






Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD|46958826 lOMoARcPSD|46958826 FINAL EXAM QUESTIONS
Question 1: Decide if the following statements are true or false and give brief
explanations to your choice.
a) Trên thị trường một loại hàng hoá, khi cung tăng đồng thời cầu giảm sẽ làm cho giá và
lượng cân bằng của loại hàng hoá này đều giảm (giả định các yếu tố khác không đổi).
In the market of a good, when supply increases and demand decreases, both equilibrium
price and quantity of the good will decrease (all other things being equal).
b) Trên thị trường của một loại hàng hóa, nếu chính phủ quy định giá sàn sẽ gây ra
hiện tượng dư thừa hàng hóa (giả định các yếu tố khác không đổi).
In the market of a good, if the government sets the price floor, it will cause a surplus of
the good (all other things being equal).
c) Khi nhu cầu về hàng may mặc giảm, mức tiền công và lượng lao động cân bằng trên
thị trường đồ may mặc sẽ giảm (giả định các yếu tố khác không đổi).
As demand for garments decreases, the equilibrium labor wage and quantity in the
apparel market will decrease (all other things being equal).
d) Trên thị trường của một loại hàng hóa, chính phủ quy định giá trần sẽ gây ra hiện
tượng dư thừa hàng hóa (giả định các yếu tố khác không đổi).
In the market of a good, if the government sets the floor price ceiling, it will cause a
surplus of the good (all other things being equal).
e) Khi thời tiết băng giá, cung và cầu về cá tươi giảm làm cho giá và lượng cân bằng
trên thị trường cá tươi giảm (giả định các yếu tố khác không đổi).
In the icy weather condition, the supply and demand for fresh fish decreases, causing the
equilibrium price and quantity in the fresh fish market to decrease (assuming all other
things being equal).
f) Khi kinh doanh mặt hàng có cầu kém co dãn thì việc tăng giá bán sẽ làm giảm
doanh thu (giả định các yếu tố khác không đổi).
When trading a commodity with inelastic demand, an increase in price will reduce sales
(assuming all other things being equal).
g) Trong ngắn hạn, hãng độc quyền muốn tối đa hóa lợi nhuận sẽ luôn bán một mức
sản lượng nhỏ hơn mức sản lượng mang lại doanh thu tối đa.
In the short run, the monopolist that wants to maximize profits will always sell a volume
of output smaller than the volume of maximum revenue.
h) Khi giá đầu vào để sản xuất ra một loại sản phẩm tăng sẽ gây ra hiện tượng trượt
dọc trên đường cung của sản phẩm đó (giả định các yếu tố khác không đổi).
An increase in input prices to produce a product will cause points on the supply curve of
the product to move a long the curve (assuming all other things being equal).
i) Khi thu nhập của người tiêu dùng tăng thì giá và lượng cân bằng trên thị trường của
mọi loại hàng hóa đều tăng (giả định các yếu tố khác không đổi).
As the consumer's income increases, the equilibrium price and quantity of all goods
increase (assuming all other things being equal).
j) Việc giá nguyên liệu để sản xuất ra một loại sản phẩm giảm sẽ gây ra hiện tượng trượt
dọc các điểm trên đường cung của sản phẩm đó (giả định các yếu tố khác không đổi).
A decrease in the price of a raw material to produce a product will cause points on the
supply curve of the product to move a long the curve (assuming all other things being equal).
k) Trên thị trường của một loại hàng hóa, chính phủ quy định giá trần sẽ gây ra hiện
tượng dư thừa hàng hóa (giả định các yếu tố khác không đổi).
In the market for a good, it the government sets the price ceiling, it will cause a surplus of
the good (assuming all other things being equal). lOMoARcPSD|46958826
l) Trên thị trường của một loại hàng hóa, nếu chính phủ quy định giá sàn sẽ gây ra
hiện tượng dư thừa hàng hóa (giả định các yếu tố khác không đổi).
In the market for a good, if the government sets the price floor, it will cause a surplus of
the good (assuming all other things being equal).
m) Nếu ATC > MC thì khi tăng sản lượng sẽ làm cho ATC giảm tương ứng với sự gia tăng của sản lượng.
Given ATC > MC, an increase in output will cause ATC to decrease corresponding to the increase.
n) Điều kiện cần và đủ để một hãng bất kỳ lựa chọn mức sản lượng để tối đa hóa lợi
nhuận là khi giá bán P = MC.
A necessary and sufficient condition for any firm to choose the level of output to
maximize profits is the selling price P = MC.
o) Nếu ATC < MC thì khi tăng sản lượng sẽ làm cho ATC giảm tương ứng với sự gia
tăng của mức sản lượng đó.
Given ATC < MC, an increase in output will cause ATC to decrease corresponding to the increase.
p) Khác với hãng cạnh tranh hoàn hảo, hãng độc quyền luôn có đường cầu dốc xuống.
Unlike a perfectly competitive firm, a monopolist always has a downward sloping demand curve.
q) Khi chi phí chế biến thịt bò đóng hộp tăng thì giá và lượng cân bằng trên thị trường
thịt bò đóng hộp đều tăng lên (giả định các yếu tố khác không đổi).
As the cost of processing canned beef increases, both the equilibrium price and quantity
in the canned beef market increase (all other things being equal).
r) Trong ngắn hạn, hãng cạnh tranh hoàn hảo sản xuất bị thua lỗ cần phải đóng cửa ngay.
In the short term, a perfectly competitive firm suffering from production losses needs to be closed immediately.
s) Hãng cạnh tranh hoàn hảo lựa chọn điều kiện tối đa hóa lợi nhuận khi giá bán bằng chi phí cận biên.
A perfectly competitive firm makes a choice of the condition to maximize profit when
price is equal to marginal cost.
t) Trong điều kiện đầu vào vốn không đổi, sản phẩm cận biên của lao động co xu
hướng giảm dần khi số lượng lao động được thuê tăng lên.
Given constant capital input, the marginal product of labor tends to decrease as the number of labours increases.
Câu 2: Giải thích các thuật ngữ kinh tế sau
Question 2: Explain the following economic terms. a) Economics b) Microeconomics c) Macroeconomics d) Positive Economics e) Normative Economics f) Opportunity costs g) Law of demand h) Law of supply i) Quantity Demanded j) Quantity Supplied k) Scarce resources l) Goods market m) Market supply lOMoARcPSD|46958826 n) Market demand o) Surplus p) Substitutues q) Compliments
r) Diminishing marginal product s) Shortage t) Market equilibrium u) Revenue v) Economic cost w) Average total costs x) Total fixed costs y) Total Variable Costs z) Marginal Costs aa) Marginal Revenue bb)Price ceiling cc) Price floor dd)Price taker ee) Price maker ff) Equilibrium price gg)Economic profits hh)Perfect competitive market ii) Pure monopoly market jj) Price elasticity of demand
Câu 3: Có biểu cầu về hai loại hàng hoá M và N trên thị trường như sau:
Question 3: Given the table of two types of goods M and N in the markets as follows
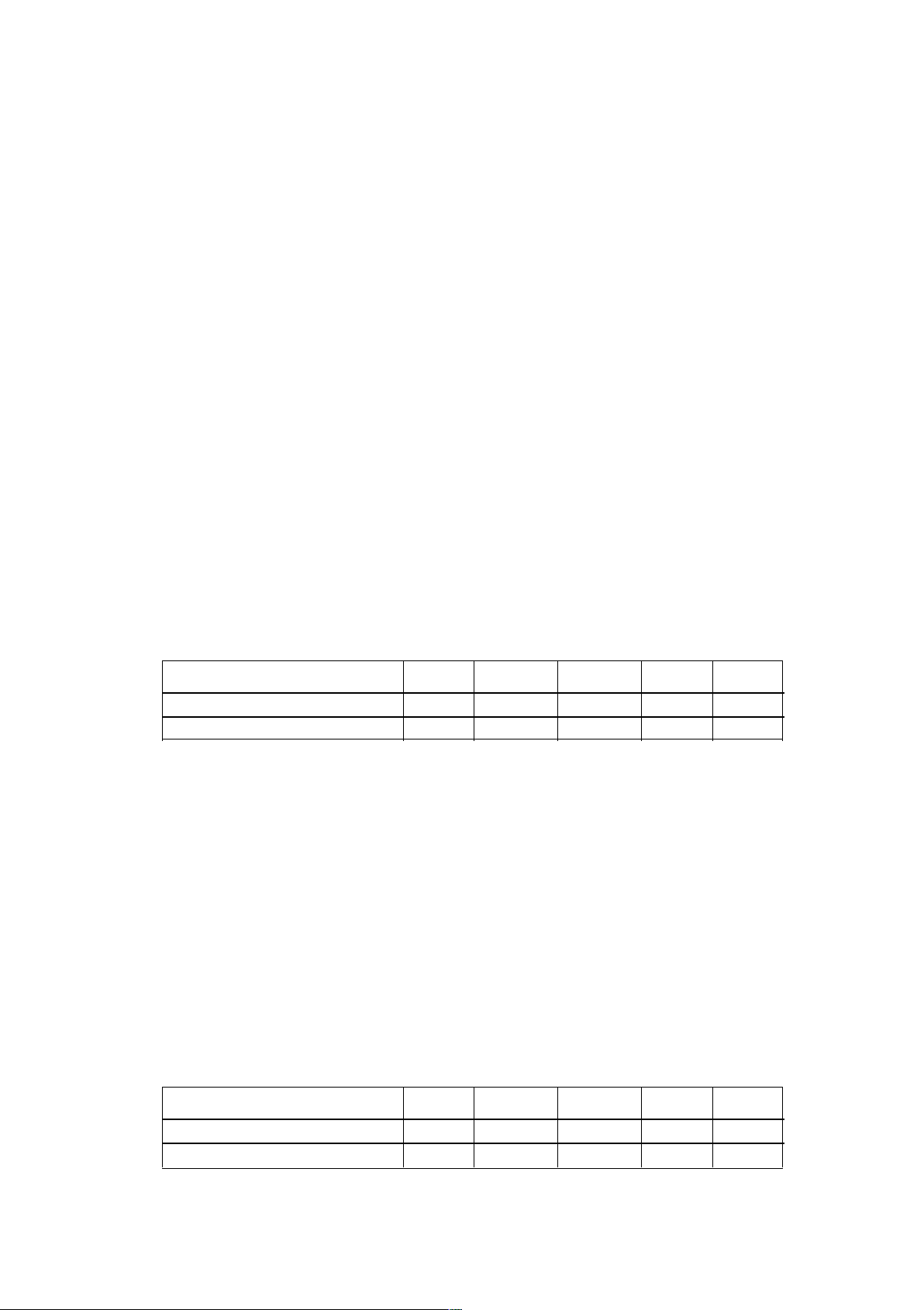
Price (thousand USD/tấn) 10 12 14 16 18 QD(M) (ton/day) 280 270 260 250 240 QD (N) (ton/day) 190 188 186 184 182
a) Viết phương trình và vẽ đồ thị đường cầu của hai loại hàng hoá đó. Cho nhận xét về
độ dốc của hai đường cầu trên.
Find the equation and draw the demand curve graph for the two goods. Give comments on
the slope of the two above demand curves.
b) Giả sử mức cung hai loại hàng này trên thị trường là cố định và đều bằng 120
tấn/ngày, hãy tính mức giá cân bằng của hai loại hàng này.
Assuming the supply of these two commodities in the market is fixed and equal to 120
tons/day, calculate the equilibrium price of these two commodities.
c) Với dữ kiện đã cho ở đầu bài, giả sử hai đường cầu đó cắt nhau tại điểm E, tại E độ
co dãn của cầu theo giá của hai loại hàng hoá trên có bằng nhau không? vì sao?
Given the data given in the table, suppose the two demand curves intersect at point E, are
the price elasticities of demand for the two commodities equal? why?
Câu 3: Có biểu cầu về hai loại hàng hoá M và N trên thị trường như sau:
Question 3: Given the table of two types of goods M and N in the markets as follows
Price (thousand USD/tấn) 10 12 14 16 18 QD(M) (ton/day) 280 270 260 250 240 QD (N) (ton/day) 190 188 186 184 182
a) Viết phương trình và vẽ đồ thị đường cầu của hai loại hàng hoá đó. Cho nhận xét về
độ dốc của hai đường cầu trên. lOMoARcPSD|46958826
Find the equation and draw the demand curve graph for the two goods. Give comments on
the slope of the two above demand curves.
b) Giả sử mức cung hai loại hàng này trên thị trường là cố định và đều bằng 120
tấn/ngày, hãy tính mức giá cân bằng của hai loại hàng này.
Assuming the supply of these two goods in the market is fixed and equal to 120 tons/day,
calculate the equilibrium price of these two commodities.
c) Với dữ kiện đã cho ở đầu bài, giả sử hai đường cầu đó cắt nhau tại điểm E, tại E độ
co dãn của cầu theo giá của hai loại hàng hoá trên có bằng nhau không? vì sao?
Given the data given in the table, suppose the two demand curves intersect at point E, are
the price elasticities of demand for the two goods equal? why?
Câu 3: Có số liệu về giá, lượng cung và lượng cầu của hàng hóa X tại bảng sau:
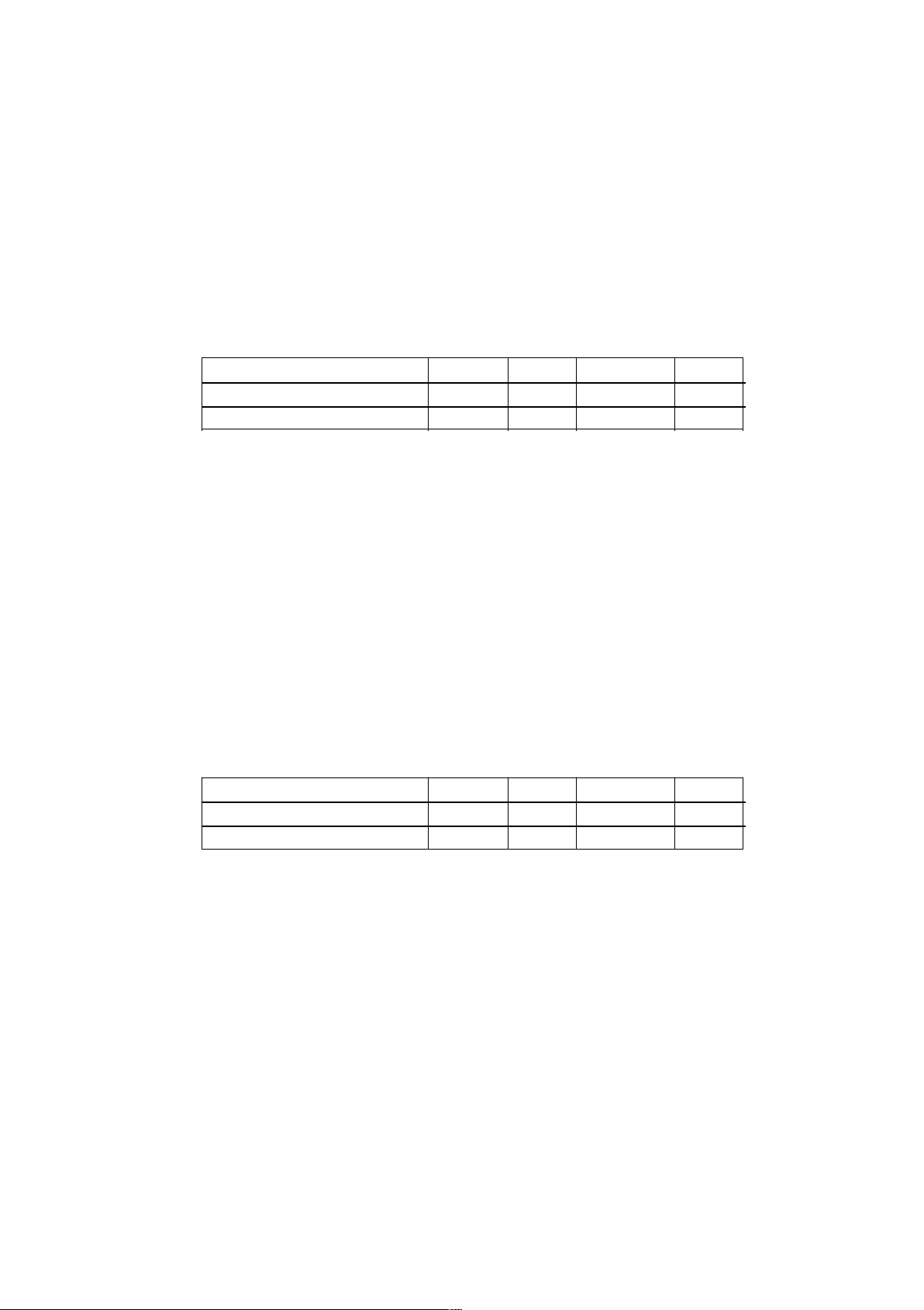
Question 3: Given the table of price, supply and demand for the good X as follows Price (USD) 100 120 140 160 QD (products/week) 60 56 52 48 QS (products/week) 39 42 45 48
a) Xác định giá và lượng cân bằng của hàng hóa X, tính hệ số co dãn của cầu theo giá
tại mức giá cân bằng. Vẽ đồ thị minh họa.
b) Tính lượng dư thừa và thiếu hụt; tính hệ số co dãn của cầu theo giá tại các mức giá P = 120USD, P = 150USD.
c) Giả sử chính phủ đánh thuế 12USD/sản phẩm bán ra, hãy tính giá và lượng cân
bằng mới, vẽ đồ thị minh họa.
a) Determine the equilibrium price and quantity of the good X and compute the own price
elasticity of demand at the equilibrium price. Draw a graph to illustrate.
b) Calculate the excess and shortage; calculate the own price elasticity of demand at the prices
P = 120 USD/unit, P = 150 USD/unit.
c) Given the government tax of $12 per product sold, calculate a new equilibrium price and
quantity, and draw a graph to illustrate.
Câu 3: Có số liệu về giá, lượng cung và lượng cầu của hàng hóa X tại bảng sau:
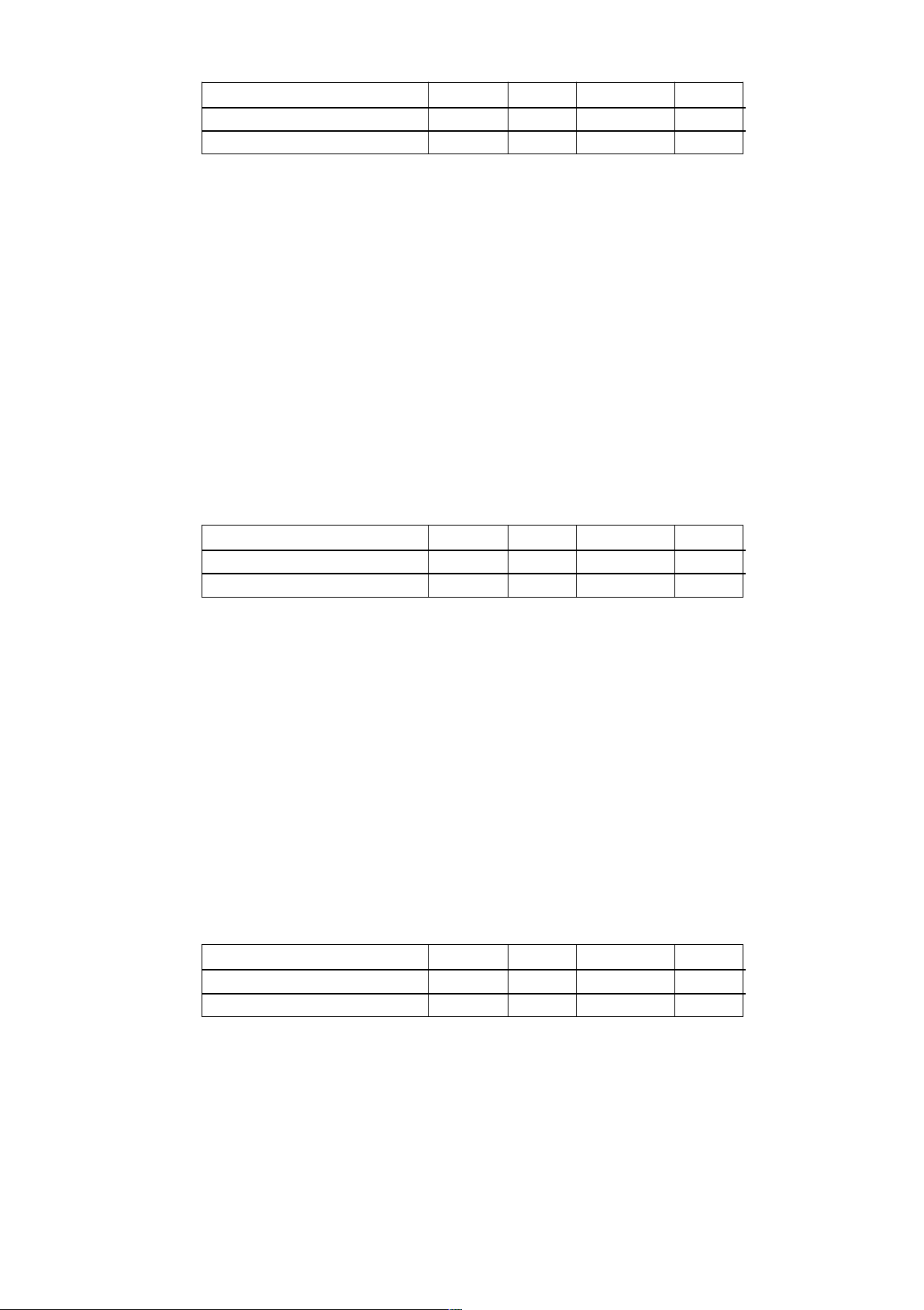
Question 3: Given the table of price, supply and demand for the good X as follows Price (USD) 110 120 130 140 QD (products/week) 64 60 56 52 QS (products/week) 40 48 56 64
a) Viết phương trình đường cầu và đường cung. Xác định giá và lượng cân bằng của hàng hóa
X, tính hệ số co dãn của cầu theo giá tại mức giá cân bằng. Vẽ đồ thị minh họa.
b) Tính lượng dư thừa, thiếu hụt, và tính hệ số co dãn của cầu theo giá tại các mức giá P = 115USD; P = 140USD.
c) Giả sử chính phủ đánh thuế 3,75USD/sản phẩm bán ra, hãy tính giá và lượng cân
bằng mới, vẽ đồ thị minh họa.
a) Find the equation for the demand and supply curves. Determine the equilibrium price and
quantity of the good X and compute the own price elasticity of demand at the equilibrium
price. Draw a graph to illustrate.
b) Calculate the surplus or shortage and compute the price elasticity of demand at prices P = 115 USD/unit; P = 140USD/unit.
c) Given the government tax of $ 3.75 per product sold, calculate a new equilibrium price and
quantity, and draw a graph to illustrate.
Câu 3: Có số liệu về giá, lượng cung và lượng cầu của hàng hóa X tại bảng sau: lOMoARcPSD|46958826
Question 3: Given the table of price, supply and demand for the good X as follows Price (USD)/ per unit 100 120 140 160 QD (products/week) 60 56 52 48 QS (products/week) 39 42 45 48
a) Xác định giá và lượng cân bằng của hàng hóa X, tính hệ số co dãn của cầu theo giá
tại mức giá cân bằng. Vẽ đồ thị minh họa.
b) Tính lượng dư thừa và thiếu hụt; tính hệ số co dãn của cầu theo giá tại các mức giá P = 100USD/unit, P = 125USD/unit.
c) Giả sử chính phủ đánh thuế 6USD/sản phẩm bán ra, hãy tính giá và lượng cân bằng mới,
vẽ đồ thị minh họa.
a) Determine the equilibrium price and quantity of the good X and compute the price
elasticity of demand at the equilibrium price. Draw a graph to illustrate.
b) Calculate the excess and shortage; calculate the price elasticity of demand at the prices P
= 100 USD/ unit, P = 120 USD/ unit.
c) c) Given the government tax of $6 per product sold, calculate a new equilibrium price and
quantity, and draw a graph to illustrate.
Câu 3: Có số liệu về giá, lượng cung và lượng cầu của hàng hóa X trong bảng sau:
Question 3: Given the table of price, supply and demand for the good X as follows Price (USD) 100 120 140 160 QD (products/week) 60 56 52 48 QS (products/week) 39 42 45 48
a) Xác định giá và lượng cân bằng của hàng hóa X, tính hệ số co dãn của cầu theo giá
tại mức giá cân bằng. Vẽ đồ thị minh họa.
b) Tính lượng dư thừa và thiếu hụt; tính hệ số co dãn của cầu theo giá tại các mức giá P = 125USD/unit, P = 135USD/unit.
c) Giả sử chính phủ đánh thuế 6USD/sản phẩm bán ra, hãy tính giá và lượng cân bằng
mới, vẽ đồ thị minh họa.
a) Determine the equilibrium price and quantity of the good X and compute the price
elasticity of demand at the equilibrium price. Draw a graph to illustrate.
b) Calculate the excess and shortage; calculate the price elasticity of demand at the prices P
= 125 USD/unit, P = 135 USD/ unit.
c) Given the government tax of $6 per product sold, calculate a new equilibrium price and
quantity, and draw a graph to illustrate.
Câu 3: Có số liệu về giá, lượng cung và lượng cầu của hàng hóa X tại bảng sau:
Question 3: Given the table of price, supply and demand for goods X as follows Price (USD) 110 120 130 140 QD (products/week) 64 60 56 52 QS (products/week) 40 48 56 64
a) Viết phương trình đường cầu và đường cung. Xác định giá và lượng cân bằng của hàng
hóa X, tính hệ số co dãn của cầu theo giá tại mức giá cân bằng. Vẽ đồ thị minh họa.
b) Tính lượng dư thừa, thiếu hụt, và tính hệ số co dãn của cầu theo giá tại các mức giá P = 110USD; P = 135USD.
c) Giả sử chính phủ đánh thuế 10USD/sản phẩm bán ra, hãy tính giá và lượng cân bằng mới,
vẽ đồ thị minh họa.
a) Write the equation for the demand and supply curves. Determine the equilibrium price
and quantity of the good X and compute the price elasticity of demand at the equilibrium
price. Draw a graph to illustrate. lOMoARcPSD|46958826
b) Calculate the surplus or shortage and compute the price elasticity of demand at prices P =
110 USD/ unit; P = 135USD/ unit.
c) Given the government tax of $10 per product sold, calculate a new equilibrium price and
quantity, and draw a graph to illustrate.
Câu 4: Một hãng độc quyền sản xuất trong ngắn hạn có hàm cầu là Q = 220 - 20P.
a) Nếu hãng bán sản phẩm với giá là P = 7 thì doanh thu của hãng là bao nhiêu? Tính
hệ số co dãn của cầu theo giá tại mức giá này rồi cho nhận xét?
b) Hãng đang bán với giá là P = 7,5 hãng dự định tăng giá để tăng lợi nhuận. Hãng có
thực hiện không? Vì sao? (Cho ATC = 6).
c) Hãng đang bán với giá là P = 9, hãng dự định tăng giá để tăng doanh thu. Hãng lựa
chọn như vậy có được không? Vì sao?
Question 4: A monopoly firm producing in the short-run has a demand function:
Q = 220 - 20P. (Quantity is measured in unit, price is measured in $/ USD).
a) If the firm sells the product at price P = $7/unit, what is its revenue? Calculate the own
price elasticity of demand at this price level and give comments.
b) The firm sells the product at price P = $7.5/unit and intends to increase the price to
increase profits. Does the firm do it? Why? (given ATC = $6/unit).
c) The firm sells the product at price P = $9/unit and intends to increase the price to increase
revenue. Is it possible to do that? Why?
Câu 4: Một hãng độc quyền sản xuất trong ngắn hạn có hàm cầu là Q = 114 - 10P.
a) Khi giá bán là P = 5 thì doanh thu là bao nhiêu. Tính độ co dãn của cầu theo giá tại
mức giá này và cho nhận xét.
b) Hãng đang bán với giá P = 4,5, hãng dự định tăng giá để tăng lợi nhuận. Hãng có
thực hiện được không, vì sao? Cho ATC = 4.
c) Hãng đang bán với giá P = 6, hãng quyết định giảm giá để tăng doanh thu. Quyết
định đó của hãng đúng hay sai, vì sao?
Question 4: A monopoly firm in the short-run has a demand function: Q = 114 - 10P.
(Quantity is measured in unit, price is measured in $/ USD).
a) If the firm sells the product at price P = $5/unit, what is its revenue? Calculate the own
price elasticity of demand at this price level and give comments.
b) The firm sells the product at price P = $4.5/unit firms and intends to increase the price to
increase profits. Does the firm do it? Why? (given ATC = $4).
c) The firm sells the product at price P = $6/unit and intends to increase the price to increase
revenue. Is it a correct decision? Why?
Câu 4: Một hãng độc quyền sản xuất trong ngắn hạn có hàm cầu là Q = 130 - 10P.
a) Khi giá bán là P = 9 thì doanh thu là bao nhiêu. Tính độ co dãn của cầu theo giá tại
mức giá này và cho nhận xét.
b) Hãng đang bán với giá P = 8, hãng dự định tăng giá để tăng lợi nhuận. Hãng có thực
hiện được không, vì sao? Cho ATC = 6.
c) Hãng đang bán với giá P = 8,5, hãng quyết định giảm giá để tăng doanh thu. Quyết
định đó của hãng đúng hay sai? Vì sao?
Question 4: A monopoly firm producing in the short-run has a demand function:
Q = 130 - 10P. (Quantity is measured in unit, price is measured in $/ USD). lOMoARcPSD|46958826
a) If the firm sells the product at price P = $9/unit, what is its revenue? Calculate the own
price elasticity of demand at this price and then give a comment.
b) The firm sells the product at price P = $8 unit firms and intends to increase the price to
increase profits. Does the firm do it? Why? (given ATC = $6).
c) The firm sells the product at price P = $8.5/unit and intends to increase the price to
increase revenue. Is it a correct decision? Why?
Câu 4: Một hãng sản xuất trong ngắn hạn có hàm cầu là: QD = 92 - 2P và ATC = 20.
a) Hãng đang bán với giá P = 18, doanh thu của hãng là bao nhiêu? Tính hệ số co dãn
của cầu theo giỏ tại mức giỏ này và cho nhận xét.
b) Hãng đang bán với giá P = 20 hãng dự định tăng giá để tăng doanh thu, dự định đó
đúng hay sai, vì sao?
c) Hãng đang bán với giá P = 22, hãng dự định tăng giá để tăng lợi nhuận, hãng có
thực hiện được không, vì sao?
Question 4: A monopoly firm producing in the short-run has the demand function as
QD = 92 - 2P and ATC = 20/unit. (Quantity is measured in unit, price is measured in $/ USD).
a) If the firm sells the product at price P = $18/unit, what is its revenue? Calculate the own
price elasticity of demand at this price level and give comments.
b) The firm is selling the product at price P = $20/unit, the firm intends to increase prices to
increase revenue. Is that intention right or wrong? Why?
c) The firm is selling the product at price P = $22/unit, the firm intends to increase the price to
increase profits, can the do it, why?
Câu 4: Một hãng độc quyền sản xuất trong ngắn hạn có hàm cầu là Q = 210 - 12P.
a) Khi giá bán là P = 8 thì doanh thu là bao nhiêu. Tính độ co dãn của cầu theo giá tại
mức giá này và cho nhận xét.
b) Hãng đang bán với giá P = 9, hãng dự định tăng giá để tăng lợi nhuận. Hãng có thực
hiện được không, vì sao? Cho ATC = 8.
c) Hãng đang bán với giá P = 7, hãng quyết định giảm giá để tăng doanh thu. Quyết
định đó của hãng đúng hay sai, vì sao?
Question 4: A monopoly firm producing in the short-run has the demand function
as QD = 210 - 12P. (Quantity is measured in unit, price is measured in $/ USD).
a) If the firm sells the product at price P = $10/unit, what is its revenue? Calculate the own
price elasticity of demand at this price level and give comments.
b) The firm is selling the product at price P = $12/unit, the firm intends to increase prices to
increase revenue. Is that intention right or wrong? Why?
c) The firm is selling the product at price P = $8/unit, the firm intends to increase the price to
increase profits, can the do it, why?
Câu 4: Một hãng độc quyền sản xuất trong ngắn hạn có hàm cầu là Q = 640 - 30P.
a) Nếu hãng bán sản phẩm với giá là P = 7 thì doanh thu của hãng là bao nhiêu? Tính
hệ số co dãn của cầu theo giá tại mức giá này rồi cho nhận xét?
b) Hãng đang bán với giá là P = 7,5 hãng dự định tăng giá để tăng lợi nhuận. Hãng có
thực hiện không? Vì sao? (Cho ATC = 6).
c) Hãng đang bán với giá là P = 9, hãng dự định tăng giá để tăng doanh thu. Hãng lựa
chọn như vậy có được không? Vì sao?
Question 4: A monopoly firm producing in the short run has the demand function as QD = 630
- 30P. (Quantity is measured in unit, price is measured in $/ USD). lOMoARcPSD|46958826
a) If the firm sells the product at price P = $10/unit, what is its revenue? Calculate the price
elasticity of demand at this price level and give comments.
b) The firm sells the product at a price P = $15/unit the firm intends to increase the price to
increase profit. Can the firm do it? Why? Given ATC = $6/unit.
c) The firm sells the product at a price P = $16/unit, the firm intends to increase the price to
increase revenue. Is it a correct decision? Why?
Câu 4: Một hãng độc quyền sản xuất trong ngắn hạn có hàm cầu là QD = 200 - 10P
(quantity measurement is unit).
a) Khi giá bán là P = 5 thì doanh thu là bao nhiêu. Tính độ co dãn của cầu theo giá tại
mức giá này và cho nhận xét.
b) Hãng đang bán với giá P = 4,5, hãng dự định tăng giá để tăng lợi nhuận. Hãng có
thực hiện được không, vì sao? Cho ATC = 4.
c) Hãng đang bán với giá P = 6, hãng quyết định giảm giá để tăng doanh thu. Quyết
định đó của hãng đúng hay sai, vì sao?
Question 4: A monopoly firm in the short run has the demand function as QD = 200 - 10P
(Quantity is measured in unit, price is measured in $/ USD).
a) If the firm sells the product at price P = $5/unit, what is its revenue? Calculate the price
elasticity of demand at this price level and give comments.
b) The firm sells the product at a price P = $4.5/unit the firm intends to increase the price to
increase profit. Can the firm do it? Why? Given ATC = $6/unit.
c) The firm sells the product at a price P = $6/unit, the firm intends to increase the price to
increase revenue. Is it a correct decision? Why?
Câu 4: Một hãng cạnh tranh hoàn hảo sản xuất trong ngắn hạn có hàm tổng chi phí là: TC=Q2+4Q+144.
a) Viết phương trình đường cung và các đường ATC, AVC, AFC của hãng. Tìm
phương trình đường cung của hãng.
b) Xác định mức giá hoà vốn và mức giá đóng cửa sản xuất của hãng.
c) Tính lợi nhuận tối đa của hãng tại các mức giá thị trường là P = 20/unit; P = 56/unit. Cho nhận
xét về các kết quả tính được.
Question 4: A perfectly competitive firm with short run production has the total cost function
as TC = Q2 + 4Q + 144. (Quantity is measured in unit, price is measured in $/ USD).
a) Find the fuctions of the ATC, AVC, and AFC curves of the firm. Identify the firm's supply curve function.
b) Determine the break-even price and the production shut-down price of the firm.
c) Calculate the firm's maximum profit at market prices of P = $20/unit; P = $56/unit. Give comments on the results.
Câu 4: Một hãng cạnh tranh hoàn hảo sản xuất trong ngắn hạn có hàm tổng chi phí là: TC=Q2+4Q+256.
a) Viết phương trình đường cung và các đường ATC, AVC, AFC của hãng. Tìm
phương trình đường cung của hãng.
b) Xác định mức giá hoà vốn và mức giá đóng cửa sản xuất của hãng.
c) Tính lợi nhuận tối đa của hãng tại các mức giá thị trường là P = 28; P = 46. Cho nhận
xét về các kết quả tính được.
Question 4: A perfectly competitive firm in the short run has the total cost function as TC = Q2
+ 4Q + 256. (Quantity is measured in unit, price is measured in $/ USD). lOMoARcPSD|46958826
a) Find the functions of the ATC, AVC, and AFC curves of the firm. Identify the firm's supply curve function.
b) Determine the break-even price and the production shut-down price of the firm.
c) Calculate the firm's maximum profit at market prices of P = $28/unit; P = $46/unit. Give comments on the results.
Câu 4: Một hãng cạnh tranh hoàn hảo sản xuất trong ngắn hạn có hàm tổng chi phí là: TC=Q2+4Q+100.
a) Viết phương trình đường cung và các đường ATC, AVC, AFC của hãng. Tìm
phương trình đường cung của hãng.
b) Xác định mức giá hoà vốn và mức giá đóng cửa sản xuất của hãng.
c) Tính lợi nhuận tối đa của hãng tại các mức giá thị trường là P = 20; P = 50. Cho
nhận xét về các kết quả tính được.
Question 4: A perfectly competitive firm in the short run has the total cost function as TC = Q2
+ 4Q + 100. (Quantity is measured in unit, price is measured in $/ USD).
a) Find the fuctions of the ATC, AVC, and AFC curves of the firm. Identify the firm's supply curve function.
b) Determine the break-even price and the production shut-down price of the firm.
c) Calculate the firm's maximum profit at market prices of P = $20/unit; P = $50/unit. Give comments on the results.
Câu 4: Một hãng cạnh tranh hoàn hảo sản xuất trong ngắn hạn có hàm tổng chi phí là: TC=Q2+4Q+400.
a) Viết phương trình đường cung và các đường ATC, AVC, AFC của hãng. Tìm
phương trình đường cung của hãng.
b) Xác định mức giá hoà vốn và mức giá đóng cửa sản xuất của hãng.
c) Tính lợi nhuận tối đa của hãng tại các mức giá thị trường là P = 40/unit; P = 60/unit. Cho nhận
xét về các kết quả tính được.
Question 4: A perfectly competitive firm in the short run has the total cost function as TC = Q2
+ 4Q + 400. (Quantity is measured in unit, price is measured in $/ USD).
a) Find the fuctions of the ATC, AVC, and AFC curves of the firm. Identify the firm's supply curve function.
b) Determine the break-even price and the production shut-down price of the firm.
c) Calculate the firm's maximum profit at market prices of P = $40/unit; P = $60/unit. Give comments on the results.
Câu 4: Một hãng sản xuất trong dài hạn có hàm sản xuất là Q = 20 K.L. Hãng sử dụng hai
đầu vào là vốn K và lao động L. Giá của các đầu vào tương ứng là r = 4USD/một đơn vị
vốn; w = 6USD/một đơn vị lao động.
a) Tỷ lệ thay thế kỹ thuật cận biên tại điểm lựa chọn cơ cấu đầu vào tối ưu để tối thiểu
hóa chi phí bằng bao nhiêu?
b) Để sản xuất ra một mức sản lượng Q0 = 500, hãng sẽ lựa chọn mức chi phí tối thiểu là bao nhiêu?
c) Nếu giá của đầu vào vốn tăng gấp 2 lần còn các yếu tố khác cố định, khi đó hãy tính lại
câu (b) và cho nhận xét về kết quả tính được.
Question 4: A firm producing in the long run has the production function of Q = 20.K.L. The
firm has two inputs, capital K and labor L. The price of the inputs is r = 4USD/unit of capital; w
= 6USD/unit of labor respectively. (Quantity is measured in unit, price is measured in $/ USD). lOMoARcPSD|46958826
a) What is the marginal rate of technical substitution at the optimal input bundle to minimize the cost?
b) In order to produce an output Q0 = 500, what minimum cost will the firm choose?
c) Given the fact that the cost of capital input doubles while other factors are constant,
reanswer question (b) and give comments on the result.
Câu 4: Một người tiêu dùng có số tiền là M = 340 sử dụng để mua 2 loại hàng hoá thông thường X và
Y. Giá của hai loại hàng hoá này tương ứng là PX = 4/unit và PY = 8/unit. Hàm lợi ích của người
tiêu dùng này là UX,Y = 20XY. (Quantity is measured in unit, price is measured in $/ USD).
a) Tính tỷ lệ thay thế cận biên trong tiêu dùng tại điểm lựa chọn tiêu dùng tối ưu.
b) Lợi ích tối đa mà người tiêu dùng có thể đạt được là bao nhiêu?
c) Giả sử ngân sách của người tiêu dùng này tăng lên gấp n lần (n > 0) và giá của cả hai
loại hàng hoá không đổi thì lợi ích tối đa của người tiêu dùng sẽ là bao nhiêu?
Question 4: A consumer has an amount of money M = $340 and uses it to buy two common
goods X and Y. The prices of these two goods are PX = $4/unit and PY = $8/unit respectively.
The utility function of this consumer is UX, Y = 20XY. (Quantity is measured in unit, price is measured in $/ USD).
a) Calculate the marginal rate of substitution in consumption at the point of optimal consumption.
b) What maximum benefit can the consumer achieve?
c) Assuming this consumer's budget grows n times (n > 0) and the prices of both goods remain
the same, what would be the maximum benefit of the consumer?




