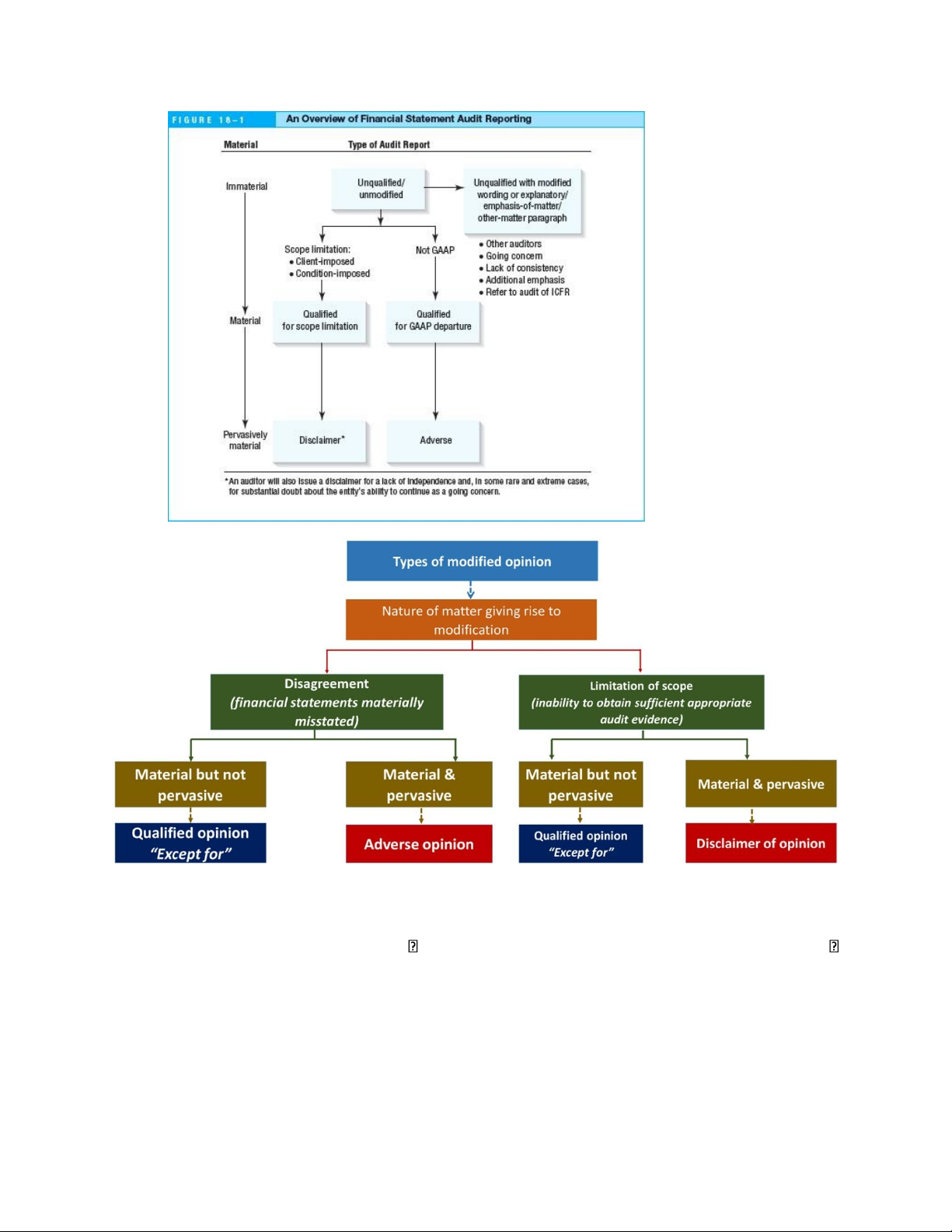
CHAP 18: Reports on audited financial statements:
1. Elements of Financial statements audit: 8 elements 1. Report title 2. Addressee 3. Introductory paragraph 4. Scope paragraph 5. Opinion paragraph
6. Explanatory paragraph referring to the audit of ICFR 7. Name of auditor 8. Audit report date
BEST: The standard unqualified report is issued when the auditor has gathered sufficient
evidence, the audit has been performed in accordance with PCAOB standards, and the financial statements conform to GAAP.
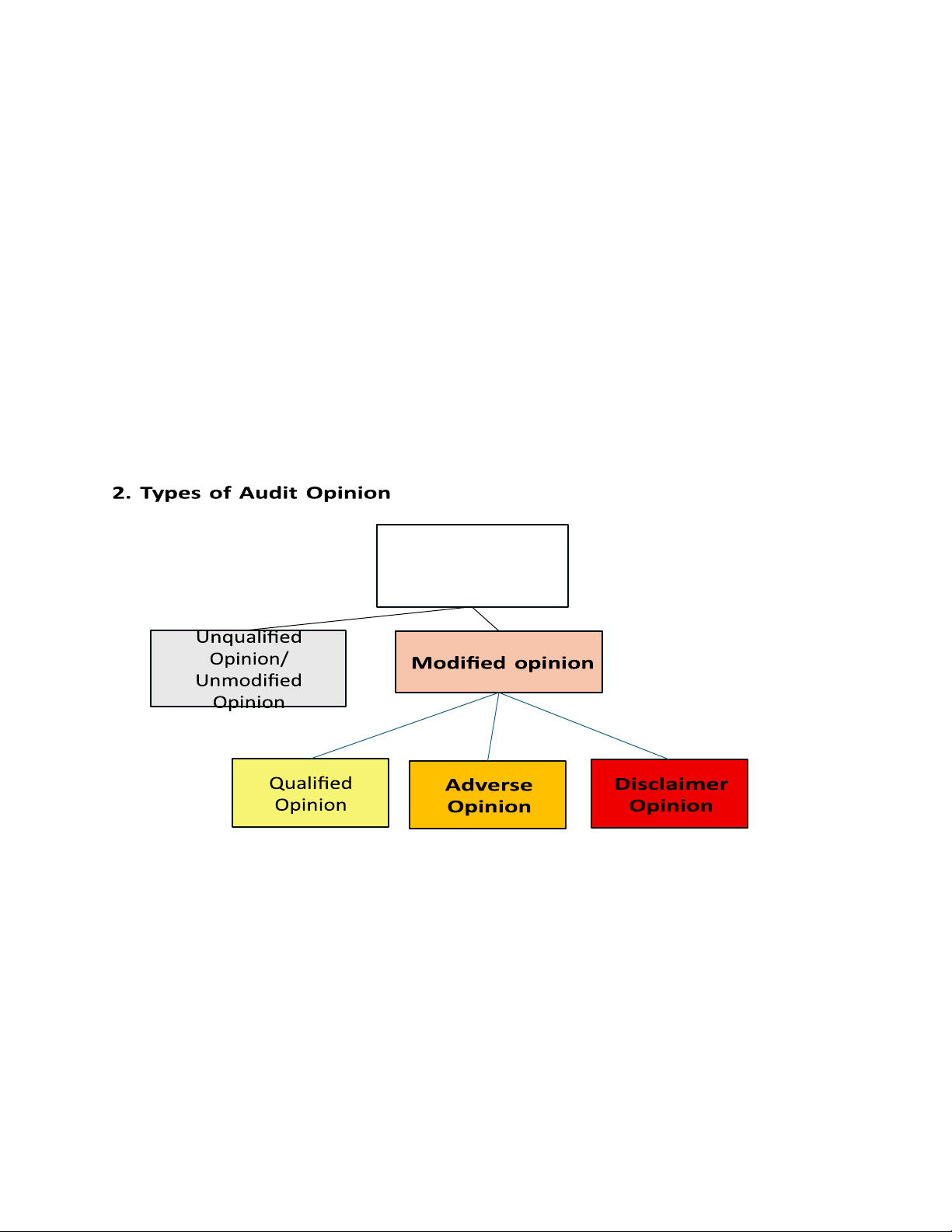
Unqualified: issuers (public companies)
Unmodified: non-issuers (private companies)
- Conditions for Departure from Unqualified/Unmodified report Scope limitations
Departure from GAAP Lack of Auditor
Independence - Departures: lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392 Qualified “except for” Adverse Disclaimer
- Pervasiveness – mức độ lan rộng, ảnh hưởng sâu rộng của một vấn đề sai sót hoặc thiếu
sót đến toàn bộ báo cáo tài chính.
Are not confined to specific elements, accounts, or items of the financial statements: .
Không chỉ giới hạn ở một phần, một tài khoản, hay một mục cụ thể trong báo cáo tài
chính; ➡ Nghĩa là ảnh hưởng rải rác hoặc lan rộng khắp các phần của BCTC, không chỉ ở một chỗ.
If so confined, represent or could represent a substantial proportion of the financial
statements; or Nếu có giới hạn, thì phần đó phải là một phần rất quan trọng hoặc
chiếm tỷ trọng lớn của BCTC; ➡ Ví dụ: sai sót chỉ nằm ở tài sản cố định, nhưng tài sản
cố định chiếm 70% tổng tài sản → vẫn bị xem là "pervasive".
With regard to disclosures, are fundamental to users’ understanding of the financial
statements. Nếu liên quan đến thuyết minh, thì thiếu sót đó làm ảnh hưởng nghiêm
trọng đến sự hiểu biết của người đọc BCTC. ➡ Ví dụ: thiếu thuyết minh về cam kết nợ
lớn hoặc kiện tụng quan trọng có thể làm người đọc hiểu sai bản chất hoạt động.
Nếu một vấn đề là material (trọng yếu) nhưng không pervasive, thì có thể: •
Ra ý kiến ngoại trừ (qualified opinion).
Nhưng nếu một vấn đề là material và pervasive, thì có thể phải: •
Ra ý kiến bất lợi (adverse opinion) hoặc từ chối đưa ra ý kiến (disclaimer) tùy tình huống. lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
- Các điều kiện đặc biệt khiến auditors phải đưa ra các loại ý kiến kiểm toán khác với ý kiến
chuẩn (unqualified/unmodified) o Scope limitation: không thể thu thập đầy đủ bằng
chứng, không đủ thông tin không chắc chắn về tính đúng đắn của bctc. qualified/disclaimer + Qualified: ví dụ + Disclaimer: ví dụ
o Not in Conformity with GAAP (Không tuân thủ nguyên tắc kế toán GAAP): qualified/adverse lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
+ Qualified: áp dụng một chính sách kết toán không đúng với chuẩn mực kế
toán ở một số khoản mục nhỏ, như ghi nhận doanh thu sớm hơn thời điểm hợp lý.
+ Adverse: sai sót trọng yếu và lan tỏa. VD: ghi nhận doanh thu giả để tăng lợi
nhuận hoặc không thuyết minh về các khoản nợ quan trọng
o Auditor Not Independent (Kiểm toán viên không độc lập): disclaimer of opinion
luôn, vì khi không độc lập, auditor mất thích khách quan, mọi ý kiến đều không đáng tin cậy
- Special reporting issues (những vấn đề đặc biệt trong báo cáo kiểm toán): thường được
đề cập trong Other-Matter/Emphasis-of-matter bất kể ý kiến kiểm toán là gì o Different
reports on comparative financial statements: khi bctc giữa 2 hoặc nhiềm năm mà ý kiến
kiểm toán giữa các năm khác nhau
– kiểm toán viên phải nêu rõ từng loại ý kiến cho từng năm kế toán
o Change in report on prior-period financial statements
Ý kiến kiểm toán trong năm trước đó bị thay đổi do có thông tin mới hoặc điều chỉnh restatement
Khi ý kiến kiểm toán của kỳ trước bị thay đổi, vì: Có sự điều chỉnh hồi tố
(restatement), Có thông tin mới phát hiện được trong kỳ hiện tại. Phải đề cập
đến thay đổi này trong đoạn gọi là “Other-Matter paragraph” hoặc “Emphasis- of-Matter paragraph”.
o Report by a predecessor auditor: có thể tham khảo báo cáo của auditor
predecesspr trong đoạn Other matter -
The predecessor auditor should do the following before reissuing a report on prior-year
financial statements published for comparative purposes:
1. Read the financial statements of the current period.
2. Compare the prior-period financial statements reported on with the current-year financial statements.
3. Obtain a letter of representation from the current-year or successor auditor.
3. Adjustments to the Standard Unqualified/Unmodified Financial statement audit report
- Reference to report on audit of ICFR: - Going concern:
Không thay đổi opinion nếu thông tin đã được thuyết minh đầy đủ.
Thêm một đoạn “Emphasis-of-Matter” để nhấn mạnh yếu tố này. - Lack of consistency:
Changes affecting Consistency: → Phải thêm đoạn Emphasis-ofMatter:
+ Change in accounting principles: Ví dụ đổi từ FIFO sang weightedaverage.
+ Change in reporting entity: Ví dụ hợp nhất thêm công ty con mới. + Correction of a
mistatement in Financial Statements: Điều chỉnh sai sót trọng yếu của kỳ trước. lOMoAR cPSD| 59085392
Changes not affecting consistency: → Không cần ghi chú đặc biệt: + Change in accounting
estimates: Ví dụ thay đổi tuổi thọ tài sản cố định.
+ Change in classification and reclassification: Ví dụ chuyển khoản mục từ chi phí sang vốn.
+ Change expected to have a material future effect: Nếu chỉ ảnh hưởng trong tương lai thì
không cần ghi chú hiện tại. - Additional emphasis 4. Other informations
- Other Information in Documents Containing Audited Financial Statements (các thông tin
không thuộc phần báo cáo tài chính nhưng nằm trong cùng một tài liệu với báo cáo kiểm
toán). Ví dụ trong Báo cáo thường niên (Annual Report) hoặc Hồ sơ đăng ký phát hành
(Registration Statement), ngoài báo cáo tài chính còn có: Thư của CEO
Phân tích của ban quản lý
Thông tin về thị trường, sản phẩm, định hướng tương lai, v.v.
o Trách nhiệm của auditors: phải đọc phần thông tin khác đó Phải xem xét thông tin
có mâu thuẫn hoặc không nhất quán với báo cáo tài chính đã kiểm toán không
o Không có trách nhiệm: kiểm tra tính đúng sai của thông tin, không thực hiện thử
tục kiểm toán, không chịu trách nhiệm nếu thông tin khác có sai sót mà không mâu thuẫn với bctc.
5. Special reports: báo cáo đặc biệt trong kiểm toán
- Financial statements prepared on a basis of accounting other than GAAP
Báo cáo lập theo chuẩn mực riêng biệt phục vụ cho mục đích riêng biệt + Regulatory basis:
cơ sở quy định pháp lý – được lập theo yêu cầu của cơ quan quản lý nhà nước. VD: Báo
cáo cho cơ quan thuế, quản lý ngành + Tax basis + Cash basis
+ Contractual: Ngân hàng yêu cầu doanh nghiệp lập báo cáo tài chính phản ánh riêng dòng
tiền từ dự án vay vốn.
- Specified elements, accounts, or items of a financial statement
- Compliance with aspects of contractual agreements or regulatory requirements